Foreign Intelligence on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Intelligence assessment, is a specific phase of the
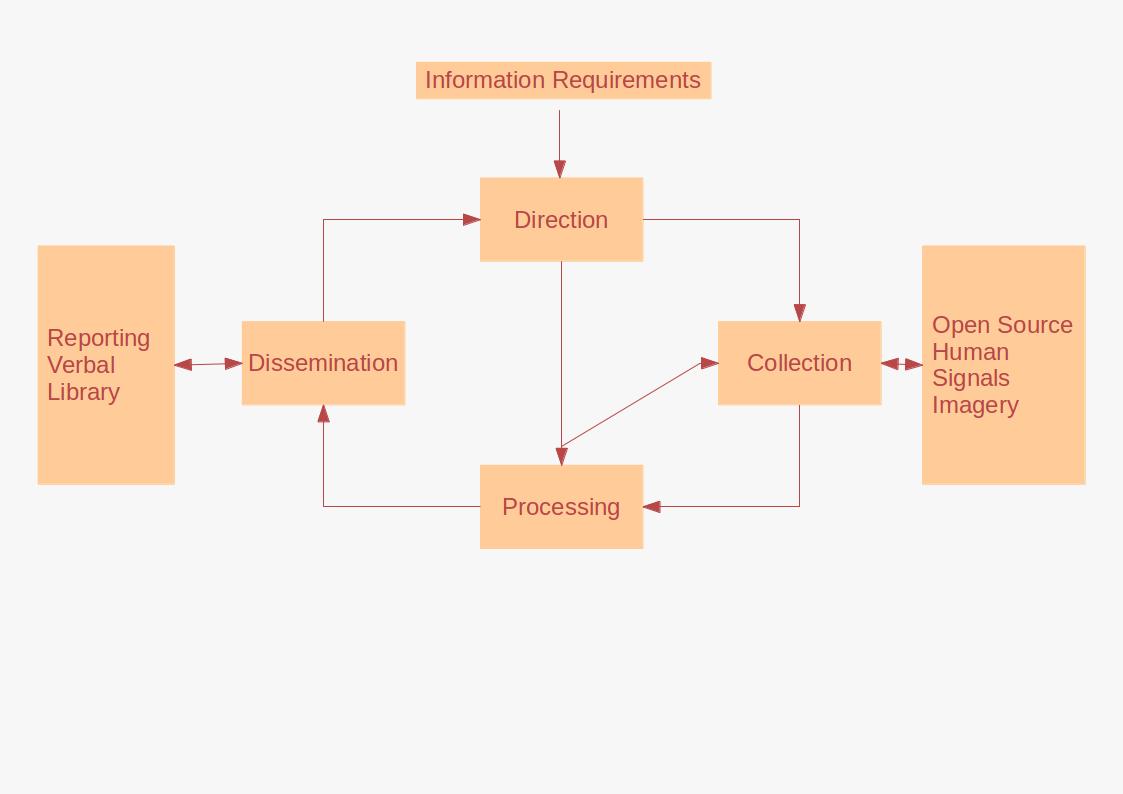 Intelligence assessment is based on a customer requirement or need, which may be a standing requirement or tailored to a specific circumstance or a Request for Information (RFI). The "requirement" is passed to the assessing agency and worked through the
Intelligence assessment is based on a customer requirement or need, which may be a standing requirement or tailored to a specific circumstance or a Request for Information (RFI). The "requirement" is passed to the assessing agency and worked through the
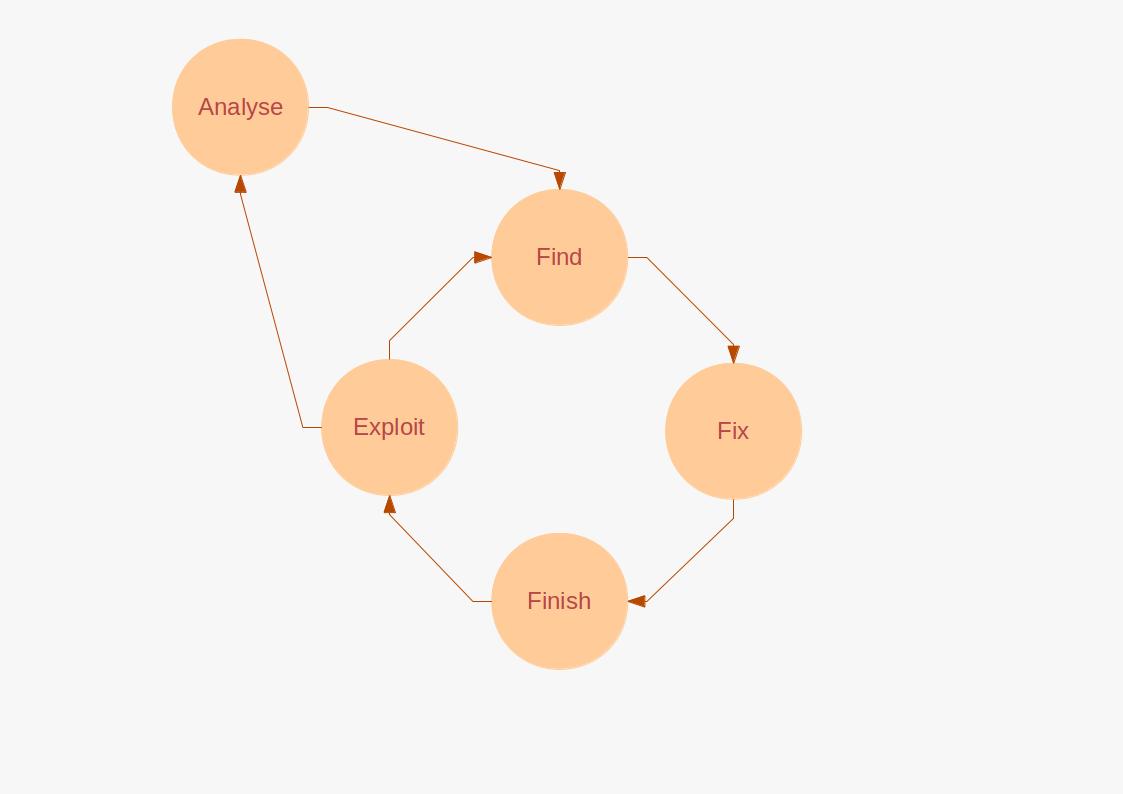 This approach, known as Find-Fix-Finish-Exploit-Assess (F3EA), is complementary to the intelligence cycle and focused on the intervention itself, where the subject of the assessment is clearly identifiable and provisions exist to make some form of intervention against that subject, the target-centric assessment approach may be used.
* Find
** The subject for action, or target, is identified and efforts are initially made to find the target for further development. This activity will identify where intervention against the target will have the most beneficial effects.
* Fix
** When the decision is made to intervene, action is taken to fix the target, confirming that the intervention will have a high probability of success and restricting the ability of the target to take independent action.
* Finish
** During the finish stage, the intervention is executed, potentially an arrest or detention or the placement of other collection methods.
* Exploit
** Following the intervention, exploitation of the target is carried out, which may lead to further refinement of the process for related targets. The output from the exploit stage will also be passed into other intelligence assessment activities.
This approach, known as Find-Fix-Finish-Exploit-Assess (F3EA), is complementary to the intelligence cycle and focused on the intervention itself, where the subject of the assessment is clearly identifiable and provisions exist to make some form of intervention against that subject, the target-centric assessment approach may be used.
* Find
** The subject for action, or target, is identified and efforts are initially made to find the target for further development. This activity will identify where intervention against the target will have the most beneficial effects.
* Fix
** When the decision is made to intervene, action is taken to fix the target, confirming that the intervention will have a high probability of success and restricting the ability of the target to take independent action.
* Finish
** During the finish stage, the intervention is executed, potentially an arrest or detention or the placement of other collection methods.
* Exploit
** Following the intervention, exploitation of the target is carried out, which may lead to further refinement of the process for related targets. The output from the exploit stage will also be passed into other intelligence assessment activities.
Intelligence Literature: Suggested Reading List (CIA)
The Literature of Intelligence: A Bibliography of Materials, with Essays, Reviews, and Comments by J. Ransom Clark, Emeritus Professor of Political Science, Muskingum College
{{DEFAULTSORT:Intelligence Assessment Data collection Intelligence analysis
intelligence cycle
The intelligence cycle is an idealized model of how intelligence (information gathering), intelligence is processed in civilian and military intelligence agency, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement organizations. It is a closed path (gra ...
which oversees the development of behavior forecasts or recommended courses of action to the leadership of an organization, based on wide ranges of available overt and covert intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. It can be described as t ...
(also known as "intel").
There are two types of assessment;
* In the beginning of the intelligence cycle, during the direction phase (also known as tasking or planning), intelligence officers assess past intelligence, identify gaps in information, and determine what new intelligence is needed.
* Intelligence assessment also occurs toward the end of the intelligence cycle, during the analysis & production phase. This phase comes after collection and processing but before dissemination to policymakers.
Assessments develop in response to leadership declaration requirements to inform decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
. Assessment may be executed on behalf of a state
State most commonly refers to:
* State (polity), a centralized political organization that regulates law and society within a territory
**Sovereign state, a sovereign polity in international law, commonly referred to as a country
**Nation state, a ...
, military
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a d ...
or commercial organisation with ranges of information sources available to each.
An intelligence assessment reviews available information and previous assessments for relevance and currency. Where there requires additional information, the analyst may direct some collection.
Process
 Intelligence assessment is based on a customer requirement or need, which may be a standing requirement or tailored to a specific circumstance or a Request for Information (RFI). The "requirement" is passed to the assessing agency and worked through the
Intelligence assessment is based on a customer requirement or need, which may be a standing requirement or tailored to a specific circumstance or a Request for Information (RFI). The "requirement" is passed to the assessing agency and worked through the intelligence cycle
The intelligence cycle is an idealized model of how intelligence (information gathering), intelligence is processed in civilian and military intelligence agency, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement organizations. It is a closed path (gra ...
, a structured method for responding to the RFI.
The RFI may indicate in what format the requester prefers to consume the product.
The RFI is reviewed by a Requirements Manager, who will then direct appropriate tasks to respond to the request. This will involve a review of existing material, the tasking of new analytical product or the collection of new information to inform an analysis.
New information may be collected through one or more of the various collection disciplines; human source, electronic and communications intercept, imagery
Imagery is visual symbolism, or figurative language that evokes a mental image or other kinds of sense impressions, especially in a literary work, but also in other activities such as. Imagery in literature can also be instrumental in conveying ...
or open sources. The nature of the RFI and the urgency placed on it may indicate that some collection types are unsuitable due to the time taken to collect or validate the information gathered. Intelligence gathering disciplines and the sources and methods used are often highly classified
Classified may refer to:
General
*Classified information, material that a government body deems to be sensitive
*Classified advertising or "classifieds"
Music
*Classified (rapper) (born 1977), Canadian rapper
* The Classified, a 1980s American ro ...
and compartmentalised, with analysts requiring an appropriate high level of security clearance
A security clearance is a status granted to individuals allowing them access to classified information (state or organizational secrets) or to restricted areas, after completion of a thorough background check. The term "security clearance" is ...
.
The process of taking known information about situations and entities of importance to the RFI, characterizing what is known and attempting to forecast future events is termed " all source" assessment, analysis or processing. The analyst uses multiple sources to mutually corroborate, or exclude, the information collected, reaching a conclusion along with a measure of confidence around that conclusion.
Where sufficient current information already exists, the analysis may be tasked directly without reference to further collection.
The analysis is then communicated back to the requester in the format directed, although subject to the constraints on both the RFI and the methods used in the analysis, the format may be made available for other uses as well and disseminated accordingly. The analysis will be written to a defined classification level with alternative versions potentially available at a number of classification levels for further dissemination.
Target-centric intelligence cycle
The F3EA Cycle
 This approach, known as Find-Fix-Finish-Exploit-Assess (F3EA), is complementary to the intelligence cycle and focused on the intervention itself, where the subject of the assessment is clearly identifiable and provisions exist to make some form of intervention against that subject, the target-centric assessment approach may be used.
* Find
** The subject for action, or target, is identified and efforts are initially made to find the target for further development. This activity will identify where intervention against the target will have the most beneficial effects.
* Fix
** When the decision is made to intervene, action is taken to fix the target, confirming that the intervention will have a high probability of success and restricting the ability of the target to take independent action.
* Finish
** During the finish stage, the intervention is executed, potentially an arrest or detention or the placement of other collection methods.
* Exploit
** Following the intervention, exploitation of the target is carried out, which may lead to further refinement of the process for related targets. The output from the exploit stage will also be passed into other intelligence assessment activities.
This approach, known as Find-Fix-Finish-Exploit-Assess (F3EA), is complementary to the intelligence cycle and focused on the intervention itself, where the subject of the assessment is clearly identifiable and provisions exist to make some form of intervention against that subject, the target-centric assessment approach may be used.
* Find
** The subject for action, or target, is identified and efforts are initially made to find the target for further development. This activity will identify where intervention against the target will have the most beneficial effects.
* Fix
** When the decision is made to intervene, action is taken to fix the target, confirming that the intervention will have a high probability of success and restricting the ability of the target to take independent action.
* Finish
** During the finish stage, the intervention is executed, potentially an arrest or detention or the placement of other collection methods.
* Exploit
** Following the intervention, exploitation of the target is carried out, which may lead to further refinement of the process for related targets. The output from the exploit stage will also be passed into other intelligence assessment activities.
The F3EAD Cycle
The F3EAD cycle—Find, Fix, Finish, Exploit, Analyze, and Disseminate—is an alternative intelligence cycle commonly used within Western militaries, particularly in operations that result in lethal action, such as drone strikes and special forces missions. * Analyze ** The collected information is analyzed to identify patterns, assess credibility, and produce intelligence reports. * Disseminate ** The output from the exploit stage is disseminated to key stakeholders and other intelligence assessment activities.Intelligence information cycle theory around the world
United States Intelligence Community
The U.S. intelligence community (IC) follows a structured six-step intelligence cycle; * Planning & Direction * Collection (Espionage) * Processing & Exploitation * Analysis & Production *Dissemination
To disseminate (from Latin, lat. ''disseminare'' "scattering seeds"), in the field of communication, is to broadcast a message to the public without direct feedback from the audience.
Meaning
Dissemination takes on the theory of the traditional ...
, and Feedback.
The IC has a heavy reliance on technological collection (SIGINT
Signals intelligence (SIGINT) is the act and field of intelligence-gathering by interception of ''signals'', whether communications between people (communications intelligence—abbreviated to COMINT) or from electronic signals not directly u ...
, IMINT, MASINT) alongside HUMINT
Human intelligence (HUMINT, pronounced ) is intelligence-gathering by means of human sources and interpersonal communication. It is distinct from more technical intelligence-gathering disciplines, such as signals intelligence (SIGINT), imager ...
.
Centralized analysis through agencies like the CIA, DIA, and NSA, but intelligence dissemination is highly structured through national security briefings.
The Intelligence Information Cycle leverages secrecy theory and U.S. regulation of classified intelligence to re-conceptualize the traditional intelligence cycle under the following four assumptions:
# Intelligence is secret information
# Intelligence is a public good
# Intelligence moves cyclically
# Intelligence is hoarded
Information is transformed from privately held to secretly held to public based on who has control over it. For example, the private information
Privacy (, ) is the ability of an individual or group to seclude themselves or information about themselves, and thereby express themselves selectively.
The domain of privacy partially overlaps with security, which can include the concepts of a ...
of a source becomes secret information (intelligence) when control over its dissemination is shared with an intelligence officer, and then becomes public information when the intelligence officer further disseminates it to the public by any number of means, including formal reporting, threat warning, and others. The fourth assumption, intelligence is hoarded, causes conflict points where information transitions from one type to another. The first conflict point, collection, occurs when private transitions to secret information (intelligence). The second conflict point, dissemination, occurs when secret transitions to public information. Thus, conceiving of intelligence using these assumptions demonstrates the cause of collection techniques (to ease the private-secret transition) and dissemination conflicts, and can inform ethical standards of conduct among all agents in the intelligence process.
United Kingdom
The UK intelligence process is similar but often less bureaucratic, withMI6
The Secret Intelligence Service (SIS), commonly known as MI6 ( Military Intelligence, Section 6), is the foreign intelligence service of the United Kingdom, tasked mainly with the covert overseas collection and analysis of human intelligenc ...
(SIS) focusing on HUMINT, GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ) is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the United Kingdom. Primar ...
on SIGINT, and MI5
MI5 ( Military Intelligence, Section 5), officially the Security Service, is the United Kingdom's domestic counter-intelligence and security agency and is part of its intelligence machinery alongside the Secret Intelligence Service (MI6), Gov ...
on domestic security. The Joint Intelligence Committee (JIC) plays a key role in assessing intelligence for policymakers, rather than each agency handling it independently.
Russia (FSB/GRU/SVR)
The Russian approach integrates intelligence directly into active measures (deception, subversion, and disinformation) more than Western counterparts. Analysis and dissemination tend to be more centralized, with intelligence feeding directly into the Kremlin’s strategic decision-making.China (MSS and PLA Intelligence)
China’s Ministry of State Security (MSS) and military intelligence units prioritize long-term strategic intelligence gathering, especially industrial espionage and cyber warfare. The fusion of intelligence and policy-making is stronger, with theChinese Communist Party
The Communist Party of China (CPC), also translated into English as Chinese Communist Party (CCP), is the founding and One-party state, sole ruling party of the People's Republic of China (PRC). Founded in 1921, the CCP emerged victorious in the ...
exerting tight control over the process.
France (DGSE & DRM)
The French intelligence cycle closely resembles the U.S. and UK models, but with a greater focus on economic intelligence to support national industries. More autonomy is given to field operatives to gather and assess intelligence in real-time without excessive central oversight.Israel (Mossad, Aman, Shin Bet)
Intelligence operations in Israel are highly operationally integrated, meaning the cycle often skips steps (e.g., collection may immediately lead to direct action, such as assassinations or preemptive strikes). Intelligence is designed for rapid-action scenarios, given Israel’s security threats.See also
* All-source intelligence *Intelligence cycle
The intelligence cycle is an idealized model of how intelligence (information gathering), intelligence is processed in civilian and military intelligence agency, intelligence agencies, and law enforcement organizations. It is a closed path (gra ...
* List of intelligence gathering disciplines
This is a list of intelligence gathering disciplines.
HUMINT
Human intelligence (HUMINT) are gathered from a person in the location in question. Sources can include the following:
* Advisors or foreign internal defense (FID) personnel wor ...
* Military intelligence
Military intelligence is a military discipline that uses information collection and analysis List of intelligence gathering disciplines, approaches to provide guidance and direction to assist Commanding officer, commanders in decision making pr ...
* Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing, or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as ...
* Threat assessment
* Futures studies
Futures studies, futures research or futurology is the systematic, interdisciplinary and holistic study of social and technological advancement, and other environmental trends, often for the purpose of exploring how people will live and wor ...
* Intelligence literature
References
External links
Intelligence Literature: Suggested Reading List (CIA)
The Literature of Intelligence: A Bibliography of Materials, with Essays, Reviews, and Comments by J. Ransom Clark, Emeritus Professor of Political Science, Muskingum College
{{DEFAULTSORT:Intelligence Assessment Data collection Intelligence analysis