Gabii on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
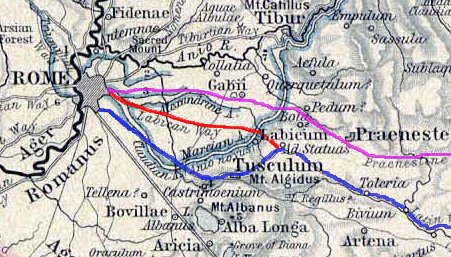
 Gabii was an ancient city of
Gabii was an ancient city of
 Definitive settlement at Gabii is believed to have begun with Latial IIA (900-830 BC) when the cemeteries of Castiglione, some 60 tombs of only IIA, and Osteria del'Osa, over 600 tombs primarily of II and III (900-630 BC), and some of IV (730-580 BC), began. Both of these necropoli are dated entirely before the foundation of Rome and well before the classical city of Gabii. The location of the settlements producing these cemeteries was an issue of some mystery until aerial reconnaissance revealed a string of six "Iron Age hamlets" on the isthmus and more along the ridge to the east. Latial IIA is regarded as pre-urban and IIB as proto-urban; that is, at some time during 830-730 BC the settlements acquired a common geopolitical identity. By the end of IV (580 BC) the name Gabii must have been in place as the name of the city, as by then the history was well into the events of its legends.
The most archaeological work has been done on the cemetery of Osteria dell'Osa. The tombs are divided into 14 groups, each exhibiting a set of distinctive traditions and each believed to represent one community of roughly 100 persons, round numbers. The earliest two, contemporaneous and dated to IIA, termed the northern and southern groups from their location within the cemetery, evidence the presence of a male warrior class. At the center of the cluster is a small set of male-only cremation burials, some in hut-urns. Around them is a greater group of inhumations of men, women and children. The richer cremation burials included grave gifts of miniaturized bronze tools and weapons and miniaturized pottery forms. The inhumations lacked weapons. Women were buried with jewelry and spindle-whorls (used in weaving).Cornell (1995), pp. 51-53.
The northern group (25 tombs) covered the mouth of the burial jar (dolium) with a
Definitive settlement at Gabii is believed to have begun with Latial IIA (900-830 BC) when the cemeteries of Castiglione, some 60 tombs of only IIA, and Osteria del'Osa, over 600 tombs primarily of II and III (900-630 BC), and some of IV (730-580 BC), began. Both of these necropoli are dated entirely before the foundation of Rome and well before the classical city of Gabii. The location of the settlements producing these cemeteries was an issue of some mystery until aerial reconnaissance revealed a string of six "Iron Age hamlets" on the isthmus and more along the ridge to the east. Latial IIA is regarded as pre-urban and IIB as proto-urban; that is, at some time during 830-730 BC the settlements acquired a common geopolitical identity. By the end of IV (580 BC) the name Gabii must have been in place as the name of the city, as by then the history was well into the events of its legends.
The most archaeological work has been done on the cemetery of Osteria dell'Osa. The tombs are divided into 14 groups, each exhibiting a set of distinctive traditions and each believed to represent one community of roughly 100 persons, round numbers. The earliest two, contemporaneous and dated to IIA, termed the northern and southern groups from their location within the cemetery, evidence the presence of a male warrior class. At the center of the cluster is a small set of male-only cremation burials, some in hut-urns. Around them is a greater group of inhumations of men, women and children. The richer cremation burials included grave gifts of miniaturized bronze tools and weapons and miniaturized pottery forms. The inhumations lacked weapons. Women were buried with jewelry and spindle-whorls (used in weaving).Cornell (1995), pp. 51-53.
The northern group (25 tombs) covered the mouth of the burial jar (dolium) with a

 The most conspicuous ruin remaining at the site of Gabii is a temple, generally attributed to Juno, which had six Ionic or Corinthian columns in the front and six on each side, excluding the back. The temple was composed of a single room ('' cella''), and it was made of ''lapis Gabinus'', a fire-resistant rock that was found in the quarries around Gabii and that also made its way into some of the buildings of Rome itself. The temple was situated in the middle of a podium, which had a colonnade of Doric columns along the back and extending around the sides. This colonnade stood in front of rooms of unknown function, perhaps multi-functional, for such uses as temple shops. The temple was excavated and published by the Spanish School at Rome in the 1960s and 1970s.
The temple was constructed 150-100 BC. A painted inscription (''IVN'') on an antefix identifies it as a temple of Juno. Around the rear of the temple (on the cliff side), which faced and towered above the road, were about 55 pits for planting trees representing a sacred grove. The site began as sacred in the 7th century BC featuring such a grove in which one tree was especially worshipped. In the 4th century BC a small shrine was constructed next to the grove around and in connection with which caches of anatomical
The most conspicuous ruin remaining at the site of Gabii is a temple, generally attributed to Juno, which had six Ionic or Corinthian columns in the front and six on each side, excluding the back. The temple was composed of a single room ('' cella''), and it was made of ''lapis Gabinus'', a fire-resistant rock that was found in the quarries around Gabii and that also made its way into some of the buildings of Rome itself. The temple was situated in the middle of a podium, which had a colonnade of Doric columns along the back and extending around the sides. This colonnade stood in front of rooms of unknown function, perhaps multi-functional, for such uses as temple shops. The temple was excavated and published by the Spanish School at Rome in the 1960s and 1970s.
The temple was constructed 150-100 BC. A painted inscription (''IVN'') on an antefix identifies it as a temple of Juno. Around the rear of the temple (on the cliff side), which faced and towered above the road, were about 55 pits for planting trees representing a sacred grove. The site began as sacred in the 7th century BC featuring such a grove in which one tree was especially worshipped. In the 4th century BC a small shrine was constructed next to the grove around and in connection with which caches of anatomical
 New fieldwork has been undertaken to the east of Gabii along the lines of the ancient city wall where a sanctuary has been excavated by Marco Fabbri close to one of the city's gates. Other work at the site has been carried out by Stefano Musco, the local inspector of the Soprintendenza Speciale per i Beni Archeologici di Roma
New fieldwork has been undertaken to the east of Gabii along the lines of the ancient city wall where a sanctuary has been excavated by Marco Fabbri close to one of the city's gates. Other work at the site has been carried out by Stefano Musco, the local inspector of the Soprintendenza Speciale per i Beni Archeologici di Roma
SSBAR
. These excavators, led by Marco Fabbri, reported the discovery of an Archaic building that they identified as a 'regia' in March 2010.
the discovery, in July 2009, of a half-ton lead encased inhumation burial that has tentatively been dated to the Roman Imperial period, likely the second or third centuries A.D. Evidence for early elite burials, in this case those of infants, also emerged in 2009, suggesting the development of social hierarchy in the eighth through sixth centuries BC. The discovery of an important but fragmentary Republican Latin inscription also came in 2009 and was published in 2011.Fortson and Potter 2011 The excavations of the Gabii Project continued in 2010 and 2011, during which time substantial portions of several ancient city blocks were brought to light. Not only is evidence for multi-period infrastructure clearly present, but the remains of urban architecture of the later first millennium BC have also become apparent. The award of a major collaborative research grant from the
Lazio e Sabina VI: Atti del Convegno. Sesto Incontro di Studi sul Lazio e la Sabina. Roma 4-6 marzo 2009'
', edited by G. Ghini, 237-48. Rome: Edizioni Quasar. * Jeffrey A. Becker and J. Nowlin. 2011. "Orientalizing Infant Burials from Gabii, Italy." ''BABESCH'' 86:27-39. * Benjamin Fortson and avid Potter. 2011. "A Fragmentary Early Republican Public Inscription from Gabii." ''Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik'' 178:255-60. * Sophie Hellas. 2014. "Gabii/Latium. Die Befestigungen von archaischer bis in mittelrepublikanische Zeit." ''Kölner und Bonner Archaeologica'' 3/2013:145-166. * M. Mogetta and J. A. Becker, 2014.
Archaeological Research at Gabii, Italy: The Gabii Project Excavations 2009-2011
" ''American Journal of Archaeology'' 118(1): 171-88. * M. Mogetta, 2014. "From Latin Planned Urbanism to Roman Colonial Layouts: the Town-planning of Gabii and its Cultural Implications." In E. Robinson (ed.), ''Papers on Italian Urbanism in the First Millennium B.C.'' (Journal of Roman Archaeology, Suppl. 97): 145-74. Portsmouth, R.I.: Journal of Roman Archaeology.

 Gabii was an ancient city of
Gabii was an ancient city of Latium
Latium ( , ; ) is the region of central western Italy in which the city of Rome was founded and grew to be the capital city of the Roman Empire.
Definition
Latium was originally a small triangle of fertile, volcanic soil (Old Latium) on whic ...
, located due east of Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
along the Via Praenestina
The Via Praenestina (modern Italian: Via Prenestina) was an ancient Roman road in central Italy.
Initially called Via Gabiana, from Gabii, the ancient city of Old Latium to which it ran, it received a new name having been extended as far as Pr ...
, which was in early times known as the ''Via Gabina''.
It was on the south-eastern perimeter of an extinct volcanic crater lake
A volcanic crater lake is a lake in a volcanic crater, crater that was formed by explosive eruption, explosive activity or a caldera, collapse during a types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruption.
Formation
Lakes in calderas fill large crate ...
, approximately circular in shape, named the ''Lacus Gabinus'', and then during later times called the ''Lago di Castiglione'', "lake of the fortification", after ''Castiglione'', a mediaeval tower erected on the site of the ancient acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens ...
, or ''arx'', of Gabii. A necropolis
A necropolis (: necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'' ().
The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distan ...
is adjacent on that side of the lake. At present, the former lake is entirely agricultural land. The ruins of the ancient city project from the fields next to the cliffs overlooking it, on both sides of the via. A ''municipium
In ancient Rome, the Latin term (: ) referred to a town or city. Etymologically, the was a social contract among ('duty holders'), or citizens of the town. The duties () were a communal obligation assumed by the in exchange for the privileges ...
'' in Roman times, Gabii is currently located in the of Osteria dell'Osa from the ''comune'' of Monte Compatri, of which it is a part, in the Province of Rome, Region of Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants an ...
. The site is under new seasonal archaeological excavation.
Historical geography
To what degree the lake was sedimented in ancient times remains unknown. Some of the earliest huts are down in the crater. Two streams flowing north to south flanked the lake on the west: the ''Fosso del'Osa'', and the east: ''Fosso di San Giuliano''. These originated in another body of water, believed to be ''Lacus Regillus'', on the south side of the road. The streams cut the road on either side of Gabii and were crossed by bridges; in other words, Gabii was constructed at a defensible location on an isthmus between two lakes. The isthmus was isolated by streams on either side. The quadrangle so formed contained its own water supply and straddled a major route on the east flank of Rome. It could not, as history demonstrated, be ignored by Rome. The two streams flow north to the Anio river, which flows west into theTiber river
The Tiber ( ; ; ) is the List of rivers of Italy, third-longest river in Italy and the longest in Central Italy, rising in the Apennine Mountains in Emilia-Romagna and flowing through Tuscany, Umbria, and Lazio, where it is joined by the R ...
on the north side of Rome.
In 1846 Gell reported that the Osa came from "a large marshy plain, extending almost to the Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. The course after the first six miles from Rome is not taken by any modern road, but it can be clearly traced from remains of pavement and buildings. It seems possibl ...
." Passing by Lake Gabino it was connected to the latter by "artificial canals", which were in the process of draining the lake:The water of the lake has been very much lowered by this canal, and more draining is yet in contemplation, although there are already many square miles of uncultivated ground in the vicinity.The draining of the lake was a project of the Borghese family, which had purchased it in 1614 from the Colonna family. Octavian Blewitt's handbook was able to report in 1850 (only four years later):
The lake was drained a few years ago by prince Borghese, who has converted it from the state of a pestilential marsh into a district of great fertility.Near the river a small inn had been placed, the Osteria dell'Osa ("Inn of the Osa"), north of which was the main necropolis of Gabii. The habitation today has expanded into the center of a . The marshy plain was the last trace of the quasi-legendary lake near which the
Battle of Lake Regillus
The Battle of Lake Regillus was a legendary Roman victory over the Latin League shortly after the establishment of the Roman Republic and as part of a wider Latin War (498–493 BC), Latin War. The Latins were led by an elderly Lucius Tar ...
decided whether the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
would continue or the kings of Rome would be restored by the intervention of the Latin League
The Latin League ( – 338 BC)Stearns, Peter N. (2001). ''The Encyclopedia of World History''. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 76–78. . was an ancient confederation of about 30 villages and tribes in the region of Latium near the ancient city of Rome, o ...
, to which Gabii belonged. The site of the battle is still a matter of dispute, which, on the unwarranted assumption that the location of the battle reveals the location of the lake, has extended into a dispute over the location of the lake. To modern topographers the deep lake basin, now kept dry, and the aqueducts that drew water, and still draw water, from its sources leave no doubt that the lake was located in the basin.
Lake Regillus varied in size and depth over the centuries but was certainly between the ''Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east-southeast from Rome. The course after the first six miles from Rome is not taken by any modern road, but it can be clearly traced from remains of pavement and buildings. It seems possibl ...
'' and the ''Via Praenestina
The Via Praenestina (modern Italian: Via Prenestina) was an ancient Roman road in central Italy.
Initially called Via Gabiana, from Gabii, the ancient city of Old Latium to which it ran, it received a new name having been extended as far as Pr ...
'' east of Finocchio and north of Colonna (ancient Labicum), the last remnant at Pantana Borghese having been drained by the Borghese family in conjunction with the restitution of the first part of the Acqua Alexandrina as the Acqua Felice under Pope Sixtus V
Pope Sixtus V (; 13 December 1521 – 27 August 1590), born Felice Piergentile, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 24 April 1585 to his death, in August 1590. As a youth, he joined the Franciscan order, where h ...
in the years 1585–1587. The two roads joined on the outskirts of Rome. The Pantana was the low point; from springs on its hillside exuded the water that filled the lake. During the thousand years of the post-classical period a much smaller Rome (totally abandoned at one point under the Goths) had lived on a greatly reduced water supply due to the broken and unrepaired aqueducts.
Gabii had kept its lake until the completion of the Acqua Alexandrina in 226 AD. The Romans captured springs or mountain streams for drinking water; they never fed the waters of the marsh into the aqueduct. It led from springs over the Pantana through underground conduits on the south side of the ''Via Praenestina'' to the outskirts of Rome, where it was carried on arched conduits above ground into the city. The Acqua Felice had more altitude at this point. By 226 the lake must have receded enough to have left a corridor along the road, as the Romans would not have been able to sink a conduit under the swamp. Having its source water drained away, the lake receded drastically. The aqueduct is still in use. In 1915 it shunted some per day into the city of Rome. If these sources were not diverted, Lake Regillus would soon return.
Meanwhile, the basin marks the location of the former lake. It is now entirely agricultural land, except that the community of Lago Regillo has been placed in it near Gabii. Osteria del Finocchio marks the western limit, as it is heavily settled and is on higher ground. Lake Regillus therefore cannot have been in the vicinity of Frascati
Frascati () is a city and in the Metropolitan City of Rome Capital in the Lazio region of central Italy. It is located south-east of Rome, on the Alban Hills close to the ancient city of Tusculum. Frascati is closely associated with science, ...
, regardless of where the battle was fought.
Prehistory
Scattered surface pottery has been found from the Middle Bronze Age outside the necropolis located below Castiglione, from which nothing can be deduced concerning the settlement at Gabii. The Late Bronze Age is missing. The Final Bronze Age is represented by minimal Latial I (1000-900 BC) material around the inside of the crater on the southern side, indicating low-density settlement at the water's edge there.Smith (1996), p. 61. Definitive settlement at Gabii is believed to have begun with Latial IIA (900-830 BC) when the cemeteries of Castiglione, some 60 tombs of only IIA, and Osteria del'Osa, over 600 tombs primarily of II and III (900-630 BC), and some of IV (730-580 BC), began. Both of these necropoli are dated entirely before the foundation of Rome and well before the classical city of Gabii. The location of the settlements producing these cemeteries was an issue of some mystery until aerial reconnaissance revealed a string of six "Iron Age hamlets" on the isthmus and more along the ridge to the east. Latial IIA is regarded as pre-urban and IIB as proto-urban; that is, at some time during 830-730 BC the settlements acquired a common geopolitical identity. By the end of IV (580 BC) the name Gabii must have been in place as the name of the city, as by then the history was well into the events of its legends.
The most archaeological work has been done on the cemetery of Osteria dell'Osa. The tombs are divided into 14 groups, each exhibiting a set of distinctive traditions and each believed to represent one community of roughly 100 persons, round numbers. The earliest two, contemporaneous and dated to IIA, termed the northern and southern groups from their location within the cemetery, evidence the presence of a male warrior class. At the center of the cluster is a small set of male-only cremation burials, some in hut-urns. Around them is a greater group of inhumations of men, women and children. The richer cremation burials included grave gifts of miniaturized bronze tools and weapons and miniaturized pottery forms. The inhumations lacked weapons. Women were buried with jewelry and spindle-whorls (used in weaving).Cornell (1995), pp. 51-53.
The northern group (25 tombs) covered the mouth of the burial jar (dolium) with a
Definitive settlement at Gabii is believed to have begun with Latial IIA (900-830 BC) when the cemeteries of Castiglione, some 60 tombs of only IIA, and Osteria del'Osa, over 600 tombs primarily of II and III (900-630 BC), and some of IV (730-580 BC), began. Both of these necropoli are dated entirely before the foundation of Rome and well before the classical city of Gabii. The location of the settlements producing these cemeteries was an issue of some mystery until aerial reconnaissance revealed a string of six "Iron Age hamlets" on the isthmus and more along the ridge to the east. Latial IIA is regarded as pre-urban and IIB as proto-urban; that is, at some time during 830-730 BC the settlements acquired a common geopolitical identity. By the end of IV (580 BC) the name Gabii must have been in place as the name of the city, as by then the history was well into the events of its legends.
The most archaeological work has been done on the cemetery of Osteria dell'Osa. The tombs are divided into 14 groups, each exhibiting a set of distinctive traditions and each believed to represent one community of roughly 100 persons, round numbers. The earliest two, contemporaneous and dated to IIA, termed the northern and southern groups from their location within the cemetery, evidence the presence of a male warrior class. At the center of the cluster is a small set of male-only cremation burials, some in hut-urns. Around them is a greater group of inhumations of men, women and children. The richer cremation burials included grave gifts of miniaturized bronze tools and weapons and miniaturized pottery forms. The inhumations lacked weapons. Women were buried with jewelry and spindle-whorls (used in weaving).Cornell (1995), pp. 51-53.
The northern group (25 tombs) covered the mouth of the burial jar (dolium) with a travertine
Travertine ( ) is a form of terrestrial limestone deposited around mineral springs, especially hot springs. It often has a fibrous or concentric appearance and exists in white, tan, cream-colored, and rusty varieties. It is formed by a process ...
slab, made ovicaprine food offerings, left serpentine fibulae, razors of quadrangular shape and spearheads with sockets for wooden handles. The pottery is decorated. The southern group (30 tombs) used an impasto
Impasto is a technique used in painting, where paint is laid on an area of the surface thickly, usually thick enough that the brush or painting-knife strokes are visible. Paint can also be mixed right on the canvas. When dry, impasto provides tex ...
lid on the burial jars, left serpent-fibulae of a different-style, a razor of lunate shape and one-piece cast spears. The pottery is undecorated.
Urbanization of the area probably did not begin before the start of the second half of the 8th century BC. This process most likely finished by the end of the 7th century BC, and, at its height, the city's borders enclosed .
Legend and legendary history
The early date of the prehistoric Gabii suggests that the Roman writers could have little traditional memory of its foundation or of who founded it. The surviving traditions are therefore in thelegend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess certain qualities that give the ...
category; there may or may not be elements of truth in them. The tradition is two-fold: Gabii was founded either by the Latin kings of Alba Longa (according to Vergil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Roman poet of the Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' ...
and Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus (,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.
...
) and therefore was aboriginal Latin in ethnic descent, or by the Sicels
The Sicels ( ; or ''Siculī'') were an Indo-European tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily, their namesake, during the Iron Age. They spoke the Siculian language. After the defeat of the Sicels at the Battle of Nomae in 450 BC and the death of ...
as the Siculi, a substrate population of east Italy expelled by the Italics to Sicily. They became one of the three major indigenous tribes of ancient Sicily, giving their name to it.
The legend of a Siculian foundation of Rome comes from fragments of early Roman annalists, who asserted that the Siculi occupied several cities of Latium before the arrival of the ''aborigines'' (Latins): Rome, Tibur, Fescennium, Falerii, Antemnae, Caenina and a few others. Gabii is mentioned as one of them by Gaius Julius Solinus
__NOTOC__
Gaius Julius Solinus, better known simply as Solinus, was a Latin grammarian, geographer, and compiler who probably flourished in the early 3rd century AD. Historical scholar Theodor Mommsen dates him to the middle of the 3rd century. ...
. According to him two Siculian brothers founded it and named it by combining their names, ''Galatus'' and ''Bins''. Fanciful etymologies such as the above are not taken seriously but there is a sober case for a Sicilian and Siculian influence on early Latium. For example, the Cloelii claimed to be from Alba Longa
Alba Longa (occasionally written Albalonga in Italian sources) was an ancient Latins (Italic tribe), Latin city in Central Italy in the vicinity of Lake Albano in the Alban Hills. The ancient Romans believed it to be the founder and head of the ...
and used the cognomen
A ''cognomen'' (; : ''cognomina''; from ''co-'' "together with" and ''(g)nomen'' "name") was the third name of a citizen of ancient Rome, under Roman naming conventions. Initially, it was a nickname, but lost that purpose when it became hereditar ...
''Siculus''. Prisons called ''lautumia'' were cut into the sides of the early Capitoline Hill
The Capitolium or Capitoline Hill ( ; ; ), between the Roman Forum, Forum and the Campus Martius, is one of the Seven Hills of Rome.
The hill was earlier known as ''Mons Saturnius'', dedicated to the god Saturn (mythology), Saturn. The wo ...
. Syracuse used quarries, called ''latomiai'', for a similar purpose. Most of the similarities can be attributed to an influence on early Rome from Greek Sicily; however, the case of a Sicul substrate also is possible.
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', ...
relates the legend that Romulus
Romulus (, ) was the legendary founder and first king of Rome. Various traditions attribute the establishment of many of Rome's oldest legal, political, religious, and social institutions to Romulus and his contemporaries. Although many of th ...
and Remus were raised by Faustulus, the servant of Amulius
In Roman mythology, Amulius () was king of Alba Longa who ordered the death of his infant, twin grandnephews Romulus, the eventual founder and king of Rome, and Remus. He was deposed and killed by them after they survived and grew to adulth ...
, in Gabii, where they learned everything from literature to the use of Greek
Greek may refer to:
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all kno ...
weapons. From there they went on to found Rome.
War with Rome under Tarquinius Superbus
TheLatin League
The Latin League ( – 338 BC)Stearns, Peter N. (2001). ''The Encyclopedia of World History''. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 76–78. . was an ancient confederation of about 30 villages and tribes in the region of Latium near the ancient city of Rome, o ...
(''Latini'') was brought under Roman jurisdiction by the last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus
Lucius Tarquinius Superbus (died 495 BC) was the legendary seventh and final king of Rome, reigning 25 years until the popular uprising that led to the establishment of the Roman Republic.Livy, ''ab urbe condita libri'', wikisource:From_the_ ...
. Addressing their council and claiming that, because all the Latin cities were founded from Alba Longa
Alba Longa (occasionally written Albalonga in Italian sources) was an ancient Latins (Italic tribe), Latin city in Central Italy in the vicinity of Lake Albano in the Alban Hills. The ancient Romans believed it to be the founder and head of the ...
and Tullus Hostilius
Tullus Hostilius (; r. 672–640 BC) was the legendary third king of Rome. He succeeded Numa Pompilius and was succeeded by Ancus Marcius. Unlike his predecessor, Tullus was known as a warlike king who, according to the Roman historian Livy, b ...
had made a treaty by which Alba was ceded to Rome along with all its colonies, Rome had a legal claim over the Latins, he offered them protection from any chance devastation that should inflict their country and a share in Roman prosperity if they would resume the treaty, which they did. Thenceforward Latin troops fought beside Roman within the Roman army.
Gabii reneged from the Latin treaty with Rome for unknown reasons. Tarquinius' son, Sextus Tarquinius
Sextus Tarquinius was one of the sons of the last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. In the original account of the Tarquin dynasty presented by Fabius Pictor, he is the second son, between Titus Tarquinius, Titus and Arruns Tarquinius ( ...
, went to Gabii, pretending to be in revolt against his father and asking for assistance. He was accepted, and after successfully commanding various military expeditions, he was appointed as the leading general of the army of Gabii. As general, he commanded a number of minor but successful skirmishes against Roman forces, with the complicity of the Roman king.Livy
Titus Livius (; 59 BC – AD 17), known in English as Livy ( ), was a Roman historian. He wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people, titled , covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome before the traditional founding i ...
, ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' (; 'from the founding of Rome, founding of the City'), or (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is ...
'', 1.54
He sent a message to the king asking what to do next. Receiving the messenger in the garden the king said nothing at all (for which he might have been held liable later) but strolled around lopping off the heads of the tallest poppies with a stick. Sextus took this to be a message to destroy the aristocrats of Gabii including Antistius Petro whom according to legend Sextus accused of plotting with Tarquinius Superbus Sextus' return to Rome dead or alive, thereby provoking the Gabines to stone Antistius to death. Tarquinius Superbus was able to take advantage of the ensuing confusion and bring Gabii into submission without battle.
Dionysius of Halicarnassus
Dionysius of Halicarnassus (,
; – after 7 BC) was a Greek historian and teacher of rhetoric, who flourished during the reign of Emperor Augustus. His literary style was ''atticistic'' – imitating Classical Attic Greek in its prime.
...
states that Tarquin was lenient with Gabii, and their subsequent treaty, whose original text was written on a bullock's skin and draped over a wooden shield, was said by Dionysius of Halicarnassus to be still extant in his day in the Roman temple of Sancus.
After the overthrow of the Roman monarchy, Sextus fled to Gabii but was killed by the leaders of the city in revenge for his past actions.
History under Roman control
Gabii was an ally of Rome after 493 BC. In the late Republican period, the city became depopulated due to the extensive use of the ''lapis Gabinus'' quarry, which was just under the archaic city.Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises tha ...
mentioned it in the 1st century BC as a small and insignificant place.
The Augustan poets used Gabii when demonstrating a city that had fallen from its old heights.Princeton encyclopedia (1976). From inscriptions we learn that from the time of Augustus
Gaius Julius Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian (), was the founder of the Roman Empire, who reigned as the first Roman emperor from 27 BC until his death in A ...
or Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
onwards it enjoyed a municipal organization. Its baths were well known, and Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
, who was responsible for much of the renewed prosperity of the small towns of Latium, appears to have been a very liberal patron, building a senate-house (Curia Aelia Augusta
Curia (: curiae) in ancient Rome referred to one of the original groupings of the citizenry, eventually numbering 30, and later every Roman citizen was presumed to belong to one. While they originally probably had wider powers, they came to meet ...
) and an aqueduct.
After the 3rd century, Gabii practically disappears from history, though its bishops continue to be mentioned in ecclesiastical documents till the close of the 9th century.

Cultural influences
Gabii's importance in the earliest history of Rome is also apparent elsewhere: the adoption of the '' cinctus Gabinus'' (a method of draping the toga that leaves both arms free) by the Romans for certain ceremonies, the unique role it played for theaugur
An augur was a priest and official in the ancient Rome, classical Roman world. His main role was the practice of augury, the interpretation of the will of the List of Roman deities, gods by studying events he observed within a predetermined s ...
s as seen from the specific term '' ager Gabinus'' used by these priests (Varro, Ling. 5,33), and its presence in a Roman formula of ''devotio
In ancient Roman religion, the ''devotio'' was an extreme form of '' votum'' in which a Roman general vowed to sacrifice his own life in battle along with the enemy to chthonic gods in exchange for a victory. The most extended description of t ...
''.
Archaeology
Temple of Juno
 The most conspicuous ruin remaining at the site of Gabii is a temple, generally attributed to Juno, which had six Ionic or Corinthian columns in the front and six on each side, excluding the back. The temple was composed of a single room ('' cella''), and it was made of ''lapis Gabinus'', a fire-resistant rock that was found in the quarries around Gabii and that also made its way into some of the buildings of Rome itself. The temple was situated in the middle of a podium, which had a colonnade of Doric columns along the back and extending around the sides. This colonnade stood in front of rooms of unknown function, perhaps multi-functional, for such uses as temple shops. The temple was excavated and published by the Spanish School at Rome in the 1960s and 1970s.
The temple was constructed 150-100 BC. A painted inscription (''IVN'') on an antefix identifies it as a temple of Juno. Around the rear of the temple (on the cliff side), which faced and towered above the road, were about 55 pits for planting trees representing a sacred grove. The site began as sacred in the 7th century BC featuring such a grove in which one tree was especially worshipped. In the 4th century BC a small shrine was constructed next to the grove around and in connection with which caches of anatomical
The most conspicuous ruin remaining at the site of Gabii is a temple, generally attributed to Juno, which had six Ionic or Corinthian columns in the front and six on each side, excluding the back. The temple was composed of a single room ('' cella''), and it was made of ''lapis Gabinus'', a fire-resistant rock that was found in the quarries around Gabii and that also made its way into some of the buildings of Rome itself. The temple was situated in the middle of a podium, which had a colonnade of Doric columns along the back and extending around the sides. This colonnade stood in front of rooms of unknown function, perhaps multi-functional, for such uses as temple shops. The temple was excavated and published by the Spanish School at Rome in the 1960s and 1970s.
The temple was constructed 150-100 BC. A painted inscription (''IVN'') on an antefix identifies it as a temple of Juno. Around the rear of the temple (on the cliff side), which faced and towered above the road, were about 55 pits for planting trees representing a sacred grove. The site began as sacred in the 7th century BC featuring such a grove in which one tree was especially worshipped. In the 4th century BC a small shrine was constructed next to the grove around and in connection with which caches of anatomical terra cotta
Terracotta, also known as terra cotta or terra-cotta (; ; ), is a clay-based Vitrification#Ceramics, non-vitreous ceramicOED, "Terracotta""Terracotta" MFA Boston, "Cameo" database fired at relatively low temperatures. It is therefore a term used ...
statuettes were found. This type of statuette modeled an organ or section of the human body and was given as a votive offering at a healing sanctuary, of which a great many have been found in Latium, in hope that divinity would turn its attention to healing the organ of the dedicator. Also found were some votive pedestals inscribed to ''Fortuna.'' A pavement was inscribed to ''Jupiter Jurarius'' ("of oaths"), indicating possible state functions of the site. There were two other shrines at the location.
The subsequent temple to Juno remained in use during the empire, after the town was abandoned.
Forum
To the east of the temple lay the supposed area of the forum, where excavations were made by Gavin Hamilton in 1792. Hamilton discovered a large cache of statues that were initially placed in the Borghese collection, although many of them subsequently were carried off toParis
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of ci ...
by Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
, and still remain in the Louvre. The statues and busts are especially numerous and interesting (38 in all); besides the deities Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is often called Earth's "twin" or "sister" planet for having almost the same size and mass, and the closest orbit to Earth's. While both are rocky planets, Venus has an atmosphere much thicker ...
, Diana, Nemesis
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Nemesis (; ) also called Rhamnousia (or Rhamnusia; ), was the goddess who personified retribution for the sin of hubris: arrogance before the gods.
Etymology
The name ''Nemesis'' is derived from the Greek ...
, etc., they comprise Agrippa, Tiberius
Tiberius Julius Caesar Augustus ( ; 16 November 42 BC – 16 March AD 37) was Roman emperor from AD 14 until 37. He succeeded his stepfather Augustus, the first Roman emperor. Tiberius was born in Rome in 42 BC to Roman politician Tiberius Cl ...
, Germanicus
Germanicus Julius Caesar (24 May 15 BC – 10 October AD 19) was a Roman people, Roman general and politician most famously known for his campaigns against Arminius in Germania. The son of Nero Claudius Drusus and Antonia the Younger, Germanicu ...
, Caligula
Gaius Caesar Augustus Germanicus (31 August 12 – 24 January 41), also called Gaius and Caligula (), was Roman emperor from AD 37 until his assassination in 41. He was the son of the Roman general Germanicus and Augustus' granddaughter Ag ...
, Claudius
Tiberius Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; ; 1 August 10 BC – 13 October AD 54), or Claudius, was a Roman emperor, ruling from AD 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, Claudius was born to Nero Claudius Drusus, Drusus and Ant ...
, Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
, Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
and Plotina, Hadrian
Hadrian ( ; ; 24 January 76 – 10 July 138) was Roman emperor from 117 to 138. Hadrian was born in Italica, close to modern Seville in Spain, an Italic peoples, Italic settlement in Hispania Baetica; his branch of the Aelia gens, Aelia '' ...
and Sabina, Marcus Aurelius
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus ( ; ; 26 April 121 – 17 March 180) was Roman emperor from 161 to 180 and a Stoicism, Stoic philosopher. He was a member of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty, the last of the rulers later known as the Five Good Emperors ...
, Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; ; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the ...
, Geta
Geta may refer to:
Places
*Geta (woreda), a woreda in Ethiopia's Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples' Region
*Geta, Åland, a municipality in Finland
*Geta, Nepal, a town in Attariya Municipality, Kailali District, Seti Zone, Nepal
*Get� ...
, Gordian III
Gordian III (; 20 January 225 – February 244) was Roman emperor from 238 to 244. At the age of 13, he became the youngest sole emperor of the united Roman Empire. Gordian was the son of Maecia Faustina and her husband Junius Balbus, who d ...
and others. The inscriptions relate mainly to local and municipal matters.
Tower of Castiglione
The citadel of Gabii is now marked by the ruins of the medieval tower of Castiglione.Fieldwork since the 1990s
 New fieldwork has been undertaken to the east of Gabii along the lines of the ancient city wall where a sanctuary has been excavated by Marco Fabbri close to one of the city's gates. Other work at the site has been carried out by Stefano Musco, the local inspector of the Soprintendenza Speciale per i Beni Archeologici di Roma
New fieldwork has been undertaken to the east of Gabii along the lines of the ancient city wall where a sanctuary has been excavated by Marco Fabbri close to one of the city's gates. Other work at the site has been carried out by Stefano Musco, the local inspector of the Soprintendenza Speciale per i Beni Archeologici di RomaSSBAR
. These excavators, led by Marco Fabbri, reported the discovery of an Archaic building that they identified as a 'regia' in March 2010.
Gabii Project
In early 2007 the multi-institution Gabii Project, led by Nicola Terrenato of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, was launched. It began its investigations by conducting a large-scale geophysical survey of the former urban center of Gabii. This survey had two prongs: a magnetometry survey and a core-sampling survey including both manual and machine collected cores. The survey data revealed a regularized pattern of streets latent in the subsurface layers, together with archaeological deposits. The Gabii Project commenced large-scale excavations in two areas of the site in June 2009. In late March 2010 the Gabii Project reportethe discovery, in July 2009, of a half-ton lead encased inhumation burial that has tentatively been dated to the Roman Imperial period, likely the second or third centuries A.D. Evidence for early elite burials, in this case those of infants, also emerged in 2009, suggesting the development of social hierarchy in the eighth through sixth centuries BC. The discovery of an important but fragmentary Republican Latin inscription also came in 2009 and was published in 2011.Fortson and Potter 2011 The excavations of the Gabii Project continued in 2010 and 2011, during which time substantial portions of several ancient city blocks were brought to light. Not only is evidence for multi-period infrastructure clearly present, but the remains of urban architecture of the later first millennium BC have also become apparent. The award of a major collaborative research grant from the
National Endowment for the Humanities
The National Endowment for the Humanities (NEH) is an independent federal agency of the U.S. government, established by thNational Foundation on the Arts and the Humanities Act of 1965(), dedicated to supporting research, education, preserv ...
supports the next phase of excavations from 2012 to 2015.
See also
* Praxiteles *Roman art
The art of Ancient Rome, and the territories of its Republic and later Empire, includes architecture, painting, sculpture and mosaic work. Luxury objects in metal-work, gem engraving, ivory carvings, and glass are sometimes considered to be m ...
* Tall poppy syndrome
*Sextus Tarquinius
Sextus Tarquinius was one of the sons of the last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus. In the original account of the Tarquin dynasty presented by Fabius Pictor, he is the second son, between Titus Tarquinius, Titus and Arruns Tarquinius ( ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * Jeffrey A. Becker, Marcello Mogetta, and Nicola Terrenato. "A new plan for an ancient Italian city: Gabii revealed."American Journal of Archaeology
The ''American Journal of Archaeology'' (AJA), the peer-reviewed journal of the Archaeological Institute of America, has been published since 1897 (continuing the ''American Journal of Archaeology and of the History of the Fine Arts'' founded by t ...
113.4 (October 2009):629-42.
* Nicola Terrenato, A. Gallone, Jeffrey A. Becker, and S. Kay. 2010. "Urbanistica Ortogonale a Gabii: Risultati delle nuove prospezioni geofisiche e prospettive per il futuro." In Lazio e Sabina VI: Atti del Convegno. Sesto Incontro di Studi sul Lazio e la Sabina. Roma 4-6 marzo 2009'
', edited by G. Ghini, 237-48. Rome: Edizioni Quasar. * Jeffrey A. Becker and J. Nowlin. 2011. "Orientalizing Infant Burials from Gabii, Italy." ''BABESCH'' 86:27-39. * Benjamin Fortson and avid Potter. 2011. "A Fragmentary Early Republican Public Inscription from Gabii." ''Zeitschrift für Papyrologie und Epigraphik'' 178:255-60. * Sophie Hellas. 2014. "Gabii/Latium. Die Befestigungen von archaischer bis in mittelrepublikanische Zeit." ''Kölner und Bonner Archaeologica'' 3/2013:145-166. * M. Mogetta and J. A. Becker, 2014.
Archaeological Research at Gabii, Italy: The Gabii Project Excavations 2009-2011
" ''American Journal of Archaeology'' 118(1): 171-88. * M. Mogetta, 2014. "From Latin Planned Urbanism to Roman Colonial Layouts: the Town-planning of Gabii and its Cultural Implications." In E. Robinson (ed.), ''Papers on Italian Urbanism in the First Millennium B.C.'' (Journal of Roman Archaeology, Suppl. 97): 145-74. Portsmouth, R.I.: Journal of Roman Archaeology.
External links
* * {{Authority control Cities and towns in Lazio Roman sites in Lazio Former populated places in Italy Latin cities Catholic titular sees in Europe Archaeological sites in Lazio Roman towns and cities in Italy Monte Compatri