Fayum Depression on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Faiyum Oasis ( ''Wāḥat al-Fayyum'') is a depression or basin in the desert immediately west of the
The Faiyum Oasis ( ''Wāḥat al-Fayyum'') is a depression or basin in the desert immediately west of the
 When the
When the

The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction
{{Authority control Faiyum Governorate Geography of ancient Egypt Oases of Egypt

 The Faiyum Oasis ( ''Wāḥat al-Fayyum'') is a depression or basin in the desert immediately west of the
The Faiyum Oasis ( ''Wāḥat al-Fayyum'') is a depression or basin in the desert immediately west of the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
river, 62 miles south of Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
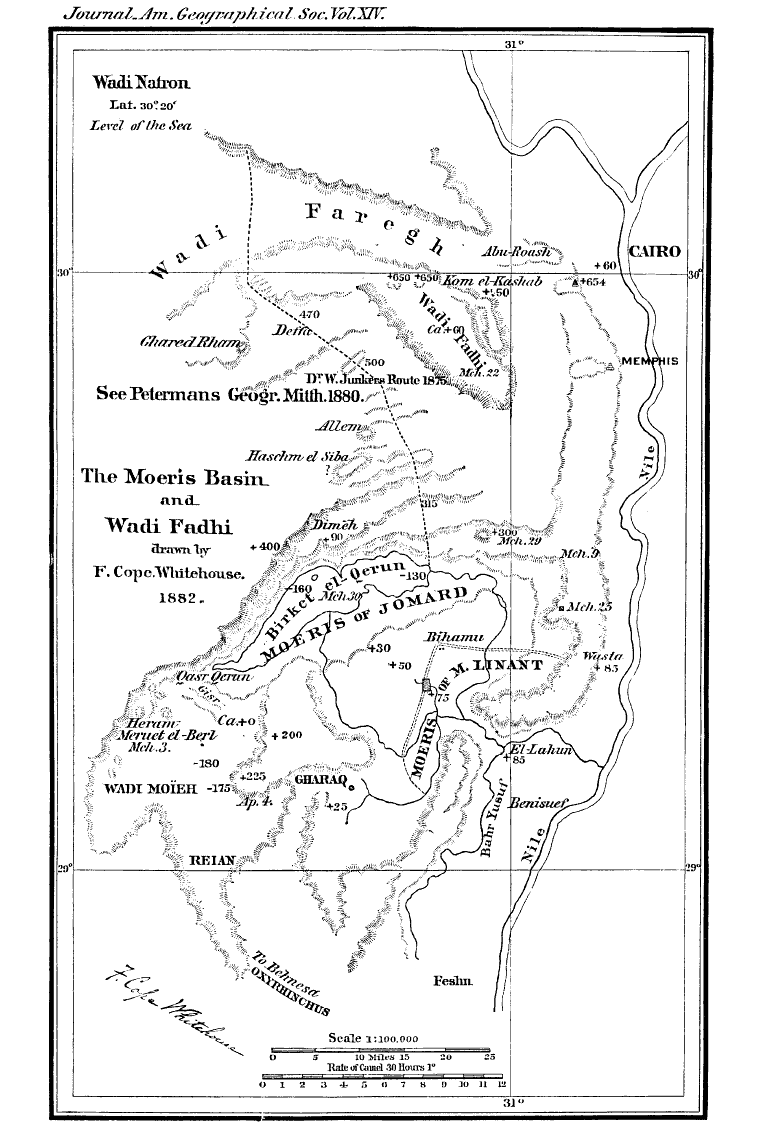
, Egypt. The extent of the basin area is estimated at between 1,270 km2 (490 mi2) and 1,700 km2 (656 mi2). The basin floor comprises fields watered by a channel of the Nile, the Bahr Yussef
The Bahr Yussef (; "the waterway of Joseph") is a canal which connects the Nile River with Faiyum Oasis in Egypt.
In ancient times it was called Tomis () by the Greeks, which was derived from its Egyptian name ''Tm.t'' ("ending canal"). That nam ...
, as it drains into a desert hollow to the west of the Nile Valley
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river i ...
. The Bahr Yussef veers west through a narrow neck of land north of Ihnasya, between the archaeological sites of El Lahun and Gurob near Hawara; it then branches out, providing agricultural land in the Faiyum basin, draining into the large saltwater Lake Moeris (Birket Qarun). In prehistory it was a freshwater lake, but is today a saltwater lake. It is a source for tilapia and other fish for the local area.
Differing from typical oases, whose fertility depends on water obtained from springs, the cultivated land in the Faiyum is formed of Nile mud brought by the Bahr Yussef
The Bahr Yussef (; "the waterway of Joseph") is a canal which connects the Nile River with Faiyum Oasis in Egypt.
In ancient times it was called Tomis () by the Greeks, which was derived from its Egyptian name ''Tm.t'' ("ending canal"). That nam ...
canal, 24 km (15 miles) in length. Between the beginning of Bahr Yussef at El Lahun to its end at the city of Faiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
, several canals branch off to irrigate the Faiyum Governorate. The drainage water flows into Lake Moeris.
History
 When the
When the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
was a hot, dry hollow near the end of the Messinian Salinity Crisis
In the Messinian salinity crisis (also referred to as the Messinian event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event) the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partial or nearly complete desiccation (drying-up) throughout the latter part of ...
in the late Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, Faiyum was a dry hollow, and the Nile
The Nile (also known as the Nile River or River Nile) is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the List of river sy ...
flowed past it at the bottom of a canyon
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency t ...
(which was deep or more where Cairo
Cairo ( ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Egypt and the Cairo Governorate, being home to more than 10 million people. It is also part of the List of urban agglomerations in Africa, largest urban agglomeration in Africa, L ...
is today). After the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern ...
reflooded at the end of the Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
, the Nile canyon became an arm of the sea reaching inland further than Aswan
Aswan (, also ; ) is a city in Southern Egypt, and is the capital of the Aswan Governorate.
Aswan is a busy market and tourist centre located just north of the Aswan Dam on the east bank of the Nile at the first cataract. The modern city ha ...
. Over geological time that sea arm gradually filled with silt and became the Nile Valley.
Eventually, the Nile valley bed silted up high enough to let the Nile periodically overflow into the Faiyum Hollow, forming a lake. The lake is first recorded from about 3000 BC, around the time of Menes
Menes ( ; ; , probably pronounced *; and Μήν) was a pharaoh of the Early Dynastic Period of ancient Egypt, credited by classical tradition with having united Upper and Lower Egypt, and as the founder of the First Dynasty.
The identity of M ...
(Narmer). However, for the most part, it would only be filled with high flood waters. Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
settlements bordered the lake, and the town of Crocodilopolis (now Faiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
) grew up on the south where the higher ground created a ridge.
In 2300 BC, the waterway from the Nile River to the natural lake was widened and deepened to make a canal now known as the Bahr Yussef
The Bahr Yussef (; "the waterway of Joseph") is a canal which connects the Nile River with Faiyum Oasis in Egypt.
In ancient times it was called Tomis () by the Greeks, which was derived from its Egyptian name ''Tm.t'' ("ending canal"). That nam ...
. This canal fed into the lake. This was meant to serve three purposes: control the flooding of the Nile, regulate the water level of the Nile during dry seasons, and serve the surrounding area with irrigation. There is evidence the pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
s of the Twelfth Dynasty of Egypt
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is a series of rulers reigning from 1991–1802 BC (190 years), at what is often considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom (Dynasties XI–XIV). The dynasty period ...
used the natural lake of Faiyum as a reservoir to store surpluses of water for use during the dry periods. The immense waterworks undertaken by the ancient Egyptian pharaohs of the twelfth dynasty to transform the lake into a vast water reservoir gave the impression that the lake was an artificial excavation, as classic geographers and travellers reported. The lake was eventually abandoned due to the nearest branch of the Nile dwindling in size from 230 BC.
Faiyum was known to the ancient Egyptians as the twenty-first nome of Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ', shortened to , , locally: ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the Nile River valley south of the delta and the 30th parallel North. It thus consists of the entire Nile River valley from Cairo south to Lake N ...
, Atef-Pehu ("Northern Sycamore"). Its capital was Sh-d-y-t (usually written "Shedyt"), called by the Greeks ''Crocodilopolis'', and refounded by Ptolemy II Philadelphus
Ptolemy II Philadelphus (, ''Ptolemaîos Philádelphos'', "Ptolemy, sibling-lover"; 309 – 28 January 246 BC) was the pharaoh of Ptolemaic Egypt from 284 to 246 BC. He was the son of Ptolemy I, the Macedonian Greek general of Alexander the G ...
as Arsinoe.
This region has the earliest evidence for farming in Egypt, and was a center of royal pyramid and tomb-building in the Twelfth Dynasty during the Middle Kingdom, and again during the rule of the Ptolemaic Kingdom
The Ptolemaic Kingdom (; , ) or Ptolemaic Empire was an ancient Greek polity based in Ancient Egypt, Egypt during the Hellenistic period. It was founded in 305 BC by the Ancient Macedonians, Macedonian Greek general Ptolemy I Soter, a Diadochi, ...
. Faiyum became one of the breadbaskets of the Roman world.
For the first three centuries AD, the people of Faiyum and elsewhere in Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, ...
not only embalmed their dead but also placed a portrait of the deceased over the face of the mummy wrappings, shroud or case. The Egyptians continued their practice of burying their dead, despite the Roman preference for cremation
Cremation is a method of Disposal of human corpses, final disposition of a corpse through Combustion, burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India, Nepal, and ...
. Preserved by the dry desert environment, these Fayum mummy portraits make up the richest body of portraiture to have survived from antiquity. They provide a window into a society of peoples of mixed origins—Egyptians, Greeks
Greeks or Hellenes (; , ) are an ethnic group and nation native to Greece, Greek Cypriots, Cyprus, Greeks in Albania, southern Albania, Greeks in Turkey#History, Anatolia, parts of Greeks in Italy, Italy and Egyptian Greeks, Egypt, and to a l ...
, Romans, Syrians
Syrians () are the majority inhabitants of Syria, indigenous to the Levant, most of whom have Arabic, especially its Levantine Arabic, Levantine and Mesopotamian Arabic, Mesopotamian dialects, as a mother tongue. The culture of Syria, cultural ...
, Libyans
Demographics of Libya is the demography of Libya, specifically covering population density, Ethnic group, ethnicity, and Religion in Libya, religious affiliations, as well as other aspects of the Libyan population. All figures are from the Uni ...
and others—that flourished 2000 years ago in the Faiyum. The Faiyum portraits were painted on wood in a pigmented wax technique called encaustic painting
Encaustic painting, also known as hot wax painting, is a form of painting that involves a heated wax medium to which colored pigments have been added. The molten mix is applied to a surface—usually prepared wood, though canvas and other mate ...
.
In the late 1st millennium, the arable area shrank. Settlements around the edge of the basin were abandoned. These sites include some of the best-preserved from the late Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
, notably Karanis, and from the Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also known as the Eastern Roman Empire, was the continuation of the Roman Empire centred on Constantinople during late antiquity and the Middle Ages. Having survived the events that caused the fall of the Western Roman E ...
and early Arab
Arabs (, , ; , , ) are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in West Asia and North Africa. A significant Arab diaspora is present in various parts of the world.
Arabs have been in the Fertile Crescent for thousands of years ...
Periods, though recent redevelopment has greatly reduced the archaeological features. In addition to the mummy portraits, the villages of the Faiyum have also proven to be a source of papyrus
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can a ...
fragments containing literature and documents in Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
, Greek, and Egyptian scripts.
"Colonial-type" village names (villages named after towns elsewhere in Egypt and places outside Egypt) show that much land was brought into cultivation in the Faiyum in the Greek and Roman periods.
According to the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition, in 1910 over 1,000 km2 (400 mile2) of the Faiyum Oasis was cultivated, the chief crops being cereal
A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize ( Corn). Edible grains from other plant families, ...
s and cotton
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ...
. The completion of the Aswan Low Dam ensured a supply of water, which enabled 20,000 acres (80 km2) of land, previously unirrigated and untaxed, to be brought under cultivation in the years 1903–1905. Three crops were obtained in twenty months. The province was noted for its figs, grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began approximately 8,0 ...
s, and olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'' ("European olive"), is a species of Subtropics, subtropical evergreen tree in the Family (biology), family Oleaceae. Originating in Anatolia, Asia Minor, it is abundant throughout the Mediterranean ...
s. Rose
A rose is either a woody perennial plant, perennial flowering plant of the genus ''Rosa'' (), in the family Rosaceae (), or the flower it bears. There are over three hundred Rose species, species and Garden roses, tens of thousands of cultivar ...
trees were numerous, and most of the attar of roses (rose oil) of Egypt was manufactured in the province. Faiyum also raised its own variety of sheep
Sheep (: sheep) or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are a domesticated, ruminant mammal typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus '' Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to d ...
.
Archaeology
In the vicinity of the lake are many ruins of ancient villages and cities. Mounds north of the city ofFaiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
mark the site of Crocodilopolis/Arsinoe. Archaeological remains across the region extend from the prehistoric period to modern times, e.g. the Monastery of the Archangel Gabriel at Naqlun.
The cult of Sobek
In antiquity, the Fajyum was a center of the cult of the crocodile godSobek
Sobek (), also known as Suchus (), was an ancient Egyptian deities, ancient Egyptian deity with a complex and elastic history and nature. He is associated with the Nile crocodile and is often represented as a crocodile-headed humanoid, if not a ...
. In many settlements, temples were dedicated to local manifestations of the god and associated divinities. The priests of Sobek were key players in social and economic life; for example by organizing religious festivals or by purchasing goods from local producers. The development of temples dedicated to the Sobek cult can be studied particularly well in Bakchias, Narmouthis, Soknopaiou Nesos, Tebtunis, and Theadelphia, since many written sources (papyri
Papyrus ( ) is a material similar to thick paper that was used in ancient times as a writing surface. It was made from the pith of the papyrus plant, ''Cyperus papyrus'', a wetland sedge. ''Papyrus'' (plural: ''papyri'' or ''papyruses'') can ...
, ostraka
An ostracon (Greek: ''ostrakon'', plural ''ostraka'') is a piece of pottery, usually broken off from a vase or other earthenware vessel. In an archaeological or epigraphical context, ''ostraca'' refer to sherds or even small pieces of ston ...
, inscriptions) on the daily life of the priests are available there.
Egyptian temples have been operating at the edges of the Fayyum at least until the early third century and in some cases in the fourth century. The institutionalized Sobek cults existed alongside early Christian communities, which settled in the region from the third century onwards and built their first churches in the Fayyum settlements by the fourth century.
Birket Qarun lake
Birket Qarun (Arabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
for ''Lake of Qarun''), is located in the Faiyum Oasis and has an abundant population of fish
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can ...
, notably bulti, of which considerable quantities are sent to Cairo. In ancient times this lake was much larger, and the ancient Greeks and Romans called it Lake Moeris.
Cities and towns
The largest city isFaiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
, which is also the capital of the Faiyum Governorate. Other towns include Sinnuris and Tamiya to the north of Faiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
, and Sanhur and Ibsheway on the road to the lake.
In popular culture
The oasis is the setting for about a quarter of Paolo Coelho's '' The Alchemist'', one of the top 20 best-selling books in the world. It also appears as one of the main regions in the Assassin's Creed: Origins game.See also
*Bahr Yussef
The Bahr Yussef (; "the waterway of Joseph") is a canal which connects the Nile River with Faiyum Oasis in Egypt.
In ancient times it was called Tomis () by the Greeks, which was derived from its Egyptian name ''Tm.t'' ("ending canal"). That nam ...
canal
*Faiyum
Faiyum ( ; , ) is a city in Middle Egypt. Located southwest of Cairo, in the Faiyum Oasis, it is the capital of the modern Faiyum Governorate. It is one of Egypt's oldest cities due to its strategic location.
Name and etymology
Originally f ...
* Fayum (fossil deposit)
*Faiyum Governorate
Faiyum ( ) is one of the governorates of Egypt in the middle of the country. Its capital is the city of Faiyum, located about 81 mi (130 km) south west of Cairo. It has a population of 3,848,708 (2020).
Etymology
The name Faiyum com ...
* Farafra
* Fayum mummy portraits
* Lake Moeris
* Monastery of the Archangel Gabriel at Naqlun
* Pedestals of Biahmu
* Phiomia (an extinct relative of the elephant, named after Faiyum)
*Roman Egypt
Roman Egypt was an imperial province of the Roman Empire from 30 BC to AD 642. The province encompassed most of modern-day Egypt except for the Sinai. It was bordered by the provinces of Crete and Cyrenaica to the west and Judaea, ...
Notes
References
The Hydraulics of Open Channel Flow: An Introduction
{{Authority control Faiyum Governorate Geography of ancient Egypt Oases of Egypt