Gavotte From Hamlet (Prokofiev) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The gavotte (also gavot, gavote, or gavotta) is a French dance, taking its name from a
The gavotte (also gavot, gavote, or gavotta) is a French dance, taking its name from a
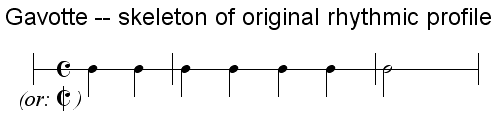 The phrases of the 18th-century French court gavotte begin in the middle of the
The phrases of the 18th-century French court gavotte begin in the middle of the  In the ballroom the gavotte was often paired with a preceding triple-time
In the ballroom the gavotte was often paired with a preceding triple-time 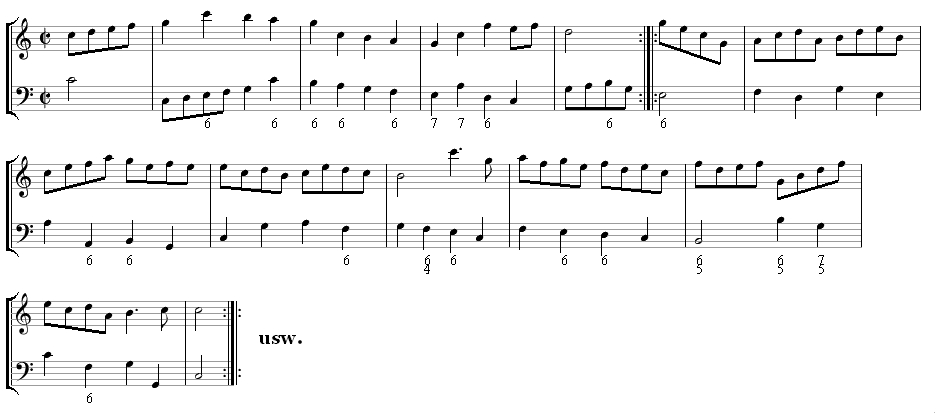 In the Baroque suite the gavotte is played after (or sometimes before) the
In the Baroque suite the gavotte is played after (or sometimes before) the
 The gavotte became popular in the court of
The gavotte became popular in the court of
 The gavotte (also gavot, gavote, or gavotta) is a French dance, taking its name from a
The gavotte (also gavot, gavote, or gavotta) is a French dance, taking its name from a folk dance
A folk dance is a dance that reflects the life of the people of a certain country or region. Not all ethnic dances are folk dances. For example, Ritual, ritual dances or dances of ritual origin are not considered to be folk dances. Ritual dances ...
of the Gavot, the people of the Pays de Gap region of Dauphiné
The Dauphiné ( , , ; or ; or ), formerly known in English as Dauphiny, is a former province in southeastern France, whose area roughly corresponded to that of the present departments of Isère, Drôme and Hautes-Alpes. The Dauphiné was ...
in the southeast of France, where the dance originated, according to one source. According to another reference, the word ''gavotte'' is a generic term for a variety of French folk dances, and most likely originated in Lower Brittany
Lower Brittany (; ) denotes the parts of Brittany west of Ploërmel, where the Breton language has been traditionally spoken, and where the culture associated with this language is most prolific. The name is in distinction to Upper Brittany, th ...
in the west, or possibly Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
in the southeast or the French Basque Country
The French Basque Country (; ; ), or Northern Basque Country (, or , ), is a region lying on the west of the French department of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques. Since 1 January 2017, it constitutes the Basque Municipal Community (; ) presided ...
in the southwest of France. It is notated in or time
Time is the continuous progression of existence that occurs in an apparently irreversible process, irreversible succession from the past, through the present, and into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequ ...
and is usually of moderate tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition ...
, though the folk dances also use meters such as and .
In late 16th-century Renaissance dance
Renaissance dances belong to the broad group of historical dances, specifically those during the Renaissance period. During that period, there was a distinction between country dances and court dances. Court dances required the dancers to be trai ...
, the gavotte is first mentioned as the last of a suite of branle
A branle ( , ), also bransle, brangle, brawl(e), brall(e), braul(e), brando (in Italy), bran (in Spain), or brantle (in Scotland), is a type of France, French dance popular from the early 16th century to the present, danced by couples in either ...
s. Popular at the court of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
, it became one of many optional dances in the classical suite of dances. Many were composed by Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( – 22 March 1687) was a French composer, dancer and instrumentalist of Italian birth, who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his life working in the court o ...
, Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; ; – ) was a French composer and music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of French opera a ...
and Gluck
Christoph Willibald ( Ritter von) Gluck (; ; 2 July 1714 – 15 November 1787) was a composer of Italian and French opera in the early classical period. Born in the Upper Palatinate and raised in Bohemia, both part of the Holy Roman Empire at ...
, and the 17th-century cibell A cibell or cebell is a gavotte-like musical piece in duple metre, predominantly heard in Baroque music. It is named after the chorus praising the goddess Cybele in Jean Baptiste Lully's '' Atys''. Later cibells have been written either for voiceTh ...
is a variety. The dance was popular in France throughout the 18th century and spread widely. In early courtly use the gavotte involved kissing, but this was replaced by the presentation of flowers.
The gavotte of the 16th, 17th, and 18th centuries has nothing in common with the 19th-century column-dance called the "gavotte" but may be compared with the rigaudon
The rigaudon (, ), anglicized as rigadon or rigadoon, is a French baroque dance with a lively duple metre. The music is similar to that of a bourrée, but the rigaudon is rhythmically simpler with regular phrases (eight measure phrases are most ...
and the bourrée
The bourrée (; ; also in England, borry or bore) is a dance of French origin and the words and music that accompany it. The bourrée resembles the gavotte in that it is in Duple and quadruple meter, double time and often has a dactyl (poetry), ...
.
Etymology
The term ''gavotte'' for a lively dance originated in the 1690s fromOld Provençal
Old Occitan (, ), also called Old Provençal, was the earliest form of the Occitano-Romance languages, as attested in writings dating from the 8th to the 14th centuries. Old Occitan generally includes Early and Old Occitan. Middle Occitan is somet ...
''gavoto'' (mountaineer's dance) from ''gavot'', a local name for an Alpine resident, said to mean literally "boor", "glutton", from ''gaver'' (to stuff, force-feed poultry) from Old Provençal ''gava'' (crop). The word is cognate to French ''gavache'' (coward, dastard). The Italianized form is ''gavotta''.
Musical characteristics
 The phrases of the 18th-century French court gavotte begin in the middle of the
The phrases of the 18th-century French court gavotte begin in the middle of the bar
Bar or BAR may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bar (establishment), selling alcoholic beverages
* Candy bar
** Chocolate bar
* Protein bar
Science and technology
* Bar (river morphology), a deposit of sediment
* Bar (tropical cyclone), a laye ...
, creating a half-measure (half-bar) upbeat
Up beat may refer to:
*Upbeat, in music, the last beat in the previous bar which immediately precedes the downbeat
*Anacrusis, a note (or sequence of notes) which precedes the first downbeat in a bar in a musical phrase
* ''Upbeat'' (album), by t ...
. However the music for the earlier court gavotte, first described by Thoinot Arbeau
Thoinot Arbeau is the anagrammatic pen name of French cleric Jehan Tabourot (March 17, 1520 – July 23, 1595). Tabourot is most famous for his ''Orchésographie'', a study of late sixteenth-century French Renaissance social dance. He was born ...
in 1589, invariably began on the downbeat of a duple measure. Later composers also wrote gavottes that began on the downbeat
''DownBeat'' (styled in all caps) is an American music magazine devoted to "jazz, blues and beyond", the last word indicating its expansion beyond the jazz realm that it covered exclusively in previous years. The publication was established in 1 ...
rather than on the half-measure: an example is Jean-Philippe Rameau
Jean-Philippe Rameau (; ; – ) was a French composer and music theory, music theorist. Regarded as one of the most important French composers and music theorists of the 18th century, he replaced Jean-Baptiste Lully as the dominant composer of ...
's ''Gavotte Variée'' in A minor for keyboard. Various folk gavottes found in mid-20th-century Brittany are danced to music in , , , and time.
 In the ballroom the gavotte was often paired with a preceding triple-time
In the ballroom the gavotte was often paired with a preceding triple-time minuet
A minuet (; also spelled menuet) is a social dance of French origin for two people, usually written in time. The English word was adapted from the Italian ''minuetto'' and the French ''menuet''.
The term also describes the musical form tha ...
: both dances are stately, and the gavotte's lifted step contrasted with the shuffling minuet step The minuet step is the dance step performed in the dance minuet. It "is composed of four plain straight Steps or Walks, and may be performed forwards, backward, sideways, &c." or in a square. The steps are often referred to by direction to distingu ...
. It had a steady rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular r ...
, not broken up into faster notes.
 In the Baroque suite the gavotte is played after (or sometimes before) the
In the Baroque suite the gavotte is played after (or sometimes before) the sarabande
The sarabande (from ) is a dance in triple metre, or the music written for such a dance.
History
The Sarabande evolved from a Spanish dance with Arab influences, danced by a lively double line of couples with castanets. A dance called ''zara ...
. Like most dance movements of the Baroque period it is typically in binary form
Binary form is a musical form in 2 related sections, both of which are usually repeated. Binary is also a structure used to choreograph dance. In music this is usually performed as A-A-B-B.
Binary form was popular during the Baroque music, Baro ...
but this may be extended by a second melody in the same metre
The metre (or meter in US spelling; symbol: m) is the base unit of length in the International System of Units (SI). Since 2019, the metre has been defined as the length of the path travelled by light in vacuum during a time interval of of ...
, often one called the ''musette'', having a pedal drone
Drone or The Drones may refer to:
Science and technology Vehicle
* Drone, a type of uncrewed vehicle, a class of robot
** Unmanned aerial vehicle or aerial drone
*** Unmanned combat aerial vehicle
** Unmanned ground vehicle or ground drone
** Unma ...
to imitate the French bagpipes, played after the first to create a grand ternary form
Ternary form, sometimes called song form, is a three-part musical form consisting of an opening section (A), a following section (B) and then a repetition of the first section (A). It is usually schematized as A–B–A. Prominent examples inclu ...
; A–(A)–B–A. There is a ''Gavotte en Rondeau'' ("Gavotte in rondo
The rondo or rondeau is a musical form that contains a principal theme (music), theme (sometimes called the "refrain") which alternates with one or more contrasting themes (generally called "episodes", but also referred to as "digressions" or "c ...
form") in J.S. Bach's Partita
Partita (also ''partie'', ''partia'', ''parthia'', or ''parthie'') closely resemble the dance suites of the Baroque music, Baroque Period (and are often used synonymously with Suite (music), suites) with the addition of a prelude movement at the ...
No. 3 in E Major for solo violin, BWV 1006.
The gavotte could be played at a variety of tempo
In musical terminology, tempo (Italian for 'time'; plural 'tempos', or from the Italian plural), measured in beats per minute, is the speed or pace of a given musical composition, composition, and is often also an indication of the composition ...
s: Johann Gottfried Walther
Johann Gottfried Walther (18 September 1684 – 23 March 1748) was a German music theorist, organist, composer, and lexicographer of the Baroque era.
Life and work
Walther was born at Erfurt. Not only was his life almost exactly contempor ...
wrote that the gavotte is "often quick but occasionally slow".
Renaissance
The gavotte is first described in the late 16th century as a suite or miscellany of double branles danced in a line or circle to music in duple time, "with little springs in the manner of the Haut Barrois" branle and with some of the steps "divided" with figures borrowed from thegalliard
The ''galliard'' (; ; ) was a form of Renaissance dance and Renaissance music, music popular all over Europe in the 16th century. It is mentioned in dance manuals from England, Portugal, France, Spain, Germany, and Italy.
Dance form
The ''gal ...
.
The basic gavotte step, as described by Arbeau, is that of the common or double branle, a line of dancers moving alternately to the left and right with a ''double à gauche'' and ''double à droite'', each requiring a count of four. In the double branle these composite steps consist of; a ''pied largi'' (firm outward step), a ''pied approche'' (the other foot drawn near to the first), another ''pied largi'' and a ''pied joint'' (the other foot drawn against the first).
In the gavotte's ''double à gauche'' a skip (''petit saut'') is inserted after each of the four components; the second ''pied largi'' is replaced by a ''marque pied croisé'' (the following foot crosses over the left with toe contacting the floor); the final ''pied approche'' is replaced by a ''grève croisée'' (the right foot crosses over the left, raised).
The ''double à droite'' begins with a ''pieds joints'' and ''petit saut'', followed by two quick steps, a ''marque pied gauche croisé'' and ''marque pied droit croisé'', during beat two, a ''grève droit croisée'' and ''petit saut'' on beat three and on the last beat ''pieds joints'' and a ''capriole'' (leap into the air with entrechat
Because ballet History of ballet, became formalized in France, a significant part of ballet terminology is in the French language.
A
À la seconde
() (Literally "to second") If a step is done "à la seconde", it is done to the side. 'Second posi ...
).
Baroque
 The gavotte became popular in the court of
The gavotte became popular in the court of Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
where Jean-Baptiste Lully
Jean-Baptiste Lully ( – 22 March 1687) was a French composer, dancer and instrumentalist of Italian birth, who is considered a master of the French Baroque music style. Best known for his operas, he spent most of his life working in the court o ...
was the leading court composer. Gaétan Vestris
Gaetano Apolline Baldassarre Vestris (18 April 1729 – 23 September 1808), French ballet dancer, was born in Florence and made his debut at the opera in 1749.
Life
Born of an Italian theatrical family, he studied dance with Louis Dupré at th ...
did much to define the dance. Subsequently many composers of the Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
period incorporated the dance as one of many optional additions to the standard instrumental suite
Suite may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Suite (music), a set of musical pieces considered as one composition
** Suite (Bach), a list of suites composed by J. S. Bach
** Suite (Cassadó), a mid-1920s composition by Gaspar Cassadó
** ''Suite' ...
of the era. The examples in suites and partitas by Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (German: Help:IPA/Standard German, �joːhan zeˈbasti̯an baχ ( – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque music, Baroque period. He is known for his prolific output across a variety ...
are well known.
Movements of early 18th-century musical works entitled ''Tempo di gavotta'' sometimes indicated the sense of a gavotte rhythm or movement, without fitting the number of measures or strains typical of the actual dance. Examples of these can be found in the works of Arcangelo Corelli
Arcangelo Corelli (, also , ; ; 17 February 1653 – 8 January 1713) was an List of Italian composers, Italian composer and violinist of the middle Baroque music, Baroque era. His music was key in the development of the modern genres of Sonata a ...
or Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (German: Help:IPA/Standard German, �joːhan zeˈbasti̯an baχ ( – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque music, Baroque period. He is known for his prolific output across a variety ...
.
George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
wrote a number of gavottes, including the fifth-and-final movement, Allegro, of the Concerto Grosso in B-flat major, Op. 3, No. 2, HWV 313.
Later examples
Composers in the 19th century wrote gavottes that began, like the 16th-century gavotte, on thedownbeat
''DownBeat'' (styled in all caps) is an American music magazine devoted to "jazz, blues and beyond", the last word indicating its expansion beyond the jazz realm that it covered exclusively in previous years. The publication was established in 1 ...
rather than on the half-measure upbeat. The famous Gavotte in D by Gossec is such an example, as is the Gavotte in Massenet's ''Manon'' but not the one in Ambroise Thomas's ''Mignon
''Mignon'' () is an 1866 ''opéra comique'' (or opera in its second version) in three acts by Ambroise Thomas. The original French libretto was by Jules Barbier and Michel Carré, based on Goethe's 1795-96 novel '' Wilhelm Meisters Lehrjahre''. ...
''. A gavotte also occurs in the second act of ''The Gondoliers
''The Gondoliers; or, The King of Barataria'' is a Savoy Opera, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It premiered at the Savoy Theatre on 7 December 1889 and ran for a very successful 554 performances (at that time t ...
'' and the Act I finale of ''Ruddigore
''Ruddigore; or, The Witch's Curse'', originally called ''Ruddygore'', is a comic opera in two acts, with music by Arthur Sullivan and libretto by W. S. Gilbert. It is one of the Savoy Operas and the tenth of fourteen comic operas written tog ...
'', both by Gilbert and Sullivan
Gilbert and Sullivan refers to the Victorian-era theatrical partnership of the dramatist W. S. Gilbert (1836–1911) and the composer Arthur Sullivan (1842–1900) and to the works they jointly created. The two men collaborated on fourteen com ...
.
Edvard Grieg
Edvard Hagerup Grieg ( , ; 15 June 18434 September 1907) was a Norwegian composer and pianist. He is widely considered one of the leading Romantic music, Romantic era composers, and his music is part of the standard classical repertoire worldwid ...
's suite '' From Holberg's Time'', based on eighteenth-century dance forms, features a "Gavotte" as its third movement (1884).
Australian composer Fred Werner used a gavotte he composed for teaching students.
Igor Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky ( – 6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and American citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential 20th-century c ...
's ballet ''Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; ) is a classical character that originated in commedia dell'arte of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept ...
'' features a "Gavotta con due variazioni", as number 18, and movement VI in the suite (1922).
Sergei Prokofiev
Sergei Sergeyevich Prokofiev; alternative transliterations of his name include ''Sergey'' or ''Serge'', and ''Prokofief'', ''Prokofieff'', or ''Prokofyev''. , group=n ( – 5 March 1953) was a Russian composer, pianist, and conductor who l ...
employs a gavotte instead of a minuet in his Symphony No. 1 (''Classical''), Op. 25 (1917), and includes another one as the second of his Ten Piano Pieces Op. 12 (1913), and another as the third of his Four Piano Pieces, Op. 32 (1918).
Leonard Bernstein
Leonard Bernstein ( ; born Louis Bernstein; August 25, 1918 – October 14, 1990) was an American conductor, composer, pianist, music educator, author, and humanitarian. Considered to be one of the most important conductors of his time, he was th ...
's ''Candide
( , ) is a French satire written by Voltaire, a philosopher of the Age of Enlightenment, first published in 1759. The novella has been widely translated, with English versions titled ''Candide: or, All for the Best'' (1759); ''Candide: or, The ...
'' has a "Venice Gavotte" in act 2.
"The Ascot Gavotte" is a song in the 1956 musical ''My Fair Lady
''My Fair Lady'' is a musical theatre, musical with a book and lyrics by Alan Jay Lerner and music by Frederick Loewe. The story, based on George Bernard Shaw's 1913 play ''Pygmalion (play), Pygmalion'' and on the Pygmalion (1938 film), 1938 film ...
'' by Alan Jay Lerner
Alan Jay Lerner (August 31, 1918 – June 14, 1986) was an American lyricist and librettist. In collaboration with Frederick Loewe, and later Burton Lane, he created some of the world's most popular and enduring works of musical theatre bot ...
and Frederick Loewe
Frederick Loewe ( ; born Friedrich "Fritz" Löwe, ; June 10, 1901 – February 14, 1988
.
In popular culture
* Early 20th century musicianSamuel Siegel
Samuel Siegel (born 1875, Des Moines, Iowa — died January 14, 1948, Los Angeles, California) was an American mandolin virtuoso and composer who played mandolin on 29 records for Victor Records, including 9 pieces of his own composition and two ...
recorded a ragtime
Ragtime, also spelled rag-time or rag time, is a musical style that had its peak from the 1890s to 1910s. Its cardinal trait is its Syncopation, syncopated or "ragged" rhythm. Ragtime was popularized during the early 20th century by composers ...
mandolin
A mandolin (, ; literally "small mandola") is a Chordophone, stringed musical instrument in the lute family and is generally Plucked string instrument, plucked with a plectrum, pick. It most commonly has four Course (music), courses of doubled St ...
tune "Gavotte".
* Carly Simon
Carly Elisabeth Simon (born June 25, 1943) is an American musician, singer, songwriter, and author. She rose to fame in the 1970s with a string of hit records; her 13 Billboard Hot 100, top 40 U.S. hits include "Anticipation (song), Anticipatio ...
's song "You're So Vain
"You're So Vain" is a song by the American singer-songwriter Carly Simon, released as a single in November 1972. The lyrics describe a self-absorbed lover, whose identity has long been a matter of speculation. Simon said the song refers to three ...
" includes the lyric "You had one eye in the mirror as you watched yourself gavotte". In this context it means "moving in a pretentious manner".
* The Stephen Sondheim
Stephen Joshua Sondheim (; March22, 1930November26, 2021) was an American composer and lyricist. Regarded as one of the most important figures in 20th-century musical theater, he is credited with reinventing the American musical. He received Lis ...
musical ''Sunday in the Park with George
''Sunday in the Park with George'' is a 1984 musical with music and lyrics by Stephen Sondheim and book by James Lapine. It was inspired by the French pointillist painter Georges Seurat's painting '' A Sunday Afternoon on the Island of La G ...
'' uses the word ''gavotte'' as a satirical device in the otherwise irregular, non-steadily rhythmical, song "It's Hot Up Here" to start the second act, "We're stuck up here in this gavotte".
* The Johnny Mercer
John Herndon Mercer (November 18, 1909 – June 25, 1976) was an American lyricist, songwriter, and singer, as well as a record label executive who co-founded Capitol Records with music industry businessmen Buddy DeSylva and Wallichs Music Cit ...
song "Strip Polka
"Strip Polka" is a 1942 novelty song
A novelty song is a type of song built upon some form of novel concept, such as a gimmick, a piece of humor, or a sample of popular culture. Novelty songs partially overlap with comedy songs, which are ...
" includes the lyric "Oh, she hates corny waltzes and she hates the gavotte".
* Geneticist W. D. Hamilton
William Donald Hamilton (1 August 1936 – 7 March 2000) was a British evolutionary biologist, recognised as one of the most significant evolutionary theorists of the 20th century. Hamilton became known for his theoretical work expounding a ...
in his paper "Gamblers since life began: barnacles, aphids, elms." in ''The Quarterly Review of Biology
''The Quarterly Review of Biology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of biology. It was established in 1926 by Raymond Pearl. In the 1960s it was purchased by the Stony Brook Foundation when the editor H. Bentley Glass ...
'' (1975) referred to the drilled formality of the mechanisms of individual reproduction as "the gavotte of chromosomes".
* Philosopher Stephen David Ross
Stephen David Ross (born 1935) is an American philosopher, currently Distinguished Research Professor of Philosophy, Interpretation, and Culture and of Comparative Literature at Binghamton University. He has published over 30 books in interdiscipl ...
characterises metaphysical aporia
In philosophy, an aporia () is a conundrum or state of puzzlement. In rhetoric, it is a declaration of doubt, made for rhetorical purpose and often feigned. The notion of an aporia is principally found in ancient Greek philosophy, but it also p ...
as "the disruptive side of a tradition that needs both repetition and its annihilation for intelligibility. It is a site at which same and other dance their unending gavotte of life and death."
*Agustín Barrios
Agustín Pío Barrios (also known as Agustín Barrios Mangoré and Nitsuga—Agustín spelled backwards—Mangoré; May 5, 1885 – August 7, 1944) was a Paraguayan virtuoso classical guitarist and composer, largely regarded as one of the greates ...
wrote a solo guitar piece, "Madrigal Gavotte", which is a combination of the two styles.
* In the anime ''Kiniro no Corda'' (''La Corda d'Oro
is a Japanese role-playing game series targeted at a female demographic audience from Koei. The title is Italian for ''The Golden String''.
The story was adapted into a manga by the game's character designer, Yuki Kure, which is ...
''), "Gavotte in D" by Gossec is heard many times, though referred to only as "Gavotte".
* In the 1990 novel ''Good Omens
''Good Omens: The Nice and Accurate Prophecies of Agnes Nutter, Witch'' is a 1990 novel written by the English authors Terry Pratchett and Neil Gaiman.
The novel is a comedy about the birth of the son of Satan and the coming of the End Times. ...
'' by Terry Pratchett
Sir Terence David John Pratchett (28 April 1948 – 12 March 2015) was an English author, humorist, and Satire, satirist, best known for the ''Discworld'' series of 41 comic fantasy novels published between 1983 and 2015, and for the Apocalyp ...
and Neil Gaiman
Neil Richard MacKinnon Gaiman (; born Neil Richard Gaiman; 10 November 1960) is an English author of short fiction, novels, comic books, audio theatre, and screenplays. His works include the comic series ''The Sandman (comic book), The Sandma ...
, it is noted that one cannot determine how many angels can dance on the head of a pin
"How many angels can dance on the head of a pin?" (alternatively "How many angels can stand on the point of a pin?") is a phrase that when used in modern contexts can be used as a metaphor for wasting time debating topics of no practical value ...
, because angels do not dance—the exception being the Principality
A principality (or sometimes princedom) is a type of monarchy, monarchical state or feudalism, feudal territory ruled by a prince or princess. It can be either a sovereign state or a constituent part of a larger political entity. The term "prin ...
Aziraphale, who once learned to do the gavotte in a discreet gentlemen's club in Portland Place
Portland Place is a street in the Marylebone district of central London. Named after the 3rd Duke of Portland, the unusually wide street is home to the BBC's headquarters Broadcasting House, the Chinese and Polish embassies, the Royal Insti ...
in the late 1880s.
*In the Broadway musical ''1776
Events January–February
* January 1 – American Revolutionary War – Burning of Norfolk: The town of Norfolk, Virginia is destroyed, by the combined actions of the British Royal Navy and occupying Patriot forces.
* January ...
'' during the song "Cool, Considerate Men", reference is made to "Mr. Adams' new gavotte"—a reference regarding John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Before Presidency of John Adams, his presidency, he was a leader of ...
' ideas for a declaration of independence from Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-west coast of continental Europe, consisting of the countries England, Scotland, and Wales. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the List of European ...
.
*In the 1967 film '' How to Succeed in Business Without Really Trying'' the song "A Secretary Is Not a Toy" refers to a gavotte. The song discourages personal indiscretions with secretaries at the firm. The reference to a gavotte is meant to be ironic, as the original dance accompanying the song from the Broadway show was a modified gavotte.
*In the manga and anime ''One Piece
''One Piece'' (stylized in all caps) is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Eiichiro Oda. It follows the adventures of Monkey D. Luffy and his crew, the Straw Hat Pirates, as he explores the Grand Line in search of the myt ...
'', the skeleton musician character Brooke (and his "zombie," Ryuuma, which was given life by Brooke's shadow) has a signature technique, ''Gavotte Bond en Avant''.
*In the Robert Pinsky
Robert Pinsky (born October 20, 1940) is an American poet, essayist, literary critic, and translator. He was the first United States Poet Laureate to serve three terms. Recognized worldwide, Pinsky's work has earned numerous accolades. Pinsky ...
poem "Impossible To Tell", the gavotte is mentioned in the first line.
*In John Updike
John Hoyer Updike (March 18, 1932 – January 27, 2009) was an American novelist, poet, short-story writer, art critic, and literary critic. One of only four writers to win the Pulitzer Prize for Fiction more than once (the others being Booth Tar ...
's novel ''Bech at Bay
Henry Bech is a fictional character created by American author John Updike. Bech first appeared in assorted short stories, stories which were later compiled in the books ''Bech: A Book'' (1970), ''Bech Is Back'' (1982), and ''Bech at Bay'' (1998). ...
'', for the protagonist, "It embarrassed him that for these young Czechs American writing, its square dance of lame old names, should appear such a lively gavotte, prancing carefree into the future."
*In the mid-nineteenth-century novel ''The Scout'', William Gilmore Simms
William Gilmore Simms (April 17, 1806 – June 11, 1870) was a poet, novelist, politician and historian from the American South. His writings achieved great prominence during the 19th century, with Edgar Allan Poe pronouncing him the best novelis ...
describes a lonely sentry: "He sang, and whistled, and soliloquized; and, not unfrequently, relieved the dull measured step of the sentinel by the indulgence of such a gavotte as a beef-eating British soldier of the 'prince's own' might be supposed capable of displaying in that period of buckram movement."
* Describing American foreign policy in the wake of the September 11 attacks
The September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11, were four coordinated Islamist terrorist suicide attacks by al-Qaeda against the United States in 2001. Nineteen terrorists hijacked four commercial airliners, crashing the first two into ...
, author Norman Podhoretz
Norman Podhoretz (; born January 16, 1930) is an American magazine editor, writer, and conservative political commentator, who identifies his views as " paleo- neoconservative", but only "because (he's) been one for so long".John Ashbery
John Lawrence Ashbery (July 28, 1927 – September 3, 2017) was an American poet and art critic.
Ashbery is considered the most influential American poet of his time. Oxford University literary critic John Bayley wrote that Ashbery "sounded, in ...
includes the sentence: "A gavotte of dust-motes / came to replace my seeing."
*In the poem "12/2/80" from ''Waltzing Matilda'' (1981), Alice Notley
Alice Elizabeth Notley (November 8, 1945 – May 19, 2025) was an American poet. Notley came to prominence as a member of the second generation of the New York School of poetry—although she always denied being involved with the New York Schoo ...
writes: "A leaf if local / only when falling. // 'What? like a gavotte?' / the common evergreen rustle: / hours & regulations & so on ...",
* Chas & Dave
Chas & Dave (often billed as Chas 'n' Dave) were an English pop rock duo, formed in London by Chas Hodges and Dave Peacock (musician), Dave Peacock.
They were most notable as creators and performers of a musical style labelled ''rockney'' (a p ...
produced a song called "Give it Gavotte" which uses this style on their 1982 album '' Job Lot''
* In "The Wild Wood", the third chapter of Kenneth Grahame
Kenneth Grahame ( ; 8 March 1859 – 6 July 1932) was a British writer. He is best remembered for the classic of children's literature ''The Wind in the Willows'' (1908). Born in Scotland, he spent most of his childhood with his grandmother in ...
's 1908 novel ''The Wind in the Willows
''The Wind in the Willows'' is a children's novel by the British novelist Kenneth Grahame, first published in 1908. It details the story of Mole, Ratty, and Badger as they try to help Mr. Toad, after he becomes obsessed with motorcars and get ...
'', one of the lines describing the blooming spring is "Comfrey, the purple hand-in-hand with the white, crept forth to take its place in the line; and at last one morning the diffident and delaying dog-rose stepped delicately on the stage, and one knew, as if string-music had announced it in stately chords that strayed into a gavotte, that June at last was here."
References
Further reading
*Guilcher, Jean-Michel. 1963. ''La tradition populaire de danse en Basse-Bretagne''. Études Européennes 1. Paris and The Hague: Mouton. Second edition, 1976, Paris: Mouton. . New, expanded edition, 1995, Spézet-Douarnenez: Coop-Breizh. . Douarnenez: Chasse-Marée-Armen. . Reprinted 1997. *Semmens, Richard T. 1997. "Branles, Gavottes and Contredanses in the Later Seventeenth and Early Eighteenth Centuries". ''Dance Research
Dance research is the study of dance, including dance history, ethnochoreology, dance theory, dance anthropology, and dance science.
Dance research as an academic discipline is relatively new. In 1967, the first volume of the ''CORD Dance Re ...
'' 15, no. 2 (Winter): 35–62.
External links
* * * * * {{Authority control French dances French music history Breton dances Baroque dance Renaissance music Baroque music Dance forms in classical music