Gadolinium(III) Oxide on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gadolinium(III) oxide (archaically gadolinia) is an

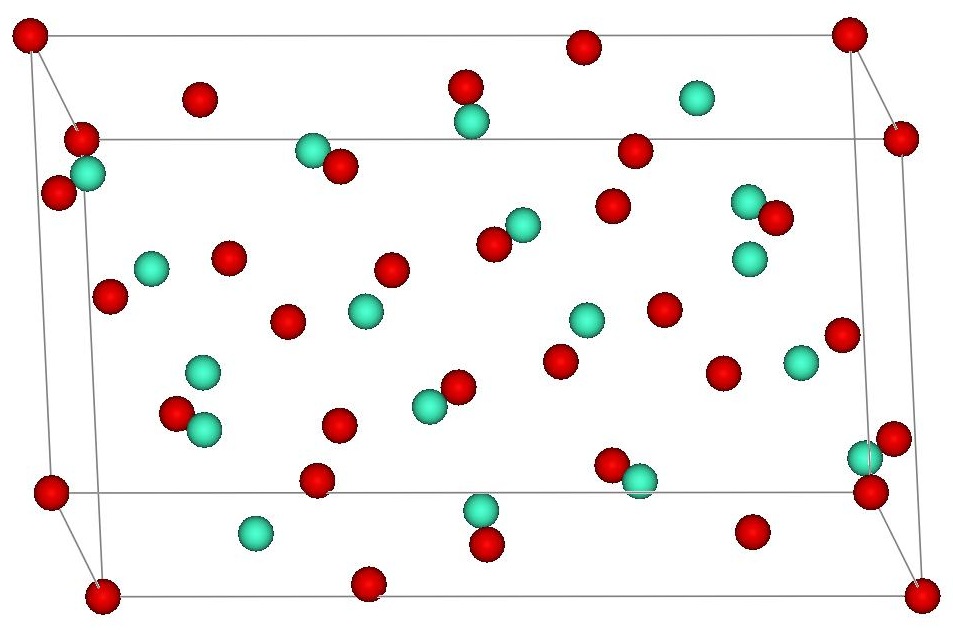 Gadolinium oxide adopts two structures. The cubic ( cI80, Ia), No. 206) structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide and heavy trivalent lanthanide sesquioxides. The cubic structure features two types of gadolinium sites, each with a coordination number of 6 but with different coordination geometries. The second polymorph is
Gadolinium oxide adopts two structures. The cubic ( cI80, Ia), No. 206) structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide and heavy trivalent lanthanide sesquioxides. The cubic structure features two types of gadolinium sites, each with a coordination number of 6 but with different coordination geometries. The second polymorph is
inorganic compound
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bondsthat is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemistry''.
Inorgan ...
with the formula
In science, a formula is a concise way of expressing information symbolically, as in a mathematical formula or a ''chemical formula''. The informal use of the term ''formula'' in science refers to the general construct of a relationship betwe ...
Gd2O3. It is one of the most commonly available forms of the rare-earth element gadolinium, derivatives, of which are potential contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
.
Structure

 Gadolinium oxide adopts two structures. The cubic ( cI80, Ia), No. 206) structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide and heavy trivalent lanthanide sesquioxides. The cubic structure features two types of gadolinium sites, each with a coordination number of 6 but with different coordination geometries. The second polymorph is
Gadolinium oxide adopts two structures. The cubic ( cI80, Ia), No. 206) structure is similar to that of manganese(III) oxide and heavy trivalent lanthanide sesquioxides. The cubic structure features two types of gadolinium sites, each with a coordination number of 6 but with different coordination geometries. The second polymorph is monoclinic
In crystallography, the monoclinic crystal system is one of the seven crystal systems. A crystal system is described by three Vector (geometric), vectors. In the monoclinic system, the crystal is described by vectors of unequal lengths, as in t ...
( Pearson symbol mS30, space group C2/m, No. 12). At room temperature, the cubic structure is more stable. The phase change to the monoclinic structure takes place at 1200 °C. Above 2100 °C to the melting point at 2420 °C, a hexagonal phase dominates.
Preparation and chemistry
Gadolinium oxide can be formed by thermal decomposition of the hydroxide, nitrate, carbonate, or oxalates. Gadolinium oxide forms on the surface of gadolinium metal. Gadolinium oxide is a rather basic oxide, indicated by its ready reaction with carbon dioxide to give carbonates. It dissolves readily in the common mineral acids with the complication that the oxalate, fluoride, sulfate and phosphate are very insoluble in water and may coat the grains of oxide, thereby preventing the complete dissolution.Nanoparticles of Gd2O3
Several methods are known for the synthesis of gadolinium oxidenanoparticle
A nanoparticle or ultrafine particle is a particle of matter 1 to 100 nanometres (nm) in diameter. The term is sometimes used for larger particles, up to 500 nm, or fibers and tubes that are less than 100 nm in only two directions. At ...
s, mostly based on precipitation of the hydroxide by the reaction of gadolinium ions with hydroxide, followed by thermal dehydration to the oxide. The nanoparticles are always coated with a protective material to avoid the formation of larger polycrystalline aggregates.
Nanoparticles of gadolinium oxide is a potential contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ...
(MRI). A dextran-coated preparation of 20–40 nm sized gadolinium oxide particles had a relaxivity of 4.8 s−1mM−1 per gadolinium ion at 7.05 T (an unusually high field compared to the clinically used MRI scanners which mostly range from 0.5 to 3 T). Smaller particles, between 2 and 7 nm, were tested as an MRI agent.
Potential applications
* Gadolinium(III) oxide is a host material in some solid-state lasers. Doped with rare-earth ions such asneodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth element, rare-earth metals. It is a hard (physics), hard, sli ...
or erbium
Erbium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements. It is a lanthanide, a rare- ...
, Gd₂O₃ can produce lasers with high efficiency and specific wavelengths, which are important in various applications, including telecommunications and medical procedures.
* Gd₂O₃ is used in some solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs).
References
{{Gadolinium compounds Gadolinium compounds Sesquioxides Crystals in space group 206 Crystals in space group 12