gastroesophageal reflux on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is a chronic upper
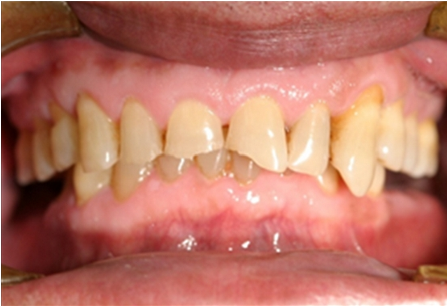
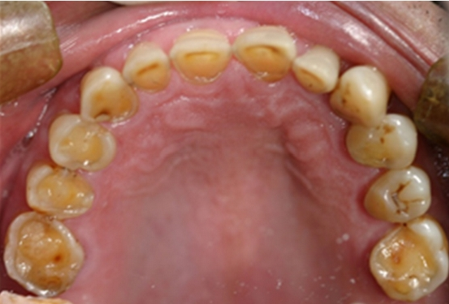 Acid reflux into the mouth can cause breakdown of the enamel, especially on the inside surface of the teeth. A dry mouth, acid or burning sensation in the mouth, bad breath and redness of the palate may occur. Less common symptoms of GERD include difficulty in swallowing, water brash, chronic cough, hoarse voice, nausea and vomiting.
Signs of enamel erosion are the appearance of a smooth, silky-glazed, sometimes dull, enamel surface with the absence of perikymata, together with intact enamel along the gum margin. It will be evident in people with restorations as tooth structure typically dissolves much faster than the restorative material, causing it to seem as if it "stands above" the surrounding tooth structure.
Acid reflux into the mouth can cause breakdown of the enamel, especially on the inside surface of the teeth. A dry mouth, acid or burning sensation in the mouth, bad breath and redness of the palate may occur. Less common symptoms of GERD include difficulty in swallowing, water brash, chronic cough, hoarse voice, nausea and vomiting.
Signs of enamel erosion are the appearance of a smooth, silky-glazed, sometimes dull, enamel surface with the absence of perikymata, together with intact enamel along the gum margin. It will be evident in people with restorations as tooth structure typically dissolves much faster than the restorative material, causing it to seem as if it "stands above" the surrounding tooth structure.
 A small amount of acid reflux is typical even in healthy people (as with infrequent and minor
A small amount of acid reflux is typical even in healthy people (as with infrequent and minor
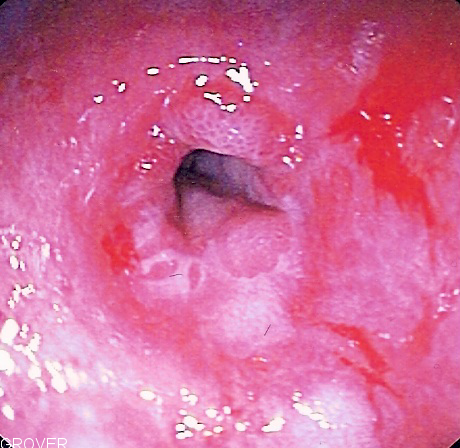 The diagnosis of GERD is usually made when typical symptoms are present. Reflux can be present in people without symptoms and the diagnosis requires both symptoms or complications and reflux of stomach content.
Other investigations may include
The diagnosis of GERD is usually made when typical symptoms are present. Reflux can be present in people without symptoms and the diagnosis requires both symptoms or complications and reflux of stomach content.
Other investigations may include
gastrointestinal disease
Gastrointestinal diseases (abbrev. GI diseases or GI illnesses) refer to diseases involving the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract, namely the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum; and the accessory or ...
in which stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
, resulting in symptoms and/or complications. Symptoms include dental corrosion, dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
, heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Ly ...
, odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the ...
, regurgitation, non-cardiac chest pain, extraesophageal symptoms such as chronic cough, hoarseness
A hoarse voice, also known as dysphonia or hoarseness, is when the voice involuntarily sounds breathy, raspy, or strained, or is softer in volume or lower in pitch. A hoarse voice can be associated with a feeling of unease or scratchiness in the ...
, reflux-induced laryngitis, or asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
. In the long term, and when not treated, complications such as esophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stoma ...
, esophageal stricture, and Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, intersper ...
may arise.
Risk factors include obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
, pregnancy
Pregnancy is the time during which one or more offspring gestation, gestates inside a woman's uterus. A multiple birth, multiple pregnancy involves more than one offspring, such as with twins.
Conception (biology), Conception usually occurs ...
, smoking
Smoking is a practice in which a substance is combusted, and the resulting smoke is typically inhaled to be tasted and absorbed into the bloodstream of a person. Most commonly, the substance used is the dried leaves of the tobacco plant, whi ...
, hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs (typically the stomach) slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryng ...
, and taking certain medications. Medications that may cause or worsen the disease include benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), colloquially known as "benzos", are a class of central nervous system (CNS) depressant, depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed t ...
s, calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, NSAID
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a therapeutic drug class which reduces pain, decreases inflammation, decreases fever, and prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of ...
s, and certain asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wh ...
medicines. Acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus ( archaic spelling) ( see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, ...
, which is at the junction between the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and the esophagus. Diagnosis among those who do not improve with simpler measures may involve gastroscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered ...
, upper GI series, esophageal pH monitoring
In gastroenterology, esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document ...
, or esophageal manometry
An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), esophageal body and lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
Indications
An EMS is typically done to evaluate susp ...
.
Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and sometimes surgery for those who do not improve with the first two measures. Lifestyle changes include not lying down for three hours after eating, lying down on the left side, raising the pillow or bedhead height, losing weight, and stopping smoking. Foods that may precipitate GERD symptoms include coffee, alcohol, chocolate, fatty foods, acidic foods, and spicy foods.
* Medications include antacid
An antacid is a substance which neutralization (chemistry), neutralizes gastric acid, stomach acidity and is used to relieve heartburn, indigestion, or an upset stomach. Some antacids have been used in the treatment of constipation and diarrhe ...
s, H2 receptor blockers, proton pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. The body eventually synthesizes ne ...
s, and prokinetics
A prokinetic agent (also prokineticin, gastroprokinetic agent, gastrokinetic agent or propulsive) is a type of drug which enhances gastrointestinal motility by increasing the frequency or strength of contractions, but without disrupting their rhyt ...
.
In the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
, between 10 and 20% of the population is affected by GERD. It is highly prevalent in North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
with 18% to 28% of the population suffering from the condition. Occasional gastroesophageal reflux without troublesome symptoms or complications is even more common. The classic symptoms of GERD were first described in 1925, when Friedenwald and Feldman commented on heartburn and its possible relationship to a hiatal hernia. In 1934 gastroenterologist Asher Winkelstein described reflux and attributed the symptoms to stomach acid.
Signs and symptoms
Adults
The most common symptoms of GERD in adults are an acidic taste in the mouth, regurgitation, andheartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Ly ...
. Less common symptoms include pain with swallowing/sore throat
Sore throat, also known as throat pain, is pain or irritation of the throat. The majority of sore throats are caused by a virus, for which antibiotics are not helpful.
For sore throat caused by bacteria (GAS), treatment with antibiotics may hel ...
, increased salivation (also known as water brash), nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat.
Over 30 d ...
, chest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
, coughing
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ...
, and globus sensation. The acid reflux can induce asthma attack symptoms like shortness of breath, cough, and wheezing in those with underlying asthma.
GERD sometimes causes injury to the esophagus. These injuries may include one or more of the following:
* Reflux esophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stoma ...
– inflammation of esophageal epithelium which can cause ulcers near the junction of the stomach and esophagus
* Esophageal strictures – the persistent narrowing of the esophagus caused by reflux-induced inflammation
* Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, intersper ...
– intestinal metaplasia
Metaplasia () is the transformation of a cell type to another cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus. In simplistic terms, it is as if the ...
(changes of the epithelial cells from squamous to intestinal columnar epithelium) of the distal esophagus
* Esophageal adenocarcinoma – a form of cancer
GERD sometimes causes injury of the larynx (LPR). Other complications can include aspiration pneumonia
Aspiration pneumonia is a type of lung infection that is due to a relatively large amount of material from the stomach or mouth entering the lungs. Signs and symptoms often include fever and cough of relatively rapid onset. Complications may incl ...
.
Children and babies
GERD may be difficult to detect ininfant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of ...
s and child
A child () is a human being between the stages of childbirth, birth and puberty, or between the Development of the human body, developmental period of infancy and puberty. The term may also refer to an unborn human being. In English-speaking ...
ren since they cannot describe what they are feeling and indicators must be observed. Symptoms may vary from typical adult symptoms. GERD in children may cause repeated vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
, effortless spitting up, coughing
A cough is a sudden expulsion of air through the large breathing passages which can help clear them of fluids, irritants, foreign particles and microbes. As a protective reflex, coughing can be repetitive with the cough reflex following three ...
, and other respiratory problems, such as wheezing. Inconsolable crying, refusing food, crying for food and then pulling off the bottle or breast only to cry for it again, failure to gain adequate weight, bad breath, and burping
Burping (also called belching and eructation) is the release of gas from the upper digestive tract (esophagus and stomach) of animals through the mouth. It is usually audible.
In humans, burping can be caused by normal eating processes, or as ...
are also common. Children may have one symptom or many; no single symptom is universal in all children with GERD.
Of the estimated 4 million babies born in the US each year, up to 35% of them may have difficulties with reflux in the first few months of their lives, known as 'spitting up'. About 90% of infants will outgrow their reflux by their first birthday.
Mouth

 Acid reflux into the mouth can cause breakdown of the enamel, especially on the inside surface of the teeth. A dry mouth, acid or burning sensation in the mouth, bad breath and redness of the palate may occur. Less common symptoms of GERD include difficulty in swallowing, water brash, chronic cough, hoarse voice, nausea and vomiting.
Signs of enamel erosion are the appearance of a smooth, silky-glazed, sometimes dull, enamel surface with the absence of perikymata, together with intact enamel along the gum margin. It will be evident in people with restorations as tooth structure typically dissolves much faster than the restorative material, causing it to seem as if it "stands above" the surrounding tooth structure.
Acid reflux into the mouth can cause breakdown of the enamel, especially on the inside surface of the teeth. A dry mouth, acid or burning sensation in the mouth, bad breath and redness of the palate may occur. Less common symptoms of GERD include difficulty in swallowing, water brash, chronic cough, hoarse voice, nausea and vomiting.
Signs of enamel erosion are the appearance of a smooth, silky-glazed, sometimes dull, enamel surface with the absence of perikymata, together with intact enamel along the gum margin. It will be evident in people with restorations as tooth structure typically dissolves much faster than the restorative material, causing it to seem as if it "stands above" the surrounding tooth structure.
Barrett's esophagus
GERD may lead toBarrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal ( metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells that line the lower part of the esophagus. The cells change from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium, intersper ...
, a type of intestinal metaplasia
Metaplasia () is the transformation of a cell type to another cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abnormal stimulus. In simplistic terms, it is as if the ...
, which is in turn a precursor condition for esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer (American English) or oesophageal cancer (British English) is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include dysphagia, difficulty in swallowing and weigh ...
. The risk of progression from Barrett's to dysplasia is uncertain, but is estimated at 20% of cases. Due to the risk of chronic heartburn progressing to Barrett's, EGD every five years is recommended for people with chronic heartburn, or who take drugs for chronic GERD.
Causes
 A small amount of acid reflux is typical even in healthy people (as with infrequent and minor
A small amount of acid reflux is typical even in healthy people (as with infrequent and minor heartburn
Heartburn is a burning sensation felt behind the breastbone. It is a symptom that is commonly linked to acid reflux and is often triggered by food, particularly fatty, sugary, spicy, chocolate, citrus, onion-based and tomato-based products. Ly ...
), but gastroesophageal reflux becomes gastroesophageal reflux disease when signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms are diagnostic indications of an illness, injury, or condition.
Signs are objective and externally observable; symptoms are a person's reported subjective experiences.
A sign for example may be a higher or lower temperature ...
develop into a recurrent problem. Frequent acid reflux is due to poor closure of the lower esophageal sphincter
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus ( archaic spelling) ( see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), colloquially known also as the food pipe, food tube, or gullet, ...
, which is at the junction between the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of Human, humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical t ...
and the esophagus.
Factors that can contribute to GERD:
* Hiatal hernia
A hiatal hernia or hiatus hernia is a type of hernia in which abdominal organs (typically the stomach) slip through the diaphragm into the middle compartment of the chest. This may result in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or laryng ...
, which increases the likelihood of GERD due to mechanical and motility factors.
* Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, considered by multiple organizations to be a disease, in which excess Adipose tissue, body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it can potentially have negative effects on health. People are classifi ...
: increasing body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (Mass versus weight, weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the human body weight, body mass divided by the square (algebra), square of the human height, body height, and is ...
is associated with more severe GERD. In a large series of 2,000 patients with symptomatic reflux disease, it has been shown that 13% of changes in esophageal acid exposure is attributable to changes in body mass index.
* GERD can be a symptom of mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS).
Factors that have been linked with GERD, but not conclusively:
* Obstructive sleep apnea
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is the most common sleep-related breathing disorder and is characterized by recurrent episodes of complete or partial airway obstruction, obstruction of the respiratory tract#Upper respiratory tract, upper airway lea ...
* Gallstones
A gallstone is a stone formed within the gallbladder from precipitated bile components. The term cholelithiasis may refer to the presence of gallstones or to any disease caused by gallstones, and choledocholithiasis refers to the presence of ...
, which can impede the flow of bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
into the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
, which can affect the ability to neutralize gastric acid
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid – of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. In humans, the pH is between one and three, much lower than most other a ...
In 1999, a review of existing studies found that, on average, 40% of GERD patients also had '' H. pylori'' infection. The eradication of ''H. pylori'' can lead to an increase in acid secretion, leading to the question of whether ''H. pylori''-infected GERD patients are any different from non-infected GERD patients. A double-blind
In a blind or blinded experiment, information which may influence the participants of the experiment is withheld until after the experiment is complete. Good blinding can reduce or eliminate experimental biases that arise from a participants' expec ...
study, reported in 2004, found no clinically significant difference between these two types of patients with regard to the subjective or objective measures of disease severity.
The etiology
Etiology (; alternatively spelled aetiology or ætiology) is the study of causation or origination. The word is derived from the Greek word ''()'', meaning "giving a reason for" (). More completely, etiology is the study of the causes, origins ...
of GERD appears to include the reflux of bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is pro ...
from the stomach into the esophagus leading to the production of reactive oxygen species
In chemistry and biology, reactive oxygen species (ROS) are highly Reactivity (chemistry), reactive chemicals formed from diatomic oxygen (), water, and hydrogen peroxide. Some prominent ROS are hydroperoxide (H2O2), superoxide (O2−), hydroxyl ...
and oxidative stress
Oxidative stress reflects an imbalance between the systemic manifestation of reactive oxygen species and a biological system's ability to readily detoxify the reactive intermediates or to repair the resulting damage. Disturbances in the normal ...
and then inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
and induction of DNA damage. In experimental models of GERD it was found that '' Lactobacilli'' facilitate the repair of such DNA damage indicating that administration of these potentially probiotic
Probiotics are live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, generally by improving or restoring the microbiota in the gut. Probiotics are considered generally safe to consume, but may cause bacteria– host interactions ...
bacteria may be useful in patients suffering with GERD for preventing progression to Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ; AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
.
Diagnosis
 The diagnosis of GERD is usually made when typical symptoms are present. Reflux can be present in people without symptoms and the diagnosis requires both symptoms or complications and reflux of stomach content.
Other investigations may include
The diagnosis of GERD is usually made when typical symptoms are present. Reflux can be present in people without symptoms and the diagnosis requires both symptoms or complications and reflux of stomach content.
Other investigations may include esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD) or oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD), also called by various other names, is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract down to the duodenum. It is considered ...
(EGD). Barium swallow
An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as bariu ...
X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s should not be used for diagnosis. Esophageal manometry
An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), esophageal body and lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
Indications
An EMS is typically done to evaluate susp ...
is not recommended for use in the diagnosis, being recommended only prior to surgery. Ambulatory esophageal pH monitoring
In gastroenterology, esophageal pH monitoring is the current gold standard for diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It provides direct physiologic measurement of acid in the esophagus and is the most objective method to document ...
may be useful in those who do not improve after PPIs and is not needed in those in whom Barrett's esophagus is seen. Investigation for ''H. pylori'' is not usually needed.
The current gold standard for diagnosis of GERD is esophageal pH monitoring. It is the most objective test to diagnose the reflux disease and allows monitoring GERD patients in their response to medical or surgical treatment. One practice for diagnosis of GERD is a short-term treatment with proton-pump inhibitors, with improvement in symptoms suggesting a positive diagnosis. Short-term treatment with proton-pump inhibitors may help predict abnormal 24-hour pH monitoring results among patients with symptoms suggestive of GERD.
Endoscopy
Endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
, the examination of the stomach with a fibre-optic scope, is not routinely needed if the case is typical and responds to treatment. It is recommended when people either do not respond well to treatment or have alarm symptoms, including dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or l ...
, anemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availabl ...
, blood in the stool
Blood in stool looks different depending on how early it enters the digestive tract—and thus how much digestive action it has been exposed to—and how much there is. The term can refer either to melena, with a black appearance, typically or ...
(detected chemically), wheezing
A wheeze is a clinical symptom of a continuous, coarse, whistling sound produced in the respiratory airways during breathing. For wheezes to occur, part of the respiratory tree must be narrowed or obstructed (for example narrowing of the lower ...
, weight loss, or voice changes. Some physicians advocate either once-in-a-lifetime or 5- to 10-yearly endoscopy for people with longstanding GERD, to evaluate the possible presence of dysplasia or Barrett's esophagus.
Biopsies performed during gastroscopy may show:
* Edema and basal hyperplasia (nonspecific inflammatory changes)
* Lymphocytic inflammation (nonspecific)
* Neutrophilic inflammation (usually due to reflux or '' Helicobacter'' gastritis
Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Othe ...
)
* Eosinophilic inflammation (usually due to reflux): The presence of intraepithelial eosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
may suggest a diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis (EE) if eosinophils are present in high enough numbers. Less than 20 eosinophils per high-power microscopic field in the distal
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provi ...
esophagus, in the presence of other histologic features of GERD, is more consistent with GERD than EE.Mills, S (ed.) 2009.Sternberg's Diagnostic Pathology. 5th Edition.
* Goblet cell intestinal metaplasia or Barrett's esophagus
* Elongation of the papillae
* Thinning of the squamous cell layer
* Dysplasia
Dysplasia is any of various types of abnormal growth or development of cells (microscopic scale) or organs (macroscopic scale), and the abnormal histology or anatomical structure(s) resulting from such growth. Dysplasias on a mainly microscopic ...
* Carcinoma
Carcinoma is a malignancy that develops from epithelial cells. Specifically, a carcinoma is a cancer that begins in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body, and that arises from cells originating in the endodermal, mesoder ...
Reflux changes that are not erosive in nature lead to "nonerosive reflux disease".
Severity
Severity may be documented with the Johnson-DeMeester's scoring system: 0 – None 1 – Minimal – occasional episodes 2 – Moderate – medical therapy visits 3 – Severe – interference with daily activitiesDifferential diagnosis
Other causes ofchest pain
Chest pain is pain or discomfort in the chest, typically the front of the chest. It may be described as sharp, dull, pressure, heaviness or squeezing. Associated symptoms may include pain in the shoulder, arm, upper abdomen, or jaw, along with n ...
such as heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, ...
should be ruled out before making the diagnosis. Another kind of acid reflux, which causes respiratory
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies gr ...
and laryngeal signs and symptoms, is called laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) or extraesophageal reflux disease (EERD). Unlike GERD, LPR rarely produces heartburn, and is sometimes called ''silent reflux''. Differential diagnosis of GERD can also include dyspepsia, peptic ulcer disease, esophageal and gastric cancer, and food allergies.
Treatment
The treatments for GERD may include food choices, lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgery. Initial treatment is frequently with a proton-pump inhibitor such asomeprazole
Omeprazole, sold under the brand names Prilosec and Losec, among others, is a medication used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It is also used to prevent up ...
. In some cases, a person with GERD symptoms can manage them by taking over-the-counter drugs
Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid presc ...
.
* This is often safer and less expensive than taking prescription drugs. Some guidelines recommend trying to treat symptoms with an H2 antagonist before using a proton-pump inhibitor because of cost and safety concerns.
Medical nutrition therapy and lifestyle changes
Medical nutrition therapy plays an essential role in managing the symptoms of the disease by preventing reflux, preventing pain and irritation, and decreasing gastric secretions. Some foods such as chocolate, mint, high-fat food, and alcohol have been shown to relax the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the risk of reflux. Weight loss is recommended for the overweight or obese, as well as avoidance of bedtime snacks or lying down immediately after meals (meals should occur at least 2–3 hours before bedtime), elevation of the head of the bed on 6-inch blocks, avoidance of smoking, and avoidance of tight clothing that increases pressure in the stomach. It may be beneficial to avoid spices, citrus juices, tomatoes andsoft drink
A soft drink (see #Terminology, § Terminology for other names) is a class of non-alcoholic drink, usually (but not necessarily) Carbonated water, carbonated, and typically including added Sweetness, sweetener. Flavors used to be Natural flav ...
s, and to consume small frequent meals and drink liquids between meals. Some evidence suggests that reduced sugar intake and increased fiber intake can help. Although moderate exercise may improve symptoms in people with GERD, vigorous exercise may worsen them. Breathing exercises may relieve GERD symptoms.
Medications
The primary medications used for GERD are proton-pump inhibitors, H2 receptor blockers and antacids with or withoutalginic acid
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. When the alginic acid binds with sodium and calcium ions, the resulting salts are kn ...
. The use of acid suppression therapy is a common response to GERD symptoms and many people get more of this kind of treatment than their case merits. The overuse of acid suppression is a problem because of the side effects and costs.
Proton-pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs), such asomeprazole
Omeprazole, sold under the brand names Prilosec and Losec, among others, is a medication used in the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Zollinger–Ellison syndrome. It is also used to prevent up ...
, are the most effective, followed by H2 receptor blockers. If a once-daily PPI is only partially effective they may be used twice a day. They should be taken one half to one hour before a meal. There is no significant difference between PPIs. When these medications are used long-term, the lowest effective dose should be taken.
* They may also be taken only when symptoms occur in those with frequent problems. H2 receptor blockers lead to roughly a 40% improvement.
Antacids
The evidence for antacids is weaker with a benefit of about 10% ( NNT=13) while a combination of an antacid andalginic acid
Alginic acid, also called algin, is a naturally occurring, edible polysaccharide found in brown algae. It is hydrophilic and forms a viscous gum when hydrated. When the alginic acid binds with sodium and calcium ions, the resulting salts are kn ...
(such as Gaviscon) may improve symptoms by 60% (NNT=4). Metoclopramide
Metoclopramide is a medication used to treat nausea, vomiting, gastroparesis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It is also used to treat migraine headaches.
Common side effects include feeling tired, diarrhea, akathisia, and tardive dyski ...
(a prokinetic) is not recommended either alone or in combination with other treatments due to concerns around adverse effects. The benefit of the prokinetic mosapride is modest.
Other agents
Sucralfate has similar effectiveness to H2 receptor blockers; however, sucralfate needs to be taken multiple times a day, thus limiting its use. Baclofen, an agonist of the GABAB receptor, while effective, has similar issues of needing frequent dosing in addition to greater adverse effects compared to other medications.Surgery
The standard surgical treatment for severe GERD is the Nissen fundoplication. In this procedure, the upper part of the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophageal sphincter to strengthen the sphincter and prevent acid reflux and to repair a hiatal hernia. It is recommended only for those who do not improve with PPIs. Quality of life is improved in the short term compared to medical therapy, but there is uncertainty in the benefits of surgery versus long-term medical management with proton pump inhibitors. When comparing different fundoplication techniques, partial posterior fundoplication surgery is more effective than partial anterior fundoplication surgery, and partial fundoplication has better outcomes than total fundoplication. Esophagogastric dissociation is an alternative procedure that is sometimes used to treat neurologically impaired children with GERD. Preliminary studies have shown it may have a lower failure rate and a lower incidence of recurrent reflux. In 2012 the U.S.Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respo ...
(FDA) approved a device called the LINX, which consists of a series of metal beads with magnetic cores that are placed surgically around the lower esophageal sphincter, for those with severe symptoms that do not respond to other treatments. Improvement of GERD symptoms is similar to those of the Nissen fundoplication, although there is no data regarding long-term effects. Compared to Nissen fundoplication procedures, the procedure has shown a reduction in complications such as gas bloat syndrome that commonly occur. Adverse responses include difficulty swallowing, chest pain, vomiting, and nausea. Contraindications that would advise against use of the device are patients who are or may be allergic
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, alle ...
to titanium
Titanium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in ...
, stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element; it has symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive, but large pieces are slo ...
, or ferrous iron materials. A warning advises that the device should not be used by patients who could be exposed to, or undergo, magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI) because of serious injury to the patient and damage to the device.
Some patients who are at an increased surgical risk or do not tolerate PPIs may qualify for a more recently developed incisionless procedure known as a TIF transoral incisionless fundoplication. Benefits of this procedure may last for up to six years.
Special populations
Pregnancy
GERD is a common condition that develops during pregnancy, but usually resolves after delivery. The severity of symptoms tend to increase throughout the pregnancy. In pregnancy, dietary modifications and lifestyle changes may be attempted, but often have little effect. Some lifestyle changes that can be implemented are elevating the head of the bed, eating small portions of food at regularly scheduled intervals, reduce fluid intake with a meal, avoid eating three hours before bedtime, and refrain from lying down after eating. Calcium-based antacids are recommended if these changes are not effective; aluminum- and magnesium hydroxide-based antacids are also safe. Antacids that contain sodium bicarbonate or magnesium trisilicate should be avoided in pregnancy. Sucralfate has been studied in pregnancy and proven to be safe as iscimetidine
Cimetidine, sold under the brand name Tagamet among others, is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is mainly used in the treatment of heartburn and peptic ulcers.
With the development of proton pump ...
and PPIs.
Babies
Babies may see relief with smaller, more frequent feedings, more frequent burping during feedings, holding the baby in an upright position 30 minutes after feeding, keeping the baby's head elevated while laying on the back, removing milk and soy from the mother's diet or feeding the baby milk protein-free formula. They may also be treated with medicines such as PPIs or H2 receptor blockers. PPIs, however, have not been found to be effective in this population and there is a lack of evidence for safety. The role of anoccupational therapist
Occupational therapists (OTs) are health care professionals specializing in occupational therapy and occupational science. OTs and occupational therapy assistants (OTAs) use evidence-based practice, scientific bases and a Holism, holistic perspec ...
with an infant with GERD includes positioning during and after feeding. One technique used is called the log-roll technique, which is practiced when changing an infant's clothing or diapers. Placing an infant on their back while having their legs lifted is not recommended since it causes the acid to flow back up the esophagus
The esophagus (American English), oesophagus (British English), or œsophagus (Œ, archaic spelling) (American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, see spelling difference) all ; : ((o)e)(œ)sophagi or ((o)e)(œ)sophaguses), c ...
. Instead, the occupational therapist would suggest rolling the child on the side, keeping the shoulders and hips aligned to avoid acid rising up the baby's esophagus. Another technique used is feeding the baby on their side with an upright position instead of lying flat on their back. The final positioning technique used for infants is to keep them on their stomach or upright for 20 minutes after feeding.
Epidemiology
In Western populations, GERD affects approximately 10% to 20% of the population and 0.4% newly develop the condition. For instance, an estimated 3.4 million to 6.8 million Canadians have GERD. The prevalence rate of GERD in developed nations is also tightly linked with age, with adults aged 60 to 70 being the most commonly affected. In the United States 20% of people have symptoms in a given week and 7% every day. No data supports sex predominance with regard to GERD.History
An obsolete treatment is vagotomy ("highly selective vagotomy"), the surgical removal ofvagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve (CN X), plays a crucial role in the autonomic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating involuntary functions within the human body. This nerve carries both sensory and motor fibe ...
branches that innervate the stomach lining. This treatment has been largely replaced by medication. Vagotomy by itself tended to worsen contraction of the pyloric sphincter of the stomach, and delayed stomach emptying. Historically, vagotomy was combined with pyloroplasty or gastroenterostomy to counter this problem.
Research
A number of endoscopic devices have been tested to treat chronic heartburn. * Endocinch puts stitches in the lower esophogeal sphincter (LES) to create small pleats to help strengthen the muscle. However, long-term results were disappointing, and the device is no longer sold by Bard. * The Stretta procedure uses electrodes to apply radio-frequency energy to the LES. A 2015 systematic review and meta-analysis in response to the systematic review (no meta-analysis) conducted by SAGES did not support the claims that Stretta was an effective treatment for GERD. A 2012 systematic review found that it improves GERD symptoms. * NDO Surgical Plicator creates a plication, or fold, of tissue near the gastroesophageal junction, and fixates the plication with a suture-based implant. The company ceased operations in mid-2008, and the device is no longer on the market. * Transoral incisionless fundoplication, which uses a device called Esophyx, may be effective.See also
* Acid perfusion test * EndoStim Electrical Stimulation Therapy *Esophageal motility disorder
An esophageal motility disorder (EMD) is any medical disorder resulting from dysfunction of the coordinated movement of esophagus, which causes dysphagia (i.e. difficulty in swallowing, regurgitation of food).
Primary motility disorders are:
* ...
* Esophageal motility study
An esophageal motility study (EMS) or esophageal manometry is a test to assess motor function of the upper esophageal sphincter (UES), esophageal body and lower esophageal sphincter (LES).
Indications
An EMS is typically done to evaluate susp ...
References
Further reading
* ** * * {{Authority control Medical conditions related to obesity Stomach disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate Gastrointestinal motility disorders