Fenestration (architecture) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A window is an opening in a wall, door,

 The Romans were the first known to use
The Romans were the first known to use
 A ''foldup'' has two equal sashes similar to a standard double-hung but folds upward allowing air to pass through nearly the full-frame opening. The window is balanced using either springs or counterbalances, similar to a double-hung. The sashes can be either offset to simulate a double-hung, or in-line. The inline versions can be made to fold inward or outward. The inward swinging foldup windows can have fixed screens, while the outward swinging ones require movable screens. The windows are typically used for screen rooms, kitchen pass-throughs, or egress.
A ''foldup'' has two equal sashes similar to a standard double-hung but folds upward allowing air to pass through nearly the full-frame opening. The window is balanced using either springs or counterbalances, similar to a double-hung. The sashes can be either offset to simulate a double-hung, or in-line. The inline versions can be made to fold inward or outward. The inward swinging foldup windows can have fixed screens, while the outward swinging ones require movable screens. The windows are typically used for screen rooms, kitchen pass-throughs, or egress.
 A
A
 Also known as a louvered window, the jalousie window consists of parallel slats of glass or acrylic that open and close like a Venetian blind, usually using a crank or a lever. They are used extensively in tropical architecture. A jalousie door is a door with a jalousie window.
Also known as a louvered window, the jalousie window consists of parallel slats of glass or acrylic that open and close like a Venetian blind, usually using a crank or a lever. They are used extensively in tropical architecture. A jalousie door is a door with a jalousie window.
 A skylight is a window built into a roof structure. This type of window allows for natural daylight and moonlight.
A skylight is a window built into a roof structure. This type of window allows for natural daylight and moonlight.
 A ''roof window'' is a sloped window used for daylighting, built into a
A ''roof window'' is a sloped window used for daylighting, built into a
 A stained glass window is a window composed of pieces of colored glass, transparent, translucent or opaque, frequently portraying persons or scenes. Typically the glass in these windows is separated by lead glazing bars. Stained glass windows were popular in Victorian houses and some Wrightian houses, and are especially common in churches.
A stained glass window is a window composed of pieces of colored glass, transparent, translucent or opaque, frequently portraying persons or scenes. Typically the glass in these windows is separated by lead glazing bars. Stained glass windows were popular in Victorian houses and some Wrightian houses, and are especially common in churches.
 ''Double-paned windows'' have two parallel panes (slabs of glass) with a separation of typically about 1 cm; this space is permanently sealed and filled at the time of manufacture with dry air or other dry nonreactive gas. Such windows provide a marked improvement in thermal insulation (and usually in acoustic insulation as well) and are resistant to fogging and frosting caused by temperature differential. They are widely used for residential and commercial construction in intemperate climates. In the UK, double-paned and triple-paned are referred to as double- glazing and triple-glazing. Triple-paned windows are now a common type of glazing in central to northern Europe. Quadruple glazing is now being introduced in Scandinavia.
''Double-paned windows'' have two parallel panes (slabs of glass) with a separation of typically about 1 cm; this space is permanently sealed and filled at the time of manufacture with dry air or other dry nonreactive gas. Such windows provide a marked improvement in thermal insulation (and usually in acoustic insulation as well) and are resistant to fogging and frosting caused by temperature differential. They are widely used for residential and commercial construction in intemperate climates. In the UK, double-paned and triple-paned are referred to as double- glazing and triple-glazing. Triple-paned windows are now a common type of glazing in central to northern Europe. Quadruple glazing is now being introduced in Scandinavia.
 A hexagonal window is a hexagon-shaped window, resembling a bee cell or crystal lattice of graphite. The window can be vertically or horizontally oriented, openable or dead. It can also be regular or elongately-shaped and can have a separator ( mullion). Typically, the cellular window is used for an attic or as a decorative feature, but it can also be a major architectural element to provide the natural lighting inside buildings.
A hexagonal window is a hexagon-shaped window, resembling a bee cell or crystal lattice of graphite. The window can be vertically or horizontally oriented, openable or dead. It can also be regular or elongately-shaped and can have a separator ( mullion). Typically, the cellular window is used for an attic or as a decorative feature, but it can also be a major architectural element to provide the natural lighting inside buildings.
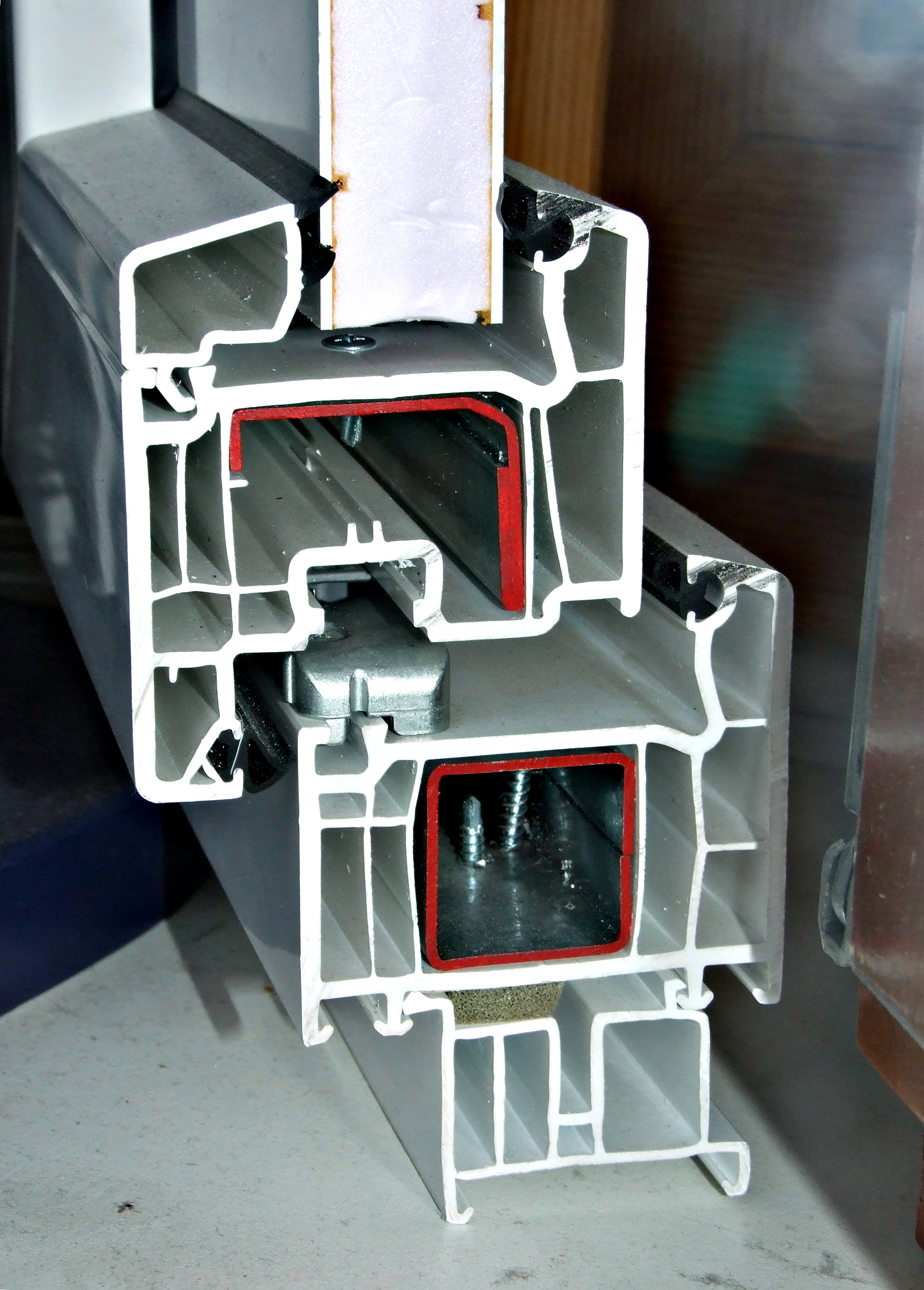 Windows can be a significant source of heat transfer.Carmody, J., Selkowitz, S., Lee, E. S., Arasteh, D., & Willmert, T. (2004). ''Window Systems for High-Performance Buildings''. New York, NY: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Therefore, insulated glazing units consist of two or more panes to reduce the transfer of heat.
Windows can be a significant source of heat transfer.Carmody, J., Selkowitz, S., Lee, E. S., Arasteh, D., & Willmert, T. (2004). ''Window Systems for High-Performance Buildings''. New York, NY: W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Therefore, insulated glazing units consist of two or more panes to reduce the transfer of heat.
 A special class of PVC window frames, uPVC window frames, became widespread since the late 20th century, particularly in Europe: there were 83.5 million installed by 1998 with numbers still growing as of 2012.
A special class of PVC window frames, uPVC window frames, became widespread since the late 20th century, particularly in Europe: there were 83.5 million installed by 1998 with numbers still growing as of 2012.
File:Window grill from a palace of Ramesses III MET 14.6.232-dia1.jpg,
Roman Glass from Metropolitan Museum of Art
{{Authority control Architectural elements Glass
roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
, or vehicle
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered land vehicle, human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velo ...
that allows the exchange of light
Light, visible light, or visible radiation is electromagnetic radiation that can be visual perception, perceived by the human eye. Visible light spans the visible spectrum and is usually defined as having wavelengths in the range of 400– ...
and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material
A material is a matter, substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an Physical object, object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical property, physical ...
, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock
Lock(s) or Locked may refer to:
Common meanings
*Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance
*Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal
Arts and entertainme ...
the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts.
Types include the eyebrow window, fixed windows, hexagonal windows, single-hung, and double-hung sash windows, horizontal sliding sash windows, casement window
A casement window is a window that is attached to its frame by one or more hinges at the side. They are used singly or in pairs within a common frame, in which case they are hinged on the outside. Casement windows are often held open using a c ...
s, awning windows, hopper windows, tilt, and slide windows (often door-sized), tilt and turn windows, transom windows, sidelight windows, jalousie or louvered windows, clerestory windows, lancet windows, skylights, roof windows, roof lantern
A roof lantern is a Daylighting (architecture), daylighting architectural element. Architectural lanterns are part of a larger roof and provide natural light into the space or room below. In contemporary use it is an architectural skylight stru ...
s, bay windows, oriel windows, thermal, or Diocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
, windows, picture windows, rose window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' wa ...
s, emergency exit windows, stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ...
windows, French windows, panel windows, double/triple-paned windows, and witch window
In American vernacular architecture, a witch window (also known as a Vermont window, among other names) is a window (usually a double-hung sash window, occasionally a single-sided casement window) placed in the gable-end wall of a houseGeorge Nas ...
s.
Etymology
The English language-word ''window'' originates from theOld Norse
Old Norse, also referred to as Old Nordic or Old Scandinavian, was a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants ...
, from 'wind' and 'eye'. In Norwegian, Nynorsk
Nynorsk (; ) is one of the two official written standards of the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. From 12 May 1885, it became the state-sanctioned version of Ivar Aasen's standard Norwegian language (''Landsmål''), parallel to the Da ...
, and Icelandic, the Old Norse form has survived to this day (in Icelandic only as a less used word for a type of small open "window", not strictly a synonym for , the Icelandic word for 'window'). In Swedish, the word remains as a term for a hole through the roof of a hut, and in the Danish language
Danish (, ; , ) is a North Germanic languages, North Germanic language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family spoken by about six million people, principally in and around Denmark. Communities of Danish speakers are a ...
and Norwegian , the direct link to ''eye'' is lost, just as for ''window''. The Danish (but not the ) word is pronounced fairly similarly to ''window''.
''Window'' is first recorded in the early 13th century, and originally referred to an unglazed hole in a roof. ''Window'' replaced the Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
, which literally means 'eye-hole', and 'eye-door'. Many Germanic languages, however, adopted the Latin word to describe a window with glass, such as standard Swedish , or German . The use of ''window'' in English is probably because of the Scandinavian influence on the English language by means of loanword
A loanword (also a loan word, loan-word) is a word at least partly assimilated from one language (the donor language) into another language (the recipient or target language), through the process of borrowing. Borrowing is a metaphorical term t ...
s during the Viking Age
The Viking Age (about ) was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonising, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. The Viking Age applies not only to their ...
. In English, the word ''fenester'' was used as a parallel until the mid-18th century. ''Fenestration'' is still used to describe the arrangement of windows within a façade, as well as '' defenestration'', meaning 'to throw out of a window'.
History

glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
for windows, a technology likely first produced in Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, ...
, in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
AD. Presentations of windows can be seen in ancient Egyptian wall art and sculptures from Assyria. Paper windows were economical and widely used in ancient China, Korea, and Japan. In England, glass
Glass is an amorphous (non-crystalline solid, non-crystalline) solid. Because it is often transparency and translucency, transparent and chemically inert, glass has found widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in window pane ...
became common in the windows of ordinary homes only in the early 17th century whereas windows made up of panes of flattened animal horn were used as early as the 14th century. In the 19th century American west, greased paper windows came to be used by pioneering settlers. Modern-style floor-to-ceiling windows became possible only after the industrial plate glass making processes were fully perfected.
Technologies
In the 13th century BC, the earliest windows were unglazed openings in a roof to admit light during the day. Later, windows were covered with animal hide, cloth, or wood. Shutters that could be opened and closed came next. Over time, windows were built that both protected the inhabitants from the elements and transmitted light, using multiple small pieces of translucent material, such as flattened pieces of translucent animal horn, paper sheets, thin slices ofmarble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is ty ...
(such as fengite), or pieces of glass, set in frameworks of wood, iron or lead. In the Far East, paper was used to fill windows.
The Romans were the first known users of glass for windows, exploiting a technology likely first developed in Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, ...
. Specifically, in Alexandria
Alexandria ( ; ) is the List of cities and towns in Egypt#Largest cities, second largest city in Egypt and the List of coastal settlements of the Mediterranean Sea, largest city on the Mediterranean coast. It lies at the western edge of the Nile ...
100 CE, cast-glass windows, albeit with poor optical properties, began to appear, but these were small thick productions, little more than blown-glass jars (cylindrical shapes) flattened out into sheets with circular striation patterns throughout. (Compare traditional church windows made of stained glass
Stained glass refers to coloured glass as a material or art and architectural works created from it. Although it is traditionally made in flat panels and used as windows, the creations of modern stained glass artists also include three-dimensio ...
.) It would be over a millennium before window glass became transparent enough to see through clearly, as we expect now. (However, ancient Roman windows were still very useful, as they presented "an often-overlooked advance in heating technology (allowing solar heat to enter a home or building while preventing the warmed air from escaping).") In 1154, Al-Idrisi described glass windows as a feature of the palace belonging to the king of the Ghana Empire.
Over the centuries techniques were developed to shear through one side of a blown glass cylinder and produce thinner rectangular window panes from the same amount of glass material. This gave rise to tall narrow windows, usually separated by a vertical support called a mullion. Mullioned glass windows were the windows of choice among the European well-to-do, whereas paper windows were economical and widely used in ancient China, Korea, and Japan. In England, glass became common in the windows of ordinary homes only in the early 17th century, whereas windows made up of panes of flattened animal horn were used as early as the 14th century.
Modern-style floor-to-ceiling windows became possible only after the industrial plate glass-making processes were perfected in the late 19th century. Modern windows are usually filled using glass, although transparent plastic is also used.
Fashions and trends
The introduction of lancet windows into Western European church architecture from the 12th century CE built on a tradition of arched windows inserted between columns, and led not only to tracery and elaborate stained-glass windows but also to a long-standing motif of pointed or rounded window-shapes in ecclesiastical buildings, still seen in many churches today. Peter Smith discusses overall trends in early-modern rural Welsh window architecture:Up to about 1680 windows tended to be horizontal in proportion, a shape suitable for lighting the low-ceilinged rooms that had resulted from the insertion of the upper floor into the hall-house. After that date vertically proportioned windows came into fashion, partly at least as a response to the Renaissance taste for the high ceiling. Since 1914 the wheel has come full circle and a horizontally proportioned window is again favoured.The spread of plate-glass technology made possible the introduction of picture windows (in Levittown, Pennsylvania, founded 1951–1952). Many modern day windows may have a window screen or mesh, often made of
aluminum
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has ...
or fibreglass, to keep bugs out when the window is opened. Windows are primarily designed to facilitate a vital connection with the outdoors, offering those within the confines of the building visual access to the everchanging events occurring outside. The provision of this connection serves as an integral safeguard for the health and well-being of those inhabiting buildings, lest they experience the detrimental effects of enclosed buildings devoid of windows. Among the myriad criteria for the design of windows, several pivotal criteria have emerged in daylight standards: location, time, weather, nature, and people. Of these criteria, windows that are designed to provide views of nature
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the Ecosphere (planetary), ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the Scientific law, laws, elements and phenomenon, phenomena of the physic ...
are considered to be the most important by people.
Types
Cross
A cross-window is a rectangular window usually divided into four lights by a mullion and transom that form a Latin cross.Eyebrow
The term ''eyebrow window'' is used in two ways: a curved top window in a wall or an eyebrow dormer; and a row of small windows usually under the front eaves such as the James-Lorah House in Pennsylvania.Fixed
A ''fixed window'' is a window that cannot be opened, whose function is limited to allowing light to enter (unlike an unfixed window, which can open and close). Clerestory windows in church architecture are often fixed. Transom windows may be fixed or operable. This type of window is used in situations where light or vision alone is needed as no ventilation is possible in such windows without the use of trickle vents or overglass vents.Single-hung sash
A ''single-hung sash window'' is a window that has one sash that is movable (usually the bottom one) and the other fixed. This is the earlier form of sliding sash window and is also cheaper.Double-hung sash
A sash window is the traditional style of window in the United Kingdom, and many other places that were formerly colonized by the UK, with two parts (sashes) that overlap slightly and slide up and down inside the frame. The two parts are not necessarily the same size; where the upper sash is smaller (shorter) it is termed a cottage window. Currently, most new double-hung sash windows use spring balances to support the sashes, but traditionally, counterweights held in boxes on either side of the window were used. These were and are attached to the sashes using pulleys of either braided cord or, later, purpose-made chain. Three types of spring balances are called a tape or clock spring balance; channel or block-and-tackle balance, and a spiral or tube balance. Double-hung sash windows were traditionally often fitted with shutters. Sash windows can be fitted with simplex hinges that let the window be locked into hinges on one side, while the rope on the other side is detached—so the window can be opened for fire escape or cleaning.Foldup
 A ''foldup'' has two equal sashes similar to a standard double-hung but folds upward allowing air to pass through nearly the full-frame opening. The window is balanced using either springs or counterbalances, similar to a double-hung. The sashes can be either offset to simulate a double-hung, or in-line. The inline versions can be made to fold inward or outward. The inward swinging foldup windows can have fixed screens, while the outward swinging ones require movable screens. The windows are typically used for screen rooms, kitchen pass-throughs, or egress.
A ''foldup'' has two equal sashes similar to a standard double-hung but folds upward allowing air to pass through nearly the full-frame opening. The window is balanced using either springs or counterbalances, similar to a double-hung. The sashes can be either offset to simulate a double-hung, or in-line. The inline versions can be made to fold inward or outward. The inward swinging foldup windows can have fixed screens, while the outward swinging ones require movable screens. The windows are typically used for screen rooms, kitchen pass-throughs, or egress.
Horizontal sliding sash
A ''horizontal sliding sash window'' has two or more sashes that overlap slightly but slide horizontally within the frame. In the UK, these are sometimes calledYorkshire
Yorkshire ( ) is an area of Northern England which was History of Yorkshire, historically a county. Despite no longer being used for administration, Yorkshire retains a strong regional identity. The county was named after its county town, the ...
sash windows, presumably because of their traditional use in that county.
Casement
casement window
A casement window is a window that is attached to its frame by one or more hinges at the side. They are used singly or in pairs within a common frame, in which case they are hinged on the outside. Casement windows are often held open using a c ...
is a window with a hinged sash that swings in or out like a door comprising either a side-hung, top-hung (also called "awning window"; see below), or occasionally bottom-hung sash or a combination of these types, sometimes with fixed panels on one or more sides of the sash. In the US, these are usually opened using a crank, but in parts of Europe, they tend to use projection friction stays and espagnolette locking. Formerly, plain hinges were used with a casement stay. Handing applies to casement windows to determine direction of swing; a casement window may be left-handed, right-handed, or double. The casement window is the dominant type now found in modern buildings in the UK and many other parts of Europe.
Awning
An ''awning window'' is a casement window that is hung horizontally, hinged on top, so that it swings outward like an awning. In addition to being used independently, they can be stacked, several in one opening, or combined with fixed glass. They are particularly useful for ventilation.Hopper
A ''hopper window'' is a bottom-pivoting casement window that opens by tilting vertically, typically to the inside, resembling a hopper chute.Pivot
A ''pivot window'' is a window hung on one hinge on each of two opposite sides which allows the window to revolve when opened. The hinges may be mounted top and bottom (Vertically Pivoted) or at each jamb (Horizontally Pivoted). The window will usually open initially to a restricted position for ventilation and, once released, fully reverse and lock again for safe cleaning from inside. Modern pivot hinges incorporate a friction device to hold the window open against its weight and may have restriction and reversed locking built-in. In the UK, where this type of window is most common, they were extensively installed in high-rise social housing.Tilt and slide
A ''tilt and slide window'' is a window (more usually a door-sized window) where the sash tilts inwards at the top similar to a hopper window and then slides horizontally behind the fixed pane.Tilt and turn
A ''tilt and turn window'' can both tilt inwards at the top or open inwards from hinges at the side. This is the most common type of window in Germany, its country of origin. It is also widespread in many other European countries. In Europe, it is usual for these to be of the "turn first" type. i.e. when the handle is turned to 90 degrees the window opens in the side hung mode. With the handle turned to 180 degrees the window opens in bottom hung mode. Most usually in the UK the windows will be "tilt first" i.e. bottom hung at 90 degrees for ventilation and side hung at 180 degrees for cleaning the outer face of the glass from inside the building.Transom
A transom window is a window above a door. In an exterior door the transom window is often fixed, in an interior door, it can open either by hinges at top or bottom, or rotate on hinges. It provided ventilation before forced air heating and cooling. A fan-shaped transom is known as a fanlight, especially in the British Isles.Side light
Windows beside a door or window are called side-, wing-, margen-lights, and flanking windows.Jalousie window
 Also known as a louvered window, the jalousie window consists of parallel slats of glass or acrylic that open and close like a Venetian blind, usually using a crank or a lever. They are used extensively in tropical architecture. A jalousie door is a door with a jalousie window.
Also known as a louvered window, the jalousie window consists of parallel slats of glass or acrylic that open and close like a Venetian blind, usually using a crank or a lever. They are used extensively in tropical architecture. A jalousie door is a door with a jalousie window.
Clerestory
A clerestory window is a window set in aroof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
structure or high in a wall, used for daylighting.
Skylight
 A skylight is a window built into a roof structure. This type of window allows for natural daylight and moonlight.
A skylight is a window built into a roof structure. This type of window allows for natural daylight and moonlight.
Roof
 A ''roof window'' is a sloped window used for daylighting, built into a
A ''roof window'' is a sloped window used for daylighting, built into a roof
A roof (: roofs or rooves) is the top covering of a building, including all materials and constructions necessary to support it on the walls of the building or on uprights, providing protection against rain, snow, sunlight, extremes of tempera ...
structure. It is one of the few windows that could be used as an exit. Larger roof windows meet building codes for emergency evacuation.
Roof lantern
A roof lantern is a multi-paned glass structure, resembling a small building, built on a roof for day or moon light. Sometimes includes an additional clerestory. May also be called acupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, usually dome-like structure on top of a building often crowning a larger roof or dome. Cupolas often serve as a roof lantern to admit light and air or as a lookout.
The word derives, via Ital ...
.
Bay
A bay window is a multi-panel window, with at least three panels set at different angles to create a protrusion from the wall line.Oriel
An ''oriel window'' is a form of bay window. This form most often appears in Tudor-style houses and monasteries. It projects from the wall and does not extend to the ground. Originally a form of porch, they are often supported by brackets or corbels.Thermal
Thermal, orDiocletian
Diocletian ( ; ; ; 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia. As with other Illyri ...
, windows are large semicircular windows (or niches) which are usually divided into three lights (window compartments) by two mullions. The central compartment is often wider than the two side lights on either side of it.
Picture
A ''picture window'' is a large fixed window in a wall, typically without glazing bars, or glazed with only perfunctory glazing bars ( muntins) near the edge of the window. Picture windows provide an unimpeded view, as if framing a picture.Multi-lite
A ''multi-lite window'' is a window glazed with small panes of glass separated by wooden or lead ''glazing bars'', or '' muntins'', arranged in a decorative ''glazing pattern'' often dictated by the building's architectural style. Due to the historic unavailability of large panes of glass, the multi-lit (or ''lattice window'') was the most common window style until the beginning of the 20th century, and is still used in traditional architecture.Emergency exit/egress
An '' emergency exit window'' is a window big enough and low enough so that occupants can escape through the opening in an emergency, such as a fire. In many countries, exact specifications for emergency windows in bedrooms are given in many building codes. Specifications for such windows may also allow for the entrance of emergency rescuers. Vehicles, such as buses, aircraft, and trains frequently have emergency exit windows as well.Stained glass
 A stained glass window is a window composed of pieces of colored glass, transparent, translucent or opaque, frequently portraying persons or scenes. Typically the glass in these windows is separated by lead glazing bars. Stained glass windows were popular in Victorian houses and some Wrightian houses, and are especially common in churches.
A stained glass window is a window composed of pieces of colored glass, transparent, translucent or opaque, frequently portraying persons or scenes. Typically the glass in these windows is separated by lead glazing bars. Stained glass windows were popular in Victorian houses and some Wrightian houses, and are especially common in churches.
French
A French door has two columns of upright rectangular glass panes (lights) extending its full length; and two of these doors on an exterior wall and without a mullion separating them, that open outward with opposing hinges to a terrace or porch, are referred to as a French window. Sometimes these are set in pairs or multiples thereof along the exterior wall of a very large room, but often, one French window is placed centrally in a typically sized room, perhaps among other fixed windows flanking the feature. French windows are known as ''porte-fenêtre'' in France and ''portafinestra'' in Italy, and frequently are used in modern houses.Double-paned
 ''Double-paned windows'' have two parallel panes (slabs of glass) with a separation of typically about 1 cm; this space is permanently sealed and filled at the time of manufacture with dry air or other dry nonreactive gas. Such windows provide a marked improvement in thermal insulation (and usually in acoustic insulation as well) and are resistant to fogging and frosting caused by temperature differential. They are widely used for residential and commercial construction in intemperate climates. In the UK, double-paned and triple-paned are referred to as double- glazing and triple-glazing. Triple-paned windows are now a common type of glazing in central to northern Europe. Quadruple glazing is now being introduced in Scandinavia.
''Double-paned windows'' have two parallel panes (slabs of glass) with a separation of typically about 1 cm; this space is permanently sealed and filled at the time of manufacture with dry air or other dry nonreactive gas. Such windows provide a marked improvement in thermal insulation (and usually in acoustic insulation as well) and are resistant to fogging and frosting caused by temperature differential. They are widely used for residential and commercial construction in intemperate climates. In the UK, double-paned and triple-paned are referred to as double- glazing and triple-glazing. Triple-paned windows are now a common type of glazing in central to northern Europe. Quadruple glazing is now being introduced in Scandinavia.
Hexagonal window
 A hexagonal window is a hexagon-shaped window, resembling a bee cell or crystal lattice of graphite. The window can be vertically or horizontally oriented, openable or dead. It can also be regular or elongately-shaped and can have a separator ( mullion). Typically, the cellular window is used for an attic or as a decorative feature, but it can also be a major architectural element to provide the natural lighting inside buildings.
A hexagonal window is a hexagon-shaped window, resembling a bee cell or crystal lattice of graphite. The window can be vertically or horizontally oriented, openable or dead. It can also be regular or elongately-shaped and can have a separator ( mullion). Typically, the cellular window is used for an attic or as a decorative feature, but it can also be a major architectural element to provide the natural lighting inside buildings.
Guillotine window
A ''guillotine window'' is a window that opens vertically. Guillotine windows have more than one sliding frame, and open from bottom to top or top to bottom.Terms
EN 12519 is the European standard that describes windows terms officially used in EU Member States. The main terms are: * Light, or Lite, is the area between the outer parts of a window ( transom, sill and jambs), usually filled with a glass pane. Multiple panes are divided by mullions when load-bearing, muntins when not. * Lattice light is a compound window pane madeup of small pieces of glass held together in a lattice. * Fixed window is a unit of one non-moving lite. The terms ''single-light'', ''double-light'', etc., refer to the number of these glass panes in a window. * Sash unit is a window consisting of at least one sliding glass component, typically composed of two lites (known as a ''double-light''). * Replacement window in the United States means a framed window designed to slip inside the original window frame from the inside after the old sashes are removed. In Europe, it usually means a complete window including a replacement outer frame. * New construction window, in the US, means a window with a nailing fin that is inserted into a rough opening from the outside before applying siding and inside trim. A nailing fin is a projection on the outer frame of the window in the same plane as the glazing, which overlaps the prepared opening, and can thus be 'nailed' into place. In the UK and mainland Europe, windows in new-build houses are usually fixed with long screws into expanding plastic plugs in the brickwork. A gap of up to 13 mm is left around all four sides, and filled with expanding polyurethane foam. This makes the window fixing weatherproof but allows for expansion due to heat. * Lintel is a beam over the top of a window, also known as a transom. * Window sill is the bottom piece in a window frame. Window sills slant outward to drain water away from the inside of the building. * Secondary glazing is an additional frame applied to the inside of an existing frame, usually used on protected or listed buildings to achieve higher levels of thermal and sound insulation without compromising the look of the building * Decorative millwork is the moulding, cornices and lintels often decorating the surrounding edges of the window.Labeling
The United States NFRC Window Label lists the following terms: * Thermal transmittance (U-factor), best values are around U-0.15 (equal to 0.8 W/m2/K) * Solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), ratio of solar heat (infrared) passing through the glass to incident solar heat * Visible transmittance (VT), ratio of transmitted visible light divided by incident visible light * Air leakage (AL), measured in cubic foot per minute per linear foot of crack between sash and frame * Condensation resistance (CR), measured between 1 and 100 (the higher the number, the higher the resistance of the formation of condensation) The European harmonised standard hEN 14351–1, which deals with doors and windows, defines 23 characteristics (divided into ''essential'' and ''non essential''). Two other, preliminary European Norms that are under development deal with internal pedestrian doors (prEN 14351–2), smoke and fire resisting doors, and openable windows (prEN 16034).Construction
Grids or muntins
These are the pieces of framing that separate a larger window into smaller panes. In older windows, large panes of glass were quite expensive, so muntins let smaller panes fill a larger space. In modern windows, light-colored muntins still provide a useful function by reflecting some of the light going through the window, making the window itself a source of diffuse light (instead of just the surfaces and objects illuminated within the room). By increasing the indirect illumination of surfaces near the window, muntins tend to brighten the area immediately around a window and reduce the contrast of shadows within the room.Frame and sash construction
Frames and sashes can be made of the following materials: Composites (also known as Hybrid Windows) are start since early 1998 and combine materials like aluminium + pvc or wood to obtain aesthetics of one material with the functional benefits of another. A special class of PVC window frames, uPVC window frames, became widespread since the late 20th century, particularly in Europe: there were 83.5 million installed by 1998 with numbers still growing as of 2012.
A special class of PVC window frames, uPVC window frames, became widespread since the late 20th century, particularly in Europe: there were 83.5 million installed by 1998 with numbers still growing as of 2012.
Glazing and filling
Low-emissivity coated panes reduce heat transfer byradiation
In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or a material medium. This includes:
* ''electromagnetic radiation'' consisting of photons, such as radio waves, microwaves, infr ...
, which, depending on which surface is coated, helps prevent heat loss (in cold climates) or heat gains (in warm climates).
High thermal resistance can be obtained by evacuating or filling the insulated glazing units with gases such as argon
Argon is a chemical element; it has symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as abu ...
or krypton
Krypton (from 'the hidden one') is a chemical element; it has symbol (chemistry), symbol Kr and atomic number 36. It is a colorless, odorless noble gas that occurs in trace element, trace amounts in the Earth's atmosphere, atmosphere and is of ...
, which reduces conductive heat transfer due to their low thermal conductivity. Performance of such units depends on good window seals and meticulous frame construction to prevent entry of air and loss of efficiency.
Modern double-pane and triple-pane windows often include one or more low-e coatings to reduce the window's U-factor (its insulation value, specifically its rate of heat loss). In general, soft-coat low-e coatings tend to result in a lower solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC) than hard-coat low-e coatings.
Modern windows are usually glazed with one large sheet of glass per sash, while windows in the past were glazed with multiple panes separated by ''glazing bars'', or ''muntins'', due to the unavailability of large sheets of glass. Today, glazing bars tend to be decorative, separating windows into small panes of glass even though larger panes of glass are available, generally in a pattern dictated by the architectural style at use. Glazing bars are typically wooden, but occasionally lead glazing bars soldered in place are used for more intricate glazing patterns.
Other construction details
Many windows have movablewindow covering
Window coverings are considered any type of materials used to cover a window to manage sunlight, privacy, additional weatherproofing or for purely Window treatment, decorative purposes.
Description and design
Window coverings comprise materia ...
s such as blinds or curtains to keep out light, provide additional insulation, or ensure privacy.
Windows allow natural light to enter, but too much can have negative effects such as glare and heat gain. Additionally, while windows let the user see outside, there must be a way to maintain privacy on in the inside.Howell, Sandra C. (1976). ''Designing for the Elderly; Windows''. Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Department of Architecture. Design Evaluation Project. Window coverings are practical accommodations for these issues.
Impact of the sun
Sun incidence angle
Historically, windows are designed with surfaces parallel to vertical building walls. Such a design allows considerable solar light and heat penetration due to the most commonly occurring incidence of sun angles. In passive solar building design, an extended eave is typically used to control the amount of solar light and heat entering the window(s). An alternative method is to calculate an optimum window mounting angle that accounts for summer sun load minimization, with consideration of actual latitude of the building. This process has been implemented, for example, in the Dakin Building in Brisbane, California—in which most of the fenestration is designed to reflect summer heat load and help prevent summer interior over-illumination and glare, by canting windows to nearly a 45 degree angle.Solar window
Photovoltaic windows not only provide a clear view and illuminate rooms, but also convert sunlight to electricity for the building. In most cases, translucent photovoltaic cells are used.Passive solar
''Passive solar windows'' allow light and solar energy into a building while minimizing air leakage and heat loss. Properly positioning these windows in relation to sun, wind, and landscape—while properly shading them to limit excess heat gain in summer and shoulder seasons, and providing thermal mass to absorb energy during the day and release it when temperatures cool at night—increases comfort and energy efficiency. Properly designed in climates with adequate solar gain, these can even be a building's primary heating system.Coverings
Awindow covering
Window coverings are considered any type of materials used to cover a window to manage sunlight, privacy, additional weatherproofing or for purely Window treatment, decorative purposes.
Description and design
Window coverings comprise materia ...
is a shade or screen that provides multiple functions. Some coverings, such as drapes and blinds provide occupants with privacy. Some window coverings control solar heat gain and glare. There are external shading devices and internal shading devices.Beckett, H. E., & Godfrey, J. A. (1974). ''Windows: Performance, design and installation''. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold Company. Low-e window film
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent m ...
is a low-cost alternative to window replacement to transform existing poorly-insulating windows into energy-efficient windows. For high-rise buildings, smart glass can provide an alternative.
Gallery
Ancient Egyptian
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
sandstone
Sandstone is a Clastic rock#Sedimentary clastic rocks, clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of grain size, sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate mineral, silicate grains, Cementation (geology), cemented together by another mineral. Sand ...
window grill from a palace of Ramesses III, now in the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art, colloquially referred to as the Met, is an Encyclopedic museum, encyclopedic art museum in New York City. By floor area, it is the List of largest museums, third-largest museum in the world and the List of larg ...
(New York City)
File:GBM - Glas Fenster.jpg, Fragment of a Roman window glass plate dated to 1st to 4th century CE. Note the obvious curvature; this is not a flat pane
File:Window art in Kalleshvara Temple at Aralaguppe (edited angles and cropped).jpg, Indian window of the Kalleshvara Temple (India)
File:师俭堂.JPG, Chinese latticed window in Zhenze (Jiangsu
Jiangsu is a coastal Provinces of the People's Republic of China, province in East China. It is one of the leading provinces in finance, education, technology, and tourism, with its capital in Nanjing. Jiangsu is the List of Chinese administra ...
, China)
File:Atenas, varios 10.jpg, Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
window of the Little Metropolis (Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southe ...
, Greece)
File:Jameh Mosque of Nishapur - October 13 2013 45.JPG, Islamic
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
window of the Jameh Mosque of Nishapur (Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district.
Ni ...
, Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran (IRI) and also known as Persia, is a country in West Asia. It borders Iraq to the west, Turkey, Azerbaijan, and Armenia to the northwest, the Caspian Sea to the north, Turkmenistan to the nort ...
)
File:David et Salomon, vitrail roman, Cathédrale de Strasbourg.jpg, Part of a Romanesque stained glass window with Kings David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
and Solomon
Solomon (), also called Jedidiah, was the fourth monarch of the Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Kingdom of Israel and Judah, according to the Hebrew Bible. The successor of his father David, he is described as having been the penultimate ...
from Cathédrale Notre-Dame de Strasbourg (Strasbourg
Strasbourg ( , ; ; ) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est Regions of France, region of Geography of France, eastern France, in the historic region of Alsace. It is the prefecture of the Bas-Rhin Departmen ...
, France)
File:Chartres RosetteNord 121 DSC08241.jpg, North transept windows in the Chartres Cathedral ( Chartres, France)
File:Béringuier-Bonnefoy fenêtre (2).jpg, Flamboyant Gothic window of a stair tower (Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
, France)
File:Valdai IverskyMon asv2018 img41.jpg, Russian window of the Valday Iversky Monastery ( Lake Valdayskoye, Novgorod Oblast, Russia)
File:Flickr - fusion-of-horizons - stavropoleos (124).jpg, Brâncovenesc window of the Stavropoleos Monastery (Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ) is the capital and largest city of Romania. The metropolis stands on the River Dâmbovița (river), Dâmbovița in south-eastern Romania. Its population is officially estimated at 1.76 million residents within a greater Buc ...
, Romania)
File:Fenetre-assezat-cour (2).jpg, Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
window of the Hôtel d'Assézat (Toulouse
Toulouse (, ; ; ) is a city in southern France, the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Haute-Garonne department and of the Occitania (administrative region), Occitania region. The city is on the banks of the Garonne, River Garonne, from ...
, France)
File:0756a - Milano - Palazzo Sormani-Andreani - Foto Giovanni Dall'Orto 5-May-2007 (edited).jpg, Baroque
The Baroque ( , , ) is a Western Style (visual arts), style of Baroque architecture, architecture, Baroque music, music, Baroque dance, dance, Baroque painting, painting, Baroque sculpture, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished from ...
window of the Palazzo Sormani (Milan
Milan ( , , ; ) is a city in northern Italy, regional capital of Lombardy, the largest city in Italy by urban area and the List of cities in Italy, second-most-populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of nea ...
, Italy)
File:Zwinger Wallpavillon Gartenseite, Dresden.jpg, Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpte ...
windows of the Zwinger (Dresden
Dresden (; ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; , ) is the capital city of the States of Germany, German state of Saxony and its second most populous city after Leipzig. It is the List of cities in Germany by population, 12th most p ...
, Germany)
File:South gate of the Petit Trianon 004.JPG, Louis XVI
Louis XVI (Louis-Auguste; ; 23 August 1754 – 21 January 1793) was the last king of France before the fall of the monarchy during the French Revolution. The son of Louis, Dauphin of France (1729–1765), Louis, Dauphin of France (son and heir- ...
round window of the Petit Trianon
The Petit Trianon (; French for 'small Trianon') is a Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical style château located on the grounds of the Palace of Versailles in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, France. It was built between 1762 and 1768 ...
(Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; ) is a former royal residence commissioned by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, Yvelines, Versailles, about west of Paris, in the Yvelines, Yvelines Department of Île-de-France, Île-de-France region in Franc ...
, France), with a festoon-derived ornament at the top
File:Window of a lateral façade of the Romanian Athenaeum, on Strada Benjamin Franklin (Bucharest, Romania).jpg, Neoclassical group of windows, on a lateral side of the Romanian Athenaeum (Bucharest)
File:Window of a very beautiful Gothic Revival house on the Jean-Louis Calderon street from Bucharest (Romania).jpg, Gothic Revival
Gothic Revival (also referred to as Victorian Gothic or neo-Gothic) is an Architectural style, architectural movement that after a gradual build-up beginning in the second half of the 17th century became a widespread movement in the first half ...
window of a house on Strada Jean-Louis Calderon (Bucharest)
File:P1340760 Paris II place et passage du Caire rwk.jpg, Egyptian Revival windows of a building in Place du Caire (Paris)
File:60, Bulevardul Dacia, Bucharest (Romania) 1.jpg, Romanian Revival window of a house on Bulevardul Dacia (Bucharest)
File:Window, 55 rue Molitor, Paris 25 February 2017.jpg, 19th century Eclectic Classicist windows on Rue Molitor (Paris)
File:9, Strada Dianei, Bucharest (Romania) 3.jpg, Beaux-Arts window of the Stroescu House on Strada Dianei (Bucharest)
File:Stillemans32.jpg, Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French (), is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design that first Art Deco in Paris, appeared in Paris in the 1910s just before World War I and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920 ...
house with stained glass windows on Stillemansstraat (Sint-Niklaas
Sint-Niklaas (; , ) is a Belgium, Belgian City status in Belgium, city and Municipalities in Belgium, municipality located in the Flemish Region, Flemish Provinces of Belgium, province of East Flanders. The municipality comprises the city of Sin ...
, Belgium)
File:Reliance Building (Burnham Hotel) - Chicago, Illinois.JPG, Chicago windows of the Reliance Building (Chicago)
File:Maison Horta, détail de la façade.JPG, Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau ( ; ; ), Jugendstil and Sezessionstil in German, is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and ...
windows of the Horta Museum (Brussels)
File:Fischerkirche (window), Born a. Darß.jpg, Window with shutters of the Lutheran wooden church in Born auf dem Darß (Germany)
File:Restaurant Amigos de Acapulco (window), Chico.jpg, Serving window of a Mexican restaurant in the city of Chico (California)
File:Windows of the Cité de la musique, Paris July 2015.jpg, Postmodern windows of the Cité de la musique (Paris)
File:Windows (7004083002).jpg, Contemporary windows of Cathedral Plaza Bucharest
File:Fönster - Entré - Ystad-2021.jpg, Very high windows in the entrance to a residential building in Ystad
See also
* Airflow window * Architectural glass * Crown glass * Demerara window * Display window * Fortochka * Glass mullion system * Greased paper window * Insulated glazing * Plate glass * Porthole *Rose window
Rose window is often used as a generic term applied to a circular window, but is especially used for those found in Gothic cathedrals and churches. The windows are divided into segments by stone mullions and tracery. The term ''rose window'' wa ...
* Window tax
* Window treatment
* Witch window
In American vernacular architecture, a witch window (also known as a Vermont window, among other names) is a window (usually a double-hung sash window, occasionally a single-sided casement window) placed in the gable-end wall of a houseGeorge Nas ...
References
External links
Roman Glass from Metropolitan Museum of Art
{{Authority control Architectural elements Glass