finfish on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting
A/RES/71/313
FAO Fisheries Department
The Fishery Resources Monitoring System (FIRMS)
{{Authority control pt:Pesca se:Guolásteapmi

 Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. The term excludes seawater and brackish water, but it does include non-salty mi ...
waterbodies (about 10% of all catch) and the oceans (about 90%). About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing
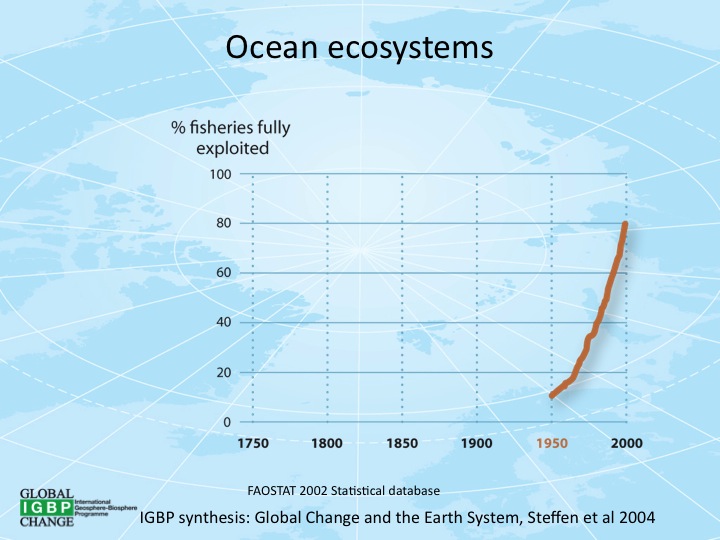
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.
Because of their economic and social importance, fisheries are governed by complex fisheries management
The management of fisheries is broadly defined as the set of tasks which guide vested parties and managers in the optimal use of aquatic renewable resources, primarily fish. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nation ...
practices and legal regimes that vary widely across countries. Historically, fisheries were treated with a "first-come, first-served
Queueing theory is the mathematical study of Queue area, waiting lines, or wikt:queue, queues. A queueing model is constructed so that queue lengths and waiting time can be predicted. Queueing theory is generally considered a branch of operatio ...
" approach, but recent threats from human overfishing and environmental issues have required increased regulation of fisheries to prevent conflict and increase profitable economic activity on the fishery. Modern jurisdiction over fisheries is often established by a mix of international treaties and local laws.
Declining fish populations, marine pollution
Marine pollution occurs when substances used or spread by humans, such as industrial waste, industrial, agricultural pollution, agricultural, and municipal solid waste, residential waste; particle (ecology), particles; noise; excess carbon dioxi ...
, and the destruction of important coastal ecosystems have introduced increasing uncertainty in important fisheries worldwide, threatening economic security
Economic security or financial security is the condition of having stable income or other resources to support a standard of living now and in the foreseeable future. It includes:
* probable continued solvency
* predictability of the future cash ...
and food security
Food security is the state of having reliable access to a sufficient quantity of affordable, healthy Human food, food. The availability of food for people of any class, gender, ethnicity, or religion is another element of food protection. Simila ...
in many parts of the world. These challenges are further complicated by the changes in the ocean caused by climate change, which may extend the range of some fisheries while dramatically reducing the sustainability of other fisheries.
Definitions
According to theFAO
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; . (FAO) is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition ...
, "...a fishery is an activity leading to harvesting of fish. It may involve capture of wild fish or raising of fish through aquaculture." It is typically defined in terms of the "people involved, species or type of fish, area of water or seabed, method of fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment (Freshwater ecosystem, freshwater or Marine ecosystem, marine), but may also be caught from Fish stocking, stocked Body of water, ...
, class of boats, purpose of the activities or a combination of the foregoing features".
The definition often includes a combination of mammal and fish fishers in a region, the latter fishing for similar species with similar gear types. Some government and private organizations, especially those focusing on recreational fishing
Recreational fishing, also called sport fishing or game fishing, is fishing for leisure, exercise or competition. It can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is occupational fishing activities done for profit; or subsistence fishing, ...
include in their definitions not only the fishers, but the fish and habitats upon which the fish depend.
The term ''fish''
* Inbiology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
– the term ''fish'' is most strictly used to describe any aquatic vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
that has gill
A gill () is a respiration organ, respiratory organ that many aquatic ecosystem, aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow r ...
s throughout life, and can also refer to those that have limbs (if any) or appendage
An appendage (or outgrowth) is an external body part or natural prolongation that protrudes from an organism's body such as an arm or a leg. Protrusions from single-celled bacteria and archaea are known as cell-surface appendages or surface app ...
s in the shape of fish fin
Fins are moving appendages protruding from the body of fish that interact with water to generate thrust and help the fish swim. Apart from the tail or caudal fin, fish fins have no direct connection with the back bone and are supported o ...
s. Many types of aquatic animals commonly referred to as "fish" are not fish in this strict sense; examples include shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
, cuttlefish
Cuttlefish, or cuttles, are Marine (ocean), marine Mollusca, molluscs of the order (biology), suborder Sepiina. They belong to the class (biology), class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique ...
, starfish
Starfish or sea stars are Star polygon, star-shaped echinoderms belonging to the class (biology), class Asteroidea (). Common usage frequently finds these names being also applied to brittle star, ophiuroids, which are correctly referred to ...
, crayfish
Crayfish are freshwater crustaceans belonging to the infraorder Astacidea, which also contains lobsters. Taxonomically, they are members of the superfamilies Astacoidea and Parastacoidea. They breathe through feather-like gills. Some spe ...
and jellyfish
Jellyfish, also known as sea jellies or simply jellies, are the #Life cycle, medusa-phase of certain gelatinous members of the subphylum Medusozoa, which is a major part of the phylum Cnidaria. Jellyfish are mainly free-swimming marine animal ...
. In the strict sense, all vertebrates are cladistic
Cladistics ( ; from Ancient Greek 'branch') is an approach to biological classification in which organisms are categorized in groups ("clades") based on hypotheses of most recent common ancestry. The evidence for hypothesized relationships is ...
ally fish, although colloquially "fish" is a paraphyletic
Paraphyly is a taxonomic term describing a grouping that consists of the grouping's last common ancestor and some but not all of its descendant lineages. The grouping is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In co ...
term that only refers to non-tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
vertebrates. In earlier times, even biologist
A biologist is a scientist who conducts research in biology. Biologists are interested in studying life on Earth, whether it is an individual Cell (biology), cell, a multicellular organism, or a Community (ecology), community of Biological inter ...
s did not make any distinction — for instance, 16th century
The 16th century began with the Julian calendar, Julian year 1501 (represented by the Roman numerals MDI) and ended with either the Julian or the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian year 1600 (MDC), depending on the reckoning used (the Gregorian calend ...
natural historians often classified seals, whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s, amphibian
Amphibians are ectothermic, anamniote, anamniotic, tetrapod, four-limbed vertebrate animals that constitute the class (biology), class Amphibia. In its broadest sense, it is a paraphyletic group encompassing all Tetrapod, tetrapods, but excl ...
s, crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large, semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term "crocodile" is sometimes used more loosely to include ...
s and even hippopotamus
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Sahar ...
es, as well as a host of marine invertebrates, as fish.
* In fisheries – the term ''fish'' is used as a collective term, and includes mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s and any aquatic animal
An aquatic animal is any animal, whether vertebrate or invertebrate, that lives in a body of water for all or most of its lifetime. Aquatic animals generally conduct gas exchange in water by extracting dissolved oxygen via specialised respirato ...
s that are harvested for economic value
In economics, economic value is a measure of the benefit provided by a goods, good or service (economics), service to an Agent (economics), economic agent, and value for money represents an assessment of whether financial or other resources are ...
.
* True fish – The biological definition of a fish (mentioned above) is sometimes called a "true fish", the vast majority of which are teleost
Teleostei (; Ancient Greek, Greek ''teleios'' "complete" + ''osteon'' "bone"), members of which are known as teleosts (), is, by far, the largest group of ray-finned fishes (class Actinopterygii), with 96% of all neontology, extant species of f ...
s. True fish are also referred to as ''finfish'' or ''fin fish'' to distinguish them from other invertebrate aquatic life harvested in fisheries or aquaculture.
Types
Thefishing industry
The fishing industry includes any industry or activity that takes, cultures, processes, preserves, stores, transports, markets or sells fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, sub ...
which harvests fish from fisheries can be divided into three main sectors: commercial, recreational or subsistence. They can be saltwater or freshwater, wild or farmed. About 85 percent of total marine fisheries production was finfish, mainly anchoveta (4.9 million tonnes), Alaska pollock (3.4 million tonnes) and skipjack tuna (3.1 million tonnes). Examples are the salmon
Salmon (; : salmon) are any of several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the genera ''Salmo'' and ''Oncorhynchus'' of the family (biology), family Salmonidae, native ...
fishery of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
, the cod
Cod (: cod) is the common name for the demersal fish genus ''Gadus'', belonging to the family (biology), family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gad ...
fishery off the Lofoten
Lofoten ( , ; ; ) is an archipelago and a Districts of Norway, traditional district in the county of Nordland, Norway. Lofoten has distinctive scenery with dramatic mountains and peaks, open sea and sheltered bays, beaches, and untouched lands. T ...
islands, the tuna fishery of the Eastern Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the conti ...
, or the shrimp farm fisheries in China. Capture fisheries can be broadly classified as industrial scale, small-scale or artisanal, and recreational.
Close to 90% of the world's fishery catches come from oceans and seas, as opposed to inland waters. These marine catches have remained relatively stable since the mid-nineties (between 80 and 86 million tonnes). Most marine fisheries are based near the coast
A coast (coastline, shoreline, seashore) is the land next to the sea or the line that forms the boundary between the land and the ocean or a lake. Coasts are influenced by the topography of the surrounding landscape and by aquatic erosion, su ...
. This is not only because harvesting from relatively shallow waters is easier than in the open ocean, but also because fish are much more abundant near the coastal shelf, due to the abundance of nutrients available there from coastal upwelling and land runoff. However, productive wild fisheries also exist in open oceans, particularly by seamount
A seamount is a large submarine landform that rises from the ocean floor without reaching the water surface (sea level), and thus is not an island, islet, or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly a ...
s, and inland in lakes and rivers.
Most fisheries are wild fisheries, but farmed fisheries are increasing. Farming can occur in coastal areas, such as with oyster farms, or the aquaculture of salmon, but more typically fish farming occurs inland, in lakes, ponds, tanks and other enclosures.
There are commercial fisheries worldwide for finfish, mollusk
Mollusca is a phylum of protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The ...
s, crustacean
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquatic arthrop ...
s and echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any animal of the phylum Echinodermata (), which includes starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars and sea cucumbers, as well as the sessile sea lilies or "stone lilies". While bilaterally symmetrical as ...
s, and by extension, aquatic plant
Aquatic plants, also referred to as hydrophytes, are vascular plants and Non-vascular plant, non-vascular plants that have adapted to live in aquatic ecosystem, aquatic environments (marine ecosystem, saltwater or freshwater ecosystem, freshwater ...
s such as kelp
Kelps are large brown algae or seaweeds that make up the order (biology), order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genus, genera. Despite its appearance and use of photosynthesis in chloroplasts, kelp is technically not a plant but a str ...
. However, a very small number of species support the majority of the world's fisheries. Some of these species are herring
Herring are various species of forage fish, belonging to the Order (biology), order Clupeiformes.
Herring often move in large Shoaling and schooling, schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate wate ...
, cod
Cod (: cod) is the common name for the demersal fish genus ''Gadus'', belonging to the family (biology), family Gadidae. Cod is also used as part of the common name for a number of other fish species, and one species that belongs to genus ''Gad ...
, anchovy, tuna, flounder
Flounders are a group of flatfish species. They are demersal fish, found at the bottom of oceans around the world; some species will also enter estuary, estuaries.
Taxonomy
The name "flounder" is used for several only distantly related speci ...
, mullet, squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also ...
, shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchi ...
, salmon, crab
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura (meaning "short tailed" in Greek language, Greek), which typically have a very short projecting tail-like abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomen, usually hidden entirely under the Thorax (arthropo ...
, lobster
Lobsters are Malacostraca, malacostracans Decapoda, decapod crustaceans of the family (biology), family Nephropidae or its Synonym (taxonomy), synonym Homaridae. They have long bodies with muscular tails and live in crevices or burrows on th ...
, oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but no ...
and scallops. All except these last four provided a worldwide catch of well over a million
1,000,000 (one million), or one thousand thousand, is the natural number following 999,999 and preceding 1,000,001. The word is derived from the early Italian ''millione'' (''milione'' in modern Italian), from ''mille'', "thousand", plus the ...
tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the s ...
s in 1999, with herring and sardine
Sardine and pilchard are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring suborder Clupeoidei. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century; a somewhat dubious etymology says it com ...
s together providing a harvest of over 22 million metric tons in 1999. Many other species are harvested in smaller numbers.
In 2022 small-scale fisheries contribute an estimated 40 percent of the global catch and support 90 percent of the capture fisheries workforce, with women representing 40 percent. 500 million people rely on small-scale fisheries for their livelihoods, including 53 million involved in subsistence fishing, of which 45 percent are women.
In 2022 inland fisheries produced 11.3 million tonnes, harvested mainly in Asia (63.4 percent) and Africa (29.4 percent), where they are important for food security. Lead producers were India (1.9 million tonnes), Bangladesh (1.3 million tonnes), China (1.2 million tonnes), Myanmar (0.9 million tonnes) and Indonesia (0.5 million tonnes). Inland fisheries figures are likely underestimated due to the difficulties most countries face in collecting these data.
Economic importance
Directly or indirectly, the livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends on fisheries andaquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
. Overfishing
Overfishing is the removal of a species of fish (i.e. fishing) from a body of water at a rate greater than that the species can replenish its population naturally (i.e. the overexploitation of the fishery's existing Fish stocks, fish stock), resu ...
, including the taking of fish beyond sustainable levels, is reducing fish stocks and employment in many world regions. It was estimated in 2014 that global fisheries were adding US$270 billion a year to global GDP, but by full implementation of sustainable fishing, that figure could rise by as much as US$50 billion. In 2022 77% of the global workforce was in Asia, 16% in Africa and 5% in Latin America and the Caribbean.
In addition to commercial and subsistence fishing, recreational (sport) fishing is popular and economically important in many regions.
Production
Total fish production in 2016 reached an all-time high of 171 million tonnes, of which 88 percent was utilized for direct human consumption, thanks to relatively stable capture fisheries production, reduced wastage and continued aquaculture growth. This production resulted in a record-high per capita consumption of 20.3 kg in 2016. Since 1961 the annual global growth in fish consumption has been twice as high as population growth. While annual growth of aquaculture has declined in recent years, significant double-digit growth is still recorded in some countries, particularly in Africa and Asia. FAO predicted in 2018 the following major trends for the period up to 2030: * World fish production, consumption and trade are expected to increase, but with a growth rate that will slow over time. * Despite reduced capture fisheries production in China, world capture fisheries production is projected to increase slightly through increased production in other areas if resources are properly managed. Expanding world aquaculture production, although growing more slowly than in the past, is anticipated to fill the supply–demand gap. * Prices will all increase in nominal terms while declining in real terms, although remaining high. * Food fish supply will increase in all regions, while per capita fish consumption is expected to decline in Africa, which raises concerns in terms of food security. * Trade in fish and fish products is expected to increase more slowly than in the past decade, but the share of fish production that is exported is projected to remain stable.Management
Global goals
International attention to these issues has been captured in Sustainable Development Goal 14 "Life Below Water" which sets goals for international policy focused on preserving coastal ecosystems and supporting more sustainable economic practices for coastal communities, including in their fishery andaquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. Nelu ...
practices.United Nations (2017) Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on 6 July 2017, Work of the Statistical Commission pertaining to the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable DevelopmentA/RES/71/313
Law
Environmental issues
Climate change
See also
* Fisheries co-management * Fisheries science * National Fish Habitat Initiative * Ocean fisheries * Population dynamics of fisheries * Regional Fisheries Management Organisation * Sea Fish Industry Authority * Tanka peopleReferences
Free content sources
External links
FAO Fisheries Department
The Fishery Resources Monitoring System (FIRMS)
{{Authority control pt:Pesca se:Guolásteapmi