Flexor hallucis brevis muscle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle is a
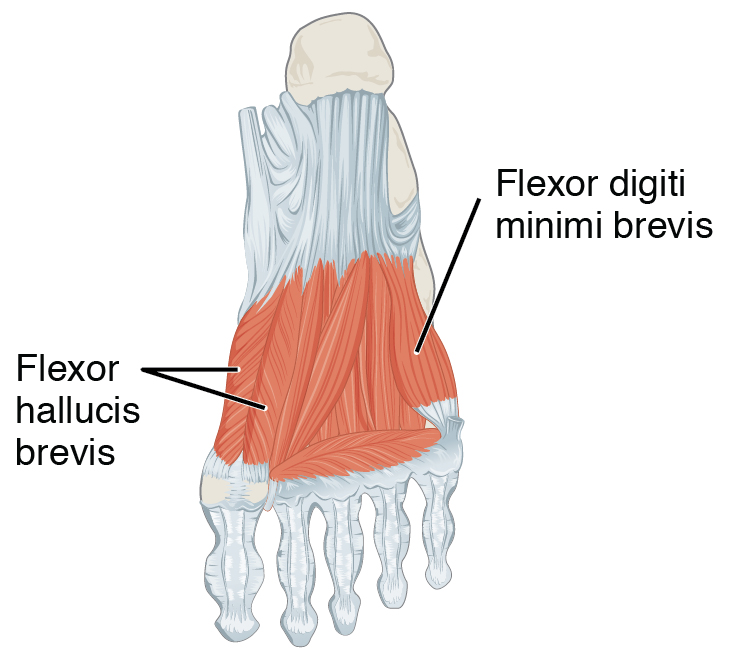 Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third
Image:Gray269.png, Bones of the right foot. Plantar surface.
File:Slide1ABA.JPG, Flexor hallucis brevis muscle
File:Slide8ABA.JPG, Flexor hallucis brevis muscle
PTCentral
{{Authority control Foot muscles Muscles of the lower limb
muscle
Muscle is a soft tissue, one of the four basic types of animal tissue. There are three types of muscle tissue in vertebrates: skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle. Muscle tissue gives skeletal muscles the ability to muscle contra ...
of the foot
The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up o ...
that flexes the big toe
Toes are the Digit (anatomy), digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ' ...
.
Structure
 Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third
Flexor hallucis brevis muscle arises, by a pointed tendinous process, from the medial part of the under surface of the cuboid bone, from the contiguous portion of the third cuneiform
Cuneiform is a Logogram, logo-Syllabary, syllabic writing system that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Near East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. Cuneiform script ...
, and from the prolongation of the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle which is attached to that bone. It divides in front into two portions, which are inserted into the medial and lateral sides of the base of the first phalanx of the great toe, a sesamoid bone being present in each tendon at its insertion. The medial portion is blended with the abductor hallucis muscle previous to its insertion; the lateral portion (sometimes described as the first plantar interosseus) with the adductor hallucis muscle
The Adductor hallucis (adductor obliquus hallucis) arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.
Structure Oblique head
The ''obliqu ...
. The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle lies in a groove between the two. Its tendon usually contains two sesamoid bones at the point under the first metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation
The medial and lateral head of the flexor hallucis brevis is innervated by the medial plantar nerve. Both heads are represented by spinal segments S1, S2.Variation
Origin subject to considerable variation; it often receives fibers from the calcaneus or long plantar ligament. Attachment to the cuboid bone sometimes wanting. Slip to first phalanx of the second toe.Function
Flexor hallucis brevis flexes the first metatarsophalangeal joint, or thebig toe
Toes are the Digit (anatomy), digits of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ' ...
. It helps to maintain the medial longitudinal arch. It assists with the toe-off phase of gait providing increased push-off.
Clinical significance
Sesamoid bones contained within the tendon of flexor hallucis brevis muscle may become damaged duringexercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardio ...
.
Additional images
References
External links
PTCentral
{{Authority control Foot muscles Muscles of the lower limb