Gastrodiscoides on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Gastrodiscoides'' is
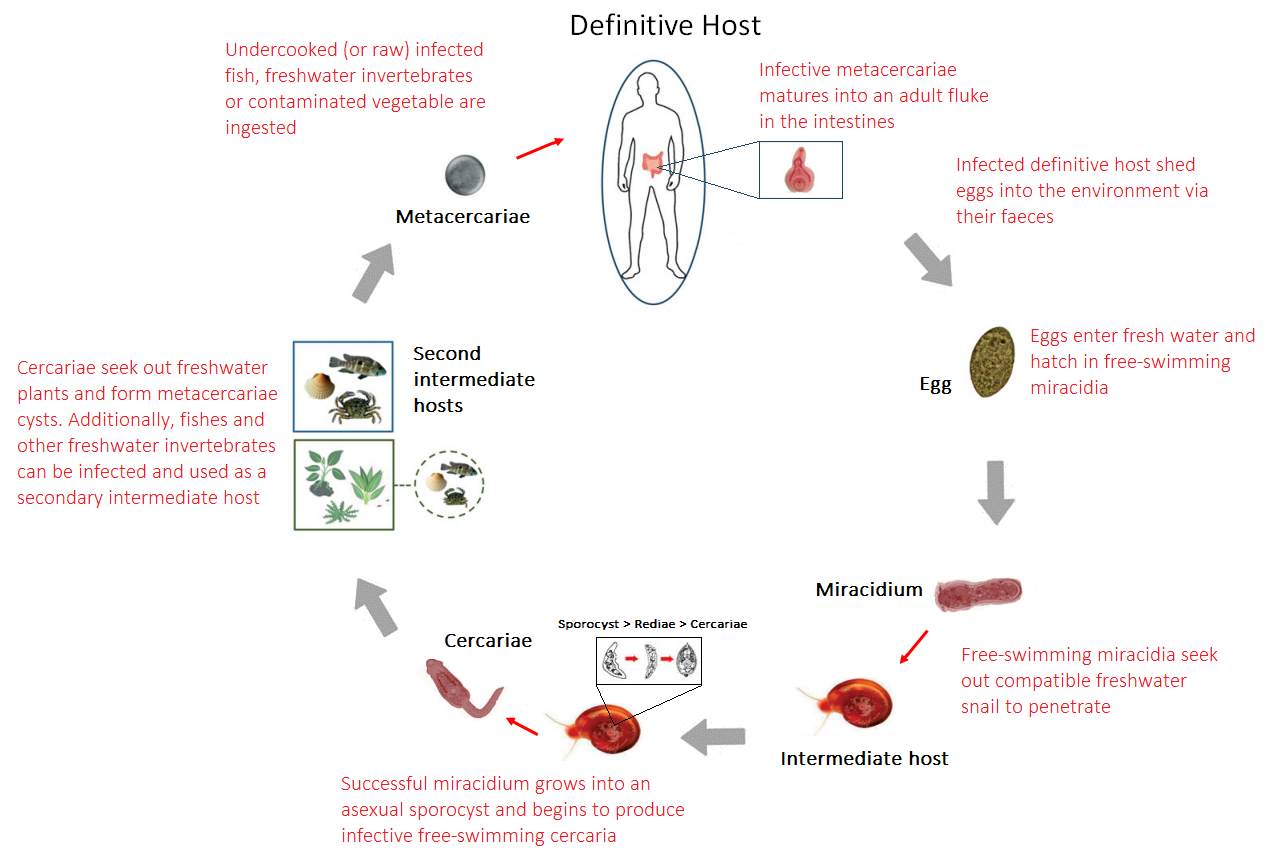 Humans are now considered as the accidental host because humans are not the primary requirement for the life cycle; pigs are recognised as the principal
Humans are now considered as the accidental host because humans are not the primary requirement for the life cycle; pigs are recognised as the principal
 Gastrodiscoidiasis is an infection that is usually
Gastrodiscoidiasis is an infection that is usually
Gastrodiscoides taxonomy at UniProtGastrodiscoides hominis taxonomy at UniProtTaxonomy and nomenclature in ITIS ReportNCBI Taxonomic BrowserClassification at Encyclopedia of LifeTaxonomy at ZipcodeZooTaxonomy at TaxonomiconMolecular data at NEHU NEPIDInformation at Comparative Toxicogenomics DatabaseTaxonomy at Fauna EuropaeaMolecular database at BOLDSYSTEMS
NCBI Taxonomy BrowserUniversal Biological Indexer and Organizer Clinical Description at BioPortalDescription at Expert Consult
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q3099212, from2=Q2379790 Plagiorchiida Plagiorchiida genera Monotypic platyhelminthes genera
genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
of zoonotic
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a virus, bacterium, parasite, fungi, or prion) that can jump from a non-human vertebrate to a human. When h ...
trematode
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate Endoparasites, internal parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host ( ...
under the class
Class, Classes, or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used d ...
Trematoda
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is a mol ...
. It has only one species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
, ''Gastrodiscoides hominis''. It is a parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
of a variety of vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, including human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
s. The first definitive specimen was described from a human subject in 1876. It is prevalent in Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, Burma
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and ha ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a tot ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, and the Volga Delta
The Volga Delta is the largest river delta in Europe and occurs where Europe's largest river system, the Volga River, drains into the Caspian Sea in Russia's Astrakhan Oblast, north-east of the republic of Kalmykia. The delta is located in the ...
of Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
, with isolated cases from Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
, such as Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
. It is especially notable in the Assam
Assam (, , ) is a state in Northeast India, northeastern India, south of the eastern Himalayas along the Brahmaputra Valley, Brahmaputra and Barak River valleys. Assam covers an area of . It is the second largest state in Northeast India, nor ...
, Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Benga ...
, Bihar
Bihar ( ) is a states and union territories of India, state in Eastern India. It is the list of states and union territories of India by population, second largest state by population, the List of states and union territories of India by are ...
, Madhya Pradesh
Madhya Pradesh (; ; ) is a state in central India. Its capital is Bhopal and the largest city is Indore, Indore. Other major cities includes Gwalior, Jabalpur, and Sagar, Madhya Pradesh, Sagar. Madhya Pradesh is the List of states and union te ...
, Odisha
Odisha (), formerly Orissa (List of renamed places in India, the official name until 2011), is a States and union territories of India, state located in East India, Eastern India. It is the List of states and union territories of India by ar ...
and Uttar Pradesh
Uttar Pradesh ( ; UP) is a States and union territories of India, state in North India, northern India. With over 241 million inhabitants, it is the List of states and union territories of India by population, most populated state in In ...
states of India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
.
It is also known as the colonic fluke, particularly when infecting other animals. Its natural habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
is the colon of pig
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities cons ...
s, and has also been found in rhesus monkey
The rhesus macaque (''Macaca mulatta''), colloquially rhesus monkey, is a species of Old World monkey. There are between six and nine recognised subspecies split between two groups, the Chinese-derived and the Indian-derived. Generally brown or g ...
s, orang-utans, fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, field rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include '' Neotoma'' (pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandicoo ...
s and Napu mouse-deer. In humans the habitat is on the wall of the caecum
The cecum ( caecum, ; plural ceca or caeca, ) is a pouch within the peritoneum that is considered to be the beginning of the large intestine. It is typically located on the right side of the body (the same side of the body as the appendix, ...
. Humans are considered an accidental host, as the parasite can survive without humans. It causes a helminthic disease called gastrodiscoidiasis.
History of discovery
''G. humanis'' is unique amonghelminths
Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are a polyphyletic group of large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other par ...
because it was first discovered and described from a human infection. The worm was discovered and described by two British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
medical doctors
A physician, medical practitioner (British English), medical doctor, or simply doctor is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through the study, diagnosis, prognosis a ...
, Timothy Richard Lewis and James McConnell, in 1876, from the caecum of an indigenous Assamese man in India. Their description of the internal structure was inaccurate and incomplete. They claimed that the parasite had one testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, p ...
and one ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
. They placed it in the genus ''Amphistomum'', because of its obvious location of posterior sucker; the species was named ''Amphistomum hominis'', as it was found in human. In 1902, F. Fischoeder recognised the affinity with other species and tentatively placed it in the genus ''Gastrodiscus'' (Leuckart, 1877). However, the generic name was largely recognised as a synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
; it was then known as ''Amphistomum (Gastrodiscus) hominis''. With a fresh look, J. W. W. Stephens re-described the parasite in 1906, and clearly noted the overlooked relatively small ovary and interpretation of the posterior testis as an ovary in the original description.
A new helminthologist at the London School of Tropical Medicine, Robert T. Leiper, re-examined the parasite in 1913. He noted the distinctive characters such as a tuberculated genital cone, the position of the genital orifice, a smooth ventral disc, and the testes in tandem position. These outstanding features prompted him to create an entirely new genus, ''Gastrodiscoides'', for the specimen. This taxonomic revision had criticism, as some of the descriptions were later found to be flawed, such as the position of testes; these criticisms prevented it from coming into general acceptance. It was later observed that the parasite was much more common to pigs and other mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
than in humans. The first report of infection of pigs was in Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; ; ; ; ) is a historical exonym and endonym, exonym for part of Vietnam, depending on the contexts, usually for Southern Vietnam. Sometimes it referred to the whole of Vietnam, but it was commonly used to refer t ...
, Vietnam
Vietnam, officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam (SRV), is a country at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of about and a population of over 100 million, making it the world's List of countries and depende ...
, in 1911. In 1913, it was further confirmed that the rate of porcine
The pig (''Sus domesticus''), also called swine (: swine) or hog, is an omnivorous, domesticated, even-toed, hoofed mammal. It is named the domestic pig when distinguishing it from other members of the genus '' Sus''. Some authorities consid ...
infection was as high as 5%. Then a large number of living flukes was recovered from dead Napu mouse-deer at the Zoological Gardens of the Zoological Society of London
The Zoological Society of London (ZSL) is a charity and organization devoted to the worldwide animal conservation, conservation of animals and their habitat conservation, habitats. It was founded in 1826. Since 1828, it has maintained London Zo ...
. The mouse-deer was Prince of Wales
Prince of Wales (, ; ) is a title traditionally given to the male heir apparent to the History of the English monarchy, English, and later, the British throne. The title originated with the Welsh rulers of Kingdom of Gwynedd, Gwynedd who, from ...
's collection from Malay. The shortcomings of Leiper's descriptions did not prevent the generic name ''Gastrodiscoides'' becoming more and more advocated in the early 1920s. The currently accepted nomenclature was fortified by the British parasitologist J. J. C. Buckley, at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine
The London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) is a public university, public research university in Bloomsbury, central London, and a constituent college, member institution of the University of London that specialises in public hea ...
(where he was then a Milner Research Fellow), whose descriptions were based on high incidence of the parasitism
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The en ...
among the native Assamese ethnic groups in Northeastern India. His first report in 1939, followed by a body of evidences in support of Leiper's proposition, enabled him to vindicate the validity of a separate genus, ''Gastrodiscoides'', hence the binomial
Binomial may refer to:
In mathematics
*Binomial (polynomial), a polynomial with two terms
*Binomial coefficient, numbers appearing in the expansions of powers of binomials
*Binomial QMF, a perfect-reconstruction orthogonal wavelet decomposition
* ...
name ''Gastrodiscoides hominis''. His report was the pioneer description of the life cycle of the fluke and the prevalence of gastrodiscoidiasis. In his survey of three villages in Assam, there was found a surprisingly high incidence, with over 40% of the population was infected. J. J. C. Buckley's report is the most useful to the modern classification of ''G. hominis''.
Description
It is typically an amphistome with the ventral sucker close to the posterior end. The body isbilaterally symmetrical
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, the face of a human being has a plane of symme ...
and is acoelomate
The coelom (or celom) is the main body cavity in many animals and is positioned inside the body to surround and contain the digestive tract and other organs. In some animals, it is lined with mesothelium. In other animals, such as molluscs, it r ...
. It is dorsoventrally flatted, with a unique pyramidal shape. The body is covered by a tegument bearing numerous tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
s. The alimentary canal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
is incomplete, consisting of a pair of lateral pouches arising from the oral sucker and a pharyngeal tube, which bifurcates into two gut caeca. The bladder
The bladder () is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys. In placental mammals, urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra during urination. In humans, the bladder is a distens ...
is in the middle behind the ventral sucker. The genus is hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
, as both male and female reproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
are present.
It is a large fluke, vase
A vase ( or ) is an open container. It can be made from a number of materials, such as ceramics, glass, non- rusting metals, such as aluminium, brass, bronze, or stainless steel. Even wood has been used to make vases, either by using tree specie ...
-shaped, and bright-pink in colour. In average it measures 5-8 mm long and 3-5 mm wide. The disc-shaped body is divisible into anterior conical and posterior discoidal regions. The anterior region is a conical projection bearing a prominent oral sucker. The posterior portion is relatively broad, up to 8 mm wide, discoidal, and ventrally excavated. It is an amphistome worm such that the ventral sucker is close to the posterior end. The body covering, called a tegument, is smooth in appearance, but contains a fine structure in a series of concentric folds bearing numerous tightly packed tubercle
In anatomy, a tubercle (literally 'small tuber', Latin for 'lump') is any round nodule, small eminence, or warty outgrowth found on external or internal organs of a plant or an animal.
In plants
A tubercle is generally a wart-like projectio ...
s. Ventral surface contains a specialised region of the tegument. Ciliated and non-ciliated papillae are arranged around the oral sucker. The incomplete alimentary canal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. ...
consists of a pair of lateral pouches arising from the oral sucker and a slightly tortuous pharyngeal tube, which bifurcates into two gut caeca. The large excretory bladder is in the middle, behind the ventral sucker. The species, being hermaphrodite
A hermaphrodite () is a sexually reproducing organism that produces both male and female gametes. Animal species in which individuals are either male or female are gonochoric, which is the opposite of hermaphroditic.
The individuals of many ...
, has both male and female reproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are al ...
s, arranged in the posterior region. The testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone.
The ...
lie in alongside the bifurcation of the caeca, and a common genital pore is on the cone just anterior to the bifurcation. The oval-shaped ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are end ...
lies just posterior to the testes in the middle, and the loosely coiled uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, f ...
opens to the genital pore. Vitelline glands are scattered around the caeca.
Biology
 Humans are now considered as the accidental host because humans are not the primary requirement for the life cycle; pigs are recognised as the principal
Humans are now considered as the accidental host because humans are not the primary requirement for the life cycle; pigs are recognised as the principal definitive host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include ...
. Infection causes a helminthic disease called gastrodiscoidiasis. It is a digenetic trematode with a complex life cycle involving asexual reproduction
Asexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that does not involve the fusion of gametes or change in the number of chromosomes. The offspring that arise by asexual reproduction from either unicellular or multicellular organisms inherit the f ...
in an intermediate host
In biology and medicine, a host is a larger organism that harbours a smaller organism; whether a parasitic, a mutualistic, or a commensalist ''guest'' (symbiont). The guest is typically provided with nourishment and shelter. Examples include ...
, presumably aquatic snails
A snail is a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gas ...
, and sexual reproduction
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete ( haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote tha ...
in the vertebrate host. As a hermaphrodite, eggs are produced by self-fertilisation
Autogamy or self-fertilization refers to the fusion of two gametes that come from one individual. Autogamy is predominantly observed in the form of self-pollination, a reproductive mechanism employed by many flowering plants. However, species of ...
and are released along the faeces of the host. Eggs measure ~146 by 66 μm, are rhomboid
Traditionally, in two-dimensional geometry, a rhomboid is a parallelogram in which adjacent sides are of unequal lengths and angles are non-right angled.
The terms "rhomboid" and "parallelogram" are often erroneously conflated with each oth ...
al in shape, transparent, and green in colour. Each egg contains about 24 vitelline cells and a central unembryonated ovum
The egg cell or ovum (: ova) is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete is not capa ...
. Eggs in a wet environment hatch into miracidia in 9-14 days.
In water, eggs hatch into miracidia, which then infect a mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
, in which larva
A larva (; : larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into their next life stage. Animals with indirect development such as insects, some arachnids, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase ...
l development and fission occurs. The miracidium grows into the sporocyst stage. It is generally conceived that the unfertilised eggs are ingested by the snail, but there has been no direct observation. In an experimental infection of the mollusc
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum ...
''Helicorbis coenosus'', miracidum develops into cercaria
A cercaria (plural cercariae) is a larval form of the trematode class of parasites. It develops within the germinal cells of the Trematode life cycle stages, sporocyst or redia. A cercaria has a tapering head with large penetration glands. It may ...
after 28-153 days of ingestion
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms, inge ...
. In the snail, mother and daughter rediae are found in the digestive gland, and are about 148-747/45-140 μm in size, sausage-shaped, and lack collar and locomotory organs.
Infective cercariae are produced and are released on water plants or directly infect other aquatic animals, such as fish. The cercariae released from the snail form metacercarial cysts on water plants. The complete life cycle is not yet observed in nature, and the tiny snail, ''H. coenosus'', remains the most commonly accepted vector, as it is coincidentally found in abundance in the pigsties. In some circumstances, fishes and other aquatic animals are found to be infected. It is hypothesised that the free cercaria in water bodies accidentally find and penetrate these animals as second intermediate host, where they encyst as metacercaria. These are directly infective to mammals
A mammal () is a vertebrate animal of the class Mammalia (). Mammals are characterised by the presence of milk-producing mammary glands for feeding their young, a broad neocortex region of the brain, fur or hair, and three middle e ...
upon consumption, while they get attached to vegetation, where night soil
Night soil is a historical euphemism for Human waste, human excreta collected from cesspit, cesspools, privies, pail closets, pit latrines, privy middens, septic tanks, etc. This material was removed from the immediate area, usually at night, by ...
is used.
Humans ingest the metacercaria either by the infected fish or contaminated vegetable. The parasite travels through the digestive tract into the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In mammals, it may be the principal site for iron absorption.
The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest p ...
, then continues down to reach the caecum, where it self-fertilizes and lay eggs, continuing the cycle.
Heavy infection in humans is suspected to cause diarrhoea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, abdominal pain, colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content ou ...
, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
, anaemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availab ...
, and even death.
Pathogenicity and pathology
 Gastrodiscoidiasis is an infection that is usually
Gastrodiscoidiasis is an infection that is usually asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
and affects the small intestine in animals, such as pigs, to a very mild symptom, but when it occurs in humans it can cause serious health problems and even death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
. It is suspected to cause diarrhoea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
, fever
Fever or pyrexia in humans is a symptom of an anti-infection defense mechanism that appears with Human body temperature, body temperature exceeding the normal range caused by an increase in the body's temperature Human body temperature#Fever, s ...
, abdominal pain, colic
Colic or cholic () is a form of pain that starts and stops abruptly. It occurs due to muscular contractions of a hollow tube (small and large intestine, gall bladder, ureter, etc.) in an attempt to relieve an obstruction by forcing content ou ...
, and an increased mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
production. In severe cases, where there are large amounts of eggs present, tissue reactions can occur in the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
or mesenteric lymphatics, and even death may occur if left neglected. Indeed, a number of mortality among native Assamese children is attributed to this infection. In pigs, pathological symptoms include infiltration with eosinophils
Eosinophils, sometimes called eosinophiles or, less commonly, acidophils, are a variety of white blood cells and one of the immune system components responsible for combating multicellular parasites and certain infections in vertebrates. Along wi ...
, lymphocytes
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), and ...
, and plasma cells
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells or effector B cells, are white blood cells that originate in the lymphoid organs as B cells and secrete large quantities of proteins called antibodies in response to being presented specific substances c ...
. The submucosa can show oedema
Edema (American English), also spelled oedema (British English), and also known as fluid retention, swelling, dropsy and hydropsy, is the build-up of fluid in the body's tissue. Most commonly, the legs or arms are affected. Symptoms may inclu ...
and thickening, resulting in a subacute inflammation
Inflammation (from ) is part of the biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and loss of function (Latin ''calor'', '' ...
of the caecum and mucoid diarrhoea.
Epidemiology
Human gastrodiscoidiasis isendemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
in Assam, and to a lesser extent in the Philippines. The highest incidence so far recorded is among children in Kamrup district of Assam, where the prevalence was as high as 41%. First described from a native Assamese patient, it was initially believed to have a distribution restricted to NE India and the southeast Asia. Later investigations revealed that it is widespread, and is further spread by infected persons to other parts of the world, such as Guyana
Guyana, officially the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, is a country on the northern coast of South America, part of the historic British West Indies. entry "Guyana" Georgetown, Guyana, Georgetown is the capital of Guyana and is also the co ...
. The level of infection in laboratory animals can be very high among Asian mammals. Regions of high incidence can be attributed to low standard of sanitation, such as rural farms and villages where night soils are used. Infection in both humans and animals is most common through the ingestion of vegetation found in contaminated water. It is also assumed that transmission from infected fish that is under-cooked or eaten raw, as common among southeast Asian. There is a unique case report of a seven-year-old Nigerian
Nigerians or the Nigerian people are citizens of Nigeria or people with ancestry from Nigeria. The name Nigeria was derived from the Niger River running through the country. This name was allegedly coined in the late 19th century by British jo ...
who showed symptoms of malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
and anaemia
Anemia (also spelt anaemia in British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen. This can be due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin availab ...
and was eventually diagnosed with infections of ''G. hominis'' and ''Ascaris lumbricoides''. The child quickly recovered after proper medication.
Diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis is made by examination of the fæces and the detection of eggs. Adult worms are easily identified from other helminths by their distinctive appearance. The eggs are readily distinguished from those of othertrematodes
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as trematodes, and commonly as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is a moll ...
by their rhomboid shape and distinct green colour. Patients do not often directly show any symptoms, and if one appears, it indicates that the infection is already at a very high level. There is no prescribed treatment, but the traditional practice of soap enema
An enema, also known as a clyster, is the rectal administration of a fluid by injection into the Large intestine, lower bowel via the anus.Cullingworth, ''A Manual of Nursing, Medical and Surgical'':155 The word ''enema'' can also refer to the ...
has been very effective in removing the worms. It works to flush the flukes from the colon which removes the parasite entirely, as it does not reproduce within the host. Some drugs that have been proven effective are tetrachloroethylene
Tetrachloroethylene, also known as perchloroethylene or under the systematic name tetrachloroethene, and abbreviations such as perc (or PERC), and PCE, is a chlorocarbon with the formula . It is a non-flammable, stable, colorless and heavy liqu ...
, at a dosage of 0.1 mg/kg on an empty stomach, and a more preferred drug, praziquantel
Praziquantel, sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections in mammals, birds, amphibians, reptiles, and fish. In humans specifically, it is used to treat schist ...
, which eliminates the parasite with 3 doses at 25 mg/kg in one day. Mebendazole
Mebendazole (MBZ), sold under the brand name Vermox among others, is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm infection, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections and hydatid di ...
was found to be efficient in deworming
Deworming (sometimes known as worming, drenching or dehelmintization) is the giving of an anthelmintic drug (a wormer, dewormer, or drench) to a human or animals to rid them of helminths parasites, such as roundworm, flukes and tapeworm. Pu ...
the parasite from a Nigerian girl who was shedding thousands of parasite eggs in stools even with a single dose of 500 mg. Prevention of this disease is not difficult when simple sanitary measures are taken. Night soil should never be used as a fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
because it could contain any number of parasites. Vegetables should be washed thoroughly, and meat properly cooked.
References
External links
Gastrodiscoides taxonomy at UniProt
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q3099212, from2=Q2379790 Plagiorchiida Plagiorchiida genera Monotypic platyhelminthes genera