French Horns on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The French horn (since the 1930s known simply as the horn in professional music circles) is a
 As the name indicates, humans originally used to blow on the actual
As the name indicates, humans originally used to blow on the actual
 Despite the introduction of valves, the single F horn proved difficult for use in the highest range, where the partials grew closer and closer, making accuracy a great challenge. An early solution was simply to use a horn of higher pitch—usually B. The use of the F versus the B horn was extensively debated among horn players of the late 19th century, until the German horn maker Eduard Kruspe (namesake of his family's brass instrument firm) produced a prototype of the "double horn" in 1897.
The double horn also combines two instruments into a single frame: the original horn in F, and a second, higher horn keyed in B. By using a fourth valve (usually operated by the thumb), the horn player can quickly switch from the deep, warm tones of the F horn to the higher, brighter tones of the B horn, or vice versa, as the horn player may choose to have the horn set into B by default by making a simple adjustment to the valves. The two sets of tones are commonly called "sides" of the horn. Using the fourth valve not only changes the basic length (and thus the harmonic series and pitch) of the instrument, it also causes the three main valves to use proportionate slide lengths.
In the US, the two most common styles ("wraps") of double horns are named Kruspe and Geyer/Knopf, after the first instrument makers who developed and standardized them. The Kruspe wrap locates the B change valve above the first valve, near the thumb. The Geyer wrap has the change valve behind the third valve, near the little finger (although the valve's trigger is still played with the thumb). In effect, the air flows in a completely different direction on the other model. Kruspe wrap horns tend to be larger in the bell throat than the Geyer wrap horns. Traditionally, Kruspe models are constructed from
Despite the introduction of valves, the single F horn proved difficult for use in the highest range, where the partials grew closer and closer, making accuracy a great challenge. An early solution was simply to use a horn of higher pitch—usually B. The use of the F versus the B horn was extensively debated among horn players of the late 19th century, until the German horn maker Eduard Kruspe (namesake of his family's brass instrument firm) produced a prototype of the "double horn" in 1897.
The double horn also combines two instruments into a single frame: the original horn in F, and a second, higher horn keyed in B. By using a fourth valve (usually operated by the thumb), the horn player can quickly switch from the deep, warm tones of the F horn to the higher, brighter tones of the B horn, or vice versa, as the horn player may choose to have the horn set into B by default by making a simple adjustment to the valves. The two sets of tones are commonly called "sides" of the horn. Using the fourth valve not only changes the basic length (and thus the harmonic series and pitch) of the instrument, it also causes the three main valves to use proportionate slide lengths.
In the US, the two most common styles ("wraps") of double horns are named Kruspe and Geyer/Knopf, after the first instrument makers who developed and standardized them. The Kruspe wrap locates the B change valve above the first valve, near the thumb. The Geyer wrap has the change valve behind the third valve, near the little finger (although the valve's trigger is still played with the thumb). In effect, the air flows in a completely different direction on the other model. Kruspe wrap horns tend to be larger in the bell throat than the Geyer wrap horns. Traditionally, Kruspe models are constructed from
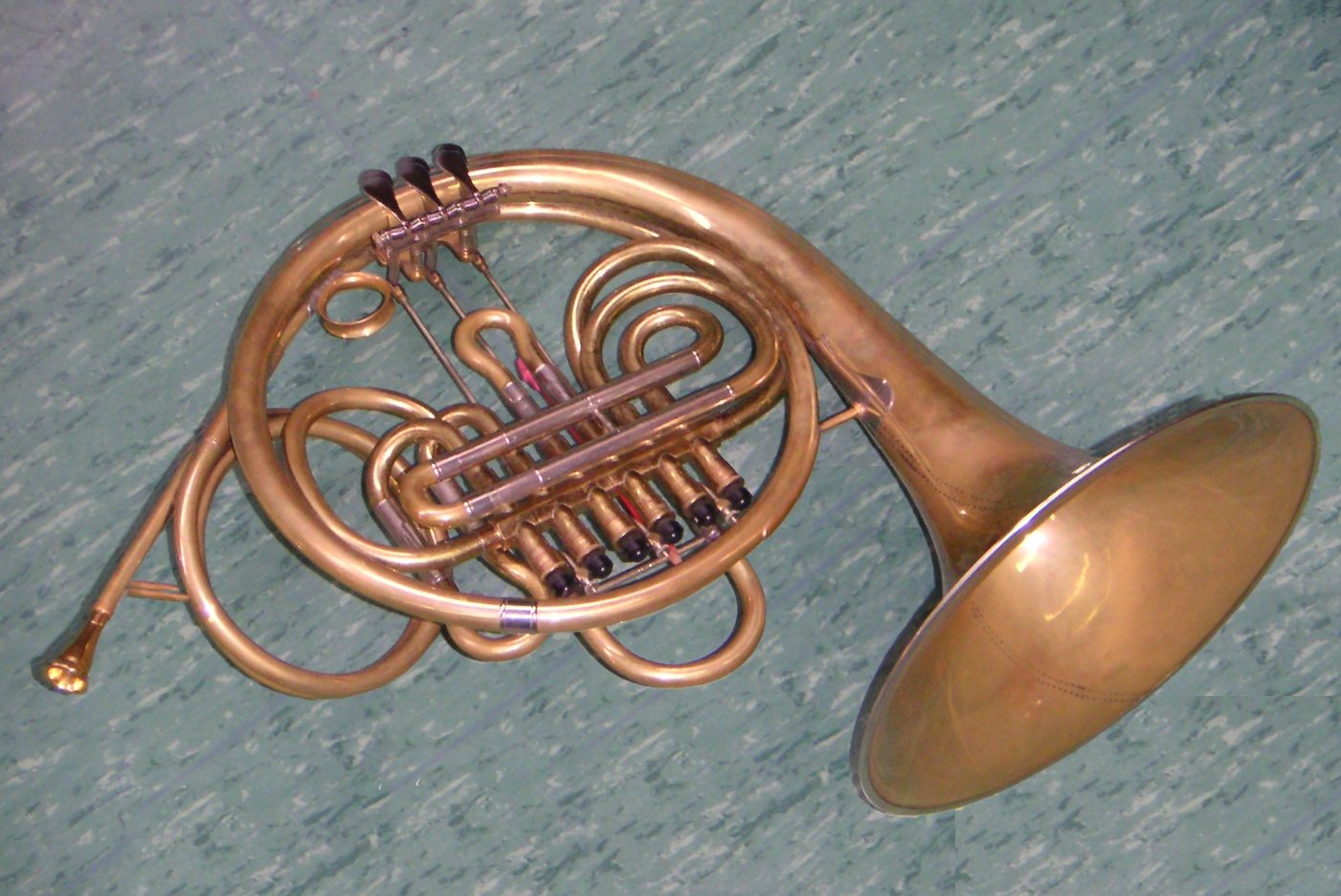 The
The
 Discussion of the repertoire of horns must recognize the different needs of orchestras and concert bands in contrast to marching bands, as above, but also the use of horns in a wide variety of music, including chamber music and jazz.
Discussion of the repertoire of horns must recognize the different needs of orchestras and concert bands in contrast to marching bands, as above, but also the use of horns in a wide variety of music, including chamber music and jazz.
File:French horn.jpg, A modern full double horn
File:Viennese horn.jpg, A
Homepage of the International Horn Society
one of the largest organizations of horn players in the world.
British Horn Society
UK-based organisation for horn playing
First steps of making a horn by hand
(QuickTime Movie) at Finke Horns
by musicologist Edmund A. Bowles
at Paxman, compiled with the assistance of Simon de Souza
How to dismantle a valve
at Finke Horns
Horn Etudes
- List of horn etudes {{DEFAULTSORT:French horn Concert band instruments F instruments German musical instruments Horns Orchestral instruments Jazz instruments
brass instrument
A brass instrument is a musical instrument that produces sound by Sympathetic resonance, sympathetic vibration of air in a tubular resonator in sympathy with the vibration of the player's lips. The term ''labrosone'', from Latin elements meani ...
made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell. The double horn in F/B (technically a variety of German horn
The German horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell, and in bands and orchestras is the most widely used of three types of horn, the other two being the French horn (in the less common, narrower meaning ...
) is the horn most often used by players in professional orchestras and bands, although the descant and triple horn have become increasingly popular. A musician who plays a horn is known as a horn player
This list of horn players and pedagogues includes notable players of French horn, German horn, natural horn, Vienna horn, tenor (alto) horn, and alphorn.
B
* Radek Baborák, born 1976, former Principal horn Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra, Mu ...
or hornist.
Pitch is controlled through the combination of the following factors: speed of air through the instrument (controlled by the player's lungs and thoracic diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles ...
); diameter and tension of lip aperture (by the player's lip muscles—the embouchure
Embouchure () or lipping is the use of the lips, facial muscles, tongue, and teeth in playing a wind instrument. This includes shaping the lips to the mouthpiece (woodwind), mouthpiece of a woodwind or brass instrument. The word is of French lan ...
) in the mouthpiece; plus, in a modern horn, the operation of valves
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fittings, ...
by the left hand, which route the air into extra sections of tubing. Most horns have lever-operated rotary valve
A rotary valve (also called rotary-motion valve) is a type of valve in which the rotation of a passage or passages in a transverse plug regulates the flow of liquid or gas through the attached pipes. The common stopcock is the simplest form of ro ...
s, but some, especially older horns, use piston valve
A piston valve is a device used to control the motion of a fluid or gas along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder.
Examples of piston valves are:
* The valves used in many brass instruments
* ...
s (similar to a trumpet
The trumpet is a brass instrument commonly used in classical and jazz musical ensemble, ensembles. The trumpet group ranges from the piccolo trumpet—with the highest Register (music), register in the brass family—to the bass trumpet, pitche ...
's) and the Vienna horn
The Vienna horn () is a type of musical horn used primarily in Vienna, Austria, for playing orchestral or classical music. It is used throughout Vienna, including the Vienna Philharmonic and ''Wiener Staatsoper''.
History
During the nineteenth ...
uses double-piston valves, or pumpenvalves. The backward-facing orientation of the bell relates to the perceived desirability to create a subdued sound in concert situations, in contrast to the more piercing quality of the trumpet. A horn without valves is known as a natural horn, changing pitch along the natural harmonics
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harm ...
of the instrument (similar to a bugle
The bugle is a simple signaling brass instrument with a wide conical bore. It normally has no valves or other pitch-altering devices, and is thus limited to its natural harmonic notes, and pitch is controlled entirely by varying the air a ...
). Pitch may also be controlled by the position of the hand in the bell, in effect reducing the bell's diameter. The pitch of any note can easily be raised or lowered by adjusting the hand position in the bell. The key of a natural horn can be changed by adding different crook
Crook is slang for criminal.
Crook or Crooks may also refer to:
Places Canada
* Crooks Inlet, former name of Kangiqturjuaq, Nunavut
England
* Crook, County Durham, a town
* Crook, Cumbria, a village and civil parish
* Crook Hill, Derby ...
s of different lengths.
Three valves control the flow of air in the ''single horn'', which is tuned to F or less commonly B. The more common ''double horn'' has a fourth, trigger valve, usually operated by the thumb, which routes the air to one set of tubing tuned to F or another tuned to B which expands the horn range to over four octaves
In music, an octave (: eighth) or perfect octave (sometimes called the diapason) is an interval between two notes, one having twice the frequency of vibration of the other. The octave relationship is a natural phenomenon that has been referr ...
and blends with flutes or clarinet
The clarinet is a Single-reed instrument, single-reed musical instrument in the woodwind family, with a nearly cylindrical bore (wind instruments), bore and a flared bell.
Clarinets comprise a Family (musical instruments), family of instrume ...
s in a woodwind ensemble
A wind quintet, also known as a woodwind quintet, is a group of five wind players (most commonly flute, oboe, clarinet, French horn and bassoon).
Unlike the string quartet (of 4 string instruments) with its homogeneous blend of sound color, the i ...
. Triple horns with five valves are also made, usually tuned in F, B, and a descant
A descant, discant, or is any of several different things in music, depending on the period in question; etymologically, the word means a voice (''cantus'') above or removed from others. The ''Harvard Dictionary of Music'' states:
A descant ...
E or F. There are also double horns with five valves tuned in B, descant E or F, and a stopping valve, which greatly simplifies the complicated and difficult hand-stopping technique, though these are rarer. Also common are ''descant'' doubles, which typically provide B and alto F branches.
A crucial element in playing the horn deals with the mouthpiece. The mouthpiece is usually placed about 2/3 on the lips with more on the upper. Because of differences in the formation of the lips and teeth of different players, some tend to play with the mouthpiece slightly off center. Although the exact side-to-side placement of the mouthpiece varies for most horn players, the up-and-down placement of the mouthpiece is generally two-thirds on the upper lip and one-third on the lower lip. When playing higher notes, the majority of players exert a small degree of additional pressure on the lips using the mouthpiece. However, this is undesirable from the perspective of both endurance and tone: excessive mouthpiece pressure makes the horn sound forced and harsh and decreases the player's stamina due to the resulting constricted flow of blood to the lips and lip muscles. Added pressure from the lips to the mouthpiece can also result in tension in the face resulting in what brass players often call "pushing". As mentioned before, this results in an undesirable sound, and loss of stamina.
Name
The name "French horn" first came into use in the late 17th century. At that time, French makers were preeminent in the manufacture of hunting horns and were credited with creating the now-familiar, circular "hoop" shape of the instrument. As a result, these instruments were often called, even in English, by their French names: ''trompe de chasse'' or ''cor de chasse'' (—the clear modern distinction between ''trompes'' rumpetsand ''cors'' ornsdid not exist at that time). German makers first devised ''crooks'' to make such horns playable in different keys—so musicians came to use "French" and "German" to distinguish the simple hunting horn from the newer horn with crooks, which in England was also called the Italian name ''corno cromatico'' (chromatic horn). More recently, "French horn" is often used colloquially, though the adjective has normally been avoided when referring to the European orchestral horn, ever since the German horn began replacing the French-style instrument in British orchestras around 1930. TheInternational Horn Society
The International Horn Society (IHS) is an international organization dedicated to players of the horn founded in June 1970. Its goal is to promote horn playing, education and fellowship. The society aims to bring together horn players, educators, ...
has recommended since 1971 that the instrument be simply called the ''horn''.
There is also a more specific use of "French horn" to describe a particular horn type, differentiated from the German horn
The German horn is a brass instrument made of tubing wrapped into a coil with a flared bell, and in bands and orchestras is the most widely used of three types of horn, the other two being the French horn (in the less common, narrower meaning ...
and Vienna horn
The Vienna horn () is a type of musical horn used primarily in Vienna, Austria, for playing orchestral or classical music. It is used throughout Vienna, including the Vienna Philharmonic and ''Wiener Staatsoper''.
History
During the nineteenth ...
. In this sense, "French horn" refers to a narrow-bore instrument () with three Périnet (piston) valves. It retains the narrow bell-throat and mouthpipe crooks of the orchestral hand horn of the late 18th century, and most often has an "ascending" third valve. This is a whole-tone valve arranged so that with the valve in the "up" position the valve loop is engaged, but when the valve is pressed the loop is cut out, raising the pitch by a whole tone.
History
 As the name indicates, humans originally used to blow on the actual
As the name indicates, humans originally used to blow on the actual horn
Horn may refer to:
Common uses
* Horn (acoustic), a tapered sound guide
** Horn antenna
** Horn loudspeaker
** Vehicle horn
** Train horn
*Horn (anatomy), a pointed, bony projection on the head of various animals
* Horn (instrument), a family ...
s of animals before starting to emulate naturally occurring horns with metal ones. The use of animal horns survives with the shofar
A shofar ( ; from , ) is an ancient musical horn, typically a ram's horn, used for Jewish ritual purposes. Like the modern bugle, the shofar lacks pitch-altering devices, with all pitch control done by varying the player's embouchure. The ...
, a ram's horn, which plays an important role in Jewish religious rituals.
Early metal horns were less complex than modern horns, consisting of valveless brass tubes, wound around a few times, with a slightly flared opening (the bell). These early "hunting" horns (French: ) were originally played on a hunt
Hunting is the Human activity, human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, and killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to obtain the animal's body for meat and useful animal products (fur/hide (sk ...
, often while mounted, and the sound they produced was called a . Change of pitch on these hunting horns was controlled entirely by the lips, as the use of valves and insertion of a hand in the bell to change pitch were later innovations. Without valves, only the notes within the harmonic series are available. By combining a long length with a narrow bore, the French horn's design allows the player to easily reach the higher overtones which differ by whole tones or less, thus making it capable of playing melodies before valves were invented.
Early horns were commonly pitched in B alto, A, A, G, F, E, E, D, C, and B basso. Since the only notes available were those on the harmonic series of one of those pitches, horn-players had no ability to play in different keys. The remedy for this limitation was the use of crooks, i.e., sections of tubing of differing length that, when inserted, altered the length of the instrument, and thus its pitch.
In the mid-18th century, horn players began to insert the right hand into the bell to change the length of the instrument, adjusting the tuning up to the distance between two adjacent harmonics depending on how much of the opening was covered.
In 1818 the German makers Heinrich Stölzel
Heinrich David Stölzel (7 September 1777 – 16 February 1844) was a German horn player who developed some of the first valves for brass instruments. He developed the first valve for a brass musical instrument, the Stölzel valve, in 1818, a ...
and Friedrich Blümel patented the first valved horn, using rotary valves. François Périnet introduced piston valves in France about 1839. The use of valves initially aimed to overcome problems associated with changing crooks during a performance. Valves' unreliability, musical taste, and players' distrust, among other reasons, slowed their adoption into the mainstream. Many traditional conservatories and players refused to use them at first, claiming that the valveless horn, or ''natural horn'', was a better instrument. Some musicians who specialize in period instruments use a natural horn to play in original performance styles, to try to recapture the sound of an older piece's original performances.
The use of valves, however, opened up a great deal more flexibility for playing in different keys; in effect, the horn became an entirely different instrument, fully chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are used to characterize scales. The terms are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, es ...
for the first time. Valves were originally used primarily as a means to play in different keys without crooks, not for harmonic playing. That is reflected in compositions for horns, which only began to include chromatic passages in the late-19th century. There were many different versions of early valves, most being variants of the piston and rotary systems used in modern horns. Early valves by Blühmel are cited as possibly the first rotary valve, but the first confirmed rotary valve design was in 1832 by Joseph Riedl in Vienna.
Types
Horns may be classified into single horn, double horn, compensating double horn, and triple horn as well as having the option of detachable bells.Single horn
Single horns use a single set of tubes connected to the valves. This allows for simplicity of use and a much lighter weight. They are usually in the keys of F or B, although many F horns have longer slides to tune them to E, and almost all B horns have a valve to put them in the key of A. The problem with single horns is the inevitable choice between accuracy or tone – while the F horn has the "typical" horn sound, above third-space C accuracy is a concern for the majority of players because, by its nature, one plays high in the horn's harmonic series where the overtones are closer together. This led to the development of the B horn, which, although easier to play accurately, has a less desirable sound in the mid and especially the low register where it is not able to play all of the notes. The solution has been the development of the double horn, which combines the two into one horn with a single lead pipe and bell. Both main types of single horns are still used today as student models because they are cheaper and lighter than double horns. In addition, the single B horns are sometimes used in solo and chamber performances and the single F survives orchestrally as the Vienna horn. Additionally, single F alto and B alto descants are used in the performance of some baroque horn concertos and F, B and F alto singles are occasionally used byjazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
performers.
Dennis Brain
Dennis Brain (17 May 19211 September 1957) was a British French horn, horn player. From a musical family – his father and grandfather were horn players – he attended the Royal Academy of Music in London. During the Second World War he served ...
's benchmark recordings of the Mozart Horn Concerti were made on a single B instrument by Gebr. Alexander
Gebrüder Alexander (Brothers Alexander), of Mainz, Germany, is a manufacturer of instruments, founded in 1782 by Franz Ambros Alexander and still in business today. The company claims to be the oldest musical instrument manufacturing company in ...
, now on display at the Royal Academy of Music
The Royal Academy of Music (RAM) in London, England, is one of the oldest music schools in the UK, founded in 1822 by John Fane and Nicolas-Charles Bochsa. It received its royal charter in 1830 from King George IV with the support of the firs ...
in London.
Double horn
 Despite the introduction of valves, the single F horn proved difficult for use in the highest range, where the partials grew closer and closer, making accuracy a great challenge. An early solution was simply to use a horn of higher pitch—usually B. The use of the F versus the B horn was extensively debated among horn players of the late 19th century, until the German horn maker Eduard Kruspe (namesake of his family's brass instrument firm) produced a prototype of the "double horn" in 1897.
The double horn also combines two instruments into a single frame: the original horn in F, and a second, higher horn keyed in B. By using a fourth valve (usually operated by the thumb), the horn player can quickly switch from the deep, warm tones of the F horn to the higher, brighter tones of the B horn, or vice versa, as the horn player may choose to have the horn set into B by default by making a simple adjustment to the valves. The two sets of tones are commonly called "sides" of the horn. Using the fourth valve not only changes the basic length (and thus the harmonic series and pitch) of the instrument, it also causes the three main valves to use proportionate slide lengths.
In the US, the two most common styles ("wraps") of double horns are named Kruspe and Geyer/Knopf, after the first instrument makers who developed and standardized them. The Kruspe wrap locates the B change valve above the first valve, near the thumb. The Geyer wrap has the change valve behind the third valve, near the little finger (although the valve's trigger is still played with the thumb). In effect, the air flows in a completely different direction on the other model. Kruspe wrap horns tend to be larger in the bell throat than the Geyer wrap horns. Traditionally, Kruspe models are constructed from
Despite the introduction of valves, the single F horn proved difficult for use in the highest range, where the partials grew closer and closer, making accuracy a great challenge. An early solution was simply to use a horn of higher pitch—usually B. The use of the F versus the B horn was extensively debated among horn players of the late 19th century, until the German horn maker Eduard Kruspe (namesake of his family's brass instrument firm) produced a prototype of the "double horn" in 1897.
The double horn also combines two instruments into a single frame: the original horn in F, and a second, higher horn keyed in B. By using a fourth valve (usually operated by the thumb), the horn player can quickly switch from the deep, warm tones of the F horn to the higher, brighter tones of the B horn, or vice versa, as the horn player may choose to have the horn set into B by default by making a simple adjustment to the valves. The two sets of tones are commonly called "sides" of the horn. Using the fourth valve not only changes the basic length (and thus the harmonic series and pitch) of the instrument, it also causes the three main valves to use proportionate slide lengths.
In the US, the two most common styles ("wraps") of double horns are named Kruspe and Geyer/Knopf, after the first instrument makers who developed and standardized them. The Kruspe wrap locates the B change valve above the first valve, near the thumb. The Geyer wrap has the change valve behind the third valve, near the little finger (although the valve's trigger is still played with the thumb). In effect, the air flows in a completely different direction on the other model. Kruspe wrap horns tend to be larger in the bell throat than the Geyer wrap horns. Traditionally, Kruspe models are constructed from nickel silver
Nickel silver, maillechort, German silver, argentan, new silver, nickel brass, albata, or alpacca is a cupronickel (copper with nickel) alloy with the addition of zinc. The usual formulation is 60% copper, 20% nickel and 20% zinc. Nickel silver ...
(also called German silver, an alloy of copper, nickel and zinc, containing no actual silver) while Geyer horns tend to be of yellow brass; although these differences in finish aren't as prevalent today - horns of both finishes can be found in either wrap. Both models have their own strengths and weaknesses, and while the choice of instrument is very personal, an orchestral horn section is usually found to have either one or the other, owing to the differences in tone color, response, and projection of the two different styles.
In Europe the most popular horns are arguably those made by Gebr. Alexander, of Mainz (particularly the Alexander 103), and those made by Paxman in London. In Germany and the Benelux
The Benelux Union (; ; ; ) or Benelux is a politico-economic union, alliance and formal international intergovernmental cooperation of three neighbouring states in Western Europe: Belgium, the Netherlands, and Luxembourg. The name is a portma ...
countries, the Alex 103 is extremely popular. These horns do not fit strictly into the Kruspe or Knopf camps, but have features of both. Alexander prefers the traditional medium bell size, which they have produced for many years, whereas Paxman do offer their models in a range of bell throat sizes. In the United States, the Conn 8D, a mass-produced instrument based on the Kruspe design, has been extremely popular in many areas (New York, Los Angeles, Cleveland, Philadelphia). Since roughly the early 1990s, however, for reasons ranging from changing tastes to a general dislike of Conn's newer 8Ds, orchestras have been moving away from the popular Conn 8D. Geyer model horns (by Carl Geyer, Karl Hill, Keith Berg, Steve Lewis, Jerry Lechniuk, Dan Rauch, and Ricco-Kuhn) are used in other areas (San Francisco, Chicago, Pittsburgh, Boston, Houston). The CF Schmidt double, with its unique piston change valve, is occasionally found in sections playing Geyer/Knopf model equipment.
Compensating double horn
A full double horn has two full-length sets of slides (one set for the B side and a longer set for the F side); a compensating double horn only has full-length slides for the B side and a shorter set of slides whose length can be added to the B slides to give the necessary tubing length for playing in F. As for the full double horn, the air is routed through the appropriate slide(s) by use of the fourth valve. Compensating double horns are lighter than full double horns because of this design.Triple horn
A triple horn has more tubing, adding a descant horn to the double horn and hence giving more assistance for the high range. The descant horn is most commonly in F, sounding an octave higher than the normal F horn.Detachable bell
The horn, although not large, is awkward in its shape and does not lend itself well to transport where space is shared or limited, especially on planes. To compensate, horn makers can make the bell detachable; this allows for smaller and more manageable horn cases.Related horns
The variety in horn history necessitates consideration of the natural horn, Vienna horn, mellophone, marching horn, and Wagner tuba.Natural horn
Thenatural horn
The natural horn is a musical instrument that is the predecessor to the modern-day (French) horn (differentiated by its lack of valves). Throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the natural horn evolved as a separation from the tr ...
is the ancestor of the modern horn. It is essentially descended from hunting horns, with its pitch controlled by air speed, aperture (opening of the lips through which air passes) and the use of the right hand moving around, as well as in and out of the bell. Although a few recent composers have written specifically for the natural horn (e.g., György Ligeti
György Sándor Ligeti (; ; 28 May 1923 – 12 June 2006) was a Hungarian-Austrian composer of contemporary classical music. He has been described as "one of the most important avant-garde music, avant-garde composers in the latter half of the ...
's ''Hamburg Concerto
''Hamburg Concerto'' (') for solo French horn, horn and chamber orchestra with four obbligato natural horns is one of György Ligeti's last works, composed in 1998–99 and revised in 2003.
The work was commissioned by the ZEIT-Stiftung, ZEIT-Fo ...
'' and sections of Paul Dukas
Paul Abraham Dukas ( 1 October 1865 – 17 May 1935) was a French composer, critic, scholar and teacher. A studious man of retiring personality, he was intensely self-critical, having abandoned and destroyed many of his compositions. His best-k ...
' ''Villanelle
A villanelle, also known as villanesque,Kastner 1903 p. 279 is a nineteen-line poetic form consisting of five tercets followed by a quatrain. There are two refrains and two repeating rhymes, with the first and third lines of the first tercet re ...
for Horn and Piano''), today it is played primarily as a period instrument
In the historically informed performance movement, musicians perform classical music using restored or replicated versions of the instruments for which it was originally written. Often performances by such musicians are said to be "on authentic ...
. The natural horn can only play from a single harmonic series at a time because there is only one length of tubing available to the horn player. A proficient player can indeed alter the pitch by partially or fully muting the bell with the right hand, thus enabling the player to reach some notes that are not part of the instrument's natural harmonic series – of course this technique also affects the quality of the tone. The player has a choice of key by using crooks to change the length of tubing.
Vienna horn
 The
The Vienna horn
The Vienna horn () is a type of musical horn used primarily in Vienna, Austria, for playing orchestral or classical music. It is used throughout Vienna, including the Vienna Philharmonic and ''Wiener Staatsoper''.
History
During the nineteenth ...
is a special horn used primarily in Vienna
Vienna ( ; ; ) is the capital city, capital, List of largest cities in Austria, most populous city, and one of Federal states of Austria, nine federal states of Austria. It is Austria's primate city, with just over two million inhabitants. ...
, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
. Instead of using rotary valve
A rotary valve (also called rotary-motion valve) is a type of valve in which the rotation of a passage or passages in a transverse plug regulates the flow of liquid or gas through the attached pipes. The common stopcock is the simplest form of ro ...
s or piston valve
A piston valve is a device used to control the motion of a fluid or gas along a tube or pipe by means of the linear motion of a piston within a chamber or cylinder.
Examples of piston valves are:
* The valves used in many brass instruments
* ...
s, it uses the pumpenvalve (or Vienna valve), which is a double-piston operating inside the valve slides, and usually situated on the opposite side of the corpus from the player's left hand, and operated by a long pushrod. Unlike the modern horn, which has grown considerably larger internally (for a bigger, broader, and louder tone), and considerably heavier (with the addition of valves and tubing in the case of the double horn) the Vienna horn very closely mimics the size and weight of the natural horn, (although the valves do add some weight, they are lighter than rotary valves) even using crooks in the front of the horn, between the mouthpiece and the instrument. Although instead of the full range of keys, Vienna horn players usually use an F crook and it is looked down upon to use others, though switching to an A or B crook for higher pitched music does happen on occasion. Vienna horns are often used with funnel shaped mouthpieces similar to those used on the natural horn, with very little (if any) backbore and a very thin rim. The Viennese horn requires very specialized technique and can be quite challenging to play, even for accomplished players of modern horns. The Vienna horn has a warmer, softer sound than the modern horn. Its pumpenvalves facilitate a continuous transition between notes (glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a wikt:glide, glide from one pitch (music), pitch to another (). It is an Italianized Musical terminology, musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In ...
); conversely, a more precise operating of the valves is required to avoid notes that sound out of tune.
Mellophone
Two instruments are called a ''mellophone''. The first is an instrument shaped somewhat like a horn, in that it is formed in a circle and is often referred to as a "classic" or "concert" mellophone. It has piston valves and is played with the right hand on the valves. Most are pitched in the key of F, with facility to switch to E, either by changing crooks/leadpipes, or by a valve dedicated to this purpose. Older examples often included the ability to be played in the keys of D and/or C as well. Manufacturing of this instrument sharply decreased in the middle of the 20th century, and this mellophone (or mellophonium) rarely appears today. The second instrument is used in modern brass bands and marching bands, and is more accurately called a "marching mellophone". A derivative of the Falto horn
The Tenor horn (British English; Alto horn in American English, Althorn in Germany; occasionally referred to as E horn) is a brass instrument in the saxhorn family and is usually pitched in E. It has a bore that is mostly conical, like the flu ...
, it is keyed in F. It is shaped like a flugelhorn, with piston valves played with the right hand and a forward-pointing bell. These horns are generally considered better marching instrument
A marching band is a group of instrumental musicians who play while marching. Historically they were used in armed forces and many marching bands remain military bands. Others are still associated with military units or emulate a military style ...
s than regular horns because their position is more stable on the mouth, they project better, and they weigh less. It is primarily used as the middle voice of drum and bugle corps Drum and bugle corps is a name used to describe several related musical ensembles.
* Drum and bugle corps (modern), a musical marching unit
* Drum and bugle corps (classic), musical ensembles that descended from military bugle and drum units retur ...
. Though they are usually played with a V-cup cornet-like mouthpiece, their range overlaps the common playing range of the horn. This mouthpiece switch makes the mellophone louder, less mellow, and more brassy and brilliant, making it more appropriate for marching bands. Often now with the use of converters, traditional conical horn mouthpieces are used to achieve the more mellow sound of a horn to make the marching band sound more like a concert band.
As they are pitched in F or G and their range overlaps that of the horn, mellophones can be used in place of the horn in brass and marching band settings. Mellophones are, however, sometimes unpopular with horn players because the mouthpiece change can be difficult and requires a different embouchure
Embouchure () or lipping is the use of the lips, facial muscles, tongue, and teeth in playing a wind instrument. This includes shaping the lips to the mouthpiece (woodwind), mouthpiece of a woodwind or brass instrument. The word is of French lan ...
. Mouthpiece adapters are available so that a horn mouthpiece can fit into the mellophone lead pipe (some of them are designed to where the end is bent at a 45-degree angle so that they can use the same embouchure), but this does not compensate for the many differences that a horn player must adapt to. The "feel" of the mellophone can be foreign to a horn player. Another unfamiliar aspect of the mellophone is that it is designed to be played with the right hand instead of the left (though it can be played with the left). Intonation can also be an issue with the mellophone.
While horn players may be asked to play the mellophone, it is unlikely that the instrument was ever intended as a substitute for the horn, mainly because of the fundamental differences described. As an instrument it compromises between the ability to sound like a horn, while being used like a trumpet or flugelhorn, a tradeoff that sacrifices acoustic properties for ergonomics.
Marching horn
The marching horn is quite similar to the mellophone in shape and appearance, but it is pitched in the key of B, the same as the B side of a double horn orvalve trombone
The valve trombone is a brass instrument in the trombone family that has a set of valves to vary the pitch instead of (or in addition to) a slide. Although it has been built in sizes from alto to contrabass, it is the tenor valve trombone pitched ...
(which is also the same as a bass trumpet
The bass trumpet is a type of low trumpet which was first developed during the 1820s in Germany. It is usually pitched in 8' C or 9' B today, but is sometimes built in E and is treated as a transposing instrument sounding either an octave, a sixth ...
, an octave below a normal trumpet). It is also available in F alto, one octave above the F side of a double horn (or the high F side of a triple horn). The marching horn is also played with a horn mouthpiece (unlike the mellophone, which needs an adapter to fit the horn mouthpiece). These instruments are primarily used in marching bands so that the sound comes from a forward-facing bell, as dissipation of the sound from the backward-facing bell becomes a concern in open-air environments. Many college marching bands and drum corps, however, use mellophones instead, which, with many marching bands, better balance the tone of the other brass instruments; additionally, mellophones require less special training of trumpeters, who considerably outnumber horn players. Some college marching bands use marching French horns when accompanying choirs as to not overpower their singing.
Wagner tuba
The Wagner tuba is a rare brass instrument that is essentially a horn modified to have a larger bell throat and a vertical bell. Despite its name and its somewhat tuba-shaped appearance, it is generally not considered part of thetuba
The tuba (; ) is the largest and lowest-pitched musical instrument in the brass instrument, brass family. As with all brass instruments, the sound is produced by lip vibrationa buzzinto a mouthpiece (brass), mouthpiece. It first appeared in th ...
family, because the instrument's relatively narrow bore causes it to play more like a horn. Invented for Richard Wagner
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, essayist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most o ...
specifically for his work ''Der Ring des Nibelungen
(''The Ring of the Nibelung''), WWV 86, is a cycle of four German-language epic music dramas composed by Richard Wagner. The works are based loosely on characters from Germanic heroic legend, namely Norse legendary sagas and the . The compo ...
'', it has since been written for by various other composers, including Bruckner, Stravinsky
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky ( – 6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and American citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of ...
and Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; ; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer and conductor best known for his Tone poems (Strauss), tone poems and List of operas by Richard Strauss, operas. Considered a leading composer of the late Roman ...
. It uses a horn mouthpiece and is available as a single tuba in B or F, or, more recently, as a double tuba similar to the double horn. It is usually played in a range similar to that of the euphonium
The euphonium ( ; ; ) is a tenor- and baritone-voiced valved brass instrument. The euphonium is a member of the large family of valved bugles, along with the tuba and flugelhorn, characterised by a wide conical bore. Most instruments have thr ...
, but its possible range is the same as that of the horn, extending from low F, below the bass clef staff to high C above the treble staff when read in F. The low pedal tones are substantially easier to play on the Wagner tuba than on the horn. Wagner viewed the regular horn as a woodwind rather than a brass instrument, evidenced by his placing of the horn parts in his orchestral scores in the woodwind group and not in their usual place above the trumpets in the brass section.
Repertoire
 Discussion of the repertoire of horns must recognize the different needs of orchestras and concert bands in contrast to marching bands, as above, but also the use of horns in a wide variety of music, including chamber music and jazz.
Discussion of the repertoire of horns must recognize the different needs of orchestras and concert bands in contrast to marching bands, as above, but also the use of horns in a wide variety of music, including chamber music and jazz.
Orchestra and concert band
The horn is most often used as an orchestral and concert band instrument, with its singular tone being employed by composers to achieve specific effects.Leopold Mozart
Johann Georg Leopold Mozart (November 14, 1719 – May 28, 1787) was a German composer, violinist, and music theorist. He is best known today as the father and teacher of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, and for his violin textbook ''Versuch einer grün ...
, for example, used horns to signify the hunt, as in his ''Jagdsinfonie
The ''Jagdsinfonie'' or ''Sinfonia da Caccia for 4 Horns and Strings'' is a work by Leopold Mozart in the key of G major. It is scored for corni di caccia, or hunting horns, strings, and gunshots, a naturalism not atypical of this composer. So ...
'' (hunting symphony). Telemann
Georg Philipp Telemann (; – 25 June 1767) was a German Baroque composer and multi-instrumentalist. He is one of the most prolific composers in history, at least in terms of surviving works. Telemann was considered by his contemporaries to be ...
wrote much for the horn, and it features prominently in the work of Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel ( ; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well-known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concerti.
Born in Halle, Germany, H ...
and in Bach
Johann Sebastian Bach (German: �joːhan zeˈbasti̯an baχ ( – 28 July 1750) was a German composer and musician of the late Baroque period. He is known for his prolific output across a variety of instruments and forms, including the or ...
's '' Brandenburg Concerto no. 1''. Once the technique of hand-stopping
Hand-stopping is a technique by which a natural horn or a natural trumpet can be made to produce notes outside of its normal harmonic series. By inserting the hand, cupped, into the bell, the player can reduce the pitch of a note by a semitone or ...
had been developed, allowing fully chromatic playing, composers began to write seriously for the horn. Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic music, Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and ...
made great use of the horn's uniquely haunting and distant sound in his symphonies, notably the famous ''Nachtmusik'' (serenade) section of his Symphony No. 7.
Many composers have written works that have become favorites in the horn repertoire. These include Poulenc (''Elegie'') and Saint-Saëns (''Morceau de Concert for horn and orchestra'', op. 94 and ''Romance'', op. 36). Others, particularly Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
, whose friend Joseph Leutgeb was a noted horn player, wrote extensively for the instrument, including concerti
A concerto (; plural ''concertos'', or ''concerti'' from the Italian plural) is, from the late Baroque era, mostly understood as an instrumental composition, written for one or more soloists accompanied by an orchestra or other ensemble. The ty ...
and other solo works. Mozart's ''A Musical Joke
''A Musical Joke'' () K. 522, (divertimento for two horns in F, and string quartet) is a composition by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart; he entered it in his ' (''Catalogue of All My Works'') on 14 June 1787. Commentators have opined that the pie ...
'' satirizes the limitations of contemporary horn playing, including the risk of selecting the wrong crook by mistake.
The development of the valve horn was exploited by romantic composers such as Bruckner, Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 – 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
, and Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; ; 11 June 1864 – 8 September 1949) was a German composer and conductor best known for his Tone poems (Strauss), tone poems and List of operas by Richard Strauss, operas. Considered a leading composer of the late Roman ...
, whose father was a well-known professional horn player. Strauss's ''Till Eulenspiegel's Merry Pranks
image:Geschiebemergel.JPG, Closeup of glacial till. Note that the larger grains (pebbles and gravel) in the till are completely surrounded by the matrix of finer material (silt and sand), and this characteristic, known as ''matrix support'', is d ...
'' contains one of the best known horn solos from this period, relying on the chromatic facility of the valved horn. Schumann
Robert Schumann (; ; 8 June 181029 July 1856) was a German composer, pianist, and music critic of the early Romantic music, Romantic era. He composed in all the main musical genres of the time, writing for solo piano, voice and piano, chamber ...
's ''Konzertstück'' for four horns and orchestra is a notable three-movement work. Brahms
Johannes Brahms (; ; 7 May 1833 – 3 April 1897) was a German composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor of the mid- Romantic period. His music is noted for its rhythmic vitality and freer treatment of dissonance, often set within studied ye ...
had a lifelong love-affair with the instrument, with many prominently featured parts throughout his four symphonies. Despite his use of natural horns in his work (e.g., Horns in B♮ in the second movement of his Symphony No. 2), players today typically play Brahms's music on modern valved instruments.
Chamber music
There is an abundance ofchamber music
Chamber music is a form of classical music that is composed for a small group of Musical instrument, instruments—traditionally a group that could fit in a Great chamber, palace chamber or a large room. Most broadly, it includes any art music ...
repertoire for horn. It is a standard member of the wind quintet
A wind quintet, also known as a woodwind quintet, is a group of five wind players (most commonly flute, oboe, clarinet, French horn and bassoon).
Unlike the string quartet (of 4 string instruments) with its homogeneous blend of sound color, the i ...
and brass quintet
A brass quintet is a five-piece musical ensemble composed of brass instruments. The instrumentation for a brass quintet typically includes two trumpets or cornets, one French horn, one trombone or euphonium/baritone horn, and one tuba or bass tro ...
, and often appears in other configurations, such as Brahms' Horn Trio Horn trio can mean a work written for three horns or horns as well as one for horn and two other instruments. In the latter category, an important genre is the trio for horn, violin and piano. Although there are a few earlier examples, the traditi ...
for violin, horn and piano (for which, however, Brahms specified the natural horn). Also, the horn can be used by itself in a horn ensemble or "horn choir". The horn choir is especially practical because the extended range of the horn provides the composer or arranger with more possibilities, registerally, sonically, and contrapuntally.
Orchestral and concert band horns
A classical orchestra usually has at least two French horn players. Typically, the first horn played a high part and the second horn played a low part. Composers fromBeethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. He is one of the most revered figures in the history of Western music; his works rank among the most performed of the classical music repertoire ...
(early 1800s) onwards commonly used four horns. Here, the first and second horns played as a pair (first horn being high, second horn being low), and the third and fourth horns played as another pair (third horn being high, fourth horn being low).
Music written for the modern horn follows a similar pattern with the first and third horns being high and the second and fourth horns being low. This configuration serves multiple purposes. It is easier to play high when the adjacent player is playing low and vice versa. Pairing makes it easier to write for horns, as the third and fourth horns can take over from the first and second horns or play contrasting material. For example, if the piece is in C minor, the first and second horns might be in C, the tonic major key, which could get most of the notes, and the third and fourth horns might be in E, the relative major key, to fill in the gaps.
Many orchestral horn sections in the 2010s also have an assistant who doubles the first horn part for selected passages, joining in loud parts, playing instead of the principal if there is a first horn solo approaching, or alternating with the principal if the part is tiring to play. Often the assistant is asked to play a passage after resting a long time. Also, he or she may be asked to enter in the middle of a passage, exactly matching the sound, articulation, and overall interpretation of the principal, thus enabling the principal horn to rest a bit.
In jazz
The French horn was at first rarely used injazz
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, h ...
music. (Note that colloquially in jazz, the word "horn" refers to any wind instrument.) Notable exponents, however, began including French horn in jazz pieces and ensembles. These include composer/arranger Gil Evans
Ian Ernest Gilmore Evans (né Green; May 13, 1912 – March 20, 1988) was a Canadian Americans, Canadian–American jazz pianist, Music arranger, arranger, composer and bandleader. He is widely recognized as one of the greatest orchestrators i ...
who included the French horn as an ensemble instrument from the 1940s, first in Claude Thornhill
Claude Thornhill (August 10, 1908 – July 1, 1965) was an American pianist, arranger, composer, and bandleader. He composed the jazz and pop standards "Snowfall" and "I Wish I Had You".
Early years
Thornhill was the son of J. Chester Thornhill ...
's groups, and later with the pioneering cool jazz
Cool jazz is a style of modern jazz music inspired by bebop and big band that arose in the United States after World War II. It is characterized by relaxed tempos and a lighter tone than that used in the fast and complex bebop style. Cool jazz of ...
nonet (nine-piece group) led by trumpeter Miles Davis
Miles Dewey Davis III (May 26, 1926September 28, 1991) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th century music, 20th-century music. Davis ado ...
, and in many other projects that sometimes also featured Davis, as well as Don Ellis
Donald Johnson Ellis (July 25, 1934 – December 17, 1978) was an American jazz trumpeter, drummer, composer, and bandleader. He is best known for his extensive musical experimentation, particularly in the area of time signatures. Later in his ...
, a trumpet player from Stan Kenton
Stanley Newcomb Kenton (December 15, 1911 – August 25, 1979) was an American popular music and jazz artist. As a pianist, composer, arranger and band leader, he led an innovative and influential jazz orchestra for almost four decades. Though ...
's jazz band. Notable works of Ellis' jazz French horn include "Strawberry Soup" and other songs on the album '' Tears of Joy''. Notable improvising horn players in jazz include Julius Watkins
Julius Watkins (October 10, 1921 – April 4, 1977) was an American jazz musician who played French horn. Described by AllMusic as "virtually the father of the jazz French horn", Watkins won the ''Down Beat'' critics poll in 1960 and 1961 for Mis ...
, Willie Ruff
Willie Henry Ruff Jr. (September 1, 1931 – December 24, 2023) was an American jazz musician, specializing in the French horn and double bass, and a music scholar and educator, primarily as a Yale professor from 1971 to 2017.
Personal life
Wil ...
, John Graas
John Graas (March 14, 1917 – April 13, 1962) was an American jazz French horn player, composer, and arranger from the 1940s through 1962. He had a short but busy career on the West Coast, and became known as a pioneer of the French horn in jazz ...
, David Amram
David Werner Amram III (born November 17, 1930) is an American composer, arranger, and conductor of orchestral, chamber, and choral works, many with jazz flavorings.
, John Clark, Vincent Chancey
Vincent Chancey (born February 4, 1950) is an American jazz hornist.
Early life and education
Chancey was born and raised in Chicago. He earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in music from the SIUC School of Music in 1973 and studied under Julius W ...
, Giovanni Hoffer, Arkady Shilkloper, Adam Unsworth, and Tom Varner
Tom Varner (born June 17, 1957 in Morristown, New Jersey, Morristown, New Jersey, United States) is an American jazz French horn, horn (French horn) player and composer.
Varner grew up in Millburn, New Jersey, where he started playing in the orc ...
.
Notable horn players
* Hermann Baumann – 1964 winner of the ARD International Music Competition and former principal horn in various orchestras, including theStuttgart Radio Symphony Orchestra
The Stuttgart Radio Symphony Orchestra (German: ''Radio-Sinfonieorchester Stuttgart des SWR'') was a German radio orchestra based in Stuttgart in Germany.
History
The ensemble was founded in 1945 by American occupation authorities as the orches ...
* Radek Baborák – famous Czech horn player, former principal horn in Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra
The Berlin Philharmonic () is a German orchestra based in Berlin. It is one of the most popular, acclaimed and well-respected orchestras in the world.
Throughout the 20th century, the orchestra was led by conductors Wilhelm Furtwängler (1922� ...
, 1994 winner of the ARD International Music Competition, winner of the Concertino Praga in 1988 and 1990, holder of a Grammy Award
The Grammy Awards, stylized as GRAMMY, and often referred to as The Grammys, are awards presented by The Recording Academy of the United States to recognize outstanding achievements in music. They are regarded by many as the most prestigious ...
(1995)
* Aubrey Brain – celebrated British horn player, father of Dennis Brain and a champion of the French style of instrument
*Dennis Brain
Dennis Brain (17 May 19211 September 1957) was a British French horn, horn player. From a musical family – his father and grandfather were horn players – he attended the Royal Academy of Music in London. During the Second World War he served ...
– former principal horn of the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra
The Royal Philharmonic Orchestra (RPO) is a British symphony orchestra based in London, England.
The RPO was established by Thomas Beecham in 1946. In its early days, the orchestra secured profitable recording contracts and important engagemen ...
and the Philharmonia Orchestra
The Philharmonia Orchestra is a British orchestra based in London. It was founded in 1945 by Walter Legge, a classical music record producer for EMI Classics, EMI. Among the conductors who worked with the orchestra in its early years were Rich ...
, with whom Herbert von Karajan
Herbert von Karajan (; born ''Heribert Adolf Ernst Karajan''; 5 April 1908 – 16 July 1989) was an Austrian conductor. He was principal conductor of the Berlin Philharmonic for 34 years. During the Nazi era, he debuted at the Salzburg Festival, ...
made well-known recordings of Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age ...
's horn concertos
*Alan Civil
Alan Civil OBE (13 June 1929 – 19 March 1989) was a British horn player.
Civil began to play the horn at a young age, and joined the famous Royal Artillery Band and Orchestra at Woolwich, while still in his teens. He studied the instrument u ...
– former principal horn of the Philharmonia Orchestra
The Philharmonia Orchestra is a British orchestra based in London. It was founded in 1945 by Walter Legge, a classical music record producer for EMI Classics, EMI. Among the conductors who worked with the orchestra in its early years were Rich ...
, the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra
The Royal Philharmonic Orchestra (RPO) is a British symphony orchestra based in London, England.
The RPO was established by Thomas Beecham in 1946. In its early days, the orchestra secured profitable recording contracts and important engagemen ...
, and the BBC Symphony Orchestra
The BBC Symphony Orchestra (BBC SO) is a British orchestra based in London. Founded in 1930, it was the first permanent salaried orchestra in London, and is the only one of the city's five major symphony orchestras not to be self-governing. The ...
*John Cerminaro
John Paul Cerminaro, Jr. (born April 7, 1947) is an American horn player who is best known for his principal tenures with two notable American orchestras, the New York Philharmonic and the Los Angeles Philharmonic. He was later principal horn of ...
– former principal horn of the Seattle Symphony
The Seattle Symphony is an American orchestra based in Seattle, Washington. Since 1998, the orchestra is resident at Benaroya Hall. The orchestra also serves as the accompanying orchestra for the Seattle Opera.
History
Beginnings
The orchest ...
, New York Philharmonic
The New York Philharmonic is an American symphony orchestra based in New York City. Known officially as the ''Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc.'', and globally known as the ''New York Philharmonic Orchestra'' (NYPO) or the ''New Yo ...
, and Los Angeles Philharmonic
The Los Angeles Philharmonic (LA Phil) is an American orchestra based in Los Angeles, California. The orchestra holds a regular concert season from October until June at the Walt Disney Concert Hall and a summer season at the Hollywood Bowl from ...
*Dale Clevenger
Dale Clevenger (July 2, 1940 – January 5, 2022) was an American musician who was the Principal Horn of the Chicago Symphony Orchestra from 1966 until his retirement in June, 2013.
– former principal horn of the Chicago Symphony Orchestra
The Chicago Symphony Orchestra (CSO) is an American symphony orchestra based in Chicago, Illinois. Founded by Theodore Thomas in 1891, the ensemble has been based in the Symphony Center since 1904 and plays a summer season at the Ravinia F ...
(1966–2013)
*Vincent DeRosa
Vincent Ned DeRosa (October 5, 1920 – July 18, 2022) was an American hornist who served as a studio musician for Hollywood soundtracks and other recordings from 1935 until his retirement in 2008. Because his career spanned over 70 years, duri ...
– former principal horn for a number of Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood ...
studios and composers including John Williams
John Towner Williams (born February 8, 1932)Nylund, Rob (November 15, 2022)Classic Connection review, ''WBOI'' ("For the second time this year, the Fort Wayne Philharmonic honored American composer, conductor, and arranger John Williams, who w ...
*Stefan Dohr
Stefan Dohr (born 3 September 1965) is a German horn player and principal horn of the Berlin Philharmonic.
Biography
Born in Münster, Dohr obtained the Solo Horn position of the Frankfurt Opera House at the age of 19.
He held the same posit ...
– current principal horn, Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra
The Berlin Philharmonic () is a German orchestra based in Berlin. It is one of the most popular, acclaimed and well-respected orchestras in the world.
Throughout the 20th century, the orchestra was led by conductors Wilhelm Furtwängler (1922� ...
* Richard Dunbar – a player of the French horn, playing in the free jazz scene
*Philip Farkas
Philip Farkas (March 5, 1914 – December 21, 1992) was the principal French horn player in the Chicago Symphony Orchestra for many years, and he left in 1960 to join the music faculty at Indiana University School of Music. His books include ' ...
– former principal horn of the Chicago Symphony Orchestra
The Chicago Symphony Orchestra (CSO) is an American symphony orchestra based in Chicago, Illinois. Founded by Theodore Thomas in 1891, the ensemble has been based in the Symphony Center since 1904 and plays a summer season at the Ravinia F ...
, developer of the Holton-Farkas horn and author of several books on horn and brass playing
* Douglas Hill – former principal horn of the Madison Symphony Orchestra
The Madison Symphony Orchestra (MSO) is an orchestra headquartered in Madison, Wisconsin, Madison, Wisconsin. Its conductor is John DeMain, who began his 30th season with the orchestra in the fall of 2023. The orchestra was founded in 1925 as a s ...
, notable teacher and composer
* Julie Landsman – former Principal Horn for the Metropolitan Opera
The Metropolitan Opera is an American opera company based in New York City, currently resident at the Metropolitan Opera House (Lincoln Center), Metropolitan Opera House at Lincoln Center, situated on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. Referred ...
and well-known horn pedagogue
*Stefan de Leval Jezierski
Stefan de Leval Jezierski (born March 22, 1954) is an American French horn, horn player resident in Germany.
Biography
Born in Boston, Jezierski learned trumpet at age 12, then began to learn horn at age 14. He later studied horn with Myron Bloo ...
– longest serving horn, Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra
The Berlin Philharmonic () is a German orchestra based in Berlin. It is one of the most popular, acclaimed and well-respected orchestras in the world.
Throughout the 20th century, the orchestra was led by conductors Wilhelm Furtwängler (1922� ...
* Philip Myers – former principal horn of the New York Philharmonic
The New York Philharmonic is an American symphony orchestra based in New York City. Known officially as the ''Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc.'', and globally known as the ''New York Philharmonic Orchestra'' (NYPO) or the ''New Yo ...
* Jeff Nelsen – Canadian Brass
The Canadian Brass is a Canadian brass quintet formed in 1970 in Toronto, Ontario, by Charles Daellenbach (tuba) and Gene Watts (trombone), with horn player Graeme Page and trumpeters Stuart Laughton and Bill Phillips completing the quintet ...
hornist 2000–2004, 2007–2010; Indiana University Jacobs School of Music horn faculty since 2006
*Giovanni Punto
Jan Václav Stich, better known as Giovanni Punto (28 September 1746 in Žehušice – 16 February 1803 in Prague) was a Czechs, Czech French horn, horn player and a pioneer of the hand-stopping technique which allows natural horns to play a great ...
– horn virtuoso and hand-stopping
Hand-stopping is a technique by which a natural horn or a natural trumpet can be made to produce notes outside of its normal harmonic series. By inserting the hand, cupped, into the bell, the player can reduce the pitch of a note by a semitone or ...
pioneer, after whom the International Horn Society's annual horn playing award is named, also a violinist, concertmaster, and composer
* David Pyatt – winner of the BBC Young Musician of the Year
BBC Young Musician is a televised national music competition broadcast biennially on BBC Television and BBC Radio 3. Originally BBC Young Musician of the Year, its name was changed in 2010.
The competition, a former member of the European Uni ...
competition in 1988 and current principal horn of the London Philharmonic Orchestra
The London Philharmonic Orchestra (LPO) is a British orchestra based in London. One of five permanent symphony orchestras in London, the LPO was founded by the conductors Thomas Beecham, Sir Thomas Beecham and Malcolm Sargent in 1932 as a riv ...
*Gunther Schuller
Gunther Alexander Schuller (November 22, 1925June 21, 2015) was an American composer, conductor, horn player, author, historian, educator, publisher, and jazz musician.
Biography and works
Early years
Schuller was born in Queens, New York City ...
– former principal horn of the Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra
The Cincinnati Symphony Orchestra is an American orchestra based in Cincinnati, Ohio. Its primary concert venue is Music Hall. In addition to its symphony concerts, the orchestra gives pops concerts as the Cincinnati Pops Orchestra. The Cinc ...
and Metropolitan Opera Orchestra
The Metropolitan Opera is an American opera company based in New York City, currently resident at the Metropolitan Opera House at Lincoln Center, situated on the Upper West Side of Manhattan. Referred to colloquially as the Met, the company i ...
, and played with Miles Davis
Miles Dewey Davis III (May 26, 1926September 28, 1991) was an American jazz trumpeter, bandleader, and composer. He is among the most influential and acclaimed figures in the history of jazz and 20th century music, 20th-century music. Davis ado ...
* Lucien Thévet - Principal horn of the Paris Conservatoire Orchestra, of the Orchestre de l'Opéra Natiobal de Paris, notable teacher and author of several books on horn playing
*Barry Tuckwell
Barry Emmanuel Tuckwell, (5 March 1931 – 16 January 2020) was an Australian French horn player who spent most of his professional life in the UK and the United States. He is generally considered to have been one of the world's leading horn p ...
– former principal horn of the London Symphony Orchestra
The London Symphony Orchestra (LSO) is a British symphony orchestra based in London. Founded in 1904, the LSO is the oldest of London's orchestras, symphony orchestras. The LSO was created by a group of players who left Henry Wood's Queen's ...
and author of several books on horn playing
*Radovan Vlatković
Radovan Vlatković (born 1962) is a Croatian-born horn player. He was the former principal horn of the Berlin Radio Symphony Orchestra (now Deutsches Symphonie-Orchester Berlin). He left that post in 1990 to devote himself to a solo career and ha ...
– 1983 winner of the ARD International Music Competition, former principal horn and soloist of the Berlin Radio Symphony Orchestra
The Berlin Radio Symphony Orchestra (''Rundfunk-Sinfonieorchester Berlin'') is a German symphony orchestra based in Berlin. In Berlin, the orchestra gives concerts at the Konzerthaus Berlin and at the Berliner Philharmonie. The orchestra has a ...
, and professor at the Mozarteum University of Salzburg
Mozarteum University Salzburg (German language, German: ''Universität Mozarteum Salzburg'') is one of three affiliated but separate (it is actually a state university) entities under the "Mozarteum" name in Salzburg, Salzburg municipality; th ...
* Sarah Willis – first female brass-player in the Berlin Philharmonic Orchestra
The Berlin Philharmonic () is a German orchestra based in Berlin. It is one of the most popular, acclaimed and well-respected orchestras in the world.
Throughout the 20th century, the orchestra was led by conductors Wilhelm Furtwängler (1922� ...
, US-born, British ambassador for the horn and classical music through television programs such as ''Sarah's Music'' on Deutsche Welle
(; "German Wave"), commonly shortened to DW (), is a German state-funded television network, state-owned international broadcaster funded by the Federal Government of Germany. The service is available in 32 languages. DW's satellite tele ...
.
People who are more notable for their other achievements, but also play the horn, include actors Ewan McGregor
Ewan Gordon McGregor ( ; born 31 March 1971) is a Scottish actor. His accolades include a Golden Globe Award and a Primetime Emmy Award. In 2013, he was appointed Officer of the Order of the British Empire (OBE) for his services to drama and ...
and David Ogden Stiers
David Allen Ogden Stiers ( ; October 31, 1942 – March 3, 2018) was an American actor and conductor. He appeared in numerous productions on Broadway, and originated the role of Feldman in '' The Magic Show'', in 1974.
In 1977, Stiers was cast ...
, comedian and television host Jon Stewart
Jon Stewart (born Jonathan Stuart Leibowitz, November 28, 1962) is an American comedian, writer, producer, director, political commentator, actor, and television host. The long-running host of ''The Daily Show'' on Comedy Central from 1999 to 20 ...
, journalist Chuck Todd
Charles David Todd (born April 8, 1972) is an American television journalist who was the 12th moderator of NBC's ''Meet the Press''. During his time at NBC News between 2007 and 2025, Todd also hosted ''Meet the Press Now'', its daily edition ...
, The Who
The Who are an English Rock music, rock band formed in London in 1964. Their classic lineup (1964–1978) consisted of lead vocalist Roger Daltrey, guitarist Pete Townshend, bassist John Entwistle and drummer Keith Moon. Considered one of th ...
bassist and singer John Entwistle
John Alec Entwistle (9 October 194427 June 2002) was an English musician, best known as the bass guitarist for the rock band the Who. Entwistle's music career spanned over four decades. Nicknamed "The Ox" and "Thunderfingers", he was the band ...
, and rapper and record producer B.o.B.
Gallery
Vienna horn
The Vienna horn () is a type of musical horn used primarily in Vienna, Austria, for playing orchestral or classical music. It is used throughout Vienna, including the Vienna Philharmonic and ''Wiener Staatsoper''.
History
During the nineteenth ...
File:Hunting horn 3.jpg, A hunting horn
File:Omnitonic horn 2.jpg, A French Omnitonic horn
File:Natural Horn (instrument).JPG, A natural horn
The natural horn is a musical instrument that is the predecessor to the modern-day (French) horn (differentiated by its lack of valves). Throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the natural horn evolved as a separation from the tr ...
at the Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (abbreviated V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.8 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and named after Queen ...
File:Stanford Natural Horn.JPG, A replica of a Mozart-era natural horn
File:Cordechasse.png, A hunting horn in E
File:Cor naturel.JPG, A natural horn
File:Three valves horn.jpg, An older, French-made ''cor à pistons'' in E
File:Brain-raoux.jpg, A French-made horn with piston valves
File:Dennis-brain-alex.jpg, A horn by Alexander, once owned by Dennis Brain
File:French horn Berlin.jpg, A French horn in Berlin
File:French horn blue background.jpg, A rose gold French Horn
See also
* List of compositions for horn * List of horn makers *List of horn techniques
Some of these horn techniques are not unique to the horn, but are applicable to most or all wind instruments.
Stopped horn
This is the act of fully closing off the bell of the instrument with either the right hand or a special stopping mute. T ...
References
External links
Homepage of the International Horn Society
one of the largest organizations of horn players in the world.
British Horn Society
UK-based organisation for horn playing
First steps of making a horn by hand
(QuickTime Movie) at Finke Horns
by musicologist Edmund A. Bowles
at Paxman, compiled with the assistance of Simon de Souza
How to dismantle a valve
at Finke Horns
Horn Etudes
- List of horn etudes {{DEFAULTSORT:French horn Concert band instruments F instruments German musical instruments Horns Orchestral instruments Jazz instruments