General Perspective Projection on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
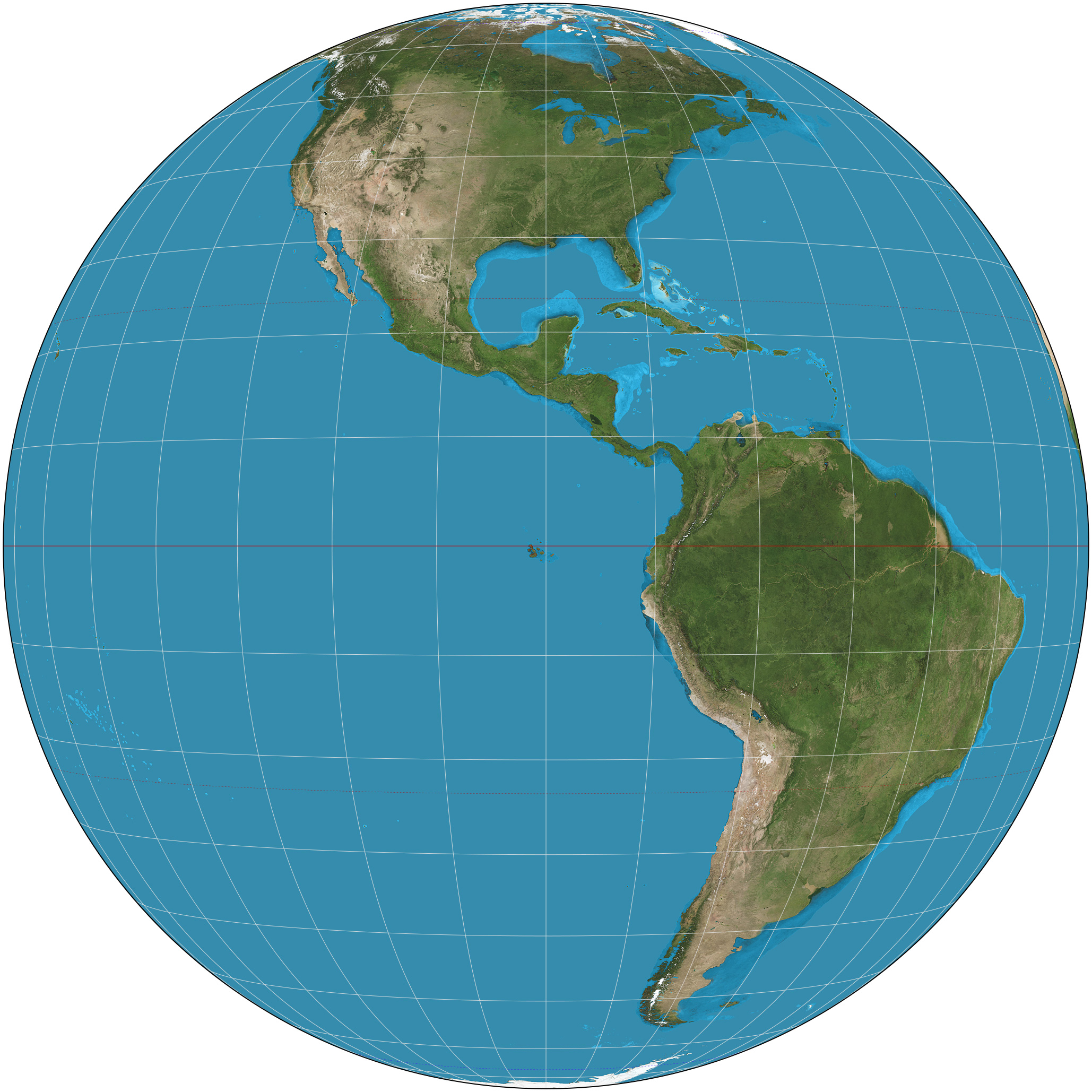 The General Perspective projection is a
The General Perspective projection is a
"Tilted perspective"
Tilted perspectives are common from aerial and low orbit photography, generally taken from at a height measured in kilometers to hundreds of kilometers, rather than the hundreds or thousands of kilometers typical of a vertical perspective. However,
 The General Perspective projection is a
The General Perspective projection is a map projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, ...
. When the Earth is photographed from space, the camera records the view as a perspective projection. When the camera is aimed toward the center of the Earth, the resulting projection is called Vertical Perspective. When aimed in other directions, the resulting projection is called a Tilted Perspective.
Perspective and usage
The Vertical Perspective is related to thestereographic projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective transform, perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point (geometry), point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (th ...
, gnomonic projection
A gnomonic projection, also known as a central projection or rectilinear projection, is a perspective projection of a sphere, with center of projection at the sphere's center, onto any plane not passing through the center, most commonly a tan ...
, and orthographic projection
Orthographic projection (also orthogonal projection and analemma) is a means of representing Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional objects in Plane (mathematics), two dimensions. Orthographic projection is a form of parallel projection in ...
. These are all true perspective projection
Linear or point-projection perspective () is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of ...
s, meaning that they result from viewing the globe from some vantage point. They are also azimuthal
An azimuth (; from ) is the horizontal angle from a cardinal direction, most commonly north, in a local or observer-centric spherical coordinate system.
Mathematically, the relative position vector from an observer (origin) to a point of inte ...
projections, meaning that the projection surface is a plane tangent to the sphere. This results in correct directions from the center to all other points. The ''point of perspective'', or vantage point, for the General Perspective Projection is at a finite distance. It depicts the earth as it appears from some relatively short distance above the surface, typically a few hundred to a few tens of thousands of kilometers.
When tilted, the General Perspective projection, also called the tilted perspective projection, is not azimuthal (see second figure below); directions are not true from the central point, and the projection plane is not tangent to the sphere.
PROJ contributors (2020). PROJ coordinate transformation software library. Open Source Geospatial Foundation"Tilted perspective"
Tilted perspectives are common from aerial and low orbit photography, generally taken from at a height measured in kilometers to hundreds of kilometers, rather than the hundreds or thousands of kilometers typical of a vertical perspective. However,
Richard Edes Harrison
Richard Edes Harrison (March 11, 1901 – January 5, 1994) was an American scientific illustrator and cartographer. He was the house cartographer of ''Fortune'' and a consultant at ''Life'' for almost two decades. He played a key role in "challe ...
pioneered the use of this projection on strategic maps showing military theaters during WWII.
Some prominent Internet mapping tools also use the tilted perspective projection. For example, Google Earth
Google Earth is a web mapping, web and computer program created by Google that renders a 3D computer graphics, 3D representation of Earth based primarily on satellite imagery. The program maps the Earth by superimposition, superimposing satelli ...
and NASA World Wind
NASA WorldWind is an open-source (released under the NOSA license and the Apache 2.0 license) virtual globe. According to the website, "WorldWind is an open source virtual globe API. WorldWind allows developers to quickly and easily c ...
show the globe as it appears from space. These applications permit a wide variety of interactive pan and zoom operations, including fly-through simulations, mimicking pictures or movies taken with a hand-held camera from an airplane or spacecraft.
History
Some forms of the projection were known to the Greeks and Egyptians 2,000 years ago. It was studied by several French and British scientists in the 18th and 19th centuries. However, the projection had little practical value at that time; computationally simpler nonperspective azimuthal projections could be used instead. Space exploration led to a renewed interest in the perspective projection. Now the concern was for a pictorial view from space, not for minimal distortion. A picture taken with a hand-held camera from the window of a spacecraft has a tilted vertical perspective, so the crewed Gemini and Apollo space missions sparked interest in this projection.Mathematics
Theformulas
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
for the general perspective projection are derived using trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The fiel ...
. They are written in terms of longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east- west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek lett ...
(''λ'') and latitude
In geography, latitude is a geographic coordinate system, geographic coordinate that specifies the north-south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from −90° at t ...
(''φ'') on the sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
. Define the radius
In classical geometry, a radius (: radii or radiuses) of a circle or sphere is any of the line segments from its Centre (geometry), center to its perimeter, and in more modern usage, it is also their length. The radius of a regular polygon is th ...
of the sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three ...
''R'' and the ''center'' point (and origin
Origin(s) or The Origin may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Comics and manga
* ''Origin'' (comics), a Wolverine comic book mini-series published by Marvel Comics in 2002
* ''The Origin'' (Buffy comic), a 1999 ''Buffy the Vampire Sl ...
) of the projection (''λ''0, ''φ''0). The equations
In mathematics, an equation is a mathematical formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for e ...
for the orthographic projection onto the (''x'', ''y'') tangent plane reduce to the following:
:
where
:
is the angular distance
Angular distance or angular separation is the measure of the angle between the orientation (geometry), orientation of two straight lines, ray (geometry), rays, or vector (geometry), vectors in three-dimensional space, or the central angle subtende ...
and denotes the distance from the perspective point to the center of earth. It is positive in the direction of the center of the projection (for the “view from space”) and negative in the opposite direction. For the stereographic projection
In mathematics, a stereographic projection is a perspective transform, perspective projection of the sphere, through a specific point (geometry), point on the sphere (the ''pole'' or ''center of projection''), onto a plane (geometry), plane (th ...
, , and for the gnomonic projection
A gnomonic projection, also known as a central projection or rectilinear projection, is a perspective projection of a sphere, with center of projection at the sphere's center, onto any plane not passing through the center, most commonly a tan ...
, .
The inverse formulas are given by:
:
where
:
If is negative and is greater than , must be subtracted from 180° to place it in the proper quadrant. For computation
A computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that is well-defined. Common examples of computation are mathematical equation solving and the execution of computer algorithms.
Mechanical or electronic devices (or, hist ...
of the inverse formulas the use of the two-argument atan2
In computing and mathematics, the function (mathematics), function atan2 is the 2-Argument of a function, argument arctangent. By definition, \theta = \operatorname(y, x) is the angle measure (in radians, with -\pi 0, \\ mu \arctan\left(\fr ...
form of the inverse tangent
In mathematics, the inverse trigonometric functions (occasionally also called ''antitrigonometric'', ''cyclometric'', or ''arcus'' functions) are the inverse functions of the trigonometric functions, under suitably restricted domains. Specific ...
function (as opposed to atan
Atan may refer to:
Mathematics
* arctangent (), a trigonometric function
** atan2, the two-argument function implementing the arctangent in many computer languages
Places
* Atan, Armenia
* Atan, Iran
Atan () is a village in Alamut-e Pain ...
) is recommended. This ensures that the sign
A sign is an object, quality, event, or entity whose presence or occurrence indicates the probable presence or occurrence of something else. A natural sign bears a causal relation to its object—for instance, thunder is a sign of storm, or me ...
of the orthographic projection as written is correct in all quadrants
Quadrant may refer to:
Companies
* Quadrant Cycle Company, 1899 manufacturers in Britain of the Quadrant motorcar
* Quadrant (motorcycles), one of the earliest British motorcycle manufacturers, established in Birmingham in 1901
* Quadrant Privat ...
.
See also
*List of map projections
This is a summary of map projections that have articles of their own on Wikipedia or that are otherwise WP:NOTABLE, notable. Because there is no limit to the number of possible map projections,
there can be no comprehensive list.
Table of proj ...
*Map projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:General Perspective Projection Map projections