Geography Of Liechtenstein on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
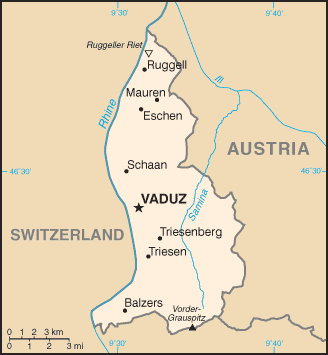

 The principality of
The principality of


 The principality of
The principality of Liechtenstein
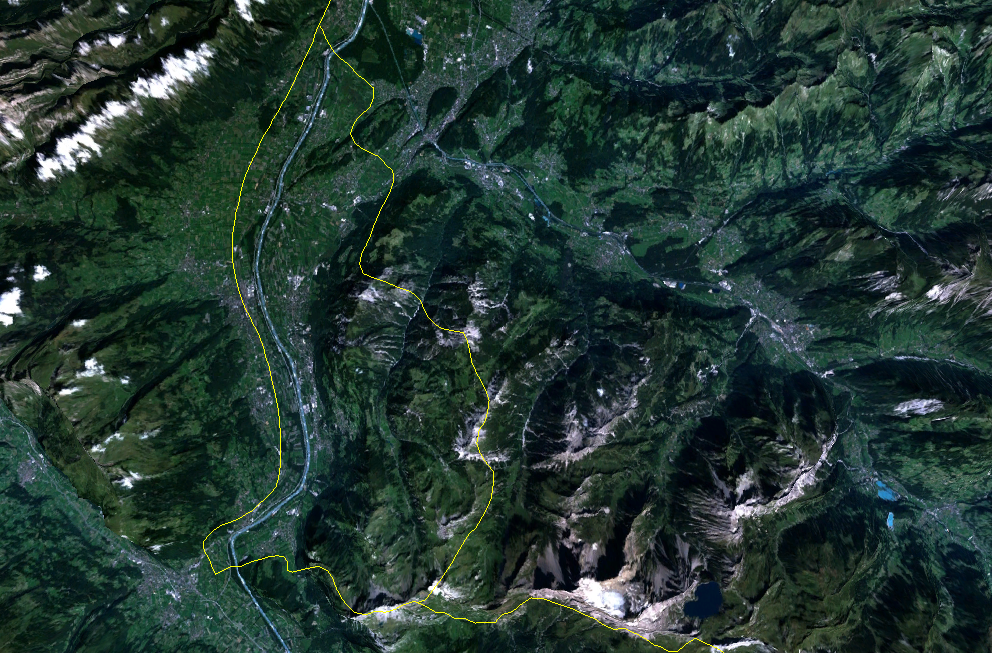
Liechtenstein (, ; ; ), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein ( ), is a Landlocked country#Doubly landlocked, doubly landlocked Swiss Standard German, German-speaking microstate in the Central European Alps, between Austria in the east ...
encompasses most of the eastern half of the Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
Valley, wedged between Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
and Switzerland
Switzerland, officially the Swiss Confederation, is a landlocked country located in west-central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the south, France to the west, Germany to the north, and Austria and Liechtenstein to the east. Switzerland ...
. The majority of the country's population is found in the western half along the Rhine River. Along with Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, Liechtenstein is one of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world.
Statistics
Geographic coordinates: Area: 160 km2 (land, 0 km2 water) Land boundaries :''total:'' 76 km :''border countries:'' Austria 35 km, Switzerland 41 km Lake :The only lake in Liechtenstein is the Gampriner Seele. Land use :''arable land:'' 21.88% :''permanent crops:'' 0% :''other:'' 78.12% (2011) Terrain :Mostly mountainous (Alps) with Rhine Valley in western third Natural resources: :Hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
potential, arable land
Extreme points:
* North - river Rhine
The Rhine ( ) is one of the List of rivers of Europe, major rivers in Europe. The river begins in the Swiss canton of Graubünden in the southeastern Swiss Alps. It forms part of the Swiss-Liechtenstein border, then part of the Austria–Swit ...
, Ruggell
Ruggell (; dialectal: ''Ruggäll'') is a municipality of Liechtenstein. It is the northernmost and lowest elevated municipality. As of 2019, it has a population of 2,322.
History
Ruggell has an ancient history, with evidence of human activity pre ...
* South - summit of Mazorakopf/Falknishorn (2,452 m), Triesen
Triesen (; dialectal: ''Tresa'') is the third largest municipality in Liechtenstein. It contains several historic churches dating from the fifteenth century. It also has a weaving mill from 1863 that is considered a historical monument. The popu ...
* East - border post 28, above Nenzinger Himmel
* West - river Rhine, Balzers
Balzers () is a municipality and village located in southern Liechtenstein. In 2024, the village had a population of 4,806. The main part of the village is situated along the east bank of the Rhine.
History and culture
Historically, the present- ...
* highest - Vorder Grauspitz
The Grauspitz (''Vorder Grauspitze'' or ''Vorder Grauspitz'' on some maps) is a mountain in the Rätikon range of the Alps, located on the border between Liechtenstein and Switzerland. With an elevation of above sea level, the Grauspitz is the ...
(2,599 m), Triesen
Triesen (; dialectal: ''Tresa'') is the third largest municipality in Liechtenstein. It contains several historic churches dating from the fifteenth century. It also has a weaving mill from 1863 that is considered a historical monument. The popu ...
* lowest - Bangserfeld (429 m), Ruggell
Ruggell (; dialectal: ''Ruggäll'') is a municipality of Liechtenstein. It is the northernmost and lowest elevated municipality. As of 2019, it has a population of 2,322.
History
Ruggell has an ancient history, with evidence of human activity pre ...
Climate
Continental; cold, cloudy winters with frequent snow or rain; cool to moderately warm, cloudy, humid summers, great variety ofmicroclimates
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often slightly but sometimes substantially. The term may refer to areas as small as a few square meters or smaller (for ...
based on elevation.
Environment - international agreements
''Party to:''Air Pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
,
Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants,
Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides,
Air Pollution-Sulphur 85, Air Pollution-Sulphur 94,
Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds,
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the variability of life, life on Earth. It can be measured on various levels. There is for example genetic variability, species diversity, ecosystem diversity and Phylogenetics, phylogenetic diversity. Diversity is not distribut ...
,
Climate Change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
,
Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
The was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that global warming is occ ...
,
Desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
,
Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
,
Hazardous Wastes
Hazardous waste is waste that must be handled properly to avoid damaging human health or the environment. Waste can be hazardous because it is toxic, reacts violently with other chemicals, or is corrosive, among other traits. As of 2022, humani ...
,
Ozone Layer Protection,
Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
,
''Signed, but not ratified:''
Law of the Sea
Law of the sea (or ocean law) is a body of international law governing the rights and duties of State (polity), states in Ocean, maritime environments. It concerns matters such as navigational rights, sea mineral claims, and coastal waters juris ...
References
Lists of coordinates