Geologic temperature record on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The geologic temperature record are changes in
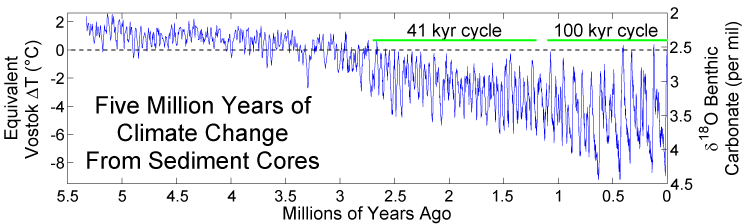 The last 3 million years have been characterized by cycles of glacials and interglacials within a gradually deepening
The last 3 million years have been characterized by cycles of glacials and interglacials within a gradually deepening
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
's environment as determined from geologic
Geology (). is a branch of natural science concerned with the Earth and other astronomical objects, the rocks of which they are composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth s ...
evidence on multi-million to billion (109) year time scales. The study of past temperatures provides an important paleoenvironmental insight because it is a component of the climate and oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
of the time.
Methods
Evidence for past temperatures comes mainly from isotopic considerations (especially ); the Mg/Ca ratio offoram
Foraminifera ( ; Latin for "hole bearers"; informally called "forams") are single-celled organisms, members of a phylum or class of Rhizarian protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses; and commonl ...
tests, and alkenones, are also useful. Often, many are used in conjunction to get a multi-proxy estimate for the temperature. This has proven crucial in studies on glacial/interglacial temperature.
Description of the temperature record
Pleistocene
 The last 3 million years have been characterized by cycles of glacials and interglacials within a gradually deepening
The last 3 million years have been characterized by cycles of glacials and interglacials within a gradually deepening ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages, and g ...
. Currently, the Earth is in an interglacial period, beginning about 20,000 years ago (20 kya).
The cycles of glaciation involve the growth and retreat of continental ice sheets in the Northern Hemisphere and involve fluctuations on a number of time scales, notably on the 21 ky, 41 ky and 100 ky scales. Such cycles are usually interpreted as being driven by predictable changes in the Earth orbit known as Milankovitch cycles
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after the Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he pr ...
. At the beginning of the Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, more widely known as the Middle Pleistocene (its previous informal name), is an Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale or a Stage (stratigraphy), stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocen ...
(0.8 million years ago, close to the Brunhes–Matuyama geomagnetic reversal
A geomagnetic reversal is a change in the Earth's Dipole magnet, dipole magnetic field such that the positions of magnetic north and magnetic south are interchanged (not to be confused with North Pole, geographic north and South Pole, geograp ...
) there has been a largely unexplained switch in the dominant periodicity of glaciations from the 41 ky to the 100 ky cycle.
The gradual intensification of this ice age over the last 3 million years has been associated with declining concentrations of the greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gases (GHGs) are the gases in the atmosphere that raise the surface temperature of planets such as the Earth. Unlike other gases, greenhouse gases absorb the radiations that a planet emits, resulting in the greenhouse effect. T ...
carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, though it remains unclear if this change is sufficiently large to have caused the changes in temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...
s.
Decreased temperatures can cause a decrease in carbon dioxide as, by Henry's Law
In physical chemistry, Henry's law is a gas law that states that the amount of dissolved gas in a liquid is directly proportional at equilibrium to its partial pressure above the liquid. The proportionality factor is called Henry's law constant ...
, carbon dioxide is more soluble in colder waters, which may account for 30ppmv of the 100ppmv decrease in carbon dioxide concentration during the last glacial maximum.
Similarly, the initiation of this deepening phase also corresponds roughly to the closure of the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama, historically known as the Isthmus of Darien, is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North America, North and South America. The country of Panama is located on the i ...
by the action of plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (, ) is the scientific theory that the Earth's lithosphere comprises a number of large tectonic plates, which have been slowly moving since 3–4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of , an idea developed durin ...
. This prevented direct ocean flow between the Pacific and Atlantic, which would have had significant effects on ocean circulation and the distribution of heat. However, modeling studies have been ambiguous as to whether this could be the direct cause of the intensification of the present ice age.
This recent period of cycling climate is part of the more extended ice age that began about with the glaciation of Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean (also known as the Antarctic Ocean), it contains the geographic South Pole. ...
.
Initial Eocene thermal maxima
In the earliest part of theEocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes ...
period, a series of abrupt thermal spikes have been observed, lasting no more than a few hundred thousand years. The most pronounced of these, the Paleocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM) is visible in the figure at right. These are usually interpreted as caused by abrupt releases of methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The abundance of methane on Earth makes ...
from clathrates (frozen methane ices that accumulate at the bottom of the ocean), though some scientists dispute that methane would be sufficient to cause the observed changes. During these events, temperatures in the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
may have reached levels more typically associated with modern temperate (i.e. mid-latitude) oceans. During the PETM, the global mean temperature seems to have risen by as much as 5–8 °C (9–14 °F) to an average temperature as high as 23 °C (73 °F), in contrast to the global average temperature of today at just under 15 °C (60 °F). Geologists and paleontologists think that during much of the Paleocene and early Eocene, the poles were free of ice caps, and palm trees and crocodiles lived above the Arctic Circle, while much of the continental United States had a sub-tropical environment.
Cretaceous thermal optimum
During the later portion of theCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
, from , average global temperatures reached their highest level during the last ~200 million years. This is likely to be the result of a favorable configuration of the continents during this period that allowed for improved circulation in the oceans and discouraged the formation of large scale ice sheet.
Fluctuations during the remainder of the Phanerozoic
ThePhanerozoic
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four eon (geology), geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and ...
eon, encompassing the last 542 million years and almost the entire time since the origination of complex multi-cellular life, has more generally been a period of fluctuating temperature between ice ages, such as the current age, and " climate optima", similar to what occurred in the Cretaceous. Roughly 4 such cycles have occurred during this time with an approximately 140 million year separation between climate optima. In addition to the present, ice ages have occurred during the Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years, from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.902 Mya. It is the s ...
-Carboniferous
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Geologic time scale, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era that spans 60 million years, from the end of the Devonian Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the ...
interval and the late Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era, and the second of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon (geology), Eon. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years f ...
-early Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of t ...
. There is also a "cooler" interval during the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately 143.1 Mya. ...
and early Cretaceous, with evidence of increased sea ice, but the lack of continents at either pole during this interval prevented the formation of continental ice sheets and consequently this is usually not regarded as a full-fledged ice age. In between these cold periods, warmer conditions were present and often referred to as climate optima. However, it has been difficult to determine whether these warmer intervals were actually hotter or colder than occurred during the Cretaceous optima.
Late Proterozoic ice ages
TheNeoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the last of the three geologic eras of the Proterozoic geologic eon, eon, spanning from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago, and is the last era of the Precambrian "supereon". It is preceded by the Mesoproterozoic era an ...
era (), provides evidence of at least two and possibly more major glaciations. The more recent of these ice ages, encompassing the Marinoan & Varangian glacial maxima (about ), has been proposed as a snowball Earth
The Snowball Earth is a historical geology, geohistorical hypothesis that proposes that during one or more of Earth's greenhouse and icehouse Earth, icehouse climates, the planet's planetary surface, surface became nearly entirely freezing, fr ...
event with continuous sea ice reaching nearly to the equator. This is significantly more severe than the ice ages during the Phanerozoic. Because this ice age terminated only slightly before the rapid diversification of life during the Cambrian explosion, it has been proposed that this ice age (or at least its end) created conditions favorable to evolution. The earlier Sturtian glacial maxima (~730 million years) may also have been a snowball Earth event though this is unproven.
The changes that lead to the initiation of snowball Earth events are not well known, but it has been argued that they necessarily led to their own end. The widespread sea ice prevents the deposition of fresh carbonates in ocean sediment
Marine sediment, or ocean sediment, or seafloor sediment, are deposits of insoluble particles that have accumulated on the seafloor. These particles either have their origins in soil and rocks and have been transported from the land to the ...
. Since such carbonates are part of the natural process for recycling carbon dioxide, short-circuiting this process allows carbon dioxide to accumulate in the atmosphere. This increases the greenhouse effect
The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature. Surface heating can happen from an internal heat source (as in the case of Jupiter) or ...
and eventually leads to higher temperatures and the retreat of sea ice.
Overall view
Direct combination of these interpreted geological temperature records is not necessarily valid, nor is their combination with other more recent temperature records, which may use different definitions. Nevertheless, an overall perspective is useful even when imprecise. In this view time is plotted backwards from the present, taken as 2015 CE. It is scaled ''linear'' in five separate segments, expanding by about an order of magnitude at each vertical break. Temperatures in the left-hand panel are very approximate, and best viewed as a qualitative indication only. Further information is given on the graph description page.Other temperature changes in Earth's past
About , there was a period of climate stasis, also known as theBoring Billion
The Boring Billion, otherwise known as the Mid Proterozoic and Earth's Middle Ages, is an informal geological time period between 1.8 and 0.8 billion years ago ( Ga) during the middle Proterozoic eon spanning from the Statherian to the Tonian ...
. During this period there was hardly any tectonic activity, no glaciations and the atmosphere composition remained stable. It is bordered by two different oxygenation and glacial events.
Temperature reconstructions based on oxygen and silicon isotopes from rock samples have predicted much hotter Precambrian sea temperatures. These predictions suggest ocean temperatures of 55–85 °C during the period of , followed by cooling to more mild temperatures of between 10-40 °C by . Reconstructed proteins from Precambrian organisms have also provided evidence that the ancient world was much warmer than today.
However, other evidence suggests that the period of was generally colder and more glaciated than the last 500 million years. This is thought to be the result of solar
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
radiation approximately 20% lower than today. Solar luminosity
The solar luminosity () is a unit of radiant flux (Power (physics), power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxy, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of ...
was 30% dimmer when the Earth formed 4.5 billion years ago, and it is expected to increase in luminosity approximately 10% per billion years in the future.
On very long time scales, the evolution of the sun is also an important factor in determining Earth's climate. According to standard solar theories, the sun will gradually have increased in brightness as a natural part of its evolution after having started with an intensity approximately 70% of its modern value. The initially low solar radiation, if combined with modern values of greenhouse gases, would not have been sufficient to allow for liquid oceans on the surface of the Earth. However, evidence of liquid water at the surface has been demonstrated as far back as . This is known as the faint young sun paradox and is usually explained by invoking much larger greenhouse gas concentrations in Earth's early history, though such proposals are poorly constrained by existing experimental evidence.
See also
*Climate state
Throughout Earth's climate history (Paleoclimate) its climate has fluctuated between two primary states: greenhouse and icehouse Earth. Both climate states last for millions of years and should not be confused with the much smaller glacial and in ...
* Global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
* Global cooling
Global cooling was a conjecture, especially during the 1970s, of imminent cooling of the Earth culminating in a period of extensive glaciation, due to the cooling effects of aerosols or orbital forcing.
Some press reports in the 1970s specu ...
* Instrumental temperature record
Global surface temperature (GST) is the average temperature of Earth's surface. More precisely, it is the weighted average of the temperatures over the ocean and land. The former is also called sea surface temperature and the latter is calle ...
* Ocean heat content
Ocean heat content (OHC) or ocean heat uptake (OHU) is the energy absorbed and stored by oceans, and is thus an important indicator of global warming. Ocean heat content is calculated by measuring ocean temperature at many different locations and ...
* Satellite temperature measurements
* Sea surface temperature
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea ...
* Thermal history of the Earth
* Timeline of glaciation
There have been five or six major ice ages in the history of Earth over the past 3 billion years.
The Late Cenozoic Ice Age began 34 million years ago, its latest phase being the Quaternary glaciation, in progress since 2.58 million years ago. ...
* List of periods and events in climate history
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geologic Temperature Record Historical geology Paleoclimatology Paleoceanography