Field of view on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The field of view (FOV) is the angular extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of
The field of view (FOV) is the angular extent of the observable world that is seen at any given moment. In the case of
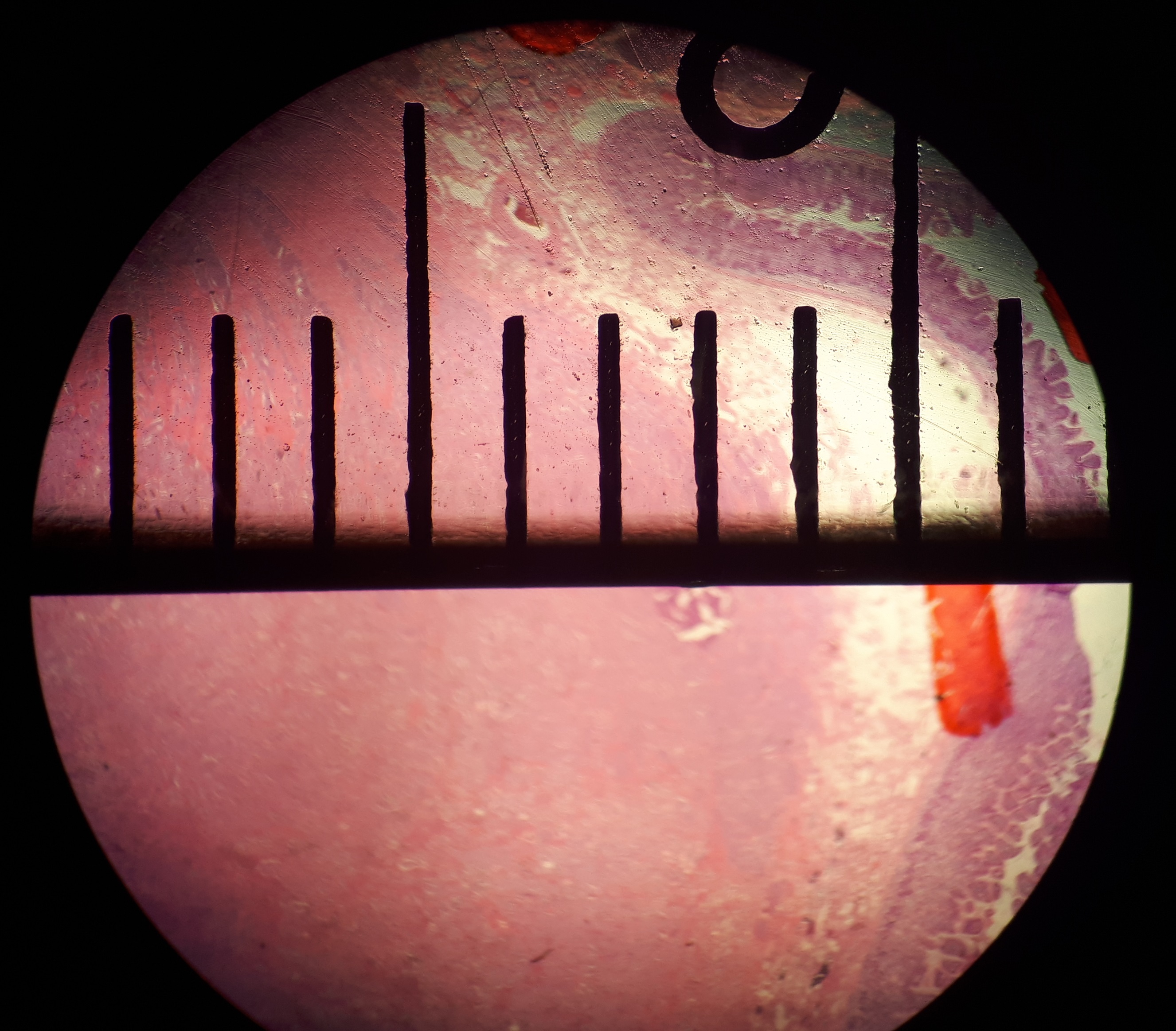 In microscopy, the field of view in high power (usually a 400-fold magnification when referenced in scientific papers) is called a high-power field, and is used as a reference point for various classification schemes.
For an objective with magnification , the FOV is related to the Field Number (FN) by
:
if other magnifying lenses are used in the system (in addition to the objective), the total for the projection is used.
In microscopy, the field of view in high power (usually a 400-fold magnification when referenced in scientific papers) is called a high-power field, and is used as a reference point for various classification schemes.
For an objective with magnification , the FOV is related to the Field Number (FN) by
:
if other magnifying lenses are used in the system (in addition to the objective), the total for the projection is used.
optical instrument
An optical instrument is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and camera ...
s or sensors, it is a solid angle through which a detector is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) is a self-propagating wave of the electromagnetic field that carries momentum and radiant energy through space. It encompasses a broad spectrum, classified by frequency or its inverse, wavelength ...
. It is further relevant in ''photography
Photography is the visual arts, art, application, and practice of creating images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It is empl ...
''.
Humans and animals
In the context of human and primate vision, the term "field of view" is typically only used in the sense of a restriction to what is visible by external apparatus, like when wearing spectacles orvirtual reality
Virtual reality (VR) is a Simulation, simulated experience that employs 3D near-eye displays and pose tracking to give the user an immersive feel of a virtual world. Applications of virtual reality include entertainment (particularly video gam ...
goggles. Note that eye movements are allowed in the definition but do not change the field of view when understood this way.
If the analogy of the eye's retina working as a sensor is drawn upon, the corresponding concept in human (and much of animal vision) is the visual field. It is defined as "the number of degrees of visual angle during stable fixation of the eyes".Strasburger, Hans; Pöppel, Ernst (2002). Visual Field. In G. Adelman & B.H. Smith (Eds): ''Encyclopedia of Neuroscience''; 3rd edition, on CD-ROM. Elsevier Science B.V., Amsterdam, New York. Note that eye movements are excluded in the visual field's definition. Humans have a slightly over 210-degree forward-facing horizontal arc of their visual field (i.e. without eye movements), (with eye movements included it is slightly larger, as you can try for yourself by wiggling a finger on the side), while some birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class (biology), class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the Oviparity, laying of Eggshell, hard-shelled eggs, a high Metabolism, metabolic rate, a fou ...
have a complete or nearly complete 360-degree visual field. The vertical range of the visual field in humans is around 150 degrees.
The range of visual abilities is not uniform across the visual field, and by implication the FoV, and varies between species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
. For example, binocular vision, which is the basis for stereopsis
Binocular vision is seeing with two eyes, which increases the size of the Visual field, visual field. If the visual fields of the two eyes overlap, binocular #Depth, depth can be seen. This allows objects to be recognized more quickly, camouflage ...
and is important for depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions.
Depth sensation is the corresponding term for non-hum ...
, covers 114 degrees (horizontally) of the visual field in humans; the remaining peripheral ~50 degrees on each side have no binocular vision (because only one eye can see those parts of the visual field). Some birds have a scant 10 to 20 degrees of binocular vision.
Similarly, color vision and the ability to perceive shape and motion vary across the visual field; in humans color vision and form perception are concentrated in the center of the visual field, while motion perception is only slightly reduced in the periphery and thus has a relative advantage there. The physiological basis for that is the much higher concentration of color-sensitive cone cell
Cone cells or cones are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the vertebrate eye. Cones are active in daylight conditions and enable photopic vision, as opposed to rod cells, which are active in dim light and enable scotopic vision. Most v ...
s and color-sensitive parvocellular retinal ganglion cells in the fovea – the central region of the retina, together with a larger representation in the visual cortex – in comparison to the higher concentration of color-insensitive rod cell
Rod cells are photoreceptor cells in the retina of the eye that can function in lower light better than the other type of visual photoreceptor, cone cells. Rods are usually found concentrated at the outer edges of the retina and are used in ...
s and motion-sensitive magnocellular retinal ganglion cells in the visual periphery, and smaller cortical representation. Since rod cells require considerably less light to be activated, the result of this distribution is further that peripheral vision is much more sensitive at night relative to foveal vision (sensitivity is highest at around 20 deg eccentricity).
Conversions
Many optical instruments, particularly binoculars or spotting scopes, are advertised with their field of view specified in one of two ways: angular field of view, and linear field of view. Angular field of view is typically specified in degrees, while linear field of view is a ratio of lengths. For example, binoculars with a 5.8 degree (angular) field of view might be advertised as having a (linear) field of view of 102 mm per meter. As long as the FOV is less than about 10 degrees or so, the following approximation formulas allow one to convert between linear and angular field of view. Let be the angular field of view in degrees. Let be the linear field of view in millimeters per meter. Then, using the small-angle approximation: : :Machine vision
Inmachine vision
Machine vision is the technology and methods used to provide image, imaging-based automation, automatic inspection and analysis for such applications as automatic inspection, process control, and robot guidance, usually in industry. Machine vision ...
the lens focal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
and image sensor An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into s ...
size sets up the fixed relationship between the field of view and the working distance. Field of view is the area of the inspection captured on the camera’s imager. The size of the field of view and the size of the camera’s imager directly affect the image resolution (one determining factor in accuracy). Working distance is the distance between the back of the lens and the target object.
Tomography
In tomography, the field of view is the area of each tomogram. In for example computed tomography, a volume of voxels can be created from such tomograms by merging multiple slices along the scan range.Remote sensing
Inremote sensing
Remote sensing is the acquisition of information about an physical object, object or phenomenon without making physical contact with the object, in contrast to in situ or on-site observation. The term is applied especially to acquiring inform ...
, the solid angle through which a detector element (a pixel sensor) is sensitive to electromagnetic radiation at any one time, is called ''instantaneous field of view'' or IFOV. A measure of the spatial resolution of a remote sensing imaging system, it is often expressed as dimensions of visible ground area, for some known sensor altitude
Altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum (geodesy), datum and a point or object. The exact definition and reference datum varies according to the context (e.g., aviation, geometr ...
. Single pixel IFOV is closely related to concept of ''ground resolved distance'', ground sample distance, modulation transfer function, and ''resolved pixel size''.
Astronomy
Inastronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest includ ...
, the field of view is usually expressed as an angular area viewed by the instrument, in square degrees, or for higher magnification instruments, in square arc-minutes. For reference the Wide Field Channel on the Advanced Camera for Surveys on the Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the Orbiting Solar Observatory, first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most ...
has a field of view of 10 sq. arc-minutes, and the High Resolution Channel of the same instrument has a field of view of 0.15 sq. arc-minutes. Ground-based survey telescopes have much wider fields of view. The photographic plates used by the UK Schmidt Telescope had a field of view of 30 sq. degrees. The 1.8 m (71 in) Pan-STARRS telescope, with the most advanced digital camera to date has a field of view of 7 sq. degrees. In the near infra-red WFCAM on UKIRT has a field of view of 0.2 sq. degrees and the VISTA telescope has a field of view of 0.6 sq. degrees. Until recently digital cameras could only cover a small field of view compared to photographic plates, although they beat photographic plates in quantum efficiency, linearity and dynamic range, as well as being much easier to process.
Photography
In photography, the field of view is that part of the world that is visible through the camera at a particular position and orientation in space; objects outside the FOV when the picture is taken are not recorded in the photograph. It is most often expressed as the angular size of the view cone, as an angle of view. For a normal lens focused at infinity, the diagonal (or horizontal or vertical) field of view can be calculated as: : where is thefocal length
The focal length of an Optics, optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the Multiplicative inverse, inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system Converge ...
, here the sensor size and are in the same unit of length, FOV is in radians.
Microscopy
 In microscopy, the field of view in high power (usually a 400-fold magnification when referenced in scientific papers) is called a high-power field, and is used as a reference point for various classification schemes.
For an objective with magnification , the FOV is related to the Field Number (FN) by
:
if other magnifying lenses are used in the system (in addition to the objective), the total for the projection is used.
In microscopy, the field of view in high power (usually a 400-fold magnification when referenced in scientific papers) is called a high-power field, and is used as a reference point for various classification schemes.
For an objective with magnification , the FOV is related to the Field Number (FN) by
:
if other magnifying lenses are used in the system (in addition to the objective), the total for the projection is used.
Video games
The field of view invideo game
A video game or computer game is an electronic game that involves interaction with a user interface or input device (such as a joystick, game controller, controller, computer keyboard, keyboard, or motion sensing device) to generate visual fe ...
s refers to the field of view of the camera looking at the game world, which is dependent on the scaling method used.
See also
*Field of regard The field of regard (abbreviated FOR) is the total area that can be captured by a movable sensor. It should not be confused with the field of view (FOV), which is the angular cone perceivable by the sensor at a particular time instant. The field of ...
* Panorama
* Perimetry
* Peripheral vision
* Visual perception
Visual perception is the ability to detect light and use it to form an image of the surrounding Biophysical environment, environment. Photodetection without image formation is classified as ''light sensing''. In most vertebrates, visual percept ...
* Useful field of view
* 35 mm equivalent focal length
* Angle of view
* Crop factor
* Image sensor format
* Line of sight
References
{{Authority control Vision Ophthalmology Neurology Science of photography