Freedom Of Religion In Eritrea on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Religion in
Religion in
Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity
. Edinburgh: University Press, p. 65 .Henze, Paul B. (2005) ''Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia'', . The Aksumites erected a number of large Another great power came in the person of the
Another great power came in the person of the

 It is believed that before Christianity became the official religion of Abyssinia (ancient Eritrea and northern Ethiopia) in the 4th century,
It is believed that before Christianity became the official religion of Abyssinia (ancient Eritrea and northern Ethiopia) in the 4th century,
/ref>
 Religion in
Religion in Eritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
consists of a number of faiths. The two major religions in Eritrea are Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
. However, the number of adherents of each faith is subject to debate. Estimates of the Christian share of the population range from 47% and 63%, while estimates of the Muslim share of the population range from 37% to 52%.
Most Eritrean Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
belong to the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is one of the Oriental Orthodox Churches with its headquarters in Asmara, Eritrea. It was given autocephaly by Shenouda III of Alexandria, pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church, after Eritrea gained its in ...
, although a minority is affiliated with the Eritrean Catholic Church
The Eritrean Catholic Church is a '' sui iuris'' (autonomous) Eastern Catholic church based in Eritrea. As a particular church of the Catholic Church, it is in full communion with the Holy See. It was established in 2015 when its territory was ...
and various Protestant denominations
A Christian denomination is a distinct religious body within Christianity that comprises all church congregations of the same kind, identifiable by traits such as a name, particular history, organization, leadership, theological doctrine, worsh ...
. Eritrean Muslims
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
are predominantly Sunni
Sunni Islam is the largest branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr () rightfully succeeded him as the caliph of the Mu ...
.
Apart from the officially recognized denominations of Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
and Sunni Islam
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
, all other faiths and denominations are in principle required to undergo a registration process; in practice they are not allowed to register. Among other things, the government's registration system requires religious groups to submit personal information on their membership to be allowed to worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity or God. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recognition of a God. An act of worship may be performed individually, in an informal or formal group, ...
.
Faiths and denominations
There are two major religions in Eritrea:Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
(four denominations) and Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
(only the Sunni school
A school is the educational institution (and, in the case of in-person learning, the Educational architecture, building) designed to provide learning environments for the teaching of students, usually under the direction of teachers. Most co ...
). However, the number of adherents is subject to debate.
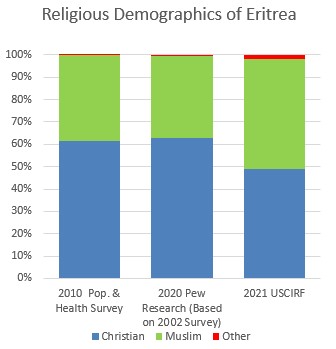
* In the 2010 Eritrea Population and Health Survey, conducted by the Eritrean National Statistics Office and the Fafo Institute for Applied International Studies, 61.4% of all survey respondents reported being Christian (56.3% Orthodox, 4.2% Catholic, and 0.8% Protestant), with 38.4% reporting being Muslim, and the remaining 0.2% adhering to traditional faiths. Among women, who made up 87.6% of those surveyed, 60.7% reported being Christian and 39.0% Muslim. In a similar survey of Eritrean women conducted in 2002, 63.0% reported being Christian (57.8% Orthodox, 4.6% Catholic, and 0.7% Protestant), with 36.6% reporting being Muslim.
*In 2015, Pew Research estimated that, by 2020, 62.9% of the population would be Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
, while 36.6% would be Muslim
Muslims () are people who adhere to Islam, a Monotheism, monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God ...
, with the rest following other religions. Pew based its estimate of Eritrea's religious composition on the 2002 survey referenced above.
* The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom
The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is a U.S. federal government commission created by the International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA) of 1998. USCIRF commissioners are appointed by the president and the lead ...
's 2021 annual report states that the country's population is "split in half between Christians (49 percent) and Muslims (49 percent)".
* In a 2016 report by Aid to the Church in Need
Aid to the Church in Need (, , ) is an international Catholic pastoral aid organization, which yearly offers financial support to more than 5,000 projects worldwide.
Aid to the Church in Need's General Secretariat and Project Headquarters is in ...
, that organization estimated around 50 percent of Eritrea's population adhered to Islam, and 48 percent followed Christianity, with all remaining religions accounting for two percent.
* According to ACS-Italia estimate, around 52% of Eritrea's population in 2017 adhered to Islam, and 46% followed Christianity, with the remaining 2% of residents practicing other religions, including traditional faiths and animism
Animism (from meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, human handiwork, and in ...
.
* The 2011 edition of the ''Encyclopedia of Global Religion'' matches the Pew Research Center estimate of 63% Christian, breaking it down further to: 58% Orthodox; 5% Roman Catholic; and less than 1% Protestant. That report further analyzed the regional distribution within Eritrea:
History of religion in Eritrea
TheKingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
, covering much of modern-day Eritrea and the Tigray Region
The Tigray Region (or simply Tigray; officially the Tigray National Regional State) is the northernmost Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob people, Irob and Kunama people. I ...
in northern Ethiopia, arose somewhere around the first or second centuries.Munro-Hay, Stuart (1991Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity
. Edinburgh: University Press, p. 65 .Henze, Paul B. (2005) ''Layers of Time: A History of Ethiopia'', . The Aksumites erected a number of large
stela
A stele ( ) or stela ( )The plural in English is sometimes stelai ( ) based on direct transliteration of the Greek, sometimes stelae or stelæ ( ) based on the inflection of Greek nouns in Latin, and sometimes anglicized to steles ( ) or stela ...
e, which served a religious purpose in pre-Christian times. Over 200 years after the kingdom's formation, it adopted Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
under King Ezana
Ezana (, ''‘Ezana'', unvocalized ዐዘነ ''‘zn''), (, ''Aezana'') was the ruler of the Kingdom of Aksum (320s – ). One of the best-documented rulers of Aksum, Ezana is important as he first adopted for his country the religion of Christ ...
. Eritrea was also one of the first Islamic settlements in Africa, as a group of Muslims facing persecution in Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above ...
migrated to the Kingdom of Aksum. Islam spread to Ethiopia and Eritrea around 615 AD with the arrival of Uthman ibn Affan
Uthman ibn Affan (17 June 656) was the third caliph of the Rashidun Caliphate, ruling from 644 until Assassination of Uthman, his assassination in 656. Uthman, a second cousin, son-in-law, and notable Companions of the Prophet, companion of ...
, one of the ''Sahabah
The Companions of the Prophet () were the Muslim disciples and followers of the Islamic prophet Muhammad who saw or met him during his lifetime. The companions played a major role in Muslim battles, society, hadith narration, and governance ...
'' (companions) of the Islamic prophet
Prophets in Islam () are individuals in Islam who are believed to spread God's message on Earth and serve as models of ideal human behaviour. Some prophets are categorized as messengers (; sing. , ), those who transmit divine revelation, mos ...
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of A ...
. Uthman had been driven out of Hejaz
Hejaz is a Historical region, historical region of the Arabian Peninsula that includes the majority of the western region of Saudi Arabia, covering the cities of Mecca, Medina, Jeddah, Tabuk, Saudi Arabia, Tabuk, Yanbu, Taif and Al Bahah, Al-B ...
and found shelter at Axum
Axum, also spelled Aksum (), is a town in the Tigray Region of Ethiopia with a population of 66,900 residents (as of 2015). It is the site of the historic capital of the Aksumite Empire.
Axum is located in the Central Zone of the Tigray Re ...
in the Tigray Region
The Tigray Region (or simply Tigray; officially the Tigray National Regional State) is the northernmost Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in Ethiopia. The Tigray Region is the homeland of the Tigrayan, Irob people, Irob and Kunama people. I ...
of Ethiopia under the protection of the Axumite king, Aṣḥama ibn Abjar.
 Another great power came in the person of the
Another great power came in the person of the Imam
Imam (; , '; : , ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a prayer leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Salah, Islamic prayers, serve as community leaders, ...
of Harar
Harar (; Harari language, Harari: ሀረር / ; ; ; ), known historically by the indigenous as Harar-Gey or simply Gey (Harari: ጌይ, ݘٛىيْ, ''Gēy'', ), is a List of cities with defensive walls, walled city in eastern Ethiopia. It is al ...
in Ethiopia, Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi
Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al-Ghazi (, Harari: አሕመድ ኢብራሂም አል-ጋዚ, ; 21 July 1506 – 10 February 1543) was the Imam of the Adal Sultanate from 1527 to 1543. Commonly named Ahmed ''Gragn'' in Amharic and ''Gurey'' in Somali, ...
, also known as Ahmad Gurey or Gragn. Al-Ghazi led Muslim forces consisting of Somali, Harari, Oromo Oromo may refer to:
* Oromo people, an ethnic group of Ethiopia and Kenya
* Oromo language, an Afroasiatic language
See also
*
*Orma (clan), Oromo tribe
*Oromia
Oromia (, ) is a Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in Ethiopia and the homelan ...
, Afar, Saho, Argobba, Hadiya, Silte and Gurage
Gurage (, Gurage: ጉራጌ) are a Semitic-speaking ethnic group inhabiting Ethiopia.G. W. E. Huntingford, "William A. Shack: The Gurage: a people of the ensete culture" They inhabit the Gurage Zone and East Gurage Zone, a fertile, semi-mounta ...
soldiers from present-day Ethiopia, Eritrea, Djibouti
Djibouti, officially the Republic of Djibouti, is a country in the Horn of Africa, bordered by Somalia to the south, Ethiopia to the southwest, Eritrea in the north, and the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden to the east. The country has an area ...
and Somalia
Somalia, officially the Federal Republic of Somalia, is the easternmost country in continental Africa. The country is located in the Horn of Africa and is bordered by Ethiopia to the west, Djibouti to the northwest, Kenya to the southwest, th ...
. In 1530 he began to attack the plateau. Within four years he laid waste to the majority of the Christian highlands, including the Tigray Region of Ethiopia. Only by surrender and conversion could people save their lives. Only the intervention of the Portuguese transformed the flow of events. They landed at Massawa
Massawa or Mitsiwa ( ) is a port city in the Northern Red Sea Region, Northern Red Sea region of Eritrea, located on the Red Sea at the northern end of the Gulf of Zula beside the Dahlak Archipelago. It has been a historically important port for ...
in 1541 and helped the Eritreans and Ethiopians to drive the Imams forces from the plateau. The Muslim forces dispersed, retreated and disappeared.
Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
was first brought to Eritrea by the Jesuits
The Society of Jesus (; abbreviation: S.J. or SJ), also known as the Jesuit Order or the Jesuits ( ; ), is a religious order (Catholic), religious order of clerics regular of pontifical right for men in the Catholic Church headquartered in Rom ...
in 1600. In 1632, this order was expelled from Eritrea for wanting to convert the country (an Orthodox country) to Catholicism. In the 19th century the Italians began to bring Eritrea under their sphere of influence and introduced Roman Catholicism again. Missionaries appeared in the 19th century and established the Lutheran
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
and Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
churches. These organizations have been allowed to continue to practice. New groups however, have been discouraged from establishing a base in Eritrea.
During Italian colonialism, Catholicism became quite widespread, mostly due to Italian settlement in Eritrea. At the beginning of the 1940s nearly 28% of the population of Italian Eritrea
Italian Eritrea (, "Colony of Eritrea") was a colony of the Kingdom of Italy in the territory of present-day Eritrea. The first Italian establishment in the area was the purchase of Assab by the Società di Navigazione Rubattino, Rubattino Shippin ...
were Catholic, most of whom were Italians
Italians (, ) are a European peoples, European ethnic group native to the Italian geographical region. Italians share a common Italian culture, culture, History of Italy, history, Cultural heritage, ancestry and Italian language, language. ...
.Bandini, Franco. ''Gli italiani in Africa, storia delle guerre coloniali 1882-1943'' Chapter: Eritrea However, the number of Italians in Eritrea decreased at the end of WW2
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies and the Axis powers. Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising ...
under British military administration (which also had religious violence between Christians and Muslims), and especially after Eritrea came under Ethiopian authority in 1950, thus diminishing the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
's importance.
Under Ethiopian rule and the Eritrean War of Independence
The Eritrean War of Independence was an War, armed conflict and insurgency aimed at achieving self-determination and independence for Eritrea from Ethiopian rule. Starting in 1961, Eritrean insurgents engaged in guerrilla warfare to liberate ...
, the role of the Ethiopian Orthodox Church
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Christian churches in Africa originating before European colonization of the continent, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church dates bac ...
was strengthened, and it legitimized Ethiopian rule in Eritrea, which was controversial. Ethiopian propaganda framed the Eritrean struggle for liberation as a "Muslim separatist movement", which strengthened feelings among Eritrean Muslims that the Ethiopian Orthodox Church was a tool of the Ethiopian state.
During Derg
The Derg or Dergue (, ), officially the Provisional Military Administrative Council (PMAC), was the military junta that ruled Ethiopia, including present-day Eritrea, from 1974 to 1987, when they formally "Civil government, civilianized" the ...
rule, the Ethiopian state had a policy of state atheism
State atheism or atheist state is the incorporation of hard atheism or non-theism into Forms of government, political regimes. It is considered the opposite of theocracy and may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments ...
, which was unpopular, especially in Eritrea. However, the Derg also co-opted many religions despite repressing them, such as with the Ethiopian Orthodox Church. They also for the first time recognized Islam in Ethiopia
Islam is the second largest religion in Ethiopia behind Christianity. In 2024, 31.5% of the population was Muslim.
Islam in Ethiopia dates back to the founding of the religion; in 615, when a group of Muslims were counseled by Muhammad to esca ...
, co-opting it with the newly founded Ethiopian Islamic Affairs Supreme Council.
Christianity
The various estimates shown above place Christianity (all denominations) as the religion of between 47% and 63% of the population of Eritrea. While elsewhere on the continent,Christianity in Africa
Christianity arrived to Africa in the 1st century AD; as of 2024, it is the largest religion on the continent. Several African Christians influenced the early development of Christianity and shaped its doctrines, including Tertullian, Perpetua, ...
was primarily introduced by European missionaries, this was not the case with the Tigray-Tigrinya people of Eritrea and Tigray Region in neighbouring Ethiopia (or with the Amhara people of Ethiopia). The ancient empire of the Kingdom of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum, or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom in East Africa and South Arabia from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, based in what is now northern Ethiopia and Eritrea, and spanning present-day Djibouti and Sudan. Emerging ...
centered in north Tigray and the central highlands of Eritrea had intimate connections with the Mediterranean world in which Christianity grew. Christianity arrived in the Eritrean and Tigrayan area in the 4th century, growing dynamically in the pre-existing Jewish/Animistic
Animism (from meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Animism perceives all things—animals, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, rivers, Weather, ...
mixed environment. The Tigrayan-Tigrinyas thus converted to Christianity centuries before most of Europe, thereby establishing one of the oldest state churches in the world. The Eritrean Orthodox have their origins in the 4th century Coptic mission of Syrian Frumentius
Saint Frumentius (; died c. 383) was a Phoenician Christian missionary and the first bishop of Axum who brought Christianity to the Kingdom of Aksum. He is sometimes known by other names, such as Abuna ("Our Father") and Aba Salama ("Father ...
in East Africa
East Africa, also known as Eastern Africa or the East of Africa, is a region at the eastern edge of the Africa, African continent, distinguished by its unique geographical, historical, and cultural landscape. Defined in varying scopes, the regi ...
, when the first Archbishop was elected for the Aksumite Empire, under Ezana of Axum
Ezana (, ''‘Ezana'', unvocalized ዐዘነ ''‘zn''), (, ''Aezana'') was the ruler of the Kingdom of Aksum (320s – ). One of the best-documented rulers of Aksum, Ezana is important as he first adopted for his country the religion of Chris ...
(r. 320–360). Among ecclesiastical buildings, most notable date from the 4th to the 14th centuries; for example Libanos, Bizen and Sina
Sina may refer to:
Relating to China
* Chin (China), or Sina (), old Chinese form of the Sanskrit name Cina ()
** Shina (word), or Sina (), archaic Japanese word for China
** Sinae, Latin name for China
Places
* Sina, Albania, or Sinë, a vi ...
.
Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church
According to surveys, Orthodox Christians make up 56-58% of the population. A large majority of the Christian population ofEritrea
Eritrea, officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa, with its capital and largest city being Asmara. It is bordered by Ethiopia in the Eritrea–Ethiopia border, south, Sudan in the west, and Dj ...
belongs to the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is one of the Oriental Orthodox Churches with its headquarters in Asmara, Eritrea. It was given autocephaly by Shenouda III of Alexandria, pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church, after Eritrea gained its in ...
, The Eritrean Church was recognized by the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria
The Coptic Orthodox Church (), also known as the Coptic Orthodox Patriarchate of Alexandria, is an Oriental Orthodox Christian church based in Egypt. The head of the church and the See of Alexandria is the pope of Alexandria on the Holy Apo ...
following independence in 1993, and in 1994 the two neighbouring churches affirmed their respective status. In April 1998 the former Archbishop Abune Phillipos
Abune Phillipos (29 September 1901 – 17 September 2002) was the first Patriarch of the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church.
Life
He was born in Endadeko, Ighelehames, Akeleguzay, Eritrea and began his religious training at the Debre Bizen Mona ...
of Asmara
Asmara ( ), or Asmera (), is the capital and most populous city of Eritrea, in the country's Central Region (Eritrea), Central Region. It sits at an elevation of , making it the List of capital cities by altitude, sixth highest capital in the wo ...
was elevated to the rank of Patriarch. He died in 2004 and was succeeded by Abune Yacob. The reign of Abune Yacob as Patriarch of Eritrea was very brief as he died not long after his enthronement, and he was succeeded by Abune Antonios as 3rd Patriarch of Eritrea. Abune Antonios was elected on 5 March 2004 and enthroned as the third Patriarch of the Orthodox Tewahedo Church of Eritrea on 24 April 2004. Pope Shenouda III
Pope Shenouda III (3 August 1923 – 17 March 2012) was the 117th Pope of Alexandria and Patriarch of the See of St. Mark. His papacy lasted 40 years, 4 months, and 4 days, from 14 November 1971 until his death.
His official title was Pope of ...
presided at the ceremony in Asmara, together with the Holy Synod
In several of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Churches and Eastern Catholic Churches, the patriarch or head bishop is elected by a group of bishops called the Holy Synod. For instance, the Holy Synod is a ruling body of the Georgian Orthodox ...
of the Eritrean Orthodox Church and a Coptic Orthodox Church delegation. Antonios was later formally deposed by the government. However, many believe that Abune Antonios was wrongly deposed and still consider him Patriarch. Many Eritrean Orthodox followers disagree with the Eritrean government making decisions in religious matters.
Catholicism
Catholics make up 4–5% of the Eritrean population. TheEritrean Catholic Church
The Eritrean Catholic Church is a '' sui iuris'' (autonomous) Eastern Catholic church based in Eritrea. As a particular church of the Catholic Church, it is in full communion with the Holy See. It was established in 2015 when its territory was ...
and Roman Catholic Church has dioceses of Asmara, Keren and Barentu. Catholics in Eritrea mainly follow the Geʽez
Geez ( or ; , and sometimes referred to in scholarly literature as Classical Ethiopic) is an ancient South Semitic language. The language originates from what is now Ethiopia and Eritrea.
Today, Geez is used as the main liturgical langu ...
variant of the Alexandrian Rite
The Alexandrian rites are a collection of ritual families and uses of Christian liturgy employed by three Oriental Orthodox churches (the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, and the Ethiopian Orthod ...
, but the Roman Rite
The Roman Rite () is the most common ritual family for performing the ecclesiastical services of the Latin Church, the largest of the ''sui iuris'' particular churches that comprise the Catholic Church. The Roman Rite governs Rite (Christianity) ...
is also used. There are four territorial jurisdictions in the country known as eparchies
Eparchy ( ''eparchía'' "overlordship") is an ecclesiastical unit in Eastern Christianity that is equivalent to a diocese in Western Christianity. An eparchy is governed by an ''eparch'', who is a bishop. Depending on the administrative structure ...
. Before the era of Italian Eritrea
Italian Eritrea (, "Colony of Eritrea") was a colony of the Kingdom of Italy in the territory of present-day Eritrea. The first Italian establishment in the area was the purchase of Assab by the Società di Navigazione Rubattino, Rubattino Shippin ...
, Roman Catholicism was already introduced into the country by Saint Justin de Jacobis
Giustino Sebastiano Pasquale de Jacobis, CM (9 October 1800 – 31 July 1860) was an Italian Catholic bishop and member of the Congregation of the Mission who served as Apostolic Vicar of Abyssinia and the Titular Bishop of Nilopolis. He is of ...
and the Vincentian Fathers
The Congregation of the Mission (), abbreviated CM and commonly called the Vincentians or Lazarists, is a Catholic society of apostolic life of pontifical right for men founded by Vincent de Paul. It is associated with the Vincentian Family, a ...
. Today the church is a distinctly Eritrean church, using the Geʽez
Geez ( or ; , and sometimes referred to in scholarly literature as Classical Ethiopic) is an ancient South Semitic language. The language originates from what is now Ethiopia and Eritrea.
Today, Geez is used as the main liturgical langu ...
language in the liturgy, although Masses continue to be celebrated also in Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance languag ...
and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
for the small Italian and Italo-Eritrean community, mainly in Asmara. When Eritrea was an Italian colony, all the colonists and the Italian military were of the Latin Church
The Latin Church () is the largest autonomous () particular church within the Catholic Church, whose members constitute the vast majority of the 1.3 billion Catholics. The Latin Church is one of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical ...
: in 1940 they constituted 11% of the total population. The Church of Our Lady of the Rosary was their main church. So, in the early 1940s, Catholicism was the religion of nearly 28% of people in the colony of Italian Eritrea.
Protestantism
Protestants, sometimes known by the slang name ''P'ent'ay
P'ent'ay (from Geʽez: ) is an originally Amharic– Tigrinya language term for Pentecostal Christians. Today, the term refers to all Evangelical Protestant denominations and organisations in Ethiopian and Eritrean societies. Alternative term ...
'', in Eritrea make up between less than 1% to 5% of the Christians. A minor church is the Kale Hiywot Church of Eritrea. Protestant denominations include Christian Brethren
The Open Brethren, sometimes called Christian Brethren, are a group of Evangelical Christian churches that arose in the late 1820s as part of the Assembly Movement within the Plymouth Brethren tradition. They originated in Ireland before spread ...
, Evangelical Church Mekane Yesus, Evangelical Lutheran Church of Eritrea. In 1926, Swedish missionaries founded the Evangelical/Lutheran Church of Eritrea. However, there was tension between the Catholic Church as the Roman Catholic Italians resisted and discouraged the spread of Protestantism in their colony and even lay prohibitions and numerous constraints on the activities of the Swedish missionaries. The Lutheran Church of Eritrea and its Swedish and Eritrean missionaries were the ones who translated the Bible
The Bible is a collection of religious texts that are central to Christianity and Judaism, and esteemed in other Abrahamic religions such as Islam. The Bible is an anthology (a compilation of texts of a variety of forms) originally writt ...
from Geʽez
Geez ( or ; , and sometimes referred to in scholarly literature as Classical Ethiopic) is an ancient South Semitic language. The language originates from what is now Ethiopia and Eritrea.
Today, Geez is used as the main liturgical langu ...
, only understood by higher clergymen, into the Tigrinya language
Tigrinya, sometimes romanized as Tigrigna, is an Ethio-Semitic languages, Ethio-Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It is primarily spoken by the Tigrinya people, ...
and other local languages and their main goal was to reach and "enlighten" as many people as possible in the world through education.
Islam
The various estimates shown above place Islam as the religion of between 37% and 52% of the population of Eritrea. Whatever the total share of the overall population, a 2009 report finds that over 99% of Eritrean Muslims areSunnis
Sunni Islam is the largest Islamic schools and branches, branch of Islam and the largest religious denomination in the world. It holds that Muhammad did not appoint any Succession to Muhammad, successor and that his closest companion Abu Bakr ...
, with less than 1% Shias
Shia Islam is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that Muhammad designated Ali ibn Abi Talib () as both his political successor (caliph) and as the spiritual leader of the Muslim community (imam). However, his right is understood to ...
.
History
The history of Islam in Eritrea can be traced back to the beginnings of the religion in the 7th century. In 615, some followers of Muhammad were said to have arrived at Massawa to seek refuge. Soon, Muslims settled in the coasts of Eritrea and built mosques and other structures. However, it was until the early 8th century when the influence of Islam began to be strongly felt. The late 7th and early 8th centuries witnessed the rise of Islamic kingdoms in the Eritrean coast. By the 9th century, Islam had spread to the eastern coasts of Eritrea and some indigenous groups in the region began adopting the religion.In the late 11th century, a Muslimsultanate
Sultan (; ', ) is a Royal and noble ranks, position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". La ...
was founded in Dahlak, which was a prosperous kingdom that had trading contacts with Ethiopia, Yemen, India, and Egypt. By the 13th century, numerous nomadic groups in Eritrea began adopting Islam and helped further propagate the faith. By the 15th century, Islam was well established and integrated among many Eritreans.
Islam later spread in Eritrea under the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Centr ...
when ethnic groups like the Tigre people
The Tigre people ( and ) are an ethnic group indigenous to Eritrea. They mainly inhabit the lowlands and northern highlands of Eritrea, with a small population in Sudan.
History
The Tigre are a nomadic agro-pastoralist community living in the ...
in mainland Eritrea began converting to Islam. Many of the inland Tigres converted to Islam in the 19th century as well as some of the Bilen. In the late 19th century, during the reign of Emperor Yohannes IV, who was a devoutly Christian Tigrayan, Muslim Tigrayans were forcibly expelled from their homes and found refuge in the nearby northern areas in what is now Eritrea, out of reach of royal Ethiopian authority.
Judaism
Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
had a heavy presence in Eritrea. Those who refused to embrace the new religion were compelled to seek refuge in the mountains of southern Ethiopia. This explains the concentration of Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
known as Beta Israel
Beta Israel, or Ethiopian Jews, is a Jewish group originating from the territory of the Amhara Region, Amhara and Tigray Region, Tigray regions in northern Ethiopia, where they are spread out across more than 500 small villages over a wide ter ...
or ''Falasha'' in Gondar
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on ...
, Ethiopia and southern Tigray. However, there was not much oppression against ethnic Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
.
The present Eritrean Jewish community is believed to be started by Yemenite Jews
Yemenite Jews, also known as Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ; ), are a Jewish diaspora group who live, or once lived, in Yemen, and their descendants maintaining their customs. After several waves of antisemitism, persecution, the vast majority ...
from Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
attracted by new commercial opportunities driven by Italian colonial expansion in the late 19th century. The Jewish population then later increased from European refugees coming to Eritrea to escape the anti-Semitic
Antisemitism or Jew-hatred is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who harbours it is called an antisemite. Whether antisemitism is considered a form of racism depends on the school of thought. Antisemi ...
regimes in Europe at the time. Many emigrated to Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
in 1948. During British administration, Eritrea was often used as a location of exile for Irgun
The Irgun (), officially the National Military Organization in the Land of Israel, often abbreviated as Etzel or IZL (), was a Zionist paramilitary organization that operated in Mandatory Palestine between 1931 and 1948. It was an offshoot of th ...
and Lehi guerrillas. Among those imprisoned were future Israeli prime minister Yitzhak Shamir
Yitzhak Shamir (, ; born Yitzhak Yezernitsky; October 22, 1915 – June 30, 2012) was an Israeli politician and the seventh prime minister of Israel, serving two terms (1983–1984, 1986–1992). Before the establishment of the State of Israel, ...
and Haim Corfu
Haim Corfu (; 6 January 1921 – 23 February 2015) was an Israeli politician, and earlier Irgun commander and assassin.
Biography
Corfu was born in Jerusalem in 1921 to an ultra-Orthodox family. He studied in religious schools and yeshivas and ...
, a founder of Beitar Jerusalem
Beitar Jerusalem Football Club (), commonly known as Beitar Jerusalem () or simply Beitar (), is an Israeli professional football club based in the city of Jerusalem, that plays in the Israeli Premier League, the top tier in Israeli football ...
. In 1961 the Eritrean War of Independence
The Eritrean War of Independence was an War, armed conflict and insurgency aimed at achieving self-determination and independence for Eritrea from Ethiopian rule. Starting in 1961, Eritrean insurgents engaged in guerrilla warfare to liberate ...
began after Eritrea was annexed by Ethiopia. It was then that Jews began to leave Eritrea. In the early 1970s, Jewish emigration increased because of ensuing violence between Eritrea and Ethiopia (up to and beyond Eritrea's official declaration of independence in 1993). Judaism is not one of the four religions recognized by the Eritrean government and indeed, as of 2006 there was only one last native Jew left in Eritrea – Sami Cohen, who tends to the Asmara Synagogue and cemetery.
Religious affiliation by geography and by ethnic group
According to a 2018 report from theUnited States Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an United States federal executive departments, executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy of the United State ...
, the population in southern and central Eritrea is primarily Christian, while the population of northern Eritrea is primarily Muslim. According to that same report, the Tigrinya Tigrinya may refer to:
* Tigrinya language
Tigrinya, sometimes romanized as Tigrigna, is an Ethio-Semitic languages, Ethio-Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It i ...
ethnic group are primarily Christian, while the Tigre and the Rashaida
The Rashaida (), also known as Bani Rasheed, are a Bedouin ethnic group inhabiting the coastal plain of the Red Sea stretching from the Sudanese city of Port Sudan to the Eritrean city of Massawa. They are the descendants of Arab tribes people f ...
groups are primarily Muslim.
The majority of Christians are found in the Eritrean Highlands
The Eritrean Highlands are a mountainous region in central Eritrea. Bordered to the south by the Mareb River, it is a northern continuation of the Ethiopian Highlands. The region has seen tremendous deforestation since the colonial period, wh ...
found in southern, central and parts of northern Eritrea. A majority of the Tigrinya who constitute almost 60% of the population are Christian. The majority of the Kunama are Catholic, with a small minority of Muslims and some who practice traditional indigenous religions. Approximately 40% of the Bilen are Christian, the majority being Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.
The majority of Muslims in Eritrea inhabit the eastern, coastal lowlands as well as the western lowlands near the border with Sudan
Sudan, officially the Republic of the Sudan, is a country in Northeast Africa. It borders the Central African Republic to the southwest, Chad to the west, Libya to the northwest, Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the east, Eritrea and Ethiopi ...
. Most belong to various Afroasiatic communities, especially the Tigre, Saho, Afar, Rashaida
The Rashaida (), also known as Bani Rasheed, are a Bedouin ethnic group inhabiting the coastal plain of the Red Sea stretching from the Sudanese city of Port Sudan to the Eritrean city of Massawa. They are the descendants of Arab tribes people f ...
, Beja and Bilen ethnic groups. About 5% of the Tigrinya Tigrinya may refer to:
* Tigrinya language
Tigrinya, sometimes romanized as Tigrigna, is an Ethio-Semitic languages, Ethio-Semitic language, which is a subgrouping within the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages. It i ...
are also Muslims; they are known as the Jeberti, though they claim a different ethnic background from the Biher-Tigrinya; the Rashaida are an Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
tribe who migrated from the Hejaz region of Saudi Arabia in the 19th century. Additionally, the majority of the Nilo-Saharan
The Nilo-Saharan languages are a proposed family of around 210 African languages spoken by somewhere around 70 million speakers, mainly in the upper parts of the Chari and Nile rivers, including historic Nubia, north of where the two tributari ...
-speaking Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an independent agency of the United States government within the executive branch, charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It is also task ...
ethnic minorities also adhere to Islam, as do some of the Kunama Nilotes.
Legal framework and restrictions
The Eritrean constitution provides for the freedom of thought, conscience, and belief; and guarantees the right to practice and manifest any religion. The constitution has not been implemented since its ratification in 1997. Since the constitution has not been implemented, the Proclamation to legally standardize and articulate religious institutions and activities is provided in Proclamation No. 73/1995 of 1995. Although Proclamation No. 73/1995 clearly enshrines the strict principle of secularism, it also states that every Eritrean national's right of freedom of thought, conscience and belief is guaranteed and respected by the law. However, Proclamation No. 73/1995 also defines that: 1) religious activities are not spread with seduction but with understanding and belief (thus explaining the hostile stance toward new religious movement and evangelical Christian group proselytism); and that 2) religious activities are carried out in accordance with and respects the law of the nation and particularly preserves the peace, stability, and unity of the people and the country. Moreover, the Proclamation is also clear on the fact that (due to the secular principles) the relation as between the government and religion and religious institutions, as well as policies that deal with religious institutions should be formulated in accordance with the law. Pursuant to this Proclamation there is the establishment of the Department of Religious Affairs within the Ministry of Internal Affairs. This is tasked with regulating religious activities and institutions. The Proclamation emphasizes that religions and religious institutions must not engage in political activities or comment on political issues which would hamper the secular character of the State. The decree additionally prohibits religious groups from initiating or offering social services based on sectarian parameters. The Proclamation requires religious groups to register with the government or cease activities. Members of religious groups that are unregistered or otherwise not in compliance with the law are subject to penalties under the provisional penal code. The Office of Religious Affairs has authority to regulate religious activities and institutions, including approval of the applications of religious groups seeking official recognition. Religious groups must renew their registration every year. In 2002, the Roman Catholic Church and the Evangelical Lutheran Church of Eritrea (affiliated with theLutheran World Federation
The Lutheran World Federation (LWF; ) is a global Communion (religion), communion of national and regional Lutheran denominations headquartered in the Ecumenical Centre in Geneva, Switzerland. The federation was founded in the Swedish city of L ...
) were required to submit registration applications and cease religious activities and services until applications were approved.
Treatment of unregistered religious groups
On 25 October 1994, the government revoked the business licenses ofJehovah’s Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a Christian denomination that is an outgrowth of the Bible Student movement founded by Charles Taze Russell in the nineteenth century. The denomination is nontrinitarian, millenarian, and restorationist. Russell co- ...
due to their refusal to recognize “the temporal government” and take part in the referendum on independence. Jehovah's Witnesses have also refused to participate in national service. Political neutrality and conscientious objection to military service are key aspects of faith for Jehovah’s Witnesses. While national service in Eritrea does include a civil component, all Eritreans are required to undertake military training and Eritreans cannot generally choose which type of service they will perform. Since the decree was issued, Jehovah’s Witnesses have been barred from obtaining government-issued identity and travel documents (required for legal recognition of marriages or land purchases); or obtaining government jobs; as well as securing business licenses.
Persecution of Jehovah's Witnesses
Fifty-four of Jehovah’s Witnesses are currently (2016) imprisoned in Eritrea. Over the past 22 years (since 1994), all except one have been held without formal charges or a hearing. Three have been in prison since 1994. On September 27, 2024, Eritrean authorities raided a private home where a meeting of Jehovah’s Witnesses was being held. The police made 24 arrests: 6 brothers, 16 sisters, and 2 minor children. Three days later, the authorities returned and arrested the 85-year-old sister who lives in the home. The 2 minor children were later released, while the 23 adults were transferred to the Mai Serwa Prison./ref>
References
{{Africa religion Religion in Eritrea,