Flank Attack on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 The use of flanking has been a consistent part of warfare since its invention. The responsibility of defending against flanks falls on the
The use of flanking has been a consistent part of warfare since its invention. The responsibility of defending against flanks falls on the
 When the terrain favors neither side, it is down to the disposition of forces in the battle line to prevent flanking attacks. As long as they have had a place on the battlefield, it was the role of
When the terrain favors neither side, it is down to the disposition of forces in the battle line to prevent flanking attacks. As long as they have had a place on the battlefield, it was the role of
 In
In military tactics
Military tactics encompasses the art of organizing and employing fighting forces on or near the battlefield. They involve the application of four battlefield functions which are closely related – kinetic or firepower, Mobility (military), mobil ...
, a flanking maneuver is a movement of an armed force around an enemy force's side, or flank
Flank may refer to:
* Flank (anatomy), part of the abdomen
** Flank steak, a cut of beef
** Part of the external anatomy of a horse
* Flank speed, a nautical term
* Flank opening, a chess opening
* A term in Australian rules football
* The ...
, to achieve an advantageous position over it. Flanking is useful because a force's fighting strength is typically concentrated in its front, therefore, to circumvent an opposing force's front and attack its flank is to concentrate one's own offense in the area where the enemy is least able to concentrate defense.
Flanking can also occur at the operational and strategic
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "troop leadership; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art o ...
levels of warfare.
Tactical flanking
The flanking maneuver is a basicmilitary tactic
Military tactics encompasses the art of organizing and employing fighting forces on or near the battlefield. They involve the application of four battlefield functions which are closely related – kinetic or firepower, mobility, protection or ...
with several variations. Flanking an enemy entails attacking from one or more sides, at an angle to the enemy's direction of engagement. There are three standard flanking maneuvers.
The first maneuver is the ambush
An ambush is a surprise attack carried out by people lying in wait in a concealed position. The concealed position itself or the concealed person(s) may also be called an "". Ambushes as a basic military tactics, fighting tactic of soldi ...
, where a unit performs a surprise attack from a concealed position. Units friendly to the ambushing unit may be hidden to the sides of the ambush site to surround the enemy, but care must be taken when setting up fields of fire to avoid friendly fire
In military terminology, friendly fire or fratricide is an attack by belligerent or neutral forces on friendly troops while attempting to attack enemy or hostile targets. Examples include misidentifying the target as hostile, cross-fire while ...
. Ambush as a tactic is typically favored by smaller, more mobile forces, usually ones with favorable terrain. An example of this would be the Battle of Beaver Dams, where the British ambushed the Americans, halting their advance further inland to Canada.
The second type is used during an attack, where a unit encounters an enemy defensive position. Upon receiving fire from the enemy, the unit commander may decide to order a flank attack. A part of the attacking unit pins the enemy in place with suppressive fire
In military science, suppressive fire is "fire that degrades the performance of an enemy force below the level needed to fulfill its mission". When used to protect exposed friendly troops advancing on the battlefield, it is commonly called cover ...
, preventing them from returning fire, retreating or changing position to meet the flank attack. The flanking force then advances to the enemy flank and attacks them at close range. Coordination to avoid friendly fire is also important in this situation. This is employed largely by forces meeting each other with equal strength.
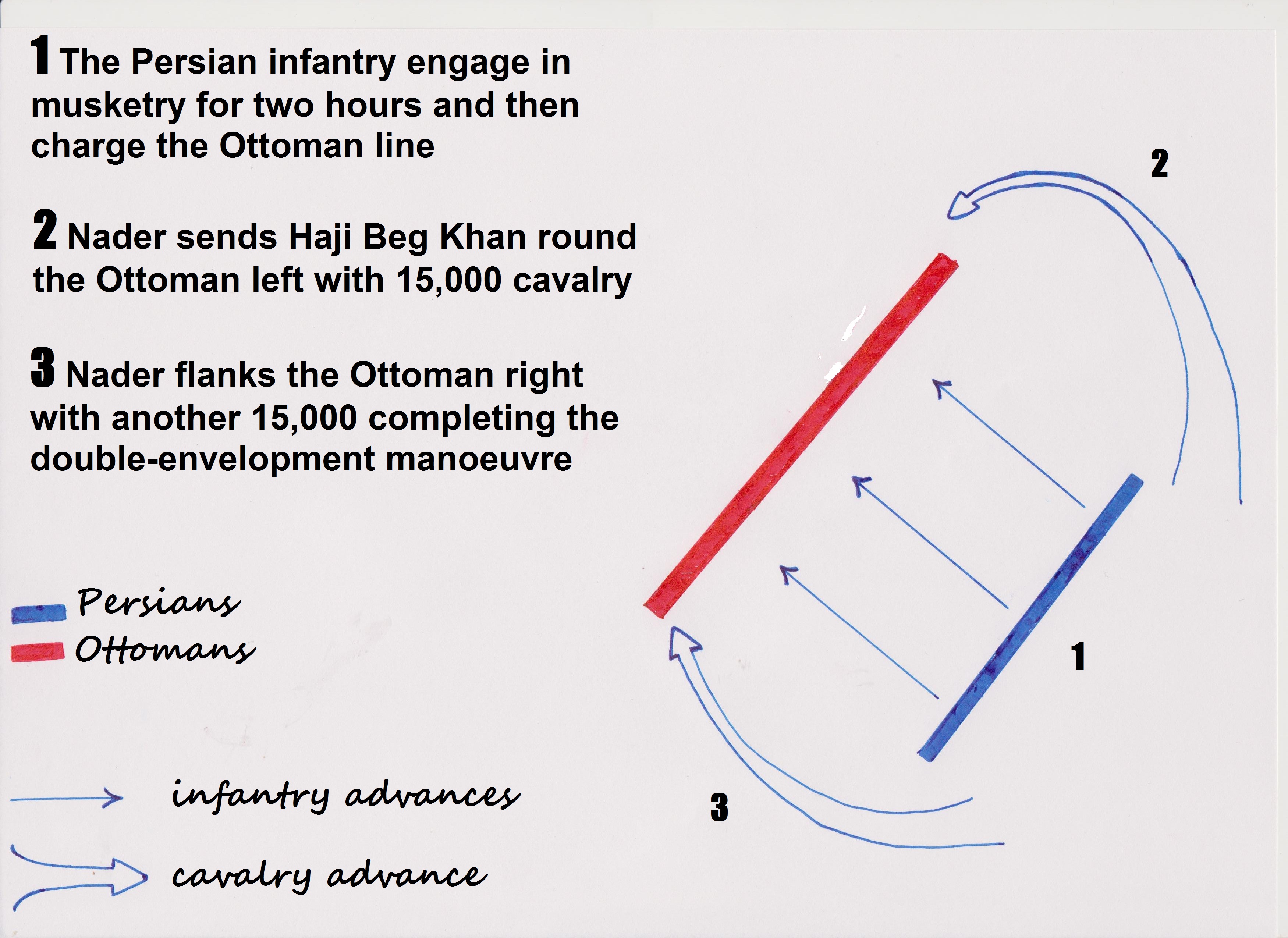
The third form of flanking maneuvers is the double envelopment, which involves simultaneous flank attacks on both sides of the enemy. An example is Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
's victory over the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of Roman civilization
*Epistle to the Romans, shortened to Romans, a letter w ...
army at the Battle of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae (; ) was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage, Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and ...
. Double envelopment can only be performed by widening friendly units
Unit may refer to:
General measurement
* Unit of measurement, a definite magnitude of a physical quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law
**International System of Units (SI), modern form of the metric system
**English units, histo ...
or formations or opening gaps between them which results in weakening the center and similar battles to that of Gaugamela. Thus, it was often employed when severely outnumbering the opponent or against those without sufficient cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
support.
Maneuvering
Flanking on land in thepre-modern
In world history, post-classical history refers to the period from about 500 CE to 1500 CE, roughly corresponding to the European Middle Ages. The period is characterized by the expansion of civilizations geographically and the developm ...
era was usually achieved with cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
(and rarely, chariots
A chariot is a type of vehicle similar to a cart, driven by a charioteer, usually using horses to provide rapid motive power. The oldest known chariots have been found in burials of the Sintashta culture in modern-day Chelyabinsk Oblast, Ru ...
) due to their speed and maneuverability, while heavily armored infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
was commonly used to pin the enemy in place, as in the Battle of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in Central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. ...
. Armored vehicles
Military vehicles are commonly armoured (or armored; see spelling differences) to withstand the impact of shrapnel, bullets, shells, rockets, and missiles, protecting the personnel inside from enemy fire. Such vehicles include armoured fighti ...
such as tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; ...
s replaced cavalry as the main force of flanking maneuvers in the 20th century, as seen in the Battle of France
The Battle of France (; 10 May – 25 June 1940), also known as the Western Campaign (), the French Campaign (, ) and the Fall of France, during the Second World War was the Nazi Germany, German invasion of the Low Countries (Belgium, Luxembour ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
.
Defense
 The use of flanking has been a consistent part of warfare since its invention. The responsibility of defending against flanks falls on the
The use of flanking has been a consistent part of warfare since its invention. The responsibility of defending against flanks falls on the commander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank as well as a job title in many army, armies. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countri ...
, who has to make the choice of how to best use terrain. In addition, the proper adjustment and positioning of soldiers is imperative in ensuring a protected flank.
Terrain
A commander could prevent being flanked by anchoring one or both parts of his line on terrain impassable to his enemies, such as gorges, lakes or mountains. Notable examples of this being theSpartans
Sparta was a prominent city-state in Laconia in ancient Greece. In antiquity, the city-state was known as Lacedaemon (), while the name Sparta referred to its main settlement in the valley of Evrotas river in Laconia, in southeastern P ...
at the Battle of Thermopylae
The Battle of Thermopylae ( ) was fought in 480 BC between the Achaemenid Empire, Achaemenid Persian Empire under Xerxes I and an alliance of Polis, Greek city-states led by Sparta under Leonidas I. Lasting over the course of three days, it wa ...
, Hannibal
Hannibal (; ; 247 – between 183 and 181 BC) was a Punic people, Carthaginian general and statesman who commanded the forces of Ancient Carthage, Carthage in their battle against the Roman Republic during the Second Punic War.
Hannibal's fat ...
at the Battle of Lake Trasimene
The Battle of Lake Trasimene was fought when a Carthaginian force under Hannibal ambushed a Roman army commanded by Gaius Flaminius on 21 June 217 BC, during the Second Punic War. The battle took place on the north shore of Lake Tra ...
, and the Romans at the Battle of Watling Street. Although not strictly impassable, woods, forests, rivers, uneven, and marshy ground can also be used to anchor a flank: Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (1216–1281 ...
at Agincourt. However, in such instances, it was still wise to have skirmishers
Skirmishers are light infantry or light cavalry soldiers deployed as a vanguard, flank guard or rearguard to screen a tactical position or a larger body of friendly troops from enemy advances. They may be deployed in a skirmish line, an irreg ...
covering the flanks.
Fortification
In exceptional circumstances, an army may be fortunate enough to be able to anchor a flank with a friendly castle, fortress, or walled city. In such circumstances, it was necessary not to fix the line to the fortress but to allow a killing space between the fortress and the battle line so that any enemy forces attempting to flank the field forces could be brought under fire from thegarrison
A garrison is any body of troops stationed in a particular location, originally to guard it. The term now often applies to certain facilities that constitute a military base or fortified military headquarters.
A garrison is usually in a city ...
. Natural strongholds formed by terrain can also be incorporated into the battle line: the Union positions of Culp's Hill
Culp's Hill,. The modern U.S. Geographic Names System refers to "Culps Hill". which is about south of the center of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, played a prominent role in the Battle of Gettysburg. It consists of two rounded peaks, separated b ...
, Cemetery Hill
Cemetery Hill is a landform on the Gettysburg Battlefield that was the scene of fighting each day of the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1–3, 1863). The northernmost part of the Army of the Potomac defensive " fish-hook" line, the hill is gent ...
on the right flank, and Big Round Top
Big Round Top is a boulder-strewn hill notable as the topographic high point of the Gettysburg Battlefield and for 1863 American Civil War engagements for which Medals of Honor were awarded. In addition to battle monuments, a historic reconstruc ...
and Little Round Top
Little Round Top is the smaller of two rocky hills south of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania—the companion to the adjacent, taller hill named Big Round Top. It was the site of an unsuccessful assault by Confederate troops against the Union left ...
on the left flank at the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was a three-day battle in the American Civil War, which was fought between the Union and Confederate armies between July 1 and July 3, 1863, in and around Gettysburg, Pennsylvania. The battle, won by the Union, ...
. If time and circumstances allowed, field fortifications could be created or expanded to protect the flanks, as the Allied forces did with the hamlet of Papelotte
Papelotte Farm (, ) is located off Chemin des Cosaques, a rural road in the Municipality of Waterloo around south of Brussels, Belgium. On 18 June 1815, during the pivotal Battle of Waterloo it served as one of the advanced defensible position ...
and the farmhouse of Hougoumont
Château d'Hougoumont (possibly originally Goumont or Gomont) is a walled manorial compound, situated at the bottom of an escarpment near the Nivelles road in the Braine-l'Alleud municipality, near Waterloo, Belgium. The site served as one o ...
on the left and right flanks at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (then in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium), marking the end of the Napoleonic Wars. The French Imperial Army (1804–1815), Frenc ...
.
Formations
 When the terrain favors neither side, it is down to the disposition of forces in the battle line to prevent flanking attacks. As long as they have had a place on the battlefield, it was the role of
When the terrain favors neither side, it is down to the disposition of forces in the battle line to prevent flanking attacks. As long as they have had a place on the battlefield, it was the role of cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from ''cheval'' meaning "horse") are groups of soldiers or warriors who Horses in warfare, fight mounted on horseback. Until the 20th century, cavalry were the most mob ...
to be placed on the flanks of the infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadl ...
battle line. With speed and greater tactical flexibility, the cavalry could both make flanking attacks and guard against them. It was the marked superiority of Hannibal's cavalry at the Battle of Cannae
The Battle of Cannae (; ) was a key engagement of the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Ancient Carthage, Carthage, fought on 2 August 216 BC near the ancient village of Cannae in Apulia, southeast Italy. The Carthaginians and ...
that allowed him to chase off the Roman cavalry and complete the encirclement of the Roman legions. With equally-matched cavalry, commanders have been content to allow inaction, with the cavalry of both sides preventing the other from action.
In a case of no cavalry, inferior cavalry or in armies whose cavalry had gone off on their own (a common complaint), the lack of resulting advantage left the outcome depending on the disposition of the infantry to guard against flanking attacks. It was the danger of being flanked by the numerically superior Persians that led Miltiades
Miltiades (; ; c. 550 – 489 BC), also known as Miltiades the Younger, was a Greek Athenian statesman known mostly for his role in the Battle of Marathon, as well as for his downfall afterwards. He was the son of Cimon Coalemos, a renowned ...
to lengthen the Athenian
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
line at the Battle of Marathon
The Battle of Marathon took place in 490 BC during the first Persian invasion of Greece. It was fought between the citizens of Athens (polis), Athens, aided by Plataea, and a Achaemenid Empire, Persian force commanded by Datis and Artaph ...
by decreasing the depth of the centre. The importance of the flank positions led to the practise, which became tradition of placing the best troops on the flanks. At the Battle of Platea, the Tegea
Tegea (; ) was a settlement in ancient Arcadia, and it is also a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the Tripoli municipality, of which it is a municipal unit with an area o ...
ns squabbled with the Athenians on who should have the privilege of holding a flank;Herodotus
Herodotus (; BC) was a Greek historian and geographer from the Greek city of Halicarnassus (now Bodrum, Turkey), under Persian control in the 5th century BC, and a later citizen of Thurii in modern Calabria, Italy. He wrote the '' Histori ...
, '' The Histories'', Book Nine, sections 26 to 28 both having conceded the honour of the right flank (the critical flank in the hoplite
Hoplites ( ) ( ) were citizen-soldiers of Ancient Greek city-states who were primarily armed with spears and shields. Hoplite soldiers used the phalanx formation to be effective in war with fewer soldiers. The formation discouraged the sold ...
system) to the Spartans. That is the source of the tradition of giving the honour of the right to the most senior regiment present, which has persisted into the modern era.
With troops confident and reliable enough to operate in separate dispersed units, the echelon formation
An echelon formation () is a (usually military) formation in which its units are arranged diagonally. Each unit is stationed behind and to the right (a "right echelon"), or behind and to the left ("left echelon"), of the unit ahead. The name of ...
may be adopted. That can take different forms with either equally strong "divisions" or a massively reinforced wing or centre supported by smaller formations in step behind it (forming either a staircase like, or arrow like arrangement). When the foremost unit engages with the enemy the echeloned units remain out of action. The idea is for the enemy to attack the exposed flanks of the foremost unit, but the units immediately echeloned behind the foremost unit would then push forward taking the flankers themselves in the flank. If the echeloned unit is being attacked in turn, the unit behind it would move forward to again attack the flanks of the would be flankers. In theory a cascade of such engagements could occur all along the line for as many units as there were in echelon. In practice, that almost never happened since most enemy commanders saw it for what it was and so resisted the temptation of the initial easy flanking attack.
That prudence was used in the manifestation of the oblique order in which one wing was massively reinforced, creating a local superiority in numbers that could obliterate that part of the enemy line that it was sent against. The weaker echeloned units was sufficient to fix the greater portion of the enemy troops into inaction. With the battle on the wing won, the reinforced flank would turn and roll up the enemy battle line from the flank.
In the Roman chequer board formation, readopted by Renaissance militaries, each of the units in the front line could be thought of as having two lines of units echeloned behind it.
As warfare increased in size and scope and armies increased, armies could no longer hope to have a contiguous battle line. To be able to maneuver, it was necessary to introduce intervals between units and these intervals could be used to flank individual units in the battle line by fast acting-units such as cavalry. To guard against that, the infantry subunits were trained to be able to form squares
In geometry, a square is a regular polygon, regular quadrilateral. It has four straight sides of equal length and four equal angles. Squares are special cases of rectangles, which have four equal angles, and of rhombuses, which have four equal si ...
rapidly that gave the cavalry no weak flank to attack. During the age of gunpowder
Gunpowder, also commonly known as black powder to distinguish it from modern smokeless powder, is the earliest known chemical explosive. It consists of a mixture of sulfur, charcoal (which is mostly carbon), and potassium nitrate, potassium ni ...
, intervals between units could be increased because of the greater reach of the weapons, which raised the possibility of cavalry finding a gap in the line to exploit. Thus, the mark of good infantry was the rapid ability to form from line to square and back again.
Operational flanking
On an operational level army, commanders may attempt to flank and wrong foot entire enemy armies, rather than just being content with doing so at a tactical battalion or brigade level. The most infamous example of such an attempt was the modifiedSchlieffen Plan
The Schlieffen Plan (, ) is a name given after the First World War to German war plans, due to the influence of Field Marshal Alfred von Schlieffen and his thinking on an invasion of France and Belgium, which began on 4 August 1914. Schlieffe ...
used by the Germans during the opening stages of the First World War
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. That was an attempt to avoid facing the French armies head on, but instead flank them by swinging through neutral Belgium.
Second fronts
Just as at the tactical level, where a commander can attempt to anchor his flanks, commanders try to do the same at the operational level. Examples are theSecond World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
's German Winter Line
The Winter Line was a series of German and Italian military fortifications in Italy, constructed during World War II by Organisation Todt and commanded by Albert Kesselring. The series of three lines was designed to defend a western section ...
in Italy anchored by the Tyrrhenian and Adriatic Sea
The Adriatic Sea () is a body of water separating the Italian Peninsula from the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula. The Adriatic is the northernmost arm of the Mediterranean Sea, extending from the Strait of Otranto (where it connects to the Ionian Se ...
s and the trench systems of the Western Front which ran from the North Sea to the Alps. Attacking such positions would be expensive in casualties and more than likely lead to stalemate. Flanking attacks into areas outside the main zone of contention might be attempted to break the stalemates.
If successful, such operations can be shattering, such as at the Inchon, and break into lightly held rear echelons of an enemy when its front line forces are committed elsewhere. Even when they are not entirely successful, such as at Anzio
Anzio (, also ; ) is a town and ''comune'' on region of Italy, about south of Rome.
Well known for its seaside resorts, it is a fishing port and a departure point for ferries and hydroplanes to the Pontine Islands of Ponza, Palmarola, and Ve ...
, the operations can relieve pressure on troops on the main battle front by forcing the enemy to divert resources to contain the new front.
The operations may have strategic objectives such as the Invasion of Italy itself, the Gallipoli
The Gallipoli Peninsula (; ; ) is located in the southern part of East Thrace, the European part of Turkey, with the Aegean Sea to the west and the Dardanelles strait to the east.
Gallipoli is the Italian form of the Greek name (), meaning ' ...
, and the Normandy
Normandy (; or ) is a geographical and cultural region in northwestern Europe, roughly coextensive with the historical Duchy of Normandy.
Normandy comprises Normandy (administrative region), mainland Normandy (a part of France) and insular N ...
landings.
Such a strategy is not new, as Hannibal attacked Rome
Rome (Italian language, Italian and , ) is the capital city and most populated (municipality) of Italy. It is also the administrative centre of the Lazio Regions of Italy, region and of the Metropolitan City of Rome. A special named with 2, ...
by going over the Alps, rather than taking the obvious route. In return, Scipio Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus (, , ; 236/235–) was a Roman general and statesman who was one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Ancient Carthage, Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest milit ...
was able to defeat Hannibal not by trying to face him in Italy but by first undermining his power base in Iberia and then attacking his home city, Carthage
Carthage was an ancient city in Northern Africa, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classic ...
.
Strategic flanking
Flank attacks on thestrategic
Strategy (from Greek στρατηγία ''stratēgia'', "troop leadership; office of general, command, generalship") is a general plan to achieve one or more long-term or overall goals under conditions of uncertainty. In the sense of the "art o ...
level are seen when a nation or group of nations surround and attack an enemy from two or more directions, such as the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not an explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are calle ...
surrounding Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany, officially known as the German Reich and later the Greater German Reich, was the German Reich, German state between 1933 and 1945, when Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party controlled the country, transforming it into a Totalit ...
in World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
. In those cases, the flanked country usually has to fight on two fronts at once, placing it at a disadvantage.
The danger of being strategically flanked has driven the political and diplomatic actions of nations even in peacetime. For example, the fear of being strategically flanked by the other in The Great Game
The Great Game was a rivalry between the 19th-century British and Russian empires over influence in Central Asia, primarily in Afghanistan, Persia, and Tibet. The two colonial empires used military interventions and diplomatic negotiations t ...
between the British and the Russian Empires led to the expansion of both of them into China and the British eastwards into South-East Asia. The British feared that British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
would be surrounded by a Persian and Central Asia satellite to Russia in the west and north and a Russian-dominated China in the east. A China under British influence would mean that the Russians would be penned in from the south and the east. Initially, the Russians were more successful than the British in gaining territorial concessions in China, but the British were able to counteract that by cultivating the emerging Empire of Japan
The Empire of Japan, also known as the Japanese Empire or Imperial Japan, was the Japanese nation state that existed from the Meiji Restoration on January 3, 1868, until the Constitution of Japan took effect on May 3, 1947. From Japan–Kor ...
as a counterweight to the Russians, a relationship that culminated in the Anglo-Japanese Alliance
The was an alliance between the United Kingdom and the Empire of Japan which was effective from 1902 to 1923. The treaty creating the alliance was signed at Lansdowne House in London on 30 January 1902 by British foreign secretary Lord Lans ...
.
The Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
had its own Great Game, with the US and USSR competing for influence in Europe, Asia, Africa and Latin America. The division of Europe, the proxy wars
In political science, a proxy war is an armed conflict where at least one of the belligerents is directed or supported by an external third-party power. In the term ''proxy war'', a belligerent with external support is the ''proxy''; both bel ...
in Asia, and events like the Cuban Missile Crisis
The Cuban Missile Crisis, also known as the October Crisis () in Cuba, or the Caribbean Crisis (), was a 13-day confrontation between the governments of the United States and the Soviet Union, when American deployments of Nuclear weapons d ...
were all of great strategic importance to the two competing hegemonies.
Historical examples
See also
* '' Battleplan'' (documentary TV series) *Pincer movement
The pincer movement, or double envelopment, is a maneuver warfare, military maneuver in which forces simultaneously attack both flanking maneuver, flanks (sides) of an enemy Military organization, formation. This classic maneuver has been im ...
* Encirclement
Encirclement is a military term for the situation when a force or target is isolated and surrounded by enemy forces. The situation is highly dangerous for the encircled force. At the military strategy, strategic level, it cannot receive Milit ...
References
{{reflist, 2 Military tactics Military strategy Assault tactics Battle of Marathon