Fechner (crater) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
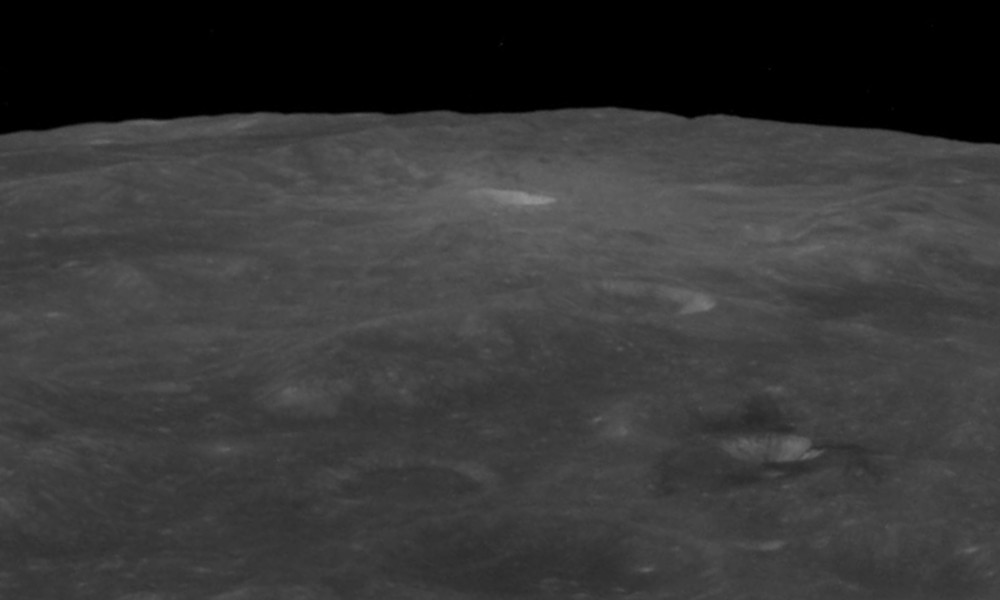 Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim.
Attached to the western rim of Fechner is Fechner T, a small, bowl-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo
Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim.
Attached to the western rim of Fechner is Fechner T, a small, bowl-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo Fechner
Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)
 Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim.
Attached to the western rim of Fechner is Fechner T, a small, bowl-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo
Fechner is a lunar impact crater that lies on the far side of the Moon's southern hemisphere, attached to the western rim of the large walled plain Planck. The eastern rim of Fechner intersects the Vallis Planck, a long, wide cleft in the surface that follows a course to the north-northwest. This valley intrudes into the southeastern rim of the crater, then continues northwards from the periphery of the northeast rim.
Attached to the western rim of Fechner is Fechner T, a small, bowl-shaped crater with a relatively high albedo ray system
A ray system comprises radial streaks of fine '' ejecta'' thrown out during the formation of an impact crater, looking somewhat like many thin spokes coming from the hub of a wheel. The rays may extend for lengths up to several times the diameter ...
. This satellite crater is surrounded by a blanket of light-hued ejecta
Ejecta (from the Latin: "things thrown out", singular ejectum) are particles ejected from an area. In volcanology, in particular, the term refers to particles including pyroclastic materials (tephra) that came out of a volcanic explosion and magma ...
that spills across the southwestern half of Fechner's interior floor. The crater rim of Fechner is relatively worn and eroded, with the eastern half of the rim reshaped due to the valley and proximity to Planck. The interior floor is marked by several small craters.
The crater is named after Gustav Theodor Fechner, a German physicist, psychologist, and philosopher (1801-1887). The name was approved by the IAU in 1970.Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature, International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN)
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Fechner.References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * Impact craters on the Moon {{Craters on the Moon: C-F