Genu Recurvatum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Genu recurvatum is a deformity in the
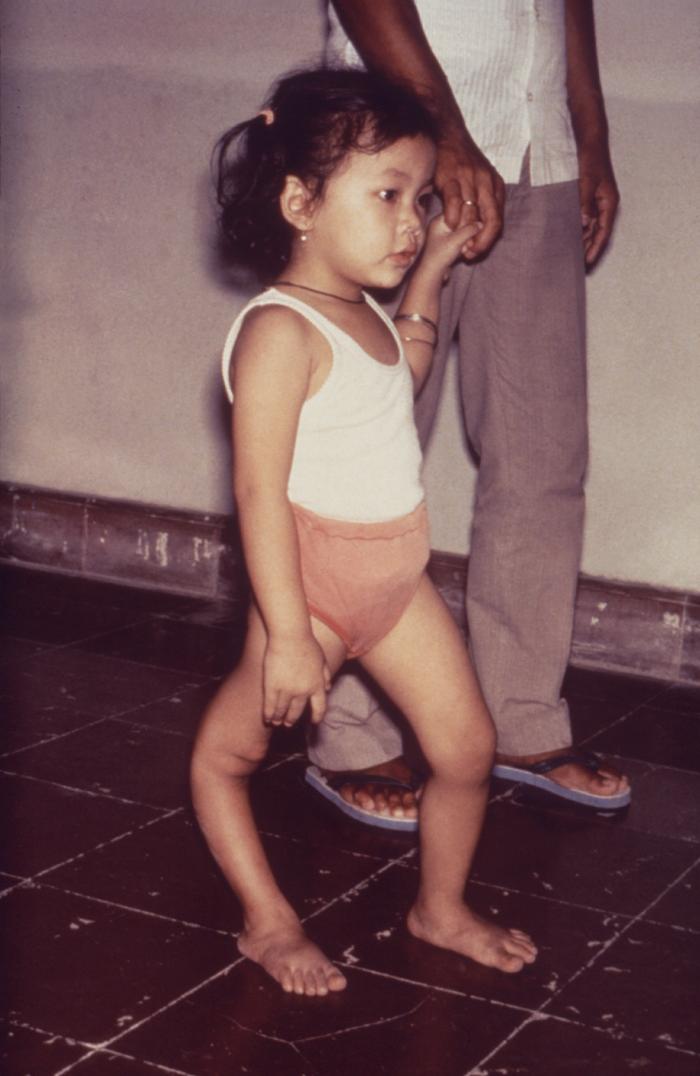 The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
*
The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
*
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
The differential diagnosis of children with joint hypermobility: a review of the literature
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Rheumatology Orthopedic problems Knee injuries and disorders Rare diseases
knee joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
, so that the knee bends backwards. In this deformity, excessive extension occurs in the tibiofemoral joint
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest joint in the ...
. Genu recurvatum is also called knee hyperextension and back knee. This deformity is more common in women and is correlated with men with extremely high testosterone. and people with familial ligamentous laxity
Ligamentous laxity or ligament laxity can appear in a variety of ways and levels of severity.
In most people, ligaments (which are the tissues that connect bones to each other) are naturally tight in such a way that the joints are restricted to ...
. Hyperextension of the knee may be mild, moderate or severe.
The normal range of motion (ROM) of the knee joint is from 0 to 135 degrees in an adult. Full knee extension should be no more than 10 degrees. In genu recurvatum, normal extension is increased. The development of genu recurvatum may lead to knee pain
Knee pain is pain in or around the knee.
The knee joint consists of an articulation between four bones: the femur, tibia, fibula and patella. There are four compartments to the knee. These are the medial and lateral tibiofemoral compartments, the ...
and knee osteoarthritis.
Causes
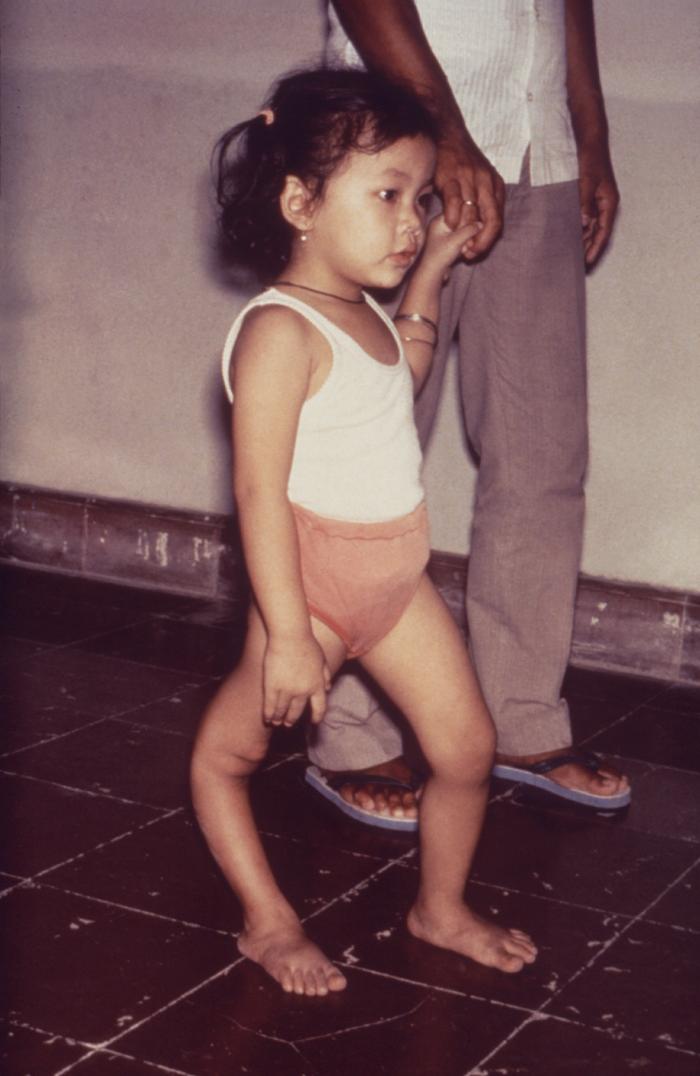 The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
*
The following factors may be involved in causing this deformity:
* Inherent laxity of the knee ligaments
* Weakness of biceps femoris muscle
* Instability of the knee joint due to ligaments and joint capsule injuries
* Inappropriate alignment of the tibia and femur
* Malunion of the bones around the knee
* Weakness in the hip extensor muscles
* Gastrocnemius muscle
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It is located superficial to the soleus in the posterior (back) compartment of the leg. It runs from its t ...
weakness (in standing position)
* Upper motor neuron lesion
An upper motor neuron lesion (also known as pyramidal insufficiency) Is an injury or abnormality that occurs in the neural pathway above the anterior horn cell of the spinal cord or motor nuclei of the cranial nerves. Conversely, a lower motor ...
(for example, hemiplegia
Hemiparesis, also called unilateral paresis, is the weakness of one entire side of the body ('' hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia, in its most severe form, is the complete paralysis of one entire side of the body. Either hemiparesis or hemiplegia ...
as the result of a cerebrovascular accident
Stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to a part of the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop ...
)
* Lower motor neuron lesion
A lower motor neuron lesion is a lesion which affects nerve fibers traveling from the lower motor neuron(s) in the anterior horn/anterior grey column of the spinal cord, or in the motor nuclei of the cranial nerves, to the relevant muscle(s).
O ...
(for example, in post-polio syndrome
Post-polio syndrome (PPS, poliomyelitis sequelae) is a group of latent symptoms of poliomyelitis (polio), occurring in more than 80% of polio infections. The symptoms are caused by the damaging effects of the viral infection on the nervous syst ...
)
* Deficit in joint proprioception
Proprioception ( ) is the sense of self-movement, force, and body position.
Proprioception is mediated by proprioceptors, a type of sensory receptor, located within muscles, tendons, and joints. Most animals possess multiple subtypes of propri ...
* Lower limb
Lower may refer to:
*Lower (album), ''Lower'' (album), 2025 album by Benjamin Booker
*Lower (surname)
*Lower Township, New Jersey
*Lower Receiver (firearms)
*Lower Wick Gloucestershire, England
See also
*Nizhny
{{Disambiguation ...
length discrepancy
* Congenital genu recurvatum
* Cerebral palsy
Cerebral palsy (CP) is a group of movement disorders that appear in early childhood. Signs and symptoms vary among people and over time, but include poor coordination, spasticity, stiff muscles, Paresis, weak muscles, and tremors. There may b ...
* Muscular dystrophy
Muscular dystrophies (MD) are a genetically and clinically heterogeneous group of rare neuromuscular diseases that cause progressive weakness and breakdown of skeletal muscles over time. The disorders differ as to which muscles are primarily affe ...
* Limited dorsiflexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
(plantar flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
contracture)
* Popliteus muscle weakness
* Connective tissue disorders. In these disorders, there are excessive joint mobility (joint hypermobility) problems. These disorders include:
** Marfan syndrome
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with dolichostenomelia, long arms, legs, Arachnodactyly, fingers, and toes. They also typically ha ...
** Loeys–Dietz syndrome
Loeys–Dietz syndrome (LDS) is an autosomal dominant genetic connective tissue disorder. It has features similar to Marfan syndrome and Ehlers–Danlos syndrome. The disorder is marked by aneurysms in the aorta, often in children, and the aorta m ...
** Ehlers–Danlos syndrome
Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) is a group of 14 genetic connective-tissue disorders. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Co ...
** Benign hypermobile joint syndrome
** Osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that bone fracture, break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other Or ...
disease
Pathophysiology
The most important factors of knee stability include: *Ligaments
A ligament is a type of fibrous connective tissue in the body that connects bones to other bones. It also connects flight feathers to bones, in dinosaurs and birds. All 30,000 species of amniotes (land animals with internal bones) have ligam ...
of the knee: The knee joint is stabilized by four main ligaments:
** Anterior cruciate ligament
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of a pair of cruciate ligaments (the other being the posterior cruciate ligament) in the human knee. The two ligaments are called "cruciform" ligaments, as they are arranged in a crossed formation. In ...
(ACL). The ACL has an important role in stabilization of knee extension movement by preventing the knee from hyperextending.
** Posterior cruciate ligament
The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is a ligament in each knee of humans and various other animals. It works as a counterpart to the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). It connects the posterior intercondylar area of the tibia to the Medial condyl ...
(PCL)
** Medial collateral ligament
The medial collateral ligament (MCL), also called the superficial medial collateral ligament (sMCL) or tibial collateral ligament (TCL), is one of the major ligaments of the knee. It is on the medial (inner) side of the knee joint and occurs in ...
(MCL)
** Lateral collateral ligament (LCL)
* Joint capsule
In anatomy, a joint capsule or articular capsule is an envelope surrounding a synovial joint.Quadriceps femoris muscle
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large ...
* Appropriate alignment of the femur
The femur (; : femurs or femora ), or thigh bone is the only long bone, bone in the thigh — the region of the lower limb between the hip and the knee. In many quadrupeds, four-legged animals the femur is the upper bone of the hindleg.
The Femo ...
and tibia
The tibia (; : tibiae or tibias), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two Leg bones, bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outsi ...
(especially in knee extension position )
Treatment
Treatment generally includes the following: * Sometimes pharmacologic therapy for initial disease treatment *Physical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is a healthcare profession, as well as the care provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through patient education, physical intervention, disease preventio ...
: physiotherapy will be beneficial in patient with complaint of pain, discomfort.
* Occupational therapy
Occupational therapy (OT), also known as ergotherapy, is a healthcare profession. Ergotherapy is derived from the Greek wiktionary:ergon, ergon which is allied to work, to act and to be active. Occupational therapy is based on the assumption t ...
* Use of appropriate assistive devices such as orthoses
* Surgery
Incidence
This condition is considered to be rare, with about 1 in 100,000 births being affected by the congenital form of genu recurvatum, although it's a common feature in some disorders, such as in joint hypermobility, which affects 1 in 30 people.See also
*Genu varum
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving th ...
* Genu valgum
Genu valgum, commonly called "knock-knee", is a condition in which the knees angle in and touch each other when the human leg, legs are straightened. Individuals with severe valgus deformity, valgus deformities are typically unable to touch thei ...
* Hypermobility
References
External links
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
The differential diagnosis of children with joint hypermobility: a review of the literature
The American Academy of Orthotists and Prosthetists
{{Congenital malformations and deformations of musculoskeletal system Rheumatology Orthopedic problems Knee injuries and disorders Rare diseases