Geology Of Cornwall on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The geology of
The geology of
 Cornwall forms the tip of the south-west peninsula of the island
Cornwall forms the tip of the south-west peninsula of the island
 The interior of the county consists of a roughly east–west spine of infertile and exposed upland, with a series of
The interior of the county consists of a roughly east–west spine of infertile and exposed upland, with a series of
 The Lizard complex is
The Lizard complex is
Royal Geological Society of Cornwall
The Geology of West Cornwall
{{Cornwall, state=collapsed * Mining in Cornwall

 The geology of
The geology of Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
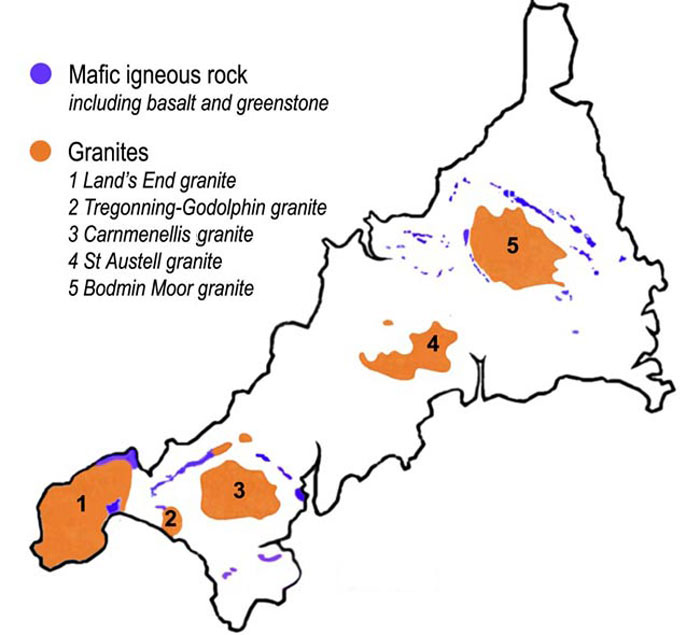
, England, is dominated by its granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
backbone, part of the Cornubian batholith, formed during the Variscan orogeny
The Variscan orogeny, or Hercynian orogeny, was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
Nomenclature
The name ''Varis ...
. Around this is an extensive metamorphic aureole (known locally as killas) formed in the mainly Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
slates that make up most of the rest of the county. There is an area of sandstone and shale of Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
age in the north east, and the Lizard peninsula
The Lizard () is a peninsula in southern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The Extreme points of the United Kingdom, southernmost point of the Great Britain, British mainland is near Lizard Point, Cornwall, Lizard Point at SW 701115; The ...
is formed of a rare section of uplifted oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramaf ...
.
Coasts
 Cornwall forms the tip of the south-west peninsula of the island
Cornwall forms the tip of the south-west peninsula of the island Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
, and is therefore exposed to the full force of the prevailing winds that blow in from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the ...
. The coastline is composed mainly of resistant rocks that give rise in many places to impressive cliffs.
The north and south coasts have different characteristics. The north coast is more exposed and therefore has a wilder nature. The prosaically-named ''High Cliff'', between Boscastle and St Gennys, is the highest sheer-drop cliff in Cornwall at 735 ft (224 m). However, there are also many extensive stretches of fine golden sand which form the beaches that are so important to the tourist industry, such as those at St Ives, Hayle
Hayle (, "estuary") is a port town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in west Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated at the mouth of the Hayle River (which discharges into St Ives Bay) and is approximately northeast of ...
, Perranporth and Newquay
Newquay ( ; ) is a town on the north coast in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is a civil parishes in England, civil parish, seaside resort, regional centre for aerospace industries with an airport and a spaceport, and a fishing port on t ...
. The only river estuary of any size on the north coast is that of the Camel
A camel (from and () from Ancient Semitic: ''gāmāl'') is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provid ...
, which provides Padstow
Padstow (; ) is a town, civil parishes in England, civil parish and fishing port on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town is situated on the west bank of the River Camel estuary, approximately northwest of Wadebridge, ...
with a safe harbour.
The south coast, dubbed the riviera, is somewhat more sheltered and there are several broad estuaries formed by drowned valleys or rias that offer safe anchorages to seafarers, such as at Falmouth and Fowey
Fowey ( ; , meaning ''beech trees'') is a port town and civil parishes in England, civil parish at the mouth of the River Fowey in south Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The town has been in existence since well before the Norman invasion, ...
. Beaches on the south coast usually consist of coarser sand and shingle, interspersed with rocky sections of wave-cut platform. Raised beaches can be identified in various places these being geological evidence of past changes in sea levels.
Interior
 The interior of the county consists of a roughly east–west spine of infertile and exposed upland, with a series of
The interior of the county consists of a roughly east–west spine of infertile and exposed upland, with a series of granite
Granite ( ) is a coarse-grained (phanerite, phaneritic) intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly coo ...
intrusions, such as Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor () is a granite moorland in north-eastern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous period of geology, geological history. It includes Brown Willy, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough To ...
, which contains the highest land within Cornwall. From east to west, and with approximately descending altitude, these are Bodmin Moor
Bodmin Moor () is a granite moorland in north-eastern Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is in size, and dates from the Carboniferous period of geology, geological history. It includes Brown Willy, the highest point in Cornwall, and Rough To ...
, the area north of St Austell
Saint Austell (, ; ) is a town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, south of Bodmin and west of the border with Devon.
At the 2021 Census in the United Kingdom, census it had a population of 20,900.
History
St Austell was a village centred ...
(including St Austell Downs), the area south of Camborne
Camborne (from Cornish language, Cornish ''Cambron'', "crooked hill") is a town in Cornwall, England. The population at the 2011 Census was 20,845. The northern edge of the parish includes a section of the South West Coast Path, Hell's Mouth, C ...
and Redruth
Redruth ( , ) is a town and civil parishes in Cornwall, civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. According to the 2011 census, the population of Redruth was 14,018 In the same year the population of the Camborne-Redruth urban area, ...
, and the Penwith
Penwith (; ) is an area of Cornwall, England, located on the peninsula of the same name. It is also the name of a former Non-metropolitan district, local government district, whose council was based in Penzance. The area is named after one ...
or Land's End
Land's End ( or ''Pedn an Wlas'') is a headland and tourist and holiday complex in western Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, on the Penwith peninsula about west-south-west of Penzance at the western end of the A30 road. To the east of it is ...
peninsula. These intrusions are the central part of the granite outcrops of south-west Britain, which include Dartmoor
Dartmoor is an upland area in southern Devon, South West England. The moorland and surrounding land has been protected by National Park status since 1951. Dartmoor National Park covers .
The granite that forms the uplands dates from the Carb ...
to the east in Devon
Devon ( ; historically also known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west ...
and the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly ( ; ) are a small archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, Isles of Scilly, St Agnes, is over farther south than the most southerly point of the Great Britain, British mainla ...
to the west, the latter now being partially submerged.
The uplands are surrounded by more fertile, mainly pastoral
The pastoral genre of literature, art, or music depicts an idealised form of the shepherd's lifestyle – herding livestock around open areas of land according to the seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. The target au ...
farmland. Near the south coast, deep wooded valleys provide sheltered conditions for a flora that likes shade and a moist, mild climate. These areas are mainly of Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
and slate
Slate is a fine-grained, foliated, homogeneous, metamorphic rock derived from an original shale-type sedimentary rock composed of clay or volcanic ash through low-grade, regional metamorphism. It is the finest-grained foliated metamorphic ro ...
. The north east of Cornwall lies on Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
rocks known as the Culm Measures
The Culm Measures are a thick sequence of geological stratum, strata originating during the Carboniferous Period that occur in south-west England, principally in Devon and Cornwall, now known as the Culm Supergroup. Its estimated thickness varies b ...
. In places these have been subjected to severe folding, as can be seen on the north coast near Crackington Haven, spectacularly at the ''Whaleback Pericline'' on the beach just south of Bude
Bude (, locally or ; Cornish language, Cornish ) is a seaside town in north Cornwall, England, in the civil parish of Bude-Stratton and at the mouth of the River Neet (also known locally as the River Strat). It was sometimes formerly known as ...
and at several other locations.
Granite
The intrusion of the granite into the surroundingsedimentary
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock formed by the cementation of sediments—i.e. particles made of minerals (geological detritus) or organic matter (biological detritus)—that have been accumulated or deposited at Earth's surface. Sedime ...
rocks gave rise to extensive metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated ...
and mineralisation, and this led to Cornwall being one of the most important mining areas in Europe until the early 20th century. It is thought that tin ore (cassiterite
Cassiterite is a tin oxide mineral, SnO2. It is generally opaque, but it is translucent in thin crystals. Its luster and multiple crystal faces produce a desirable gem. Cassiterite was the chief tin ore throughout ancient history and remains ...
) was exploited in Cornwall as early as the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age () was a historical period characterised principally by the use of bronze tools and the development of complex urban societies, as well as the adoption of writing in some areas. The Bronze Age is the middle principal period of ...
. Over the years, many other metals such as copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
, lead
Lead () is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol Pb (from Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a Heavy metal (elements), heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale, soft and Ductility, malleabl ...
, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
and silver
Silver is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag () and atomic number 47. A soft, whitish-gray, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. ...
have all been mined in Cornwall. Alteration of the granite also gave rise to extensive deposits of china clay (kaolinite
Kaolinite ( ; also called kaolin) is a clay mineral, with the chemical composition Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4. It is a layered silicate mineral, with one tetrahedral sheet of silica () linked through oxygen atoms to one octahedral sheet of alumina () ...
), especially in the area to the north of St Austell
Saint Austell (, ; ) is a town in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, south of Bodmin and west of the border with Devon.
At the 2021 Census in the United Kingdom, census it had a population of 20,900.
History
St Austell was a village centred ...
, and this remains one of Cornwall's most important industries.
Granite was used as a building stone as early as the Bronze Age. Before the 17th century the granite was not quarried as it was far too difficult to cut the stone at that time. Builders used blocks lying about on the moors, known as moorstone, instead. By the later Middle Ages the masons were adept enough at dressing moorstone to use it in church building. Moorstone blocks were also used for bridging streams and for walls, stiles, posts and troughs.
The Lizard peninsula
 The Lizard complex is
The Lizard complex is Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
's most complete Chandler, P. t al.(1984) ''A Gravity Survey of the Polyphant Ultrabasic Complex, East Cornwall'', Proceedings of the Ussher Society 6(1), pp. 116-120 example of an ophiolite
An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.
The Greek word ὄφις, ''ophis'' (''snake'') is ...
. Much of the peninsula consists of the dark green and red rock, serpentinite
Serpentinite is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of serpentine group minerals formed by serpentinization of mafic or ultramafic rocks. The ancient origin of the name is uncertain; it may be from the similarity of its texture or color ...
, which forms cliffs as at Kynance Cove, and can be carved and polished to create ornaments. This ultramafic rock
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are usua ...
forms a very infertile soil which covers the flat and marshy heaths of the Goonhilly Downs
Goonhilly Downs is a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) that forms a raised plateau in the central western area of the The Lizard, Lizard peninsula in southern Cornwall, England. It is one of 229 English national nature reserves designat ...
.
Mining and quarrying
Extraction of tin began in Cornwall in prehistoric times and continued until the late 20th century. Historically extensivetin
Tin is a chemical element; it has symbol Sn () and atomic number 50. A silvery-colored metal, tin is soft enough to be cut with little force, and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, a bar of tin makes a sound, the ...
and copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orang ...
mining has occurred in Cornwall and Devon, as well as arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol As and atomic number 33. It is a metalloid and one of the pnictogens, and therefore shares many properties with its group 15 neighbors phosphorus and antimony. Arsenic is not ...
, silver, zinc and a few other metals. Granite, slate and aggregate are still quarried and china-clay extraction continues on a large scale.
There are ample supplies of granite worth the cost of shipping out of the county and much Cornish granite has been used in distant places. It is one of the most appropriate materials for memorials and examples are found in most parts of Cornwall. there are no active metalliferous mines remaining. However, tin deposits still exist in Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
, and there is talk of reopening South Crofty tin mine.
Geological studies were made worthwhile due to the economic importance of mines and quarries: about forty distinct minerals have been identified from type localities in Cornwall, e. g. endellionite from St Endellion
St Endellion () is a civil parishes in England, civil parish and hamlet in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The hamlet and parish church are situated four miles (6.5 km) north of Wadebridge.
The parish takes its name from Saint Ende ...
.
See also
* Geography of Cornwall *Royal Geological Society of Cornwall
The Royal Geological Society of Cornwall is a geological society originally based in Penzance, Cornwall in the United Kingdom. It was founded in 1814 to promote the study of the geology of Cornwall, and is the second oldest geological society in ...
References
Bibliography
* Edmonds, E. A. t al.(1975) ''South-West England''; based on previous editions by H. Dewey (British Geological Survey
The British Geological Survey (BGS) is a partly publicly funded body which aims to advance Earth science, geoscientific knowledge of the United Kingdom landmass and its continental shelf by means of systematic surveying, monitoring and research. ...
UK Regional Geology Guide series no. 17, 4th ed.) London: HMSO
* Evans, C. D. R. & Hillis, R. R. (1990) ''Geology of the western English Channel and its western approaches'' (British Geological Survey UK Offshore Regional Report series, no. 9). London: HMSO
* Hall, A. (2005) ''West Cornwall'' (Geologists' Association Guide series no. 13, 2nd ed.) London: Geologists' Association
* Todd, A. C. & Laws, Peter (1972) ''The Industrial Archaeology of Cornwall''. Newton Abbot: David & Charles
Further reading
*Bristow, C. M. (2004) ''Cornwall's Geology and Scenery'' *English Heritage (2011) ''The Strategic Stone Study: a building stone atlas of Cornwall and the Isles of Scilly'' *Selwood, E. B., Durrance, E. M. & Bristow, C. M. (eds.) (1998) ''The Geology of Cornwall and the Isles of Scilly''External links
Royal Geological Society of Cornwall
The Geology of West Cornwall
{{Cornwall, state=collapsed * Mining in Cornwall