French-Canadian Group on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
French Canadians, referred to as Canadiens mainly before the nineteenth century, are an

 After the 1760 British conquest of New France in the
After the 1760 British conquest of New France in the
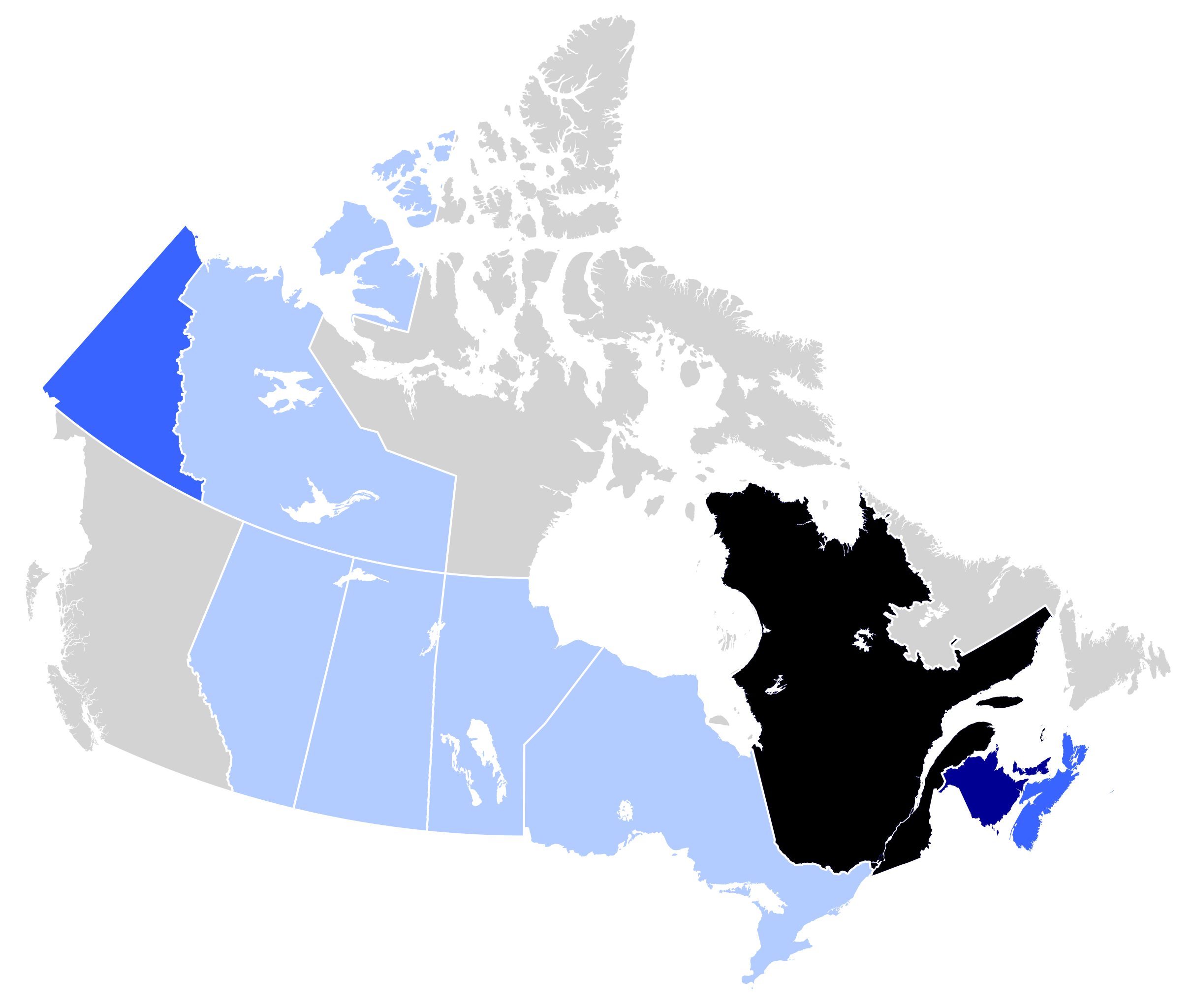 In Canada, 85% of French Canadians reside in
In Canada, 85% of French Canadians reside in
 In the United States, many cities were founded as colonial outposts of
In the United States, many cities were founded as colonial outposts of
 French Canadians express their cultural or ancestral roots using a number of different terms. In the 2021 census, French-speaking Canadians identified their ethnicity, in order of prevalence, most often as Canadian ethnicity, Canadian,
French Canadians express their cultural or ancestral roots using a number of different terms. In the 2021 census, French-speaking Canadians identified their ethnicity, in order of prevalence, most often as Canadian ethnicity, Canadian,
 Since the 1960s, French Canadians in Quebec have generally used ''Québécois'' (masculine) or ''Québécoise'' (feminine) to express their cultural and national identity, rather than ''Canadien français'' and ''Canadienne française''. Francophones who self-identify as Québécois and do not have French-Canadian ancestry may not identify as "French Canadian" (''Canadien'' or ''Canadien français''); however, by extension, though the term "French Canadian" may refer to natives of the province of Quebec or other parts of French Canada of foreign descent. Those who do have French or French-Canadian ancestry, but who support Quebec sovereignty, often find ''Canadien français'' to be archaic or even pejorative. This is a reflection of the strong social, cultural, and political ties that most Quebecers of French-Canadian origin, who constitute a majority of francophone Quebecers, maintain within Quebec. It has given Québécois an ambiguous meaning which has often played out in Québécois nation motion, political issues, as all public institutions attached to the Government of Quebec refer to all Quebec citizens, regardless of their language or their cultural heritage, as Québécois.
Academic analysis of French Canadian culture has often focused on the degree to which the Quiet Revolution, particularly the shift in the social and cultural identity of the Québécois following the Estates General of French Canada of 1966 to 1969, did or did not create a "rupture" between the Québécois and other francophones elsewhere in Canada.
Since the 1960s, French Canadians in Quebec have generally used ''Québécois'' (masculine) or ''Québécoise'' (feminine) to express their cultural and national identity, rather than ''Canadien français'' and ''Canadienne française''. Francophones who self-identify as Québécois and do not have French-Canadian ancestry may not identify as "French Canadian" (''Canadien'' or ''Canadien français''); however, by extension, though the term "French Canadian" may refer to natives of the province of Quebec or other parts of French Canada of foreign descent. Those who do have French or French-Canadian ancestry, but who support Quebec sovereignty, often find ''Canadien français'' to be archaic or even pejorative. This is a reflection of the strong social, cultural, and political ties that most Quebecers of French-Canadian origin, who constitute a majority of francophone Quebecers, maintain within Quebec. It has given Québécois an ambiguous meaning which has often played out in Québécois nation motion, political issues, as all public institutions attached to the Government of Quebec refer to all Quebec citizens, regardless of their language or their cultural heritage, as Québécois.
Academic analysis of French Canadian culture has often focused on the degree to which the Quiet Revolution, particularly the shift in the social and cultural identity of the Québécois following the Estates General of French Canada of 1966 to 1969, did or did not create a "rupture" between the Québécois and other francophones elsewhere in Canada.
 *Franco-Newfoundlanders, province of Newfoundland and Labrador, also known as Terre-Neuvien(ne)
*
*Franco-Newfoundlanders, province of Newfoundland and Labrador, also known as Terre-Neuvien(ne)
*
 During the mid-18th century, French Canadian explorers and colonists colonized other parts of North America in what are today
During the mid-18th century, French Canadian explorers and colonists colonized other parts of North America in what are today
File:Pavillon royal de la France.svg, Royal pavilion of 1534 to 1599.
File:Naval Flag of the Kingdom of France (Civil Ensign).svg, Pavilion of the merchant navy from 1600 to 1663.
File:Royal Standard of King Louis XIV.svg, Royal pavilion of 1663 to 1763.
File:Carillon drapeau.png,
File:Flag of the Patriote movement (Lower Canada).svg, Patriote flag.
File:CarillonSacreCoeur Drapeau.png,
File:Drapeau du Québec 1948.svg, Flag of Quebec in 1948.
File:Flag of Quebec.svg, Flag of Quebec.
File:Flag of Quebec.svg, Québécois.
File:Flag of the Franco Albertains.svg, Franco-Albertans.
File:Flag of the Franco-Manitobains.svg, Franco-Manitoban.
File:Franco-Ontarian flag.svg, Franco-Ontarians.
File:Bandera dels Fransaskois.svg, Fransaskois.
File:Drapeau Franco-Américain.svg, French-Canadian Americans, Franco-Americans.
File:Flag of the Franco-Colombiens.svg, Franco-Columbians.
File:Flag of the Franco-Nunavois.svg, Franco-Nunavois.
File:Flag of the FrancoTenois.svg, Franco-Ténois.
File:Flag of the Franco-Yukonnais.svg, Franco-Yukonnais.
File:Flag of Acadia.svg,
online book review
* * * * Lamarre, Jean. ''Les Canadiens français du Michigan: leur contribution dans le développement de la vallée de la Saginaw et de la péninsule de Keweenaw, 1840-1914'' (Les éditions du Septentrion, 2000)
online
* * McQuillan, D. Aidan. "Franch-Canadian Communities in the American Upper Midwest during the Nineteenth Century." ''Cahiers de géographie du Québec'' 23.58 (1979): 53-72. * * Newton, Jason L. "“These French Canadian of the Woods are Half-Wild Folk” Wilderness, Whiteness, and Work in North America, 1840–1955." ''Labour'' 77 (2016): 121-150. in New Hampshir
online
* * * Sorrell, Richard S. "The survivance of French Canadians in New England (1865–1930): History, geography and demography as destiny." ''Ethnic and Racial Studies'' 4.1 (1981): 91-109. * Szlezák, Edith. ''Franco-Americans in Massachusetts: "No French no mo' 'round here" '' (Narr Francke Attempto Verlag, 2010
online
.
''Map displaying the percentage of the US population claiming French Canadian ancestry by county''
United States Census Bureau, Census 2000 {{Authority control French-Canadian people, French diaspora in Canada, * Canadian people of French descent, * European diaspora in Canada Linguistic minorities Ethnic minorities
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
descended from French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
colonists first arriving in France's colony of Canada in 1608. The vast majority of French Canadians live in the province of Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
.
During the 17th century, French settlers originating mainly from the west and north of France settled Canada. It is from them that the French Canadian ethnicity was born. During the 17th to 18th centuries, French Canadians expanded across North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and colonized various regions, cities, and towns. As a result, people of French Canadian descent can be found across North America. Between 1840 and 1930, many French Canadians emigrated to New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, an event known as the Grande Hémorragie
The Quebec diaspora consists of Quebec immigrants and their descendants dispersed over the North American continent and historically concentrated in the New England region of the United States, Ontario, and the Canadian Prairies. The mass emigrat ...
.
Etymology
French Canadians get their name from the French colony of Canada, the most developed and densely populated region ofNew France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
during the period of French colonization in the 17th and 18th centuries. The original use of the term ''Canada'' referred to the area of present-day Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
along the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawren ...
, divided in three districts (Québec
Quebec is Canada's largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border ...
, Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, ; ) is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice River, Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence River, Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Sain ...
, and Montréal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cit ...
), as well as to the ''Pays d'en Haut
The ''Pays d'en Haut'' (; ''Upper Country'') was a territory of New France covering the regions of North America located west of Montreal. The vast territory included most of the Great Lakes region, expanding west and south over time into the ...
'' (Upper Countries), a vast and thinly settled territorial dependence north and west of Montreal which covered the whole of the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
area.
From 1535 to the 1690s, ''Canadien'' was a word used by the French to refer to the First Nations
First nations are indigenous settlers or bands.
First Nations, first nations, or first peoples may also refer to:
Indigenous groups
*List of Indigenous peoples
*First Nations in Canada, Indigenous peoples of Canada who are neither Inuit nor Mé ...
they had encountered in the St. Lawrence River valley at Stadacona
Stadacona was a 16th-century St. Lawrence Iroquoian village not far from where Quebec City was founded in 1608.
History
French explorer and navigator Jacques Cartier, while travelling and charting the Saint Lawrence River, reached the village ...
and Hochelaga; however, First Nations groups did not refer to themselves as ''Canadien''. At the end of the 17th century, ''Canadien'' became an ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
distinguishing the French inhabitants of Canada from those of France. At the end of the 18th century, to distinguish between the English-speaking population and the French-speaking population, the terms ''English Canadian
English Canadians (), or Anglo-Canadians (), refers to either Canadians of English ethnic origin and heritage or to English-speaking or Anglophone Canadians of any ethnic origin; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadians. Cana ...
'' and ''French Canadian'' emerged. During the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
of the 1960s to 1980s, inhabitants of Quebec began to identify as Québécois instead of simply French Canadian.
History

French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
settlers from Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
, Perche
Perche () (French: ''le Perche'') is a former Provinces of France, province of France, known historically for its forests and, for the past two centuries, for the Percheron draft horse, draft horse breed. Until the French Revolution, Perche was ...
, Beauce Beauce may refer to:
* Beauce, France, a natural region in north-central France
* Beaucé, a commune in the Ille-et-Vilaine department, Brittany, France
* Beauce, Quebec
Beauce (; ) is a historical and traditional region of Quebec, Canada, lo ...
, Brittany
Brittany ( ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the north-west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica in Roman Gaul. It became an Kingdom of Brittany, independent kingdom and then a Duch ...
, Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
, Anjou
Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
*County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
** Du ...
, Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vien ...
, Poitou
Poitou ( , , ; ; Poitevin: ''Poetou'') was a province of west-central France whose capital city was Poitiers. Both Poitou and Poitiers are named after the Pictones Gallic tribe.
Geography
The main historical cities are Poitiers (historical ...
, Aunis
Aunis () is a historical Provinces of France, province of France, situated in the north-west of the department of Charente-Maritime. Its historic capital is La Rochelle, which took over from Châtelaillon-Plage, Castrum Allionis (Châtelaillon) t ...
, Angoumois
Angoumois (), historically the County of Angoulême, was a county and province of France, originally inferior to the parent duchy of Aquitaine, similar to the Périgord to its east but lower and generally less forested, equally with occasional ...
, Saintonge
Saintonge may refer to:
*County of Saintonge, a historical province of France on the Atlantic coast
* Saintonge (region), a region of France corresponding to the historical province
* Saintonge ware, a medieval pottery type produced in Saintes reg ...
, and Gascony
Gascony (; ) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part of the combined Province of Guyenne and Gascon ...
were the first Europeans
Europeans are the focus of European ethnology, the field of anthropology related to the various ethnic groups that reside in the states of Europe. Groups may be defined by common ancestry, language, faith, historical continuity, etc. There are ...
to permanently colonize what is now Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
, parts of Ontario, Acadia, and select areas of Western Canada, all in Canada (see French colonization of the Americas
France began colonizing America in the 16th century and continued into the following centuries as it established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France established colonies in much of eastern North America, on several Caribbean is ...
). Their colonies of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
(also commonly called Canada) stretched across what today are the Maritime provinces
The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of ...
, southern Quebec and Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, as well as the entire Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
Valley.
The first permanent European settlements in Canada were at Port Royal
Port Royal () was a town located at the end of the Palisadoes, at the mouth of Kingston Harbour, in southeastern Jamaica. Founded in 1494 by the Spanish, it was once the largest and most prosperous city in the Caribbean, functioning as the cen ...
in 1605 and Quebec City
Quebec City is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Quebec. As of July 2021, the city had a population of 549,459, and the Census Metropolitan Area (including surrounding communities) had a populati ...
in 1608 as fur trading posts. The territories of New France were Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
(later renamed Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
), and Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
; the mid-continent Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. Whi ...
was at first governed from Canada and then attached to Louisiana. The inhabitants of the French colony of Canada (modern-day Quebec) called themselves the ''Canadiens'', and came mostly from northwestern France. The early inhabitants of Acadia, or Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
(''Acadiens)'', came mostly but not exclusively from the southwestern regions of France.
''Canadien'' explorers and fur traders would come to be known as ''coureurs des bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; ) were independent entrepreneurial French Canadians, French Canadian traders who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with Indigenous peoples of the Americas, ...
'' and ''voyageurs
Voyageurs (; ) were 18th- and 19th-century French and later French Canadians and others who transported furs by canoe at the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ...
'', while those who settled on farms in Canada would come to be known as ''habitants
Habitants () were French settlers and inhabitants of French origin who farmed the land along both shores of the St. Lawrence River and the Gulf of St. Lawrence in what is now Quebec, Canada. The term was used by the inhabitants themselves an ...
''. Many French Canadians are the descendants of the King's Daughters
The King's Daughters ( , or in the spelling of the era) were the approximately 800 young French people, French women who immigrated to New France between 1663 and 1673 as part of a program sponsored by King Louis XIV. The program was designed ...
(''Filles du Roi'') of this era. A few also are the descendants of mixed French and Algonquian marriages (see also Metis people
Metis or Métis, meaning "mixed" in French, may refer to:
Ethnic groups
* Métis, recognized Indigenous communities in Canada and the United States whose distinct culture and language emerged after early intermarriage between First Nations peopl ...
and Acadian people
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern American region of Acadia, w ...
). During the mid-18th century, French explorers and ''Canadiens'' born in French Canada colonized other parts of North America in what are today the states of Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, Vincennes, Indiana
Vincennes is a city in, and the county seat of, Knox County, Indiana, United States. It is located on the lower Wabash River in the southwestern part of the state, nearly halfway between Evansville and Terre Haute. It was founded in 1732 by F ...
, Louisville, Kentucky
Louisville is the List of cities in Kentucky, most populous city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky, sixth-most populous city in the Southeastern United States, Southeast, and the list of United States cities by population, 27th-most-populous city ...
, the Windsor-Detroit region and the Canadian prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
(primarily Southern Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
).
 After the 1760 British conquest of New France in the
After the 1760 British conquest of New France in the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
(known as the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
in Canada), the French-Canadian population remained important in the life of the colonies. The British gained Acadia by the Treaty of Utrecht
The Peace of Utrecht was a series of peace treaty, peace treaties signed by the belligerents in the War of the Spanish Succession, in the Dutch city of Utrecht between April 1713 and February 1715. The war involved three contenders for the vac ...
in 1713. It took the 1774 Quebec Act
The Quebec Act 1774 ( 14 Geo. 3. c. 83) () was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain which set procedures of governance in the Province of Quebec. One of the principal components of the act was the expansion of the province's territory t ...
for French Canadians to regain the French civil law system, and in 1791 French Canadians in Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada () was a British colonization of the Americas, British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence established in 1791 and abolished in 1841. It covered the southern portion o ...
were introduced to the parliamentary system when an elected Legislative Assembly was created. The Legislative Assembly having no real power, the political situation degenerated into the Lower Canada Rebellion
The Lower Canada Rebellion (), commonly referred to as the Patriots' Rebellion () in French, is the name given to the armed conflict in 1837–38 between rebels and the colonial government of Lower Canada (now southern Quebec). Together wit ...
s of 1837–1838, after which Lower Canada and Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada () was a Province, part of The Canadas, British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Queb ...
were unified. Some of the motivations for the union was to limit French-Canadian political power and at the same time transferring a large part of the Upper Canadian debt to the debt-free Lower Canada. After many decades of British immigration, the ''Canadiens'' became a minority in the Province of Canada
The Province of Canada (or the United Province of Canada or the United Canadas) was a British colony in British North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham, in the Report ...
in the 1850s.
French-Canadian contributions were essential in securing responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability, the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy. Governments (the equivalent of the executive br ...
for the Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for the provinces of Lower Canada and Upper Canada, two British colonization of the Americas, historical British colonies in present-day Canada. The two colonies were formed in 1791, when the British Parliament ...
and in undertaking Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
. In the late 19th and 20th centuries, French Canadians' discontent grew with their place in Canada because of a series of events: including the execution of Louis Riel
Louis Riel (; ; 22 October 1844 – 16 November 1885) was a Canadian politician, a founder of the province of Manitoba, and a political leader of the Métis in Canada, Métis people. He led two resistance movements against the Government of ...
, the elimination of official bilingualism in Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
, Canada's military participation in the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War (, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, Transvaal War, Anglo–Boer War, or South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer republics (the South African Republic and ...
, Regulation 17
Regulation 17 () was a regulation of the Government of Ontario, Canada, designed to limit instruction in French-language Catholic separate schools. The regulation was written by the Ministry of Education and was issued in July 1912 by the Progr ...
which banned French-language schools in Ontario, the Conscription Crisis of 1917
The Conscription Crisis of 1917 () was a political and military crisis in Canada during World War I. It was mainly caused by disagreement on whether men should be conscripted to fight in the war, but also brought out many issues regarding relatio ...
and the Conscription Crisis of 1944
The Conscription Crisis of 1944 was a political and military crisis following the introduction of forced military service for men in Canada during World War II. It was similar to the Conscription Crisis of 1917, but not as politically damaging.
...
.
Between the 1840s and the 1930s, some 900,000 French Canadians immigrated to the New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
region. About half of them returned home. The generations born in the United States would eventually come to see themselves as Franco-Americans. During the same period of time, numerous French Canadians also migrated and settled in Eastern and Northern Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
. The descendants of those Quebec inter-provincial migrants constitute the bulk of today's Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarians ( or if female, sometimes known as ''Ontarois'' and ''Ontaroises'') are Francophone Canadians that reside in the province of Ontario. Most are French Canadians from Ontario. In 2021, according to the Government of Ontario, ther ...
community.
Since 1968, French has been one of Canada's two official languages. It is the sole official language of Quebec and one of the official languages of New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
, Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
, the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, and Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agr ...
. The province of Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
has no official languages defined in law, although the provincial government provides French language services in many parts of the province under the ''French Language Services Act French Language Services Act may refer to:
* French Language Services Act (Ontario)
The ''French Language Services Act'' () (the ''Act'') is a law in the province of Ontario, Canada which is intended to protect the rights of Franco-Ontarians, or ...
''.
Language
There are manyvarieties
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of French spoken by francophone Canadians, for example Quebec French
Quebec French ( ), also known as Québécois French, is the predominant variety (linguistics), variety of the French language spoken in Canada. It is the dominant language of the province of Quebec, used in everyday communication, in education, ...
, Acadian French
Acadian French () is a variety of French spoken by Acadians, mostly in the region of Acadia, Canada. Acadian French has seven regional accents, including Chiac and Brayon.
Phonology
Since there was relatively little linguistic contact with F ...
, Métis French
Métis French () is one of the traditional languages of the Métis people along with Michif and Bungi, and is the French-dialect source of Michif.
Features
Métis French is a variety of Canadian French with some added characters such as Ññ ...
, and Newfoundland French
Newfoundland French or Newfoundland Peninsular French () is the French spoken on the Port au Port Peninsula (part of the so-called “French Shore”) of Newfoundland. The francophones of the region can trace their origins to Continental French ...
. The French spoken in Ontario, the Canadian West
Western Canada, also referred to as the Western provinces, Canadian West, or Western provinces of Canada, and commonly known within Canada as the West, is a Canadian region that includes the four western provinces just north of the Canada–Unit ...
, and New England can trace their roots back to Quebec French because of Quebec's diaspora. Over time, many regional accents have emerged. Canada is estimated to be home to between 32 and 36 regional French accents, 17 of which can be found in Quebec, and seven of which are found in New Brunswick. There are also people who will naturally speak using ''Québécois Standard'' or Joual
''Joual'' () is an accepted name for the linguistic features of Quebec French that are associated with the French-speaking working class in Montreal which has become a symbol of national identity for some. ''Joual'' has historically been stigma ...
which are considered sociolect
In sociolinguistics, a sociolect is a form of language ( non-standard dialect, restricted register) or a set of lexical items used by a socioeconomic class, profession, age group, or other social group.
Sociolects involve both passive acquisit ...
s.
There are about seven million French Canadians and native French speakers in Quebec. Another one million French-speaking French Canadians are distributed throughout the rest of Canada. French Canadians may also speak Canadian English
Canadian English (CanE, CE, en-CA) encompasses the Variety (linguistics), varieties of English language, English used in Canada. According to the 2016 Canadian Census, 2016 census, English was the first language of 19.4 million Canadians or ...
, especially if they live in overwhelmingly English-speaking environments. In Canada, not all those of French Canadian ancestry speak French, but the vast majority do.
Francophones living in Canadian provinces other than Quebec have enjoyed minority language
A minority language is a language spoken by a minority of the population of a territory. Such people are termed linguistic minorities or language minorities. With a total number of 196 sovereign states recognized internationally (as of 2019) and ...
rights under Canadian law since the Official Languages Act of 1969, and under the Canadian Constitution
The Constitution of Canada () is the supreme law in Canada. It outlines Canada's system of government and the civil and human rights of those who are citizens of Canada and non-citizens in Canada. Its contents are an amalgamation of various ...
since 1982, protecting them from provincial governments that have historically been indifferent towards their presence. At the provincial level, New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
formally designates French as a full official language
An official language is defined by the Cambridge English Dictionary as, "the language or one of the languages that is accepted by a country's government, is taught in schools, used in the courts of law, etc." Depending on the decree, establishmen ...
, while other provinces vary in the level of French language services they offer. All three of Canada's territories include French as an official language of the territory alongside English and local indigenous languages; however, in practice, French-language services are normally available only in the capital cities and not across the entire territory.
Religion
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
is the chief denomination amongst French Canadians. The kingdom of France forbade non-Catholic settlement in New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
from 1629 onward; thus, almost all French settlers of Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
were Catholic. In the United States, some families of French-Canadian origin have converted to Protestantism. Until the 1960s, religion was a central component of French-Canadian national identity. The Church parish was the focal point of civic life in French-Canadian society, and religious orders ran French-Canadian schools, hospitals and orphanages and were very influential in everyday life in general. During the Quiet Revolution
The Quiet Revolution () was a period of socio-political and socio-cultural transformation in French Canada, particularly in Quebec, following the 1960 Quebec general election. This period was marked by the secularization of the government, the ...
of the 1960s, however, the practice of Catholicism dropped drastically. Church attendance in Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
currently remains low. Rates of religious observance among French Canadians outside Quebec tend to vary by region, and by age. In general, however, those in Quebec are the least observant, while those in the United States of America
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguo ...
and other places away from Quebec tend to be the most observant.
Geographical distribution
People who claim some French-Canadian ancestry or heritage number some 7 million in Canada. In the United States, 2.4 million people report French-Canadian ancestry or heritage, while an additional 8.4 million claimFrench
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
ancestry; they are treated as a separate ethnic group by the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the U ...
.
Canada
 In Canada, 85% of French Canadians reside in
In Canada, 85% of French Canadians reside in Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
where they constitute the majority of the population in all regions except the far north (Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; ) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada.
Spread over nearly 14 degrees of latitude, north of the 49th parallel, the region covers on the Labrador Peninsula, making ...
). Most cities and villages in this province were built and settled by the French or French Canadians during the French colonial rule
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas colonies, protectorates, and mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "First French colonial empire", that ex ...
.
There are various urban and small centres in Canada outside Quebec that have long-standing populations of French Canadians, going back to the late 19th century, due to Interprovincial migration in Canada, interprovincial migration. Eastern Ontario, Eastern and Northern Ontario have large populations of francophones in communities such as Ottawa, Cornwall, Ontario, Cornwall, Hawkesbury, Ontario, Hawkesbury, Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Timmins, North Bay, Ontario, North Bay, Timiskaming District, Timiskaming, Welland and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor. Many also pioneered the Canadian Prairies in the late 18th century, founding the towns of Saint Boniface, Manitoba and in Alberta's Peace Country, including the region of Grande Prairie.
It is estimated that roughly 70–75% of Quebec's population descend from the French pioneers of the 17th and 18th century.
The French-speaking population have massively chosen the "Canadian" ("''Canadien'') ethnic group since the government made it possible (1986), which has made the current statistics misleading. The term ''Canadien'' historically referred only to a French-speaker, though today it is used in French to describe any Canadian citizen.
United States
 In the United States, many cities were founded as colonial outposts of
In the United States, many cities were founded as colonial outposts of New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
by French or French-Canadian explorers. They include Mobile, Alabama, Mobile (Alabama), Coeur d'Alene, Idaho, Coeur d'Alene (Idaho), Vincennes, Indiana, Vincennes (Indiana), Belleville, Illinois, Belleville (Illinois), Bourbonnais, Illinois, Bourbonnais (Illinois), Prairie du Rocher, Illinois, Prairie du Rocher (Illinois), Dubuque, Iowa, Dubuque (Iowa), Baton Rouge, Louisiana, Baton Rouge (Louisiana), New Orleans, New Orleans (Louisiana), Detroit, Detroit (Michigan), Biloxi, Mississippi, Biloxi (Mississippi), Creve Coeur, Missouri, Creve Coeur (Missouri), St. Louis, St. Louis (Missouri), Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh (Fort Duquesne, Pennsylvania), Provo, Utah, Provo (Utah), Green Bay, Wisconsin, Green Bay (Wisconsin), La Crosse, Wisconsin, La Crosse (Wisconsin), Milwaukee, Milwaukee (Wisconsin) or Prairie du Chien, Wisconsin, Prairie du Chien (Wisconsin).
The majority of the French-Canadian population in the United States is found in the New England area, although there is also a large French-Canadian presence in Plattsburgh, New York, across Lake Champlain from Burlington, Vermont. Quebec and Acadian emigrants settled in industrial cities like Fitchburg, Massachusetts, Fitchburg, Leominster, Massachusetts, Leominster, Lynn, Massachusetts, Lynn, Worcester, Massachusetts, Worcester, Haverhill, Massachusetts, Haverhill, Waltham, Massachusetts, Waltham, Lowell, Massachusetts, Lowell, Gardner, Massachusetts, Gardner, Lawrence, Massachusetts, Lawrence, Chicopee, Massachusetts, Chicopee, Somerset, Massachusetts, Somerset, Fall River, Massachusetts, Fall River, and New Bedford, Massachusetts, New Bedford in Massachusetts; Woonsocket, Rhode Island, Woonsocket in Rhode Island; Manchester, New Hampshire, Manchester and Nashua, New Hampshire, Nashua in New Hampshire; Bristol, Connecticut, Bristol, Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford, and East Hartford, Connecticut, East Hartford in Connecticut; throughout the state of Vermont, particularly in Burlington, Vermont, Burlington, St. Albans (city), Vermont, St. Albans, and Barre, Vermont (city), Barre; and Biddeford, Maine, Biddeford and Lewiston, Maine, Lewiston in Maine. Smaller groups of French Canadians settled in the Midwest, notably in the states of Michigan, Illinois, Wisconsin, Nebraska, Iowa, Missouri, and Minnesota. French Canadians also settled in central North Dakota, largely in Rolette County, North Dakota, Rolette and Bottineau County, North Dakota, Bottineau counties, and in South Dakota.
Some Métis people (Canada), Metis still speak Michif, a language influenced by French, and a mixture of other European and Native American tribal languages.
Identities
Canada
 French Canadians express their cultural or ancestral roots using a number of different terms. In the 2021 census, French-speaking Canadians identified their ethnicity, in order of prevalence, most often as Canadian ethnicity, Canadian,
French Canadians express their cultural or ancestral roots using a number of different terms. In the 2021 census, French-speaking Canadians identified their ethnicity, in order of prevalence, most often as Canadian ethnicity, Canadian, French
French may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France
** French people, a nation and ethnic group
** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices
Arts and media
* The French (band), ...
, French-speaking Quebecer, Québécois, French Canadian, and Acadian. All of these except for French were grouped together by Jantzen (2006) as "French New World" ancestries because they originate in Canada.
Jantzen (2006) distinguishes the English ''Canadian'', meaning "someone whose family has been in Canada for multiple generations", and the French ''Canadien'', used to refer to descendants of the original settlers of New France in the 17th and 18th centuries.Jantzen (2006) Footnote 5: ''"Note that Canadian and Canadien have been separated since the two terms mean different things. In English, it usually means someone whose family has been in Canada for multiple generations. In French it is referring to "Les Habitants", settlers of New France during the 17th and 18th centuries who earned their living primarily from agricultural labour."'' "Canadien" was used to refer to the French-speaking residents of New France beginning in the last half of the 17th century. The English-speaking residents who arrived later from Great Britain were called "Anglais". This usage continued until Canadian Confederation
Canadian Confederation () was the process by which three British North American provinces—the Province of Canada, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick—were united into one federation, called the Name of Canada#Adoption of Dominion, Dominion of Ca ...
in 1867. Confederation united several former British colonies into the Dominion of Canada, and from that time forward, the word "Canadian" has been used to describe both English-speaking and French-speaking citizens, wherever they live in the country.
Those reporting "French New World" ancestries overwhelmingly had ancestors that went back at least four generations in Canada.Jantzen (2006): "The reporting of French New World ancestries (Canadien, Québécois, and French-Canadian) is concentrated in the 4th+ generations; 79% of French-Canadian, 88% of Canadien and 90% of Québécois are in the 4th+generations category." Fourth generation Canadiens and Québécois showed considerable attachment to their ethno-cultural group, with 70% and 61%, respectively, reporting a strong sense of belonging.Jantzen (2005): ''"According to Table 3, the 4th+ generations are highest because of a strong sense of belonging to their ethnic or cultural group among those respondents reporting the New World ancestries of Canadien and Québécois."''
The generational profile and strength of identity of French New World ancestries contrast with those of British or Canadian ancestries, which represent the largest ethnic identities in Canada.Jantzen (2006): ''For respondents of French and New World ancestries the pattern is different. Where generational data is available, it is possible to see that not all respondents reporting these ancestries report a high sense of belonging to their ethnic or cultural group. The high proportions are focused among those respondents that are in the 4th+ generations, and unlike with the British Isles example, the difference between the 2nd and 3rd generations to the 4th+ generation is more pronounced. Since these ancestries are concentrated in the 4th+ generations, their high proportions of sense of belonging to ethnic or cultural group push up the 4th+ generational results."'' Although deeply rooted Canadians express a deep attachment to their ethnic identity, most English-speaking Canadians of British or Canadian ancestry generally cannot trace their ancestry as far back in Canada as French speakers. As a result, their identification with their ethnicity is weaker: for example, only 50% of third generation "Canadians" strongly identify as such, bringing down the overall average. The survey report notes that 80% of Canadians whose families had been in Canada for three or more generations reported "Canadian and provincial or regional ethnic identities". These identities include French New World ancestries such as "Québécois" (37% of Quebec population) and Acadians, Acadian (6% of Atlantic provinces).
Quebec
 Since the 1960s, French Canadians in Quebec have generally used ''Québécois'' (masculine) or ''Québécoise'' (feminine) to express their cultural and national identity, rather than ''Canadien français'' and ''Canadienne française''. Francophones who self-identify as Québécois and do not have French-Canadian ancestry may not identify as "French Canadian" (''Canadien'' or ''Canadien français''); however, by extension, though the term "French Canadian" may refer to natives of the province of Quebec or other parts of French Canada of foreign descent. Those who do have French or French-Canadian ancestry, but who support Quebec sovereignty, often find ''Canadien français'' to be archaic or even pejorative. This is a reflection of the strong social, cultural, and political ties that most Quebecers of French-Canadian origin, who constitute a majority of francophone Quebecers, maintain within Quebec. It has given Québécois an ambiguous meaning which has often played out in Québécois nation motion, political issues, as all public institutions attached to the Government of Quebec refer to all Quebec citizens, regardless of their language or their cultural heritage, as Québécois.
Academic analysis of French Canadian culture has often focused on the degree to which the Quiet Revolution, particularly the shift in the social and cultural identity of the Québécois following the Estates General of French Canada of 1966 to 1969, did or did not create a "rupture" between the Québécois and other francophones elsewhere in Canada.
Since the 1960s, French Canadians in Quebec have generally used ''Québécois'' (masculine) or ''Québécoise'' (feminine) to express their cultural and national identity, rather than ''Canadien français'' and ''Canadienne française''. Francophones who self-identify as Québécois and do not have French-Canadian ancestry may not identify as "French Canadian" (''Canadien'' or ''Canadien français''); however, by extension, though the term "French Canadian" may refer to natives of the province of Quebec or other parts of French Canada of foreign descent. Those who do have French or French-Canadian ancestry, but who support Quebec sovereignty, often find ''Canadien français'' to be archaic or even pejorative. This is a reflection of the strong social, cultural, and political ties that most Quebecers of French-Canadian origin, who constitute a majority of francophone Quebecers, maintain within Quebec. It has given Québécois an ambiguous meaning which has often played out in Québécois nation motion, political issues, as all public institutions attached to the Government of Quebec refer to all Quebec citizens, regardless of their language or their cultural heritage, as Québécois.
Academic analysis of French Canadian culture has often focused on the degree to which the Quiet Revolution, particularly the shift in the social and cultural identity of the Québécois following the Estates General of French Canada of 1966 to 1969, did or did not create a "rupture" between the Québécois and other francophones elsewhere in Canada.
Elsewhere in Canada
The emphasis on the French language and Quebec autonomy means that French speakers across Canada may now self-identify as ''québécois(e)'', ''acadien(ne)'', or ''Franco-canadien(ne)'', or as provincial linguistic minorities such as ''Franco-manitobain(e)'', ''Franco-ontarien(ne)'' or ''fransaskois(e)''. Education, health and social services are provided by provincial institutions, so that provincial identities are often used to identify French-language institutions:Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarians ( or if female, sometimes known as ''Ontarois'' and ''Ontaroises'') are Francophone Canadians that reside in the province of Ontario. Most are French Canadians from Ontario. In 2021, according to the Government of Ontario, ther ...
s, province of Ontario
Ontario is the southernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Located in Central Canada, Ontario is the Population of Canada by province and territory, country's most populous province. As of the 2021 Canadian census, it ...
, also referred to as Ontarien(ne)
*Franco-Manitobans, province of Manitoba
Manitoba is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population ...
, also referred to as Manitobain(e)
*Fransaskois, province of Saskatchewan, also referred to Saskois(e)
*Franco-Albertans, province of Alberta, also referred to Albertain(e)
*Franco-Columbians, province of British Columbia mostly live in the Vancouver metro area; also referred to as Franco-Colombien(ne)
*Franco-Yukonnais, territory of Yukon
Yukon () is a Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada, bordering British Columbia to the south, the Northwest Territories to the east, the Beaufort Sea to the north, and the U.S. state of Alaska to the west. It is Canada’s we ...
, also referred to as Yukonais(e)
*Franco-Ténois, territory of Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories is a federal Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2021 census population of 41,070, it is the second-largest and the most populous of Provinces and territorie ...
, also referred to as Ténois(e)
*Franco-Nunavois, territory of Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agr ...
, also referred to as Nunavois(e)
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
residing in the provinces of New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
, Prince Edward Island and Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
represent a distinct ethnic Acadian French, French-speaking culture. This group's culture and history evolved separately from the French Canadian culture, at a time when the Maritime Provinces were ''not'' part of what was referred to as Canada, and are consequently considered a distinct culture from French Canadians.
Brayons in Madawaska County, New Brunswick, Madawaska County, New Brunswick
New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to ...
and Aroostook County, Maine, Aroostook County, Maine may be identified with either the Acadians or the Québécois, or considered a distinct group in their own right, by different sources.
French Canadians outside Quebec are more likely to self-identify as "French Canadian". Identification with provincial groupings varies from province to province, with Franco-Ontarians, for example, using their provincial label far more frequently than Franco-Columbians do. Few identify ''only'' with the provincial groupings, explicitly rejecting "French Canadian" as an identity label. A population genetics ancestry study claims that for those French Canadians who trace their ancestry to the French founder population, a significant percentage, 53-78% have at least one indigenous ancestor.
United States
 During the mid-18th century, French Canadian explorers and colonists colonized other parts of North America in what are today
During the mid-18th century, French Canadian explorers and colonists colonized other parts of North America in what are today Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
(called ''Louisianais''), Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, Missouri
Missouri (''see #Etymology and pronunciation, pronunciation'') is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Ranking List of U.S. states and territories by area, 21st in land area, it border ...
, Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
, Wisconsin, Indiana, Ohio, far northern New York (state), New York and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan as well as around Detroit. They also founded such cities as New Orleans and St. Louis, Missouri, St. Louis and villages in the Mississippi Valley. French Canadians later emigrated in large numbers from Canada to the United States between the 1840s and the 1930s in search of economic opportunities in border communities and industrialized portions of New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
. French-Canadian communities in the United States remain along the Quebec
Quebec is Canada's List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, ...
border in Maine, Vermont, and New Hampshire, as well as further south in Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut. There is also a significant community of French Canadians in South Florida, particularly Hollywood, Florida, especially during the winter months. The wealth of Catholic churches named after Louis IX of France, St. Louis throughout New England is indicative of the French immigration to the area. They came to identify as French American, Franco-American, especially those who were born American.
Distinctions between French Canadian, natives of France, and other New World French identities is more blurred in the U.S. than in Canada; however, those who identify as French Canadian or Franco American generally do not regard themselves as French. Rather, they identify culturally, historically, and ethnically with the culture that originated in Quebec that is differentiated from French culture. In ''L'Avenir du français aux États-Unis'', Calvin Veltman and Benoît Lacroix found that since the French language has been so widely abandoned in the United States, the term "French Canadian" has taken on an ethnic rather than linguistic meaning.
French Canadian identities are influenced by historical events that inform regional cultures. For example, in New England, the relatively recent immigration (19th/20th centuries) is informed by experiences of language oppression and an identification with certain occupations, such as the mill workers. In the Great Lakes, many French Canadians also identify as Métis and trace their ancestry to the earliest voyageurs
Voyageurs (; ) were 18th- and 19th-century French and later French Canadians and others who transported furs by canoe at the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ...
and habitants, settlers; many also have ancestry dating to the lumber era and often a mixture of the two groups.
The main Franco-American regional identities are:
* French Canadians:
** French Canadians of the Great Lakes (including Muskrat French)
** New England French
* Creoles:
** Missouri French (and other people of French ancestry in the former Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. Whi ...
)
** Louisiana Creole people, Louisiana Creoles (who speak Colonial French)
* Cajuns
Culture
Agriculture
Traditionally, Canadiens had a subsistence agriculture in Eastern Canada (Québec). This subsistence agriculture slowly evolved in dairy farm during the end of the 19th century and the beginning of 20th century while retaining the subsistence side. By 1960, agriculture changed toward an industrial agriculture. French Canadians have selective breeding, selectively bred distinct livestock over the centuries, including Canadienne cattle, cattle, Canadian horse, horses and Chantecler chicken, chickens.Flags
From New France
After the conquest
Of French Canadian civic institutions
Of francophone groups located in native land
Of francophone groups formed by French Canadian emigration
Of other groups originating from the colonisation of New France
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
.
File:Flag of Acadiana.svg, Cajuns.
File:Flag of Franco-Terreneuviens.svg, Franco-Terreneuviens.
File:Metis Blue.svg, Métis (Canada).
File:Metis Red.svg, Métis (Canada).
File:Flag of Saint-Pierre and Miquelon.svg, Saint-Pierre-et-Miquelonais.
See also
* Canadians in France * French Americans * Quebec diaspora * List of francophone communities in Ontario * French language in Canada * Canada–France relationsReferences
Genealogical works
Below is a list of the main genealogical works retracing the origins of French Canadian families: # and Jacques Legaré, ''Répertoire des actes de baptême, mariage et sépulture et des recensements du Québec ancien'', vol. I-XLVII. Montréal : Les Presses de l'Université de Montréal, 1980. () # and collab, ''Dictionnaire généalogique des familles du Québec. Des origines à 1730'', Montréal : Les Presses de l'Université de Montréal, 1983. () # Noël Montgomery Elliot, ''Les Canadiens français 1600-1900'', vol. I-III. Toronto : 1st edition, La Bibliothèque de recherche généalogique, 1992. () # Cyprien Tanguay, ''Dictionnaire généalogique des familles canadiennes. Depuis la fondation de la colonie jusqu'à nos jours'', vol. I-VII, 1871–1890. Nouvelle édition, Montréal : Éditions Élysée, 1975. ()Further reading
* * * Breton, Raymond, and Pierre Savard, eds. ''"The Quebec and Acadian Diaspora in North America'' (1982online book review
* * * * Lamarre, Jean. ''Les Canadiens français du Michigan: leur contribution dans le développement de la vallée de la Saginaw et de la péninsule de Keweenaw, 1840-1914'' (Les éditions du Septentrion, 2000)
online
* * McQuillan, D. Aidan. "Franch-Canadian Communities in the American Upper Midwest during the Nineteenth Century." ''Cahiers de géographie du Québec'' 23.58 (1979): 53-72. * * Newton, Jason L. "“These French Canadian of the Woods are Half-Wild Folk” Wilderness, Whiteness, and Work in North America, 1840–1955." ''Labour'' 77 (2016): 121-150. in New Hampshir
online
* * * Sorrell, Richard S. "The survivance of French Canadians in New England (1865–1930): History, geography and demography as destiny." ''Ethnic and Racial Studies'' 4.1 (1981): 91-109. * Szlezák, Edith. ''Franco-Americans in Massachusetts: "No French no mo' 'round here" '' (Narr Francke Attempto Verlag, 2010
online
.
''Map displaying the percentage of the US population claiming French Canadian ancestry by county''
United States Census Bureau, Census 2000 {{Authority control French-Canadian people, French diaspora in Canada, * Canadian people of French descent, * European diaspora in Canada Linguistic minorities Ethnic minorities