Fossa Regia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
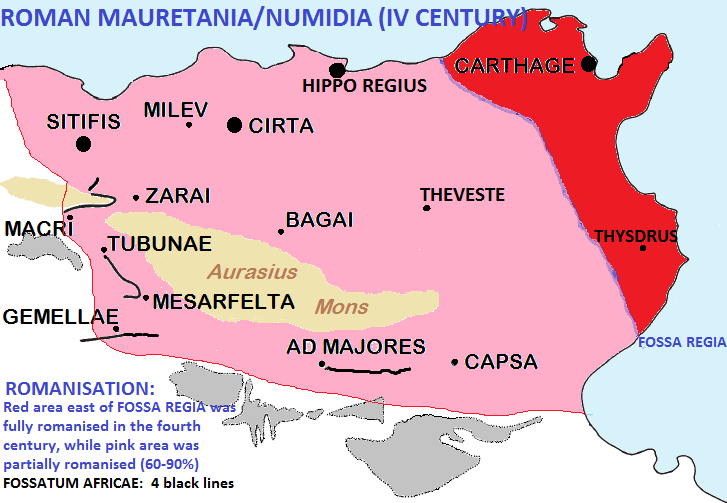 The Fossa Regia, also called the ''Fosse Scipio'', was the first part of the Limes Africanus to be built in Roman
The Fossa Regia, also called the ''Fosse Scipio'', was the first part of the Limes Africanus to be built in Roman
 The Fossa was dug by the Romans after their final conquest of Carthage at the end of the
The Fossa was dug by the Romans after their final conquest of Carthage at the end of the Camps: "Fossa Regia" (in French)
/ref> was fully Romanized with one third of the population made of Italic colonists and their descendants, according to historian
 The Fossa Regia, also called the ''Fosse Scipio'', was the first part of the Limes Africanus to be built in Roman
The Fossa Regia, also called the ''Fosse Scipio'', was the first part of the Limes Africanus to be built in Roman Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
. It was used to divide the Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–196 ...
kingdom of Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
from the territory of Carthage that was conquered by the Romans in the second century BC.
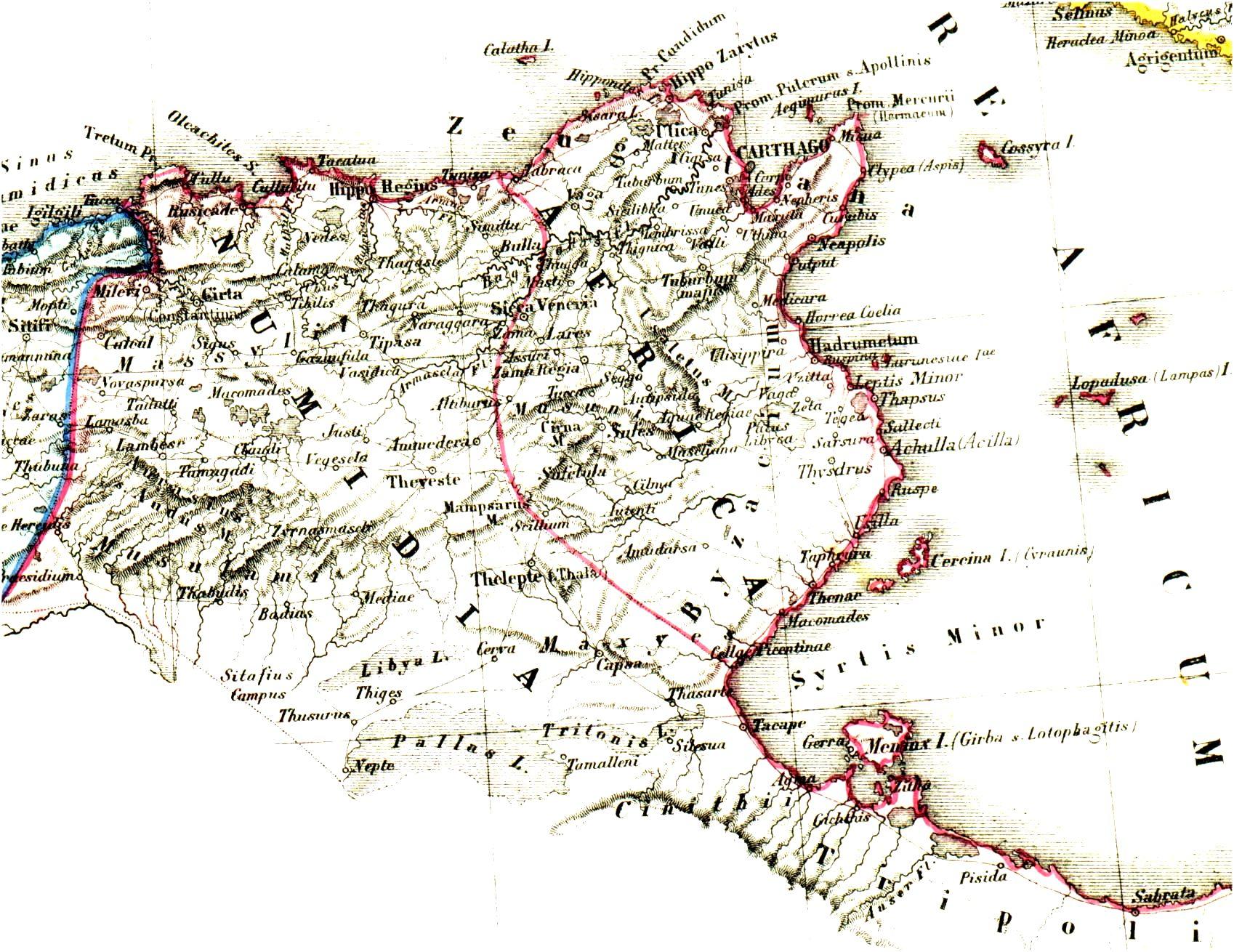
It was an irregular ditch "from Thabraca on the northern coast to Thaenae
Thenae or Thenai (), also written Thaena and Thaenae, was a Carthaginian and Roman town (') located in or near Thyna, now a suburb of Sfax on the Mediterranean coast of southeastern Tunisia.
Name
The city was founded with the Punic name ( ...
on the south-eastern coast".
History
 The Fossa was dug by the Romans after their final conquest of Carthage at the end of the
The Fossa was dug by the Romans after their final conquest of Carthage at the end of the Third Punic War
The Third Punic War (149–146 BC) was the third and last of the Punic Wars fought between Carthage and Rome. The war was fought entirely within Carthaginian territory, in what is now northern Tunisia. When the Second Punic War ended in 20 ...
in 146 BC. The construction's primary purpose was administrative, not military. It delineated the limits of the newly created Roman province of Africa
Africa was a Roman province on the northern coast of the continent of Africa. It was established in 146 BC, following the Roman Republic's conquest of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisi ...
marking the border between the Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( ) was the era of Ancient Rome, classical Roman civilisation beginning with Overthrow of the Roman monarchy, the overthrow of the Roman Kingdom (traditionally dated to 509 BC) and ending in 27 BC with the establis ...
and its then ally Numidia
Numidia was the ancient kingdom of the Numidians in northwest Africa, initially comprising the territory that now makes up Algeria, but later expanding across what is today known as Tunisia and Libya. The polity was originally divided between ...
.
After the end of Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected ret ...
in 46 BC, the western part of the ''Fossa regia'' served as the boundary between the province of ''Nova Africa'', to its west, and the province of ''Africa Vetus'' to its east. Even after these two provinces were merged into Proconsular Africa
Africa was a Roman province on the northern coast of the continent of Africa. It was established in 146 BC, following the Roman Republic's conquest of Carthage in the Third Punic War. It roughly comprised the territory of present-day Tunisi ...
in 27 BC, the ditch continued to be maintained as late as the year 74 AD under Vespasian
Vespasian (; ; 17 November AD 9 – 23 June 79) was Roman emperor from 69 to 79. The last emperor to reign in the Year of the Four Emperors, he founded the Flavian dynasty, which ruled the Empire for 27 years. His fiscal reforms and consolida ...
as shown by many stone marker posts that have been found.
East of ''Fossa regia'' there was full Latinization of the local society after Trajan
Trajan ( ; born Marcus Ulpius Traianus, 18 September 53) was a Roman emperor from AD 98 to 117, remembered as the second of the Five Good Emperors of the Nerva–Antonine dynasty. He was a philanthropic ruler and a successful soldier ...
. Under Theodosius Theodosius ( Latinized from the Greek "Θεοδόσιος", Theodosios, "given by god") is a given name. It may take the form Teodósio, Teodosie, Teodosije etc. Theodosia is a feminine version of the name.
Emperors of ancient Rome and Byzantium
...
that area/ref> was fully Romanized with one third of the population made of Italic colonists and their descendants, according to historian
Theodore Mommsen
Christian Matthias Theodor Mommsen (; ; 30 November 1817 – 1 November 1903) was a Germans, German classics, classical scholar, historian, jurist, journalist, politician and archaeologist. He is widely regarded as one of the greatest classicis ...
. The other two thirds were Romanized Berbers, all Christians and nearly all Latin speaking.
See also
*Fossatum Africae
''Fossatum Africae'' ("African ditch") is one or more linear defensive structures (sometimes called Limes (Roman Empire), ''limes'') claimed to extend over or more in North Africa, northern Africa constructed during the Roman Empire to defend an ...
* Limes Tripolitanus
The ''Limes Tripolitanus'' was a frontier zone of defence of the Roman Empire, built in the south of what is now Tunisia and the northwest of Libya. It was primarily intended as a protection for the tripolitanian cities of Leptis Magna, Sabrath ...
References
{{ReflistBibliography
* G. Di Vita-Evrard: ''La Fossa Regia et les diocèses d'Afrique proconsulaire''. In: A. Mastino (Hrsg.): L'Africa romana. Atti del III convegno di studio, 1986 * Mommsen, Theodore. ''The Provinces of the Roman Empire'' Section: Roman Africa. Ed. Barnes & Noble. New York, 2004 Africa (Roman province)