Forest Global Earth Observatory Network on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
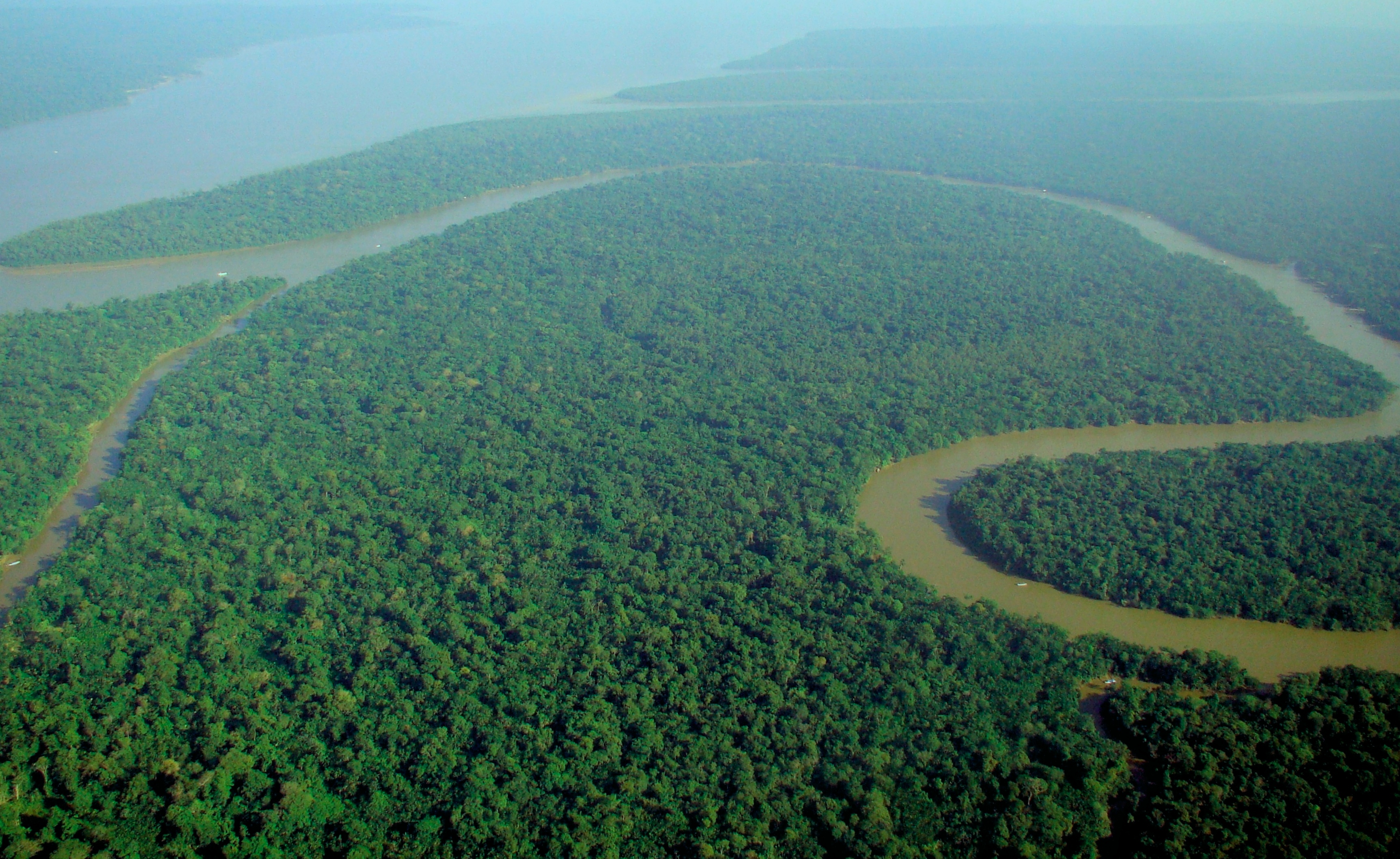 A forest is an
A forest is an
 Although the word ''forest'' is commonly used, there is no universally recognised precise definition, with more than 800 definitions of forest used around the world. Although a forest is usually defined by the presence of trees, under many definitions an area completely lacking trees may still be considered a forest if it grew trees in the past, will grow trees in the future, or was legally designated as a forest regardless of vegetation type.
There are three broad categories of definitions of forest in use: administrative,
Although the word ''forest'' is commonly used, there is no universally recognised precise definition, with more than 800 definitions of forest used around the world. Although a forest is usually defined by the presence of trees, under many definitions an area completely lacking trees may still be considered a forest if it grew trees in the past, will grow trees in the future, or was legally designated as a forest regardless of vegetation type.
There are three broad categories of definitions of forest in use: administrative,
 The word ''
The word ''
 A forest is an
A forest is an ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
characterized by a dense community
A community is a social unit (a group of people) with a shared socially-significant characteristic, such as place, set of norms, culture, religion, values, customs, or identity. Communities may share a sense of place situated in a given g ...
of tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
s. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
(FAO) defines a forest as, "Land spanning more than 0.5 hectares with trees higher than 5 meters and a canopy
Canopy may refer to:
Plants
* Canopy (biology), aboveground portion of plant community or crop (including forests)
* Canopy (grape), aboveground portion of grapes
Religion and ceremonies
* Baldachin or canopy of state, typically placed over an a ...
cover of more than 10 percent, or trees able to reach these thresholds ''in situ
is a Latin phrase meaning 'in place' or 'on site', derived from ' ('in') and ' ( ablative of ''situs'', ). The term typically refers to the examination or occurrence of a process within its original context, without relocation. The term is use ...
''. It does not include land that is predominantly under agricultural or urban use." Using this definition, '' Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'' found that forests covered , or approximately 31 percent of the world's land area in 2020.
Forests are the largest terrestrial ecosystems of Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to Planetary habitability, harbor life. This is enabled by Earth being an ocean world, the only one in the Solar System sustaining liquid surface water. Almost all ...
by area, and are found around the globe. 45 percent of forest land is in the tropical latitudes. The next largest share of forests are found in subarctic climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a continental climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of ...
s, followed by temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
, and subtropic
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones immediately to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 3 ...
al zones.
Forests account for 75% of the gross primary production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through ...
of the Earth's biosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
, and contain 80% of the Earth's plant biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
. Net primary production is estimated at 21.9 gigatonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the sh ...
s of biomass per year for tropical forest
Tropical forests are forested ecoregions with tropical climates – that is, land areas approximately bounded by the Tropic of Cancer, tropics of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn, Capricorn, but possibly affected by other factors such as prevailing ...
s, 8.1 for temperate forest
A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest terrestrial biome, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers about 3 ...
s, and 2.6 for boreal forest
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by pinophyta, coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. I ...
s.
Forests form distinctly different biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s at different latitudes and elevations, and with different precipitation and evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration (ET) refers to the combined processes which move water from the Earth's surface (open water and ice surfaces, bare soil and vegetation) into the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere. It covers both water evaporation (movement of w ...
rates. These biomes include boreal forests in subarctic climates, tropical moist forests
Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests (TSMF), also known as tropical moist forest, is a subtropical and tropical forest habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF).
Description
TSMF is generally found in large ...
and tropical dry forests
The tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forest is a habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature and is located at tropical and subtropical latitudes. Though these forests occur in climates that are warm year-round, and may receive ...
around the Equator
The equator is the circle of latitude that divides Earth into the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Southern Hemisphere, Southern Hemispheres of Earth, hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, about in circumferen ...
, and temperate forest
A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest terrestrial biome, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers about 3 ...
s at the middle latitudes
The middle latitudes, also called the mid-latitudes (sometimes spelled midlatitudes) or moderate latitudes, are spatial regions on either Hemispheres of Earth, hemisphere of Earth, located between the Tropic of Cancer (latitude ) and the Arctic ...
. Forests form in areas of the Earth with high rainfall, while drier conditions produce a transition to savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
. However, in areas with intermediate rainfall levels, forest transitions to savanna rapidly when the percentage of land that is covered by trees drops below 40 to 45 percent. Research conducted in the Amazon rainforest
The Amazon rainforest, also called the Amazon jungle or Amazonia, is a Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, moist broadleaf tropical rainforest in the Amazon biome that covers most of the Amazon basin of South America. This basin ...
shows that trees can alter rainfall rates across a region, releasing water from their leaves in anticipation of seasonal rains to trigger the wet season early. Because of this, seasonal rainfall in the Amazon begins two to three months earlier than the climate would otherwise allow. Deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal and destruction of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. Ab ...
in the Amazon and anthropogenic climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
hold the potential to interfere with this process, causing the forest to pass a threshold where it transitions into savanna.
Deforestation threatens many forest ecosystems. Deforestation occurs when humans remove trees from a forested area by cutting or burning, either to harvest timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
or to make way for farming. Most deforestation today occurs in tropical forests. The vast majority of this deforestation is because of the production of four commodities: wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin t ...
, beef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus''). Beef can be prepared in various ways; Cut of beef, cuts are often used for steak, which can be cooked to varying degrees of doneness, while trimmings are often Ground beef, grou ...
, soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean. Soy is a staple crop, the world's most grown legume, and an important animal feed.
Soy is a key source of f ...
, and palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 36% of global oils produced from o ...
. Over the past 2,000 years, the area of land covered by forest in Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
has been reduced from 80% to 34%. Large areas of forest have also been cleared in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
and in the eastern United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, in which only 0.1% of land was left undisturbed. Almost half of Earth's forest area (49 percent) is relatively intact, while 9 percent is found in fragments with little or no connectivity. Tropical rainforests and boreal coniferous forests are the least fragmented, whereas subtropical dry forests and temperate oceanic forests are among the most fragmented. Roughly 80 percent of the world's forest area is found in patches larger than . The remaining 20 percent is located in more than 34 million patches around the world – the vast majority less than in size.
Human society and forests can affect one another positively or negatively. Forests provide ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
to humans and serve as tourist attractions. Forests can also affect people's health. Human activities, including unsustainable use of forest resources, can negatively affect forest ecosystems.
Definitions
 Although the word ''forest'' is commonly used, there is no universally recognised precise definition, with more than 800 definitions of forest used around the world. Although a forest is usually defined by the presence of trees, under many definitions an area completely lacking trees may still be considered a forest if it grew trees in the past, will grow trees in the future, or was legally designated as a forest regardless of vegetation type.
There are three broad categories of definitions of forest in use: administrative,
Although the word ''forest'' is commonly used, there is no universally recognised precise definition, with more than 800 definitions of forest used around the world. Although a forest is usually defined by the presence of trees, under many definitions an area completely lacking trees may still be considered a forest if it grew trees in the past, will grow trees in the future, or was legally designated as a forest regardless of vegetation type.
There are three broad categories of definitions of forest in use: administrative, land use
Land use is an umbrella term to describe what happens on a parcel of land. It concerns the benefits derived from using the land, and also the land management actions that humans carry out there. The following categories are used for land use: fo ...
, and land cover
Land cover is the physical material at the land surface of Earth. Land covers include flora, concrete, built structures, bare ground, and temporary water. Earth cover is the expression used by ecologist Frederick Edward Clements that has as ...
. Administrative definitions are legal designations, and may not reflect the type of vegetation that grows upon the land; an area can be legally designated "forest" even if no trees grow on it. Land-use definitions are based on the primary purpose the land is used for. Under a land-use definition, any area used primarily for harvesting timber, including areas that have been cleared by harvesting, disease, fire, or for the construction of roads and infrastructure, are still defined as forests, even if they contain no trees. Land-cover definitions define forests based upon the density of trees, area of tree canopy
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only p ...
cover, or area of the land occupied by the cross-section of tree trunks (basal area
Basal area is the cross-sectional area of trees at breast height (1.3m or 4.5 ft above ground). It is a common way to describe stand density. In forest management, basal area usually refers to merchantable timber and is given on a per hectare ...
) meeting a particular threshold. This type of definition depends upon the presence of trees sufficient to meet the threshold, or at least of immature trees that are expected to meet the threshold once they mature.
Under land-cover definitions, there is considerable variation on where the cutoff points are between a forest, woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
, and savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
. Under some definitions, to be considered a forest requires very high levels of tree canopy cover, from 60% to 100%, which excludes woodlands and savannas, which have a lower canopy cover
Crown closure, in forestry, is a measure of forest canopy coverage. Crown closure and crown cover are two slightly different measures of the forest canopy and that determine the amount of light able to penetrate to the forest floor.
Crown closu ...
. Other definitions consider savannas to be a type of forest, and include all areas with tree canopies over 10%.
Some areas covered with trees are legally defined as agricultural areas, for example Norway spruce
''Picea abies'', the Norway spruce or European spruce, is a species of spruce native to Northern, Central and Eastern Europe.
It has branchlets that typically hang downwards, and the largest cones of any spruce, 9–17 cm long. It is very clo ...
plantations, under Austrian forest law, when the trees are being grown as Christmas trees and are below a certain height.
Etymology
 The word ''
The word ''forest
A forest is an ecosystem characterized by a dense ecological community, community of trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, ...
'' derives from the Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th
 A forest consists of many components that can be broadly divided into two categories: biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living). The living parts include
A forest consists of many components that can be broadly divided into two categories: biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living). The living parts include
 The main layers of all forest types are the forest floor, the understory, and the canopy. The emergent layer, above the canopy, exists in tropical rainforests. Each layer has a different set of plants and animals, depending upon the availability of sunlight, moisture, and food.
* The Forest floor is covered in dead plant material such as fallen leaves and decomposing logs, which detritivores break down into new soil. The layer of decaying leaves that covers the soil is necessary for many insects to overwinter and for amphibians, birds, and other animals to shelter and forage for food. Leaf litter also keeps the soil moist, stops erosion, and protects roots against extreme heat and cold. The Fungi, fungal mycelium that helps form the mycorrhizal network transmits nutrients from decaying material to trees and other plants. The forest floor supports a variety of plants, ferns, grasses, and tree seedlings, as well as animals such as ants, amphibians, spiders, and millipedes.
* Understory is made up of bushes, shrubs, and young trees that are adapted to living in the shade of the canopy.
* Canopy is formed by the mass of intertwined branches, twigs, and leaves of mature trees. The crowns of the dominant trees receive most of the sunlight. This is the most productive part of the trees, where maximum food is produced. The canopy forms a shady, protective "umbrella" over the rest of the forest.
* Emergent layer exists in a tropical rain forest and is composed of a few scattered trees that tower over the canopy.
In botany and countries like Germany and Poland, a different classification of forest vegetation is often used: tree, shrub, herb, and moss layers (see stratification (vegetation)).
The main layers of all forest types are the forest floor, the understory, and the canopy. The emergent layer, above the canopy, exists in tropical rainforests. Each layer has a different set of plants and animals, depending upon the availability of sunlight, moisture, and food.
* The Forest floor is covered in dead plant material such as fallen leaves and decomposing logs, which detritivores break down into new soil. The layer of decaying leaves that covers the soil is necessary for many insects to overwinter and for amphibians, birds, and other animals to shelter and forage for food. Leaf litter also keeps the soil moist, stops erosion, and protects roots against extreme heat and cold. The Fungi, fungal mycelium that helps form the mycorrhizal network transmits nutrients from decaying material to trees and other plants. The forest floor supports a variety of plants, ferns, grasses, and tree seedlings, as well as animals such as ants, amphibians, spiders, and millipedes.
* Understory is made up of bushes, shrubs, and young trees that are adapted to living in the shade of the canopy.
* Canopy is formed by the mass of intertwined branches, twigs, and leaves of mature trees. The crowns of the dominant trees receive most of the sunlight. This is the most productive part of the trees, where maximum food is produced. The canopy forms a shady, protective "umbrella" over the rest of the forest.
* Emergent layer exists in a tropical rain forest and is composed of a few scattered trees that tower over the canopy.
In botany and countries like Germany and Poland, a different classification of forest vegetation is often used: tree, shrub, herb, and moss layers (see stratification (vegetation)).
 Forests are classified differently and to different degrees of specificity. One such classification is in terms of the
Forests are classified differently and to different degrees of specificity. One such classification is in terms of the
 Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests include a substantial component of trees of the Anthophyta group. They are generally characteristic of the warmer temperate latitudes, but extend to cool temperate ones, particularly in the southern hemisphere. They include such forest types as the mixed deciduous forests of the United States and their counterparts in China and Japan; the broadleaf evergreen rainforests of Japan, Chile, and Tasmania; the sclerophyllous forests of Australia, central Chile, the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean, and California; and the southern beech Nothofagus forests of Chile and New Zealand.
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests include a substantial component of trees of the Anthophyta group. They are generally characteristic of the warmer temperate latitudes, but extend to cool temperate ones, particularly in the southern hemisphere. They include such forest types as the mixed deciduous forests of the United States and their counterparts in China and Japan; the broadleaf evergreen rainforests of Japan, Chile, and Tasmania; the sclerophyllous forests of Australia, central Chile, the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean, and California; and the southern beech Nothofagus forests of Chile and New Zealand.
 The annual net loss of forest area has decreased since 1990, but the world is not on track to meet the target of the United Nations Strategic Plan for Forests to increase forest area by 3 percent by 2030.
While deforestation is taking place in some areas, new forests are being established through natural expansion or deliberate efforts in other areas. As a result, the net loss of forest area is less than the rate of deforestation; and it, too, is decreasing: from per year in the 1990s to per year during 2010–2020. In absolute terms, the global forest area decreased by between 1990 and 2020, which is an area about the size of Libya.
The annual net loss of forest area has decreased since 1990, but the world is not on track to meet the target of the United Nations Strategic Plan for Forests to increase forest area by 3 percent by 2030.
While deforestation is taking place in some areas, new forests are being established through natural expansion or deliberate efforts in other areas. As a result, the net loss of forest area is less than the rate of deforestation; and it, too, is decreasing: from per year in the 1990s to per year during 2010–2020. In absolute terms, the global forest area decreased by between 1990 and 2020, which is an area about the size of Libya.

 Forest management has changed considerably over the last few centuries, with rapid changes from the 1980s onward, culminating in a practice now referred to as ''sustainable forest management''. Forest ecologists concentrate on forest patterns and processes, usually with the aim of elucidating cause-and-effect relationships. Foresters who practice sustainable forest management focus on the integration of ecological, social, and economic values, often in Stakeholder engagement, consultation with local communities and other stakeholders.
Forest management has changed considerably over the last few centuries, with rapid changes from the 1980s onward, culminating in a practice now referred to as ''sustainable forest management''. Forest ecologists concentrate on forest patterns and processes, usually with the aim of elucidating cause-and-effect relationships. Foresters who practice sustainable forest management focus on the integration of ecological, social, and economic values, often in Stakeholder engagement, consultation with local communities and other stakeholders.
 Humans have generally decreased the amount of forest worldwide. Anthropogenic factors that can affect forests include logging, urban sprawl, human-caused forest fires, acid rain, invasive species, and the slash and burn practices of swidden agriculture or shifting cultivation. The loss and re-growth of forests lead to a distinction between two broad types of forest: primary or old-growth forest and secondary forest. There are also many natural factors that can cause changes in forests over time, including forest fires, Forest pathology#Animals, insects, Forest pathology, diseases, weather, competition between species, etc. In 1997, the World Resources Institute recorded that only 20% of the world's original forests remained in large intact tracts of undisturbed forest. More than 75% of these intact forests lie in three countries: the boreal forests of Russia and Canada, and the rainforest of Brazil.
According to
Humans have generally decreased the amount of forest worldwide. Anthropogenic factors that can affect forests include logging, urban sprawl, human-caused forest fires, acid rain, invasive species, and the slash and burn practices of swidden agriculture or shifting cultivation. The loss and re-growth of forests lead to a distinction between two broad types of forest: primary or old-growth forest and secondary forest. There are also many natural factors that can cause changes in forests over time, including forest fires, Forest pathology#Animals, insects, Forest pathology, diseases, weather, competition between species, etc. In 1997, the World Resources Institute recorded that only 20% of the world's original forests remained in large intact tracts of undisturbed forest. More than 75% of these intact forests lie in three countries: the boreal forests of Russia and Canada, and the rainforest of Brazil.
According to
 Canada has about of forest land. More than 90% of forest land is publicly owned and about 50% of the total forest area is allocated for harvesting. These allocated areas are managed using the principles of sustainable forest management, which include extensive consultation with local stakeholders. About eight percent of Canada's forest is legally protected from resource development. Much more forest land—about 40 percent of the total forest land base—is subject to varying degrees of protection through processes such as integrated land use planning or defined management areas, such as certified forests.
By December 2006, over of forest land in Canada (about half the global total) had been certified as being sustainably managed. Clearcutting, first used in the latter half of the 20th century, is less expensive, but devastating to the environment; and companies are required by law to ensure that harvested areas are adequately regenerated. Most Canadian provinces have regulations limiting the size of new clear-cuts, although some older ones grew to over several years.
The Canadian Forest Service is the government department which looks after Forests in Canada.
Canada has about of forest land. More than 90% of forest land is publicly owned and about 50% of the total forest area is allocated for harvesting. These allocated areas are managed using the principles of sustainable forest management, which include extensive consultation with local stakeholders. About eight percent of Canada's forest is legally protected from resource development. Much more forest land—about 40 percent of the total forest land base—is subject to varying degrees of protection through processes such as integrated land use planning or defined management areas, such as certified forests.
By December 2006, over of forest land in Canada (about half the global total) had been certified as being sustainably managed. Clearcutting, first used in the latter half of the 20th century, is less expensive, but devastating to the environment; and companies are required by law to ensure that harvested areas are adequately regenerated. Most Canadian provinces have regulations limiting the size of new clear-cuts, although some older ones grew to over several years.
The Canadian Forest Service is the government department which looks after Forests in Canada.
Forests in danger
Intact Forests
with maps and reports (archived 8 September 2015)
by the
Forest area is land under natural or planted stands of trees of at least 5 meters ''in situ'', whether productive or not, and excludes tree stands in agricultural production systems
Forest area (sq. km)
data from the World Bank's World Development Indicators, made available by Google * * * {{Authority control Forests, Habitats Trees Ecosystems
Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages, a group of Low Germanic languages also commonly referred to as "Frankish" varieties
* Francia, a post-Roman ...
or Old High German, of the Medieval Latin , denoting "open wood", Carolingian scribes first used ''foresta'' in the Carolingian Empire#Capitularies, capitularies of Charlemagne, specifically to denote the royal hunting grounds of the king. The word was not endemic to the Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, e.g., native words for ''forest'' in the Romance languages derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''silva'', which denoted "forest" and " wood(land)" (cf.
The abbreviation cf. (short for either Latin or , both meaning 'compare') is generally used in writing to refer the reader to other material to make a comparison with the topic being discussed. However some sources offer differing or even contr ...
the English ''sylva'' and ''sylvan''; the Italian, Spanish, and Portuguese ''selva''; the Romanian ''silvă''; the Old French ''selve''). Cognates of forest in Romance languages—e.g., the Italian ''foresta'', Spanish and Portuguese ''floresta'', etc.—are all ultimately derivations of the French word.
The precise origin of Medieval Latin is obscure. Some authorities claim the word derives from the Late Latin
Late Latin is the scholarly name for the form of Literary Latin of late antiquity.Roberts (1996), p. 537. English dictionary definitions of Late Latin date this period from the 3rd to 6th centuries CE, and continuing into the 7th century in ...
phrase ''forestam silvam'', denoting "the outer wood"; others claim the word is a Latinisation of the Frankish *''forhist'', denoting "forest, wooded country", and was assimilated to ''forestam silvam'', pursuant to the common practice of Frankish scribes. The Old High German ''forst'' denoting "forest"; Middle Low German
Middle Low German is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented in writing since about 1225–34 (). During the Hanseatic period (from about 1300 to about 1600), Mid ...
''vorst'' denoting "forest"; Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
''fyrhþ'' denoting "forest, woodland, game preserve, hunting ground" (English ''frith
Frith is a word derived from Old English meaning "peace; protection; safety, security, freedom, refuge".
Etymology
Derived from Old English ''friðu, friþ'', it is cognate to Old Norse '' friðr'', Old Saxon '' frithu'', Old High German '' ...
''); and Old Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
''fýri'', denoting "coniferous forest
Conifers () are a group of cone-bearing seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single extant class, Pinopsida. All e ...
"; all of which derive from the Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the linguistic reconstruction, reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic languages, Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from ...
*''furhísa-'', *''furhíþija-'', denoting "a fir-wood, ''coniferous'' forest", from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists; its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-Euro ...
*''perkwu-'', denoting "a ''coniferous'' or mountain forest
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher t ...
, wooded height" all attest to the Frankish *''forhist''.
Uses of ''forest'' in English to denote any uninhabited and unenclosed area are presently considered archaic. The Norman rulers of England introduced the word as a legal term, as seen in Latin texts such as Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter"), sometimes spelled Magna Charta, is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the Archbishop of Canterbury, Cardin ...
, to denote uncultivated land that was legally designated for hunting by feudal nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. T ...
(see royal forest
A royal forest, occasionally known as a kingswood (), is an area of land with different definitions in England, Wales, Scotland and Ireland. The term ''forest'' in the ordinary modern understanding refers to an area of wooded land; however, the ...
).
These hunting forests did not necessarily contain any trees. Because that often included significant areas of woodland, "forest" eventually came to connote woodland in general, regardless of tree density. By the beginning of the fourteenth century, English texts used the word in all three of its senses: common, legal, and archaic. Other English words used to denote "an area with a high density of trees" are ''firth'', ''frith'', ''holt'', ''weald'', ''wold'', ''wood'', and ''woodland''. Unlike ''forest'', these are all derived from Old English and were not borrowed from another language. Some present classifications reserve ''woodland'' for denoting a locale with more open space between trees, and distinguish kinds of woodlands as ''open forests'' and ''closed forests'', premised on their crown covers. Finally, ''sylva'' (plural ''sylvae'' or, less classically, ''sylvas'') is a peculiar English spelling of the Latin ''silva'', denoting a "woodland", and has precedent in English, including its plural forms. While its use as a synonym
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means precisely or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are a ...
of ''forest'', and as a Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
ate word denoting a woodland, may be admitted; in a specific technical sense it is restricted to denoting the ''species'' of trees that comprise the woodlands of a region, as in its sense in the subject of silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, as well as quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests ...
. The resorting to ''sylva'' in English indicates more precisely the denotation that the use of ''forest'' intends.
Evolutionary history
The first known forests on Earth arose in theMiddle Devonian
In the geological timescale, the Middle Devonian epoch (from 393.3 ± 1.2 million years ago to 382.7 ± 1.6 million years ago) occurred during the Devonian period, after the end of the Emsian age.
The Middle Devonian epoch is subdivided into two ...
(approximately 390 million years ago
Million years ago, abbreviated as Mya, Myr (megayear) or Ma (megaannum), is a unit of time equal to (i.e. years), or approximately 31.6 teraseconds.
Usage
Myr is in common use in fields such as Earth science and cosmology. Myr is also used w ...
), with the evolution of cladoxylopsid
The cladoxylopsids are an extinct group of plants related to ferns and sphenopsids.
They had a central trunk, from the top of which several lateral branches were attached. Fossils of these plants originate in the Middle Devonian to Early Carb ...
plants like ''Calamophyton
''Calamophyton'' is an extinct genus of tree, or "tree-sized plant", that was extant in the Middle Devonian period. As of 2024, a well-preserved fossilized forest of ''Calamophyton'' trees discovered in Somerset, England, represents the earliest ...
''. Appeared in the Late Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era during the Phanerozoic eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago ( Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding ...
, ''Archaeopteris
''Archaeopteris'' is an extinct genus of progymnosperm tree with fern-like leaves. A useful List of index fossils, index fossil, this tree is found in Stratum, strata dating from the Upper Devonian to Lower Carboniferous (), the oldest fossils b ...
'' was both tree-like and fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
-like plant, growing to in height or more. It quickly spread throughout the world, from the equator to subpolar latitudes. It is the first species known to cast shade due to its fronds
A frond is a large, divided leaf. In both common usage and botanical nomenclature, the leaves of ferns are referred to as fronds and some botanists restrict the term to this group. Other botanists allow the term frond to also apply to the lar ...
and forming soil from its roots. ''Archaeopteris'' was deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
, dropping its fronds onto the forest floor, the shade, soil, and forest duff from the dropped fronds creating the early forest. The shed organic matter altered the freshwater environment, slowing its flow and providing food. This promoted freshwater fish.
Ecology
Forests account for 75% of the gross primary productivity of the Earth'sbiosphere
The biosphere (), also called the ecosphere (), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be termed the zone of life on the Earth. The biosphere (which is technically a spherical shell) is virtually a closed system with regard to mat ...
, and contain 80% of the Earth's plant biomass. Biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how ...
per unit area is high compared to other vegetation communities. Much of this biomass occurs below ground in the root systems and as partially decomposed plant detritus
In biology, detritus ( or ) is organic matter made up of the decomposition, decomposing remains of organisms and plants, and also of feces. Detritus usually hosts communities of microorganisms that colonize and decomposition, decompose (Reminera ...
. The woody component of a forest contains lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidit ...
, which is relatively slow to decompose
Decomposition is the process by which dead organic substances are broken down into simpler organic or inorganic matter such as carbon dioxide, water, simple sugars and mineral salts. The process is a part of the nutrient cycle and is essen ...
compared with other organic materials such as cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the chemical formula, formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of glycosidic bond, β(1→4) linked glucose, D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important s ...
or carbohydrate. The world's forests contain about 606 gigatonnes of living biomass (above- and below-ground) and 59 gigatonnes of dead wood. The total biomass has decreased slightly since 1990, but biomass per unit area has increased.
Forest ecosystems broadly differ based on climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
; latitudes 10° north and south of the equator are mostly covered in tropical rainforest, and the latitudes between 53rd parallel north, 53°N and 67th parallel north, 67°N have boreal forest
Taiga or tayga ( ; , ), also known as boreal forest or snow forest, is a biome characterized by pinophyta, coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. The taiga, or boreal forest, is the world's largest land biome. I ...
. As a general rule, forests dominated by angiosperms (''broadleaf forests'') are more species-rich than those dominated by gymnosperms (''conifer'', ''montane'', or ''needleleaf forests''), although exceptions exist. The trees that form the principal structural and defining component of a forest may be of a great variety of species (as in tropical rainforests and temperate deciduous forests), or relatively few species over large areas (e.g., taiga and arid montane coniferous forests). The biodiversity of forests also encompasses shrubs, herbaceous plants, mosses, fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
s, lichens, fungi, and a variety of animals.
Trees rising up to in height add a vertical dimension to the area of land that can support plant and animal species, opening up numerous ecological niches for arboreal locomotion, arboreal animal species, epiphytes, and various species that thrive under the regulated microclimate created under the canopy. Forests have intricate three-dimensional structures that increase in complexity with lower levels of disturbance and greater variety of tree species.
The biodiversity of forests varies considerably according to factors such as forest type, geography, climate, and soils – in addition to human use. Most forest habitats in temperate regions support relatively few animal and plant species, and species that tend to have large geographical distributions, while the montane forests of Africa, South America, Southeast Asia, and lowland forests of Australia, coastal Brazil, the Caribbean islands, Central America, and insular Southeast Asia have many species with small geographical distributions. Areas with dense human populations and intense agricultural land use, such as Europe, parts of Bangladesh, China, India, and North America, are less intact in terms of their biodiversity. Northern Africa, southern Australia, coastal Brazil, Madagascar, and South Africa are also identified as areas with striking losses in biodiversity intactness.
Components
 A forest consists of many components that can be broadly divided into two categories: biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living). The living parts include
A forest consists of many components that can be broadly divided into two categories: biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living). The living parts include tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, e.g., including only woody plants with secondary growth, only ...
s, shrubs, vines, grasses and other herbaceous (non-woody) plants, mosses, algae, fungi, insects, mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and microorganisms living on the plants and animals and in the soil, connected by mycorrhizal networks.
Layers
 The main layers of all forest types are the forest floor, the understory, and the canopy. The emergent layer, above the canopy, exists in tropical rainforests. Each layer has a different set of plants and animals, depending upon the availability of sunlight, moisture, and food.
* The Forest floor is covered in dead plant material such as fallen leaves and decomposing logs, which detritivores break down into new soil. The layer of decaying leaves that covers the soil is necessary for many insects to overwinter and for amphibians, birds, and other animals to shelter and forage for food. Leaf litter also keeps the soil moist, stops erosion, and protects roots against extreme heat and cold. The Fungi, fungal mycelium that helps form the mycorrhizal network transmits nutrients from decaying material to trees and other plants. The forest floor supports a variety of plants, ferns, grasses, and tree seedlings, as well as animals such as ants, amphibians, spiders, and millipedes.
* Understory is made up of bushes, shrubs, and young trees that are adapted to living in the shade of the canopy.
* Canopy is formed by the mass of intertwined branches, twigs, and leaves of mature trees. The crowns of the dominant trees receive most of the sunlight. This is the most productive part of the trees, where maximum food is produced. The canopy forms a shady, protective "umbrella" over the rest of the forest.
* Emergent layer exists in a tropical rain forest and is composed of a few scattered trees that tower over the canopy.
In botany and countries like Germany and Poland, a different classification of forest vegetation is often used: tree, shrub, herb, and moss layers (see stratification (vegetation)).
The main layers of all forest types are the forest floor, the understory, and the canopy. The emergent layer, above the canopy, exists in tropical rainforests. Each layer has a different set of plants and animals, depending upon the availability of sunlight, moisture, and food.
* The Forest floor is covered in dead plant material such as fallen leaves and decomposing logs, which detritivores break down into new soil. The layer of decaying leaves that covers the soil is necessary for many insects to overwinter and for amphibians, birds, and other animals to shelter and forage for food. Leaf litter also keeps the soil moist, stops erosion, and protects roots against extreme heat and cold. The Fungi, fungal mycelium that helps form the mycorrhizal network transmits nutrients from decaying material to trees and other plants. The forest floor supports a variety of plants, ferns, grasses, and tree seedlings, as well as animals such as ants, amphibians, spiders, and millipedes.
* Understory is made up of bushes, shrubs, and young trees that are adapted to living in the shade of the canopy.
* Canopy is formed by the mass of intertwined branches, twigs, and leaves of mature trees. The crowns of the dominant trees receive most of the sunlight. This is the most productive part of the trees, where maximum food is produced. The canopy forms a shady, protective "umbrella" over the rest of the forest.
* Emergent layer exists in a tropical rain forest and is composed of a few scattered trees that tower over the canopy.
In botany and countries like Germany and Poland, a different classification of forest vegetation is often used: tree, shrub, herb, and moss layers (see stratification (vegetation)).
Types
 Forests are classified differently and to different degrees of specificity. One such classification is in terms of the
Forests are classified differently and to different degrees of specificity. One such classification is in terms of the biome
A biome () is a distinct geographical region with specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. It consists of a biological community that has formed in response to its physical environment and regional climate. In 1935, Tansley added the ...
s in which they exist, combined with leaf longevity of the dominant species (whether they are evergreen or deciduous
In the fields of horticulture and botany, the term deciduous () means "falling off at maturity" and "tending to fall off", in reference to trees and shrubs that seasonally shed Leaf, leaves, usually in the autumn; to the shedding of petals, aft ...
). Another distinction is whether the forests are composed predominantly of broadleaf trees, coniferous (needle-leaved) trees, or mixed.
* Boreal forests occupy the subarctic zone and are generally evergreen and coniferous.
* Temperate zones support both broadleaf deciduous forests (e.g., Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests, temperate deciduous forest) and evergreen coniferous forests (e.g., temperate coniferous forests and temperate rainforests). Warm temperate zones support broadleaf evergreen forests, including laurel forests.
* Tropical and subtropical forests include Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical and subtropical moist forests, Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests, tropical and subtropical dry forests, and tropical and subtropical coniferous forests.
* Forests are classified according to physiognomy based on their overall physical structure or Ecological succession, developmental stage (e.g. old growth vs. Secondary forest, second growth).
* Forests can also be classified more specifically based on the climate and the dominant tree species present, resulting in numerous different forest types (e.g., Ponderosa pine/Douglas fir forest).
The number of trees in the world, according to a 2015 estimate, is 3 trillion, of which 1.4 trillion are in the tropics or sub-tropics, 0.6 trillion in the temperate zones, and 0.7 trillion in the coniferous boreal forests. The 2015 estimate is about eight times higher than previous estimates, and is based on tree densities Forest inventory, measured on over 400,000 plots. It remains subject to a wide margin of error, not least because the samples are mainly from Europe and North America.
Forests can also be classified according to the amount of human alteration. Old-growth forest contains mainly natural patterns of biodiversity in established seral patterns, and they contain mainly species native to the region and habitat. In contrast, secondary forest is forest regrowing following timber harvest and may contain species originally from other regions or habitats.
Different global forest classification systems have been proposed, but none has gained universal acceptance. United Nations Environment Programme, UNEP-World Conservation Monitoring Centre, WCMC's forest category classification system is a simplification of other, more complex systems (e.g. UNESCO's forest and woodland 'subformations'). This system divides the world's forests into 26 major types, which reflect climatic zones as well as the principal types of trees. These 26 major types can be reclassified into 6 broader categories: temperate needleleaf, temperate broadleaf and mixed, tropical moist, tropical dry, sparse trees and parkland, and forest plantations. Each category is described in a separate section below.
Temperate needleleaf
Temperate coniferous forest, Temperate needleleaf forests mostly occupy the higher latitudes of the Northern Hemisphere, as well as some warm temperate areas, especially on nutrient-poor or otherwise unfavourable soils. These forests are composed entirely, or nearly so, of coniferous species (Coniferophyta). In the Northern Hemisphere, pines ''Pinus'', spruces ''Picea'', larches ''Larix'', firs ''Abies'', Douglas firs ''Pseudotsuga'', and hemlocks ''Tsuga'' make up the canopy; but other taxa are also important. In the Southern Hemisphere, most coniferous trees (members of Araucariaceae and Podocarpaceae) occur mixed with broadleaf species, and are classed as broadleaf-and-mixed forests.Temperate broadleaf and mixed
 Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests include a substantial component of trees of the Anthophyta group. They are generally characteristic of the warmer temperate latitudes, but extend to cool temperate ones, particularly in the southern hemisphere. They include such forest types as the mixed deciduous forests of the United States and their counterparts in China and Japan; the broadleaf evergreen rainforests of Japan, Chile, and Tasmania; the sclerophyllous forests of Australia, central Chile, the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean, and California; and the southern beech Nothofagus forests of Chile and New Zealand.
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests include a substantial component of trees of the Anthophyta group. They are generally characteristic of the warmer temperate latitudes, but extend to cool temperate ones, particularly in the southern hemisphere. They include such forest types as the mixed deciduous forests of the United States and their counterparts in China and Japan; the broadleaf evergreen rainforests of Japan, Chile, and Tasmania; the sclerophyllous forests of Australia, central Chile, the Mediterranean Basin, Mediterranean, and California; and the southern beech Nothofagus forests of Chile and New Zealand.
Tropical moist
There are many different types of Tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests, tropical moist forests, with lowland evergreen broad-leaf tropical rainforests: for example Várzea forest, várzea and Cantão#Natural Communities, igapó forests and the terra firme forests of the Amazon Basin; the peat swamp forests; dipterocarp forests of Southeast Asia; and the high forests of the Congo Basin. Seasonal tropical forests, perhaps the best description for the colloquial term "jungle", typically range from the rainforest zone 10 degrees north or south of the equator, to the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn. Forests located on mountains are also included in this category, divided largely into upper and lower Montane ecology, montane formations, on the basis of the variation of physiognomy corresponding to changes in altitude.Tropical dry
Tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests, Tropical dry forests are characteristic of areas in the tropics affected by seasonal drought. The seasonality of rainfall is usually reflected in the deciduousness of the forest canopy, with most trees being leafless for several months of the year. Under some conditions, such as less fertile soils or less predictable drought regimes, the proportion of evergreen species increases and the forests are characterised as "sclerophyllous". Deserts and xeric shrublands, Thorn forest, a dense forest of low stature with a high frequency of thorny or spiny species, is found where drought is prolonged, and especially where grazing animals are plentiful. On very poor soils, and especially where fire or herbivory are recurrent phenomena,savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
s develop.
Sparse trees and savanna
Sparse trees andsavanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland-grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) biome and ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach th ...
are forests with sparse tree-canopy
Canopy may refer to:
Plants
* Canopy (biology), aboveground portion of plant community or crop (including forests)
* Canopy (grape), aboveground portion of grapes
Religion and ceremonies
* Baldachin or canopy of state, typically placed over an a ...
cover. They occur principally in areas of transition from forested to non-forested landscapes. The two major zones in which these ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s occur are in the boreal ecosystem, boreal region and in the seasonally dry tropics. At high latitudes, north of the main zone of boreal forestland, growing conditions are not adequate to maintain a continuously closed forest cover, so tree cover is both sparse and discontinuous. This vegetation is variously called open taiga, open lichen woodland, and forest tundra. A savanna is a mixed woodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
–grassland ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
characterized by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer that consists primarily of grasses. Savannas maintain an open canopy despite a high tree density.
Plantations
Forest plantations are generally intended for the production of timber and pulpwood. Commonly mono-specific, planted with even spacing between the trees, and intensively managed, these forests are generally important as habitat for native biodiversity. Some are managed in ways that enhance their biodiversity protection functions and can provide ecosystem services such as nutrient capital maintenance, Drainage basin, watershed and soil structure protection and carbon storage.Area
Societal significance

Ecosystem services
Forests provide a diversity ofecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
including:
* Converting carbon dioxide into oxygen and biomass. A full-grown tree produces about of net oxygen per year.
* Acting as a carbon sink. Therefore, they are necessary to Climate change mitigation, mitigate climate change.
* Aiding in regulating climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in a region, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteoro ...
. For example, research from 2017 shows that forests induce rainfall. If the forest is cut, it can lead to drought, and in the tropics to occupational heat stress of outdoor workers.
* Purifying water.
* Mitigating natural hazards such as floods.
* Serving as a genetic reserve.
* Serving as a source of lumber and as recreational areas.
* Serving as a source of woodlands and trees for millions of people dependent almost entirely on forests for subsistence for their essential fuelwood, food, and fodder needs.
The main ecosystem services can be summarized in the next table:
Some researchers state that forests do not only provide benefits, but can in certain cases also incur costs to humans. Forests may impose an economic burden, diminish the enjoyment of natural areas, reduce the food-producing capacity of grazing land and cultivated land, reduce biodiversity, reduce available water for humans and wildlife, harbour dangerous or destructive wildlife, and act as reservoirs of human and livestock disease.
An important consideration regarding carbon sequestration is that forests can turn from a carbon sink to a carbon source if plant diversity, density or forest area decreases, as has been observed in different tropical forests The typical tropical forest may become a carbon source by the 2060s. An assessment of European forests found early signs of carbon sink saturation, after decades of increasing strength. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that a combination of measures aimed at increasing forest carbon stocks, andsustainable timber offtake will generate the largest carbon sequestration benefit.
Forest-dependent people
The term forest-dependent people is used to describe any of a wide variety of livelihoods that are dependent on access to forests, products harvested from forests, or ecosystem services provided by forests, including those of Indigenous peoples dependent on forests. In India, approximately 22 percent of the population belongs to forest-dependent communities, which live in close proximity to forests and practice agroforestry as a principal part of their livelihood. People of Ghana who rely ontimber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into uniform and useful sizes (dimensional lumber), including beams and planks or boards. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, window frames). ...
and bushmeat harvested from forests and Indigenous peoples of the Amazon rainforest are also examples of forest-dependent people. Though forest-dependence by more common definitions is statistically associated with poverty and rural livelihoods, elements of forest-dependence exist in communities with a wide range of characteristics. Generally, richer households derive more cash value from forest resources, whereas among poorer households, forest resources are more important for home consumption and increase community resilience.
Indigenous peoples
Forests are fundamental to the culture and livelihood of indigenous people groups that live in and depend on forests, many of which have been removed from and denied access to the lands on which they lived as part of global colonialism. Indigenous lands contain 36% or more of intact forest worldwide, host more biodiversity, and experience less deforestation. Indigenous activists have argued that degradation of forests and indigenous peoples' marginalization and land dispossession are interconnected. Other concerns among indigenous peoples include lack of Indigenous involvement in forest management and loss of knowledge related for the forest ecosystem. Since 2002, the amount of land that is legally owned by or designated for indigenous peoples has broadly increased, but land acquisition in lower-income countries by multinational corporations, often with little or no consultation of indigenous peoples, has also increased. Research in the Amazon rainforest suggests that indigenous methods of agroforestry form reservoirs of biodiversity. In the U.S. state of Wisconsin, forests managed by indigenous people have more plant diversity, fewer invasive species, higher tree regeneration rates, and higher volume of trees.Management
 Humans have generally decreased the amount of forest worldwide. Anthropogenic factors that can affect forests include logging, urban sprawl, human-caused forest fires, acid rain, invasive species, and the slash and burn practices of swidden agriculture or shifting cultivation. The loss and re-growth of forests lead to a distinction between two broad types of forest: primary or old-growth forest and secondary forest. There are also many natural factors that can cause changes in forests over time, including forest fires, Forest pathology#Animals, insects, Forest pathology, diseases, weather, competition between species, etc. In 1997, the World Resources Institute recorded that only 20% of the world's original forests remained in large intact tracts of undisturbed forest. More than 75% of these intact forests lie in three countries: the boreal forests of Russia and Canada, and the rainforest of Brazil.
According to
Humans have generally decreased the amount of forest worldwide. Anthropogenic factors that can affect forests include logging, urban sprawl, human-caused forest fires, acid rain, invasive species, and the slash and burn practices of swidden agriculture or shifting cultivation. The loss and re-growth of forests lead to a distinction between two broad types of forest: primary or old-growth forest and secondary forest. There are also many natural factors that can cause changes in forests over time, including forest fires, Forest pathology#Animals, insects, Forest pathology, diseases, weather, competition between species, etc. In 1997, the World Resources Institute recorded that only 20% of the world's original forests remained in large intact tracts of undisturbed forest. More than 75% of these intact forests lie in three countries: the boreal forests of Russia and Canada, and the rainforest of Brazil.
According to Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
's (FAO) ''Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020'', an estimated of forest have been lost worldwide through deforestation since 1990, but the rate of forest loss has declined substantially. In the most recent five-year period (2015–2020), the annual rate of deforestation was estimated at , down from annually in 2010–2015.
The forest transition
The transition of a region from forest loss to net gain in forested land is referred to as the forest transition. This change occurs through a few main pathways, including increase in commercial tree plantations, adoption of agroforestry techniques by small farmers, or spontaneous regeneration when former agricultural land is abandoned. It can be motivated by the economic benefits of forests, the ecosystem services forests provide, or cultural changes where people increasingly appreciate forests for their spiritual, aesthetic, or otherwise intrinsic value. According to the Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5 °C of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, to avoid temperature rise by more than 1.5 degrees above pre-industrial levels, there will need to be an increase in global forest cover equal to the land area of Canada () by 2050. China instituted a ban on logging, beginning in 1998, due to the erosion and flooding that it caused. In addition, ambitious tree-planting programmes in countries such as China, India, the United States, and Vietnam – combined with natural expansion of forests in some regions – have added more than of new forests annually. As a result, the net loss of forest area was reduced to per year between 2000 and 2010, down from annually in the 1990s. In 2015, a study for ''Nature Climate Change'' showed that the trend has recently been reversed, leading to an "overall gain" in global biomass and forests. This gain is due especially to reforestation in China and Russia. New forests are not equivalent to old growth forests in terms of species diversity, resilience, and carbon capture. On 7 September 2015, the FAO released a new study stating that over the last 25 years the global deforestation rate has decreased by 50% due to improved forest management, management of forests and greater government protection. There is an estimated of forest in protected areas worldwide. Of the six major world regions, South America has the highest share of forests in protected areas, at 31 percent. The area of such areas globally has increased by since 1990, but the rate of annual increase slowed in 2010–2020. Smaller areas ofwoodland
A woodland () is, in the broad sense, land covered with woody plants (trees and shrubs), or in a narrow sense, synonymous with wood (or in the U.S., the '' plurale tantum'' woods), a low-density forest forming open habitats with plenty of sunli ...
in cities may be managed as urban forestry, sometimes within public parks. These are often created for human benefits; Attention Restoration Theory argues that spending time in nature reduces stress and improves health, while Forest School (education), forest schools and Forest kindergarten, kindergartens help young people to develop social as well as scientific skills in forests. These typically need to be close to where the children live.
Canada
 Canada has about of forest land. More than 90% of forest land is publicly owned and about 50% of the total forest area is allocated for harvesting. These allocated areas are managed using the principles of sustainable forest management, which include extensive consultation with local stakeholders. About eight percent of Canada's forest is legally protected from resource development. Much more forest land—about 40 percent of the total forest land base—is subject to varying degrees of protection through processes such as integrated land use planning or defined management areas, such as certified forests.
By December 2006, over of forest land in Canada (about half the global total) had been certified as being sustainably managed. Clearcutting, first used in the latter half of the 20th century, is less expensive, but devastating to the environment; and companies are required by law to ensure that harvested areas are adequately regenerated. Most Canadian provinces have regulations limiting the size of new clear-cuts, although some older ones grew to over several years.
The Canadian Forest Service is the government department which looks after Forests in Canada.
Canada has about of forest land. More than 90% of forest land is publicly owned and about 50% of the total forest area is allocated for harvesting. These allocated areas are managed using the principles of sustainable forest management, which include extensive consultation with local stakeholders. About eight percent of Canada's forest is legally protected from resource development. Much more forest land—about 40 percent of the total forest land base—is subject to varying degrees of protection through processes such as integrated land use planning or defined management areas, such as certified forests.
By December 2006, over of forest land in Canada (about half the global total) had been certified as being sustainably managed. Clearcutting, first used in the latter half of the 20th century, is less expensive, but devastating to the environment; and companies are required by law to ensure that harvested areas are adequately regenerated. Most Canadian provinces have regulations limiting the size of new clear-cuts, although some older ones grew to over several years.
The Canadian Forest Service is the government department which looks after Forests in Canada.
Latvia
Latvia has about of forest land, which equates to about 50.5% of Latvia's total area of of forest land (46% of total forest land) is publicly owned and of forest land (54% of the total) is in private hands. Latvia's forests have been steadily increasing over the years, which is in contrast to many other nations, mostly due to the forestation of land not used for agriculture. In 1935, there were only of forest; today this has increased by more than 150%. Birch is the most common tree at 28.2%, followed by pine (26.9%), spruce (18.3%), grey alder (9.7%), aspen (8.0%), black alder (5.7%), oak/ash (1.2%), with other hardwood trees making up the rest (2.0%).United States
In the United States, most forests have historically been affected by humans to some degree, though in recent years improved forestry practices have helped regulate or moderate large-scale impacts. The United States Forest Service estimated a net loss of about between 1997 and 2020; this estimate includes conversion of forest land to other uses, including urban and suburban development, as well as afforestation and natural reversion of abandoned crop and pasture land to forest. In many areas of the United States, the area of forest is stable or increasing, particularly in many northern states. The opposite problem from flooding has plagued national forests, with loggers complaining that a lack of thinning and proper forest management has resulted in large forest fires.See also
Sources
References
External links
Forests in danger
Intact Forests
with maps and reports (archived 8 September 2015)
by the
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, , translates ...
* (archived 24 January 2008)
Forest area is land under natural or planted stands of trees of at least 5 meters ''in situ'', whether productive or not, and excludes tree stands in agricultural production systems
Forest area (sq. km)
data from the World Bank's World Development Indicators, made available by Google * * * {{Authority control Forests, Habitats Trees Ecosystems