Frank Gray (researcher) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Frank Gray (13 September 1887 – 23 May 1969) was a physicist and researcher at
 With Herbert E. Ives as co-inventor, Gray filed for two US patents in 1927: "Electro-optical system" (US 2,037,471, issued 14 April 1936) and "Electro-optical transmission" (US 1,759,504, issued 20 May 1930), and one in just his own name: "Television system" (US 2,113,254, issued 5 April 1938). He patented many other similar-sounding inventions over the years that followed.
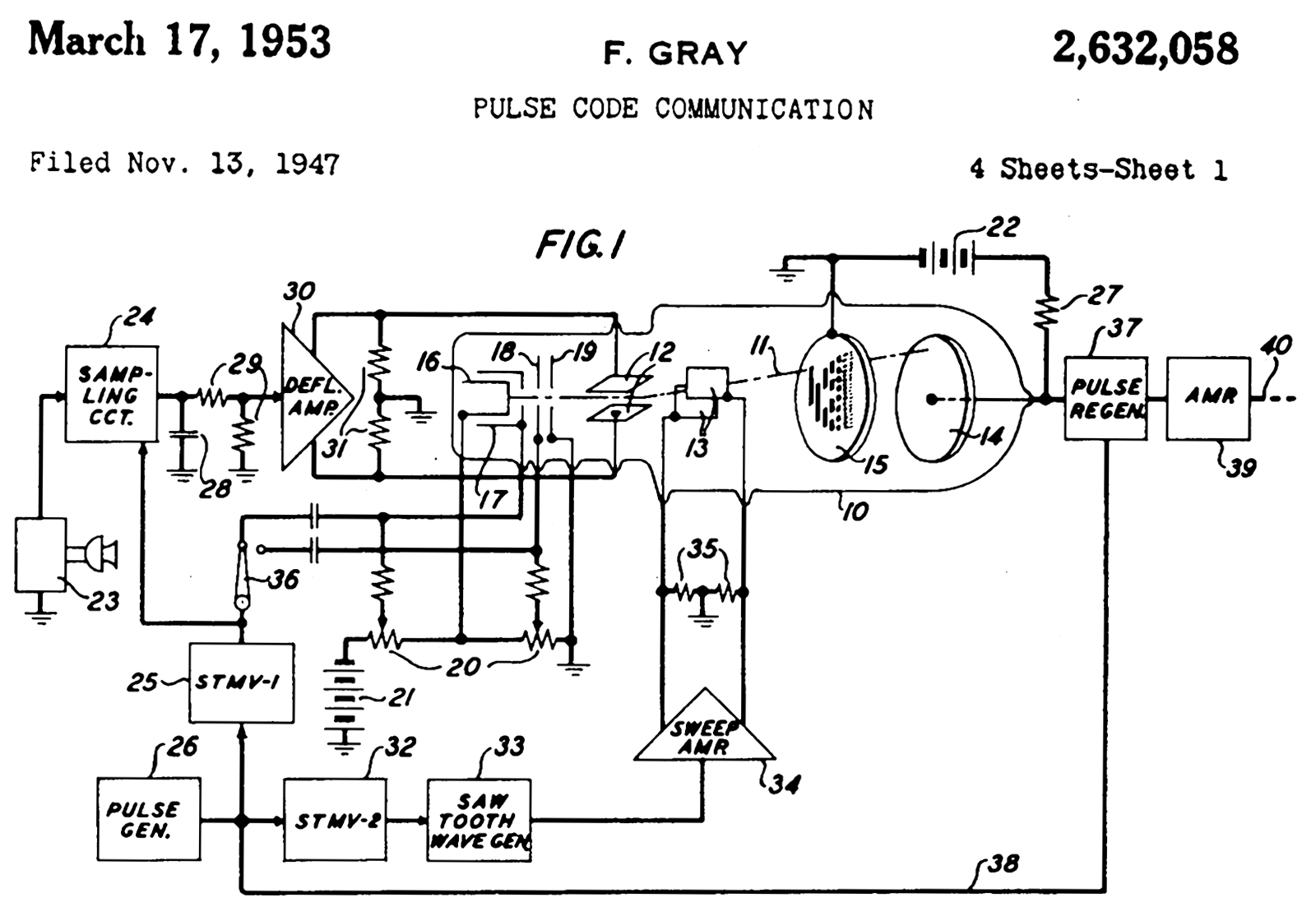
His 1953 patent "Pulse Code Communication" with the Gray code was filed in 1947.
With Herbert E. Ives as co-inventor, Gray filed for two US patents in 1927: "Electro-optical system" (US 2,037,471, issued 14 April 1936) and "Electro-optical transmission" (US 1,759,504, issued 20 May 1930), and one in just his own name: "Television system" (US 2,113,254, issued 5 April 1938). He patented many other similar-sounding inventions over the years that followed.
His 1953 patent "Pulse Code Communication" with the Gray code was filed in 1947.
Science Newsletter, 16 April 1927 (reproduced at Science News Online)
"How New Television Process Works" with Gray's flying-spot scanner innovation
1930 booklet by AT&T, wit
photo of Frank Gray
1887 births 1969 deaths 20th-century American physicists Television pioneers Scientists at Bell Labs {{US-engineer-stub
Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, commonly referred to as ''Bell Labs'', is an American industrial research and development company owned by Finnish technology company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, Murray Hill, New Jersey, the compa ...
who made numerous innovations in television, both mechanical and electronic, and is remembered for the Gray code
The reflected binary code (RBC), also known as reflected binary (RB) or Gray code after Frank Gray (researcher), Frank Gray, is an ordering of the binary numeral system such that two successive values differ in only one bit (binary digit).
For ...
.
The Gray code, or reflected binary code (RBC), appearing in Gray's 1953 patent, is a binary numeral system
A binary number is a number expressed in the base-2 numeral system or binary numeral system, a method for representing numbers that uses only two symbols for the natural numbers: typically "0" ( zero) and "1" ( one). A ''binary number'' may als ...
often used in electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, but with many applications in mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
.
Gray conducted pioneering research on the development of television
Television (TV) is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. Additionally, the term can refer to a physical television set rather than the medium of transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertising, ...
; he proposed an early form of " flying spot scanner" for early TV systems in 1927, and helped develop a two-way mechanically scanned TV system in 1930.
With Pierre Mertz, Gray wrote the classic paper on the mathematics of raster scan
A raster scan, or raster scanning, is the rectangular pattern of image capture and reconstruction in television. By analogy, the term is used for raster graphics, the pattern of image storage and transmission used in most computer bitmap image s ...
systems in 1934. He later participated in the early days of the digital revolution, with Raymond W. Sears, William M. Goodall, John Robinson Pierce
John Robinson Pierce (March 27, 1910 – April 2, 2002), was an American engineer and author. He did extensive work concerning radio communication, microwave technology, computer music, psychoacoustics, and science fiction. Additionally to hi ...
, and others at Bell Labs, by providing the binary code used by Sears in his PCM tube, a beam deflection tube of the type that Sears and Pierce collaborated on, which was used in Goodall's "Television by pulse code modulation".
Early life
Gray graduated fromPurdue University
Purdue University is a Public university#United States, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, United States, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded ...
in 1911 with a degree in Physics.
Patents
 With Herbert E. Ives as co-inventor, Gray filed for two US patents in 1927: "Electro-optical system" (US 2,037,471, issued 14 April 1936) and "Electro-optical transmission" (US 1,759,504, issued 20 May 1930), and one in just his own name: "Television system" (US 2,113,254, issued 5 April 1938). He patented many other similar-sounding inventions over the years that followed.
His 1953 patent "Pulse Code Communication" with the Gray code was filed in 1947.
With Herbert E. Ives as co-inventor, Gray filed for two US patents in 1927: "Electro-optical system" (US 2,037,471, issued 14 April 1936) and "Electro-optical transmission" (US 1,759,504, issued 20 May 1930), and one in just his own name: "Television system" (US 2,113,254, issued 5 April 1938). He patented many other similar-sounding inventions over the years that followed.
His 1953 patent "Pulse Code Communication" with the Gray code was filed in 1947.
References
External links
Science Newsletter, 16 April 1927 (reproduced at Science News Online)
"How New Television Process Works" with Gray's flying-spot scanner innovation
1930 booklet by AT&T, wit
photo of Frank Gray
1887 births 1969 deaths 20th-century American physicists Television pioneers Scientists at Bell Labs {{US-engineer-stub