Geography And Imperialism on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Geography (from
Qualitative Developmental Research Methods in Their Historical and Epistemological Contexts
FQS. Vol 7, No. 1, Art. 8 Common techniques include
 Geography is a systematic study of the Earth (other celestial bodies are specified, such as "geography of Mars", or given another name, such as
Geography is a systematic study of the Earth (other celestial bodies are specified, such as "geography of Mars", or given another name, such as
 For something to exist in the realm of geography, it must be able to be described spatially. Thus, space is the most fundamental concept at the foundation of geography. The concept is so basic, that geographers often have difficulty defining exactly what it is.
For something to exist in the realm of geography, it must be able to be described spatially. Thus, space is the most fundamental concept at the foundation of geography. The concept is so basic, that geographers often have difficulty defining exactly what it is.
 Time is usually thought to be within the domain of
Time is usually thought to be within the domain of
File:Línea de Wallace.jpg,
File:Spatial Contextual Awareness Fig 2.png, Cognitive geography
File:Qichwa conchucos 01.jpg,
Various approaches to the study of human geography have also arisen through time and include
File:Stourhead Pantheon.jpg,
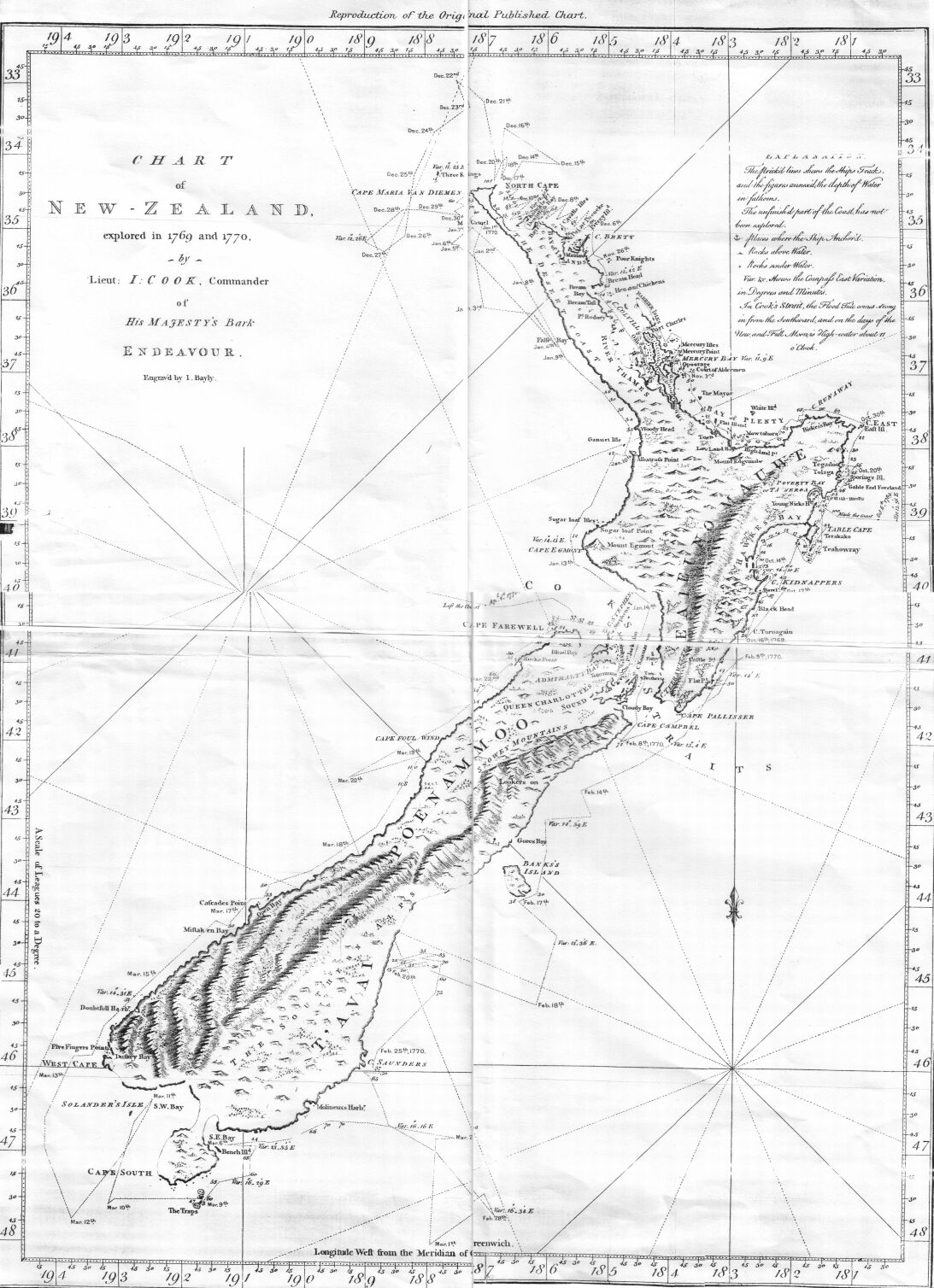 All geographic research and analysis start with asking the question "where," followed by "why there." Geographers start with the fundamental assumption set forth in Tobler's first law of geography, that "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
As spatial interrelationships are key to this synoptic science, maps are a key tool. Classical
All geographic research and analysis start with asking the question "where," followed by "why there." Geographers start with the fundamental assumption set forth in Tobler's first law of geography, that "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
As spatial interrelationships are key to this synoptic science, maps are a key tool. Classical
 Remote sensing is the art, science, and technology of obtaining information about Earth's features from measurements made at a distance. Remotely sensed data can be either passive, such as traditional
Remote sensing is the art, science, and technology of obtaining information about Earth's features from measurements made at a distance. Remotely sensed data can be either passive, such as traditional
 Qualitative cartography employs many of the same software and techniques as quantitative cartography. It may be employed to inform on map practices, or to visualize perspectives and ideas that are not strictly quantitative in nature. An example of a form of qualitative cartography is a
Qualitative cartography employs many of the same software and techniques as quantitative cartography. It may be employed to inform on map practices, or to visualize perspectives and ideas that are not strictly quantitative in nature. An example of a form of qualitative cartography is a
Deep Maps and Spatial Narratives
'. Indiana University Press. DOI: 10.2307/j.ctt1zxxzr2 This approach offers more inclusive strategies than more traditional cartographic approaches for connecting the complex layers that makeup places.
 The ideas of
The ideas of  During the
During the 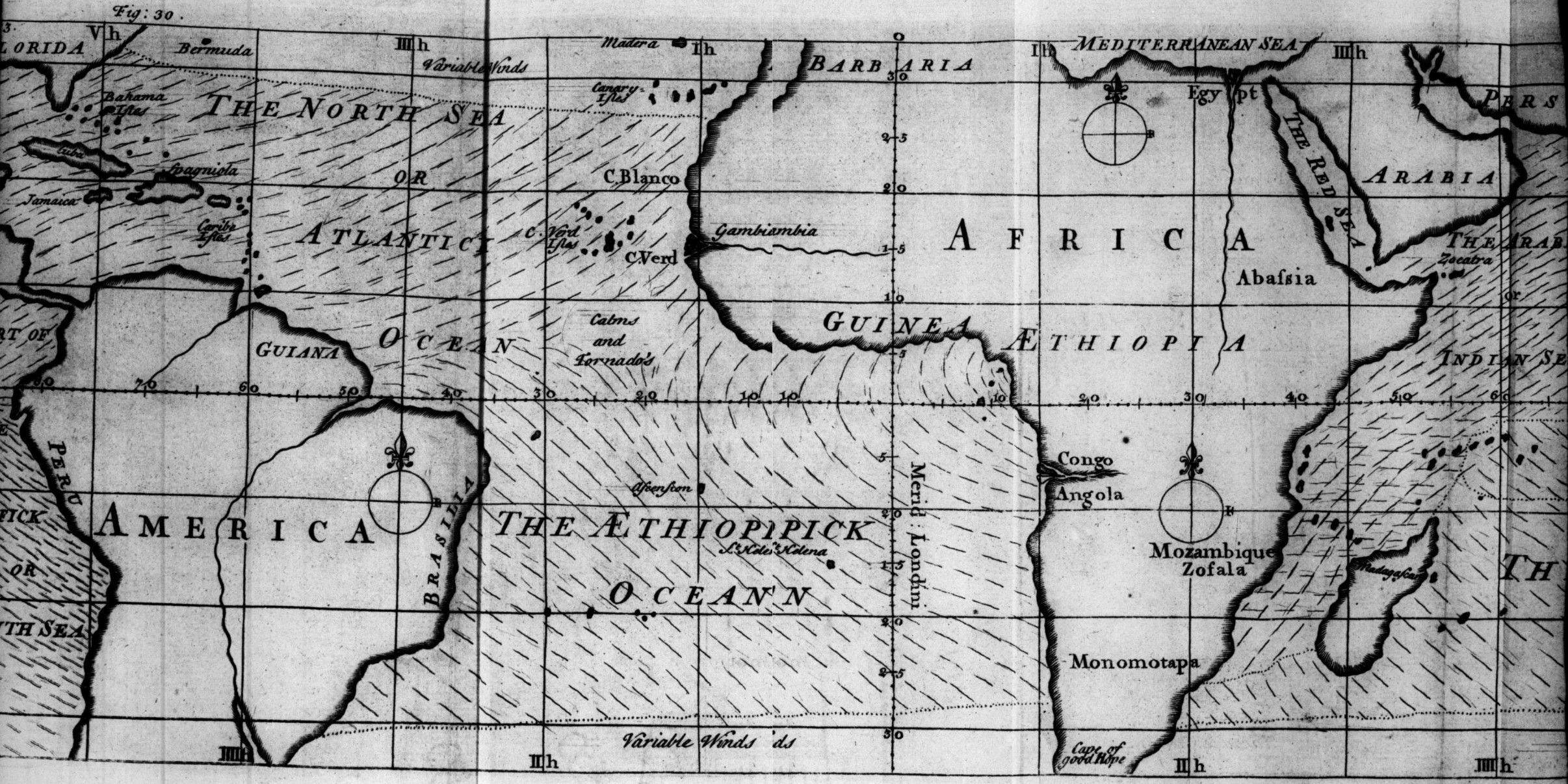 The European
The European  Over the past two centuries, the advancements in technology with computers have led to the development of
Over the past two centuries, the advancements in technology with computers have led to the development of
 The discipline of geography, especially physical geography, and geology have significant overlap. In the past, the two have often shared academic departments at universities, a point that has led to conflict over resources. Both disciplines do seek to understand the
The discipline of geography, especially physical geography, and geology have significant overlap. In the past, the two have often shared academic departments at universities, a point that has led to conflict over resources. Both disciplines do seek to understand the
 While the discipline of geography is normally concerned with the Earth, the term can also be informally used to describe the study of other worlds, such as the
While the discipline of geography is normally concerned with the Earth, the term can also be informally used to describe the study of other worlds, such as the
Geography
at the ''
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concept
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs.
Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, ...
s can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists within the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are of ...
in the field of planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of ...
. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science
Natural science or empirical science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer ...
and social science
Social science (often rendered in the plural as the social sciences) is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among members within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the ...
disciplines."
Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine, Islamic, and ...
(100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." However, the concepts of geography (such as cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
) date back to the earliest attempts to understand the world spatially, with the earliest example of an attempted world map dating to the 9th century BCE in ancient Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
. The history of geography
The History of geography includes many histories of geography which have differed over time and between different cultural and political groups. In more recent developments, geography has become a distinct academic discipline. 'Geography' derive ...
as a discipline spans cultures and millennia, being independently developed by multiple groups, and cross-pollinated by trade between these groups. The core concepts of geography consistent between all approaches are a focus on space, place, time, and scale. Today, geography is an extremely broad discipline with multiple approaches and modalities. There have been multiple attempts to organize the discipline, including the four traditions of geography, and into branches. Techniques employed can generally be broken down into quantitative
Quantitative may refer to:
* Quantitative research, scientific investigation of quantitative properties
* Quantitative analysis (disambiguation)
* Quantitative verse, a metrical system in poetry
* Statistics, also known as quantitative analysis
...
and qualitative approaches, with many studies taking mixed-methods approaches.Diriwächter, R. & Valsiner, J. (January 2006Qualitative Developmental Research Methods in Their Historical and Epistemological Contexts
FQS. Vol 7, No. 1, Art. 8 Common techniques include
cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
, remote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
, interview
An interview is a structured conversation where one participant asks questions, and the other provides answers.Merriam Webster DictionaryInterview Dictionary definition, Retrieved February 16, 2016 In common parlance, the word "interview" re ...
s, and surveying
Surveying or land surveying is the technique, profession, art, and science of determining the land, terrestrial Plane (mathematics), two-dimensional or Three-dimensional space#In Euclidean geometry, three-dimensional positions of Point (geom ...
.
Fundamentals
 Geography is a systematic study of the Earth (other celestial bodies are specified, such as "geography of Mars", or given another name, such as
Geography is a systematic study of the Earth (other celestial bodies are specified, such as "geography of Mars", or given another name, such as areography
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the di ...
in the case of Mars, or selenography
Selenography is the study of the surface and physical features of the Moon (also known as geography of the Moon, or selenodesy). Like geography and areography, selenography is a subdiscipline within the field of planetary science. Historically, ...
in the case of the Moon, or planetography for the general case), its features, and phenomena that take place on it. For something to fall into the domain of geography, it generally needs some sort of spatial component that can be placed on a map
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on ...
, such as coordinates
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the Position (geometry), position of the Point (geometry), points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as ...
, place names, or address
An address is a collection of information, presented in a mostly fixed format, used to give the location of a building, apartment, or other structure or a plot of land, generally using border, political boundaries and street names as references, ...
es. This has led to geography being associated with cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
and place names. Although many geographers are trained in toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage, and types. ''Toponym'' is the general term for a proper na ...
and cartology, this is not their main preoccupation. Geographers
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society, including how society and nature interacts. The Greek prefix "geo" means "earth" ...
study the Earth's spatial and temporal distribution of phenomena, processes, and features as well as the interaction of humans and their environment. Because space and place affect a variety of topics, such as economics, health, climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
, plants, and animals, geography is highly interdisciplinary. The interdisciplinary nature of the geographical approach depends on an attentiveness to the relationship between physical and human phenomena and their spatial patterns.
While narrowing down geography to a few key concepts is extremely challenging, and subject to tremendous debate within the discipline, several sources have approached the topic. The 1st edition of the book "Key Concepts in Geography" broke down this into chapters focusing on "Space," "Place," "Time," "Scale," and "Landscape." The 2nd edition of the book expanded on these key concepts by adding "Environmental systems," "Social Systems," "Nature," "Globalization
Globalization is the process of increasing interdependence and integration among the economies, markets, societies, and cultures of different countries worldwide. This is made possible by the reduction of barriers to international trade, th ...
," "Development," and "Risk," demonstrating how challenging narrowing the field can be. Another approach used extensively in teaching geography are the Five themes of geography established by "Guidelines for Geographic Education: Elementary and Secondary Schools," published jointly by the National Council for Geographic Education
The National Council for Geographic Education (NCGE), chartered in 1915, is a non-profit scientific and educational society in the United States that supports geography education.
History
George J. Miller, a professor at the Mankato Normal Sc ...
and the Association of American Geographers
The American Association of Geographers (AAG) is a non-profit scientific and educational society aimed at advancing the understanding, study, and importance of geography and related fields. Its headquarters is located in Washington, D.C. The ...
in 1984. These themes are Location, place, relationships within places (often summarized as Human-Environment Interaction), movement, and regions. The five themes of geography have shaped how American education approaches the topic in the years since.
Space
Absolute space
Absolute may refer to:
Companies
* Absolute Entertainment, a video game publisher
* Absolute Radio, (formerly Virgin Radio), independent national radio station in the UK
* Absolute Software Corporation, specializes in security and data risk mana ...
is the exact site, or spatial coordinates, of objects, persons, places, or phenomena under investigation. We exist in space. Absolute space leads to the view of the world as a photograph, with everything frozen in place when the coordinates were recorded. Today, geographers are trained to recognize the world as a dynamic space where all processes interact and take place, rather than a static image on a map.
Place
Place is one of the most complex and important terms in geography. In human geography, place is the synthesis of the coordinates on the Earth's surface, the activity and use that occurs, has occurred, and will occur at the coordinates, and the meaning ascribed to the space by human individuals and groups. This can be extraordinarily complex, as different spaces may have different uses at different times and mean different things to different people. In physical geography, a place includes all of the physical phenomena that occur in space, including thelithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to ch ...
, and biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
. Places do not exist in a vacuum and instead have complex spatial relationships with each other, and place is concerned how a location is situated in relation to all other locations. As a discipline then, the term place in geography includes all spatial phenomena occurring at a location, the diverse uses and meanings humans ascribe to that location, and how that location impacts and is impacted by all other locations on Earth. In one of Yi-Fu Tuan
Yi-Fu Tuan (; December 5, 1930 – August 10, 2022) was a Chinese-born American geographer and writer. He was one of the key figures in human geography and an important originator of humanistic geography.
Early life and education
Born in 193 ...
's papers, he explains that in his view, geography is the study of Earth as a home for humanity, and thus place and the complex meaning behind the term is central to the discipline of geography.
Time
 Time is usually thought to be within the domain of
Time is usually thought to be within the domain of history
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some t ...
, however, it is of significant concern in the discipline of geography. In physics, space and time are not separated, and are combined into the concept of spacetime
In physics, spacetime, also called the space-time continuum, is a mathematical model that fuses the three dimensions of space and the one dimension of time into a single four-dimensional continuum. Spacetime diagrams are useful in visualiz ...
.
Geography is subject to the laws of physics, and in studying things that occur in space, time must be considered. Time in geography is more than just the historical record of events that occurred at various discrete coordinates; but also includes modeling the dynamic movement of people, organisms, and things through space. Time facilitates movement through space, ultimately allowing things to flow through a system. The amount of time an individual, or group of people, spends in a place will often shape their attachment and perspective to that place. Time constrains the possible paths that can be taken through space, given a starting point, possible routes, and rate of travel. Visualizing time over space is challenging in terms of cartography, and includes Space-Prism, advanced 3D geovisualizations, and animated maps.
Scale
Scale in the context of a map is the ratio between a distance measured on the map and the corresponding distance as measured on the ground. This concept is fundamental to the discipline of geography, not just cartography, in that phenomena being investigated appear different depending on the scale used. Scale is the frame that geographers use to measure space, and ultimately to understand a place.Laws of geography
During the quantitative revolution, geography shifted to an empirical law-making (nomothetic
Nomothetic literally means "proposition of the law" (Greek derivation) and is used in philosophy, psychology, and law with differing meanings.
Etymology
In the general humanities usage, ''nomothetic'' may be used in the sense of "able to lay do ...
) approach. Several laws of geography have been proposed since then, most notably by Waldo Tobler
Waldo Rudolph Tobler (November 16, 1930 – February 20, 2018) was an United States, American-Switzerland, Swiss geographer and cartographer. Tobler is regarded as one of the most influential geographers and cartographers of the late 20th centur ...
and can be viewed as a product of the quantitative revolution. In general, some dispute the entire concept of laws in geography and the social sciences. These criticisms have been addressed by Tobler and others, such as Michael Frank Goodchild
Michael Frank Goodchild (born February 24, 1944) is a British-American geographer. He is an Emeritus Professor of Geography at the University of California, Santa Barbara. After nineteen years at the University of Western Ontario, including th ...
. However, this is an ongoing source of debate in geography and is unlikely to be resolved anytime soon. Several laws have been proposed, and Tobler's first law of geography is the most generally accepted in geography. Some have argued that geographic laws do not need to be numbered. The existence of a first invites a second, and many have proposed themselves as that. It has also been proposed that Tobler's first law of geography should be moved to the second and replaced with another. A few of the proposed laws of geography are below:
* Tobler's first law of geography: "Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant."
* Tobler's second law of geography
The second law of geography, according to Waldo Tobler, is " the phenomenon external to a geographic area of interest affects what goes on inside." This is an extension of his first. He first published it in 1999 in reply to a paper titled "Linear ...
: "The phenomenon external to a geographic area of interest affects what goes on inside."
* Arbia's law of geography
Arbia's law of geography states, "Everything is related to everything else, but things observed at a coarse spatial resolution are more related than things observed at a finer resolution." Originally proposed as the 2nd law of geography, this is ...
: "Everything is related to everything else, but things observed at a coarse spatial resolution are more related than things observed at a finer resolution."
* Spatial heterogeneity
Spatial heterogeneity is a property generally ascribed to a landscape or to a population. It refers to the uneven distribution of various concentrations of each species within an area. A landscape with spatial heterogeneity has a mix of concentra ...
: Geographic variables exhibit uncontrolled variance.
* The uncertainty principle: "That the geographic world is infinitely complex and that any representation must therefore contain elements of uncertainty, that many definitions used in acquiring geographic data contain elements of vagueness, and that it is impossible to measure location on the Earth's surface exactly."
Additionally, several variations or amendments to these laws exist within the literature, although not as well supported. For example, one paper proposed an amended version of Tobler's first law of geography, referred to in the text as the ''Tobler–von Thünen law'', which states: "Everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things, as a consequence of accessibility."
Sub-disciplines
Geography is a branch of inquiry that focuses on spatial information on Earth. It is an extremely broad topic and can be broken down multiple ways. There have been several approaches to doing this spanning at least several centuries, including "four traditions of geography" and into distinct branches. The Four traditions of geography are often used to divide the different historical approach theories geographers have taken to the discipline. In contrast, geography's branches describe contemporary applied geographical approaches.Four traditions
Geography is an extremely broad field. Because of this, many view the various definitions of geography proposed over the decades as inadequate. To address this, William D. Pattison proposed the concept of the "Four traditions of Geography" in 1964. These traditions are the Spatial or Locational Tradition, the Man-Land or Human-Environment Interaction Tradition (sometimes referred to asIntegrated geography
Integrated geography (also referred to as integrative geography, environmental geography or human–environment geography) is where the branches of human geography and physical geography overlap to describe and explain the spatial aspects of inte ...
), the Area Studies
Area studies, also known as regional studies, is an interdisciplinary field of research and scholarship pertaining to particular geographical, national/ federal, or cultural regions. The term exists primarily as a general description for what a ...
or Regional
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as areas, zones, lands or territories, are portions of the Earth's surface that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and ...
Tradition, and the Earth Science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
Tradition. These concepts are broad sets of geography philosophies bound together within the discipline. They are one of many ways geographers organize the major sets of thoughts and philosophies within the discipline.
Branches
In another approach to the abovementioned four traditions, geography is organized into applied branches. The UNESCOEncyclopedia of Life Support Systems The Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS) is an integrated compendium of twenty one encyclopedias.
One of the largest database repositories on the web, dedicated to the health, maintenance and future of the web of life on planet Earth, focu ...
organizes geography into the three categories of human geography
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography which studies spatial relationships between human communities, cultures, economies, and their interactions with the environment, examples of which include urban sprawl and urban ...
, physical geography
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, h ...
, and technical geography
Technical geography is the branch of geography that involves using, studying, and creating tools to obtain, analyze, interpret, understand, and communicate spatial information.
The other branches of geography, most commonly limited to human geo ...
. Some publications limit the number of branches to physical and human, describing them as the principal branches. Human geography largely focuses on the built environment
The term built environment refers to human-made conditions and is often used in architecture, landscape architecture, urban planning, public health, sociology, and anthropology, among others. These curated spaces provide the setting for human ac ...
and how humans create, view, manage, and influence space. Human geographers study people and their communities, cultures, economies, and environmental interactions by studying their relations with and across space and place. Physical geography examines the natural environment and how organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
s, climate, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
, water, and landform
A landform is a land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. They may be natural or may be anthropogenic (caused or influenced by human activity). Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement ...
s produce and interact, studying spatial patterns in the natural environment, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to ch ...
, biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
, and geosphere
There are several conflicting usages of geosphere, variously defined.
In Aristotelian physics, the term was applied to four spherical ''natural places'', concentrically nested around the center of the Earth, as described in the lectures '' Ph ...
. The difference between these approaches led to the development of integrated geography
Integrated geography (also referred to as integrative geography, environmental geography or human–environment geography) is where the branches of human geography and physical geography overlap to describe and explain the spatial aspects of inte ...
, which combines physical and human geography and concerns the interactions between the environment and humans. Technical geography involves studying and developing the tools and techniques used by geographers, such as remote sensing, cartography, and geographic information system. Technical geography
Technical geography is the branch of geography that involves using, studying, and creating tools to obtain, analyze, interpret, understand, and communicate spatial information.
The other branches of geography, most commonly limited to human geo ...
is interested in studying and applying techniques and methods to store, process, analyze, visualize, and use spatial data. It is the newest of the branches, the most controversial, and often other terms are used in the literature to describe the emerging category. These branches use similar geographic philosophies, concepts, and tools and often overlap significantly. Geographers rarely focus on just one of these topics, often using one as their primary focus and then incorporating data and methods from the other branches. Often, geographers are asked to describe what they do by individuals outside the discipline and are likely to identify closely with a specific branch, or sub-branch when describing themselves to lay people.
Physical
Physical geography (or physiography) focuses on geography as anEarth science
Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres ...
. It aims to understand the physical problems and the issues of lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the lithospheric mantle, the topmost portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time ...
, hydrosphere
The hydrosphere () is the combined mass of water found on, under, and above the Planetary surface, surface of a planet, minor planet, or natural satellite. Although Earth's hydrosphere has been around for about 4 billion years, it continues to ch ...
, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, pedosphere
The pedosphere () is the Earth's crust, outermost layer of the Earth that is composed of soil and subject to soil formation processes. It exists at the interface of the lithosphere, Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere, hydrosphere and biosphere. The ...
, and global flora
Flora (: floras or florae) is all the plant life present in a particular region or time, generally the naturally occurring (indigenous (ecology), indigenous) native plant, native plants. The corresponding term for animals is ''fauna'', and for f ...
and fauna
Fauna (: faunae or faunas) is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding terms for plants and fungi are ''flora'' and '' funga'', respectively. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively ...
patterns (biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
). Physical geography is the study of earth's seasons, climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
, atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gases that envelop an astronomical object, held in place by the gravity of the object. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A stellar atmosph ...
, soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by re ...
, streams, landforms, and oceans. Physical geographers will often work in identifying and monitoring the use of natural resources.
Biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the species distribution, distribution of species and ecosystems in geography, geographic space and through evolutionary history of life, geological time. Organisms and biological community (ecology), communities o ...
File:Cyclone Catarina from the ISS on March 26 2004.JPG, Climatology
Climatology (from Greek , ''klima'', "slope"; and , '' -logia'') or climate science is the scientific study of Earth's climate, typically defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of at least 30 years. Climate concerns the atmospher ...
and meteorology
Meteorology is the scientific study of the Earth's atmosphere and short-term atmospheric phenomena (i.e. weather), with a focus on weather forecasting. It has applications in the military, aviation, energy production, transport, agricultur ...
File:90 mile beach.jpg, Coastal geography
Coastal geography is the study of the constantly changing region between the ocean and the land, incorporating both the physical geography (i.e. coastal geomorphology, climatology and oceanography) and the human geography (sociology and history) ...
File:Gavin Plant.JPG, Environmental management
Environmental resource management or environmental management is the management of the interaction and impact of human societies on the environment. It is not, as the phrase might suggest, the management of the environment itself. Environment ...
File:Delicate Arch LaSalle.jpg, Geomorphology
Geomorphology () is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features generated by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or near Earth's surface. Geomorphologists seek to understand wh ...
File:Receding glacier-en.svg, Glaciology
Glaciology (; ) is the scientific study of glaciers, or, more generally, ice and natural phenomena that involve ice.
Glaciology is an interdisciplinary Earth science that integrates geophysics, geology, physical geography, geomorphology, clim ...
File:Meander.svg, Hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydro ...
and hydrography
Hydrography is the branch of applied sciences which deals with the measurement and description of the physical features of oceans, seas, coastal areas, lakes and rivers, as well as with the prediction of their change over time, for the primary ...
File:Khajuraho-landscape.jpg, Landscape ecology
Landscape ecology is the science of studying and improving relationships between ecological processes in the environment and particular ecosystems. This is done within a variety of landscape scales, development spatial patterns, and organizatio ...
File:World11.jpg, Oceanography
Oceanography (), also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the ocean, including its physics, chemistry, biology, and geology.
It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of to ...
File:Pangea interpretacion.png, alt=a view of the supercontinent of pangea breaking up, Palaeogeography
Palaeogeography (or paleogeography) is the study of historical geography, generally physical landscapes. Palaeogeography can also include the study of human or cultural environments. When the focus is specifically on landforms, the term pale ...
File:Soil profile.jpg, Pedology
Pedology (from Greek: πέδον, ''pedon'', "soil"; and λόγος, ''logos'', "study") is a discipline within soil science which focuses on understanding and characterizing soil formation, evolution, and the theoretical frameworks for modelin ...
File:Milankovitch Variations sv.png, Quaternary science
Quaternary science is the subfield of geology which studies the Quaternary Period commonly known as the ice age. The Quaternary Period is a time period that started around 2.58 million years ago and continues today. This period is divided in ...
Human
Human geography (or anthropogeography) is a branch of geography that focuses on studying patterns and processes that shape human society. It encompasses the human, political,cultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
, social, and economic aspects. In industry, human geographers often work in city planning, public health, or business analysis.
Cultural geography
Cultural geography is a subfield within human geography. Though the first traces of the study of different nations and cultures on Earth can be dated back to ancient geographers such as Ptolemy or Strabo, cultural geography as academic study fir ...
File:Pepsi in India.jpg, Development geography
Development geography is a branch of geography which refers to the standard of living and its quality of life of its human inhabitants. In this context, development is a process of change that affects peoples' lives. It may involve an improvement ...
File:Christaller model 1.jpg, Economic geography
Economic geography is the subfield of human geography that studies economic activity and factors affecting it. It can also be considered a subfield or method in economics.
Economic geography takes a variety of approaches to many different topi ...
File:Star of life.svg, Health geography
Health geography is the application of geographical information, perspectives, and methods to the study of health, disease, and health care. Medical geography, a sub-discipline of, or sister field of health geography, Oxford Bibliographies entry ...
File:British Empire 1897.jpg, Historical geography
Historical geography is the branch of geography that studies the ways in which geographic phenomena have changed over time. In its modern form, it is a synthesizing discipline which shares both topical and methodological similarities with histor ...
File:Internet map 1024 - transparent, inverted.png , Internet geography
File:UN General Assembly.jpg, Political geography
Political geography is concerned with the study of both the spatially uneven outcomes of political processes and the ways in which political processes are themselves affected by spatial structures. Conventionally, for the purposes of analysis, ...
and Geopolitics
Geopolitics () is the study of the effects of Earth's geography on politics and international relations. Geopolitics usually refers to countries and relations between them, it may also focus on two other kinds of State (polity), states: ''de fac ...
File:Pyramide Comores.PNG, Population geography
Population geography is the study of the distribution, composition, migration, and growth of human populations in relation to the geographic characteristics of specific area. It focuses on how populations are distributed across space, the facto ...
or Demography
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analysis examine ...
File:ReligionSymbol.svg, Religion geography
File:US-hoosier-family.jpg, Social geography
Social geography is the branch of human geography that is interested in the relationships between society and space, and is most closely related to social theory in general and sociology in particular, dealing with the relation of social phenome ...
File:Gare du Nord USFRT (Paris Metro).png, Transportation geography
Transport geography or transportation geography is a branch of geography that investigates the movement and connections between people, goods and information on the Earth's surface.
Aims and scope
Transportation geography detects, describes, and ...
File:Tourists-2.jpg, Tourism geography
Tourism geography is the study of travel and tourism, as an industry and as a social and cultural activity. Tourism geography covers a wide range of interests including the environmental impact of tourism, the geographies of tourism and leisure ...
File:Empire State Building - Flickr id 22550357694.jpg, Urban geography
Urban geography is the subdiscipline of geography that derives from a study of cities and urban processes. Urban geographers and urbanists examine various aspects of urban life and the built environment. Scholars, activists, and the public have ...
behavioral geography
Behavioral geography is an approach to human geography that examines human behavior by separating it into different parts. In addition, behavioral geography is an ideology/approach in human geography that makes use of the methods and assumptions ...
, culture theory
Culture theory is the branch of comparative anthropology and semiotics that seeks to define the heuristic concept of culture in operational and/or scientific terms.
Overview
In the 19th century, "culture" was used by some to refer to a wide a ...
, feminist geography
Feminist geography is a sub-discipline of human geography that applies the theories, methods, and critiques of feminism to the study of the human environment, society, and geographical space. Feminist geography emerged in the 1970s, when members ...
, and geosophy
Geosophy is a concept introduced to geography by J.K. Wright in 1947. The word is a compound of ‘geo’ (Greek for earth) and ‘sophia’ (Greek for wisdom). Wright defined it thus:
:Geosophy ... is the study of geographical knowledge from an ...
.
Technical
Technical geography concerns studying and developing tools, techniques, and statistical methods employed to collect, analyze, use, and understand spatial data. Technical geography is the most recently recognized, and controversial, of the branches. Its use dates back to 1749, when a book published byEdward Cave
Edward Cave (27 February 1691 – 10 January 1754) was an English printer, editor and publisher. He coined the term "magazine" for a periodical, founding ''The Gentleman's Magazine'' in 1731, and was the first publisher to successfully fashi ...
organized the discipline into a section containing content such as cartographic techniques and globes. There are several other terms, often used interchangeably with technical geography to subdivide the discipline, including "techniques of geographic analysis," "Geographic Information Technology," "Geography method's and techniques," "Geographic Information Science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represe ...
," "geoinformatics
Geoinformatics is a scientific field primarily within the domains of Computer Science and technical geography. It focuses on the programming of applications, spatial data structures, and the analysis of objects and space-time phenomena relate ...
," "geomatics
Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under another definition, it ...
," and "information geography". There are subtle differences to each concept and term; however, technical geography is one of the broadest, is consistent with the naming convention of the other two branches, has been in use since the 1700s, and has been used by the UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO ) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) with the aim of promoting world peace and International secur ...
Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems The Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS) is an integrated compendium of twenty one encyclopedias.
One of the largest database repositories on the web, dedicated to the health, maintenance and future of the web of life on planet Earth, focu ...
to divide geography into themes. As academic fields increasingly specialize in their nature, technical geography has emerged as a branch of geography specializing in geographic methods and thought. The emergence of technical geography has brought new relevance to the broad discipline of geography by serving as a set of unique methods for managing the interdisciplinary nature of the phenomena under investigation. While human and physical geographers use the techniques employed by technical geographers, technical geography is more concerned with the fundamental spatial concepts and technologies than the nature of the data. It is therefore closely associated with the spatial tradition of geography while being applied to the other two major branches. A technical geographer might work as a GIS analyst, a GIS developer working to make new software tools, or create general reference maps incorporating human and natural features.
Geodesign
Geodesign is a set of concepts and methods used to involve all stakeholders and various professions in collaboratively designing and realizing the optimal solution for spatial challenges in the built and natural environments, utilizing all availa ...
File:Meridian convergence and spehrical excess.png, Geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional spac ...
File:Worldwind.png, Geoinformatics
Geoinformatics is a scientific field primarily within the domains of Computer Science and technical geography. It focuses on the programming of applications, spatial data structures, and the analysis of objects and space-time phenomena relate ...
File:Fig 4.4.png, Geographic information science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represe ...
File:Survey instruments-2.png, Geomatics
Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under another definition, it ...
File:gislayers.jpg, Geovisualization
Geovisualization or geovisualisation (short for geographic visualization), also known as cartographic visualization, refers to a set of tools and techniques supporting the analysis of geospatial data through the use of interactive visualization.
...
File:Euclidean Voronoi diagram.svg, Statistical geography
Statistical geography is the study and practice of collecting, analysing and presenting data that has a geographic or areal dimension, such as census or demographics data. It uses techniques from spatial analysis, but also encompasses geographica ...
File:Example_krig.png, Spatial analysis
Spatial analysis is any of the formal Scientific technique, techniques which study entities using their topological, geometric, or geographic properties, primarily used in Urban design, Urban Design. Spatial analysis includes a variety of techni ...
File:Sample of time geographical description.png, Time geography
Time geography or time-space geography is an evolving transdisciplinary perspective on spatial and temporal processes and events such as social interaction, ecological interaction, social and environmental change, and biographies of individuals. ...
Methods
 All geographic research and analysis start with asking the question "where," followed by "why there." Geographers start with the fundamental assumption set forth in Tobler's first law of geography, that "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
As spatial interrelationships are key to this synoptic science, maps are a key tool. Classical
All geographic research and analysis start with asking the question "where," followed by "why there." Geographers start with the fundamental assumption set forth in Tobler's first law of geography, that "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things."
As spatial interrelationships are key to this synoptic science, maps are a key tool. Classical cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
has been joined by a more modern approach to geographical analysis, computer-based geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data ...
s (GIS).
In their study, geographers use four interrelated approaches:
* Analytical – Asks ''why'' we find features and populations in a specific geographic area.
* Descriptive – Simply specifies the locations of features and populations.
* Regional – Examines systematic relationships between categories for a specific region or location on the planet.
* Systematic – Groups geographical knowledge into categories that can be explored globally.
Quantitative methods
Quantitative methods in geography became particularly influential in the discipline during the quantitative revolution of the 1950s and 60s. These methods revitalized the discipline in many ways, allowing scientific testing of hypotheses and proposing scientific geographic theories and laws. The quantitative revolution heavily influenced and revitalized technical geography, and lead to the development of the subfield of quantitative geography.Quantitative cartography
Cartography is the art, science, and technology of making maps. Cartographers study the Earth's surface representation with abstract symbols (map making). Although other subdisciplines of geography rely on maps for presenting their analyses, the actual making of maps is abstract enough to be regarded separately. Cartography has grown from a collection of drafting techniques into an actual science. Cartographers must learncognitive psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of human mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning.
Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, whi ...
and ergonomics
Ergonomics, also known as human factors or human factors engineering (HFE), is the application of Psychology, psychological and Physiology, physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Primary goa ...
to understand which symbols convey information about the Earth most effectively and behavioural psychology
Behaviorism is a systematic approach to understand the behavior of humans and other animals. It assumes that behavior is either a reflex elicited by the pairing of certain antecedent stimuli in the environment, or a consequence of that individ ...
to induce the readers of their maps to act on the information. They must learn geodesy
Geodesy or geodetics is the science of measuring and representing the Figure of the Earth, geometry, Gravity of Earth, gravity, and Earth's rotation, spatial orientation of the Earth in Relative change, temporally varying Three-dimensional spac ...
and fairly advanced mathematics to understand how the shape of the Earth
In geodesy, the figure of the Earth is the size and shape used to model planet Earth. The kind of figure depends on application, including the precision needed for the model. A spherical Earth is a well-known historical approximation that is s ...
affects the distortion of map symbols projected onto a flat surface for viewing. It can be said, without much controversy, that cartography is the seed from which the larger field of geography grew.
Geographic information systems
Geographic information systems (GIS) deal with storing information about the Earth for automatic retrieval by a computer in an accurate manner appropriate to the information's purpose. In addition to all of the other subdisciplines of geography, GIS specialists must understandcomputer science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, ...
and database
In computing, a database is an organized collection of data or a type of data store based on the use of a database management system (DBMS), the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and a ...
systems. GIS has revolutionized the field of cartography: nearly all mapmaking is now done with the assistance of some form of GIS software
A GIS software program is a computer program to support the use of a geographic information system, providing the ability to create, store, manage, query, Spatial analysis, analyze, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data and informati ...
. The science of using GIS software and GIS techniques to represent, analyse, and predict the spatial relationships is called ''geographic information science
Geographic information science (GIScience, GISc) or geoinformation science is a scientific discipline at the crossroads of computational science, social science, and natural science that studies geographic information, including how it represe ...
'' (GISc).
Remote sensing
 Remote sensing is the art, science, and technology of obtaining information about Earth's features from measurements made at a distance. Remotely sensed data can be either passive, such as traditional
Remote sensing is the art, science, and technology of obtaining information about Earth's features from measurements made at a distance. Remotely sensed data can be either passive, such as traditional photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
, or active, such as LiDAR
Lidar (, also LIDAR, an acronym of "light detection and ranging" or "laser imaging, detection, and ranging") is a method for determining ranging, ranges by targeting an object or a surface with a laser and measuring the time for the reflected li ...
. A variety of platforms can be used for remote sensing, including satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell im ...
, aerial photography
Aerial photography (or airborne imagery) is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other flight, airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.
Platforms for aerial photography include fixed-wi ...
(including consumer drones), and data obtained from hand-held sensors. Products from remote sensing include Digital elevation model
A digital elevation model (DEM) or digital surface model (DSM) is a 3D computer graphics representation of elevation data to represent terrain or overlaying objects, commonly of a planet, Natural satellite, moon, or asteroid. A "global DEM" refer ...
and cartographic base maps. Geographers increasingly use remotely sensed data to obtain information about the Earth's land surface
Terrain (), alternatively relief or topographical relief, is the dimension and shape of a given surface of land. In physical geography, terrain is the lay of the land. This is usually expressed in terms of the elevation, slope, and orientati ...
, ocean, and atmosphere, because it: (a) supplies objective information at a variety of spatial scales (local to global), (b) provides a synoptic view of the area of interest, (c) allows access to distant and inaccessible sites, (d) provides spectral information outside the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the full range of electromagnetic radiation, organized by frequency or wavelength. The spectrum is divided into separate bands, with different names for the electromagnetic waves within each band. From low to high ...
, and (e) facilitates studies of how features/areas change over time. Remotely sensed data may be analyzed independently or in conjunction with other digital data layers (e.g., in a geographic information system). Remote sensing aids in land use, land cover (LULC) mapping, by helping to determine both what is naturally occurring on a piece of land and what human activities are taking place on it.
Geostatistics
Geostatistics
Geostatistics is a branch of statistics focusing on spatial or spatiotemporal datasets. Developed originally to predict probability distributions of ore grades for mining operations, it is currently applied in diverse disciplines including pet ...
deal with quantitative data
Quantitative research is a research strategy that focuses on quantifying the collection and analysis of data. It is formed from a deductive approach where emphasis is placed on the testing of theory, shaped by empiricist and positivist philoso ...
analysis, specifically the application of a statistical methodology to the exploration of geographic phenomena. Geostatistics is used extensively in a variety of fields, including hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and drainage basin sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is called a hydro ...
, geology, petroleum exploration, weather analysis, urban planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportatio ...
, logistics, and epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
. The mathematical basis for geostatistics derives from cluster analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the data analyzing technique in which task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more Similarity measure, similar (in some specific sense defined by the ...
, linear discriminant analysis
Linear discriminant analysis (LDA), normal discriminant analysis (NDA), canonical variates analysis (CVA), or discriminant function analysis is a generalization of Fisher's linear discriminant, a method used in statistics and other fields, to fi ...
and non-parametric statistical tests, and a variety of other subjects. Applications of geostatistics rely heavily on geographic information system
A geographic information system (GIS) consists of integrated computer hardware and Geographic information system software, software that store, manage, Spatial analysis, analyze, edit, output, and Cartographic design, visualize Geographic data ...
s, particularly for the interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
(estimate) of unmeasured points. Geographers are making notable contributions to the method of quantitative techniques.
Qualitative methods
Qualitative methods in geography are descriptive rather than numerical or statistical in nature. They add context to concepts, and explore human concepts like beliefs and perspective that are difficult or impossible to quantify. Human geography is much more likely to employ qualitative methods than physical geography. Increasingly, technical geographers are attempting to employ GIS methods to qualitative datasets.Qualitative cartography
Chorochromatic map
A Chorochromatic map (), also known as an area-class, Qualitative data, qualitative area, or mosaic map, is a type of thematic map that portray regions of categorical or nominal data using variations in color Map symbol, symbols. Chorochromatic ...
of nominal data, such as land cover or dominant language group in an area. Another example is a deep map
A deep map is a map with greater information than a two-dimensional image of places, names, and topography.
One such kind of intensive exploration of place was popularised by author William Least Heat-Moon with his book ''PrairyErth: A Deep Ma ...
, or maps that combine geography and storytelling to produce a product with greater information than a two-dimensional image of places, names, and topography.Bodenhamer, David J.; John Corrigan; Trevor M. Harris. 2015. Deep Maps and Spatial Narratives
'. Indiana University Press. DOI: 10.2307/j.ctt1zxxzr2 This approach offers more inclusive strategies than more traditional cartographic approaches for connecting the complex layers that makeup places.
Ethnography
Ethnographical research techniques are used by human geographers. Incultural geography
Cultural geography is a subfield within human geography. Though the first traces of the study of different nations and cultures on Earth can be dated back to ancient geographers such as Ptolemy or Strabo, cultural geography as academic study fir ...
, there is a tradition of employing qualitative research
Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This ...
techniques, also used in anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, society, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including archaic humans. Social anthropology studies patterns of behav ...
and sociology. Participant observation
Participant observation is one type of data collection method by practitioner-scholars typically used in qualitative research and ethnography. This type of methodology is employed in many disciplines, particularly anthropology (including cultur ...
and in-depth interviews provide human geographers with qualitative data.
Geopoetics
Geopoetics is an interdisciplinary approach that combines geography andpoetry
Poetry (from the Greek language, Greek word ''poiesis'', "making") is a form of literature, literary art that uses aesthetics, aesthetic and often rhythmic qualities of language to evoke meaning (linguistics), meanings in addition to, or in ...
to explore the interconnectedness between humans, space, place, and the environment. Geopoetics is employed as a mixed methods
Multimethodology or multimethod research includes the use of more than one method of data collection or research in a research study or set of related studies. Mixed methods research is more specific in that it includes the mixing of qualitative ...
tool to explain the implications of geographic research. It is often employed to address and communicate the implications of complex topics, such as the anthropocene
''Anthropocene'' is a term that has been used to refer to the period of time during which human impact on the environment, humanity has become a planetary force of change. It appears in scientific and social discourse, especially with respect to ...
.
Interviews
Geographers employ interviews to gather data and acquire valuable understandings from individuals or groups regarding their encounters, outlooks, and opinions concerning spatial phenomena. Interviews can be carried out through various mediums, including face-to-face interactions, phone conversations, online platforms, or written exchanges. Geographers typically adopt a structured or semi-structured approach during interviews involving specific questions or discussion points when utilized for research purposes. These questions are designed to extract focused information about the research topic while being flexible enough to allow participants to express their experiences and viewpoints, such as through open-ended questions.Origin and history
The concept of geography is present in all cultures, and therefore the history of the discipline is a series of competing narratives, with concepts emerging at various points across space and time. The oldest knownworld map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of t ...
s date back to ancient Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-sp ...
from the 9th century BC. The best known Babylonia
Babylonia (; , ) was an Ancient history, ancient Akkadian language, Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Kuwait, Syria and Iran). It emerged as a ...
n world map, however, is the ''Imago Mundi
''Imago Mundi'' ( ), or in full ''Imago Mundi: International Journal for the History of Cartography'', is a semiannual peer-reviewed academic journal about mapping, established in 1935 by Leo Bagrow. It covers the history of early maps, cartogra ...
'' of 600 BC. The map as reconstructed by Eckhard Unger
Eckhard Unger ( Landsberg an der Warthe, 11 April 1884 – 24 July 1966) was a German assyriologist.
Unger who was the curator of the Istanbul museum described the remains of Balawat Gates that are still in the Istanbul Museum. Unger was fully ...
shows Babylon
Babylon ( ) was an ancient city located on the lower Euphrates river in southern Mesopotamia, within modern-day Hillah, Iraq, about south of modern-day Baghdad. Babylon functioned as the main cultural and political centre of the Akkadian-s ...
on the Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
, surrounded by a circular landmass showing Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
, Urartu
Urartu was an Iron Age kingdom centered around the Armenian highlands between Lake Van, Lake Urmia, and Lake Sevan. The territory of the ancient kingdom of Urartu extended over the modern frontiers of Turkey, Iran, Iraq, and Armenia.Kleiss, Wo ...
, and several cities, in turn surrounded by a "bitter river" (Oceanus
In Greek mythology, Oceanus ( ; , also , , or ) was a Titans, Titan son of Uranus (mythology), Uranus and Gaia, the husband of his sister the Titan Tethys (mythology), Tethys, and the father of the River gods (Greek mythology), river gods ...
), with seven islands arranged around it so as to form a seven-pointed star. The accompanying text mentions seven outer regions beyond the encircling ocean. The descriptions of five of them have survived. In contrast to the ''Imago Mundi'', an earlier Babylonian world map
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of Earth. World maps, because of their scale, must deal with the problem of projection. Maps rendered in two dimensions by necessity distort the display of the three-dimensional surface of t ...
dating back to the 9th century BC depicted Babylon as being further north from the center of the world, though it is not certain what that center was supposed to represent.
 The ideas of
The ideas of Anaximander
Anaximander ( ; ''Anaximandros''; ) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Ancient Greek philosophy, Greek philosopher who lived in Miletus,"Anaximander" in ''Chambers's Encyclopædia''. London: George Newnes Ltd, George Newnes, 1961, Vol. ...
(c. 610–545 BC): considered by later Greek writers to be the true founder of geography, come to us through fragments quoted by his successors. Anaximander is credited with the invention of the gnomon
A gnomon (; ) is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields, typically to measure directions, position, or time.
History
A painted stick dating from 2300 BC that was ...
, the simple, yet efficient Greek instrument that allowed the early measurement of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
. Thales
Thales of Miletus ( ; ; ) was an Ancient Greek philosophy, Ancient Greek Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic Philosophy, philosopher from Miletus in Ionia, Asia Minor. Thales was one of the Seven Sages of Greece, Seven Sages, founding figure ...
is also credited with the prediction of eclipses. The foundations of geography can be traced to ancient cultures, such as the ancient, medieval, and early modern Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
. The Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, who were the first to explore geography as both art and science, achieved this through Cartography
Cartography (; from , 'papyrus, sheet of paper, map'; and , 'write') is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an imagined reality) can ...
, Philosophy
Philosophy ('love of wisdom' in Ancient Greek) is a systematic study of general and fundamental questions concerning topics like existence, reason, knowledge, Value (ethics and social sciences), value, mind, and language. It is a rational an ...
, and Literature
Literature is any collection of Writing, written work, but it is also used more narrowly for writings specifically considered to be an art form, especially novels, Play (theatre), plays, and poetry, poems. It includes both print and Electroni ...
, or through Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
. There is some debate about who was the first person to assert that the Earth is spherical in shape, with the credit going either to Parmenides
Parmenides of Elea (; ; fl. late sixth or early fifth century BC) was a Pre-Socratic philosophy, pre-Socratic ancient Greece, Greek philosopher from Velia, Elea in Magna Graecia (Southern Italy).
Parmenides was born in the Greek colony of Veli ...
or Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of P ...
. Anaxagoras
Anaxagoras (; , ''Anaxagóras'', 'lord of the assembly'; ) was a Pre-Socratic Greek philosopher. Born in Clazomenae at a time when Asia Minor was under the control of the Persian Empire, Anaxagoras came to Athens. In later life he was charged ...
was able to demonstrate that the profile of the Earth was circular by explaining eclipse
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three ...
s. However, he still believed that the Earth was a flat disk, as did many of his contemporaries. One of the first estimates of the radius of the Earth was made by Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; ; – ) was an Ancient Greek polymath: a Greek mathematics, mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theory, music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of A ...
.
The first rigorous system of latitude and longitude
A geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or geodetic coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest, and most widely used type of the various ...
lines is credited to Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; , ; BC) was a Ancient Greek astronomy, Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hippar ...
. He employed a sexagesimal
Sexagesimal, also known as base 60, is a numeral system with 60 (number), sixty as its radix, base. It originated with the ancient Sumerians in the 3rd millennium BC, was passed down to the ancient Babylonians, and is still used—in a modified fo ...
system that was derived from Babylonian mathematics
Babylonian mathematics (also known as Assyro-Babylonian mathematics) is the mathematics developed or practiced by the people of Mesopotamia, as attested by sources mainly surviving from the Old Babylonian period (1830–1531 BC) to the Seleucid ...
. The meridians were subdivided into 360°, with each degree further subdivided into 60 (minutes
Minutes, also known as minutes of meeting, protocols or, informally, notes, are the instant written record of a meeting or hearing. They typically describe the events of the meeting and may include a list of attendees, a statement of the activit ...
). To measure the longitude at different locations on Earth, he suggested using eclipses to determine the relative difference in time. The extensive mapping by the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
as they explored new lands would later provide a high level of information for Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
to construct detailed atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of world map, maps of Earth or of a continent or region of Earth. Advances in astronomy have also resulted in atlases of the celestial sphere or of other planets.
Atlases have traditio ...
es. He extended the work of Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; , ; BC) was a Ancient Greek astronomy, Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hippar ...
, using a grid system on his maps and adopting a length of 56.5 miles for a degree.
From the 3rd century onwards, Chinese
Chinese may refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people identified with China, through nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**Han Chinese, East Asian ethnic group native to China.
**'' Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic ...
methods of geographical study and writing of geographical literature became much more comprehensive than what was found in Europe at the time (until the 13th century). Chinese geographers such as Liu An
Liú Ān (, c. 179–122 BC) was a Chinese cartographer, monarch, and philosopher. A Han dynasty Chinese prince, ruling the Huainan Kingdom, and an advisor to his nephew, Emperor Wu of Han (武帝). He is best known for editing the (139 BC) ''Hu ...
, Pei Xiu
Pei Xiu (224–3 April 271), courtesy name Jiyan, was a Chinese cartographer, geographer, politician, and writer of the state of Cao Wei during the late Three Kingdoms period and Jin dynasty (265–420), Jin dynasty of China. He was very m ...
, Jia Dan Jia Dan (, 730 – 805), courtesy name Dunshi () and formally Duke Yuanjing of Wei (), was a Chinese cartographer, military general, and politician from Cangzhou, Hebei during the Tang dynasty.
Background
Jia Dan was born in 730, during the reign ...
, Shen Kuo
Shen Kuo (; 1031–1095) or Shen Gua, courtesy name Cunzhong (存中) and Art name#China, pseudonym Mengqi (now usually given as Mengxi) Weng (夢溪翁),Yao (2003), 544. was a Chinese polymath, scientist, and statesman of the Song dynasty (960� ...
, Fan Chengda Fan Chengda (, 1126–1193), courtesy name Zhineng (), was a Chinese geographer, poet, and politician. One of the best-known Chinese poets of the Song Dynasty, he served as a government official, and was an academic authority in geography, especiall ...
, Zhou Daguan
Zhou Daguan (; ; c. 1270–?) was a Chinese diplomat of the Yuan dynasty of China, serving under Temür Khan (Emperor Chengzong of Yuan). He is most well known for his accounts of the customs of Cambodia and the Angkor temple complexes during hi ...
, and Xu Xiake
Xu Xiake (, January 5, 1587 – March 8, 1641), born Xu Hongzu (), courtesy name Zhenzhi (), was a Chinese explorer, geographer, and travel writer of the Ming dynasty, known best for his famous geographical treatise, and noted for his bravery ...
wrote important treatises, yet by the 17th century advanced ideas and methods of Western-style geography were adopted in China.
 During the
During the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ...
, the fall of the Roman empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire, also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome, was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vast ...
led to a shift in the evolution of geography from Europe to the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
. Muslim geographers such as Muhammad al-Idrisi
Abu Abdullah Muhammad al-Idrisi al-Qurtubi al-Hasani as-Sabti, or simply al-Idrisi (; ; 1100–1165), was an Arab Muslim geographer and cartographer who served in the court of King Roger II at Palermo, Sicily. Muhammad al-Idrisi was born in C ...
produced detailed world maps (such as Tabula Rogeriana
The (, lit. "The Excursion of One Eager to Penetrate the Distant Horizons"), commonly known in the West as the (lit. "''The Book of Roger''" in Latin), is an atlas commissioned by the Norman King Roger II in 1138 and completed by the Arab ...
), while other geographers such as Yaqut al-Hamawi
Yāqūt Shihāb al-Dīn ibn-ʿAbdullāh al-Rūmī al-Ḥamawī (1179–1229) () was a Muslim scholar of Byzantine ancestry active during the late Abbasid period (12th–13th centuries). He is known for his , an influential work on geography con ...
, Abu Rayhan Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (; ; 973after 1050), known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian peoples, Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative religion, Co ...
, Ibn Battuta
Ibn Battuta (; 24 February 13041368/1369), was a Maghrebi traveller, explorer and scholar. Over a period of 30 years from 1325 to 1354, he visited much of Africa, the Middle East, Asia and the Iberian Peninsula. Near the end of his life, Ibn ...
, and Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732–808 Hijri year, AH) was an Arabs, Arab Islamic scholar, historian, philosopher and sociologist. He is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest social scientists of the Middle Ages, and cons ...
provided detailed accounts of their journeys and the geography of the regions they visited. Turkish geographer Mahmud al-Kashgari
Mahmud ibn Husayn ibn Muhammad al-Kashgari; ; , Мәһмуд Қәшқири; , Махмуд Қашғарий was an 11th-century Kara-Khanid scholar and lexicographer of the Turkic languages from Kashgar.
His father, Husayn, was the mayor of ...
drew a world map on a linguistic basis, and later so did Piri Reis
Muhiddin Piri ( 1470 – 1553), better known as Piri Reis (), was an Ottoman cartographer, admiral, navigator, corsair, and geographer. He is primarily known today for his cartographic works, including his 1513 world map and the '' Kitab-ı ...
(Piri Reis map
The Piri Reis map is a world map compiled in 1513 by the Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis. Approximately one third of the map survives, housed in the Topkapı Palace in Istanbul. After the empire's 1517 conquest of Egypt, Piri Re ...
). Further, Islamic scholars translated and interpreted the earlier works of the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
and the Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
and established the House of Wisdom
The House of Wisdom ( ), also known as the Grand Library of Baghdad, was believed to be a major Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid-era public academy and intellectual center in Baghdad. In popular reference, it acted as one of the world's largest publ ...
in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
for this purpose. Abū Zayd al-Balkhī, originally from Balkh
Balkh is a town in the Balkh Province of Afghanistan. It is located approximately to the northwest of the provincial capital city Mazar-i-Sharif and approximately to the south of the Amu Darya and the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border. In 2021 ...
, founded the "Balkhī school" of terrestrial mapping in Baghdad
Baghdad ( or ; , ) is the capital and List of largest cities of Iraq, largest city of Iraq, located along the Tigris in the central part of the country. With a population exceeding 7 million, it ranks among the List of largest cities in the A ...
. Suhrāb, a late tenth century Muslim geographer accompanied a book of geographical coordinates, with instructions for making a rectangular world map with equirectangular projection
The equirectangular projection (also called the equidistant cylindrical projection or la carte parallélogrammatique projection), and which includes the special case of the plate carrée projection (also called the geographic projection, lat/l ...
or cylindrical equidistant projection.
Abu Rayhan Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (; ; 973after 1050), known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian peoples, Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative religion, Co ...
(976–1048) first described a polar equi-azimuthal equidistant projection
The azimuthal equidistant projection is an azimuthal map projection. It has the useful properties that all points on the map are at proportionally correct distances from the center point, and that all points on the map are at the correct azimuth ...
of the celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
. He was regarded as the most skilled when it came to mapping cities and measuring the distances between them, which he did for many cities in the Middle East and the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
. He often combined astronomical readings and mathematical equations to develop methods of pin-pointing locations by recording degrees of latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
and longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
. He also developed similar techniques when it came to measuring the heights of mountains, depths of the valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains and typically containing a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
s, and expanse of the horizon
The horizon is the apparent curve that separates the surface of a celestial body from its sky when viewed from the perspective of an observer on or near the surface of the relevant body. This curve divides all viewing directions based on whethe ...
. He also discussed human geography
Human geography or anthropogeography is the branch of geography which studies spatial relationships between human communities, cultures, economies, and their interactions with the environment, examples of which include urban sprawl and urban ...
and the planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to Abiogenesis, develop and sustain an environment hospitable to life. Life may be abiogenesis, generated directly on a planet or satellite endogenously. Res ...
of the Earth. He also calculated the latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
of Kath, Khwarezm
Khwarazm (; ; , ''Xwârazm'' or ''Xârazm'') or Chorasmia () is a large oasis region on the Amu Darya river delta in western Central Asia, bordered on the north by the (former) Aral Sea, on the east by the Kyzylkum Desert, on the south by ...
, using the maximum altitude of the Sun, and solved a complex geodesic
In geometry, a geodesic () is a curve representing in some sense the locally shortest path ( arc) between two points in a surface, or more generally in a Riemannian manifold. The term also has meaning in any differentiable manifold with a conn ...
equation to accurately compute the Earth's circumference
Earth's circumference is the distance around Earth. Measured around the equator, it is . Measured passing through the poles, the circumference is .
Treating the Earth as a sphere, its circumference would be its single most important measuremen ...
, which was close to modern values of the Earth's circumference. His estimate of 6,339.9 km for the Earth radius
Earth radius (denoted as ''R''🜨 or ''R''E) is the distance from the center of Earth to a point on or near its surface. Approximating the figure of Earth by an Earth spheroid (an oblate ellipsoid), the radius ranges from a maximum (equato ...
was only 16.8 km less than the modern value of 6,356.7 km. In contrast to his predecessors, who measured the Earth's circumference by sighting the Sun simultaneously from two different locations, al-Biruni
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (; ; 973after 1050), known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern ...
developed a new method of using trigonometric
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The field ...
calculations based on the angle between a plain
In geography, a plain, commonly known as flatland, is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and ...
and mountain top, which yielded more accurate measurements of the Earth's circumference, and made it possible for it to be measured by a single person from a single location.
 The European
The European Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (), also known as the Age of Exploration, was part of the early modern period and overlapped with the Age of Sail. It was a period from approximately the 15th to the 17th century, during which Seamanship, seafarers fro ...
during the 16th and the 17th centuries, where many new lands were discovered and accounts by European explorers such as Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
, Marco Polo
Marco Polo (; ; ; 8 January 1324) was a Republic of Venice, Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in ''The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known a ...
, and James Cook
Captain (Royal Navy), Captain James Cook (7 November 1728 – 14 February 1779) was a British Royal Navy officer, explorer, and cartographer famous for his three voyages of exploration to the Pacific and Southern Oceans, conducted between 176 ...
revived a desire for both accurate geographic detail and more solid theoretical foundations in Europe. In 1650, the first edition of the ''Geographia Generalis
''Geographia Generalis'' is a seminal work in the field of geography authored by Bernhardus Varenius, first published in 1650. This influential text laid the foundations for modern geographical science and was pivotal in the development of geogr ...
'' was published by Bernhardus Varenius
Bernhardus Varenius (Bernhard Varen) (1622, Hitzacker, Holy Roman Empire1650) was a German geographer.
Life
His early years (from 1627) were spent at Uelzen, where his father was court preacher to the duke of Brunswick. Varenius studied at th ...
, which was later edited and republished by others including Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton () was an English polymath active as a mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author. Newton was a key figure in the Scientific Revolution and the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment that followed ...
. This textbook sought to integrate new scientific discoveries and principles into classical geography and approach the discipline like the other sciences emerging, and is seen by some as the division between ancient and modern geography in the West.
The ''Geographia Generalis'' contained both theoretical background and practical applications related to ship navigation. The remaining problem facing both explorers and geographers was finding the latitude and longitude of a geographic location. While the problem of latitude was solved long ago, but that of longitude remained; agreeing on what zero meridians should be was only part of the problem. It was left to John Harrison
John Harrison ( – 24 March 1776) was an English carpenter and clockmaker who invented the marine chronometer, a long-sought-after device for solving the History of longitude, problem of how to calculate longitude while at sea.
Harrison's sol ...
to solve it by inventing the chronometer H-4 in 1760, and later in 1884 for the International Meridian Conference
The International Meridian Conference was a conference held in October 1884 in Washington, D.C., in the United States, to determine a prime meridian for international use. The conference was held at the request of President of the United State ...
to adopt by convention the Greenwich meridian
The Greenwich meridian is a prime meridian, a geographical reference line that passes through the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, in London, England. From 1884 to 1974, the Greenwich meridian was the international standard prime meridian, ...
as zero meridians.
The 18th and 19th centuries were the times when geography became recognized as a discrete academic discipline
An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined (in part) and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, a ...
, and became part of a typical university curriculum in Europe (especially Paris and Berlin
Berlin ( ; ) is the Capital of Germany, capital and largest city of Germany, by both area and List of cities in Germany by population, population. With 3.7 million inhabitants, it has the List of cities in the European Union by population withi ...
). The development of many geographic societies also occurred during the 19th century, with the foundations of the Société de Géographie
The Société de Géographie (; ), is the world's oldest geographical society. It was founded in 1821 as the first Geographic Society. Since 1878, its headquarters have been at 184 Boulevard Saint-Germain, Paris. The entrance is marked by two gig ...
in 1821, the Royal Geographical Society
The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers), often shortened to RGS, is a learned society and professional body for geography based in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1830 for the advancement of geographical scien ...
in 1830, Russian Geographical Society
The Russian Geographical Society (), or RGO, is a learned society based in Saint Petersburg, Russia. It promotes geography, exploration and nature protection with research programs in fields including oceanography, ethnography, ecology and stati ...
in 1845, American Geographical Society
The American Geographical Society (AGS) is an organization of professional geographers, founded in 1851 in New York City. Most fellows of the society are United States, Americans, but among them have always been a significant number of fellows f ...
in 1851, the Royal Danish Geographical Society
The Royal Danish Geographical Society (RDGS, ) is a scientific society. The society aims to furthethe knowledge of the Earth and its inhabitants and to disseminate interest in the science of geography.
It was founded 18 November 1876 on the initia ...
in 1876 and the National Geographic Society
The National Geographic Society, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States, is one of the largest nonprofit scientific and educational organizations in the world.
Founded in 1888, its interests include geography, archaeology, natural sc ...
in 1888. The influence of Immanuel Kant
Immanuel Kant (born Emanuel Kant; 22 April 1724 – 12 February 1804) was a German Philosophy, philosopher and one of the central Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment thinkers. Born in Königsberg, Kant's comprehensive and systematic works ...
, Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 1769 – 6 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, natural history, naturalist, List of explorers, explorer, and proponent of Romanticism, Romantic philosophy and Romanticism ...
, Carl Ritter
Carl Ritter (August 7, 1779September 28, 1859) was a German geographer. Along with Alexander von Humboldt, he is considered one of the founders of modern geography, as they established it as an independent scientific discipline. From 1825 until ...
, and Paul Vidal de la Blache
Paul Vidal de La Blache (, Pézenas, Hérault, 22 January 1845 – Tamaris-sur-Mer, Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, 5 April 1918) was a French geographer. He is considered to be the founder of modern French geography and also the founder of the Fr ...
can be seen as a major turning point in geography from philosophy to an academic subject. Geographers such as Richard Hartshorne
Richard Hartshorne (; December 12, 1899 – November 5, 1992) was a prominent American geographer, and professor at the University of Wisconsin-Madison, who specialized in economic and political geography and the philosophy of geography. He is ...
and Joseph Kerski have regarded both Humboldt and Ritter as the founders of modern geography, as Humboldt and Ritter were the first to establish geography as an independent scientific discipline.
 Over the past two centuries, the advancements in technology with computers have led to the development of
Over the past two centuries, the advancements in technology with computers have led to the development of geomatics
Geomatics is defined in the ISO/TC 211 series of standards as the "discipline concerned with the collection, distribution, storage, analysis, processing, presentation of geographic data or geographic information". Under another definition, it ...
and new practices such as participant observation and geostatistics being incorporated into geography's portfolio of tools. In the West during the 20th century, the discipline of geography went through four major phases: environmental determinism
Environmental determinism (also known as climatic determinism or geographical determinism) is the study of how the physical environment predisposes societies and states towards particular economic or social developmental (or even more gener ...
, regional geography
Regional geography is one of the major traditions of geography. It focuses on the interaction of different cultural and natural geofactors in a specific land or landscape, while its counterpart, systematic geography, concentrates on a specific geo ...
, the quantitative revolution
In geography, the quantitative revolution (QR) was a paradigm shift that sought to develop a more rigorous and systematic methodology for the discipline. It came as a response to the inadequacy of regional geography to explain general spatial d ...
, and critical geography
Critical geography is theoretically informed geographical scholarship that promotes social justice, liberation, and leftist politics. Critical geography is also used as an umbrella term for Marxist, feminist, postmodern, posts ...
. The strong interdisciplinary links between geography and the sciences of geology and botany
Botany, also called plant science, is the branch of natural science and biology studying plants, especially Plant anatomy, their anatomy, Plant taxonomy, taxonomy, and Plant ecology, ecology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who s ...
, as well as economics, sociology, and demographics
Demography () is the statistical study of human populations: their size, composition (e.g., ethnic group, age), and how they change through the interplay of fertility (births), mortality (deaths), and migration.
Demographic analysis examin ...
, have also grown greatly, especially as a result of earth system science
Earth system science (ESS) is the application of systems science to the Earth. In particular, it considers interactions and 'feedbacks', through material and energy fluxes, between the Earth's sub-systems' cycles, processes and "spheres"—atmosp ...
that seeks to understand the world in a holistic view. New concepts and philosophies have emerged from the rapid advancement of computers, quantitative methods, and interdisciplinary approaches. The 1962 book ''Theoretical Geography
A theory is a systematic and rational form of abstract thinking about a phenomenon, or the conclusions derived from such thinking. It involves contemplative and logical reasoning, often supported by processes such as observation, experimentation, ...
'' by William Bunge
William Wheeler Bunge Jr. (born 1928, La Crosse, Wisconsin; died October 31, 2013, Canada) was an American geographer active mainly as a quantitative geographer and spatial theorist. He also became a radical geographer and anti-war activist in th ...
, which argued for a nomothetic
Nomothetic literally means "proposition of the law" (Greek derivation) and is used in philosophy, psychology, and law with differing meanings.
Etymology
In the general humanities usage, ''nomothetic'' may be used in the sense of "able to lay do ...
approach to geography and that from a purely spatial perspective there was no real difference between human and physical geography, has been described by Kevin R. Cox as "perhaps the seminal text of the spatial-quantitative revolution."In 1970, Waldo Tobler
Waldo Rudolph Tobler (November 16, 1930 – February 20, 2018) was an United States, American-Switzerland, Swiss geographer and cartographer. Tobler is regarded as one of the most influential geographers and cartographers of the late 20th centur ...
proposed the first law of geography
First most commonly refers to:
* First, the ordinal form of the number 1
First or 1st may also refer to:
Acronyms
* Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array
* Far Infrared a ...
, "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." This law summarizes the first assumption geographers make about the world.
Related fields
Geology
 The discipline of geography, especially physical geography, and geology have significant overlap. In the past, the two have often shared academic departments at universities, a point that has led to conflict over resources. Both disciplines do seek to understand the
The discipline of geography, especially physical geography, and geology have significant overlap. In the past, the two have often shared academic departments at universities, a point that has led to conflict over resources. Both disciplines do seek to understand the rocks
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks form the Earth's ...
on the Earth's surface and the processes that change them over time. Geology employs many of the tools and techniques of technical geographers, such as GIS and remote sensing to aid in geological mapping
A geological map or geologic map is a special-purpose map made to show various geological features. Rock units or geologic strata are shown by color or symbols. Bedding planes and structural features such as faults, folds, are shown with s ...
. However, geology includes research that goes beyond the spatial component, such as the chemical analysis of rocks and biogeochemistry
Biogeochemistry is the Branches of science, scientific discipline that involves the study of the chemistry, chemical, physics, physical, geology, geological, and biology, biological processes and reactions that govern the composition of the natu ...
.
History
The discipline of History has significant overlap with geography, especially human geography. Like geology, history and geography have shared university departments. Geography provides the spatial context within which historical events unfold. The physical geographic features of a region, such as its landforms, climate, and resources, shape human settlements, trade routes, and economic activities, which in turn influence the course of historical events. Thus, a historian must have a strong foundation in geography. Historians employ the techniques of technical geographers to createhistorical atlas
A historical atlas is a collection of maps and possibly illustrations that depict the historical geography of a particular region at a defined time period. These atlases typically include maps that show the political and cultural boundaries of ...
es and maps.
Planetary science
 While the discipline of geography is normally concerned with the Earth, the term can also be informally used to describe the study of other worlds, such as the
While the discipline of geography is normally concerned with the Earth, the term can also be informally used to describe the study of other worlds, such as the planet
A planet is a large, Hydrostatic equilibrium, rounded Astronomical object, astronomical body that is generally required to be in orbit around a star, stellar remnant, or brown dwarf, and is not one itself. The Solar System has eight planets b ...
s of the Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Sola ...
and even beyond. The study of systems larger than the Earth itself usually forms part of Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
or Cosmology
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the wo ...
, while the study of other planets is usually called planetary science
Planetary science (or more rarely, planetology) is the scientific study of planets (including Earth), celestial bodies (such as moons, asteroids, comets) and planetary systems (in particular those of the Solar System) and the processes of ...
. Alternative terms such as areography (geography of Mars)
Areography, also known as the geography of Mars, is a subfield of planetary science that entails the delineation and characterization of regions on Mars. Areography is mainly focused on what is called physical geography on Earth; that is the di ...
have been employed to describe the study of other celestial objects. Ultimately, geography may be considered a subdiscipline within planetary science, and planetary science link geography with fields like astronomy and physics.
See also
* * * * * *References
External links
Geography
at the ''
Encyclopaedia Britannica
An encyclopedia is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge, either general or special, in a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into article (publishing), articles or entries that are arranged Alp ...
'' website
{{Use Oxford spelling, date=August 2016
Earth sciences
Social sciences
Main topic articles