Field-programmable gate arrays on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a
Xilinx, Inc.
Retrieved January 15, 2009. The XC2064 had 64 configurable logic blocks (CLBs), with two three-input
Xilinx unveil revolutionary 65nm FPGA architecture: the Virtex-5 family
. May 15, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009. In 1987, the
FPGA Market to Pass $2.7 Billion by '10, In-Stat Says
. May 24, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009. * 2010 estimates: $2.75 billion * 2013: $5.4 billion * 2020 estimate: $9.8 billion
Gartner Dataquest Analyst Gives ASIC, FPGA Markets Clean Bill of Health
. June 13, 2005. Retrieved February 5, 2009. * 2008: 90,000
 The most common FPGA architecture consists of an array of
The most common FPGA architecture consists of an array of
 An alternate approach to using hard-macro processors is to make use of
An alternate approach to using hard-macro processors is to make use of
FPGA manufacturer claims to beat Moore's Law
" October 27, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2011. Following the introduction of its 28 nm 7-series FPGAs, Xilinx said that several of the highest-density parts in those FPGA product lines will be constructed using multiple dies in one package, employing technology developed for 3D construction and stacked-die assemblies. Xilinx's approach stacks several (three or four) active FPGA dies side by side on a silicon

 A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a
A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by a customer or a designer after manufacturinghence the term '' field-programmable''. The FPGA configuration is generally specified using a hardware description language
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, and most commonly, digital logic circuits.
A hardware description language e ...
(HDL), similar to that used for an application-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-effici ...
(ASIC). Circuit diagram
A circuit diagram (wiring diagram, electrical diagram, elementary diagram, electronic schematic) is a graphical representation of an electrical circuit. A pictorial circuit diagram uses simple images of components, while a schematic diagram ...
s were previously used to specify the configuration, but this is increasingly rare due to the advent of electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together ...
tools.
FPGAs contain an array of programmable logic block
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates.
Logic blocks ...
s, and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects allowing blocks to be wired together. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or act as simple logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic ga ...
s like AND and XOR
Exclusive or or exclusive disjunction is a logical operation that is true if and only if its arguments differ (one is true, the other is false).
It is symbolized by the prefix operator J and by the infix operators XOR ( or ), EOR, EXOR, , , ...
. In most FPGAs, logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops
Flip-flops are a type of light sandal, typically worn as a form of casual footwear. They consist of a flat sole held loosely on the foot by a Y-shaped strap known as a toe thong that passes between the first and second toes and around both side ...
or more complete blocks of memory. Many FPGAs can be reprogrammed to implement different logic functions, allowing flexible reconfigurable computing
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with very flexible high speed computing fabrics like FPGA, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA ...
as performed in computer software
Software is a set of computer programs and associated documentation and data. This is in contrast to hardware, from which the system is built and which actually performs the work.
At the lowest programming level, executable code consists ...
.
FPGAs have a remarkable role in embedded system
An embedded system is a computer system—a combination of a computer processor, computer memory, and input/output peripheral devices—that has a dedicated function within a larger mechanical or electronic system. It is ''embedded'' ...
development due to their capability to start system software development simultaneously with hardware, enable system performance simulations at a very early phase of the development, and allow various system trials and design iterations before finalizing the system architecture.
History
The FPGA industry sprouted fromprogrammable read-only memory
A programmable read-only memory (PROM) is a form of digital memory where the contents can be changed once after manufacture of the device. The data is then permanent and cannot be changed. It is one type of read-only memory (ROM). PROMs are used ...
(PROM) and programmable logic devices
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manuf ...
(PLDs). PROMs and PLDs both had the option of being programmed in batches in a factory or in the field (field-programmable).
Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
was founded in 1983 and delivered the industry's first reprogrammable logic device in 1984 – the EP300 – which featured a quartz window in the package that allowed users to shine an ultra-violet lamp on the die to erase the EPROM
An EPROM (rarely EROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power ...
cells that held the device configuration.
Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
produced the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array
A gate array is an approach to the design and manufacture of application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) using a prefabricated chip with components that are later interconnected into logic devices (e.g. NAND gates, flip-flops, etc.) accord ...
in 1985the XC2064. The XC2064 had programmable gates and programmable interconnects between gates, the beginnings of a new technology and market.Funding Universe.Xilinx, Inc.
Retrieved January 15, 2009. The XC2064 had 64 configurable logic blocks (CLBs), with two three-input
lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array that replaces runtime computation with a simpler array indexing operation. The process is termed as "direct addressing" and LUTs differ from hash tables in a way that, to retrieve a value v w ...
s (LUTs).Clive Maxfield, Programmable Logic DesignLine,Xilinx unveil revolutionary 65nm FPGA architecture: the Virtex-5 family
. May 15, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009. In 1987, the
Naval Surface Warfare Center
*
A Naval Surface Warfare Center (NSWC) is part of the Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA) operated by the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the ...
funded an experiment proposed by Steve Casselman to develop a computer that would implement 600,000 reprogrammable gates. Casselman was successful and a patent related to the system was issued in 1992.
Altera and Xilinx continued unchallenged and quickly grew from 1985 to the mid-1990s when competitors sprouted up, eroding a significant portion of their market share. By 1993, Actel (now Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-bas ...
) was serving about 18 percent of the market.
The 1990s were a period of rapid growth for FPGAs, both in circuit sophistication and the volume of production. In the early 1990s, FPGAs were primarily used in telecommunication
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than tha ...
s and networking
Network, networking and networked may refer to:
Science and technology
* Network theory, the study of graphs as a representation of relations between discrete objects
* Network science, an academic field that studies complex networks
Mathematics
...
. By the end of the decade, FPGAs found their way into consumer, automotive, and industrial applications.
By 2013, Altera (31 percent), Actel (10 percent) and Xilinx (36 percent) together represented approximately 77 percent of the FPGA market.
Companies like Microsoft have started to use FPGAs to accelerate high-performance, computationally intensive systems (like the data centers that operate their Bing search engine
Microsoft Bing (commonly known as Bing) is a web search engine owned and operated by Microsoft. The service has its origins in Microsoft's previous search engines: MSN Search, Windows Live Search and later Live Search. Bing provides a variety ...
), due to the performance per watt
In computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consu ...
advantage FPGAs deliver. Microsoft began using FPGAs to accelerate
In mechanics, acceleration is the rate of change of the velocity of an object with respect to time. Accelerations are vector quantities (in that they have magnitude and direction). The orientation of an object's acceleration is given by the ...
Bing in 2014, and in 2018 began deploying FPGAs across other data center workloads for their Azure cloud computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage ( cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Large clouds often have functions distributed over m ...
platform.
Growth
The following timelines indicate progress in different aspects of FPGA design.Gates
* 1987: 9,000 gates, Xilinx * 1992: 600,000, Naval Surface Warfare Department * Early 2000s: millions * 2013: 50 million, XilinxMarket size
* 1985: First commercial FPGA : Xilinx XC2064 * 1987: $14 million * : >$385 million * 2005: $1.9 billionDylan McGrath, ''EE Times'',FPGA Market to Pass $2.7 Billion by '10, In-Stat Says
. May 24, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009. * 2010 estimates: $2.75 billion * 2013: $5.4 billion * 2020 estimate: $9.8 billion
Design starts
A ''design start'' is a new custom design for implementation on an FPGA. * 2005: 80,000Dylan McGrath, ''EE Times'',Gartner Dataquest Analyst Gives ASIC, FPGA Markets Clean Bill of Health
. June 13, 2005. Retrieved February 5, 2009. * 2008: 90,000
Design
Contemporary FPGAs have amplelogic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic ga ...
s and RAM blocks to implement complex digital computations. FPGAs can be used to implement any logical function that an ASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-effici ...
can perform. The ability to update the functionality after shipping, partial re-configuration of a portion of the design and the low non-recurring engineering costs relative to an ASIC design (notwithstanding the generally higher unit cost), offer advantages for many applications.
As FPGA designs employ very fast I/O rates and bidirectional data buses
A bus (contracted from omnibus, with variants multibus, motorbus, autobus, etc.) is a road vehicle that carries significantly more passengers than an average car or van. It is most commonly used in public transport, but is also in use for ...
, it becomes a challenge to verify correct timing of valid data within setup time and hold time. Floor planning helps resource allocation within FPGAs to meet these timing constraints.
Some FPGAs have analog features in addition to digital functions. The most common analog feature is a programmable slew rate
In electronics, slew rate is defined as the change of voltage or current, or any other electrical quantity, per unit of time. Expressed in SI units, the unit of measurement is volts/ second or amperes/second, but is usually expressed in terms of ...
on each output pin, allowing the engineer to set low rates on lightly loaded pins that would otherwise ring
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
or couple unacceptably, and to set higher rates on heavily loaded high-speed channels that would otherwise run too slowly. Also common are quartz-crystal oscillator
A crystal oscillator is an electronic oscillator circuit that uses a piezoelectric crystal as a frequency-selective element. The oscillator frequency is often used to keep track of time, as in quartz wristwatches, to provide a stable clock ...
s, on-chip resistance-capacitance oscillators, and phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
s with embedded voltage-controlled oscillator
A microwave (12–18GHz) voltage-controlled oscillator
A voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) is an electronic oscillator whose oscillation frequency is controlled by a voltage input. The applied input voltage determines the instantaneous oscillat ...
s used for clock generation and management as well as for high-speed serializer-deserializer (SERDES) transmit clocks and receiver clock recovery. Fairly common are differential comparator
In electronics, a comparator is a device that compares two voltages or currents and outputs a digital signal indicating which is larger. It has two analog input terminals V_+ and V_- and one binary digital output V_\text. The output is ideally
: ...
s on input pins designed to be connected to differential signaling
Differential signalling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conduc ...
channels. A few "mixed signal
A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die.analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
s (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archi ...
s (DACs) with analog signal conditioning blocks allowing them to operate as a system-on-a-chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memor ...
(SoC). Such devices blur the line between an FPGA, which carries digital ones and zeros on its internal programmable interconnect fabric, and field-programmable analog array A field-programmable analog array (FPAA) is an integrated circuit device containing computational analog blocks (CAB) and interconnects between these blocks offering field-programmability. Unlike their digital cousin, the FPGA, the devices tend to ...
(FPAA), which carries analog values on its internal programmable interconnect fabric.
Logic blocks
 The most common FPGA architecture consists of an array of
The most common FPGA architecture consists of an array of logic block
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates.
Logic blocks ...
s (called configurable logic blocks, CLBs, or logic array blocks, LABs, depending on vendor), I/O pads, and routing channels. Generally, all the routing channels have the same width (number of wires). Multiple I/O pads may fit into the height of one row or the width of one column in the array.
"An application circuit must be mapped into an FPGA with adequate resources. While the number of CLBs/LABs and I/Os required is easily determined from the design, the number of routing tracks needed may vary considerably even among designs with the same amount of logic. (For example, a crossbar switch
In electronics and telecommunications, a crossbar switch (cross-point switch, matrix switch) is a collection of switches arranged in a matrix configuration. A crossbar switch has multiple input and output lines that form a crossed pattern of ...
requires much more routing than a systolic array
In parallel computer architectures, a systolic array is a homogeneous network of tightly coupled data processing units (DPUs) called cells or nodes. Each node or DPU independently computes a partial result as a function of the data received f ...
with the same gate count. Since unused routing tracks increase the cost (and decrease the performance) of the part without providing any benefit, FPGA manufacturers try to provide just enough tracks so that most designs that will fit in terms of lookup tables (LUTs) and I/Os can be routed
Routing is the process of selecting a path for traffic in a network or between or across multiple networks. Broadly, routing is performed in many types of networks, including circuit-switched networks, such as the public switched telephone netwo ...
. This is determined by estimates such as those derived from Rent's rule or by experiments with existing designs."
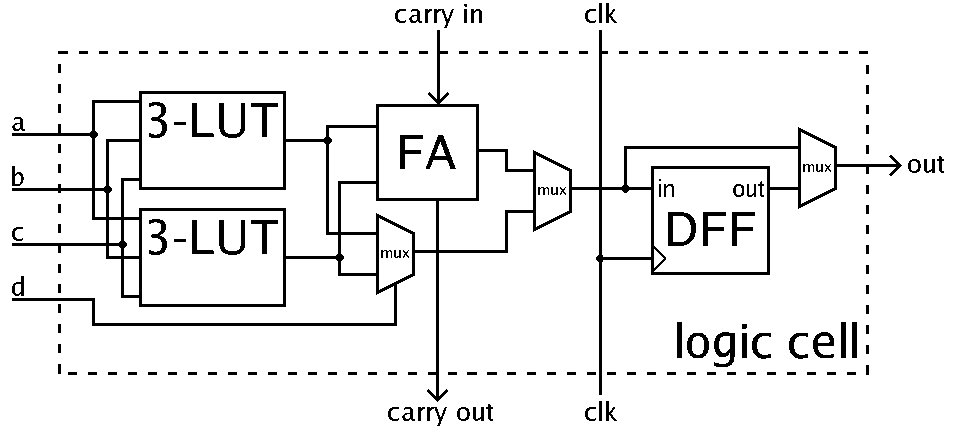
In general, a logic block consists of a few logical cells (called ALM, LE, slice etc.). A typical cell consists of a 4-input LUT, a full adder
An adder, or summer, is a digital circuit that performs addition of numbers. In many computers and other kinds of processors adders are used in the arithmetic logic units (ALUs). They are also used in other parts of the processor, where they are ...
(FA) and a D-type flip-flop. These might be split into two 3-input LUTs. In ''normal mode'' those are combined into a 4-input LUT through the first multiplexer
In electronics, a multiplexer (or mux; spelled sometimes as multiplexor), also known as a data selector, is a device that selects between several analog or digital input signals and forwards the selected input to a single output line. The sel ...
(mux). In ''arithmetic'' mode, their outputs are fed to the adder. The selection of mode is programmed into the second mux. The output can be either synchronous
Synchronization is the coordination of events to operate a system in unison. For example, the conductor of an orchestra keeps the orchestra synchronized or ''in time''. Systems that operate with all parts in synchrony are said to be synchronou ...
or asynchronous
Asynchrony is the state of not being in synchronization.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and computing
* Asynchrony (computer programming), the occurrence of events independent of the main program flow, and ways to deal wit ...
, depending on the programming of the third mux. In practice, entire or parts of the adder are stored as functions into the LUTs in order to save space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
.
Hard blocks
Modern FPGA families expand upon the above capabilities to include higher level functionality fixed in silicon. Having these common functions embedded in the circuit reduces the area required and gives those functions increased speed compared to building them from logical primitives. Examples of these include multipliers, generic DSP blocks, embedded processors, high-speed I/O logic and embeddedmemories
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, ...
.
Higher-end FPGAs can contain high speed multi-gigabit transceivers and ''hard IP cores'' such as processor core
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, ...
s, Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in ...
medium access control units, PCI
PCI may refer to:
Business and economics
* Payment card industry, businesses associated with debit, credit, and other payment cards
** Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard, a set of security requirements for credit card processors
* Prov ...
/PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common m ...
controllers, and external memory controllers. These cores exist alongside the programmable fabric, but they are built out of transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s instead of LUTs so they have ASIC-level performance
A performance is an act of staging or presenting a play, concert, or other form of entertainment. It is also defined as the action or process of carrying out or accomplishing an action, task, or function.
Management science
In the work place ...
and power consumption
Electric energy consumption is the form of energy consumption that uses electrical energy. Electric energy consumption is the actual energy demand made on existing electricity supply for transportation, residential, industrial, commercial, and ot ...
without consuming a significant amount of fabric resources, leaving more of the fabric free for the application-specific logic. The multi-gigabit transceivers also contain high performance analog input and output circuitry along with high-speed serializers and deserializers, components which cannot be built out of LUTs. Higher-level physical layer (PHY) functionality such as line coding
In telecommunication, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signals is usually called a constrained c ...
may or may not be implemented alongside the serializers and deserializers in hard logic, depending on the FPGA.
Soft core
 An alternate approach to using hard-macro processors is to make use of
An alternate approach to using hard-macro processors is to make use of soft processor
A soft microprocessor (also called softcore microprocessor or a soft processor) is a microprocessor core that can be wholly implemented using logic synthesis. It can be implemented via different semiconductor devices containing programmable logi ...
IP cores that are implemented within the FPGA logic. Nios II
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it mo ...
, MicroBlaze and Mico32 are examples of popular softcore processors. Many modern FPGAs are programmed at "run time", which has led to the idea of reconfigurable computing
Reconfigurable computing is a computer architecture combining some of the flexibility of software with the high performance of hardware by processing with very flexible high speed computing fabrics like FPGA, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA ...
or reconfigurable systems – CPUs that reconfigure themselves to suit the task at hand. Additionally, new, non-FPGA architectures are beginning to emerge. Software-configurable microprocessors such as the Stretch S5000 adopt a hybrid approach by providing an array of processor cores and FPGA-like programmable cores on the same chip.
Integration
In 2012 the coarse-grained architectural approach was taken a step further by combining thelogic block
In computing, a logic block or configurable logic block (CLB) is a fundamental building block of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) technology. Logic blocks can be configured by the engineer to provide reconfigurable logic gates.
Logic blocks ...
s and interconnects of traditional FPGAs with embedded microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circu ...
s and related peripherals to form a complete " system on a programmable chip". This work mirrors the architecture created by Ron Perloff and Hanan Potash of Burroughs Advanced Systems Group in 1982 which combined a reconfigurable CPU architecture
Processor design is a subfield of computer engineering and electronics engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware.
The design process involves choosing an instruction set and a certain ex ...
on a single chip called the SB24. Examples of such hybrid technologies can be found in the Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
Zynq-7000 all Programmable SoC, which includes a 1.0 GHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is s−1, meaning that one ...
dual-core ARM Cortex-A9
The ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore is a 32-bit multi-core processor that provides up to 4 cache-coherent cores, each implementing the ARM v7 architecture instruction set. It was introduced in 2007.
Features
Key features of the Cortex-A9 core are:
* ...
MPCore processor embedded
Embedded or embedding (alternatively imbedded or imbedding) may refer to:
Science
* Embedding, in mathematics, one instance of some mathematical object contained within another instance
** Graph embedding
* Embedded generation, a distributed ge ...
within the FPGA's logic fabric or in the Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
Arria V FPGA, which includes an 800 MHz dual-core
A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions (such ...
ARM Cortex-A9
The ARM Cortex-A9 MPCore is a 32-bit multi-core processor that provides up to 4 cache-coherent cores, each implementing the ARM v7 architecture instruction set. It was introduced in 2007.
Features
Key features of the Cortex-A9 core are:
* ...
MPCore. The Atmel
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included mi ...
FPSLIC is another such device, which uses an AVR processor in combination with Atmel's programmable logic architecture. The Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-bas ...
SmartFusion SmartFusion is a family of microcontrollers with an integrated FPGA of Actel. The device includes an ARM Cortex-M3 hard processor core (with up to 512kB of flash and 64kB of RAM) and analog peripherals such as a multi-channel ADC and DACs in addi ...
devices incorporate an ARM Cortex-M3 hard processor core (with up to 512 kB of flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Barry Allen)
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Wally West, the first Kid F ...
and 64 kB of RAM) and analog peripheral
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by th ...
s such as a multi-channel analog-to-digital converter
In electronics, an analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A-to-D) is a system that converts an analog signal, such as a sound picked up by a microphone or light entering a digital camera, into a digital signal. An ADC may also provide ...
s and digital-to-analog converter
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC, D/A, D2A, or D-to-A) is a system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse function.
There are several DAC archi ...
s to their flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
-based FPGA fabric.
Clocking
Most of the circuitry built inside of an FPGA issynchronous circuit
In digital electronics, a synchronous circuit is a digital circuit in which the changes in the state of memory elements are synchronized by a clock signal. In a sequential digital logic circuit, data are stored in memory devices called flip-fl ...
ry that requires a clock signal
In electronics and especially synchronous digital circuits, a clock signal (historically also known as ''logic beat'') oscillates between a high and a low state and is used like a metronome to coordinate actions of digital circuits.
A clock s ...
. FPGAs contain dedicated global and regional routing networks for clock and reset so they can be delivered with minimal skew. Also, FPGAs generally contain analog phase-locked loop
A phase-locked loop or phase lock loop (PLL) is a control system that generates an output signal whose phase is related to the phase of an input signal. There are several different types; the simplest is an electronic circuit consisting of a ...
and/or delay-locked loop
In electronics, a delay-locked loop (DLL) is a pseudo-digital circuit similar to a phase-locked loop (PLL), with the main difference being the absence of an internal voltage-controlled oscillator, replaced by a delay line.
A DLL can be used to ch ...
components to synthesize new clock frequencies as well as attenuate jitter
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a significa ...
. Complex designs can use multiple clocks with different frequency and phase relationships, each forming separate clock domains. These clock signals can be generated locally by an oscillator or they can be recovered from a high speed serial data stream. Care must be taken when building clock domain crossing
In digital electronic design a clock domain crossing (CDC), or simply clock crossing, is the traversal of a signal in a synchronous digital circuit from one clock domain into another. If a signal does not assert long enough and is not registered, ...
circuitry to avoid metastability
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
. FPGAs generally contain blocks of RAMs that are capable of working as dual port RAMs with different clocks, aiding in the construction of building FIFOs and dual port buffers that connect differing clock domains.
3D architectures
To shrink the size and power consumption of FPGAs, vendors such as Tabula andXilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
have introduced 3D or stacked architectures.Lawrence Latif, The Inquirer.FPGA manufacturer claims to beat Moore's Law
" October 27, 2010. Retrieved May 12, 2011. Following the introduction of its 28 nm 7-series FPGAs, Xilinx said that several of the highest-density parts in those FPGA product lines will be constructed using multiple dies in one package, employing technology developed for 3D construction and stacked-die assemblies. Xilinx's approach stacks several (three or four) active FPGA dies side by side on a silicon
interposer
An interposer is an electrical interface routing between one socket or connection to another. The purpose of an interposer is to spread a connection to a wider pitch or to reroute a connection to a different connection.
Interposer comes from t ...
– a single piece of silicon that carries passive interconnect. The multi-die construction also allows different parts of the FPGA to be created with different process technologies, as the process requirements are different between the FPGA fabric itself and the very high speed 28 Gbit/s serial transceivers. An FPGA built in this way is called a ''heterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts often used in the sciences and statistics relating to the uniformity of a substance or organism. A material or image that is homogeneous is uniform in composition or character (i.e. color, shape, siz ...
FPGA''.
Altera's heterogeneous approach involves using a single monolithic FPGA die and connecting other die/technologies to the FPGA using Intel's embedded multi-die interconnect bridge (EMIB) technology.
Programming
To define the behavior of the FPGA, the user provides a design in ahardware description language
In computer engineering, a hardware description language (HDL) is a specialized computer language used to describe the structure and behavior of electronic circuits, and most commonly, digital logic circuits.
A hardware description language e ...
(HDL) or as a schematic
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the s ...
design. The HDL form is more suited to work with large structures because it's possible to specify high-level functional behavior rather than drawing every piece by hand. However, schematic entry can allow for easier visualization of a design and its component modules.
Using an electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together ...
tool, a technology-mapped netlist
In electronic design, a netlist is a description of the connectivity of an electronic circuit. In its simplest form, a netlist consists of a list of the electronic components in a circuit and a list of the nodes they are connected to. A netwo ...
is generated. The netlist can then be fit to the actual FPGA architecture using a process called place-and-route, usually performed by the FPGA company's proprietary place-and-route software. The user will validate the map, place and route results via timing analysis
Static timing analysis (STA) is a simulation method of computing the expected timing of a synchronous digital circuit without requiring a simulation of the full circuit.
High-performance integrated circuits have traditionally been characteri ...
, simulation
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the ...
, and other verification and validation
Verification and validation (also abbreviated as V&V) are independent procedures that are used together for checking that a product, service, or system meets requirements and specifications and that it fulfills its intended purpose. These ar ...
methodologies. Once the design and validation process is complete, the binary file generated, typically using the FPGA vendor's proprietary software, is used to (re-)configure the FPGA. This file is transferred to the FPGA/CPLD via a serial interface
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication interface through which information transfers in or out sequentially one bit at a time. This is in contrast to a parallel port, which communicates multiple bits simultaneously in parallel. ...
(JTAG
JTAG (named after the Joint Test Action Group which codified it) is an industry standard for verifying designs and testing printed circuit boards after manufacture.
JTAG implements standards for on-chip instrumentation in electronic design autom ...
) or to an external memory device like an EEPROM
EEPROM (also called E2PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as ...
.
The most common HDLs are VHDL
The VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is a hardware description language (HDL) that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gat ...
and Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is a ...
as well as extensions such as SystemVerilog
SystemVerilog, standardized as IEEE 1800, is a hardware description and hardware verification language used to model, design, simulate, test and implement electronic systems. SystemVerilog is based on Verilog and some extensions, and since 20 ...
. However, in an attempt to reduce the complexity of designing in HDLs, which have been compared to the equivalent of assembly languages, there are moves to raise the abstraction level through the introduction of alternative languages. National Instruments
National Instruments Corporation, doing business as NI, is an American multinational company with international operation. Headquartered in Austin, Texas, it is a producer of automated test equipment and virtual instrumentation software. Co ...
' LabVIEW
Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench (LabVIEW) is a system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments.
The graphical language is named "G"; not to be confused with G- ...
graphical programming language (sometimes referred to as "G") has an FPGA add-in module available to target and program FPGA hardware. Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is a ...
was created to simplify the process making HDL more robust and flexible. Verilog is currently the most popular. Verilog creates a level of abstraction to hide away the details of its implementation. Verilog has a C-like syntax, unlike VHDL.
To simplify the design of complex systems in FPGAs, there exist libraries of predefined complex functions and circuits that have been tested and optimized to speed up the design process. These predefined circuits are commonly called '' intellectual property (IP) cores'', and are available from FPGA vendors and third-party IP suppliers. They are rarely free, and typically released under proprietary licenses. Other predefined circuits are available from developer communities such as OpenCores (typically released under free and open source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
licenses such as the GPL
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general us ...
, BSD
The Berkeley Software Distribution or Berkeley Standard Distribution (BSD) is a discontinued operating system based on Research Unix, developed and distributed by the Computer Systems Research Group (CSRG) at the University of California, Be ...
or similar license), and other sources. Such designs are known as "open-source hardware
Open-source hardware (OSH) consists of physical artifacts of technology designed and offered by the open-design movement. Both free and open-source software (FOSS) and open-source hardware are created by this open-source culture movement and a ...
."
In a typical design flow, an FPGA application developer will simulate the design at multiple stages throughout the design process. Initially the RTL description in VHDL
The VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL) is a hardware description language (HDL) that can model the behavior and structure of digital systems at multiple levels of abstraction, ranging from the system level down to that of logic gat ...
or Verilog
Verilog, standardized as IEEE 1364, is a hardware description language (HDL) used to model electronic systems. It is most commonly used in the design and verification of digital circuits at the register-transfer level of abstraction. It is a ...
is simulated by creating test bench
A test bench or testing workbench is an environment used to verify the correctness or soundness of a design or model.
The term has its roots in the testing of electronic devices, where an engineer would sit at a lab bench with tools for measurem ...
es to simulate the system and observe results. Then, after the synthesis
Synthesis or synthesize may refer to:
Science Chemistry and biochemistry
*Chemical synthesis, the execution of chemical reactions to form a more complex molecule from chemical precursors
**Organic synthesis, the chemical synthesis of organi ...
engine has mapped the design to a netlist, the netlist is translated to a gate-level description where simulation is repeated to confirm the synthesis proceeded without errors. Finally the design is laid out in the FPGA at which point propagation delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering ed ...
s can be added and the simulation run again with these values back-annotated onto the netlist.
More recently, OpenCL
OpenCL (Open Computing Language) is a framework for writing programs that execute across heterogeneous platforms consisting of central processing units (CPUs), graphics processing units (GPUs), digital signal processors (DSPs), field-prog ...
(Open Computing Language) is being used by programmers to take advantage of the performance and power efficiencies that FPGAs provide. OpenCL allows programmers to develop code in the C programming language and target FPGA functions as OpenCL kernels using OpenCL constructs. For further information, see high-level synthesis
High-level synthesis (HLS), sometimes referred to as C synthesis, electronic system-level (ESL) synthesis, algorithmic synthesis, or behavioral synthesis, is an automated design process that takes an abstract behavioral specification of a digital ...
and C to HDL
C to HDL tools convert C language or C-like computer code into a hardware description language (HDL) such as VHDL or Verilog. The converted code can then be synthesized and translated into a hardware device such as a field-programmable gate arra ...
.
Most FPGAs rely on an SRAM-based approach to be programmed. These FPGAs are in-system programmable and re-programmable, but require external boot devices. For example, flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
or EEPROM
EEPROM (also called E2PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as ...
devices may often load contents into internal SRAM that controls routing and logic. The SRAM approach is based on CMOS.
Rarer alternatives to the SRAM approach include:
* Fuse
Fuse or FUSE may refer to:
Devices
* Fuse (electrical), a device used in electrical systems to protect against excessive current
** Fuse (automotive), a class of fuses for vehicles
* Fuse (hydraulic), a device used in hydraulic systems to prote ...
: one-time programmable. Bipolar. Obsolete.
* Antifuse
An antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path (typically when the current through the path exceed ...
: one-time programmable. CMOS. Examples: Actel SX and Axcelerator families; Quicklogic Eclipse II family.
* PROM
A promenade dance, commonly called a prom, is a dance party for high school students. It may be offered in semi-formal black tie or informal suit for boys, and evening gowns for girls. This event is typically held near the end of the school y ...
: programmable read-only memory technology. One-time programmable because of plastic packaging. Obsolete.
* EPROM
An EPROM (rarely EROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power ...
: erasable programmable read-only memory technology. One-time programmable but with window, can be erased with ultraviolet (UV) light. CMOS. Obsolete.
* EEPROM
EEPROM (also called E2PROM) stands for electrically erasable programmable read-only memory and is a type of non-volatile memory used in computers, usually integrated in microcontrollers such as smart cards and remote keyless systems, or as ...
: electrically erasable programmable read-only memory technology. Can be erased, even in plastic packages. Some but not all EEPROM devices can be in-system programmed. CMOS.
* Flash
Flash, flashes, or FLASH may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Fictional aliases
* Flash (DC Comics character), several DC Comics superheroes with super speed:
** Flash (Barry Allen)
** Flash (Jay Garrick)
** Wally West, the first Kid F ...
: flash-erase EPROM technology. Can be erased, even in plastic packages. Some but not all flash devices can be in-system programmed. Usually, a flash cell is smaller than an equivalent EEPROM cell and is therefore less expensive to manufacture. CMOS. Example: Actel ProASIC family.
Manufacturers
In 2016, long-time industry rivalsXilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
(now part of AMD) and Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
(now an Intel subsidiary) were the FPGA market leaders. At that time, they controlled nearly 90 percent of the market.
Both Xilinx (now AMD) and Altera (now Intel) provide proprietary electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together ...
software for Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for ...
and Linux
Linux ( or ) is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds. Linux is typically packaged as a Linux distribution, which i ...
( ISE/ Vivado and Quartus
Quartus ( el, Κούαρτος, Kouartos) was an early Christian who is mentioned in the Bible.
According to church tradition, he is known as Quartus of Berytus and is numbered among the Seventy Disciples. Furthermore, he was Bishop of Beirut ...
) which enables engineers to design
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' ...
, analyze, simulate
A simulation is the imitation of the operation of a real-world process or system over time. Simulations require the use of models; the model represents the key characteristics or behaviors of the selected system or process, whereas the ...
, and synthesize (compile
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily ...
) their designs.
In March 2010, Tabula announced their FPGA technology that uses time-multiplexed logic and interconnect that claims potential cost savings for high-density applications. On March 24, 2015, Tabula officially shut down.
On June 1, 2015, Intel announced it would acquire Altera for approximately $16.7 billion and completed the acquisition on December 30, 2015.
On October 27, 2020, AMD announced it would acquire Xilinx and completed the acquisition valued at about $50 billion in February 2022.
Other manufacturers include:
* Achronix, manufacturing SRAM based FPGAS with 1.5 GHz fabric speed
*Altium
Altium Limited is an Australian multinational software company that provides electronic design automation software to engineers who design printed circuit boards. Founded as Protel Systems Pty Ltd in Australia in 1985, the company has regional ...
, provides system-on-FPGA hardware-software design environment.
* Efinix offers small to medium-sized FPGAs. They combine logic and routing interconnects into a configurable XLR cell.
* GOWIN Semiconductors, manufacturing small and medium-sized SRAM and Flash-based FPGAs. They also offer pin-compatible replacements for a few Xilinx, Altera and Lattice products.
* Lattice Semiconductor
Lattice Semiconductor Corporation is an American semiconductor company specializing in the design and manufacturing of low power, field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). Headquartered in the Silicon Forest area of Hillsboro, Oregon, the company ...
, which manufactures low-power SRAM-based FPGAs featuring integrated configuration flash, instant-on
In computing, instant-on is the ability to boot nearly instantly, allowing to go online or to use a specific application without waiting for a PC's traditional operating system to launch. Instant-on technology is today mostly used on laptops, net ...
and live reconfiguration
In discrete mathematics and theoretical computer science, reconfiguration problems are computational problems involving reachability or connectivity of state spaces.
Types of problems
Here, a state space is a discrete set of configurations of a ...
** SiliconBlue Technologies, which provides extremely low power SRAM-based FPGAs with optional integrated nonvolatile configuration memory; acquired by Lattice in 2011
*Microchip
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny M ...
:
**Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-bas ...
(previously Actel
Actel Corporation (formerly NASDAQ:ACTL) was an American manufacturer of nonvolatile, low-power field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs), mixed-signal FPGAs, and programmable logic solutions. It was headquartered in Mountain View, California, with ...
), producing antifuse, flash-based, mixed-signal
A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die.Atmel
Atmel Corporation was a creator and manufacturer of semiconductors before being subsumed by Microchip Technology in 2016. Atmel was founded in 1984. The company focused on embedded systems built around microcontrollers. Its products included mi ...
, a second source of some Altera-compatible devices; also FPSLIC mentioned above; acquired by Microchip in 2016
* QuickLogic, which manufactures Ultra Low Power Sensor Hubs, extremely low powered, low density SRAM-based FPGAs, with display bridges MIPI & RGB inputs, MIPI, RGB and LVDS outputs
Applications
An FPGA can be used to solve any problem which is computable. This is trivially proven by the fact that FPGAs can be used to implement asoft microprocessor
A soft microprocessor (also called softcore microprocessor or a soft processor) is a microprocessor core that can be wholly implemented using logic synthesis. It can be implemented via different semiconductor devices containing programmable logic ...
, such as the Xilinx MicroBlaze or Altera Nios II
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it mo ...
. Their advantage lies in that they are significantly faster for some applications because of their parallel nature and optimality in terms of the number of gates used for certain processes.
FPGAs originally began as competitors to CPLDs to implement glue logic
In electronics, glue logic is the custom logic circuitry used to interface a number of off-the-shelf integrated circuits. This is often achieved using common, inexpensive 7400- or 4000-series components. In more complex cases, a programmable lo ...
for printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich str ...
s. As their size, capabilities, and speed increased, FPGAs took over additional functions to the point where some are now marketed as full systems on chips (SoCs). Particularly with the introduction of dedicated multipliers into FPGA architectures in the late 1990s, applications which had traditionally been the sole reserve of digital signal processor hardware (DSPs) began to incorporate FPGAs instead.
The evolution of FPGAs has motivated an increase in the use of these devices, whose architecture allows the development of hardware solutions optimized for complex tasks, such as 3D MRI image segmentation, 3D discrete wavelet transform, tomographic image reconstruction, or PET/MRI systems. The developed solutions can perform intensive computation tasks with parallel processing, are dynamically reprogrammable, and have a low cost, all while meeting the hard real-time requirements associated with medical imaging.
Another trend in the use of FPGAs is hardware acceleration
Hardware acceleration is the use of computer hardware designed to perform specific functions more efficiently when compared to software running on a general-purpose central processing unit (CPU). Any transformation of data that can be calc ...
, where one can use the FPGA to accelerate certain parts of an algorithm and share part of the computation between the FPGA and a generic processor. The search engine Bing
Bing most often refers to:
* Bing Crosby (1903–1977), American singer
* Microsoft Bing, a web search engine
Bing may also refer to:
Food and drink
* Bing (bread), a Chinese flatbread
* Bing (soft drink), a UK brand
* Bing cherry, a variety ...
is noted for adopting FPGA acceleration for its search algorithm in 2014. , FPGAs are seeing increased use as AI accelerator
An AI accelerator is a class of specialized hardware accelerator or computer system designed to accelerate artificial intelligence and machine learning applications, including artificial neural networks and machine vision. Typical applications ...
s including Microsoft's so-termed "Project Catapult" and for accelerating artificial neural network
Artificial neural networks (ANNs), usually simply called neural networks (NNs) or neural nets, are computing systems inspired by the biological neural networks that constitute animal brains.
An ANN is based on a collection of connected units ...
s for machine learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of inquiry devoted to understanding and building methods that 'learn', that is, methods that leverage data to improve performance on some set of tasks. It is seen as a part of artificial intelligence.
Machine ...
applications.
Traditionally, FPGAs have been reserved for specific vertical applications where the volume of production is small. For these low-volume applications, the premium that companies pay in hardware cost per unit for a programmable chip is more affordable than the development resources spent on creating an ASIC. , new cost and performance dynamics have broadened the range of viable applications.
The company Gigabyte Technology
Gigabyte Technology (branded as GIGABYTE or sometimes GIGA-BYTE; formally GIGA-BYTE Technology Co., Ltd.) is a Taiwanese manufacturer and distributor of computer hardware.
Gigabyte's principal business is motherboards. It shipped 4.8 million mot ...
created an i-RAM card which used a Xilinx FPGA although a custom made chip would be cheaper if made in large quantities. The FPGA was chosen to bring it quickly to market and the initial run was only to be 1000 units making an FPGA the best choice. This device allows people to use computer RAM as a hard drive.
Other uses for FPGAs include:
* Space (i.e. with radiation hardening
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation ( particle radiation and high-energy electromagnetic radiation), especially for envir ...
)
* Hardware security module
A hardware security module (HSM) is a physical computing device that safeguards and manages secrets (most importantly digital keys), performs encryption and decryption functions for digital signatures, strong authentication and other cryptogra ...
s
Security
FPGAs have both advantages and disadvantages as compared to ASICs or secure microprocessors, concerninghardware security
Hardware security as a discipline originated out of cryptographic engineering and involves hardware design, access control, secure multi-party computation, secure key storage, ensuring code authenticity, measures to ensure that the supply chain tha ...
. FPGAs' flexibility makes malicious modifications during fabrication
Fabrication may refer to:
* Manufacturing, specifically the crafting of individual parts as a solo product or as part of a larger combined product.
Processes in arts, crafts and manufacturing
*Semiconductor device fabrication, the process used t ...
a lower risk. Previously, for many FPGAs, the design bitstream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
was exposed while the FPGA loads it from external memory (typically on every power-on). All major FPGA vendors now offer a spectrum of security solutions to designers such as bitstream encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can dec ...
and authentication
Authentication (from ''authentikos'', "real, genuine", from αὐθέντης ''authentes'', "author") is the act of proving an assertion, such as the identity of a computer system user. In contrast with identification, the act of indicat ...
. For example, Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
and Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
offer AES
AES may refer to:
Businesses and organizations Companies
* AES Corporation, an American electricity company
* AES Data, former owner of Daisy Systems Holland
* AES Eletropaulo, a former Brazilian electricity company
* AES Andes, formerly AES Gener ...
encryption (up to 256-bit) for bitstreams stored in an external flash memory.
FPGAs that store their configuration internally in nonvolatile flash memory, such as Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-bas ...
's ProAsic 3 or Lattice's XP2 programmable devices, do not expose the bitstream and do not need encryption
In cryptography, encryption is the process of encoding information. This process converts the original representation of the information, known as plaintext, into an alternative form known as ciphertext. Ideally, only authorized parties can dec ...
. In addition, flash memory for a lookup table
In computer science, a lookup table (LUT) is an array that replaces runtime computation with a simpler array indexing operation. The process is termed as "direct addressing" and LUTs differ from hash tables in a way that, to retrieve a value v w ...
provides single event upset
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocesso ...
protection for space applications. Customers wanting a higher guarantee of tamper resistance can use write-once, antifuse
An antifuse is an electrical device that performs the opposite function to a fuse. Whereas a fuse starts with a low resistance and is designed to permanently break an electrically conductive path (typically when the current through the path exceed ...
FPGAs from vendors such as Microsemi
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-bas ...
.
With its Stratix 10 FPGAs and SoCs, Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
introduced a Secure Device Manager and physical unclonable functions to provide high levels of protection against physical attacks.
In 2012 researchers Sergei Skorobogatov and Christopher Woods demonstrated that some FPGAs can be vulnerable to hostile intent. They discovered a critical backdoor
A back door is a door in the rear of a building. Back door may also refer to:
Arts and media
* Back Door (jazz trio), a British group
* Porta dos Fundos (literally “Back Door” in Portuguese) Brazilian comedy YouTube channel.
* Works so titl ...
vulnerability
Vulnerability refers to "the quality or state of being exposed to the possibility of being attacked or harmed, either physically or emotionally."
A window of vulnerability (WOV) is a time frame within which defensive measures are diminished, com ...
had been manufactured in silicon as part of the Actel/Microsemi ProAsic 3 making it vulnerable on many levels such as reprogramming crypto and access keys, accessing unencrypted bitstream, modifying low-level silicon features, and extracting configuration
Configuration or configurations may refer to:
Computing
* Computer configuration or system configuration
* Configuration file, a software file used to configure the initial settings for a computer program
* Configurator, also known as choice boar ...
data.
Similar technologies
Historically, FPGAs have been slower, less energy efficient and generally achieved less functionality than their fixedASIC
An application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC ) is an integrated circuit (IC) chip customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use, such as a chip designed to run in a digital voice recorder or a high-effici ...
counterparts. A study from 2006 showed that designs implemented on FPGAs need on average 40 times as much area, draw 12 times as much dynamic power, and run at one third the speed of corresponding ASIC implementations. More recently, FPGAs such as the Xilinx
Xilinx, Inc. ( ) was an American technology and semiconductor company that primarily supplied programmable logic devices. The company was known for inventing the first commercially viable field-programmable gate array (FPGA) and creating the fi ...
Virtex-7 or the Altera
Altera Corporation was a manufacturer of programmable logic devices (PLDs) headquartered in San Jose, California. It was founded in 1983 and acquired by Intel in 2015.
The main product lines from Altera were the flagship Stratix series, mid-ra ...
Stratix 5 have come to rival corresponding ASIC and ASSP ("Application-specific standard part", such as a standalone USB interface chip) solutions by providing significantly reduced power usage, increased speed, lower materials cost, minimal implementation real-estate, and increased possibilities for re-configuration 'on-the-fly'. A design that included 6 to 10 ASICs can now be achieved using only one FPGA. Advantages of FPGAs include the ability to re-program when already deployed (i.e. "in the field") to fix bugs
Bugs may refer to:
* Plural of bug
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
* Bugs Bunny, a character
* Bugs Meany, a character in the ''Encyclopedia Brown'' books
Films
* ''Bugs'' (2003 film), a science-fiction-horror film
* ''Bugs ...
, and often include shorter time to market
In commerce, time to market (TTM) is the length of time it takes from a product being conceived until its being available for sale. The reason that time to market is so important is since being late erodes the addressable market into which prod ...
and lower non-recurring engineering
Non-recurring engineering (NRE) cost refers to the one-time cost to research, design, develop and test a new product or product enhancement. When budgeting for a new product, NRE must be considered to analyze if a new product will be profitable. ...
costs. Vendors can also take a middle road via FPGA prototyping
Field-programmable gate array prototyping (FPGA prototyping), also referred to as FPGA-based prototyping, ASIC prototyping or system-on-chip (SoC) prototyping, is the method to prototype system-on-chip and application-specific integrated circu ...
: developing their prototype hardware on FPGAs, but manufacture their final version as an ASIC so that it can no longer be modified after the design has been committed. This is often also the case with new processor designs. Some FPGAs have the capability of partial re-configuration that lets one portion of the device be re-programmed while other portions continue running.
The primary differences between complex programmable logic devices (CPLDs) and FPGAs are architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
. A CPLD has a comparatively restrictive structure consisting of one or more programmable sum-of-products
In Boolean algebra, any Boolean function can be expressed in the canonical disjunctive normal form ( CDNF) or minterm canonical form and its dual canonical conjunctive normal form (CCNF) or maxterm canonical form. Other canonical forms include ...
logic arrays feeding a relatively small number of clocked registers. As a result, CPLDs are less flexible, but have the advantage of more predictable timing delays and FPGA architectures, on the other hand, are dominated by interconnect
In telecommunications, interconnection is the physical linking of a carrier's network with equipment or facilities not belonging to that network. The term may refer to a connection between a carrier's facilities and the equipment belonging to ...
. This makes them far more flexible (in terms of the range of designs that are practical for implementation on them) but also far more complex to design for, or at least requiring more complex electronic design automation
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards. The tools work together ...
(EDA) software. In practice, the distinction between FPGAs and CPLDs is often one of size as FPGAs are usually much larger in terms of resources than CPLDs. Typically only FPGAs contain more complex embedded functions such as adders, multipliers, memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
, and serializer/deserializers. Another common distinction is that CPLDs contain embedded flash memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both u ...
to store their configuration while FPGAs usually require external non-volatile memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data.
Non-volatile memory typ ...
(but not always). When a design requires simple instant-on (logic is already configured at power-up) CPLDs are generally preferred. For most other applications FPGAs are generally preferred. Sometimes both CPLDs and FPGAs are used in a single system design. In those designs, CPLDs generally perform glue logic functions, and are responsible for "booting
In computing, booting is the process of starting a computer as initiated via Computer hardware, hardware such as a button or by a software command. After it is switched on, a computer's central processing unit (CPU) has no software in its ma ...
" the FPGA as well as controlling reset and boot sequence of the complete circuit board. Therefore, depending on the application it may be judicious to use both FPGAs and CPLDs in a single design.
See also
* FPGA Mezzanine Card *List of HDL simulators
HDL simulators are software packages that simulate expressions written in one of the hardware description languages, such as VHDL, Verilog, SystemVerilog.
This page is intended to list current and historical HDL simulators, accelerators, emulat ...
References
Further reading
* * * * Mencer, Oskar et al. (2020). "The history, status, and future of FPGAs". Communications of the ACM. ACM. Vol. 63, No. 10. doi: 10.1145/3410669External links
* {{Authority control * Integrated circuits Semiconductor devices American inventions Hardware acceleration