geologic uplift on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Orogeny () is a

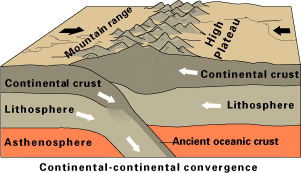 Orogeny takes place on the convergent margins of continents. The convergence may take the form of
Orogeny takes place on the convergent margins of continents. The convergence may take the form of
 Orogens show a great range of characteristics,
but they may be broadly divided into collisional orogens and noncollisional orogens (Andean-type orogens). Collisional orogens can be further divided by whether the collision is with a second continent or a continental fragment or island arc. Repeated collisions of the latter type, with no evidence of collision with a major continent or closure of an ocean basin, result in an accretionary orogen. Examples of orogens arising from collision of an island arc with a continent include
Orogens show a great range of characteristics,
but they may be broadly divided into collisional orogens and noncollisional orogens (Andean-type orogens). Collisional orogens can be further divided by whether the collision is with a second continent or a continental fragment or island arc. Repeated collisions of the latter type, with no evidence of collision with a major continent or closure of an ocean basin, result in an accretionary orogen. Examples of orogens arising from collision of an island arc with a continent include

Maps of the Acadian and Taconic orogenies
{{Authority control Geological processes Plate tectonics Mountain geomorphology Effects of gravity Events in the geological history of Earth
mountain
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
-building
A building or edifice is an enclosed Structure#Load-bearing, structure with a roof, walls and window, windows, usually standing permanently in one place, such as a house or factory. Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, a ...
process that takes place at a convergent plate margin when plate motion compresses the margin. An or develops as the compressed plate crumples and is uplifted to form one or more mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
s. This involves a series of geological processes collectively called orogenesis. These include both structural deformation of existing continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
and the creation of new continental crust through volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
. Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also ...
rising in the orogen carries less dense material upwards while leaving more dense material behind, resulting in compositional differentiation of Earth's lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
( crust and uppermost mantle). A synorogenic (or synkinematic) process or event is one that occurs during an orogeny.
The word ''orogeny'' comes . Although it was used before him, the American geologist G. K. Gilbert used the term in 1890 to mean the process of mountain-building, as distinguished from epeirogeny.
Tectonics
 Orogeny takes place on the convergent margins of continents. The convergence may take the form of
Orogeny takes place on the convergent margins of continents. The convergence may take the form of subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second p ...
(where a continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
rides forcefully over an oceanic plate
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic ...
to form a noncollisional orogeny) or continental collision (convergence of two or more continents to form a collisional orogeny).
Orogeny typically produces ''orogenic belts'' or ''orogens'', which are elongated regions of deformation bordering continental craton
A craton ( , , or ; from "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and rifting of contine ...
s (the stable interiors of continents). Young orogenic belts, in which subduction is still taking place, are characterized by frequent volcanic activity
Volcanism, vulcanism, volcanicity, or volcanic activity is the phenomenon where solids, liquids, gases, and their mixtures erupt to the surface of a solid-surface astronomical body such as a planet or a moon. It is caused by the presence of a he ...
and earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they ...
s. Older orogenic belts are typically deeply eroded
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is disti ...
to expose displaced and deformed strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum (: strata) is a layer of Rock (geology), rock or sediment characterized by certain Lithology, lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by v ...
. These are often highly metamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
and include vast bodies of intrusive igneous rock called batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive rock, intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in the Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate ...
s.
Subduction zones consume oceanic crust, thicken lithosphere, and produce earthquakes and volcanoes. Not all subduction zones produce orogenic belts; mountain building takes place only when the subduction produces compression in the overriding plate. Whether subduction produces compression depends on such factors as the rate of plate convergence and the degree of coupling between the two plates, while the degree of coupling may in turn rely on such factors as the angle of subduction and rate of sedimentation in the oceanic trench associated with the subduction zone. The Andes Mountains
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18°S ...
are an example of a noncollisional orogenic belt, and such belts are sometimes called ''Andean-type orogens''.
As subduction continues, island arc
Island arcs are long archipelago, chains of active volcanoes with intense earthquake, seismic activity found along convergent boundary, convergent plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have re ...
s, continental fragment
Continental crustal fragments, partly synonymous with microcontinents, are pieces of continents that have broken off from main continental masses to form distinct islands that are often several hundred kilometers from their place of origin.
Caus ...
s, and oceanic material may gradually accrete onto the continental margin. This is one of the main mechanisms by which continents have grown. An orogen built of crustal fragments ('' terranes'') accreted over a long period of time, without any indication of a major continent-continent collision, is called an ''accretionary orogen.'' The North American Cordillera
The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system along the Pacifi ...
and the Lachlan Orogen of southeast Australia are examples of accretionary orogens.
The orogeny may culminate with continental crust from the opposite side of the subducting oceanic plate arriving at the subduction zone. This ends subduction and transforms the accretional orogen into a Himalayan-type collisional orogen. The collisional orogeny may produce extremely high mountains, as has been taking place in the Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya ( ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the Earth's highest peaks, including the highest, Mount Everest. More than list of h ...
for the last 65 million years.
The processes of orogeny can take tens of millions of years and build mountains from what were once sedimentary basin
Sedimentary basins are region-scale depressions of the Earth's crust where subsidence has occurred and a thick sequence of sediments have accumulated to form a large three-dimensional body of sedimentary rock They form when long-term subsidence ...
s. Activity along an orogenic belt can be extremely long-lived. For example, much of the basement
A basement is any Storey, floor of a building that is not above the grade plane. Especially in residential buildings, it often is used as a utility space for a building, where such items as the Furnace (house heating), furnace, water heating, ...
underlying the United States belongs to the Transcontinental Proterozoic Provinces, which accreted to Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American craton is a large continental craton that forms the Geology of North America, ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of ...
(the ancient heart of North America) over the course of 200 million years in the Paleoproterozoic
The Paleoproterozoic Era (also spelled Palaeoproterozoic) is the first of the three sub-divisions ( eras) of the Proterozoic eon, and also the longest era of the Earth's geological history, spanning from (2.5–1.6 Ga). It is further sub ...
. The Yavapai and Mazatzal orogenies were peaks of orogenic activity during this time. These were part of an extended period of orogenic activity that included the Picuris orogeny
The Picuris orogeny was an orogenic event in what is now the Southwestern United States from 1.43 to 1.3 billion years ago in the Calymmian Period of the Mesoproterozoic. The event is named for the Picuris Mountains in northern New Mexico and ...
and culminated in the Grenville orogeny
The Grenville orogeny was a long-lived Mesoproterozoic mountain-building event associated with the assembly of the supercontinent Rodinia. Its record is a prominent orogenic belt which spans a significant portion of the North American continent, ...
, lasting at least 600 million years. A similar sequence of orogenies has taken place on the west coast of North America, beginning in the late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago ( Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding ...
(about 380 million years ago) with the Antler orogeny and continuing with the Sonoma orogeny and Sevier orogeny and culminating with the Laramide orogeny
The Laramide orogeny was a time period of mountain building in western North America, which started in the Late Cretaceous, 80 to 70 million years ago, and ended 55 to 35 million years ago. The exact duration and ages of beginning and end of the o ...
. The Laramide orogeny alone lasted 40 million years, from 75 million to 35 million years ago.
Intraplate orogeny
Stresses transmitted from plate boundaries can also lead to episodes of intracontinental transpressional orogeny. Examples in Australia include the Neoproterozoic Petermann Orogeny (630–520 Ma), and the Sprigg Orogeny (Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
– present).
Orogens
 Orogens show a great range of characteristics,
but they may be broadly divided into collisional orogens and noncollisional orogens (Andean-type orogens). Collisional orogens can be further divided by whether the collision is with a second continent or a continental fragment or island arc. Repeated collisions of the latter type, with no evidence of collision with a major continent or closure of an ocean basin, result in an accretionary orogen. Examples of orogens arising from collision of an island arc with a continent include
Orogens show a great range of characteristics,
but they may be broadly divided into collisional orogens and noncollisional orogens (Andean-type orogens). Collisional orogens can be further divided by whether the collision is with a second continent or a continental fragment or island arc. Repeated collisions of the latter type, with no evidence of collision with a major continent or closure of an ocean basin, result in an accretionary orogen. Examples of orogens arising from collision of an island arc with a continent include Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
and the collision of Australia with the Banda arc. Orogens arising from continent-continent collisions can be divided into those involving ocean closure (Himalayan-type orogens) and those involving glancing collisions with no ocean basin closure (as is taking place today in the Southern Alps
The Southern Alps (; officially Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana) are a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand, New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The n ...
of New Zealand).
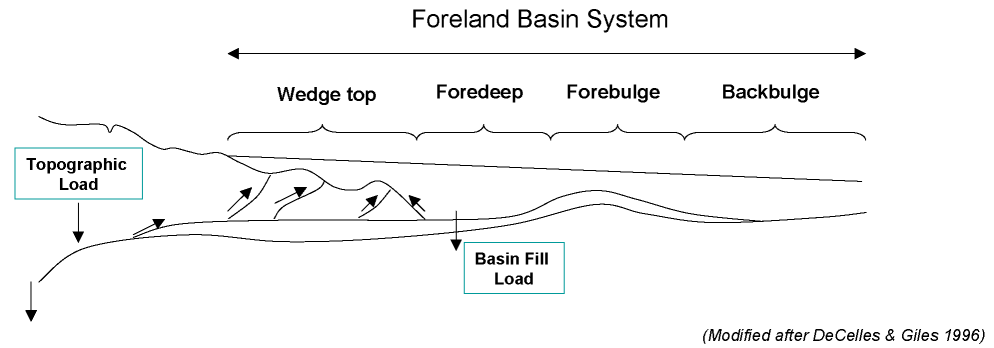
Orogens have a characteristic structure, though this shows considerable variation. A ''foreland basin'' forms ahead of the orogen due mainly to loading and resulting flexure of the lithosphere by the developing mountain belt. A typical foreland basin is subdivided into a wedge-top basin above the active orogenic wedge, the foredeep immediately beyond the active front, a forebulge high of flexural origin and a back-bulge area beyond, although not all of these are present in all foreland-basin systems. The basin migrates with the orogenic front and early deposited foreland basin sediments become progressively involved in folding and thrusting. Sediment
Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of ...
s deposited in the foreland basin are mainly derived from the erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
of the actively uplifting rocks of the mountain range, although some sediments derive from the foreland. The fill of many such basins shows a change in time from deepwater marine (''flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building ep ...
''-style) through shallow water to continental (''molasse
__NOTOC__
In geology, "molasse" () are sandstones, shales and conglomerates that form as terrestrial or shallow marine deposits in front of rising mountain chains. The molasse deposits accumulate in a foreland basin, especially on top of flys ...
''-style) sediments.
While active orogens are found on the margins of present-day continents, older inactive orogenies, such as the Algoman, Penokean and Antler
Antlers are extensions of an animal's skull found in members of the Cervidae (deer) Family (biology), family. Antlers are a single structure composed of bone, cartilage, fibrous tissue, skin, nerves, and blood vessels. They are generally fo ...
, are represented by deformed and metamorphosed rocks with sedimentary basins further inland.
Orogenic cycle
Long before the acceptance ofplate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
, geologists had found evidence within many orogens of repeated cycles of deposition, deformation, crustal thickening and mountain building, and crustal thinning to form new depositional basins. These were named ''orogenic cycles'', and various theories were proposed to explain them. Canadian geologist Tuzo Wilson first put forward a plate tectonic interpretation of orogenic cycles, now known as Wilson cycles. Wilson proposed that orogenic cycles represented the periodic opening and closing of an ocean basin, with each stage of the process leaving its characteristic record on the rocks of the orogen.
Continental rifting
The Wilson cycle begins when previously stable continental crust comes under tension from a shift inmantle convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creep of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carry heat from the interior to the planet's surface. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface.
The Earth's l ...
. Continental rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben ...
takes place, which thins the crust and creates basins in which sediments accumulate. As the basins deepen, the ocean invades the rift zone, and as the continental crust rifts completely apart, shallow marine sedimentation gives way to deep marine sedimentation on the thinned marginal crust of the two continents.
Seafloor spreading
As the two continents rift apart,seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge.
History of study
Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener ...
commences along the axis of a new ocean basin. Deep marine sediments continue to accumulate along the thinned continental margins, which are now passive margin
A passive margin is the transition between Lithosphere#Oceanic lithosphere, oceanic and Lithosphere#Continental lithosphere, continental lithosphere that is not an active plate continental margin, margin. A passive margin forms by sedimentatio ...
s.
Subduction
At some point, subduction is initiated along one or both of the continental margins of the ocean basin, producing avolcanic arc
A volcanic arc (also known as a magmatic arc) is a belt of volcanoes formed above a subducting oceanic tectonic plate, with the belt arranged in an arc shape as seen from above. Volcanic arcs typically parallel an oceanic trench, with the arc ...
and possibly an Andean-type orogen along that continental margin. This produces deformation of the continental margins and possibly crustal thickening and mountain building.
Mountain building
Mountain formation
Mountain formation occurs due to a variety of geological processes associated with large-scale movements of the Earth's crust ( tectonic plates). Folding, faulting, volcanic activity, igneous intrusion and metamorphism can all be parts of th ...
in orogens is largely a result of crustal thickening. The compressive forces produced by plate convergence result in pervasive deformation of the crust of the continental margin (thrust tectonics
Thrust tectonics or contractional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the Tectonics, tectonic processes associated with, the shortening and thickening of the Crust (geology), crust or lithosphere. It is one of the three main ...
). This takes the form of folding of the ductile deeper crust and thrust faulting in the upper brittle crust.
Crustal thickening raises mountains through the principle of isostasy
Isostasy (Greek wikt:ἴσος, ''ísos'' 'equal', wikt:στάσις, ''stásis'' 'standstill') or isostatic equilibrium is the state of gravity, gravitational mechanical equilibrium, equilibrium between Earth's crust (geology), crust (or lithosph ...
. Isostacy is the balance of the downward gravitational force
Newton's law of universal gravitation describes gravity as a force by stating that every particle attracts every other particle in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the sq ...
upon an upthrust mountain range (composed of light, continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as '' continental shelves''. This layer is sometimes called '' si ...
material) and the buoyant upward forces exerted by the dense underlying mantle.
Portions of orogens can also experience uplift as a result of delamination of the orogenic lithosphere, in which an unstable portion of cold lithospheric root drips down into the asthenospheric mantle, decreasing the density of the lithosphere and causing buoyant uplift. An example is the Sierra Nevada
The Sierra Nevada ( ) is a mountain range in the Western United States, between the Central Valley of California and the Great Basin. The vast majority of the range lies in the state of California, although the Carson Range spur lies primari ...
in California. This range of fault-block mountain
Fault blocks are very large blocks of rock, sometimes hundreds of kilometres in extent, created by Tectonics, tectonic and localized stresses in Crust (geology), Earth's crust. Large areas of bedrock are broken up into blocks by Fault (geology) ...
s experienced renewed uplift and abundant magmatism after a delamination of the orogenic root beneath them.
Mount Rundle on the Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway (Canadian French, French: ; abbreviated as the TCH or T-Can) is a transcontinental federal–provincial highway system that travels through all ten provinces of Canada, from the Pacific Ocean on the west coast to the A ...
between Banff and Canmore provides a classic example of a mountain cut in dipping-layered rocks. Millions of years ago a collision caused an orogeny, forcing horizontal layers of an ancient ocean crust to be thrust up at an angle of 50–60°. That left Rundle with one sweeping, tree-lined smooth face, and one sharp, steep face where the edge of the uplifted layers are exposed.
Although mountain building mostly takes place in orogens, a number of secondary mechanisms are capable of producing substantial mountain ranges. Areas that are rifting apart, such as mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
s and the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. It was formerly considered to be part of a l ...
, have mountains due to thermal buoyancy related to the hot mantle underneath them; this thermal buoyancy is known as dynamic topography. In strike-slip
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
orogens, such as the San Andreas Fault
The San Andreas Fault is a continental Fault (geology)#Strike-slip faults, right-lateral strike-slip transform fault that extends roughly through the U.S. state of California. It forms part of the tectonics, tectonic boundary between the Paci ...
, restraining bends result in regions of localized crustal shortening and mountain building without a plate-margin-wide orogeny. Hotspot volcanism results in the formation of isolated mountains and mountain chains that look as if they are not necessarily on present tectonic-plate boundaries, but they are essentially the product of plate tectonism. Likewise, uplift and erosion related to epeirogenesis (large-scale vertical motions of portions of continents without much associated folding, metamorphism, or deformation) can create local topographic highs.
Closure of the ocean basin
Eventually, seafloor spreading in the ocean basin comes to a halt, and continued subduction begins to close the ocean basin.Continental collision and orogeny
The closure of the ocean basin ends with a continental collision and the associated Himalayan-type orogen.Erosion
Erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
represents the final phase of the orogenic cycle. Erosion of overlying strata in orogenic belts, and isostatic adjustment to the removal of this overlying mass of rock, can bring deeply buried strata to the surface. The erosional process is called ''unroofing''. Erosion inevitably removes much of the mountains, exposing the core or ''mountain roots'' (metamorphic rocks
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, caus ...
brought to the surface from a depth of several kilometres). Isostatic movements may help such unroofing by balancing out the buoyancy of the evolving orogen. Scholars debate about the extent to which erosion modifies the patterns of tectonic deformation (see erosion and tectonics). Thus, the final form of the majority of old orogenic belts is a long arcuate strip of crystalline metamorphic rocks sequentially below younger sediments which are thrust atop them and which dip away from the orogenic core.
An orogen may be almost completely eroded away, and only recognizable by studying (old) rocks that bear traces of orogenesis. Orogens are usually long, thin, arcuate tracts of rock that have a pronounced linear structure resulting in terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its d ...
s or blocks of deformed rocks, separated generally by suture zones
Suture, literally meaning "seam", may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Suture'' (album), a 2000 album by American Industrial rock band Chemlab
* ''Suture'' (film), a 1993 film directed by Scott McGehee and David Siegel
* Suture (ban ...
or dipping thrust fault
A thrust fault is a break in the Earth's crust, across which older rocks are pushed above younger rocks.
Thrust geometry and nomenclature
Reverse faults
A thrust fault is a type of reverse fault that has a dip of 45 degrees or less.
I ...
s. These thrust faults carry relatively thin slices of rock (which are called nappe
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the ...
s or thrust sheets, and differ from tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
s) from the core of the shortening orogen out toward the margins, and are intimately associated with folds and the development of metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated ...
.
History of the concept
Before the development of geologic concepts during the 19th century, the presence of marinefossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
s in mountains was explained in Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
contexts as a result of the Biblical Deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge or Le Déluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-L ...
. This was an extension of Neoplatonic
Neoplatonism is a version of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a series of thinkers. Among the common id ...
thought, which influenced early Christian writers
Various History of Christianity#Early_Christianity_(c._27_–_fourth_century), early Christian writers wrote gospels and other books, some of which were canonized as the Development of the New Testament canon, New Testament canon developed. The A ...
.
The 13th-century Dominican scholar Albert the Great
Albertus Magnus ( 1200 – 15 November 1280), also known as Saint Albert the Great, Albert of Swabia, Albert von Bollstadt, or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop, considered one of the great ...
posited that, as erosion was known to occur, there must be some process whereby new mountains and other land-forms were thrust up, or else there would eventually be no land; he suggested that marine fossils in mountainsides must once have been at the sea-floor. Orogeny was used by Amanz Gressly
Amanz Gressly (17 July 1814 – 13 April 1865) was a Swiss geologist and Paleontology, paleontologist. He introduced the use of the term facies in geology, and is considered one of the founders of modern stratigraphy and paleoecology.
He i ...
(1840) and Jules Thurmann
Jules Thurmann (5 November 1804, Neuf-Brisach in Haut-Rhin, France – 25 July 1855, Porrentruy) was an Alsatian French-Swiss geologist and botanist.
He studied at the college in Porrentruy, then continued his education at the University of ...
(1854) as ''orogenic'' in terms of the creation of mountain elevations, as the term ''mountain building'' was still used to describe the processes. Elie de Beaumont (1852) used the evocative "Jaws of a Vise" theory to explain orogeny, but was more concerned with the height rather than the implicit structures created by and contained in orogenic belts. His theory essentially held that mountains were created by the squeezing of certain rocks. Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess (; 20 August 1831 – 26 April 1914) was an Austrian geologist and an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana (proposed in 1861) and ...
(1875) recognised the importance of horizontal movement of rocks. The concept of a ''precursor geosyncline
A geosyncline (originally called a geosynclinal) is an obsolete geology, geological concept to explain orogeny, orogens, which was developed in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, before the theory of plate tectonics was envisaged.#Sengor1982, ...
'' or initial downward warping of the solid earth (Hall, 1859) prompted James Dwight Dana
James Dwight Dana Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (February 12, 1813 – April 14, 1895) was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcano, volcanic activity, and the ...
(1873) to include the concept of ''compression'' in the theories surrounding mountain-building. With hindsight, we can discount Dana's conjecture that this contraction was due to the cooling of the Earth (aka the cooling Earth theory). The cooling Earth theory was the chief paradigm for most geologists until the 1960s. It was, in the context of orogeny, fiercely contested by proponents of vertical movements in the crust, or convection within the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between c. below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere i ...
or mantle.
Gustav Steinmann (1906) recognised different classes of orogenic belts, including the ''Alpine type orogenic belt'', typified by a flysch
Flysch () is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building ep ...
and molasse
__NOTOC__
In geology, "molasse" () are sandstones, shales and conglomerates that form as terrestrial or shallow marine deposits in front of rising mountain chains. The molasse deposits accumulate in a foreland basin, especially on top of flys ...
geometry to the sediments; ophiolite
An ophiolite is a section of Earth's oceanic crust and the underlying upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle that has been uplifted and exposed, and often emplaced onto continental crustal rocks.
The Greek word ὄφις, ''ophis'' (''snake'') is ...
sequences, tholeiitic basalts, and a nappe
In geology, a nappe or thrust sheet is a large sheetlike body of rock that has been moved more than or above a thrust fault from its original position. Nappes form in compressional tectonic settings like continental collision zones or on the ...
style fold structure.
In terms of recognising orogeny as an ''event'', Leopold von Buch
Christian Leopold von Buch (26 April 1774 – 4 March 1853), usually cited as Leopold von Buch, was a German geologist and paleontologist born in Stolpe an der Oder (now a part of Angermünde, Brandenburg) and is remembered as one of the most im ...
(1855) recognised that orogenies could be placed in time by bracketing between the youngest deformed rock and the oldest undeformed rock, a principle which is still in use today, though commonly investigated by geochronology
Geochronology is the science of Chronological dating, determining the age of rock (geology), rocks, fossils, and sediments using signatures inherent in the rocks themselves. Absolute geochronology can be accomplished through radioactive isotopes, ...
using radiometric dating.
Based on available observations from the metamorphic differences in orogenic belts of Europe and North America, H. J. Zwart (1967) proposed three types of orogens in relationship to tectonic setting and style: Cordillerotype, Alpinotype, and Hercynotype. His proposal was revised by W. S. Pitcher in 1979 in terms of the relationship to granite occurrences. Cawood et al. (2009) categorized orogenic belts into three types: accretionary, collisional, and intracratonic. Both accretionary and collisional orogens developed in converging plate margins. In contrast, Hercynotype orogens generally show similar features to intracratonic, intracontinental, extensional, and ultrahot orogens, all of which developed in continental detachment systems at converged plate margins.
# Accretionary orogens, which were produced by subduction of one oceanic plate beneath one continental plate for arc volcanism. They are dominated by calc-alkaline igneous rocks and high-T/low-P metamorphic facies series at high thermal gradients of >30 °C/km. There is a general lack of ophiolites, migmatites and abyssal sediments. Typical examples are all circum-Pacific orogens containing continental arcs.
# Collisional orogens, which were produced by subduction of one continental block beneath the other continental block with the absence of arc volcanism. They are typified by the occurrence of blueschist to eclogite facies metamorphic zones, indicating high-P/low-T metamorphism at low thermal gradients of <10 °C/km. Orogenic peridotites are present but volumetrically minor, and syn-collisional granites and migmatites are also rare or of only minor extent. Typical examples are the Alps-Himalaya orogens in the southern margin of Eurasian continent and the Dabie-Sulu orogens in east-central China.
See also
* * * * * * * *References
Further reading
* * provides a detailed history of a number of orogens, including the Caledonian Orogeny, which lasted from the lateCambrian
The Cambrian ( ) is the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 51.95 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran period 538.8 Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Ordov ...
to the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ...
, with the main collisional events occurring during Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
and Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
times.
* is one of a two-volume exposition of the geology of central Europe with a discussion of major orogens.
* Evolution of the Cordilleras of the Americas from a multidisciplinary perspective from a symposium held in Mendoza, Argentina (2006).
External links
Maps of the Acadian and Taconic orogenies
{{Authority control Geological processes Plate tectonics Mountain geomorphology Effects of gravity Events in the geological history of Earth