Fat Triglyceride Shorthand Formula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In animals,
In animals,

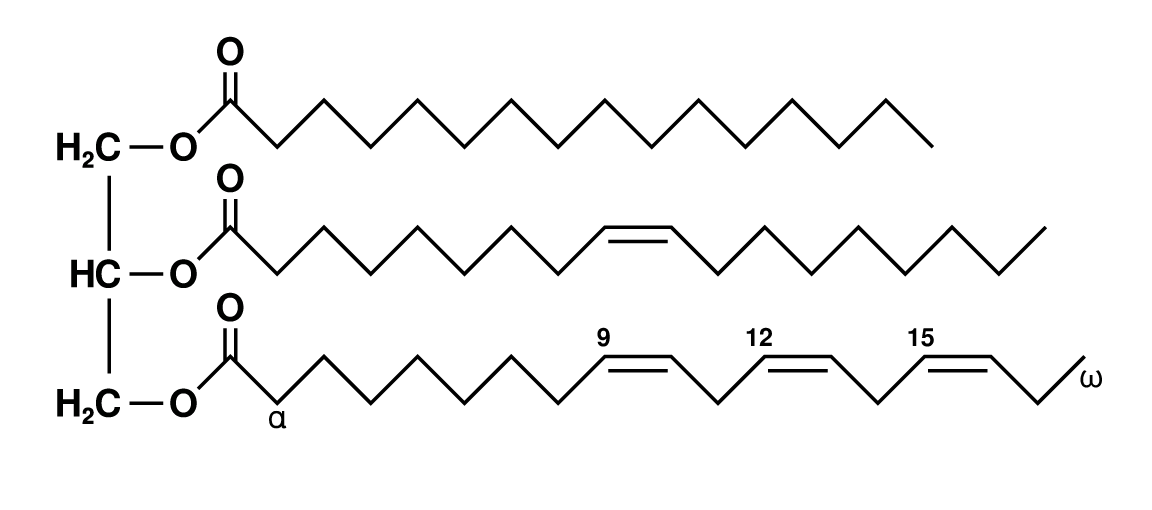 Assuming that unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs) are generally healthier than saturated ones (SFAs), another question that has gained attention in recent decades is the risks and benefits of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs, with a single double bond) versus polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs, with two or more double bonds).
The most common fatty acids in human diet are unsaturated or mono-unsaturated. Monounsaturated fats are found in animal flesh such as red meat, whole milk products, nuts, and high fat fruits such as olives and avocados. Olive oil is about 75% monounsaturated fat. The high oleic variety
Assuming that unsaturated fatty acids (UFAs) are generally healthier than saturated ones (SFAs), another question that has gained attention in recent decades is the risks and benefits of monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAs, with a single double bond) versus polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs, with two or more double bonds).
The most common fatty acids in human diet are unsaturated or mono-unsaturated. Monounsaturated fats are found in animal flesh such as red meat, whole milk products, nuts, and high fat fruits such as olives and avocados. Olive oil is about 75% monounsaturated fat. The high oleic variety

 Concerns about ''trans'' fatty acids in human diet were raised when they were found to be an unintentional byproduct of the partial hydrogenation of vegetable and fish oils. While these ''trans'' fatty acids (popularly called "trans fats") are edible, they have been implicated in many health problems.
Concerns about ''trans'' fatty acids in human diet were raised when they were found to be an unintentional byproduct of the partial hydrogenation of vegetable and fish oils. While these ''trans'' fatty acids (popularly called "trans fats") are edible, they have been implicated in many health problems.
 The hydrogenation process, invented and patented by Wilhelm Normann in 1902, made it possible to turn relatively cheap liquid fats such as
The hydrogenation process, invented and patented by Wilhelm Normann in 1902, made it possible to turn relatively cheap liquid fats such as
 In
In nutrition
Nutrition is the biochemical and physiological process by which an organism uses food to support its life. It provides organisms with nutrients, which can be metabolized to create energy and chemical structures. Failure to obtain sufficien ...
, biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a broad scope but has several unifying themes that tie it together as a single, coherent field. For instance, all organisms are made up of cells that process hereditar ...
, and chemistry, fat usually means any ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides ...
of fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s, or a mixture of such compounds, most commonly those that occur in living beings or in food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is ...
.
The term often refers specifically to triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as ...
s (triple esters of glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ...
), that are the main components of vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, ...
s and of fatty tissue in animals; or, even more narrowly, to triglycerides that are solid or semisolid at room temperature, thus excluding oils. The term may also be used more broadly as a synonym of lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids incl ...
—any substance of biological relevance, composed of carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes ...
, hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic ...
, or oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
, that is insoluble in water but soluble in non-polar solvents. In this sense, besides the triglycerides, the term would include several other types of compounds like mono-
Numeral or number prefixes are prefixes derived from numerals or occasionally other numbers. In English and many other languages, they are used to coin numerous series of words. For example:
* unicycle, bicycle, tricycle (1-cycle, 2-cycle, 3-cyc ...
and diglyceride
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as ...
s, phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids ty ...
s (such as lecithin), sterol
Sterol is an organic compound with formula , whose molecule is derived from that of gonane by replacement of a hydrogen atom in position 3 by a hydroxyl group. It is therefore an alcohol of gonane. More generally, any compounds that contain the g ...
s (such as cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
), waxes (such as beeswax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive workers ...
), and free fatty acids, which are usually present in human diet in smaller amounts.
Fats are one of the three main macronutrient groups in human diet, along with carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s and protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respon ...
s, and the main components of common food products like milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulati ...
, butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food), spread, melted a ...
, tallow
Tallow is a rendered form of beef or mutton fat, primarily made up of triglycerides.
In industry, tallow is not strictly defined as beef or mutton fat. In this context, tallow is animal fat that conforms to certain technical criteria, inclu ...
, lard
Lard is a semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering the fatty tissue of a pig.Lard
entry in the ...
, entry in the ...
salt pork
Salt pork is salt-cured pork. It is usually prepared from pork belly, or, more rarely, fatback. Salt pork typically resembles uncut side bacon, but is fattier, being made from the lowest part of the belly, and saltier, as the cure is stronger ...
, and cooking oil
Cooking oil is plant, animal, or synthetic liquid fat used in frying, baking, and other types of cooking. It is also used in food preparation and flavoring not involving heat, such as salad dressings and bread dips, and may be called edible oi ...
s. They are a major and dense source of food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals (including humans) derive from their food to sustain their metabolism, including their muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the carbohy ...
for many animals and play important structural and metabolic
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cel ...
functions, in most living beings, including energy storage, waterproofing, and thermal insulation
Thermal insulation is the reduction of heat transfer (i.e., the transfer of thermal energy between objects of differing temperature) between objects in thermal contact or in range of radiative influence. Thermal insulation can be achieved with ...
. The human body can produce the fat it requires from other food ingredients, except for a few essential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic a ...
s that must be included in the diet. Dietary fats are also the carriers of some flavor and aroma ingredients and vitamin
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nut ...
s that are not water-soluble.
Biological importance
In humans and many animals, fats serve both as energy sources and as stores for energy in excess of what the body needs immediately. Each gram of fat when burned or metabolized releases about 9 food calories (37 kJ = 8.8kcal
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of o ...
).
Fats are also sources of essential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic a ...
s, an important dietary requirement. Vitamin
A vitamin is an organic molecule (or a set of molecules closely related chemically, i.e. vitamers) that is an essential micronutrient that an organism needs in small quantities for the proper functioning of its metabolism. Essential nut ...
s A, D, E, and K are fat-soluble, meaning they can only be digested, absorbed, and transported in conjunction with fats.
Fats play a vital role in maintaining healthy skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
and hair, insulating body organs against shock, maintaining body temperature, and promoting healthy cell function. Fat also serves as a useful buffer against a host of diseases. When a particular substance, whether chemical or biotic, reaches unsafe levels in the bloodstream, the body can effectively dilute—or at least maintain equilibrium of—the offending substances by storing it in new fat tissue. This helps to protect vital organs, until such time as the offending substances can be metabolized or removed from the body by such means as excretion
Excretion is a process in which metabolic waste
is eliminated from an organism. In vertebrates this is primarily carried out by the lungs, kidneys, and skin. This is in contrast with secretion, where the substance may have specific tasks afte ...
, urination
Urination, also known as micturition, is the release of urine from the urinary bladder through the urethra to the outside of the body. It is the urinary system's form of excretion. It is also known medically as micturition, voiding, ure ...
, accidental or intentional bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily flu ...
, sebum
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest nu ...
excretion, and hair growth.
Adipose tissue
 In animals,
In animals, adipose tissue
Adipose tissue, body fat, or simply fat is a loose connective tissue composed mostly of adipocytes. In addition to adipocytes, adipose tissue contains the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of cells including preadipocytes, fibroblasts, vascular ...
, or fatty tissue is the body's means of storing metabolic energy over extended periods of time. Adipocyte
Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Adipocytes are derived from mesenchymal stem cells which give rise to adipocytes through adipogenesi ...
s (fat cells) store fat derived from the diet and from liver metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
. Under energy stress these cells may degrade their stored fat to supply fatty acids and also glycerol to the circulation
Circulation may refer to:
Science and technology
* Atmospheric circulation, the large-scale movement of air
* Circulation (physics), the path integral of the fluid velocity around a closed curve in a fluid flow field
* Circulatory system, a bio ...
. These metabolic activities are regulated by several hormones (e.g., insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the ''INS'' gene. It is considered to be the main anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabol ...
, glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to trea ...
and epinephrine
Adrenaline, also known as epinephrine, is a hormone and medication which is involved in regulating visceral functions (e.g., respiration). It appears as a white microcrystalline granule. Adrenaline is normally produced by the adrenal glands and ...
). Adipose tissue also secretes the hormone leptin
Leptin (from Greek λεπτός ''leptos'', "thin" or "light" or "small") is a hormone predominantly made by adipose cells and enterocytes in the small intestine that helps to regulate energy balance by inhibiting hunger, which in turn dimi ...
.
The location of the tissue determines its metabolic profile: visceral fat is located within the abdominal wall (i.e., beneath the wall of abdominal muscle) whereas subcutaneous fat is located beneath the skin (and includes fat that is located in the abdominal area beneath the skin but ''above'' the abdominal muscle wall). Visceral fat was recently discovered to be a significant producer of signaling chemicals (i.e., hormone
A hormone (from the Greek participle , "setting in motion") is a class of signaling molecules in multicellular organisms that are sent to distant organs by complex biological processes to regulate physiology and behavior. Hormones are required ...
s), among which several are involved in inflammatory tissue responses. One of these is resistin which has been linked to obesity, insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood suga ...
, and (more controversially) Type 2 diabetes.
Production and processing
A variety of chemical and physical techniques are used for the production and processing of fats, both industrially and in cottage or home settings. They include: * Pressing to extract liquid fats from fruits, seeds, oralga
Algae ( , ; : alga ) are any of a large and diverse group of photosynthetic, eukaryotic organisms. The name is an informal term for a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from u ...
e, e.g. olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: ...
from olive
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' ...
s
* Solvent extraction using solvents like hexane or supercritical carbon dioxide
* Rendering, the melting of fat in adipose tissue, e.g. to produce tallow, lard, fish oil, and whale oil
Whale oil is oil obtained from the blubber of whales. Whale oil from the bowhead whale was sometimes known as train oil, which comes from the Dutch word ''traan'' (" tear" or "drop").
Sperm oil, a special kind of oil obtained from the hea ...
* Churning of milk to produce butter
* Hydrogenation
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate org ...
to increase the degree of saturation of the fatty acids
* Interesterification, the rearrangement of fatty acids across different triglycerides
* Winterization to remove oil components with higher melting points
* Clarification of butter
Metabolism
Thepancreatic lipase
Triglyceride lipases () are a family of lipolytic enzymes that hydrolyse ester linkages of triglycerides. Lipases are widely distributed in animals, plants and prokaryotes.
At least three tissue-specific isozymes exist in higher vertebrates, p ...
acts at the ester bond, hydrolyzing the bond and "releasing" the fatty acid. In triglyceride form, lipids cannot be absorbed by the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine ...
. Fatty acids, monoglycerides (one glycerol, one fatty acid), and some diglycerides are absorbed by the duodenum, once the triglycerides have been broken down.
In the intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans a ...
, following the secretion of lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
s and bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), or gall, is a dark-green-to-yellowish-brown fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is produced continuously by the liver (liver b ...
, triglycerides are split into monoacylglycerol and free fatty acids in a process called lipolysis
Lipolysis is the metabolic pathway through which lipid triglycerides are hydrolyzed into a glycerol and free fatty acids. It is used to mobilize stored energy during fasting or exercise, and usually occurs in fat adipocytes. The most importa ...
. They are subsequently moved to absorptive enterocyte cells lining the intestines. The triglycerides are rebuilt in the enterocytes from their fragments and packaged together with cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
and proteins to form chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (8 ...
s. These are excreted from the cells and collected by the lymph system and transported to the large vessels near the heart before being mixed into the blood. Various tissues can capture the chylomicrons, releasing the triglycerides to be used as a source of energy. Liver cells can synthesize and store triglycerides. When the body requires fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s as an energy source, the hormone glucagon
Glucagon is a peptide hormone, produced by alpha cells of the pancreas. It raises concentration of glucose and fatty acids in the bloodstream, and is considered to be the main catabolic hormone of the body. It is also used as a medication to trea ...
signals the breakdown of the triglycerides by hormone-sensitive lipase to release free fatty acids. As the brain
The brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head ( cephalization), usually near organs for special ...
cannot utilize fatty acids as an energy source (unless converted to a ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bon ...
), the glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ...
component of triglycerides can be converted into glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usi ...
, via gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non- carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In verteb ...
by conversion into dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP, also glycerone phosphate in older texts) is the anion with the formula HOCH2C(O)CH2OPO32-. This anion is involved in many metabolic pathways, including the Calvin cycle in plants and glycolysis.Nelson, D. L.; C ...
and then into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate, also known as triose phosphate or 3-phosphoglyceraldehyde and abbreviated as G3P, GA3P, GADP, GAP, TP, GALP or PGAL, is a metabolite that occurs as an intermediate in several central pathways of all organisms.Nelson, D ...
, for brain fuel when it is broken down. Fat cells may also be broken down for that reason if the brain's needs ever outweigh the body's.
Triglycerides cannot pass through cell membranes freely. Special enzymes on the walls of blood vessels called lipoprotein lipase
Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) (EC 3.1.1.34, systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase (lipoprotein-dependent)) is a member of the lipase gene family, which includes pancreatic lipase, hepatic lipase, and endothelial lipase. It is a water-solubl ...
s must break down triglycerides into free fatty acids and glycerol. Fatty acids can then be taken up by cells via the fatty acid transporter (FAT).
Triglycerides, as major components of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and chylomicron
Chylomicrons (from the Greek χυλός, chylos, meaning ''juice'' (of plants or animals), and micron, meaning ''small particle''), also known as ultra low-density lipoproteins (ULDL), are lipoprotein particles that consist of triglycerides (8 ...
s, play an important role in metabolism
Metabolism (, from el, μεταβολή ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run c ...
as energy sources and transporters of dietary fat. They contain more than twice as much energy (approximately 9kcal/g or 38 kJ/g) as carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s (approximately 4kcal/g or 17kJ/g).
Nutritional and health aspects
The most common type of fat, in human diet and most living beings, is atriglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as ...
, an ester of the triple alcohol
Alcohol most commonly refers to:
* Alcohol (chemistry), an organic compound in which a hydroxyl group is bound to a carbon atom
* Alcohol (drug), an intoxicant found in alcoholic drinks
Alcohol may also refer to:
Chemicals
* Ethanol, one of sev ...
glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ...
and three fatty acids. The molecule of a triglyceride can be described as resulting from a condensation reaction (specifically, esterification
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glyceride ...
) between each of glycerol's –OH groups and the HO– part of the carboxyl group of each fatty acid, forming an ester bridge with elimination of a water molecule .
Other less common types of fats include diglyceride
A diglyceride, or diacylglycerol (DAG), is a glyceride consisting of two fatty acid chains covalently bonded to a glycerol molecule through ester linkages. Two possible forms exist, 1,2-diacylglycerols and 1,3-diacylglycerols. DAGs can act as ...
s and monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two differe ...
s, where the esterification is limited to two or just one of glycerol's –OH groups. Other alcohols, such as cetyl alcohol (predominant in spermaceti), may replace glycerol. In the phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids ty ...
s, one of the fatty acids is replaced by phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid (orthophosphoric acid, monophosphoric acid or phosphoric(V) acid) is a colorless, odorless phosphorus-containing solid, and inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is commonly encountered as an 85% aqueous solutio ...
or a monoester thereof.
The benefits and risks of various amounts and types of dietary fats have been the object of much study, and are still highly controversial topics.
Essential fatty acids
There are twoessential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic a ...
s (EFAs) in human nutrition: alpha-Linolenic acid (an omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their che ...
) and linoleic acid
Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are ''cis''. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 ''cis''-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.
L ...
(an omega-6 fatty acid). The adult body can synthesize other lipids that it needs from these two.
Dietary sources
Saturated vs. unsaturated fats
Different foods contain different amounts of fat with different proportions of saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. Some animal products, likebeef
Beef is the culinary name for meat from cattle (''Bos taurus'').
In prehistoric times, humankind hunted aurochs and later domesticated them. Since that time, numerous breeds of cattle have been bred specifically for the quality or quant ...
and dairy products
Dairy products or milk products, also known as lacticinia, are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, nanny goat, and ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food items in ...
made with whole or reduced fat milk like yogurt
Yogurt (; , from tr, yoğurt, also spelled yoghurt, yogourt or yoghourt) is a food produced by bacterial fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as ''yogurt cultures''. Fermentation of sugars in the milk by these bact ...
, ice cream
Ice cream is a sweetened frozen food typically eaten as a snack or dessert. It may be made from milk or cream and is flavoured with a sweetener, either sugar or an alternative, and a spice, such as cocoa or vanilla, or with fruit such as ...
, cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During product ...
and butter
Butter is a dairy product made from the fat and protein components of churned cream. It is a semi-solid emulsion at room temperature, consisting of approximately 80% butterfat. It is used at room temperature as a spread (food), spread, melted a ...
have mostly saturated fatty acids (and some have significant contents of dietary cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membran ...
). Other animal products, like pork
Pork is the culinary name for the meat of the domestic pig (''Sus domesticus''). It is the most commonly consumed meat worldwide, with evidence of pig husbandry dating back to 5000 BCE.
Pork is eaten both freshly cooked and preserved ...
, poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quail ...
, eggs, and seafood have mostly unsaturated fats. Industrialized baked goods
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot stones. The most common baked item is bread but many other types of foods can be baked. Heat is gradually transferre ...
may use fats with high unsaturated fat contents as well, especially those containing partially hydrogenated oil
Hydrogenation is a chemical reaction between molecular hydrogen (H2) and another compound or element, usually in the presence of a catalyst such as nickel, palladium or platinum. The process is commonly employed to reduce or saturate organic co ...
s, and processed foods that are deep-fried
Deep frying (also referred to as deep fat frying) is a cooking method in which food is submerged in hot fat, traditionally lard but today most commonly oil, as opposed to the shallow oil used in conventional frying done in a frying pan. Norm ...
in hydrogenated oil
Fat hydrogenation is the process of combining fat – typically liquid vegetable oils – with hydrogen, to convert some or all of the unsaturated fat into saturated fat, resulting in a solid or semi-solid fat.
Changing the degree of saturation o ...
are high in saturated fat content.
Plants and fish oil generally contain a higher proportion of unsaturated acids, although there are exceptions such as coconut oil
frameless , right , alt = A cracked coconut and a bottle of coconut oil
Coconut oil (or coconut butter) is an edible oil derived from the wick, meat, and milk of the coconut palm fruit. Coconut oil is a white solid fat; in warmer climates duri ...
and palm kernel oil
Palm kernel oil is an edible plant oil derived from the kernel of the oil palm tree '' Elaeis guineensis''. It is related to other two edible oils: ''palm oil'', extracted from the fruit pulp of the oil palm, and '' coconut oil'', extracted fro ...
. Foods containing unsaturated fats include avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Pre-Columb ...
, nuts
Nut often refers to:
* Nut (fruit), fruit composed of a hard shell and a seed, or a collective noun for dry and edible fruits or seeds
* Nut (hardware), fastener used with a bolt
Nut or Nuts may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Com ...
, olive oil
Olive oil is a liquid fat obtained from olives (the fruit of ''Olea europaea''; family Oleaceae), a traditional tree crop of the Mediterranean Basin, produced by pressing whole olives and extracting the oil. It is commonly used in cooking: ...
s, and vegetable oil
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, ...
s such as canola.
Many careful studies have found that replacing saturated fats with ''cis'' unsaturated fats in the diet reduces risk of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
s (CVDs), diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
, or death. These studies prompted many medical organizations and public health departments, including the World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level o ...
(WHO), to officially issue that advice. Some countries with such recommendations include:
* United Kingdom
* United States
* India
* Canada
* Australia
* Singapore
* New Zealand
* Hong Kong
A 2004 review concluded that "no lower safe limit of specific saturated fatty acid intakes has been identified" and recommended that the influence of varying saturated fatty acid intakes against a background of different individual lifestyles and genetic backgrounds should be the focus in future studies.
This advice is often oversimplified by labeling the two kinds of fats as ''bad fats'' and ''good fats'', respectively. However, since the fats and oils in most natural and traditionally processed foods contain both unsaturated and saturated fatty acids, the complete exclusion of saturated fat is unrealistic and possibly unwise. For instance, some foods rich in saturated fat, such as coconut and palm oil, are an important source of cheap dietary calories for a large fraction of the population in developing countries.
Concerns were also expressed at a 2010 conference of the American Dietetic Association
The Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics is a 501(c)(6) trade association in the United States. With over 112,000 members, the association claims to be the largest organization of food and nutrition professionals. It has Dietitian, registered dieti ...
that a blanket recommendation to avoid saturated fats could drive people to also reduce the amount of polyunsaturated fats, which may have health benefits, and/or replace fats by refined carbohydrates — which carry a high risk of obesity and heart disease.
For these reasons, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
, for example, recommends to consume at least 10% (7% for high-risk groups) of calories from saturated fat, with an average of 30% (or less) of total calories from all fat. A general 7% limit was recommended also by the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and death ...
(AHA) in 2006.
The WHO/FAO report also recommended replacing fats so as to reduce the content of myristic and palmitic acids, specifically.
The so-called Mediterranean diet, prevalent in many countries in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
area, includes more total fat than the diet of Northern European countries, but most of it is in the form of unsaturated fatty acids (specifically, monounsaturated and omega-3) from olive oil and fish, vegetables, and certain meats like lamb, while consumption of saturated fat is minimal in comparison.
A 2017 review found evidence that a Mediterranean-style diet could reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases, overall cancer incidence, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, and mortality rate. A 2018 review showed that a Mediterranean-like diet may improve overall health status, such as reduced risk of non-communicable diseases. It also may reduce the social and economic costs of diet-related illnesses.
A small number of contemporary reviews have challenged this negative view of saturated fats. For example, an evaluation of evidence from 1966 to 1973 of the observed health impact of replacing dietary saturated fat
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone and fatty acids that each contain a long linear or branched ...
with linoleic acid
Linoleic acid (LA) is an organic compound with the formula COOH(CH2)7CH=CHCH2CH=CH(CH2)4CH3. Both alkene groups are ''cis''. It is a fatty acid sometimes denoted 18:2 (n-6) or 18:2 ''cis''-9,12. A linoleate is a salt or ester of this acid.
L ...
found that it ''increased'' rates of death from all causes, coronary heart disease, and cardiovascular disease. These studies have been disputed by many scientists, and the consensus in the medical community is that saturated fat and cardiovascular disease are closely related. Still, these discordant studies fueled debate over the merits of substituting polyunsaturated fats for saturated fats.
Cardiovascular disease
The effect of saturated fat on cardiovascular disease has been extensively studied. The general consensus is that there is evidence of moderate-quality of a strong, consistent, and graded relationship between saturated fat intake, blood cholesterol levels, and the incidence of cardiovascular disease. The relationships are accepted as causal, including by many government and medical organizations. A 2017 review by the AHA estimated that replacement of saturated fat with polyunsaturated fat in the American diet could reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by 30%. The consumption of saturated fat is generally considered a risk factor for dyslipidemia—abnormal blood lipid levels, including high total cholesterol, high levels of triglycerides, high levels oflow-density lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall densi ...
(LDL, "bad" cholesterol) or low levels of high-density lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules ( lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are ...
(HDL, "good" cholesterol). These parameters in turn are believed to be risk indicators for some types of cardiovascular disease. These effects were observed in children too.
Several meta-analyses
A meta-analysis is a statistical analysis that combines the results of multiple scientific studies. Meta-analyses can be performed when there are multiple scientific studies addressing the same question, with each individual study reporting me ...
(reviews and consolidations of multiple previously published experimental studies) have confirmed a significant relationship between saturated fat and high serum cholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell mem ...
levels, which in turn have been claimed to have a causal relation with increased risk of cardiovascular disease (the so-called lipid hypothesis
The lipid hypothesis (also known as the cholesterol hypothesis) is a medical theory postulating a link between blood cholesterol levels and the occurrence of cardiovascular disease. A summary from 1976 described it as: "measures used to lower th ...
). However, high cholesterol may be caused by many factors. Other indicators, such as high LDL/HDL ratio, have proved to be more predictive. In a study of myocardial infarction
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ...
in 52 countries, the ApoB/ApoA1
Apolipoprotein AI (ApoA-I) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''APOA1'' gene. As the major component of HDL particles, it has a specific role in lipid metabolism.
Structure
''APOA1'' is located on chromosome 11, with its specific lo ...
(related to LDL and HDL, respectively) ratio was the strongest predictor of CVD among all risk factors. There are other pathways involving obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
, triglyceride
A triglyceride (TG, triacylglycerol, TAG, or triacylglyceride) is an ester derived from glycerol and three fatty acids (from ''tri-'' and '' glyceride'').
Triglycerides are the main constituents of body fat in humans and other vertebrates, as ...
levels, insulin sensitivity, endothelial function, and thrombogenicity, among others, that play a role in CVD, although it seems, in the absence of an adverse blood lipid profile, the other known risk factors have only a weak atherogenic effect. Different saturated fatty acids have differing effects on various lipid levels.
Cancer
The evidence for a relation between saturated fat intake andcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
is significantly weaker, and there does not seem to be a clear medical consensus about it.
* A meta-analysis published in 2003 found a significant positive relationship between saturated fat and breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipple, a newly inverted nipple, or ...
. However two subsequent reviews have found weak or insignificant relation, and noted the prevalence of confounding factors.
* Another review found limited evidence for a positive relationship between consuming animal fat and incidence of colorectal cancer.
* Other meta-analyses found evidence for increased risk of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a cancerous tumor of an ovary. It may originate from the ovary itself or more commonly from communicating nearby structures such as fallopian tubes or the inner lining of the abdomen. The ovary is made up of three different ...
by high consumption of saturated fat.
* Some studies have indicated that serum myristic acid
Myristic acid (IUPAC name: tetradecanoic acid) is a common saturated fatty acid with the molecular formula CH3(CH2)12COOH. Its salts and esters are commonly referred to as myristates or tetradecanoates. It is named after the binomial name for nu ...
and palmitic acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The ...
and dietary myristic and palmitic saturated fatty acids and serum palmitic combined with alpha-tocopherol supplementation are associated with increased risk of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is cancer of the prostate. Prostate cancer is the second most common cancerous tumor worldwide and is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related mortality among men. The prostate is a gland in the male reproductive system that su ...
in a dose-dependent manner. These associations may, however, reflect differences in intake or metabolism of these fatty acids between the precancer cases and controls, rather than being an actual cause.
Bones
Various animal studies have indicated that the intake of saturated fat has a negative effect on effects on the mineral density of bones. One study suggested that men may be particularly vulnerable.Disposition and overall health
Studies have shown that substituting monounsaturated fatty acids for saturated ones is associated with increased daily physical activity and resting energy expenditure. More physical activity, less anger, and less irritability were associated with a higher-oleic acid diet than one of apalmitic acid
Palmitic acid (hexadecanoic acid in IUPAC nomenclature) is a fatty acid with a 16-carbon chain. It is the most common saturated fatty acid found in animals, plants and microorganisms.Gunstone, F. D., John L. Harwood, and Albert J. Dijkstra. The ...
diet.
Monounsaturated vs. polyunsaturated fat
sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is the non-volatile oil pressed from the seeds of the sunflower (''Helianthus annuus''). Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient.
Sunflower oil is primarily composed ...
contains at least 70% monounsaturated fat. Canola oil
Close-up of canola blooms
Canola flower
Rapeseed oil is one of the oldest known vegetable oils. There are both edible and industrial forms produced from rapeseed, the seed of several cultivars of the plant family Brassicaceae. Historical ...
and cashew
The cashew tree (''Anacardium occidentale'') is a tropical evergreen tree native to South America in the genus '' Anacardium'' that produces the cashew seed and the cashew apple accessory fruit. The tree can grow as tall as , but the dwarf c ...
s are both about 58% monounsaturated fat. Tallow
Tallow is a rendered form of beef or mutton fat, primarily made up of triglycerides.
In industry, tallow is not strictly defined as beef or mutton fat. In this context, tallow is animal fat that conforms to certain technical criteria, inclu ...
(beef fat) is about 50% monounsaturated fat. and lard
Lard is a semi-solid white fat product obtained by rendering the fatty tissue of a pig.Lard
entry in the ...
is about 40% monounsaturated fat. Other sources include entry in the ...
hazelnut
The hazelnut is the fruit of the hazel tree and therefore includes any of the nuts deriving from species of the genus '' Corylus'', especially the nuts of the species '' Corylus avellana''. They are also known as cobnuts or filberts accordi ...
, avocado oil, macadamia nut oil, grapeseed oil, groundnut oil ( peanut oil), sesame oil
Sesame oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from sesame seeds. The oil is one of the earliest-known crop-based oils. Worldwide mass modern production is limited due to the inefficient manual harvesting process required to extract the oil. O ...
, corn oil, popcorn
Popcorn (also called popped corn, popcorns or pop-corn) is a variety of corn kernel which expands and puffs up when heated; the same names also refer to the foodstuff produced by the expansion.
A popcorn kernel's strong hull contains the se ...
, whole grain wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeolog ...
, cereal
A cereal is any grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, germ, and bran. Cereal grain crops are grown in greater quantities and provide more foo ...
, oatmeal
Oatmeal is a preparation of oats that have been de-husked, steamed, and flattened, or a coarse flour of hulled oat grains ( groats) that have either been milled (ground) or steel-cut. Ground oats are also called white oats. Steel-cut oats ...
, almond oil, sunflower oil
Sunflower oil is the non-volatile oil pressed from the seeds of the sunflower (''Helianthus annuus''). Sunflower oil is commonly used in food as a frying oil, and in cosmetic formulations as an emollient.
Sunflower oil is primarily composed ...
, hemp oil, and tea-oil camellia.
Polyunsaturated fatty acids can be found mostly in nuts, seeds, fish, seed oils, and oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not a ...
s.
Food sources of polyunsaturated fats include:
Insulin resistance and sensitivity
MUFAs (especially oleic acid) have been found to lower the incidence ofinsulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood suga ...
; PUFAs (especially large amounts of arachidonic acid) and SFAs (such as arachidic acid) increased it. These ratios can be indexed in the phospholipid
Phospholipids, are a class of lipids whose molecule has a hydrophilic "head" containing a phosphate group and two hydrophobic "tails" derived from fatty acids, joined by an alcohol residue (usually a glycerol molecule). Marine phospholipids ty ...
s of human skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m ...
and in other tissues as well. This relationship between dietary fats and insulin resistance is presumed secondary to the relationship between insulin resistance and inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving im ...
, which is partially modulated by dietary fat ratios (Omega-3
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their che ...
/ 6/ 9) with both omega 3 and 9 thought to be anti-inflammatory, and omega 6 pro-inflammatory (as well as by numerous other dietary components, particularly polyphenols
Polyphenols () are a large family of naturally occurring organic compounds characterized by multiples of phenol units. They are abundant in plants and structurally diverse. Polyphenols include flavonoids, tannic acid, and ellagitannin, some o ...
and exercise, with both of these anti-inflammatory). Although both pro- and anti-inflammatory types of fat are biologically necessary, fat dietary ratios in most US diets are skewed towards Omega 6, with subsequent disinhibition of inflammation and potentiation of insulin resistance. This is contrary to the suggestion of more recent studies, in which polyunsaturated fats are shown to be protective against insulin resistance.
The large scale KANWU study found that increasing MUFA and decreasing SFA intake could improve insulin sensitivity, but only when the overall fat intake of the diet was low. However, some MUFAs may promote insulin resistance
Insulin resistance (IR) is a pathological condition in which cells fail to respond normally to the hormone insulin.
Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the transport of glucose from blood into cells, thereby reducing blood glucose (blood suga ...
(like the SFAs), whereas PUFAs may protect against it.
Cancer
Levels of oleic acid along with other MUFAs in red blood cell membranes were positively associated with breast cancer risk. The saturation index (SI) of the same membranes was inversely associated with breast cancer risk. MUFAs and low SI in erythrocyte membranes are predictors of postmenopausal breast cancer. Both of these variables depend on the activity of the enzyme delta-9 desaturase (Δ9-d). Results from observational clinical trials on PUFA intake and cancer have been inconsistent and vary by numerous factors of cancer incidence, including gender and genetic risk. Some studies have shown associations between higher intakes and/or blood levels of omega-3 PUFAs and a decreased risk of certain cancers, including breast and colorectal cancer, while other studies found no associations with cancer risk.Pregnancy disorders
Polyunsaturated fat supplementation was found to have no effect on the incidence of pregnancy-related disorders, such as hypertension or preeclampsia, but may increase the length ofgestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during preg ...
slightly and decreased the incidence of early premature births.
Expert panels in the United States and Europe recommend that pregnant and lactating women consume higher amounts of polyunsaturated fats than the general population to enhance the DHA status of the fetus and newborn.
"Cis fat" vs. "trans fat"
In nature, unsaturated fatty acids generally have double bonds in ''cis'' configuration (with the adjacent C–C bonds on the same side) as opposed to ''trans''. Nevertheless, ''trans'' fatty acids (TFAs) occur in small amounts in meat and milk ofruminant
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. Th ...
s (such as cattle and sheep), typically 2–5% of total fat. Natural TFAs, which include conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and vaccenic acid, originate in the rumen
The rumen, also known as a paunch, is the largest stomach compartment in ruminants and the larger part of the reticulorumen, which is the first chamber in the alimentary canal of ruminant animals. The rumen's microbial favoring environment allow ...
of these animals. CLA has two double bonds, one in the ''cis'' configuration and one in ''trans'', which makes it simultaneously a ''cis''- and a ''trans''-fatty acid.

 Concerns about ''trans'' fatty acids in human diet were raised when they were found to be an unintentional byproduct of the partial hydrogenation of vegetable and fish oils. While these ''trans'' fatty acids (popularly called "trans fats") are edible, they have been implicated in many health problems.
Concerns about ''trans'' fatty acids in human diet were raised when they were found to be an unintentional byproduct of the partial hydrogenation of vegetable and fish oils. While these ''trans'' fatty acids (popularly called "trans fats") are edible, they have been implicated in many health problems.
 The hydrogenation process, invented and patented by Wilhelm Normann in 1902, made it possible to turn relatively cheap liquid fats such as
The hydrogenation process, invented and patented by Wilhelm Normann in 1902, made it possible to turn relatively cheap liquid fats such as whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
or fish oil into more solid fats and to extend their shelf-life by preventing rancidification. (The source fat and the process were initially kept secret to avoid consumer distaste.) This process was widely adopted by the food industry in the early 1900s; first for the production of margarine
Margarine (, also , ) is a spread used for flavoring, baking, and cooking. It is most often used as a substitute for butter. Although originally made from animal fats, most margarine consumed today is made from vegetable oil. The spread was orig ...
, a replacement for butter and shortening, and eventually for various other fats used in snack food, packaged baked goods, and deep fried products.
Full hydrogenation of a fat or oil produces a fully saturated fat. However, hydrogenation generally was interrupted before completion, to yield a fat product with specific melting point, hardness, and other properties. Partial hydrogenation turns some of the ''cis'' double bonds into ''trans'' bonds by an isomerization reaction
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomeriz ...
. The trans configuration is favored because it is the lower energy form.
This side reaction accounts for most of the ''trans'' fatty acids consumed today, by far. An analysis of some industrialized foods in 2006 found up to 30% "trans fats" in artificial shortening, 10% in breads and cake products, 8% in cookies and crackers, 4% in salty snacks, 7% in cake frostings and sweets, and 26% in margarine and other processed spreads. Another 2010 analysis however found only 0.2% of trans fats in margarine and other processed spreads. Up to 45% of the total fat in those foods containing man-made ''trans'' fats formed by partially hydrogenating plant fats may be ''trans'' fat. Baking shortenings, unless reformulated, contain around 30% ''trans'' fats compared to their total fats. High-fat dairy products such as butter contain about 4%. Margarines not reformulated to reduce ''trans'' fats may contain up to 15% ''trans'' fat by weight, but some reformulated ones are less than 1% trans fat.
High levels of TFAs have been recorded in popular "fast food" meals. An analysis of samples of McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation is an American multinational fast food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold ...
French fries collected in 2004 and 2005 found that fries served in New York City contained twice as much trans fat as in Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croa ...
, and 28 times as much as in Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establishe ...
, where trans fats are restricted. For Kentucky Fried Chicken products, the pattern was reversed: the Hungarian product containing twice the trans fat of the New York product. Even within the United States, there was variation, with fries in New York containing 30% more trans fat than those from Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,71 ...
.
Cardiovascular disease
Numerous studies have found that consumption of TFAs increases risk of cardiovascular disease. TheHarvard School of Public Health
The Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health is the public health school of Harvard University, located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. The school grew out of the Harvard- MIT School for Health Officers, the nation's firs ...
advises that replacing TFAs and saturated fats with ''cis'' monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats is beneficial for health.
Consuming trans fats has been shown to increase the risk of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up o ...
in part by raising levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL, often termed "bad cholesterol"), lowering levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL, often termed "good cholesterol"), increasing triglycerides in the bloodstream and promoting systemic inflammation.
The primary health risk identified for trans fat consumption is an elevated risk of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), ischemic heart disease (IHD), myocardial ischemia, or simply heart disease, involves Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the myocardium, heart muscle due to build-up o ...
(CAD). A 1994 study estimated that over 30,000 cardiac deaths per year in the United States are attributable to the consumption of trans fats. By 2006 upper estimates of 100,000 deaths were suggested. A comprehensive review of studies of trans fats published in 2006 in the New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one.
His ...
reports a strong and reliable connection between trans fat consumption and CAD, concluding that "On a per-calorie basis, trans fats appear to increase the risk of CAD more than any other macronutrient, conferring a substantially increased risk at low levels of consumption (1 to 3% of total energy intake)".
The major evidence for the effect of trans fat on CAD comes from the Nurses' Health Study – a cohort study
A cohort study is a particular form of longitudinal study that samples a cohort (a group of people who share a defining characteristic, typically those who experienced a common event in a selected period, such as birth or graduation), performing ...
that has been following 120,000 female nurses since its inception in 1976. In this study, Hu and colleagues analyzed data from 900 coronary events from the study's population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using ...
during 14 years of followup. He determined that a nurse's CAD risk roughly doubled (relative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association b ...
of 1.93, CI: 1.43 to 2.61) for each 2% increase in trans fat calories consumed (instead of carbohydrate calories). By contrast, for each 5% increase in saturated fat calories (instead of carbohydrate calories) there was a 17% increase in risk (relative risk
The relative risk (RR) or risk ratio is the ratio of the probability of an outcome in an exposed group to the probability of an outcome in an unexposed group. Together with risk difference and odds ratio, relative risk measures the association b ...
of 1.17, CI: 0.97 to 1.41). "The replacement of saturated fat or trans unsaturated fat by cis (unhydrogenated) unsaturated fats was associated with larger reductions in risk than an isocaloric replacement by carbohydrates." Hu also reports on the benefits of reducing trans fat consumption. Replacing 2% of food energy
Food energy is chemical energy that animals (including humans) derive from their food to sustain their metabolism, including their muscular activity.
Most animals derive most of their energy from aerobic respiration, namely combining the carbohy ...
from trans fat with non-trans unsaturated fat
An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double b ...
s more than halves the risk of CAD (53%). By comparison, replacing a larger 5% of food energy from saturated fat with non-trans unsaturated fats reduces the risk of CAD by 43%.
Another study considered deaths due to CAD, with consumption of trans fats being linked to an increase in mortality, and consumption of polyunsaturated fats being linked to a decrease in mortality.
Trans fat has been found to act like saturated in raising the blood level of LDL ("bad cholesterol"); but, unlike saturated fat, it also decreases levels of HDL ("good cholesterol"). The net increase in LDL/HDL ratio with trans fat, a widely accepted indicator of risk for coronary artery disease, is approximately double that due to saturated fat. One randomized crossover study
In medicine, a crossover study or crossover trial is a longitudinal study in which subjects receive a sequence of different treatments (or exposures). While crossover studies can be observational studies, many important crossover studies are co ...
published in 2003 comparing the effect of eating a meal on blood lipids of (relatively) cis and trans-fat-rich meals showed that cholesteryl ester transfer (CET) was 28% higher after the trans meal than after the cis meal and that lipoprotein concentrations were enriched in apolipoprotein
Apolipoproteins are proteins that bind lipids (oil-soluble substances such as fats, cholesterol and fat soluble vitamins) to form lipoproteins. They transport lipids in blood, cerebrospinal fluid and lymph.
The lipid components of lipoprote ...
(a) after the trans meals.
The citokyne test is a potentially more reliable indicator of CAD risk, although is still being studied. A study of over 700 nurses showed that those in the highest quartile
In statistics, a quartile is a type of quantile which divides the number of data points into four parts, or ''quarters'', of more-or-less equal size. The data must be ordered from smallest to largest to compute quartiles; as such, quartiles are ...
of trans fat consumption had blood levels of C-reactive protein
C-reactive protein (CRP) is an annular (ring-shaped) pentameric protein found in blood plasma, whose circulating concentrations rise in response to inflammation. It is an acute-phase protein of hepatic origin that increases following interleukin ...
(CRP) that were 73% higher than those in the lowest quartile.
Breast feeding
It has been established that ''trans'' fats in humanbreast milk
Breast milk (sometimes spelled as breastmilk) or mother's milk is milk produced by mammary glands located in the breast of a human female. Breast milk is the primary source of nutrition for newborns, containing fat, protein, carbohydrates (lac ...
fluctuate with maternal consumption of trans fat, and that the amount of trans fats in the bloodstream of breastfed infants fluctuates with the amounts found in their milk. In 1999, reported percentages of trans fats (compared to total fats) in human milk ranged from 1% in Spain, 2% in France, 4% in Germany, and 7% in Canada and the United States.
Other health risks
There are suggestions that the negative consequences of trans fat consumption go beyond the cardiovascular risk. In general, there is much less scientific consensus asserting that eating trans fat specifically increases the risk of other chronic health problems: * Alzheimer's disease: A study published in Archives of Neurology in February 2003 suggested that the intake of both trans fats and saturated fats promotes the development of Alzheimer disease, although not confirmed in an animal model. It has been found that trans fats impaired memory and learning in middle-age rats. The brains of rats that ate trans-fats had fewer proteins critical to healthy neurological function. Inflammation in and around the hippocampus, the part of the brain responsible for learning and memory. These are the exact types of changes normally seen at the onset of Alzheimer's, but seen after six weeks, even though the rats were still young. *Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bl ...
: There is no scientific consensus that consuming trans fats significantly increases cancer risks across the board. The American Cancer Society states that a relationship between trans fats and cancer "has not been determined." One study has found a positive connection between trans fat and prostate cancer. However, a larger study found a correlation between trans fats and a significant decrease in high-grade prostate cancer. An increased intake of trans fatty acids may raise the risk of breast cancer by 75%, suggest the results from the French part of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition.
* Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased ...
: There is a growing concern that the risk of type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes, formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urinati ...
increases with trans fat consumption. However, consensus has not been reached. For example, one study found that risk is higher for those in the highest quartile
In statistics, a quartile is a type of quantile which divides the number of data points into four parts, or ''quarters'', of more-or-less equal size. The data must be ordered from smallest to largest to compute quartiles; as such, quartiles are ...
of trans fat consumption. Another study has found no diabetes risk once other factors such as total fat intake and BMI were accounted for.
* Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
: Research indicates that trans fat may increase weight gain and abdominal fat, despite a similar caloric intake. A 6-year experiment revealed that monkeys fed a trans fat diet gained 7.2% of their body weight, as compared to 1.8% for monkeys on a mono-unsaturated fat diet. Although obesity is frequently linked to trans fat in the popular media, this is generally in the context of eating too many calories; there is not a strong scientific consensus connecting trans fat and obesity, although the 6-year experiment did find such a link, concluding that "under controlled feeding conditions, long-term TFA consumption was an independent factor in weight gain. TFAs enhanced intra-abdominal deposition of fat, even in the absence of caloric excess, and were associated with insulin resistance, with evidence that there is impaired post-insulin receptor binding signal transduction."
* Infertility in women: One 2007 study found, "Each 2% increase in the intake of energy from trans unsaturated fats, as opposed to that from carbohydrates, was associated with a 73% greater risk of ovulatory infertility...".
* Major depressive disorder
Major depressive disorder (MDD), also known as clinical depression, is a mental disorder characterized by at least two weeks of pervasive low mood, low self-esteem, and loss of interest or pleasure in normally enjoyable activities. Introdu ...
: Spanish researchers analysed the diets of 12,059 people over six years and found that those who ate the most trans fats had a 48 per cent higher risk of depression than those who did not eat trans fats. One mechanism may be trans-fats' substitution for docosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. In physiological literature, it is given the name 22:6(n-3). It can be synthesized from alpha-li ...
(DHA) levels in the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC). Very high intake of trans-fatty acids (43% of total fat) in mice from 2 to 16 months of age was associated with lowered DHA levels in the brain (p=0.001). When the brains of 15 major depressive subjects who had committed suicide were examined post-mortem and compared against 27 age-matched controls, the suicidal brains were found to have 16% less (male average) to 32% less (female average) DHA in the OFC. The OFC controls reward, reward expectation, and empathy
Empathy is the capacity to understand or feel what another person is experiencing from within their frame of reference, that is, the capacity to place oneself in another's position. Definitions of empathy encompass a broad range of social, cog ...
(all of which are reduced in depressive mood disorders) and regulates the limbic system
The limbic system, also known as the paleomammalian cortex, is a set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, immediately beneath the medial temporal lobe of the cerebrum primarily in the forebrain.Schacter, Daniel L. 2012. ' ...
.
* Behavioral irritability
Irritability (also called as crankiness) is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excess ...
and aggression
Aggression is overt or covert, often harmful, social interaction with the intention of inflicting damage or other harm upon another individual; although it can be channeled into creative and practical outlets for some. It may occur either reacti ...
: a 2012 observational analysis of subjects of an earlier study found a strong relation between dietary trans fat acids and self-reported behavioral aggression and irritability, suggesting but not establishing causality.
* Diminished memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
: In a 2015 article, researchers re-analyzing results from the 1999-2005 UCSD Statin Study argue that "greater dietary trans fatty acid consumption is linked to worse word memory in adults during years of high productivity, adults age <45".
* Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and ...
: According to a 2015 study, trans fats are one of several components of Western pattern diets which promote acne, along with carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ...
s with high glycemic load
The glycemic load (GL) of food is a number that estimates how much the food will raise a person's blood glucose level after eating it. One unit of glycemic load approximates the effect of eating one gram of glucose. Glycemic load accounts for how ...
such as refined sugars or refined starches, milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulati ...
and dairy products, and saturated fat
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone and fatty acids that each contain a long linear or branched ...
s, while omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their che ...
s, which reduce acne, are deficient in Western pattern diets.
Biochemical mechanisms
The exact biochemical process by which trans fats produce specific health problems are a topic of continuing research. Intake of dietary trans fat perturbs the body's ability to metabolizeessential fatty acid
Essential fatty acids, or EFAs, are fatty acids that humans and other animals must ingest because the body requires them for good health but cannot synthesize them.
Only two fatty acids are known to be essential for humans: alpha-linolenic a ...
s (EFAs, including Omega-3
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their che ...
) leading to changes in the phospholipid fatty acid composition of the arterial walls, thereby raising risk of coronary artery disease.
Trans double bonds are claimed to induce a linear conformation to the molecule, favoring its rigid packing as in plaque formation. The geometry of the ''cis'' double bond, in contrast, is claimed to create a bend in the molecule, thereby precluding rigid formations..
While the mechanisms through which trans fatty acids contribute to coronary artery disease are fairly well understood, the mechanism for their effects on diabetes is still under investigation. They may impair the metabolism of long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (LCPUFAs). However, maternal pregnancy trans fatty acid intake has been inversely associated with LCPUFAs levels in infants at birth thought to underlie the positive association between breastfeeding and intelligence.
Trans fats are processed by the liver
The liver is a major organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it ...
differently than other fats. They may cause liver dysfunction by interfering with delta 6 desaturase, an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecule ...
involved in converting essential fatty acids to arachidonic acid and prostaglandin
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are der ...
s, both of which are important to the functioning of cells.
Natural "trans fats" in dairy products
Some ''trans'' fatty acids occur in natural fats and traditionally processed foods. Vaccenic acid occurs in breast milk, and someisomers
In chemistry, isomers are molecules or polyatomic ions with identical molecular formulae – that is, same number of atoms of each element – but distinct arrangements of atoms in space. Isomerism is existence or possibility of isomers.
...
of conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) are found in meat and dairy products from ruminant
Ruminants ( suborder Ruminantia) are hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally through microbial actions. Th ...
s. Butter, for example, contains about 3% trans fat.
The U.S. National Dairy Council has asserted that the trans fats present in animal foods are of a different type than those in partially hydrogenated oils, and do not appear to exhibit the same negative effects. While a recent scientific review agrees with the conclusion (stating that "the sum of the current evidence suggests that the Public health implications of consuming trans fats from ruminant products are relatively limited"), it cautions that this may be due to the low consumption of trans fats from animal sources compared to artificial ones.
More recent inquiry (independent of the dairy industry) has found in a 2008 Dutch meta-analysis that all trans fats, regardless of natural or artificial origin equally raise LDL and lower HDL levels. Other studies though have shown different results when it comes to animal-based trans fats like conjugated linoleic acid (CLA). Although CLA is known for its anticancer properties, researchers have also found that the cis-9, trans-11 form of CLA can reduce the risk for cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
and help fight inflammation.
Two Canadian studies have shown that vaccenic acid, a TFA that naturally occurs in dairy products, could be beneficial compared to hydrogenated vegetable shortening
Shortening is any fat that is a solid at room temperature and used to make crumbly pastry and other food products. Although butter is solid at room temperature and is frequently used in making pastry, the term ''shortening'' seldom refers to ...
, or a mixture of pork lard and soy fat, by lowering total LDL and triglyceride levels. A study by the US Department of Agriculture showed that vaccenic acid raises both HDL and LDL cholesterol, whereas industrial trans fats only raise LDL with no beneficial effect on HDL.
Official recommendations
In light of recognized evidence and scientific agreement, nutritional authorities consider all trans fats equally harmful for health and recommend that their consumption be reduced to trace amounts. In 2003, the WHO recommended that trans fats make up no more than 0.9% of a person's diet and, in 2018, introduced a 6-step guide to eliminate industrially-produced trans-fatty acids from the global food supply. TheNational Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the Nat ...
(NAS) advises the U.S. and Canadian governments on nutritional science for use in public policy and product labeling programs. Their 2002 ''Dietary Reference Intakes for Energy, Carbohydrate, Fiber, Fat, Fatty Acids, Cholesterol, Protein, and Amino Acids'' contains their findings and recommendations regarding consumption of trans fat.
Their recommendations are based on two key facts. First, "trans fatty acids are not essential and provide no known benefit to human health", whether of animal or plant origin. Second, given their documented effects on the LDL/HDL ratio, the NAS concluded "that dietary trans fatty acids are more deleterious with respect to coronary artery disease than saturated fatty acids". A 2006 review published in the New England Journal of Medicine
''The New England Journal of Medicine'' (''NEJM'') is a weekly medical journal published by the Massachusetts Medical Society. It is among the most prestigious peer-reviewed medical journals as well as the oldest continuously published one.
His ...
(NEJM) that states "from a nutritional standpoint, the consumption of trans fatty acids results in considerable potential harm but no apparent benefit."
Because of these facts and concerns, the NAS has concluded there is no safe level of trans fat consumption. There is no adequate level, recommended daily amount or tolerable upper limit for trans fats. This is because any incremental increase in trans fat intake increases the risk of coronary artery disease.
Despite this concern, the NAS dietary recommendations have not included eliminating trans fat from the diet. This is because trans fat is naturally present in many animal foods in trace quantities, and thus its removal from ordinary diets might introduce undesirable side effects and nutritional imbalances. The NAS has, thus, "recommended that trans fatty acid consumption be as low as possible while consuming a nutritionally adequate diet". Like the NAS, the WHO has tried to balance public health goals with a practical level of trans fat consumption, recommending in 2003 that trans fats be limited to less than 1% of overall energy intake.
Regulatory action
In the last few decades, there has been substantial amount ofregulation
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology
Biology is the scientific study of life. It is a natural science with a ...
in many countries, limiting trans fat contents of industrialized and commercial food products.
Alternatives to hydrogenation
In recent years, the negative public image and strict regulations have driven many fat processing industries to replace partial hydrogenation by fat interesterification, a process that chemically scrambles the fatty acids among a mix of triglycerides. When applied to a suitable bend of oils and saturated fats, possibly followed by separation of unwanted solid or liquid triglycerides, this process can achieve results similar to those of partial hydrogenation without affecting the fatty acids themselves; in particular, without creating any new "trans fat". Researchers at theU.S. Department of Agriculture
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of com ...
have investigated whether hydrogenation can be achieved without the side effect of trans fat production. They varied the pressure
Pressure (symbol: ''p'' or ''P'') is the force applied perpendicular to the surface of an object per unit area over which that force is distributed. Gauge pressure (also spelled ''gage'' pressure)The preferred spelling varies by country a ...
under which the chemical reaction was conducted – applying 1400 kPa (200 psi) of pressure to soybean oil in a 2-liter vessel while heating it to between 140 °C and 170 °C. The standard 140 kPa (20 psi) process of hydrogenation produces a product of about 40% trans fatty acid by weight, compared to about 17% using the high-pressure method. Blended with unhydrogenated liquid soybean oil, the high-pressure-processed oil produced margarine containing 5 to 6% trans fat. Based on current U.S. labeling requirements (see below), the manufacturer could claim the product was free of trans fat. The level of trans fat may also be altered by modification of the temperature and the length of time during hydrogenation.
A University of Guelph
, mottoeng = "to learn the reasons of realities"
, established = May 8, 1964 ()As constituents: OAC: (1874) Macdonald Institute: (1903) OVC: (1922)
, type = Public university
, chancellor ...
research group has found a way to mix oils (such as olive, soybean, and canola), water, monoglyceride
Monoglycerides (also: acylglycerols or monoacylglycerols) are a class of glycerides which are composed of a molecule of glycerol linked to a fatty acid via an ester bond. As glycerol contains both primary and secondary alcohol groups two differe ...
s, and fatty acids to form a "cooking fat" that acts the same way as trans and saturated fats.
Omega-three and omega-six fatty acids
The ω−3 fatty acids have received substantial attention in recent years. Among omega-3 fatty acids, neither long-chain nor short-chain forms were consistently associated with breast cancer risk. High levels ofdocosahexaenoic acid
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid that is a primary structural component of the human brain, cerebral cortex, skin, and retina. In physiological literature, it is given the name 22:6(n-3). It can be synthesized from alpha-li ...
(DHA), however, the most abundant omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid in erythrocyte (red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
) membranes, were associated with a reduced risk of breast cancer. The DHA obtained through the consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids is positively associated with cognitive and behavioral performance. In addition, DHA is vital for the grey matter structure of the human brain, as well as retinal stimulation and neurotransmission
Neurotransmission (Latin: ''transmissio'' "passage, crossing" from ''transmittere'' "send, let through") is the process by which signaling molecules called neurotransmitters are released by the axon terminal of a neuron (the presynaptic neuron), ...
.
Interesterification
Some studies have investigated the health effects of insteresterified (IE) fats, by comparing diets with IE and non-IE fats with the same overall fatty acid composition. Several experimental studies in humans found no statistical difference on fasting blood lipids between a diet with large amounts of IE fat, having 25-40% C16:0 or C18:0 on the 2-position, and a similar diet with non-IE fat, having only 3-9% C16:0 or C18:0 on the 2-position. A negative result was obtained also in a study that compared the effects on bloodcholesterol
Cholesterol is any of a class of certain organic molecules called lipids. It is a sterol (or modified steroid), a type of lipid. Cholesterol is biosynthesized by all animal cells and is an essential structural component of animal cell membr ...
levels of an IE fat product mimicking cocoa butter and the real non-IE product.
A 2007 study funded by the Malaysian Palm Oil Board claimed that replacing natural palm oil
Palm oil is an edible vegetable oil derived from the mesocarp (reddish pulp) of the fruit of the oil palms. The oil is used in food manufacturing, in beauty products, and as biofuel. Palm oil accounted for about 33% of global oils produced fr ...
by other interesterified or partially hydrogenated fats caused adverse health effects, such as higher LDL/ HDL ratio and plasma glucose level
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood plas ...
s. However, these effects could be attributed to the higher percentage of saturated acids in the IE and partially hydrogenated fats, rather than to the IE process itself.
Role in disease
In the human body, high levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream have been linked toatherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is a pattern of the disease arteriosclerosis in which the wall of the artery develops abnormalities, called lesions. These lesions may lead to narrowing due to the buildup of atheromatous plaque. At onset there are usually ...
, heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
and stroke. However, the relative negative impact of raised levels of triglycerides compared to that of LDL:HDL ratios is as yet unknown. The risk can be partly accounted for by a strong inverse relationship between triglyceride level and HDL-cholesterol level. But the risk is also due to high triglyceride levels increasing the quantity of small, dense LDL particles.
Guidelines
The National Cholesterol Education Program has set guidelines for triglyceride levels: These levels are tested afterfasting
Fasting is the abstention from eating and sometimes drinking. From a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (see " Breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after co ...
8 to 12 hours. Triglyceride levels remain temporarily higher for a period after eating.
The AHA recommends an optimal triglyceride level of 100mg/dL (1.1mmol/L) or lower to improve heart health.
Reducing triglyceride levels
Weight loss and dietary modification are effective first-line lifestyle modification treatments for hypertriglyceridemia. For people with mildly or moderately high levels of triglycerides, lifestyle changes, including weight loss, moderate exerciseCrawford, H., Micheal. ''Current Diagnosis & Treatment Cardiology''. 3rd ed. McGraw-Hill Medical, 2009. p21 and dietary modification, are recommended. This may include restriction of carbohydrates (specificallyfructose
Fructose, or fruit sugar, is a ketonic simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and galactose, that are absorb ...
) and fat in the diet and the consumption of omega-3 fatty acid
Omega−3 fatty acids, also called Omega-3 oils, ω−3 fatty acids or ''n''−3 fatty acids, are polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) characterized by the presence of a double bond, three atoms away from the terminal methyl group in their che ...
s from algae, nuts, fish and seeds.
Medications are recommended in those with high levels of triglycerides that are not corrected with the aforementioned lifestyle modifications, with fibrates being recommended first.
Omega-3-carboxylic acids is another prescription drug used to treat very high levels of blood triglycerides.
The decision to treat hypertriglyceridemia with medication depends on the levels and on the presence of other risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Very high levels that would increase the risk of pancreatitis are treated with a drug from the fibrate class. Niacin and omega-3 fatty acids as well as drugs from the statin
Statins, also known as HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, are a class of lipid-lowering medications that reduce illness and mortality in those who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. They are the most common cholesterol-lowering drugs.
L ...
class may be used in conjunction, with statins being the main medication for moderate hypertriglyceridemia when reduction of cardiovascular risk is required.
Fat digestion and metabolism
Fats are broken down in the healthy body to release their constituents,glycerol
Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ...
and fatty acid
In chemistry, particularly in biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with an aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have an unbranched chain of an even number of carbon atoms, ...
s. Glycerol itself can be converted to glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, usi ...
by the liver and so become a source of energy. Fats and other lipids are broken down in the body by enzymes called lipase
Lipase ( ) is a family of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually tr ...
s produced in the pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an en ...
.
Many cell types can use either glucose or fatty acids as a source of energy for metabolism. In particular, heart and skeletal muscle prefer fatty acids. Despite long-standing assertions to the contrary, fatty acids can also be used as a source of fuel for brain cells through mitochondrial oxidation.
See also
* Animal fat *Diet and heart disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, hea ...
* Fatty acid synthesis
In biochemistry, fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is ...
* Food composition data Food composition data (FCD) are detailed sets of information on the nutritionally important components of foods and provide values for energy and nutrients including protein, carbohydrates, fat, vitamins and minerals and for other important food com ...
* Western pattern diet
References
{{Authority control Nutrients Macromolecules