Freeform surface machining on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
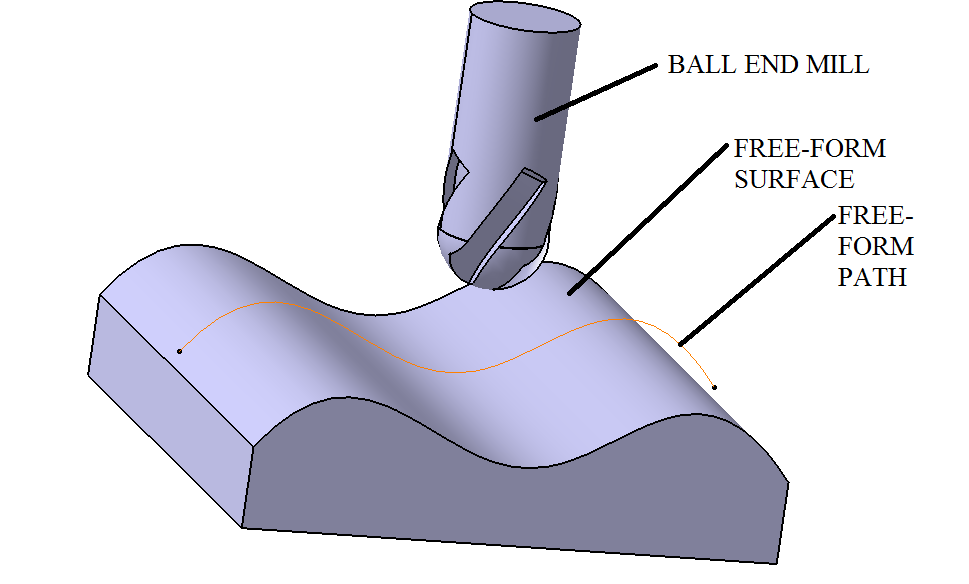 In
In
 In
In manufacturing
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of the
secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer ...
, freeform surface machining refers to the machining
Machining is a manufacturing process where a desired shape or part is created using the controlled removal of material, most often metal, from a larger piece of raw material by cutting. Machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, which util ...
of complex surfaces that are not uniformly planar. The industries which most often manufactures free-form surfaces are basically aerospace
Aerospace is a term used to collectively refer to the atmosphere and outer space. Aerospace activity is very diverse, with a multitude of commercial, industrial, and military applications. Aerospace engineering consists of aeronautics and astron ...
, automotive, die mold industries, biomedical and power sector for turbine
A turbine ( or ) (from the Greek , ''tyrbē'', or Latin ''turbo'', meaning vortex) is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced can be used for generating electrical ...
blades manufacturing. Generally 3- or 5-axis CNC milling machines are used for this purpose. The manufacturing process of freeform surfaces is not an easy job, as the tool path generation in present CAM
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
technology is generally based on geometric computation so tool path are not optimum. The geometry can also be not described explicitly so errors and discontinuities occurrence in the solid structure cannot be avoided. Free-form surfaces are machined with the help of different tool path generation method like adaptive iso-planar tool path generation, constant scallop tool path generation, adaptive iso-parametric method, iso-curvature, isophote and by other methods. The different methods are chosen based on the parameters which is needed to be optimized.
Different tool path generation methods
# Iso-planar tool path method: This is the most common and robust method used to machine free-form surface. In this process tool path generation is done by intersection of surfaces with parallel plane in Cartesian space. # Adaptive iso-planar tool path method: In this process the surface are partitioned into different regions according to their slope with the intersection planes by applying the concept of isophote. # Iso-scallop method: Scallop generated between two adjacent machining path is constant.Optimization of free-form surface machining
CAM
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
software generally creates a tool path without considering any mechanics process. These causes risk of tool damage, tool deflection and errors on surface finish. By minimizing the forces we can increase tool life. Different optimization method can be used considering process parameters like feed rate, spindle speed, steps, tool diameter, magnitude and preset maximum force. The optimization can be done for minimum machining time, minimum tool travel, minimum production cost or for good surface finish. Efficiency of surface machined is also considered by maximum scallop height and by gouging. Gouging are the main reason for discrepancies of surface accuracy and texture specification. It also causes damage to parts, surface and machine tool. Scallop height tolerance help us in measuring the quality of free-form surface. Selection of proper topology result in minimum path length. In CAM
Cam or CAM may refer to:
Science and technology
* Cam (mechanism), a mechanical linkage which translates motion
* Camshaft, a shaft with a cam
* Camera or webcam, a device that records images or video
In computing
* Computer-aided manufacturin ...
software choosing NURBS
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model using basis splines (B-splines) that is commonly used in computer graphics for representing curves and surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analy ...
to create surface is considered to be good method for presenting surface as it is accepted by both IGES
The Initial Graphics Exchange Specification (IGES) is a vendor-neutral List of file formats, file format that allows the CAD data exchange, digital exchange of information among computer-aided design (CAD) systems. It is an ASCII-based textual for ...
and STEP files of CAM software.
See also
*Freeform surface modelling
Freeform surface modelling is a technique for engineering freeform Computer representation of surfaces, surfaces with a Computer-aided design, CAD or Computer-aided industrial design, CAID system.
The technology has encompassed two main fields. ...
* CNC
* G-code
G-code (abbreviation for geometric code; also called RS-274, standardized today in ISO 6983-1) is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) and 3D printing programming language. It is used mainly in computer-aided manufacturing t ...
* Multiaxis machining
* NURBS
Non-uniform rational basis spline (NURBS) is a mathematical model using basis splines (B-splines) that is commonly used in computer graphics for representing curves and surfaces. It offers great flexibility and precision for handling both analy ...
References
{{reflist Computer-aided manufacturing