Gadahara on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gadahara (


 ''Ga-
''Ga-


 ''Ga-
''Ga-


 ''Ga-ḍa-ha-ra'' appears vertically as a monogram in the right field of the coins. Then several name appear under the arm of the ruler, including Yasada, Piroz, Kirada and Samudragupta.
It is not known with certainty whether Gadahara is actually the name of a ruler, or a clan, or a geographical region, although modern scholarship considers it is indeed the region of
''Ga-ḍa-ha-ra'' appears vertically as a monogram in the right field of the coins. Then several name appear under the arm of the ruler, including Yasada, Piroz, Kirada and Samudragupta.
It is not known with certainty whether Gadahara is actually the name of a ruler, or a clan, or a geographical region, although modern scholarship considers it is indeed the region of 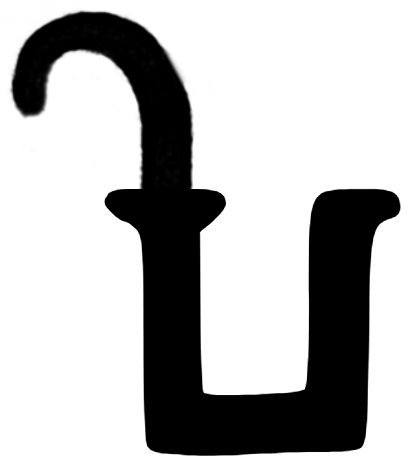

 ''Pi-ro-ysa'') or the Samudra, Some historians speculated it to
''Pi-ro-ysa'') or the Samudra, Some historians speculated it to 

 ''Samudra'') may suggest some kind of suzerainty at a time when the remnants of Kushan power were torn between these two powers.Although there may not have been any suzerainty, the
''Samudra'') may suggest some kind of suzerainty at a time when the remnants of Kushan power were torn between these two powers.Although there may not have been any suzerainty, the
File:HUNNIC TRIBES, Kidarites Kirada Circa 340-345.jpg, Another "Gadahara" coin, with the name "

 ) as a vertical monogram under the arm of the King.
File:Gadakhara Samudra coin Circa CE 350-375.jpg, "Gadakhara" coin with the name of the Samudra (Ocean) (
) as a vertical monogram under the arm of the King.
File:Gadakhara Samudra coin Circa CE 350-375.jpg, "Gadakhara" coin with the name of the Samudra (Ocean) (

 ''Samudra'') under the arm of the king. Circa 350-375 CE.
''Samudra'') under the arm of the king. Circa 350-375 CE.
Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
: ḍ
Ḍ (minuscule: ḍ) is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from D with the addition of a dot diacritic.
In the transcription of Afro-Asiatic languages such as Arabic, ⟨ḍ⟩ represents an " emphatic" consonant , and is used for that p ...
a-ha-ra''), sometimes Gadakhara (Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or ...
: ḍ
Ḍ (minuscule: ḍ) is a letter of the Latin alphabet, formed from D with the addition of a dot diacritic.
In the transcription of Afro-Asiatic languages such as Arabic, ⟨ḍ⟩ represents an " emphatic" consonant , and is used for that p ...
a-kha-ra''), is a name appearing on numerous coins at the end of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire (– CE) was a Syncretism, syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Afghanistan, Eastern Iran, India, Pakistan, Tajikistan and Uzbe ...
or the beginning of the rule of the Kidarite Huns in the area of Central and Western Punjab
Punjab (; ; also romanised as Panjāb or Panj-Āb) is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern Pakistan and no ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, in the period circa 350-375 CE.
The name Gandhara
Gandhara () was an ancient Indo-Aryan people, Indo-Aryan civilization in present-day northwest Pakistan and northeast Afghanistan. The core of the region of Gandhara was the Peshawar valley, Peshawar (Pushkalawati) and Swat valleys extending ...
.
The appearance of the names of foreign rulers such as the Kushano-Sassanian
The Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom (or Indo-Sasanians) was a polity established by the Sasanian Empire in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries. The Sasanian Empire captured the provinces of Sogdia, Bactria and Gandhara from the declining Kushan Emp ...
Piroz (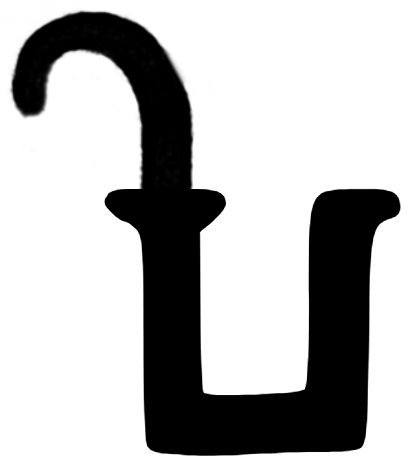

 ''Pi-ro-ysa'') or the Samudra, Some historians speculated it to
''Pi-ro-ysa'') or the Samudra, Some historians speculated it to Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', ( 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India. A military genius and a patron of arts, he is regarded among the greatest rulers in Indian history. As a son of th ...
(
 ''Samudra'') may suggest some kind of suzerainty at a time when the remnants of Kushan power were torn between these two powers.Although there may not have been any suzerainty, the
''Samudra'') may suggest some kind of suzerainty at a time when the remnants of Kushan power were torn between these two powers.Although there may not have been any suzerainty, the Samudragupta
Samudragupta (Gupta script: ''Sa-mu-dra-gu-pta'', ( 335–375 CE) was the second emperor of the Gupta Empire of ancient India. A military genius and a patron of arts, he is regarded among the greatest rulers in Indian history. As a son of th ...
's coin was minted by the ruler of the Kushan Principality of Punjab. After conquering them, the Kidarites adopted the same coinage
Coinage may refer to:
* Coins, standardized as currency
* Coining (mint), the process of manufacturing coins
* '' COINage'', a numismatics magazine
* Tin coinage, a tax on refined tin
* Coinage, a protologism or neologism
In linguistics, a neolo ...
and minted the same coins as those of Kushans of Punjab and Kushano Sassanids."In the Punjab the stylistic progression of the gold series from Kushan to Kidarite is clear: imitation staters were issued first in the name of Samudragupta, then by Kirada, 'Peroz' and finally Kidara" in
The Gadahara coins may be the last of the Kushan coins before the invasion of the Kidarites. But it is often thought that these coin actually were issued by the Kidarites
The Kidarites, or Kidara Huns, were a dynasty that ruled Bactria and adjoining parts of Central Asia and South Asia in the 4th and 5th centuries. The Kidarites belonged to a complex of peoples known collectively in India as the Huna people, Huna, ...
themselves, who were invading the Kushan realm around that time, although they seem to come chronologically just before the issues of the famous Kidarite ruler Kidara
Kidara I (Late Brahmi script: ''Ki-da-ra'') fl. 350–390 CE) was the first major ruler of the Kidarite Kingdom, which replaced the Indo-Sasanians in northwestern India, in the areas of Kushanshahr, Gandhara, Kashmir and Punjab.
Reign
Kidara ...
."Gadahara. The last branch, in course of time, yielded to Samudragupta, as is borne out by certain coins of this branch having the name Samudra. There is a good deal of similarity between the coins of the Gadaharas and the Kidara Kushanas." in
Other coin issues of Gadahara
Kirada
Kirada (Brahmi: ''Ki-ra-da'', ruled 335-345 CE), is considered by modern scholarship as the first known ruler of the Kidarites, Kidarite Huns in the area of Gandhara in northwestern India, possibly at the same time as another Kidarite ruler named ...
" (

 ''Samudra'') under the arm of the king. Circa 350-375 CE.
''Samudra'') under the arm of the king. Circa 350-375 CE.
References
{{reflist Kushan Empire