Full-mold Casting on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Full-mold casting is an evaporative-pattern casting process which is a combination of 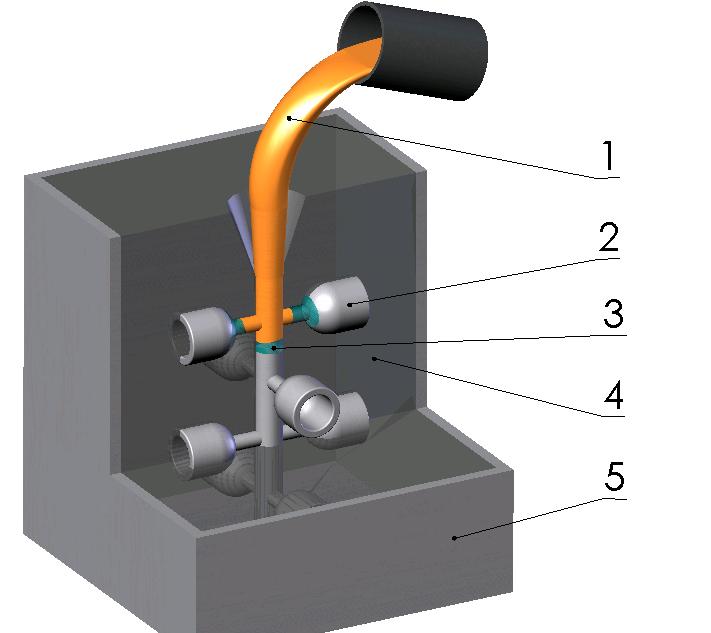
sand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand—known as ''casting sand''—as the mold material. The term "sand casting" can also refer to an object produced via the sand casting proces ...
and lost-foam casting. It uses an expanded polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
foam pattern
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated l ...
which is then surrounded by sand, much like sand casting. The metal is then poured directly into the mold, which vaporizes the foam upon contact.

Process
First, a pattern is usually made frompolystyrene foam
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is a ...
, which can be done many different ways. For small volume runs the pattern can be hand cut or machined from a solid block of foam; if the geometry is simple enough it can even be cut using a hot-wire foam cutter.
If the volume is large, then the pattern can be mass-produced by a process similar to injection molding
Injection moulding (U.S. spelling: injection molding) is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould, or mold. Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals (for ...
. Pre-expanded beads of polystyrene are injected into a preheated aluminum mold
A mold () or mould () is one of the structures that certain fungus, fungi can form. The dust-like, colored appearance of molds is due to the formation of Spore#Fungi, spores containing Secondary metabolite#Fungal secondary metabolites, fungal ...
at low pressure. Steam
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is inv ...
is then applied to the polystyrene which causes it to expand more to fill the die. The final pattern is approximately 97.5% air and 2.5% polystyrene.
The finished patterns can be hot glued to pre-made pouring basins, runners, and risers to form the final pattern.. The pattern is then coated with a refractory material. The coated pattern (2) is placed in a flask and packed carefully with green sand (4) or a chemically bonded sand.
Finally, the molten metal (1) is poured into the mold, which vaporizes the foam (3) allowing the metal to fill the entire mold. The vapor is simultaneously extracted from the flask through the sand.
The casting is allowed to cool and then dumped out of the flask (5) ready to use. The sand does not need to be reprocessed so it can be directly reused..
Details
The minimum wall thickness for a full-mold casting is . Typical dimensional tolerances are 0.3% and typical surface finishes are from 2.5 to 25 μm (100 to 1000 millionths of an inch) RMS. The size range is from to several tonnes (tons).. Full-mold casting is often used to producecylinder head
In a piston engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders, forming the roof of the combustion chamber. In sidevalve engines the head is a simple plate of metal containing the spark plugs and possibly heat dissipation fins. In more modern ...
s, engine block
In an internal combustion engine, the engine block is the structure that contains the cylinders and other components. The engine block in an early automotive engine consisted of just the cylinder block, to which a separate crankcase was attach ...
s, pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
housings, automotive brake
A brake is a machine, mechanical device that inhibits motion by absorbing energy from a moving system. It is used for Acceleration, slowing or stopping a moving vehicle, wheel, axle, or to prevent its motion, most often accomplished by means of ...
components, and manifold
In mathematics, a manifold is a topological space that locally resembles Euclidean space near each point. More precisely, an n-dimensional manifold, or ''n-manifold'' for short, is a topological space with the property that each point has a N ...
s. Commonly employed materials include aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
, steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength a ...
, nickel alloys, and copper alloy
Copper alloys are metal alloys that have copper as their principal component. They have high resistance against corrosion. Of the large number of different types, the best known traditional types are bronze, where tin is a significant addition, ...
s.
Advantages and disadvantages
This casting process is advantageous for very complex castings, that would regularly require cores. It is also dimensionally accurate, requires nodraft
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to:
Watercraft dimensions
* Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel
* Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail
* Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a v ...
, and has no parting lines so no flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* The Flash, several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Barry Allen
** Wally West, the first Kid Flash and third adult Flash ...
is formed. As compared to investment casting
Investment casting is an industrial process based on lost-wax casting, one of the oldest known metal-forming techniques. The term "lost-wax casting" can also refer to modern investment casting processes.
Investment casting has been used in vari ...
, it is cheaper because it is a simpler process and the foam is cheaper than the wax. Risers are not usually required due to the nature of the process; because the molten metal vaporizes the foam the first metal into the mold cools more quickly than the rest, which results in natural directional solidification.
The two main disadvantages are that pattern costs can be high for low volume applications and the patterns are easily damaged or distorted due to their low strength. If a die is used to create the patterns there is a large initial cost.
History
The first patent for an evaporative-pattern casting process was filed in April 1956, by H.F. Shroyer. He patented the use of foam patterns embedded in traditional green sand for metal casting.References
Notes
Bibliography
*. *. {{Metalworking navbox, castopen Casting (manufacturing)