GPSG Syntax Tree Example on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Generalized phrase structure grammar (GPSG) is a framework for describing the
 Who did you say that Hilary was fond of and eslie despised .
Who did you say that Hilary was fond of and eslie despised .
Gerald Gazdar's profile on the University of Sussex WebsiteA list of Gazdar's linguistics publications, including ones dealing with GPSG
Generative linguistics Grammar frameworks Syntactic theories Semantic theories
syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituenc ...
and semantics
Semantics is the study of linguistic Meaning (philosophy), meaning. It examines what meaning is, how words get their meaning, and how the meaning of a complex expression depends on its parts. Part of this process involves the distinction betwee ...
of natural language
A natural language or ordinary language is a language that occurs naturally in a human community by a process of use, repetition, and change. It can take different forms, typically either a spoken language or a sign language. Natural languages ...
s. It is a type of constraint-based phrase structure grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in t ...
. Constraint based grammars are based around defining certain syntactic processes as ungrammatical for a given language and assuming everything not thus dismissed is grammatical within that language. Phrase structure grammars base their framework on constituency relationships, seeing the words in a sentence as ranked, with some words dominating the others. For example, in the sentence "The dog runs", "runs" is seen as dominating "dog" since it is the main focus of the sentence. This view stands in contrast to dependency grammars, which base their assumed structure on the relationship between a single word in a sentence (the sentence head) and its dependents.
Origins
GPSG was initially developed in the late 1970s byGerald Gazdar
Gerald James Michael Gazdar, FBA (born 24 February 1950) is a British linguist and computer scientist.
Education
He was educated at Heath Mount School, Bradfield College, the University of East Anglia (BA, 1970) and the University of Reading ...
. Other contributors include Ewan Klein, Ivan Sag
Ivan Andrew Sag (November 9, 1949 – September 10, 2013) was an American linguist and cognitive scientist. He did research in areas of syntax and semantics as well as work in computational linguistics.
Personal life
Born in Alliance, Ohio on No ...
, and Geoffrey Pullum
Geoffrey Keith Pullum (; born 8 March 1945) is a British and American linguist specialising in the study of English. Pullum has published over 300 articles and books on various topics in linguistics, including phonology, morphology, semantics ...
. Their book ''Generalized Phrase Structure Grammar'', published in 1985, is the main monograph on GPSG, especially as it applies to English syntax. GPSG was in part a reaction against transformational theories of syntax. In fact, the notational extensions to context-free grammars
In formal language theory, a context-free grammar (CFG) is a formal grammar whose production rules
can be applied to a nonterminal symbol regardless of its context.
In particular, in a context-free grammar, each production rule is of the for ...
(CFGs) developed in GPSG are claimed to make transformations redundant.
Goals
One of the chief goals of GPSG is to show that the syntax of natural languages can be described by CFGs (written asID/LP grammar ID/LP Grammars are a subset of Phrase structure grammar, Phrase Structure Grammars, differentiated from other formal grammars by distinguishing between immediate dominance (ID) and linear precedence (LP) constraints. Whereas traditional phrase stru ...
s), with some suitable conventions intended to make writing such grammars easier for syntacticians. Among these conventions are a sophisticated feature structure system and so-called "meta-rules", which are rules generating the productions of a context-free grammar. GPSG further augments syntactic descriptions with semantic annotations that can be used to compute the compositional meaning of a sentence from its syntactic derivation tree. However, it has been argued (for example by Robert Berwick) that these extensions require parsing
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a String (computer science), string of Symbol (formal), symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal gramm ...
algorithms of a higher order of computational complexity
In computer science, the computational complexity or simply complexity of an algorithm is the amount of resources required to run it. Particular focus is given to computation time (generally measured by the number of needed elementary operations ...
than those used for basic CFGs.
Methodology
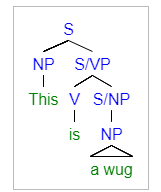
There are several ways to represent a sentence in Generalized Phrase Structure Grammar. One such method is aSyntax tree Syntax tree may refer to:
* Abstract syntax tree, used in computer science
* Concrete syntax tree, used in linguistics
{{Disambig ...
, which represents all of the words in a sentence as leaf nodes in a parsing tree, as can be seen in the provided image. However, there are several other ways of representing sentences in GPSG. Certain constituents can be illustrated without drawing a full tree by placing the constituent in question inside of brackets like so:
 Who did you say that Hilary was fond of and eslie despised .
Who did you say that Hilary was fond of and eslie despised .
Counterarguments
Evidence soon emerged, however, that CFGs could not describe all of natural language (with examples in particular from Dutch and Swiss Germancross-serial dependencies
In linguistics, cross-serial dependencies (also called crossing dependencies by some authors.) occur when the lines representing the dependency relations between two series of words cross over each other.. They are of particular interest to ling ...
), and Gazdar, along with most other syntacticians, accepted that natural languages cannot in fact be adequately described by CFGs. As a result, Generalized Phrase Structure Grammar was soon abandoned as a framework for describing natural languages, although CFGs are still used in computing languages. Most of the syntactic innovations of GPSG were subsequently incorporated into head-driven phrase structure grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar
developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor t ...
.
See also
*Lexical functional grammar
Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, an ...
*Phrase structure grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in t ...
* Transformational grammar
In linguistics, transformational grammar (TG) or transformational-generative grammar (TGG) was the earliest model of grammar proposed within the research tradition of generative grammar. Like current generative theories, it treated grammar as a sys ...
*Head-driven phrase structure grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar
developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor t ...
References
{{ReflistExternal links
Gerald Gazdar's profile on the University of Sussex Website
Generative linguistics Grammar frameworks Syntactic theories Semantic theories