Galactic cluster on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An open cluster is a type of
 The prominent open cluster the
The prominent open cluster the  The first person to use a telescope to observe the night sky and record his observations was the Italian scientist
The first person to use a telescope to observe the night sky and record his observations was the Italian scientist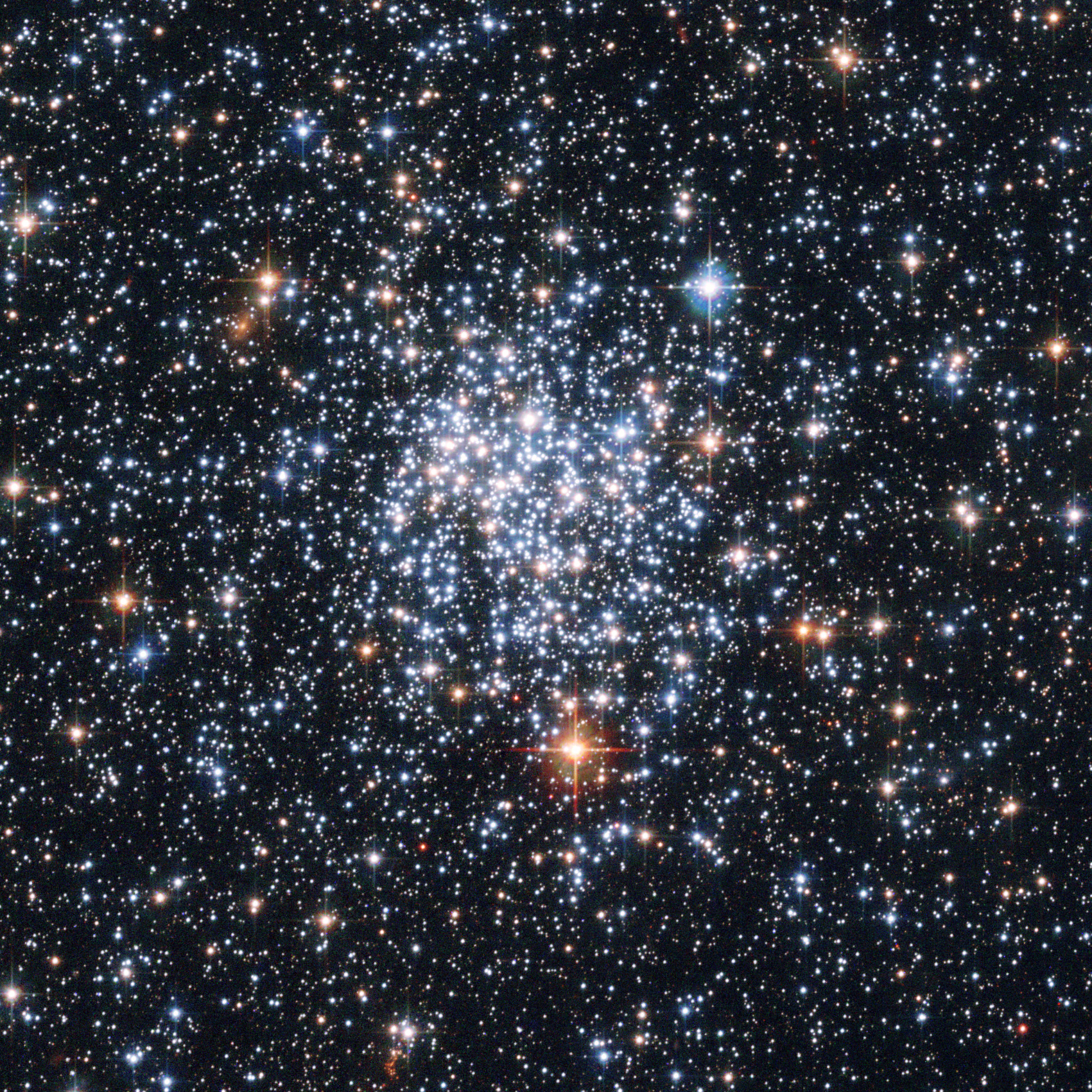  The number of clusters known continued to increase under the efforts of astronomers. Hundreds of open clusters were listed in the ''
The number of clusters known continued to increase under the efforts of astronomers. Hundreds of open clusters were listed in the ''
 The formation of an open cluster begins with the collapse of part of a
The formation of an open cluster begins with the collapse of part of a  The hottest and most massive of the newly formed stars (known as OB stars) will emit intense
The hottest and most massive of the newly formed stars (known as OB stars) will emit intense
 Open clusters range from very sparse clusters with only a few members to large
Open clusters range from very sparse clusters with only a few members to large
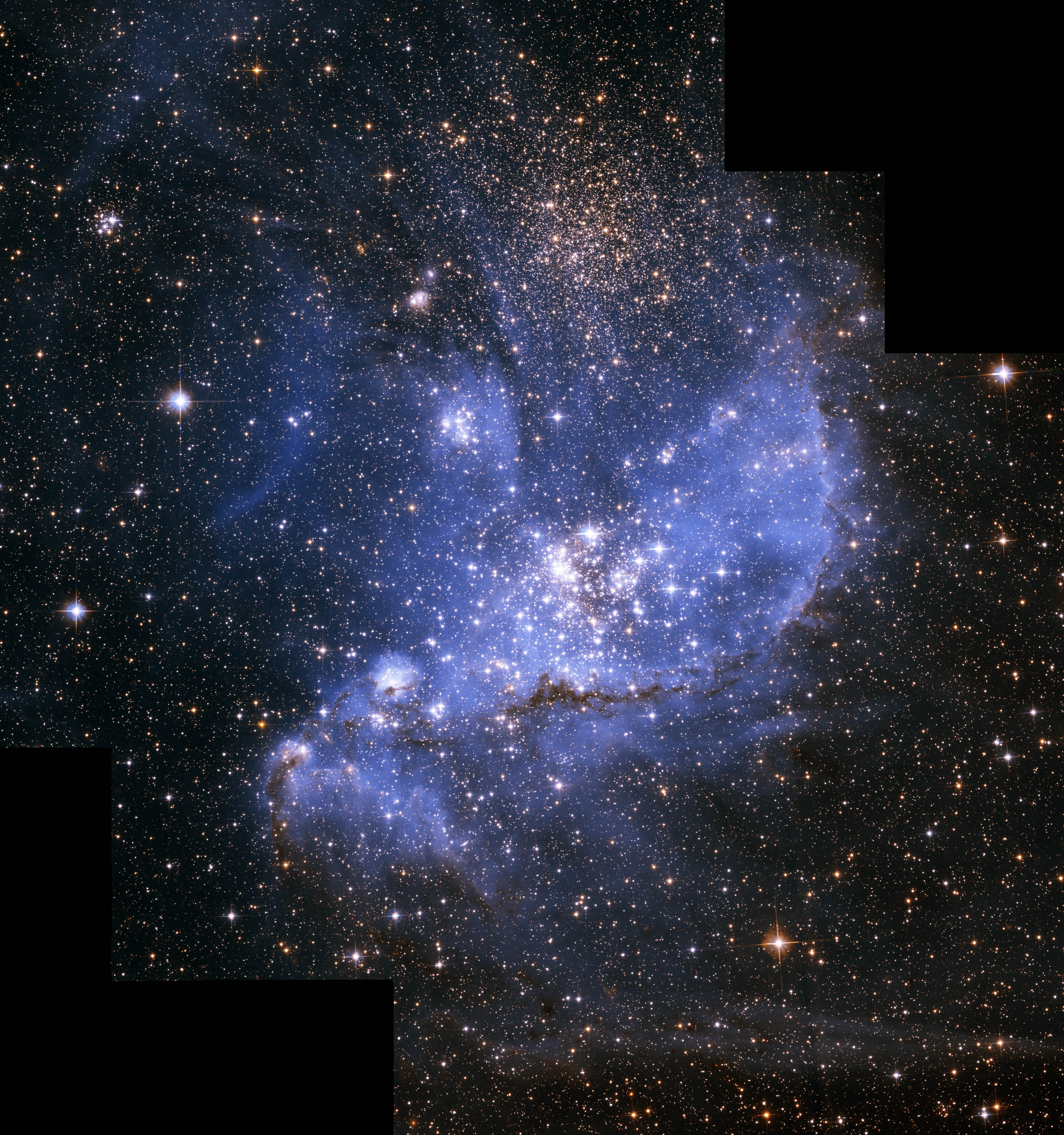 There are over 1,100 known open clusters in our galaxy, but the true total may be up to ten times higher than that. In
There are over 1,100 known open clusters in our galaxy, but the true total may be up to ten times higher than that. In
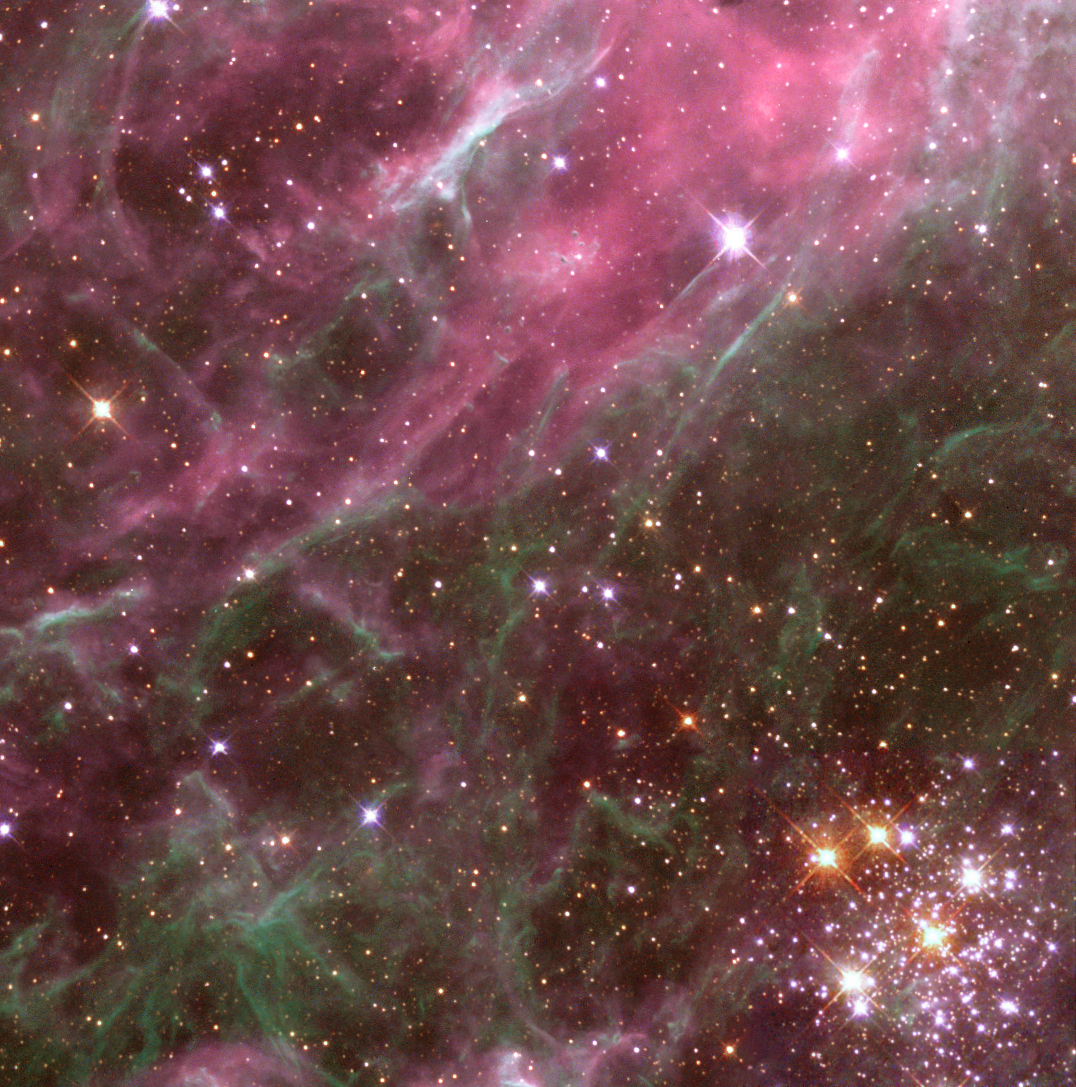 Because open clusters tend to be dispersed before most of their stars reach the end of their lives, the light from them tends to be dominated by the young, hot blue stars. These stars are the most massive, and have the shortest lives, a few tens of millions of years. The older open clusters tend to contain more yellow stars.
The frequency of
Because open clusters tend to be dispersed before most of their stars reach the end of their lives, the light from them tends to be dominated by the young, hot blue stars. These stars are the most massive, and have the shortest lives, a few tens of millions of years. The older open clusters tend to contain more yellow stars.
The frequency of
 Many open clusters are inherently unstable, with a small enough mass that the
Many open clusters are inherently unstable, with a small enough mass that the
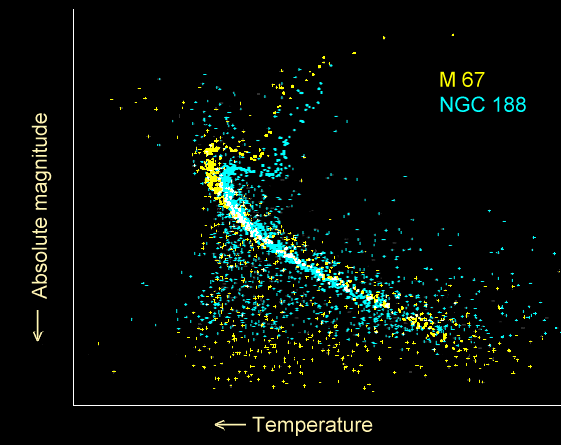 When a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is plotted for an open cluster, most stars lie on the
When a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is plotted for an open cluster, most stars lie on the
 Determining the distances to astronomical objects is crucial to understanding them, but the vast majority of objects are too far away for their distances to be directly determined. Calibration of the astronomical distance scale relies on a sequence of indirect and sometimes uncertain measurements relating the closest objects, for which distances can be directly measured, to increasingly distant objects. Open clusters are a crucial step in this sequence.
The closest open clusters can have their distance measured directly by one of two methods. First, the
Determining the distances to astronomical objects is crucial to understanding them, but the vast majority of objects are too far away for their distances to be directly determined. Calibration of the astronomical distance scale relies on a sequence of indirect and sometimes uncertain measurements relating the closest objects, for which distances can be directly measured, to increasingly distant objects. Open clusters are a crucial step in this sequence.
The closest open clusters can have their distance measured directly by one of two methods. First, the
''Cepheids in Galactic Clusters. I. CF Cass in NGC 7790.''
AJ, 128Majaess, D.; Carraro, G.; Moni Bidin, C.; Bonatto, C.; Berdnikov, L.; Balam, D.; Moyano, M.; Gallo, L.; Turner, D.; Lane, D.; Gieren, W.; Borissova, J.; Kovtyukh, V.; Beletsky, Y. (2013)
''Anchors for the cosmic distance scale: the Cepheids U Sagittarii, CF Cassiopeiae, and CEab Cassiopeiae''
A&A, 260
The Jewel Box (also known as NGC 4755 or Kappa Crucis Cluster) – open cluster in the Crux constellation @ SKY-MAP.ORG
Open Clusters – Information and amateur observations
{{DEFAULTSORT:Open Cluster Open clusters Star clusters
star cluster
A star cluster is a group of stars held together by self-gravitation. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters, tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound; and open cluster ...
made of tens to a few thousand star
A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by Self-gravitation, self-gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night sk ...
s that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud
A molecular cloud—sometimes called a stellar nursery if star formation is occurring within—is a type of interstellar cloud of which the density and size permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen ...
and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
galaxy, and many more are thought to exist. Each one is loosely bound by mutual gravitational attraction and becomes disrupted by close encounters with other clusters and clouds of gas as they orbit the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
. This can result in a loss of cluster members through internal close encounters and a dispersion into the main body of the galaxy. Open clusters generally survive for a few hundred million years, with the most massive ones surviving for a few billion years. In contrast, the more massive globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
s of stars exert a stronger gravitational attraction on their members, and can survive for longer. Open clusters have been found only in spiral
In mathematics, a spiral is a curve which emanates from a point, moving further away as it revolves around the point. It is a subtype of whorled patterns, a broad group that also includes concentric objects.
Two-dimensional
A two-dimension ...
and irregular galaxies, in which active star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in interstellar space—sometimes referred to as "stellar nurseries" or "star-forming regions"—Jeans instability, collapse and form stars. As a branch of astronomy, sta ...
is occurring.
Young open clusters may be contained within the molecular cloud from which they formed, illuminating it to create an H II region
An H II region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light year ...
. Over time, radiation pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of ...
from the cluster will disperse the molecular cloud. Typically, about 10% of the mass of a gas cloud will coalesce into stars before radiation pressure drives the rest of the gas away.
Open clusters are key objects in the study of stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is consi ...
. Because the cluster members are of similar age and chemical composition
A chemical composition specifies the identity, arrangement, and ratio of the chemical elements making up a compound by way of chemical and atomic bonds.
Chemical formulas can be used to describe the relative amounts of elements present in a com ...
, their properties (such as distance, age, metallicity
In astronomy, metallicity is the Abundance of the chemical elements, abundance of Chemical element, elements present in an object that are heavier than hydrogen and helium. Most of the normal currently detectable (i.e. non-Dark matter, dark) matt ...
, extinction
Extinction is the termination of an organism by the death of its Endling, last member. A taxon may become Functional extinction, functionally extinct before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to Reproduction, reproduce and ...
, and velocity) are more easily determined than they are for isolated stars. A number of open clusters, such as the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as Seven Sisters and Messier 45 (M45), is an Asterism (astronomy), asterism of an open cluster, open star cluster containing young Stellar classification#Class B, B-type stars in the northwest of the constellation Tau ...
, the Hyades and the Alpha Persei Cluster
The Alpha Persei Cluster, also known as Melotte 20 or Collinder 39, is an open cluster of stars in the northern constellation of Perseus (constellation), Perseus. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue-hued spectral type B stars. ...
, are visible with the naked eye. Some others, such as the Double Cluster
The Double Cluster, also known as Caldwell 14, consists of the open clusters NGC 869 and NGC 884 (often designated h Persei and χ (chi) Persei, respectively), which are close together in the constellation Perseus. Both visible to the ...
, are barely perceptible without instruments, while many more can be seen using binoculars
Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held ...
or telescopes
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
. The Wild Duck Cluster
The Wild Duck Cluster (also known as Messier 11, or NGC 6705) is an open cluster of stars in the constellation Scutum (the Shield). It was discovered by Gottfried Kirch in 1681. Charles Messier included it in his catalogue of diffuse objects i ...
, M11, is an example.
Historical observations
 The prominent open cluster the
The prominent open cluster the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as Seven Sisters and Messier 45 (M45), is an Asterism (astronomy), asterism of an open cluster, open star cluster containing young Stellar classification#Class B, B-type stars in the northwest of the constellation Tau ...
, in the constellation Taurus, has been recognized as a group of stars since antiquity, while the Hyades (which also form part of Taurus) is one of the oldest open clusters. Other open clusters were noted by early astronomers as unresolved fuzzy patches of light. In his ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' ( ) is a 2nd-century Greek mathematics, mathematical and Greek astronomy, astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy ( ) in Koine Greek. One of the most i ...
'', the Roman astronomer Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzant ...
mentions the Praesepe cluster, the Double Cluster
The Double Cluster, also known as Caldwell 14, consists of the open clusters NGC 869 and NGC 884 (often designated h Persei and χ (chi) Persei, respectively), which are close together in the constellation Perseus. Both visible to the ...
in Perseus
In Greek mythology, Perseus (, ; Greek language, Greek: Περσεύς, Romanization of Greek, translit. Perseús) is the legendary founder of the Perseid dynasty. He was, alongside Cadmus and Bellerophon, the greatest Greek hero and slayer of ...
, the Coma Star Cluster
The Coma Star Cluster (also known as Melotte 111 or Collinder 256) is a nearby open cluster located in the constellation Coma Berenices. The cluster contains about 40 brighter stars (between magnitudes 5 and 10) with a common proper motion. The ...
and the Ptolemy Cluster
Messier 7 or M7, also designated NGC 6475 and sometimes known as the Ptolemy Cluster, is an open cluster of stars in the constellation of Scorpius. The cluster is easily detectable with the naked eye, close to the "stinger" of Scorpius. With a ...
, while the Persian astronomer Al-Sufi wrote of the Omicron Velorum cluster. However, it would require the invention of the telescope
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption, or Reflection (physics), reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally, it was an optical instrument using len ...
to resolve these "nebulae" into their constituent stars. Indeed, in 1603 Johann Bayer
Johann Bayer (; 1572 – 7 March 1625) was a German lawyer and uranographer (celestial cartographer). He was born in Rain in 1572. In 1592, aged 20, he began his study of philosophy and law at the University of Ingolstadt, after which he ...
gave three of these clusters designations as if they were single stars.
 The first person to use a telescope to observe the night sky and record his observations was the Italian scientist
The first person to use a telescope to observe the night sky and record his observations was the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642), commonly referred to as Galileo Galilei ( , , ) or mononymously as Galileo, was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a poly ...
in 1609. When he turned the telescope toward some of the nebulous patches recorded by Ptolemy, he found they were not a single star, but groupings of many stars. For Praesepe, he found more than 40 stars. Where previously observers had noted only 6–7 stars in the Pleiades, he found almost 50. In his 1610 treatise ''Sidereus Nuncius
''Sidereus Nuncius'' (usually ''Sidereal Messenger'', also ''Starry Messenger'' or ''Sidereal Message'') is a short astronomical treatise (or ''pamphlet'') published in Neo-Latin by Galileo Galilei on March 13, 1610. It was the first published ...
'', Galileo Galilei wrote, "the galaxy is nothing else but a mass of innumerable stars planted together in clusters." Influenced by Galileo's work, the Sicilian astronomer Giovanni Hodierna became possibly the first astronomer to use a telescope to find previously undiscovered open clusters. In 1654, he identified the objects now designated Messier 41, Messier 47, NGC 2362
NGC 2362, also known as Caldwell 64, is an open cluster of stars in the southern constellation of Canis Major. It was discovered by the Italian court astronomer Giovanni Batista Hodierna, who published his finding in 1654. William Herschel called ...
and NGC 2451.
It was realized as early as 1767 that the stars in a cluster were physically related, when the English naturalist the Reverend John Michell
John Michell (; 25 December 1724 – 21 April 1793) was an English natural philosopher and clergyman who provided pioneering insights into a wide range of scientific fields including astronomy, geology, optics, and gravitation. Considered "on ...
calculated that the probability of even just one group of stars like the Pleiades being the result of a chance alignment as seen from Earth was just 1 in 496,000. Between 1774 and 1781, French astronomer Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects'', referred to with th ...
published a catalogue of celestial objects that had a nebulous appearance similar to comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that warms and begins to release gases when passing close to the Sun, a process called outgassing. This produces an extended, gravitationally unbound atmosphere or Coma (cometary), coma surrounding ...
s. This catalogue included 26 open clusters. In the 1790s, English astronomer William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel ( ; ; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline Herschel. Born in the Electorate of Hanover ...
began an extensive study of nebulous celestial objects. He discovered that many of these features could be resolved into groupings of individual stars. Herschel conceived the idea that stars were initially scattered across space, but later became clustered together as star systems because of gravitational attraction. He divided the nebulae into eight classes, with classes VI through VIII being used to classify clusters of stars.
 The number of clusters known continued to increase under the efforts of astronomers. Hundreds of open clusters were listed in the ''
The number of clusters known continued to increase under the efforts of astronomers. Hundreds of open clusters were listed in the ''New General Catalogue
The ''New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' (abbreviated NGC) is an astronomical catalogue of deep-sky objects compiled by John Louis Emil Dreyer in 1888. The NGC contains 7,840 objects, including galaxy, galaxies, star cluste ...
'', first published in 1888 by the Danish–Irish astronomer J. L. E. Dreyer, and the two supplemental Index Catalogues, published in 1896 and 1905. Telescopic observations revealed two distinct types of clusters, one of which contained thousands of stars in a regular spherical distribution and was found all across the sky but preferentially towards the center of the Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galax ...
. The other type consisted of a generally sparser population of stars in a more irregular shape. These were generally found in or near the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
of the Milky Way. Astronomers dubbed the former globular cluster
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
s, and the latter open clusters. Because of their location, open clusters are occasionally referred to as ''galactic clusters'', a term that was introduced in 1925 by the Swiss-American astronomer Robert Julius Trumpler.
Micrometer measurements of the positions of stars in clusters were made as early as 1877 by the German astronomer E. Schönfeld and further pursued by the American astronomer E. E. Barnard prior to his death in 1923. No indication of stellar motion was detected by these efforts. However, in 1918 the Dutch–American astronomer Adriaan van Maanen was able to measure the proper motion of stars in part of the Pleiades cluster by comparing photographic plates taken at different times. As astrometry
Astrometry is a branch of astronomy that involves precise measurements of the positions and movements of stars and other Astronomical object, celestial bodies. It provides the kinematics and physical origin of the Solar System and this galaxy, th ...
became more accurate, cluster stars were found to share a common proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
through space. By comparing the photographic plates of the Pleiades cluster taken in 1918 with images taken in 1943, van Maanen was able to identify those stars that had a proper motion
Proper motion is the astrometric measure of changes in the apparent places of stars or other celestial objects as they move relative to the center of mass of the Solar System. It is measured relative to the distant stars or a stable referenc ...
similar to the mean motion of the cluster, and were therefore more likely to be members. Spectroscopic measurements revealed common radial velocities, thus showing that the clusters consist of stars bound together as a group.
The first color–magnitude diagrams of open clusters were published by Ejnar Hertzsprung in 1911, giving the plot for the Pleiades and Hyades star cluster
A star cluster is a group of stars held together by self-gravitation. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters, tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound; and open cluster ...
s. He continued this work on open clusters for the next twenty years. From spectroscopic data, he was able to determine the upper limit of internal motions for open clusters, and could estimate that the total mass of these objects did not exceed several hundred times the mass of the Sun. He demonstrated a relationship between the star colors and their magnitudes, and in 1929 noticed that the Hyades and Praesepe clusters had different stellar populations than the Pleiades. This would subsequently be interpreted as a difference in ages of the three clusters.
Formation
 The formation of an open cluster begins with the collapse of part of a
The formation of an open cluster begins with the collapse of part of a giant molecular cloud
A molecular cloud—sometimes called a stellar nursery if star formation is occurring within—is a type of interstellar cloud of which the density and size permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydrogen ...
, a cold dense cloud of gas and dust containing up to many thousands of times the mass of the Sun
The solar mass () is a frequently used unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is approximately equal to the mass of the Sun. It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies a ...
. These clouds have densities that vary from 102 to 106 molecules of neutral hydrogen per cm3, with star formation occurring in regions with densities above 104 molecules per cm3. Typically, only 1–10% of the cloud by volume is above the latter density. Prior to collapse, these clouds maintain their mechanical equilibrium through magnetic fields, turbulence and rotation.
Many factors may disrupt the equilibrium of a giant molecular cloud, triggering a collapse and initiating the burst of star formation that can result in an open cluster. These include shock waves from a nearby supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last stellar evolution, evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion ...
, collisions with other clouds and gravitational interactions. Even without external triggers, regions of the cloud can reach conditions where they become unstable against collapse. The collapsing cloud region will undergo hierarchical fragmentation into ever smaller clumps, including a particularly dense form known as infrared dark clouds, eventually leading to the formation of up to several thousand stars. This star formation begins enshrouded in the collapsing cloud, blocking the protostars from sight but allowing infrared observation. In the Milky Way galaxy, the formation rate of open clusters is estimated to be one every few thousand years.
 The hottest and most massive of the newly formed stars (known as OB stars) will emit intense
The hottest and most massive of the newly formed stars (known as OB stars) will emit intense ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of t ...
, which steadily ionizes the surrounding gas of the giant molecular cloud, forming an H II region
An H II region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light year ...
. Stellar wind
A stellar wind is a flow of gas ejected from the stellar atmosphere, upper atmosphere of a star. It is distinguished from the bipolar outflows characteristic of young stars by being less collimated, although stellar winds are not generally spheri ...
s and radiation pressure
Radiation pressure (also known as light pressure) is mechanical pressure exerted upon a surface due to the exchange of momentum between the object and the electromagnetic field. This includes the momentum of light or electromagnetic radiation of ...
from the massive stars begins to drive away the hot ionized gas at a velocity matching the speed of sound in the gas. After a few million years the cluster will experience its first core-collapse supernova
A supernova (: supernovae or supernovas) is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. A supernova occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star, or when a white dwarf is triggered into runaway nuclear fusion. The original obj ...
e, which will also expel gas from the vicinity. In most cases these processes will strip the cluster of gas within ten million years, and no further star formation will take place. Still, about half of the resulting protostellar objects will be left surrounded by circumstellar disk
A Circumstellar disc (or circumstellar disk) is a torus, pancake or ring-shaped accretion disk of matter composed of gas, dust, planetesimals, asteroids, or collision fragments in orbit around a star. Around the youngest stars, they are the res ...
s, many of which form accretion disks.
As only 30 to 40 percent of the gas in the cloud core forms stars, the process of residual gas expulsion is highly damaging to the star formation process. All clusters thus suffer significant infant weight loss, while a large fraction undergo infant mortality. At this point, the formation of an open cluster will depend on whether the newly formed stars are gravitationally bound to each other; otherwise an unbound stellar association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more visible stars. An association is primarily identified by commonalities in i ...
will result. Even when a cluster such as the Pleiades does form, it may hold on to only a third of the original stars, with the remainder becoming unbound once the gas is expelled. The young stars so released from their natal cluster become part of the Galactic field population.
Because most if not all stars form in clusters, star cluster
A star cluster is a group of stars held together by self-gravitation. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters, tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound; and open cluster ...
s are to be viewed as the fundamental building blocks of galaxies. The violent gas-expulsion events that shape and destroy many star clusters at birth leave their imprint in the morphological and kinematical structures of galaxies. Most open clusters form with at least 100 stars and a mass of 50 or more solar masses. The largest clusters can have over 104 solar masses, with the massive cluster Westerlund 1 being estimated at 5 × 104 solar masses and R136
R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue) is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. W ...
at almost 5 x 105, typical of globular clusters. While open clusters and globular clusters form two fairly distinct groups, there may not be a great deal of intrinsic difference between a very sparse globular cluster such as Palomar 12
Palomar 12 is a globular cluster in the constellation Capricornus, and is a member of the Palomar Globular Clusters group.
First discovered on the National Geographic Society – Palomar Observatory Sky Survey plates by Robert George Harri ...
and a very rich open cluster. Some astronomers believe the two types of star clusters form via the same basic mechanism, with the difference being that the conditions that allowed the formation of the very rich globular clusters containing hundreds of thousands of stars no longer prevail in the Milky Way.
It is common for two or more separate open clusters to form out of the same molecular cloud. In the Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a dwarf galaxy and satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around , the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, Sagittarius Dwarf ...
, both Hodge 301 and R136
R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue) is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. W ...
have formed from the gases of the Tarantula Nebula
The Tarantula Nebula (also known as 30 Doradus) is a large H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), forming its south-east corner (from Earth, Earth's perspective).
Discovery
The Tarantula Nebula was observed by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaill ...
, while in our own galaxy, tracing back the motion through space of the Hyades and Praesepe, two prominent nearby open clusters, suggests that they formed in the same cloud about 600 million years ago. Sometimes, two clusters born at the same time will form a binary cluster. The best known example in the Milky Way is the Double Cluster
The Double Cluster, also known as Caldwell 14, consists of the open clusters NGC 869 and NGC 884 (often designated h Persei and χ (chi) Persei, respectively), which are close together in the constellation Perseus. Both visible to the ...
of NGC 869 and NGC 884 (also known as h and χ Persei), but at least 10 more double clusters are known to exist. New research indicates the Cepheid
A Cepheid variable () is a type of variable star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature. It changes in brightness, with a well-defined stable period (typically 1–100 days) and amplitude. Cepheids are important cosmi ...
-hosting M25 may constitute a ternary star cluster together with NGC 6716 and Collinder 394. Many more binary clusters are known in the Small
Small means of insignificant size
Size in general is the Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or dimensions of a thing. More specifically, ''geometrical size'' (or ''spatial size'') can refer to three geometrical measures: length, area, or ...
and Large Magellanic Clouds—they are easier to detect in external systems than in our own galaxy because projection effects can cause unrelated clusters within the Milky Way to appear close to each other.
Morphology and classification
 Open clusters range from very sparse clusters with only a few members to large
Open clusters range from very sparse clusters with only a few members to large agglomeration
Agglomeration may refer to:
* Urban agglomeration, in standard English
* Megalopolis, in Chinese English, as defined in China's ''Standard for basic terminology of urban planning'' (GB/T 50280—98). Also known as "city cluster".
* Economies of agg ...
s containing thousands of stars. They usually consist of quite a distinct dense core, surrounded by a more diffuse 'corona' of cluster members. The core is typically about 3–4 light year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year (ly or lyr), is a unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equal to exactly , which is approximately 9.46 trillion km or 5.88 trillion mi. As defined by t ...
s across, with the corona extending to about 20 light years from the cluster center. Typical star densities in the center of a cluster are about 1.5 stars per cubic light year. For comparison, stellar density near the Sun is about 0.003 stars per cubic light year.
Open clusters are often classified according to a scheme developed by Robert Trumpler in 1930. The Trumpler scheme gives a cluster a three-part designation, with a Roman numeral
Roman numerals are a numeral system that originated in ancient Rome and remained the usual way of writing numbers throughout Europe well into the Late Middle Ages. Numbers are written with combinations of letters from the Latin alphabet, ea ...
from I-IV for little to very disparate, an Arabic numeral
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numerals. ...
from 1 to 3 for the range in brightness of members (from small to large range), and ''p'', ''m'' or ''r'' to indication whether the cluster is poor, medium or rich in stars. An 'n' is appended if the cluster lies within nebulosity.
Under the Trumpler scheme, the Pleiades are classified as I3rn, and the nearby Hyades are classified as II3m.
Numbers and distribution
 There are over 1,100 known open clusters in our galaxy, but the true total may be up to ten times higher than that. In
There are over 1,100 known open clusters in our galaxy, but the true total may be up to ten times higher than that. In spiral galaxies
Spiral galaxies form a class of galaxy originally described by Edwin Hubble in his 1936 work ''The Realm of the Nebulae''
, open clusters are largely found in the spiral arms where gas densities are highest and so most star formation occurs, and clusters usually disperse before they have had time to travel beyond their spiral arm. Open clusters are strongly concentrated close to the galactic plane, with a scale height
In atmospheric, earth, and planetary sciences, a scale height, usually denoted by the capital letter ''H'', is a distance ( vertical or radial) over which a physical quantity decreases by a factor of e (the base of natural logarithms, approx ...
in our galaxy of about 180 light years, compared with a galactic radius of approximately 50,000 light years.
In irregular galaxies, open clusters may be found throughout the galaxy, although their concentration is highest where the gas density is highest. Open clusters are not seen in elliptical galaxies
An elliptical galaxy is a type of galaxy with an approximately ellipsoidal shape and a smooth, nearly featureless image. They are one of the three main classes of galaxy described by Edwin Hubble in his Hubble sequence and 1936 work ''The Re ...
: Star formation ceased many millions of years ago in ellipticals, and so the open clusters which were originally present have long since dispersed.
In the Milky Way Galaxy, the distribution of clusters depends on age, with older clusters being preferentially found at greater distances from the Galactic Center
The Galactic Center is the barycenter of the Milky Way and a corresponding point on the rotational axis of the galaxy. Its central massive object is a supermassive black hole of about 4 million solar masses, which is called Sagittarius A*, a ...
, generally at substantial distances above or below the galactic plane
The galactic plane is the plane (geometry), plane on which the majority of a disk-shaped galaxy's mass lies. The directions perpendicular to the galactic plane point to the galactic poles. In actual usage, the terms ''galactic plane'' and ''galac ...
. Tidal force
The tidal force or tide-generating force is the difference in gravitational attraction between different points in a gravitational field, causing bodies to be pulled unevenly and as a result are being stretched towards the attraction. It is the ...
s are stronger nearer the center of the galaxy, increasing the rate of disruption of clusters, and also the giant molecular clouds which cause the disruption of clusters are concentrated towards the inner regions of the galaxy, so clusters in the inner regions of the galaxy tend to get dispersed at a younger age than their counterparts in the outer regions.
Stellar composition
 Because open clusters tend to be dispersed before most of their stars reach the end of their lives, the light from them tends to be dominated by the young, hot blue stars. These stars are the most massive, and have the shortest lives, a few tens of millions of years. The older open clusters tend to contain more yellow stars.
The frequency of
Because open clusters tend to be dispersed before most of their stars reach the end of their lives, the light from them tends to be dominated by the young, hot blue stars. These stars are the most massive, and have the shortest lives, a few tens of millions of years. The older open clusters tend to contain more yellow stars.
The frequency of binary star
A binary star or binary star system is a system of two stars that are gravitationally bound to and in orbit around each other. Binary stars in the night sky that are seen as a single object to the naked eye are often resolved as separate stars us ...
systems has been observed to be higher within open clusters than outside open clusters. This is seen as evidence that single stars get ejected from open clusters due to dynamical interactions.
Some open clusters contain hot blue stars which seem to be much younger than the rest of the cluster. These blue straggler
A blue straggler is a type of star that is more luminous and bluer than expected. Typically identified in a stellar cluster, they have a higher effective temperature than the main sequence turnoff point for the cluster, where ordinary stars b ...
s are also observed in globular clusters, and in the very dense cores of globulars they are believed to arise when stars collide, forming a much hotter, more massive star. However, the stellar density in open clusters is much lower than that in globular clusters, and stellar collisions cannot explain the numbers of blue stragglers observed. Instead, it is thought that most of them probably originate when dynamical interactions with other stars cause a binary system to coalesce into one star.
Once they have exhausted their supply of hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
through nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction, reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei combine to form a larger nuclei, nuclei/neutrons, neutron by-products. The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manifested as either the rele ...
, medium- to low-mass stars shed their outer layers to form a planetary nebula
A planetary nebula is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated to planets. The ...
and evolve into white dwarf
A white dwarf is a Compact star, stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very density, dense: in an Earth sized volume, it packs a mass that is comparable to the Sun. No nuclear fusion takes place i ...
s. While most clusters become dispersed before a large proportion of their members have reached the white dwarf stage, the number of white dwarfs in open clusters is still generally much lower than would be expected, given the age of the cluster and the expected initial mass distribution of the stars. One possible explanation for the lack of white dwarfs is that when a red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface t ...
expels its outer layers to become a planetary nebula, a slight asymmetry in the loss of material could give the star a 'kick' of a few kilometres per second
The metre per second is the unit of both speed (a scalar quantity) and velocity (a vector quantity, which has direction and magnitude) in the International System of Units (SI), equal to the speed of a body covering a distance of one metre in ...
, enough to eject it from the cluster.
Because of their high density, close encounters between stars in an open cluster are common. For a typical cluster with 1,000 stars with a 0.5 parsec half-mass radius, on average a star will have an encounter with another member every 10 million years. The rate is even higher in denser clusters. These encounters can have a significant impact on the extended circumstellar disks of material that surround many young stars. Tidal perturbations of large disks may result in the formation of massive planets and brown dwarf
Brown dwarfs are substellar objects that have more mass than the biggest gas giant planets, but less than the least massive main sequence, main-sequence stars. Their mass is approximately 13 to 80 Jupiter mass, times that of Jupiter ()not big en ...
s, producing companions at distances of 100 AU or more from the host star.
Eventual fate
 Many open clusters are inherently unstable, with a small enough mass that the
Many open clusters are inherently unstable, with a small enough mass that the escape velocity
In celestial mechanics, escape velocity or escape speed is the minimum speed needed for an object to escape from contact with or orbit of a primary body, assuming:
* Ballistic trajectory – no other forces are acting on the object, such as ...
of the system is lower than the average velocity
Velocity is a measurement of speed in a certain direction of motion. It is a fundamental concept in kinematics, the branch of classical mechanics that describes the motion of physical objects. Velocity is a vector (geometry), vector Physical q ...
of the constituent stars. These clusters will rapidly disperse within a few million years. In many cases, the stripping away of the gas from which the cluster formed by the radiation pressure of the hot young stars reduces the cluster mass enough to allow rapid dispersal.
Clusters that have enough mass to be gravitationally bound once the surrounding nebula has evaporated can remain distinct for many tens of millions of years, but, over time, internal and external processes tend also to disperse them. Internally, close encounters between stars can increase the velocity of a member beyond the escape velocity of the cluster. This results in the gradual 'evaporation' of cluster members.
Externally, about every half-billion years or so an open cluster tends to be disturbed by external factors such as passing close to or through a molecular cloud. The gravitational tidal force
The tidal force or tide-generating force is the difference in gravitational attraction between different points in a gravitational field, causing bodies to be pulled unevenly and as a result are being stretched towards the attraction. It is the ...
s generated by such an encounter tend to disrupt the cluster. Eventually, the cluster becomes a stream of stars, not close enough to be a cluster but all related and moving in similar directions at similar speeds. The timescale over which a cluster disrupts depends on its initial stellar density, with more tightly packed clusters persisting longer. Estimated cluster half lives Half-life is a mathematical and scientific description of exponential or gradual decay.
Half-life, half life or halflife may also refer to:
Film
* ''Half-Life'' (film), a 2008 independent film by Jennifer Phang
* '' Half Life: A Parable for t ...
, after which half the original cluster members will have been lost, range from 150–800 million years, depending on the original density.
After a cluster has become gravitationally unbound, many of its constituent stars will still be moving through space on similar trajectories, in what is known as a stellar association
A stellar association is a very loose star cluster, looser than both open clusters and globular clusters. Stellar associations will normally contain from 10 to 100 or more visible stars. An association is primarily identified by commonalities in i ...
, moving cluster, or moving group. Several of the brightest stars in the 'Plough
A plough or ( US) plow (both pronounced ) is a farm tool for loosening or turning the soil before sowing seed or planting. Ploughs were traditionally drawn by oxen and horses but modern ploughs are drawn by tractors. A plough may have a wooden ...
' of Ursa Major
Ursa Major, also known as the Great Bear, is a constellation in the Northern Sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear", referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa M ...
are former members of an open cluster which now form such an association, in this case the Ursa Major Moving Group
The Ursa Major Moving Group, also known as Collinder 285 and the Ursa Major association, is the closest Stellar kinematics#Moving groups, stellar moving group – a set of stars with common velocities in space and thought to have a common orig ...
. Eventually their slightly different relative velocities will see them scattered throughout the galaxy. A larger cluster is then known as a stream, if we discover the similar velocities and ages of otherwise well-separated stars.
Studying stellar evolution
 When a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is plotted for an open cluster, most stars lie on the
When a Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is plotted for an open cluster, most stars lie on the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
. The most massive stars have begun to evolve away from the main sequence and are becoming red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The stellar atmosphere, outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface t ...
s; the position of the turn-off from the main sequence can be used to estimate the age of the cluster.
Because the stars in an open cluster are all at roughly the same distance from Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
, and were born at roughly the same time from the same raw material, the differences in apparent brightness among cluster members are due only to their mass. This makes open clusters very useful in the study of stellar evolution, because when comparing one star with another, many of the variable parameters are fixed.
The study of the abundances of lithium
Lithium (from , , ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the ...
and beryllium
Beryllium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a steel-gray, hard, strong, lightweight and brittle alkaline earth metal. It is a divalent element that occurs naturally only in combination with ...
in open-cluster stars can give important clues about the evolution of stars and their interior structures. While hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
nuclei cannot fuse to form helium
Helium (from ) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol He and atomic number 2. It is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, inert gas, inert, monatomic gas and the first in the noble gas group in the periodic table. Its boiling point is ...
until the temperature reaches about 10 million K, lithium and beryllium are destroyed at temperatures of 2.5 million K and 3.5 million K respectively. This means that their abundances depend strongly on how much mixing occurs in stellar interiors. Through study of their abundances in open-cluster stars, variables such as age and chemical composition can be fixed.
Studies have shown that the abundances of these light elements are much lower than models of stellar evolution predict. While the reason for this underabundance is not yet fully understood, one possibility is that convection
Convection is single or Multiphase flow, multiphase fluid flow that occurs Spontaneous process, spontaneously through the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoy ...
in stellar interiors can 'overshoot' into regions where radiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
is normally the dominant mode of energy transport.
Astronomical distance scale
 Determining the distances to astronomical objects is crucial to understanding them, but the vast majority of objects are too far away for their distances to be directly determined. Calibration of the astronomical distance scale relies on a sequence of indirect and sometimes uncertain measurements relating the closest objects, for which distances can be directly measured, to increasingly distant objects. Open clusters are a crucial step in this sequence.
The closest open clusters can have their distance measured directly by one of two methods. First, the
Determining the distances to astronomical objects is crucial to understanding them, but the vast majority of objects are too far away for their distances to be directly determined. Calibration of the astronomical distance scale relies on a sequence of indirect and sometimes uncertain measurements relating the closest objects, for which distances can be directly measured, to increasingly distant objects. Open clusters are a crucial step in this sequence.
The closest open clusters can have their distance measured directly by one of two methods. First, the parallax
Parallax is a displacement or difference in the apparent position of an object viewed along two different sightline, lines of sight and is measured by the angle or half-angle of inclination between those two lines. Due to perspective (graphica ...
(the small change in apparent position over the course of a year caused by the Earth moving from one side of its orbit around the Sun to the other) of stars in close open clusters can be measured, like other individual stars. Clusters such as the Pleiades, Hyades and a few others within about 500 light years are close enough for this method to be viable, and results from the Hipparcos
''Hipparcos'' was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions and distances of ...
position-measuring satellite yielded accurate distances for several clusters.
The other direct method is the so-called moving cluster method. This relies on the fact that the stars of a cluster share a common motion through space. Measuring the proper motions of cluster members and plotting their apparent motions across the sky will reveal that they converge on a vanishing point
A vanishing point is a point (geometry), point on the projection plane, image plane of a graphical perspective, perspective rendering where the two-dimensional perspective projections of parallel (geometry), parallel lines in three-dimensional ...
. The radial velocity of cluster members can be determined from Doppler shift
The Doppler effect (also Doppler shift) is the change in the frequency of a wave in relation to an observer who is moving relative to the source of the wave. The ''Doppler effect'' is named after the physicist Christian Doppler, who described t ...
measurements of their spectra, and once the radial velocity, proper motion and angular distance from the cluster to its vanishing point are known, simple trigonometry
Trigonometry () is a branch of mathematics concerned with relationships between angles and side lengths of triangles. In particular, the trigonometric functions relate the angles of a right triangle with ratios of its side lengths. The fiel ...
will reveal the distance to the cluster. The Hyades are the best-known application of this method, which reveals their distance to be 46.3 parsec
The parsec (symbol: pc) is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to or (AU), i.e. . The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and ...
s.
Once the distances to nearby clusters have been established, further techniques can extend the distance scale to more distant clusters. By matching the main sequence
In astronomy, the main sequence is a classification of stars which appear on plots of stellar color index, color versus absolute magnitude, brightness as a continuous and distinctive band. Stars on this band are known as main-sequence stars or d ...
on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram for a cluster at a known distance with that of a more distant cluster, the distance to the more distant cluster can be estimated. The nearest open cluster is the Hyades: The stellar association consisting of most of the Plough stars is at about half the distance of the Hyades, but is a stellar association rather than an open cluster as the stars are not gravitationally bound to each other. The most distant known open cluster in our galaxy is Berkeley 29, at a distance of about 15,000 parsecs. Open clusters, especially super star clusters, are also easily detected in many of the galaxies of the Local Group
The Local Group is the galaxy group that includes the Milky Way, where Earth is located. It has a total diameter of roughly , and a total mass of the order of .
It consists of two collections of galaxies in a " dumbbell" shape; the Milky Way ...
and nearby: e.g., NGC 346 and the SSCs R136
R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue) is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. W ...
and NGC 1569 A and B.
Accurate knowledge of open cluster distances is vital for calibrating the period–luminosity relationship shown by variable star
A variable star is a star whose brightness as seen from Earth (its apparent magnitude) changes systematically with time. This variation may be caused by a change in emitted light or by something partly blocking the light, so variable stars are ...
s such as Cepheid
A Cepheid variable () is a type of variable star that pulsates radially, varying in both diameter and temperature. It changes in brightness, with a well-defined stable period (typically 1–100 days) and amplitude. Cepheids are important cosmi ...
stars, which allows them to be used as standard candle
The cosmic distance ladder (also known as the extragalactic distance scale) is the succession of methods by which astronomers determine the distances to celestial objects. A ''direct'' distance measurement of an astronomical object is possible ...
s. These luminous stars can be detected at great distances, and are then used to extend the distance scale to nearby galaxies in the Local Group. Indeed, the open cluster designated NGC 7790 hosts three classical Cepheids
Classical Cepheids are a type of Cepheid variable star. They are young, population I variable stars that exhibit regular radial Stellar pulsation, pulsations with periods of a few days to a few weeks and visual amplitudes ranging from a few tenth ...
.Sandage, Allan (1958)''Cepheids in Galactic Clusters. I. CF Cass in NGC 7790.''
AJ, 128Majaess, D.; Carraro, G.; Moni Bidin, C.; Bonatto, C.; Berdnikov, L.; Balam, D.; Moyano, M.; Gallo, L.; Turner, D.; Lane, D.; Gieren, W.; Borissova, J.; Kovtyukh, V.; Beletsky, Y. (2013)
''Anchors for the cosmic distance scale: the Cepheids U Sagittarii, CF Cassiopeiae, and CEab Cassiopeiae''
A&A, 260
RR Lyrae variables
RR Lyrae variables are periodic variable stars, commonly found in globular clusters. They are used as standard candles to measure (extra) galactic distances, assisting with the cosmic distance ladder. This class is named after the prototype an ...
are too old to be associated with open clusters, and are instead found in globular clusters
A globular cluster is a spheroidal conglomeration of stars that is bound together by gravity, with a higher concentration of stars towards its center. It can contain anywhere from tens of thousands to many millions of member stars, all orbiting ...
.
Planets
The stars in open clusters can host exoplanets, just like stars outside open clusters. For example, the open cluster NGC 6811 contains two known planetary systems, Kepler-66 and Kepler-67. Additionally, severalhot Jupiter
Hot Jupiters (sometimes called hot Saturns) are a class of gas giant exoplanets that are inferred to be physically similar to Jupiter (i.e. Jupiter analogue, Jupiter analogues) but that have very short orbital periods (). The close proximity to t ...
s are known to exist in the Beehive Cluster
The Beehive Cluster (also known as Praesepe (Latin for "manger", "cot" or "crib"), M44, NGC 2632, or Cr 189), is an open cluster in the constellation Cancer. One of the nearest open clusters to Earth, it contains a larger population of stars tha ...
.
See also
*List of open clusters
This is a list of open clusters located in the Milky Way. An open cluster is an association of up to a few thousand stars that all formed from the same giant molecular cloud. There are over 1,000 known open clusters in the Milky Way galaxy, but th ...
* Moving groups
* Open cluster family
* Open cluster remnant
References
Further reading
* *External links
The Jewel Box (also known as NGC 4755 or Kappa Crucis Cluster) – open cluster in the Crux constellation @ SKY-MAP.ORG
Open Clusters – Information and amateur observations
{{DEFAULTSORT:Open Cluster Open clusters Star clusters