Fastest-growing religion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Growth of religion involves the spread of individual
Accessed July 2013. A comprehensive religious forecast for 2050 by the
Library of Congress (2014) Statistical data on conversion to and from Islam are scarce. According to a study published in 2011 by Pew Research, what little information is available may suggest that religious conversion has no net impact on the Muslim population, as the number of people who

People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011
''. Religions & Christianity in Today's China, Vol. II, 2012, No. 3, pp. 29–54, . of which 173 million (13%) practice some form of Taoist-defined folk faith. Further in detail, 12 million people have passed some formal initiation into Taoism, or adhere to the official
 According to a 2011
According to a 2011
link
(saying "Not only do Protestants presently constitute 13 percent of the world's population—about 800 million people—but since 1900 Protestantism has spread rapidly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.") The significant growth of Christianity in non-Western countries led to regional distribution changes of Christians. In 1900, Europe and the Americas were home to the vast majority of the world's Christians (93%). Besides, Christianity has grown enormously in Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. In 2010, 26% of the world's Christians lived in Europe, followed by 24.4% in Latin America and the Caribbean, 23.8% in Sub-Saharan Africa, 13.2% in Asia and the Pacific, 12.3% in North America, and 1% in the Middle East and North Africa. The study also suggested that by 2050, the global Christian population will change considerably. By 2050, 38% of the world's Christians will live in the Sub-Saharan Africa, followed by 23% in Latin America and The
The 
Sreda.org2012 Survey Maps
. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27 August 2012. ''Retrieved 24 September 2012''. According to study by According to the ''
According to the ''
Fler kristna väljer att bli muslimer
'', November 19, 2007 (Accessed November 19, 2007)
United States
 Druze is a major religion in the Levant region. Druzites or Al-Muwaḥḥidūn are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group; the number of Druzites worldwide is between 800,000 and one million, with the vast majority residing in the Levant. Even though the faith originally developed out of Isma'ilism, Ismaili Islam, Druze do not identify as a branch of Islam and view themselves as a separate religion. The Druze faith does not accept converts to their faith, nor practice proselytism. Over the centuries a number of the Druze conversion to Christianity, Druze embraced Christianity, Islam and other religions.
The Druzites reside primarily in Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan. Syria is home to the largest Druzite community in the world, according to a study published by Columbia University, the number of Syrian Druze increased from 684,000 in 2010 to 730,000 in mid of 2018. The Lebanese Druze have the lowest fertility among all age groups after the Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians.
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2017, the Israeli Druze population growth rate of 1.4%, which is lower than the Islam in Israel, Muslim population growth rate (2.5%) and the total population growth (1.7%), but higher than the Arab Christian population growth rate (1.0%). At the end of 2017, the average age of the Israeli Druze was 27.9. About 26.3% of the Israeli Druze population are under 14 years old and about 6.1% of the Israeli Druze are 65 years and over. Since the year 2000, the Israeli Druze community has witnessed a significant decrease in Total fertility rate, fertility-rate and a significant increase in life expectancy. The fertility rate for Israeli Druze in 2017 is 2.1 children per woman, while the fertility rate among Israeli Jews, Jewish women (3.2) and Muslim women (3.4) and the fertility rate among Christianity in Israel, Israeli Christian women (1.9).
Druze is a major religion in the Levant region. Druzites or Al-Muwaḥḥidūn are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group; the number of Druzites worldwide is between 800,000 and one million, with the vast majority residing in the Levant. Even though the faith originally developed out of Isma'ilism, Ismaili Islam, Druze do not identify as a branch of Islam and view themselves as a separate religion. The Druze faith does not accept converts to their faith, nor practice proselytism. Over the centuries a number of the Druze conversion to Christianity, Druze embraced Christianity, Islam and other religions.
The Druzites reside primarily in Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan. Syria is home to the largest Druzite community in the world, according to a study published by Columbia University, the number of Syrian Druze increased from 684,000 in 2010 to 730,000 in mid of 2018. The Lebanese Druze have the lowest fertility among all age groups after the Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians.
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2017, the Israeli Druze population growth rate of 1.4%, which is lower than the Islam in Israel, Muslim population growth rate (2.5%) and the total population growth (1.7%), but higher than the Arab Christian population growth rate (1.0%). At the end of 2017, the average age of the Israeli Druze was 27.9. About 26.3% of the Israeli Druze population are under 14 years old and about 6.1% of the Israeli Druze are 65 years and over. Since the year 2000, the Israeli Druze community has witnessed a significant decrease in Total fertility rate, fertility-rate and a significant increase in life expectancy. The fertility rate for Israeli Druze in 2017 is 2.1 children per woman, while the fertility rate among Israeli Jews, Jewish women (3.2) and Muslim women (3.4) and the fertility rate among Christianity in Israel, Israeli Christian women (1.9).
 According to the
According to the
 According to the same study "globally, Muslims have the highest fertility rate, an average of 3.1 children per woman – well above replacement level (2.1)", and "in all major regions where there is a sizable Muslim population, Muslim fertility exceeds non-Muslim fertility". From 1990 to 2010, the global Muslim population increased at an average annual rate of 2.2%. By 2030 Muslims are projected to represent about 26.4% of the global population (out of a total of 7.9 billion people). According to a 2019 study by the
According to the same study "globally, Muslims have the highest fertility rate, an average of 3.1 children per woman – well above replacement level (2.1)", and "in all major regions where there is a sizable Muslim population, Muslim fertility exceeds non-Muslim fertility". From 1990 to 2010, the global Muslim population increased at an average annual rate of 2.2%. By 2030 Muslims are projected to represent about 26.4% of the global population (out of a total of 7.9 billion people). According to a 2019 study by the
, The Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life, 27 January 2011 People switching their religions will likely have no effect on the growth of the Muslim population, as the number of people who
Europe: Integrating Islam
', Resurgent Islam is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. The Vatican's 2008 yearbook of statistics revealed that for the first time, Islam has outnumbered the Roman Catholics globally. It stated that, "Islam has overtaken Roman Catholicism as the biggest single religious denomination in the world", and stated that, "It is true that while Muslim families, as is well known, continue to make a lot of children, Christian ones on the contrary tend to have fewer and fewer". According to ''Foreign Policy'', high birth rates were cited as the reason for the Muslim population growth. With 3.1 children per woman, Muslims have higher fertility levels than the world's overall population between 2010 and 2015. High fertility is a major driver of projected Muslim population growth around the world and in particular regions. Between 2010 and 2015, with exception of the Middle East and North Africa, Muslim fertility of any other region in the world was higher than the rate for the region as a whole. While Muslim birth rates are expected to experience a decline, it will remain above replacement level and higher fertility than the world's overall by 2050. As per U.N.'s global population forecasts, as well as the
Pew Research projections, over time fertility rates generally converge toward the
replacement level. Globally, Muslims were younger (median age of 23) than the overall population (median age of 28) as of 2010. While decline of Muslim birth rates in coming years have also been well documented. According to David Ignatius, there is major decline in Muslim fertility rates as pointed out by Nicholas Eberstadt. Based on the data from 49 Muslim-majority countries and territories, he found that Muslims' birth rate has significantly dropped for 41% between 1975 and 1980 to 2005–10 while the global population decline was 33% during that period. It also stated that over a 50% decline was found in 22 Muslim countries and over a 60% decline in Iran, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Bangladesh, Tunisia, Libya, Albania, Qatar and Kuwait.
Resurgent Islam is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. The Vatican's 2008 yearbook of statistics revealed that for the first time, Islam has outnumbered the Roman Catholics globally. It stated that, "Islam has overtaken Roman Catholicism as the biggest single religious denomination in the world", and stated that, "It is true that while Muslim families, as is well known, continue to make a lot of children, Christian ones on the contrary tend to have fewer and fewer". According to ''Foreign Policy'', high birth rates were cited as the reason for the Muslim population growth. With 3.1 children per woman, Muslims have higher fertility levels than the world's overall population between 2010 and 2015. High fertility is a major driver of projected Muslim population growth around the world and in particular regions. Between 2010 and 2015, with exception of the Middle East and North Africa, Muslim fertility of any other region in the world was higher than the rate for the region as a whole. While Muslim birth rates are expected to experience a decline, it will remain above replacement level and higher fertility than the world's overall by 2050. As per U.N.'s global population forecasts, as well as the
Pew Research projections, over time fertility rates generally converge toward the
replacement level. Globally, Muslims were younger (median age of 23) than the overall population (median age of 28) as of 2010. While decline of Muslim birth rates in coming years have also been well documented. According to David Ignatius, there is major decline in Muslim fertility rates as pointed out by Nicholas Eberstadt. Based on the data from 49 Muslim-majority countries and territories, he found that Muslims' birth rate has significantly dropped for 41% between 1975 and 1980 to 2005–10 while the global population decline was 33% during that period. It also stated that over a 50% decline was found in 22 Muslim countries and over a 60% decline in Iran, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Bangladesh, Tunisia, Libya, Albania, Qatar and Kuwait.
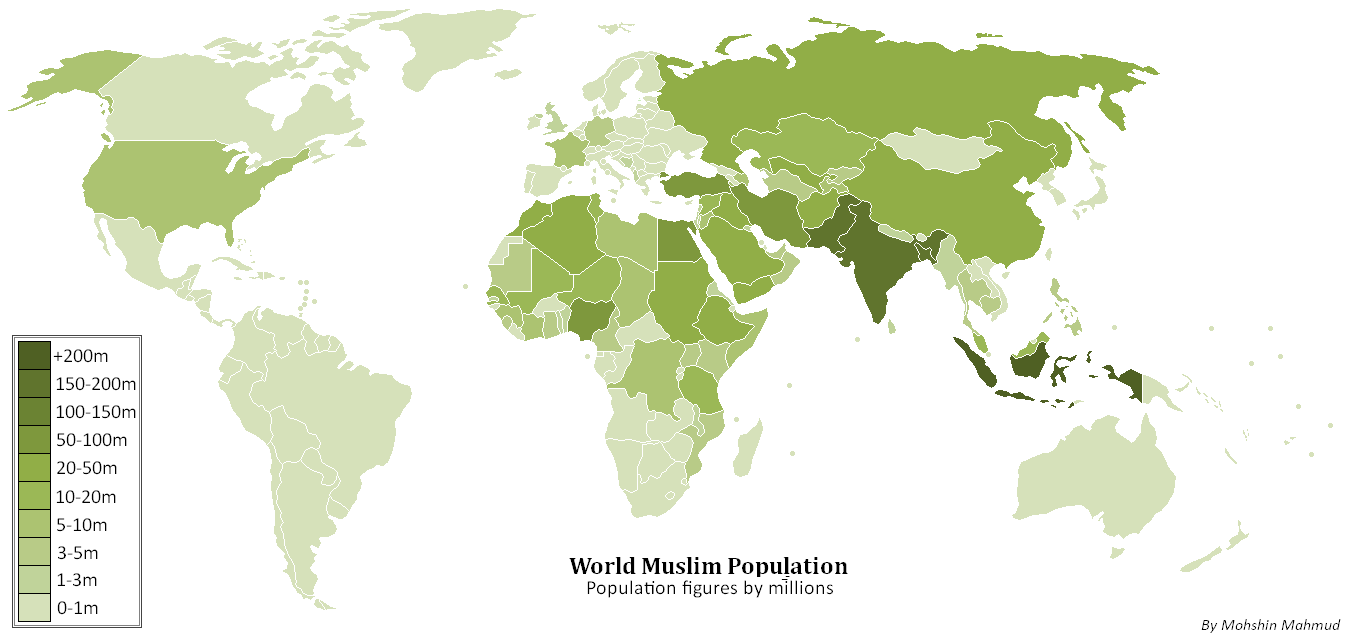 According to the religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, between 2010 and 2050 modest net gains through religious conversion are expected for Muslims (3 million) and most of the net gains through religious conversion for Muslims found in Sub Saharan Africa (2.9 million). The study also reveals that, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate among Muslims by 2050 there will be near parity between Muslims (2.8 billion, or 30% of the population) and Christians (2.9 billion, or 31%), possibly for the first time in history. While both religions will grow but Muslim population will exceed the Christian population and by 2100, Muslim population (35%) will be 1% more than the Christian population (34%). By the end of 2100 Muslims are expected to outnumber Christians. According to the same study, Muslims population growth is twice of world's overall population growth due to young age and relatively high fertility rate and as a result Muslims are projected to rise to 30% (2050) of the world's population from 23% (2010).
While the total Fertility Rate of Muslims in North America is 2.7 children per woman in the 2010 to 2015 period, well above the regional average (2.0) and the replacement level (2.1). Europe's Muslim population also has higher fertility (2.1) than other religious groups in the region, well above the regional average (1.6). A new study of Population Reference Bureau by demographers Charles Westoff and Tomas Frejka suggests that the fertility gap between Muslims and non-Muslims is shrinking and although the Muslim immigrants do have more children than other Europeans their fertility tends to decline over time, often faster than among non-Muslims.
Generally, there are few reports about how many people leave Islam in Muslim majority countries. The main reason for this is the social and legal repercussions associated with Apostasy in Islam, leaving Islam in many Muslim majority countries, up to and including the death penalty for apostasy. On the other hand, the increasingly large Ex-Muslim, ex-Muslim communities in the Western world that adhere to no religion have been well documented. A 2007 Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) report argued that some Muslim population projections are overestimated, as they assume that all descendants of Muslims will become Muslims even in cases of mixed parenthood. Equally, Darren E. Sherkat questioned in ''Foreign Affairs'' whether some of the Muslim growth projections are accurate as they do not take into account the increasing number of non-religious Muslims. Quantitative research is lacking, but he believes the European trend mirrors the American: data from the General Social Survey in the United States show that 32 percent of those raised Muslim no longer embrace Islam in adulthood, and 18 percent hold no religious identification. Many Muslims who leave Islam face social rejection or imprisonment and sometimes murder or other penalties. According to
According to the religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, between 2010 and 2050 modest net gains through religious conversion are expected for Muslims (3 million) and most of the net gains through religious conversion for Muslims found in Sub Saharan Africa (2.9 million). The study also reveals that, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate among Muslims by 2050 there will be near parity between Muslims (2.8 billion, or 30% of the population) and Christians (2.9 billion, or 31%), possibly for the first time in history. While both religions will grow but Muslim population will exceed the Christian population and by 2100, Muslim population (35%) will be 1% more than the Christian population (34%). By the end of 2100 Muslims are expected to outnumber Christians. According to the same study, Muslims population growth is twice of world's overall population growth due to young age and relatively high fertility rate and as a result Muslims are projected to rise to 30% (2050) of the world's population from 23% (2010).
While the total Fertility Rate of Muslims in North America is 2.7 children per woman in the 2010 to 2015 period, well above the regional average (2.0) and the replacement level (2.1). Europe's Muslim population also has higher fertility (2.1) than other religious groups in the region, well above the regional average (1.6). A new study of Population Reference Bureau by demographers Charles Westoff and Tomas Frejka suggests that the fertility gap between Muslims and non-Muslims is shrinking and although the Muslim immigrants do have more children than other Europeans their fertility tends to decline over time, often faster than among non-Muslims.
Generally, there are few reports about how many people leave Islam in Muslim majority countries. The main reason for this is the social and legal repercussions associated with Apostasy in Islam, leaving Islam in many Muslim majority countries, up to and including the death penalty for apostasy. On the other hand, the increasingly large Ex-Muslim, ex-Muslim communities in the Western world that adhere to no religion have been well documented. A 2007 Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) report argued that some Muslim population projections are overestimated, as they assume that all descendants of Muslims will become Muslims even in cases of mixed parenthood. Equally, Darren E. Sherkat questioned in ''Foreign Affairs'' whether some of the Muslim growth projections are accurate as they do not take into account the increasing number of non-religious Muslims. Quantitative research is lacking, but he believes the European trend mirrors the American: data from the General Social Survey in the United States show that 32 percent of those raised Muslim no longer embrace Islam in adulthood, and 18 percent hold no religious identification. Many Muslims who leave Islam face social rejection or imprisonment and sometimes murder or other penalties. According to
,
. Retrieved 18 September 2012. Eric Kaufman of In 2010 Islam in Asia, Asia was home for (62%) of the world's Muslims, and about (20%) of the world's Muslims lived in the Middle East and North Africa, (16%) in Sub Saharan Africa, and 2% in Europe. By 2050 Asia will be home to (52.8%) of the world's Muslims, and about (24.3%) of the world's Muslims will live in Sub Saharan Africa, (20%) the Middle East and North Africa, and 2% in Europe. As per the Pew Research study, Muslim populations will grow in absolute number in all regions of the world between 2010 and 2050. The Muslim population in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to reach nearly 1.5 billion by 2050, up from roughly 1 billion in 2010. The growth of Muslims is also expected in the Middle East-North Africa region, It is projected to increase from about 300 million in 2010 to more than 550 million in 2050. Besides, the Islam in Africa, Muslim population in sub-Saharan Africa is forecast to grow from about 250 million in 2010 to nearly 670 million in 2050 which is more than double. The absolute number of Muslims is also expected to increase in regions with smaller Muslim populations such as Europe and North America, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate. In Europe Muslim population will be nearly double (from 5.9% to 10.2%). In Islam in the Americas, North America, it will grow 1% to 2%. In Asia Pacific region, Muslims will surpass the Hindus by the time. In Latin America and Caribbean Muslim population will stay 0.1% by 2050.
In 2010 Indonesia, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nigeria was home for (47.8%) of the world's Muslims.
In 2010 Islam in Asia, Asia was home for (62%) of the world's Muslims, and about (20%) of the world's Muslims lived in the Middle East and North Africa, (16%) in Sub Saharan Africa, and 2% in Europe. By 2050 Asia will be home to (52.8%) of the world's Muslims, and about (24.3%) of the world's Muslims will live in Sub Saharan Africa, (20%) the Middle East and North Africa, and 2% in Europe. As per the Pew Research study, Muslim populations will grow in absolute number in all regions of the world between 2010 and 2050. The Muslim population in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to reach nearly 1.5 billion by 2050, up from roughly 1 billion in 2010. The growth of Muslims is also expected in the Middle East-North Africa region, It is projected to increase from about 300 million in 2010 to more than 550 million in 2050. Besides, the Islam in Africa, Muslim population in sub-Saharan Africa is forecast to grow from about 250 million in 2010 to nearly 670 million in 2050 which is more than double. The absolute number of Muslims is also expected to increase in regions with smaller Muslim populations such as Europe and North America, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate. In Europe Muslim population will be nearly double (from 5.9% to 10.2%). In Islam in the Americas, North America, it will grow 1% to 2%. In Asia Pacific region, Muslims will surpass the Hindus by the time. In Latin America and Caribbean Muslim population will stay 0.1% by 2050.
In 2010 Indonesia, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nigeria was home for (47.8%) of the world's Muslims.
 According to Rodney Stark, Islam was spread after military conquests after Arab armies began overtaking Christian regions from Syria to North Africa and Spain, as well as Zoroastrian, Buddhist and Hindu regions in Central Asia, parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia via military invasions, traders and Sufi missionaries.McLeod, John, ''The History of India'', Greenwood Press (2002), , pp. 41–42. According to some scholars, the Jizya (poll tax) was the most important factor in the mass conversion to Islam, the tax paid by all non-Muslims (Dhimmis – which translated means "protected persons") in Islamic empires.H. Patrick Glenn, Legal Traditions of the World. Oxford University Press, 2007, pp. 218–219. While other scholars oppose this belief, because the jizya was not of great value, and those who could not pay it were exempt from it, (such as Christians under the Ottoman Empire's authority, Hindus and Buddhists under regime of Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim invaders, Coptic Christians under administration of the Muslim conquest of Egypt, Muslim Arabs, Zoroastrians living under Muslim conquest of Persia, Islamic rule in ancient Persia,"The Zoroastrians who remained in Persia (modern Iran) after the Arab–Muslim conquest (7th century CE) had a long history as outcasts. Although they purchased some toleration by paying the jizya (poll tax), not abolished until 1882, they were treated as an inferior race, had to wear distinctive garb, and were not allowed to ride horses or bear arms
According to Rodney Stark, Islam was spread after military conquests after Arab armies began overtaking Christian regions from Syria to North Africa and Spain, as well as Zoroastrian, Buddhist and Hindu regions in Central Asia, parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia via military invasions, traders and Sufi missionaries.McLeod, John, ''The History of India'', Greenwood Press (2002), , pp. 41–42. According to some scholars, the Jizya (poll tax) was the most important factor in the mass conversion to Islam, the tax paid by all non-Muslims (Dhimmis – which translated means "protected persons") in Islamic empires.H. Patrick Glenn, Legal Traditions of the World. Oxford University Press, 2007, pp. 218–219. While other scholars oppose this belief, because the jizya was not of great value, and those who could not pay it were exempt from it, (such as Christians under the Ottoman Empire's authority, Hindus and Buddhists under regime of Muslim conquest in the Indian subcontinent, Muslim invaders, Coptic Christians under administration of the Muslim conquest of Egypt, Muslim Arabs, Zoroastrians living under Muslim conquest of Persia, Islamic rule in ancient Persia,"The Zoroastrians who remained in Persia (modern Iran) after the Arab–Muslim conquest (7th century CE) had a long history as outcasts. Although they purchased some toleration by paying the jizya (poll tax), not abolished until 1882, they were treated as an inferior race, had to wear distinctive garb, and were not allowed to ride horses or bear arms
Gabars Gabars
''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2007. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. 29 May 2007. and also with Jewish communities in the medieval Arab world) some scholars indicate that some Muslim rulers in India did not consistently collect the jizya (poll tax) from Dhimmis. Under Islamic law, Muslims are required to pay Zakat, one of the five pillars of Islam. Muslims take 2.5% out of their salaries and use the funds give to the needy. Since non-Muslims are not required to pay Zakat nor entitled to benefit from it, they had to support their own poor and in addition they had to pay Jizya if they wanted the same protections the Muslims received. In India, Islam was brought by various traders and rulers from Afghanistan and other places. According to other scholars, many converted for a whole host of reasons, the main statement of which was evangelization by Muslims, though there were several instances where some were pressured to convert owing to internal violence and friction between the Christian and Muslim communities, according to historian Philip Jenkins. However John L. Esposito, a scholar on the subject of Islam in ''The Oxford History of Islam'' states that the spread of Islam "was often peaceful and sometimes even received favorably by Christians". In a 2008 conference on religion at Yale University's ''The MacMillan Center Initiative on Religion, Politics, and Society'' which hosted a speech from Hugh N. Kennedy, Hugh Kennedy, he stated forced conversions played little part in the history of the spread of the faith. However, the poll tax known as Jizyah may have played a part in converting people over to Islam but as ''Britannica'' notes "The rate of taxation and methods of collection varied greatly from province to province and were greatly influenced by local pre-Islamic customs" and there were even cases when Muslims had the tax levied against them, on top of Zakat. Hugh N. Kennedy, Hugh Kennedy has also discussed the Jizyah issue and stated that Muslim governments discouraged conversion but were unable to prevent it.Conference on Religion and Violence. 16 February 2008.
His speech can be found here:
There were...clear reasons why Muslim governments would not want to encourage conversion to Islam. They were sometimes effectively unable to prevent conversion but they were certainly not going to use force to achieve it. (Page 5)
Long‐Range Population Projections for Israel: 2009‐2059
Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2014-04-21. The overall growth rate of Israeli Jews, Jews in Israel is 1.7% annually. The Jewish diaspora, diaspora countries, by contrast, have low Jewish birth rates, an increasingly elderly age composition, and a negative balance of people leaving Judaism versus those joining. There is also a trend of Orthodox movements reaching out to Jewish secularism, secular Jews in order to give them a stronger Jewish identity so there is less chance of Intermarriage in Judaism, intermarriage. As a result of the efforts by these and other Jewish groups over the past 25 years, there has been a trend (known as the Baal teshuva movement) for secular Jews to become more religiously observant, though the demographic implications of the trend are unknown. Additionally, there is also a growing rate of conversion to Jews by Choice of gentiles who make the decision to head in the direction of becoming Jews. Rates of Interfaith marriage, interreligious marriage vary widely: In the United States, it is just under 50 percent, in the United Kingdom, around 53 percent; in France; around 30 percent, and in Australia and Mexico, as low as 10 percent. In the United States, only about a third of children from intermarriages affiliate with Jewish religious practice. The result is that most countries in the Diaspora have steady or slightly declining religiously Historical Jewish population comparisons, Jewish populations as Jews continue to assimilate into the countries in which they live.
In 1939, the core Jewish population reached its historical peak of 17 million (0.8% of the global population). Because of the Holocaust, the number had been reduced to 11 million by the end of 1945. The population grew again to around 13 million by the 1970s, but has since recorded near-zero growth until around 2005 due to low fertility rates and to Jewish assimilation, assimilation. Since 2005, the world's Jewish population has been growing modestly at a rate of around 0.78% (in 2013). This increase primarily reflects the rapid growth of Haredi and some Orthodox Jews, Orthodox sectors, who are becoming a growing proportion of Jews.
According to the
Rates of Interfaith marriage, interreligious marriage vary widely: In the United States, it is just under 50 percent, in the United Kingdom, around 53 percent; in France; around 30 percent, and in Australia and Mexico, as low as 10 percent. In the United States, only about a third of children from intermarriages affiliate with Jewish religious practice. The result is that most countries in the Diaspora have steady or slightly declining religiously Historical Jewish population comparisons, Jewish populations as Jews continue to assimilate into the countries in which they live.
In 1939, the core Jewish population reached its historical peak of 17 million (0.8% of the global population). Because of the Holocaust, the number had been reduced to 11 million by the end of 1945. The population grew again to around 13 million by the 1970s, but has since recorded near-zero growth until around 2005 due to low fertility rates and to Jewish assimilation, assimilation. Since 2005, the world's Jewish population has been growing modestly at a rate of around 0.78% (in 2013). This increase primarily reflects the rapid growth of Haredi and some Orthodox Jews, Orthodox sectors, who are becoming a growing proportion of Jews.
According to the

 As of around 2020, there were about 8 million Bahá'ís in the world. In 2013, two scholars of demography wrote that, "The Baha'i Faith is the only religion to have grown faster in every United Nations region over the past 100 years than the general population; Bahaʼi [sic] was thus the fastest-growing religion between 1910 and 2010, growing at least twice as fast as the population of almost every UN region."
The largest proportions of the total world Bahá'í population were found in sub-Saharan Africa (29.9%) and South Asia (26.8%), followed by Southeast Asia (12.7%) and Latin America (12.2%). Lesser populations are found in North America (7.6%) and the Middle East/North Africa (6.2%), while the smallest populations in Europe (2.0%), Australasia (1.6%), and Northeast Asia (0.9%). In 2015, the internationally recognized religion was the second-largest international religion in Iran, Panama, Belize, Bolivia, Zambia, and Papua New Guinea; and the third-largest in Chad, and Kenya.
From the Bahá'í Faith's origins in the 19th century until the 1950s, the vast majority of Baháʼís were found in Iran; converts from outside Iran were mostly found in India and the Western world. From having roughly 200,000 Baháʼís in 1950, the religion grew to having over 4 million by the late 1980s, with a widespread international distribution. Most of the growth in the late 20th century was seeded out of North America by means of the planned migration of individuals. Yet, rather than being a cultural spread from either Iran or North America, in 2001, sociologist David Barrett wrote that the Baháʼí Faith is, "A world religion with no racial or national focus". However, the growth has not been even. From the late 1920s to the late 1980s the religion was harassed and banned in the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc, and then again from the 1970s into the 1990s across some countries in sub-Saharan Africa. The most intense opposition has been in Iran and neighboring Shia Islam, Shia-majority countries, considered by some scholars and watch agencies as a case of attempted genocide. Meanwhile in other times or places the religion has experienced surges in growth. Before it was banned in certain countries, the religion "hugely increased" in sub-Saharan Africa. In 1989 the Universal House of Justice named Bolivia, Bangladesh, Haiti, India, Liberia, Peru, the Philippines, and Taiwan as countries where growth in the religion had been notable in the previous decades. Bahá'í sources state "more than five million" Bahá'ís in 1991-2. However, since around 2001 the Universal House of Justice has prioritized statistics of the community by their levels of activity rather than simply their population of avowed adherents or numbers of local assemblies.
Because Bahá'ís do not represent the majority of the population in any country, and most often represent only a tiny fraction of countries' total populations, there are problems of under-reporting. In addition, there are examples where the adherents have their highest density among minorities in societies who face their own challenges.
As of around 2020, there were about 8 million Bahá'ís in the world. In 2013, two scholars of demography wrote that, "The Baha'i Faith is the only religion to have grown faster in every United Nations region over the past 100 years than the general population; Bahaʼi [sic] was thus the fastest-growing religion between 1910 and 2010, growing at least twice as fast as the population of almost every UN region."
The largest proportions of the total world Bahá'í population were found in sub-Saharan Africa (29.9%) and South Asia (26.8%), followed by Southeast Asia (12.7%) and Latin America (12.2%). Lesser populations are found in North America (7.6%) and the Middle East/North Africa (6.2%), while the smallest populations in Europe (2.0%), Australasia (1.6%), and Northeast Asia (0.9%). In 2015, the internationally recognized religion was the second-largest international religion in Iran, Panama, Belize, Bolivia, Zambia, and Papua New Guinea; and the third-largest in Chad, and Kenya.
From the Bahá'í Faith's origins in the 19th century until the 1950s, the vast majority of Baháʼís were found in Iran; converts from outside Iran were mostly found in India and the Western world. From having roughly 200,000 Baháʼís in 1950, the religion grew to having over 4 million by the late 1980s, with a widespread international distribution. Most of the growth in the late 20th century was seeded out of North America by means of the planned migration of individuals. Yet, rather than being a cultural spread from either Iran or North America, in 2001, sociologist David Barrett wrote that the Baháʼí Faith is, "A world religion with no racial or national focus". However, the growth has not been even. From the late 1920s to the late 1980s the religion was harassed and banned in the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc, and then again from the 1970s into the 1990s across some countries in sub-Saharan Africa. The most intense opposition has been in Iran and neighboring Shia Islam, Shia-majority countries, considered by some scholars and watch agencies as a case of attempted genocide. Meanwhile in other times or places the religion has experienced surges in growth. Before it was banned in certain countries, the religion "hugely increased" in sub-Saharan Africa. In 1989 the Universal House of Justice named Bolivia, Bangladesh, Haiti, India, Liberia, Peru, the Philippines, and Taiwan as countries where growth in the religion had been notable in the previous decades. Bahá'í sources state "more than five million" Bahá'ís in 1991-2. However, since around 2001 the Universal House of Justice has prioritized statistics of the community by their levels of activity rather than simply their population of avowed adherents or numbers of local assemblies.
Because Bahá'ís do not represent the majority of the population in any country, and most often represent only a tiny fraction of countries' total populations, there are problems of under-reporting. In addition, there are examples where the adherents have their highest density among minorities in societies who face their own challenges.
The Graduate Center of the City University of New York A 2012 study by the Pew Research Center, Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life reports, "The number of Americans who do not identify with any religion continues to grow at a rapid pace. One-fifth of the U.S. public – and a third of adults under 30 – are religiously unaffiliated today, the highest percentages ever in Pew Research Center polling." A similar pattern has been found in other countries such as Australia, Canada, and Mexico. According to statistics in Canada, the number of "Nones" increased by about 60% between 1985 and 2004. In Australia, census data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics give "no religion" the largest gains in absolute numbers over the 15 years from 1991 to 2006, from 2,948,888 (18.2% of the population that answered the question) to 3,706,555 (21.0% of the population that answered the question). According to INEGI, in Mexico, the number of atheists grows annually by 5.2%, while the number of Catholics grows by 1.7%. In New Zealand, 39% of the population are irreligious, making it the country with the largest irreligious population percentage in the Oceania region. According to a religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, the percentage of the world's population that is unaffiliated or nonreligious is expected to drop, from 16% of the world's total population in 2010 to 13% in 2050. The decline is largely due to the advanced age (median age of 34) and low fertility among unaffiliated or Nonreligious (1.7 children per woman in the 2010–2015 period). Sociologist Phil Zuckerman's global studies on atheism have indicated that global atheism may be in decline due to irreligious countries having the lowest birth rates in the world and religious countries having higher birth rates in general. According to Pew Research Center, Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life, by 2050 unaffiliated or nonreligious are expected to account for 27% of North America total population (up from 17.1% as in 2010), and 23% of Europe total population (up from 18% as in 2010). The religiously unaffiliated are stationed largely in the Asia-Pacific region, where 76% resided in that region in 2010, and is expected to be 68% by 2050. The share of the global unaffiliated population living in Europe is projected to grow from 12% in 2010 to 13% in 2050. The proportion of the global religiously unaffiliated living in North America will rise from 5% in 2010, to 9% in 2050. According to the Pew Research Center, religious conversion may have a modest impact on religiously unaffiliated population between 2010 and 2050; religiously unaffiliated are expected to gain 61 million adherents. The largest net movement is expected to be into the religiously unaffiliated category between 2010 and 2050.
Religious Projections for the Next 200 Years
fro
World Network of Religious Futurists
/ref>
Religion on the Move!: New Dynamics of Religious Expansion in a Globalizing World
', BRILL, 21 November 2012, Afe Adogame, Shobana Shankar, 2012. * The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the global religious landscape, revealing the size and distribution o
major religious groups as of 2023.
Think religion is in decline? Look at who is 'going forth and multiplying'
, ''Vancouver Sun'', 2014
''Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?: Demography and Politics in the Twenty-First Century''
by Eric Kaufmann, Belfer Center, Harvard University/Birkbeck College, University of London (PDF) *
Religious Projections for the Next 200 Years
fro
World Network of Religious Futurists
{{DEFAULTSORT:Claims To Be The Fastest-Growing Religion Religious studies Religious demographics
religion
Religion is a range of social system, social-cultural systems, including designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics in religion, ethics, or ...
s and the increase in the numbers of religious adherents around the world. In sociology, desecularization
In sociology, desecularization (also spelled desecularisation) is a resurgence or growth of religion after a period of secularization. The theory of desecularization is a reaction to the theory known as the '' secularization thesis,'' which posits ...
is the proliferation or growth of religion, most commonly after a period of previous secularization. Statistics commonly measure the absolute number of adherents, the percentage of the absolute growth per-year, and the growth of converts
Conversion or convert may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''The Convert'', a 2023 film produced by Jump Film & Television and Brouhaha Entertainment
* "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman''
* ...
in the world.
Studies in the 21st century suggest that, in terms of percentage and worldwide spread, Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world ...
is the fastest-growing major religion in the world."The Future of Global Muslim Population: Projections from 2010 to 2013"Accessed July 2013. A comprehensive religious forecast for 2050 by the
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
predicts that the global Muslim population will grow at a faster rate than the Christian
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a Monotheism, monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus in Christianity, Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the wo ...
population – primarily due to the average younger age, and higher fertility rate
The total fertility rate (TFR) of a population is the average number of children that are born to a woman over her lifetime, if they were to experience the exact current age-specific fertility rates (ASFRs) through their lifetime, and they were t ...
of Muslims. Religious conversion has no net impact on the Muslim population growth. In fact, conversion will have little impact on the size of religious groups. Pew projects that religious people will increase by 2050 due to increasing fertility rates in religious countries and decreasing fertility rates in less religious countries.
It is projected that birth rate – rather than conversion – will prove the main factor in the growth of any given religion. While according to other various scholars and sources Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
– a Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
Christian movement – is the fastest growing religion in the world, this growth is primarily due to religious conversion.
Counting the number of converts to a religion can prove difficult. Although some national censuses ask people about their religion, they do not ask if they have converted to their presently espoused faith. Additionally, in some countries, legal and social consequences make conversion difficult. For example, individuals can receive capital punishment
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty and formerly called judicial homicide, is the state-sanctioned killing of a person as punishment for actual or supposed misconduct. The sentence (law), sentence ordering that an offender b ...
if they openly leave Islam in some Muslim countries.Laws Criminalizing ApostasyLibrary of Congress (2014) Statistical data on conversion to and from Islam are scarce. According to a study published in 2011 by Pew Research, what little information is available may suggest that religious conversion has no net impact on the Muslim population, as the number of people who
convert to Islam
Reversion to Islam, also known within Islam as reversion, is adopting Islam as a religion or faith. Conversion requires a formal statement of the ''Shahada, shahādah'', the credo of Islam, whereby the prospective convert must state that "there i ...
is roughly similar to those who leave Islam.
Some religions proselytise
Proselytism () is the policy of attempting to convert people's religious or political beliefs. Carrying out attempts to instill beliefs can be called proselytization.
Proselytism is illegal in some countries. Some draw distinctions between Chris ...
vigorously (Christianity and Islam, for example), while others (such as Judaism
Judaism () is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic, Monotheism, monotheistic, ethnic religion that comprises the collective spiritual, cultural, and legal traditions of the Jews, Jewish people. Religious Jews regard Judaism as their means of o ...
and Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
) do not generally encourage conversions into their ranks. Some faiths grow exponentially at first (especially, for example, along trade routes
or for reasons of social prestige),
only for their zeal to wane (note the flagging case of Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
). The growth of a religion can interact with factors such as persecution
Persecution is the systematic mistreatment of an individual or group by another individual or group. The most common forms are religious persecution, racism, and political persecution, though there is naturally some overlap between these term ...
, entrenched rival religions (such as established religions), and religious market saturation
In economics, market saturation is a situation in which a Product (business), product has become Diffusion_(business), diffused (distributed) within a Market (economics), market; the actual level of saturation can depend on consumer purchasing p ...
.
Growth of religious groups
Buddhism
Buddhism
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or ...
is based on the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha (),*
*
*
was a śramaṇa, wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist lege ...
, commonly known as the Buddha, who was born in modern day Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
and lived and taught in India in the 5th century BC. The majority of Buddhists live in Asia; Europe and North America also have populations exceeding one million. According to scholars of religious demographics, there are between 488 million, 495 million, and 535 million Buddhists in the world.
According to Johnson and Grim, Buddhism has grown from a total of 138 million adherents in 1910, of which 137 million were in Asia, to 495 million in 2010, of which 487 million are in Asia. According to them, there was a fast annual growth of Buddhism in Pakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
, Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
and several Western European countries (1910–2010). More recently (2000–2010), the countries with highest growth rates are Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, and some African countries. The Australian Bureau of Statistics
The Australian Bureau of Statistics (ABS) is an List of Australian Government entities, Australian Government agency that collects and analyses statistics on economic, population, Natural environment, environmental, and social issues to advi ...
, through statistical analysis, held Buddhism to be the fastest-growing spiritual tradition in Australia in terms of percentage gain, with a growth of 79.1% for the period 1996 to 2001 (200,000→358,000).
Buddhism is the majority and state religion in seven countries: Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, also known historically as Ceylon, is an island country in South Asia. It lies in the Indian Ocean, southwest of the Bay of Bengal, separated from the Indian subcontinent, ...
, Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, Thailand
Thailand, officially the Kingdom of Thailand and historically known as Siam (the official name until 1939), is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. With a population of almost 66 million, it spa ...
, Cambodia
Cambodia, officially the Kingdom of Cambodia, is a country in Southeast Asia on the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula. It is bordered by Thailand to the northwest, Laos to the north, and Vietnam to the east, and has a coastline ...
, Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , ...
and Laos
Laos, officially the Lao People's Democratic Republic (LPDR), is the only landlocked country in Southeast Asia. It is bordered by Myanmar and China to the northwest, Vietnam to the east, Cambodia to the southeast, and Thailand to the west and ...
.
Buddhism is the majority religion in the following nine countries: Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, Laos, Bhutan, Mongolia
Mongolia is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south and southeast. It covers an area of , with a population of 3.5 million, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by po ...
, Japan and Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
.
Special administrative areas in China are Buddhist majority areas such as Macau
Macau or Macao is a special administrative regions of China, special administrative region of the People's Republic of China (PRC). With a population of about people and a land area of , it is the most List of countries and dependencies by p ...
, Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
and Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups s ...
.
Kalmykia
Kalmykia, officially the Republic of Kalmykia,; , ''Khalmg Tanghch'' is a republic of Russia, located in the Volga region of European Russia. The republic is part of the Southern Federal District, and borders Dagestan to the south and Stavr ...
is the only Buddhist majority region in Europe. It is an autonomous republic in Russia.
According to a 2012 Pew Research Center survey, over the next four decades the number of Buddhists around the world is expected to decrease from 487 million in 2010 to 486 million in 2050. The decline is due to several factors such as the low fertility level among Buddhists (1.6 children per woman), and the old age (median age of 34), compared to the overall population. According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
published on 2010, religious conversion may have little impact on the Buddhists population between 2010 and 2050; Buddhists are expected to lose 2.9 million adherents between 2010 and 2050.
According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, between 2010 and 2015 "an estimated 32 million babies were born to Buddhist mothers and roughly 20 million Buddhists died, meaning that the natural increase in the Buddhists population – i.e., the number of births minus the number of deaths – was 12 million over this period". According to the same study Buddhists "are projected to decline in absolute number, dropping 7% from nearly 500 million in 2015 to 462 million in 2060. Low fertility rates and aging populations in countries such as China, Thailand and Japan are the main demographic reasons for the expected shrinkage in the Buddhist population in the years ahead".
Chinese traditional religion
According to a survey ofreligion in China
Religion in China is diverse and most Chinese people are either non-religious or practice a combination of Buddhism and Taoism with a Confucian worldview, which is collectively termed as Chinese folk religion.
The People's Republic of C ...
in the year 2010, the number of people practicing some form of Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion comprises a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. This includes the veneration of ''Shen (Chinese folk religion), shen'' ('spirits') and Chinese ancestor worship, ances ...
is near to 950 million (70% of the Chinese),2010 Chinese Jesus Life Survey conducted by Dr. Yang Fenggang, Purdue University's Center on Religion and Chinese Society. Statistics published in: Katharina Wenzel-Teuber, David Strait. People's Republic of China: Religions and Churches Statistical Overview 2011
''. Religions & Christianity in Today's China, Vol. II, 2012, No. 3, pp. 29–54, . of which 173 million (13%) practice some form of Taoist-defined folk faith. Further in detail, 12 million people have passed some formal initiation into Taoism, or adhere to the official
Chinese Taoist Association
Chinese Taoist Association (CTA; ), founded in April 1957, is the official government supervisory organ of Taoism in the People's Republic of China.
History
In 1980, the Central Committee of the Chinese Communist Party approved a request by t ...
. Comparing this with other surveys, evidence suggests that nowadays three-fifths to four-fifths of the Chinese believe in folk religion. This shows a significant growth from the 300–400 million people practicing Chinese traditional religion that were estimated in the 1990s and early 2000s.
This growth reverses the rapid decline that Chinese traditional religion faced in the 20th century. Moreover, Chinese religion has also spread throughout the world following the emigration of Chinese populations, with 672,000 adherents in Canada as of 2010.
According to scholars Miikka Ruokanen and Paulos Huang of University of Helsinki
The University of Helsinki (, ; UH) is a public university in Helsinki, Finland. The university was founded in Turku in 1640 as the Royal Academy of Åbo under the Swedish Empire, and moved to Helsinki in 1828 under the sponsorship of Alexander ...
, the rebirth of traditional religion in China is faster and larger than the spread of other religions in the country, such as Buddhism and Christianity:
The number of adherents of the Chinese traditional religion is difficult to count, because of :Chen, Jeung. 2012. p. 200
The Chinese folk religion
Chinese folk religion comprises a range of traditional religious practices of Han Chinese, including the Chinese diaspora. This includes the veneration of ''Shen (Chinese folk religion), shen'' ('spirits') and Chinese ancestor worship, ances ...
is a "diffused religion" rather than "institutional". It is a meaning system of social solidarity and identity, ranging from the kinship systems to the community, the state, and the economy, that serves to integrate Chinese culture
Chinese culture () is one of the Cradle of civilization#Ancient China, world's earliest cultures, said to originate five thousand years ago. The culture prevails across a large geographical region in East Asia called the Sinosphere as a whole ...
.
Christianity
 According to a 2011
According to a 2011 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, there are 2.2 billion Christians around the world in 2010, up from about 600 million in 1910. And according to a 2012 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, within the next four decades, Christians will remain the world's largest religion; if current trends continue, by 2050 the number of Christians will reach 3 billion (or 31.4%). According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, by 2060 Christians will remain the world's largest religion; and the number of Christians will reach 3.05 billion (or 31.8%). According to scholar Mark Juergensmeyer
Mark Juergensmeyer (born 1940 in Carlinville, Illinois) is an American Sociology, sociologist and scholar specialized in global studies and religious studies, and a writer best known for his studies on comparative religion, religious violence, an ...
of University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Berkeley, California, United States. Founded in 1868 and named after t ...
, the global Christian population increased at an average annual rate of 2.3%, while Roman Catholicism
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
is growing by 1.3% annually, Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
is growing by 3.3% annually, and Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
and Pentecostalism
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
is growing by 7% annually. According to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP) is a nonpartisan international affairs think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C., with operations in Europe, South Asia, East Asia, and the Middle East, as well as the United States. Foun ...
, Christianity (growth rate, 1.38%) is one of the six fastest-growing religions in the world, with high birth rates and conversions in the global South
Global North and Global South are terms that denote a method of grouping countries based on their defining characteristics with regard to socioeconomics and politics. According to UN Trade and Development (UNCTAD), the Global South broadly com ...
were being cited as the major reasons of the Christian population growth.
By 2050, the Christian population is expected to exceed 3 billion. Christians have 2.7 children per woman, which is above replacement level (2.1). The birth rate is expected to be the main factor in the growth of Christianity. According to Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
study, by 2050 the number of Christians in absolute number is expected to grow to more than double in the next few decades, from 517 million to 1.1 billion in Sub Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African countries and territ ...
, from 531 million to 665 million in Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
and Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America ...
, from 287 million to 381 million in Asia
Asia ( , ) is the largest continent in the world by both land area and population. It covers an area of more than 44 million square kilometres, about 30% of Earth's total land area and 8% of Earth's total surface area. The continent, which ...
, and from 266 million to 287 million in North America. By 2050, Christianity is expected to remain the majority of population and the largest religious group in Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
and Caribbean (89%), North America (66%), Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
(65.2%) and Sub Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lie south of the Sahara. These include Central Africa, East Africa, Southern Africa, and West Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the African countries and territ ...
(59%).
Europe was the home for the world's largest Christian population for the past 1,000 years, but since 2015 Christians in Africa and Latin America respectively surpass the Europe Christian population because of the high fertility rate there. in 2018 a new data from the Gordon Theological Seminary shows that, for the first time ever, more number of Christians live in Africa than on any other single continent: "The results show Africa on top with 631 million Christian residents, Latin America in 2nd place with 601 million Christians, and Europe in 3rd place with 571 million Christians". In 2017 Christianity added nearly 50 million people due to factors such as birth rate and religious conversion. According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, between 2010 and 2015 "an estimated 223 million babies were born to Christian mothers and roughly 107 million Christians died, meaning that the natural increase in the Christian population – i.e., the number of births minus the number of deaths – was 116 million over this period".
According to Mark Jürgensmeyer of the University of California
The University of California (UC) is a public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university, research university system in the U.S. state of California. Headquartered in Oakland, California, Oakland, the system is co ...
, popular Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. According to various scholars and sources Pentecostalism – a Protestant Christian movement – is the fastest growing religion in the world, this growth is primarily due to religious conversion. According to Pulitzer Center
The Pulitzer Center on Crisis Reporting is an American news media organization established in 2006 that sponsors independent reporting on global issues that other media outlets are less willing or able to undertake on their own. The center's goal ...
35,000 people become Pentecostal or "Born again
To be born again, or to experience the new birth, is a phrase, particularly in evangelical Christianity, that refers to a "spiritual rebirth", or a regeneration of the human spirit. In contrast to one's physical birth, being "born again" is d ...
" every day. According to scholar Keith Smith of Georgia State University
Georgia State University (Georgia State, State, or GSU) is a Public university, public research university in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. Founded in 1913, it is one of the University System of Georgia's four research universities. It is al ...
"many scholars claim that Pentecostalism is the fastest growing religious phenomenon in human history", and according to scholar Peter L. Berger of Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a Private university, private research university in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. BU was founded in 1839 by a group of Boston Methodism, Methodists with its original campus in Newbury (town), Vermont, Newbur ...
"the spread of Pentecostal Christianity may be the fastest growing movement in the history of religion". Changes in worldwide Protestantism over the last century have been significant. Since 1900, due primarily to conversion, Protestantism has spread rapidly in Africa, Asia, Oceania and Latin America. That caused Protestantism to be called a primarily non-Western religion. Much of the growth has occurred after World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
, when decolonization of Africa
The decolonisation of Africa was a series of political developments in Africa that spanned from the mid-1950s to 1975, during the Cold War. Colonial governments gave way to sovereign states in a process often marred by violence, political turm ...
and abolition of various restrictions against Protestants in Latin American countries occurred. According to one source, Protestants constituted respectively 2.5%, 2%, 0.5% of Latin Americans, Africans and Asians. In 2000, percentage of Protestants on mentioned continents was 17%, more than 27% and 5.5%, respectively.Jay Diamond, Larry. Plattner, Marc F. and Costopoulos, Philip J. ''World Religions and Democracy''. 2005, page 119link
(saying "Not only do Protestants presently constitute 13 percent of the world's population—about 800 million people—but since 1900 Protestantism has spread rapidly in Africa, Asia, and Latin America.") The significant growth of Christianity in non-Western countries led to regional distribution changes of Christians. In 1900, Europe and the Americas were home to the vast majority of the world's Christians (93%). Besides, Christianity has grown enormously in Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and the Pacific. In 2010, 26% of the world's Christians lived in Europe, followed by 24.4% in Latin America and the Caribbean, 23.8% in Sub-Saharan Africa, 13.2% in Asia and the Pacific, 12.3% in North America, and 1% in the Middle East and North Africa. The study also suggested that by 2050, the global Christian population will change considerably. By 2050, 38% of the world's Christians will live in the Sub-Saharan Africa, followed by 23% in Latin America and
the Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, a ...
, 16% in Europe, 13% in Asia and the Pacific and 10% of the world's Christians will live in North America.
In mid-2005 Christianity adds about 65.1 million people annually due to factors such as birth rate and religious conversion, while losing 27.4 million people annually due to factors such as death rate and religious apostasy. Most of the net growth in the numbers of Christians is in Africa, Latin America and Asia.
Christianity is still the largest religion in Western Europe, according to a 2018 study by the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
, 71.0% of the Western European population identified themselves as Christians
A Christian () is a person who follows or adheres to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians form the largest religious community in the world. The words '' Christ'' and ''C ...
, however, most of them are non-practicing and non- church-attending. According to the same study, a large majority of those who raised as Christians (83%) in Western Europe, still identified themselves as Christians today. On the other hand, Central and Eastern European
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountains, and ...
countries did not experience a decline in the percentage of Christians, as the proportion of Christians in these countries have mostly been stable or even increasing. Christianity is still the largest religion in Central and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural and socio-economic connotations. Its eastern boundary is marked by the Ural Mountain ...
, according to a 2017 study by the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
, the share of adults who identify themselves as Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism ...
in Russia, Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the List of European countries by area, second-largest country in Europe after Russia, which Russia–Ukraine border, borders it to the east and northeast. Ukraine also borders Belarus to the nor ...
and Bulgaria has been significantly increased between 1991 and 2015. According to scholar Barry John Tolmay of University of Pretoria
The University of Pretoria (, ) is a multi-campus public university, public research university in Pretoria, the administrative and ''de facto'' capital of South Africa. The university was established in 1908 as the Pretoria campus of the Johan ...
there are increasing signs of a Christian revival in Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, Slovakia
Slovakia, officially the Slovak Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the west, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's m ...
and Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
.
According to a 2005 paper submitted to a meeting of the American Political Science Association
The American Political Science Association (APSA) is a professional association of political scientists in the United States. Founded in 1903 in the Tilton Memorial Library (now Tilton Hall) of Tulane University in New Orleans, it publishes four ...
, most of Christianity's growth has occurred in non-Western countries
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also constitute the West. ...
. The paper concludes that the Pentecostalism movement is the fastest-growing religion worldwide. Protestantism is growing primarily as a result of historic missionary activity and the recently high fertility
Fertility in colloquial terms refers the ability to have offspring. In demographic contexts, fertility refers to the actual production of offspring, rather than the physical capability to reproduce, which is termed fecundity. The fertility rate ...
rate in Africa, and due primarily to conversion in China. According to scholar Paul Freston of Wilfrid Laurier University
Wilfrid Laurier University (commonly referred to as WLU or simply Laurier) is a Public university, public university in Ontario, Canada, with campuses in Waterloo, Ontario, Waterloo, Brantford, Ontario, Brantford and Milton, Ontario, Milton. The ...
Pentecostalism continues to grow in Latin America, "both by conversion and by high birth rates". According to scholar Francis Fukuyama
Francis Yoshihiro Fukuyama (; born October 27, 1952) is an American political scientist, political economist, and international relations scholar, best known for his book '' The End of History and the Last Man'' (1992). In this work he argues th ...
of Stanford University
Leland Stanford Junior University, commonly referred to as Stanford University, is a Private university, private research university in Stanford, California, United States. It was founded in 1885 by railroad magnate Leland Stanford (the eighth ...
"converts to Protestantism find their incomes, education levels, hygiene and social networks expanding". According to scholar Terence Chong, since 1980s Protestantism is expanding in Singapore, Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, and South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
. According to a 2014 study by the Pew Research Center, around 9% of Latin Americans were raised as Protestant, but nearly 19% now identify themselves as Protestants.
 The
The US Department of State
The United States Department of State (DOS), or simply the State Department, is an executive department of the U.S. federal government responsible for the country's foreign policy and relations. Equivalent to the ministry of foreign affairs o ...
estimated in 2005 that Protestants in Vietnam may have grown by 600% over the previous 10 years. According to Pew Research Center, "largely through the efforts of missionaries and churches, Christianity has grown rapidly in South Korea
South Korea, officially the Republic of Korea (ROK), is a country in East Asia. It constitutes the southern half of the Korea, Korean Peninsula and borders North Korea along the Korean Demilitarized Zone, with the Yellow Sea to the west and t ...
over the past century", and has grown from 1% in 1900, to 20.7% in 1985 and to 29.3% in 2010, And the Catholic Church has increased its membership by 70% in the last ten years, according to Pew Research Center, "the growth of Catholics has occurred across all age groups, among men and women and across all education levels. In Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, the percentage of Christians among Singaporeans increased from 12.7%, in 1990, to 17.5%, in 2010. According to scholar Michael Nai-Chiu Poon of University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university whose main campus is located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was founded by ...
conversion to Christianity is increasing among Chinese Singaporeans
Chinese Singaporeans, Singaporean Chinese or Sino-Singaporeans () are Singaporeans of Han Chinese ancestry. Chinese Singaporeans constitute 75.9% of the Singaporean resident population according to the official census, making them the large ...
.
In recent years, the number of Chinese Christians has increased significantly; Christians were 4 million before 1949 (3 million Catholics and 1 million Protestants), and are reaching 67 million today. Christianity is reportedly the fastest growing religion in China with an average annual rate of 7% as of 2015. Some reports also show that the number of the Chinese Indonesians
Chinese Indonesians (), or simply ''Orang Tionghoa'' or ''Tionghoa'', are Indonesians whose ancestors arrived from China at some stage in the last eight centuries. Chinese Indonesians are the fourth largest community of Overseas Chinese in th ...
Christians have increased, according to scholar Gavin W. Jones of Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public university, public research university and member of the Group of Eight (Australian universities), Group of Eight, located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton, A ...
, "there has been a rapid growth in the number of Chinese Christians" in Indonesia, and "conversion of Chinese to Christianity accelerated in the 1960s, especially in East Java
East Java (, , ) is a Provinces of Indonesia, province of Indonesia located in the easternmost third of Java island. It has a land border only with the province of Central Java to the west; the Java Sea and the Indian Ocean border its northern ...
, and for Indonesia as a whole the proportion of Chinese who were Catholics rose from 2 percent in 1957 to 6 percent in 1969". Professor Aris Ananta reported in 2008 that "anecdotal evidence suggests that more Buddhist Chinese have become Christians as they increased their standards of education, because Christianity, unlike Buddhism, is often associated with 'modernity' and Western education", although there are no stats to support this.
According to a poll conducted by the Gallup Organization
Gallup, Inc. is an American multinational analytics and advisory company based in Washington, D.C. Founded by George Gallup in 1935, the company became known for its public opinion polls conducted worldwide. Gallup provides analytics and man ...
in 2006, Christianity has increased significantly in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, particularly among youth, and a high number of teens are becoming Christians.
In 1900, there were only 8.7 million adherents of Christianity in Africa, while in 2010 there were 390 million. It is expected that by 2025 there will be 600 million Christians in Africa. In Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, the percentage of Christians has grown from 21.4%, in 1953, to 50.8%, in 2010. In South Africa, Pentecostalism has grown from 0.2%, in 1951, to 7.6%, in 2001. According to Pew Research Center the number of Catholics in Africa has increased from one million in 1901 to 329,882,000 in 2010. From 2015 to 2016, Africa saw an increase of more than 6,265,000 Catholics.

Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
membership in 2013 was 1.254 billion, which is 17.7% of the world population, an increase from 437 million, in 1950Froehle, pp. 4–5 and 654 million, in 1970. The main growth areas have been Asia and Africa, 39% and 32%, respectively, since 2000.
Since 2010, the rate of increase was of 0.3% in the Americas and Europe. On the other hand, Eric Kaufman, of University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The ...
, argued that the main reason for the expansion of Catholicism and conservative Protestantism along with other religions is because their religions tend to be "pro-natal" and they have more children, and not due to religious conversion.
The total Protestant population has reached 1.17 billion in 2024. Protestantism is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. Evangelical Christian
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
denominations also are among the fastest-growing denominations in some Catholic Christian countries, such as Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population ...
and France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
(France going from 2% to 3% of the population). In Brazil, the total number of Protestants jumped from 16.2% in 2000 to 22.2% in 2010 (for the first time, the percentage of Catholics in Brazil is less than 70%). These cases do not contribute to a growth of Christianity overall, but rather to a substitution of a brand of Christianity with another one.
According to the records of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
, its membership has grown every decade since its beginning in the 1830s, it is among the top ten largest Christian denominations in the U.S., and it was the fastest growing church in the U.S. in 2012.
The 19th century saw at least 250,000 Jews
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
convert to Christianity
Conversion to Christianity is the religious conversion of a previously non-Christian person that brings about changes in what sociologists refer to as the convert's "root reality" including their social behaviors, thinking and ethics. The sociol ...
according to existing records of various societies. Data from the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
has it that, as of 2013, about 1.6 million adult American Jews
American Jews (; ) or Jewish Americans are American citizens who are Jewish, whether by culture, ethnicity, or religion. According to a 2020 poll conducted by Pew Research, approximately two thirds of American Jews identify as Ashkenazi, 3% id ...
identify themselves as Christians, most as Protestants. According to the same data, most of the Jews who identify themselves as some sort of Christian (1.6 million) were raised as Jews or are Jews by ancestry. According to a 2012 study, 17% of Jews in Russia identify themselves as Christians.Arena – Atlas of Religions and Nationalities in RussiaSreda.org2012 Survey Maps
. "Ogonek", № 34 (5243), 27 August 2012. ''Retrieved 24 September 2012''. According to study by
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
in 2021, around 19% of American those who say they were raised Jewish or who had at least one Jewish parent now identify as Christian.
According to the historian Geoffrey Blainey
Geoffrey Norman Blainey, (born 11 March 1930) is an Australian historian, academic, best selling author and commentator.
Blainey is noted for his authoritative texts on the economic and social history of Australia, including ''The Tyranny of ...
from the University of Melbourne
The University of Melbourne (colloquially known as Melbourne University) is a public university, public research university located in Melbourne, Australia. Founded in 1853, it is Australia's second oldest university and the oldest in the state ...
, since the 1960s there has been a substantial increase in the number of conversions from Islam to Christianity, mostly to the Evangelical
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
and Pentecostal
Pentecostalism or classical Pentecostalism is a movement within the broader Evangelical wing of Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes direct personal experience of God in Christianity, God through Baptism with the Holy Spirit#Cl ...
forms. According to Blainey, this is due to several reasons, including the lack of ties of Evangelical Christianity
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide, interdenominational movement within Protestantism, Protestant Christianity that emphasizes evangelism, or the preaching and spreading of th ...
with colonial powers in contrast to Roman Catholic and Mainline Protestant Churches, as well as the rising of Islamism
Islamism is a range of religious and political ideological movements that believe that Islam should influence political systems. Its proponents believe Islam is innately political, and that Islam as a political system is superior to communism ...
, which lead some Muslims to look towards other religions such as Christianity through evangelical activity in the visual and audio media, as well as irreligion. Many Muslims who convert to Christianity face social and governmental persecution. Khalil Bilici, while admitting that the limitations of their 2007 study database are too small, found a good number of Middle Eastern people are likely to convert to Christianity after leaving Islam.
 According to the ''
According to the ''World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denomination ...
'' estimate significantly more people have converted to Christianity from Islam in the 21st century than at any other point in Islamic history.Garrison, David; 2014; "A Wind in the House of Islam: How God Is Drawing Muslims Around The World To Faith in Jesus Christ"; WIGTake Resources The 2015 ''Believers in Christ from a Muslim Background: A Global Census study'' published by Baylor University institute for studies of religion estimates that 10.2 million Muslims converted to Christianity based on global missionary data. Countries with the largest numbers of Muslims converted to Christianity according to this study include Indonesia (6,500,000), Nigeria (600,000), Iran (500,000 versus only 500 in 1979), the United States (450,000), Ethiopia (400,000) and Algeria (380,000). Indonesia is home to the largest Christian community made up of converts from their former Islamic faith; according to various sources, since the mid and late 1960s, between two million to 2.5 million Muslims converted to Christianity.
Christians of Muslim background communities can be found in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
, Albania
Albania ( ; or ), officially the Republic of Albania (), is a country in Southeast Europe. It is located in the Balkans, on the Adriatic Sea, Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea, and shares land borders with Montenegro to ...
, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
, Australia, Austria
Austria, formally the Republic of Austria, is a landlocked country in Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine Federal states of Austria, states, of which the capital Vienna is the List of largest cities in Aust ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, is a Boundaries between the continents, transcontinental and landlocked country at the boundary of West Asia and Eastern Europe. It is a part of the South Caucasus region and is bounded by ...
, Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, Belgium
Belgium, officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. Situated in a coastal lowland region known as the Low Countries, it is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeas ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina, sometimes known as Bosnia-Herzegovina and informally as Bosnia, is a country in Southeast Europe. Situated on the Balkans, Balkan Peninsula, it borders Serbia to the east, Montenegro to the southeast, and Croatia to th ...
, Bulgaria, Canada, Denmark
Denmark is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe. It is the metropole and most populous constituent of the Kingdom of Denmark,, . also known as the Danish Realm, a constitutionally unitary state that includes the Autonomous a ...
, Egypt
Egypt ( , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a country spanning the Northeast Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to northe ...
, Ethiopia
Ethiopia, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a landlocked country located in the Horn of Africa region of East Africa. It shares borders with Eritrea to the north, Djibouti to the northeast, Somalia to the east, Ken ...
, Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
(Abkhazia
Abkhazia, officially the Republic of Abkhazia, is a List of states with limited recognition, partially recognised state in the South Caucasus, on the eastern coast of the Black Sea, at the intersection of Eastern Europe and West Asia. It cover ...
), Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
, Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, para.1-63 India (kashmir
Kashmir ( or ) is the Northwestern Indian subcontinent, northernmost geographical region of the Indian subcontinent. Until the mid-19th century, the term ''Kashmir'' denoted only the Kashmir Valley between the Great Himalayas and the Pir P ...
), Iran, Iraq
Iraq, officially the Republic of Iraq, is a country in West Asia. It is bordered by Saudi Arabia to Iraq–Saudi Arabia border, the south, Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq border, the east, the Persian Gulf and ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a landlocked country primarily in Central Asia, with a European Kazakhstan, small portion in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the Kazakhstan–Russia border, north and west, China to th ...
, Kosovo
Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo, is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe with International recognition of Kosovo, partial diplomatic recognition. It is bordered by Albania to the southwest, Montenegro to the west, Serbia to the ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan, officially the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia lying in the Tian Shan and Pamir Mountains, Pamir mountain ranges. Bishkek is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Kyrgyzstan, largest city. Kyrgyz ...
, Lebanon
Lebanon, officially the Republic of Lebanon, is a country in the Levant region of West Asia. Situated at the crossroads of the Mediterranean Basin and the Arabian Peninsula, it is bordered by Syria to the north and east, Israel to the south ...
, Malaysia
Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ...
, Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocc ...
, the Netherlands
, Terminology of the Low Countries, informally Holland, is a country in Northwestern Europe, with Caribbean Netherlands, overseas territories in the Caribbean. It is the largest of the four constituent countries of the Kingdom of the Nether ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country located on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. It borders Norway to the west and north, and Finland to the east. At , Sweden is the largest Nordic count ...
,Svenska Dagbladet (SvD), Fler kristna väljer att bli muslimer
'', November 19, 2007 (Accessed November 19, 2007)
Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
, Tanzania
Tanzania, officially the United Republic of Tanzania, is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It is bordered by Uganda to the northwest; Kenya to the northeast; the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to t ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan, officially the Republic of Tajikistan, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Dushanbe is the capital city, capital and most populous city. Tajikistan borders Afghanistan to the Afghanistan–Tajikistan border, south, Uzbekistan to ...
, Tunisia
Tunisia, officially the Republic of Tunisia, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered by Algeria to the west and southwest, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Tunisia also shares m ...
,International Religious Freedom Report 2007: TunisiaUnited States
Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor
The Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor Affairs (DRL) is a bureau within the United States Department of State. The bureau is under the purview of the Under Secretary of State for Civilian Security, Democracy, and Human Rights.
History ...
(September 14, 2007). ''This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no Exclusive exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly Waiver, waived, or may be inapplicable. Because no one holds ...
.'' Turkey
Turkey, officially the Republic of Türkiye, is a country mainly located in Anatolia in West Asia, with a relatively small part called East Thrace in Southeast Europe. It borders the Black Sea to the north; Georgia (country), Georgia, Armen ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the United States, Uzbekistan
, image_flag = Flag of Uzbekistan.svg
, image_coat = Emblem of Uzbekistan.svg
, symbol_type = Emblem of Uzbekistan, Emblem
, national_anthem = "State Anthem of Uzbekistan, State Anthem of the Republ ...
, and other countries. According to the Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank focused on Foreign policy of the United States, U.S. foreign policy and international relations. Founded in 1921, it is an independent and nonpartisan 501(c)(3) nonprofit organi ...
in 2007, experts estimated that thousands of Muslims in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
converted to Christianity annually, but were not publicized due to fear of retribution.
According to scholar Rob Scott of University of Tasmania
The University of Tasmania (UTAS) is a public research university, primarily located in Tasmania, Australia. Founded in 1890, it is Australia's fourth oldest university. Christ College (University of Tasmania), Christ College, one of the unive ...
in 2010 there were "approximately 180,000 Arab American
Arab Americans ( or ) are Americans who trace ancestry to any of the various waves of immigrants from the Arabic-speaking countries. In the United States census, Arabs are racially classified as White Americans which is defined as "A person ha ...
s and about 130,000 Iranian American
Iranian-Americans, also known as Persian-Americans, are Americans, United States citizens or nationals who are of Iranian peoples, Iranian ancestry, or who hold Iranian Multiple citizenship, citizenship.
Most Iranian-Americans arrived in the U ...
s who converted from Islam to Christianity", Scholar Dudley Woodberry form Fuller Theological Seminary
Fuller Theological Seminary is an Evangelical seminary in Pasadena, California, with regional campuses in the western United States. It is egalitarian in nature.
Fuller has a student body of approximately 2,300 students from 90 countries and ...
estimated approximately that 20,000 Muslims converts to Christianity annually in the United States. Also according to the historian Daniel Pipes of Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and University of Chicago, and a researcher specializing in criticism of Islam, "reports of widespread conversions of Muslims to Christianity come from regions as disparate as Algeria, Albania, Syria, and Kurdistan", in northern Iraq and Algeria, the conversions of Kurds and Berbers to Christianity are unusually high. According to Guinness, approximately 12.5 million more people who converted to Islam than people who converted to Christianity between 1990 and 2000. According to scholar Ladan Boroumand "Iran today is witnessing the highest rate of Christianization in the world", and according to scholar Shay Khatiri of Johns Hopkins University "Islam is the fastest shrinking religion in there [Iran], while Christianity is growing the fastest", and in 2018 "up to half a million Iranians are Christian converts from Muslim families, and most of these Christians are evangelicals", and he adds "recent estimates claim that the number might have climbed up to somewhere between 1 million and 3 million". Converting to Christianity is growing among Muslims in the Albanian diaspora, Iranian diaspora, and Syrian diaspora, and among Muslim Maghrebis in France, and Kurds in Germany, Kurds and Turks in Germany. According to scholars Felix Wilfred from the University of Madras and Chris Hann from the University of Cambridge and Max Planck Institute for Social Anthropology, since the fall of communism, the number of Muslim converts to Christianity in Kyrgyzstan has been increased. Some scholars and media reports indicate that in the Middle East there been increasing numbers of conversions to Christianity among the Berbers, Kurds, Persians, and Turkish people, Turks, and among some religious minorities such as Alawites and Druze. Churches in Europe say that there is an increase in the number of Muslims converting to Christianity among immigrants.
Religious conversions are projected to have a "modest impact on changes in the religious groups including Christian population" between 2010 and 2050; and may negatively affect the Christian population growth, growth of Christian population and its share of the world's populations "slightly". According to the same study Christianity, is expected to lose a net of 66 million adherents (40 million converts versus 106 million apostate) mostly to religiously unaffiliated category between 2010 and 2050. It is also expected that Christianity may have the largest net losses in terms of religious conversion. However, these forecasts lack reliable data on religious conversion in China, but according to media reports and expert assessments, it is possible that the rapid growth of Christianity in China may maintain, or even increase, the current numerical advantage of Christianity as the largest religion in the world. This scenario (Chinese scenario) is based primarily on sensitivity tests. Large increases in the developing world (around 23,000 per day) have been accompanied by substantial Decline of Christianity in the Western world, declines in the developed world, mainly in Western Europe and North America. By 2050, Christianity is expected to remain the majority religion in the United States (66.4%, down from 78.3% in 2010), and the number of Christians in absolute numbers is expected to grow from 243 million to 262 million.
According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
, Christianity is declining in the United States while non-Christian faiths are growing. The 2014 Religious Landscape Study finds a large majority (87.6%) of those who were raised as Christians in the United States still identify as such, while the rest who no longer identify as Christians mostly identify as religiously unaffiliated, and the number of those leaving Christianity in the United States is greater than the number of converts; however, the number of those convert to evangelical Christianity in the United States is greater than the number of those leaving that faith. While on the other hand, in 2017, scholars Landon Schnabel and Sean Bock at Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and Indiana University argued that while "Mainline Protestant" churches has declined in the United States since the late 1980s, but many of them do not leave Christianity, but rather convert to another Christian denomination, in particularly to evangelicalism. Schnabel and Bock argued also that evangelicalism and Christian fundamentalism, Conservative Christianity has persisted and expanded in the United States. And according to Eric Kaufmann from Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
and University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The ...
, Christian fundamentalism is expanding in the United States.
According to study published by the missionary statistician and professor David B. Barrett of Columbia University, and professor of global Christianity, historian George Thomas Kurian, and both are work on ''World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denomination ...
'', approximately 2.7 million converting to Christianity annually from another religion, ''World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denomination ...
'' also cited that Christianity ranks at first place in net gains through religious conversion. On the other hand, demographer Conrad Hackett of Pew Research Center stated that the World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denomination ...
gives a higher estimate for percent Christian when compared to other cross-national data sets. While according to the book ''The Oxford Handbook of Religious Conversion'', which written by professor of the Christian mission, Charles E. Farhadian, and professor of psychology, Lewis Rambo, in mid-2005 approximately 15.5 million converted to Christianity from another religion, while approximately 11.7 million left Christianity, most of them becoming irreligious, resulting in a net gain of 3.8 million.
According to scholar Philip Jenkins Christianity is growing rapidly in China and some other Asian countries and sub-Saharan Africa. According to a study by a scholar Fenggang Yang from Purdue University, Christianity is "spreading among the Chinese of South-East Asia", and "Evangelical and Pentecostal Christianity is growing more quickly in China", also according to him, more than half of them have university degrees. According to a report by the Singapore Management University, more people in Southeast Asia are converting to Christianity, and these new converts are mostly Chinese business managers. According to scholar Juliette Koning and Heidi Dahles of Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam there is a "rapid expansion of charismatic Christianity from the 1980s onwards. Singapore, Mainland China, Hong Kong
Hong Kong)., Legally Hong Kong, China in international treaties and organizations. is a special administrative region of China. With 7.5 million residents in a territory, Hong Kong is the fourth most densely populated region in the wor ...
, Taiwan, Indonesia, and Malaysia are said to have the fastest-growing Christian communities and the majority of the new believers are "upwardly mobile, urban, middle-class Chinese". Asia has the second largest Pentecostal-charismatic Christians of any continent, with the number growing from 10 million to 135 million between 1970 and 2000". According to the ''Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank focused on Foreign policy of the United States, U.S. foreign policy and international relations. Founded in 1921, it is an independent and nonpartisan 501(c)(3) nonprofit organi ...
'' the "number of Chinese Protestants has grown by an average of 10 percent annually since 1979". According to scholar Todd Hartch of Eastern Kentucky University, by 2005, around 6 million Africans converted to Christianity annually. While the exact number of Dalit converts to Christianity in India is not available, scholar William R. Burrow of Colorado State University estimated that about 8% of Dalit have converted to Christianity. According to a 2021 study by the Pew Research Center, Christianity in India gained an increase from conversion, most of the Christian converts in India are former Hindus.
It has been reported also that increasing numbers of young people or educated people are becoming Christians in several countries such as China, Indonesia, Iran, Japan, Singapore
Singapore, officially the Republic of Singapore, is an island country and city-state in Southeast Asia. The country's territory comprises one main island, 63 satellite islands and islets, and one outlying islet. It is about one degree ...
, and South Korea. It has also been reported that conversion into Christianity is significantly increasing among Korean, Chinese, and Japanese in the United States. By 2012 percentage of Christians on mentioned communities was 71%, more than 30% and 37%, respectively. According to the ''World Christian Encyclopedia
''World Christian Encyclopedia'' is a reference work, with its third edition published by Edinburgh University Press in November 2019. The ''WCE'' is known for providing membership statistics for major world religions and Christian denomination ...
'', between 1965 and 1985 about 2.5 million Indonesians converted from Islam to Christianity. Many people who convert to Christianity face Persecution of Christians, persecution.
Deism
The 2001 American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS) survey estimated that between 1990 and 2001 the number of self-identifying deism, deists grew from 6,000 to 49,000, representing about 0.02% of the US population at the time.Druze
 Druze is a major religion in the Levant region. Druzites or Al-Muwaḥḥidūn are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group; the number of Druzites worldwide is between 800,000 and one million, with the vast majority residing in the Levant. Even though the faith originally developed out of Isma'ilism, Ismaili Islam, Druze do not identify as a branch of Islam and view themselves as a separate religion. The Druze faith does not accept converts to their faith, nor practice proselytism. Over the centuries a number of the Druze conversion to Christianity, Druze embraced Christianity, Islam and other religions.
The Druzites reside primarily in Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan. Syria is home to the largest Druzite community in the world, according to a study published by Columbia University, the number of Syrian Druze increased from 684,000 in 2010 to 730,000 in mid of 2018. The Lebanese Druze have the lowest fertility among all age groups after the Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians.
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2017, the Israeli Druze population growth rate of 1.4%, which is lower than the Islam in Israel, Muslim population growth rate (2.5%) and the total population growth (1.7%), but higher than the Arab Christian population growth rate (1.0%). At the end of 2017, the average age of the Israeli Druze was 27.9. About 26.3% of the Israeli Druze population are under 14 years old and about 6.1% of the Israeli Druze are 65 years and over. Since the year 2000, the Israeli Druze community has witnessed a significant decrease in Total fertility rate, fertility-rate and a significant increase in life expectancy. The fertility rate for Israeli Druze in 2017 is 2.1 children per woman, while the fertility rate among Israeli Jews, Jewish women (3.2) and Muslim women (3.4) and the fertility rate among Christianity in Israel, Israeli Christian women (1.9).
Druze is a major religion in the Levant region. Druzites or Al-Muwaḥḥidūn are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group; the number of Druzites worldwide is between 800,000 and one million, with the vast majority residing in the Levant. Even though the faith originally developed out of Isma'ilism, Ismaili Islam, Druze do not identify as a branch of Islam and view themselves as a separate religion. The Druze faith does not accept converts to their faith, nor practice proselytism. Over the centuries a number of the Druze conversion to Christianity, Druze embraced Christianity, Islam and other religions.
The Druzites reside primarily in Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Jordan. Syria is home to the largest Druzite community in the world, according to a study published by Columbia University, the number of Syrian Druze increased from 684,000 in 2010 to 730,000 in mid of 2018. The Lebanese Druze have the lowest fertility among all age groups after the Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians.
According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics in 2017, the Israeli Druze population growth rate of 1.4%, which is lower than the Islam in Israel, Muslim population growth rate (2.5%) and the total population growth (1.7%), but higher than the Arab Christian population growth rate (1.0%). At the end of 2017, the average age of the Israeli Druze was 27.9. About 26.3% of the Israeli Druze population are under 14 years old and about 6.1% of the Israeli Druze are 65 years and over. Since the year 2000, the Israeli Druze community has witnessed a significant decrease in Total fertility rate, fertility-rate and a significant increase in life expectancy. The fertility rate for Israeli Druze in 2017 is 2.1 children per woman, while the fertility rate among Israeli Jews, Jewish women (3.2) and Muslim women (3.4) and the fertility rate among Christianity in Israel, Israeli Christian women (1.9).
Hinduism
Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Hypernymy and hyponymy, umbrella term for a range of Indian religions, Indian List of religions and spiritual traditions#Indian religions, religious and spiritual traditions (Sampradaya, ''sampradaya''s) that are unified ...
is the third largest religion in the world. Hindus made up about 17% of the world's population in 2010. According to Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
99% of Hindus lived in the Indo-Pacific region in 2010. According to Pew Forum, Hindus are anticipated to continue to be concentrated primarily in the Indo-Pacific region in 2050. Hinduism is the largest religion in the countries of Religion in India, India, Religion in Nepal, Nepal, Religion in Mauritius, Mauritius and Guyana. Approximately 90% of the world's Hindus live in India. 79.8% of India's population is Hindu, accounting for about 90% of Hindus worldwide. Hinduism's 10-year growth rate is estimated at 15% (based on the period 1991 to 2001), corresponding to a yearly growth close to 2%. According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, between 2010 and 2015 "an estimated 109 million babies were born to Hindu mothers and roughly 42 million Hindus died, meaning that the natural increase in the Hindus population – i.e., the number of births minus the number of deaths – was 67 million over this period".
 According to the
According to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP) is a nonpartisan international affairs think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C., with operations in Europe, South Asia, East Asia, and the Middle East, as well as the United States. Foun ...
, Hinduism (1.52%) is one of the six fastest-growing religions in the world, with high birth rates in India being cited as the major reasons of the Hindu population growth.
Hinduism is a growing religion in countries such as Ghana, Russia, and the United States. According to 2011 census, Hinduism has become the fastest-growing religion in Australia since 2006, due to migration from India and Fiji.
Generally, the term "conversion" is not applicable to Hindu traditions. According to Arvind Sharma, Hinduism "is typically quite comfortable with multiple religious participation, multiple religious affiliations, and even with multiple religious identities." However, some Hindu groups are known for running religious conversion which has been termed as Ghar Wapsi. According to proponents of Hindutva, such as Sangh Parivar, the process is called "reconversion" of Christians and Muslims who were previously converted.
Islam
Modern growth
Islam is the fastest-growing religion in the world due to the high birth rate of Muslims across the world compared to non-Muslims. In 1990, 1.1 billion people were Muslims, while in 2010, 1.6 billion people were Muslims. According to theCarnegie Endowment for International Peace
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP) is a nonpartisan international affairs think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C., with operations in Europe, South Asia, East Asia, and the Middle East, as well as the United States. Foun ...
, as of 2007 estimated that the fastest-growing religion of the world to be Islam (1.84%), high birth rates as the reason for the growths. According to the BBC, a comprehensive American study concluded in 2009 that the number of Muslims worldwide stood at about 23% of the world's population with 60% of the world's Muslims living in Asia.
 According to the same study "globally, Muslims have the highest fertility rate, an average of 3.1 children per woman – well above replacement level (2.1)", and "in all major regions where there is a sizable Muslim population, Muslim fertility exceeds non-Muslim fertility". From 1990 to 2010, the global Muslim population increased at an average annual rate of 2.2%. By 2030 Muslims are projected to represent about 26.4% of the global population (out of a total of 7.9 billion people). According to a 2019 study by the
According to the same study "globally, Muslims have the highest fertility rate, an average of 3.1 children per woman – well above replacement level (2.1)", and "in all major regions where there is a sizable Muslim population, Muslim fertility exceeds non-Muslim fertility". From 1990 to 2010, the global Muslim population increased at an average annual rate of 2.2%. By 2030 Muslims are projected to represent about 26.4% of the global population (out of a total of 7.9 billion people). According to a 2019 study by the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
; "around the globe, Muslims have higher fertility rates than Christians on average. Muslim women's low educational attainment is a likely factor; demographers find that higher educational attainment among women is tied to lower fertility rates".
On the other hand, in 2010, the Pew Forum found "that statistical data for Muslim conversions is scarce and as per their little available information, there is no substantial net gain or loss of Muslims due to religious conversion. It also stated that "the number of people who embrace Islam and the number of those who leave Islam are roughly equal. Thus, this report excludes religious conversion as a direct factor from the projection of Muslim population growth.""The Future of the Global Muslim Population, Related Factors: Conversion", The Pew Forum on Religion and Public Life, 27 January 2011 People switching their religions will likely have no effect on the growth of the Muslim population, as the number of people who
convert to Islam
Reversion to Islam, also known within Islam as reversion, is adopting Islam as a religion or faith. Conversion requires a formal statement of the ''Shahada, shahādah'', the credo of Islam, whereby the prospective convert must state that "there i ...
is roughly similar to those who leave Islam. Another study found that the number of people who will leave Islam is 9,400,000 and the number of converts to Islam is 12,620,000 so the net gain to Islam through conversion should be 3 million between 2010 and 2050, mostly from Sub-Saharan Africa (2.9 million). The growth of Islam from 2010 to 2020 has been estimated at 1.70% due to high birthrates in Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. The report also shows that the fall in the birth rate of Muslims slowed down the growth rate from 1990 to 2010. It is due to the fall of the fertility rate in many Muslim majority countries. Despite the decline, Muslims still have the highest birth rate among the world's major religious groups. According to the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace
The Carnegie Endowment for International Peace (CEIP) is a nonpartisan international affairs think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C., with operations in Europe, South Asia, East Asia, and the Middle East, as well as the United States. Foun ...
, the World Christian Database as of 2007 has Islam as the fastest-growing religion in the world. A 2007 Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) report argued that some Muslim population projections are overestimated, as they assume that all descendants of Muslims will become Muslims even in cases of mixed parenthood.Esther Pan, Europe: Integrating Islam
',
Council on Foreign Relations
The Council on Foreign Relations (CFR) is an American think tank focused on Foreign policy of the United States, U.S. foreign policy and international relations. Founded in 1921, it is an independent and nonpartisan 501(c)(3) nonprofit organi ...
, 2005-07-13
According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, between 2010 and 2015 "an estimated 213 million babies were born to Muslim mothers and roughly 61 million Muslims died, meaning that the natural increase in the Muslim population – i.e., the number of births minus the number of deaths – was 152 million over this period", and it added small net gains through religious conversion into Islam (420,000). According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, by 2060 Muslims will remain the Major religious groups#Largest religious groups, second world's largest religion; and if current trends continue, the number of Muslims will reach 2.9 billion (or 31.1%).
It was reported in 2013 that around 5,000 British people convert to Islam every year, with most of them being women. According to an earlier 2001 census, surveys found that there was an increase of 60,000 conversions to Islam in the United Kingdom. Many converts to Islam said that they suffered from hostility from their families after converting. According to a report by CNN, "Islam has drawn converts from all walks of life, most notably African-Americans". Studies estimated about 30,000 converting to Islam annually in the United States. According to The New York Times, an estimated 25% of American Muslims are converts, these converts are mostly African American. According to The Huffington Post, "observers estimate that as many as 20,000 Americans convert to Islam annually.", most of them are women and African-Americans. Experts say that conversions to Islam have doubled in the past 25 years in France, among the six million Muslims in France, about 100,000 are converts. On the other hand, according to Pew Research, the number of American converts to Islam is roughly equal to the number of American Muslims who leave Islam and this is unlike other religions in the United States where the number of those who leave these religions is greater than the number of those who convert to it, and most people who leave Islam become unaffiliated, according to same study ex-Muslims were more likely to be Christians compare to ex-Hindus or ex-Jews.
 Resurgent Islam is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. The Vatican's 2008 yearbook of statistics revealed that for the first time, Islam has outnumbered the Roman Catholics globally. It stated that, "Islam has overtaken Roman Catholicism as the biggest single religious denomination in the world", and stated that, "It is true that while Muslim families, as is well known, continue to make a lot of children, Christian ones on the contrary tend to have fewer and fewer". According to ''Foreign Policy'', high birth rates were cited as the reason for the Muslim population growth. With 3.1 children per woman, Muslims have higher fertility levels than the world's overall population between 2010 and 2015. High fertility is a major driver of projected Muslim population growth around the world and in particular regions. Between 2010 and 2015, with exception of the Middle East and North Africa, Muslim fertility of any other region in the world was higher than the rate for the region as a whole. While Muslim birth rates are expected to experience a decline, it will remain above replacement level and higher fertility than the world's overall by 2050. As per U.N.'s global population forecasts, as well as the
Pew Research projections, over time fertility rates generally converge toward the
replacement level. Globally, Muslims were younger (median age of 23) than the overall population (median age of 28) as of 2010. While decline of Muslim birth rates in coming years have also been well documented. According to David Ignatius, there is major decline in Muslim fertility rates as pointed out by Nicholas Eberstadt. Based on the data from 49 Muslim-majority countries and territories, he found that Muslims' birth rate has significantly dropped for 41% between 1975 and 1980 to 2005–10 while the global population decline was 33% during that period. It also stated that over a 50% decline was found in 22 Muslim countries and over a 60% decline in Iran, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Bangladesh, Tunisia, Libya, Albania, Qatar and Kuwait.
Resurgent Islam is one of the most dynamic religious movements in the contemporary world. The Vatican's 2008 yearbook of statistics revealed that for the first time, Islam has outnumbered the Roman Catholics globally. It stated that, "Islam has overtaken Roman Catholicism as the biggest single religious denomination in the world", and stated that, "It is true that while Muslim families, as is well known, continue to make a lot of children, Christian ones on the contrary tend to have fewer and fewer". According to ''Foreign Policy'', high birth rates were cited as the reason for the Muslim population growth. With 3.1 children per woman, Muslims have higher fertility levels than the world's overall population between 2010 and 2015. High fertility is a major driver of projected Muslim population growth around the world and in particular regions. Between 2010 and 2015, with exception of the Middle East and North Africa, Muslim fertility of any other region in the world was higher than the rate for the region as a whole. While Muslim birth rates are expected to experience a decline, it will remain above replacement level and higher fertility than the world's overall by 2050. As per U.N.'s global population forecasts, as well as the
Pew Research projections, over time fertility rates generally converge toward the
replacement level. Globally, Muslims were younger (median age of 23) than the overall population (median age of 28) as of 2010. While decline of Muslim birth rates in coming years have also been well documented. According to David Ignatius, there is major decline in Muslim fertility rates as pointed out by Nicholas Eberstadt. Based on the data from 49 Muslim-majority countries and territories, he found that Muslims' birth rate has significantly dropped for 41% between 1975 and 1980 to 2005–10 while the global population decline was 33% during that period. It also stated that over a 50% decline was found in 22 Muslim countries and over a 60% decline in Iran, Oman, the United Arab Emirates, Algeria, Bangladesh, Tunisia, Libya, Albania, Qatar and Kuwait.
 According to the religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, between 2010 and 2050 modest net gains through religious conversion are expected for Muslims (3 million) and most of the net gains through religious conversion for Muslims found in Sub Saharan Africa (2.9 million). The study also reveals that, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate among Muslims by 2050 there will be near parity between Muslims (2.8 billion, or 30% of the population) and Christians (2.9 billion, or 31%), possibly for the first time in history. While both religions will grow but Muslim population will exceed the Christian population and by 2100, Muslim population (35%) will be 1% more than the Christian population (34%). By the end of 2100 Muslims are expected to outnumber Christians. According to the same study, Muslims population growth is twice of world's overall population growth due to young age and relatively high fertility rate and as a result Muslims are projected to rise to 30% (2050) of the world's population from 23% (2010).
While the total Fertility Rate of Muslims in North America is 2.7 children per woman in the 2010 to 2015 period, well above the regional average (2.0) and the replacement level (2.1). Europe's Muslim population also has higher fertility (2.1) than other religious groups in the region, well above the regional average (1.6). A new study of Population Reference Bureau by demographers Charles Westoff and Tomas Frejka suggests that the fertility gap between Muslims and non-Muslims is shrinking and although the Muslim immigrants do have more children than other Europeans their fertility tends to decline over time, often faster than among non-Muslims.
Generally, there are few reports about how many people leave Islam in Muslim majority countries. The main reason for this is the social and legal repercussions associated with Apostasy in Islam, leaving Islam in many Muslim majority countries, up to and including the death penalty for apostasy. On the other hand, the increasingly large Ex-Muslim, ex-Muslim communities in the Western world that adhere to no religion have been well documented. A 2007 Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) report argued that some Muslim population projections are overestimated, as they assume that all descendants of Muslims will become Muslims even in cases of mixed parenthood. Equally, Darren E. Sherkat questioned in ''Foreign Affairs'' whether some of the Muslim growth projections are accurate as they do not take into account the increasing number of non-religious Muslims. Quantitative research is lacking, but he believes the European trend mirrors the American: data from the General Social Survey in the United States show that 32 percent of those raised Muslim no longer embrace Islam in adulthood, and 18 percent hold no religious identification. Many Muslims who leave Islam face social rejection or imprisonment and sometimes murder or other penalties. According to
According to the religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, between 2010 and 2050 modest net gains through religious conversion are expected for Muslims (3 million) and most of the net gains through religious conversion for Muslims found in Sub Saharan Africa (2.9 million). The study also reveals that, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate among Muslims by 2050 there will be near parity between Muslims (2.8 billion, or 30% of the population) and Christians (2.9 billion, or 31%), possibly for the first time in history. While both religions will grow but Muslim population will exceed the Christian population and by 2100, Muslim population (35%) will be 1% more than the Christian population (34%). By the end of 2100 Muslims are expected to outnumber Christians. According to the same study, Muslims population growth is twice of world's overall population growth due to young age and relatively high fertility rate and as a result Muslims are projected to rise to 30% (2050) of the world's population from 23% (2010).
While the total Fertility Rate of Muslims in North America is 2.7 children per woman in the 2010 to 2015 period, well above the regional average (2.0) and the replacement level (2.1). Europe's Muslim population also has higher fertility (2.1) than other religious groups in the region, well above the regional average (1.6). A new study of Population Reference Bureau by demographers Charles Westoff and Tomas Frejka suggests that the fertility gap between Muslims and non-Muslims is shrinking and although the Muslim immigrants do have more children than other Europeans their fertility tends to decline over time, often faster than among non-Muslims.
Generally, there are few reports about how many people leave Islam in Muslim majority countries. The main reason for this is the social and legal repercussions associated with Apostasy in Islam, leaving Islam in many Muslim majority countries, up to and including the death penalty for apostasy. On the other hand, the increasingly large Ex-Muslim, ex-Muslim communities in the Western world that adhere to no religion have been well documented. A 2007 Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) report argued that some Muslim population projections are overestimated, as they assume that all descendants of Muslims will become Muslims even in cases of mixed parenthood. Equally, Darren E. Sherkat questioned in ''Foreign Affairs'' whether some of the Muslim growth projections are accurate as they do not take into account the increasing number of non-religious Muslims. Quantitative research is lacking, but he believes the European trend mirrors the American: data from the General Social Survey in the United States show that 32 percent of those raised Muslim no longer embrace Islam in adulthood, and 18 percent hold no religious identification. Many Muslims who leave Islam face social rejection or imprisonment and sometimes murder or other penalties. According to Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ...
professor Robert D. Putnam, there is increasing numbers of Americans who are leaving their faith and becoming unaffiliated and the average Iranian American is slightly less religious than the average American. According to Public Affairs Alliance of Iranian Americans, the number of Iranian Americans Muslims decreased from 42% in 2008 to 31% in 2012 according to a telephone survey around the Los Angeles region. A June 2020 online survey found a much smaller percentage of Iranians stating they believe in Islam, with half of those surveyed indicating they had lost their religious faith. The poll, conducted by the Netherlands-based GAMAAN (Group for Analyzing and Measuring Attitudes in Iran), using online polling to provide greater anonymity for respondents, surveyed 50,000 Iranians and found 32% identified as Shia, 5% as Sunni and 3% as Sufi Muslim. A survey conducted by Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
in 2017 found that conversion has a negative impact on the growth of the Islam in Europe, Muslim population in Europe, with roughly 160,000 more people leaving Islam than converting into Islam between 2010 and 2016.
By 2010 an estimated 44 million Muslims were living in Europe (6%), up from 4.1% in 1990. By 2030, Muslims are expected to make up 8% of Europe's population including an estimated 19 million in the EU (3.8%),Pew Forum, The Future of the Global Muslim Population, January 2011,
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
notes that "the data that we have isn't pointing in the direction of 'Eurabia' at all", and predicts that the percentage of Muslims is estimated to rise to 8% in 2030, due to immigration and above-average birth rates. And only two western European countries – France and Belgium – will become around 10 percent Muslim, by 2030. According to Justin Vaïsse the fertility rate of Muslim immigrants declines with integration. He further points out that Muslims are not a monolithic or cohesive group, Most academics who have analysed the demographics dismiss the predictions that the EU will have Muslim majorities.
It is completely reasonable to assume that the overall Muslim population in Europe will increase, and Muslim citizens have and will have a significant impact on European life. The prospect of a homogeneous Muslim community per se, or a Muslim majority in Europe is however out of the question.Summary about Europe0. Retrieved 18 September 2012. Eric Kaufman of
University of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a collegiate university, federal Public university, public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The ...
denied the claims of Eurabia. According to him, Muslims will be a significant minority rather than majority in Europe and as per their projections for 2050 in the Western Europe, there will be 10–15 per cent Muslim population in high immigration countries such as Germany, France and the UK. Eric Kaufman also argue that the main reason why Islam is expanding along with other religions, is not because of conversion to Islam, but primarily to the nature of the religion, as he calls it "pro-natal", where Muslims tend to have more children. Doug Saunders states that by 2030 Muslims and Non-Muslims birth rates will be equal in Germany, Greece, Spain and Denmark without taking account of the Muslims immigration to these countries. He also states that Muslims & Non-Muslims fertility rate difference will decrease from 0.7 to 0.4 and this different will continue to shrink as a result of which Muslims and non-Muslims fertility rate will be identical by 2050.
It is often reported from various sources, including the German domestic intelligence service (Bundesnachrichtendienst), that Salafism is the fastest-growing Islamic movement in the world.
 In 2010 Islam in Asia, Asia was home for (62%) of the world's Muslims, and about (20%) of the world's Muslims lived in the Middle East and North Africa, (16%) in Sub Saharan Africa, and 2% in Europe. By 2050 Asia will be home to (52.8%) of the world's Muslims, and about (24.3%) of the world's Muslims will live in Sub Saharan Africa, (20%) the Middle East and North Africa, and 2% in Europe. As per the Pew Research study, Muslim populations will grow in absolute number in all regions of the world between 2010 and 2050. The Muslim population in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to reach nearly 1.5 billion by 2050, up from roughly 1 billion in 2010. The growth of Muslims is also expected in the Middle East-North Africa region, It is projected to increase from about 300 million in 2010 to more than 550 million in 2050. Besides, the Islam in Africa, Muslim population in sub-Saharan Africa is forecast to grow from about 250 million in 2010 to nearly 670 million in 2050 which is more than double. The absolute number of Muslims is also expected to increase in regions with smaller Muslim populations such as Europe and North America, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate. In Europe Muslim population will be nearly double (from 5.9% to 10.2%). In Islam in the Americas, North America, it will grow 1% to 2%. In Asia Pacific region, Muslims will surpass the Hindus by the time. In Latin America and Caribbean Muslim population will stay 0.1% by 2050.
In 2010 Indonesia, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nigeria was home for (47.8%) of the world's Muslims.
In 2010 Islam in Asia, Asia was home for (62%) of the world's Muslims, and about (20%) of the world's Muslims lived in the Middle East and North Africa, (16%) in Sub Saharan Africa, and 2% in Europe. By 2050 Asia will be home to (52.8%) of the world's Muslims, and about (24.3%) of the world's Muslims will live in Sub Saharan Africa, (20%) the Middle East and North Africa, and 2% in Europe. As per the Pew Research study, Muslim populations will grow in absolute number in all regions of the world between 2010 and 2050. The Muslim population in the Asia-Pacific region is expected to reach nearly 1.5 billion by 2050, up from roughly 1 billion in 2010. The growth of Muslims is also expected in the Middle East-North Africa region, It is projected to increase from about 300 million in 2010 to more than 550 million in 2050. Besides, the Islam in Africa, Muslim population in sub-Saharan Africa is forecast to grow from about 250 million in 2010 to nearly 670 million in 2050 which is more than double. The absolute number of Muslims is also expected to increase in regions with smaller Muslim populations such as Europe and North America, due to young age & relatively high fertility rate. In Europe Muslim population will be nearly double (from 5.9% to 10.2%). In Islam in the Americas, North America, it will grow 1% to 2%. In Asia Pacific region, Muslims will surpass the Hindus by the time. In Latin America and Caribbean Muslim population will stay 0.1% by 2050.
In 2010 Indonesia, India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Nigeria was home for (47.8%) of the world's Muslims.
Historical growth within the Middle East
There exist different views among scholars about the spread of Islam. Islam began in Arabia and from 633 AD until the late 10th century it was spread through Early Muslim conquests, conquests, far-reaching trade and missionary activity.Gabars Gabars
''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2007. Britannica Concise Encyclopedia. 29 May 2007. and also with Jewish communities in the medieval Arab world) some scholars indicate that some Muslim rulers in India did not consistently collect the jizya (poll tax) from Dhimmis. Under Islamic law, Muslims are required to pay Zakat, one of the five pillars of Islam. Muslims take 2.5% out of their salaries and use the funds give to the needy. Since non-Muslims are not required to pay Zakat nor entitled to benefit from it, they had to support their own poor and in addition they had to pay Jizya if they wanted the same protections the Muslims received. In India, Islam was brought by various traders and rulers from Afghanistan and other places. According to other scholars, many converted for a whole host of reasons, the main statement of which was evangelization by Muslims, though there were several instances where some were pressured to convert owing to internal violence and friction between the Christian and Muslim communities, according to historian Philip Jenkins. However John L. Esposito, a scholar on the subject of Islam in ''The Oxford History of Islam'' states that the spread of Islam "was often peaceful and sometimes even received favorably by Christians". In a 2008 conference on religion at Yale University's ''The MacMillan Center Initiative on Religion, Politics, and Society'' which hosted a speech from Hugh N. Kennedy, Hugh Kennedy, he stated forced conversions played little part in the history of the spread of the faith. However, the poll tax known as Jizyah may have played a part in converting people over to Islam but as ''Britannica'' notes "The rate of taxation and methods of collection varied greatly from province to province and were greatly influenced by local pre-Islamic customs" and there were even cases when Muslims had the tax levied against them, on top of Zakat. Hugh N. Kennedy, Hugh Kennedy has also discussed the Jizyah issue and stated that Muslim governments discouraged conversion but were unable to prevent it.Conference on Religion and Violence. 16 February 2008.
His speech can be found here:
There were...clear reasons why Muslim governments would not want to encourage conversion to Islam. They were sometimes effectively unable to prevent conversion but they were certainly not going to use force to achieve it. (Page 5)
Judaism
Today, the majority of the world's Jewish population is concentrated in two countries, the United States and Israel, in 2013, the United States and Israel were collectively home to more than 80 percent of the global Jewish population, each country having approximately 41 percent of the world's Jews. Israel is the only country with a Jewish population that is consistently growing through natural population growth and extensive immigration, although the Jewish populations of other countries, in Europe and North America, have recently increased through immigration. In the Jewish Diaspora, Diaspora, in almost every country the Jewish population in general is either declining or steady, but Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox and Haredi Jewish communities, whose members often shun birth control for religious reasons, have experienced rapid population growth. Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox and Conservative Judaism discourage proselytism to non-Jews, but many Jewish groups have tried to reach out to the assimilated Jewish communities of the Diaspora in order for them to reconnect to their Jewish roots. Additionally, while in principle Reform Judaism favors seeking new members for the faith, this position has not translated into active proselytism, instead of taking the form of an effort to reach out to non-Jewish spouses of Interfaith marriage in Judaism, intermarried couples. Studies have shown that Haredi Judaism, Haredi Jews population is rising rapidly due to the young age and very high fertility-rate, especially in Israel.Ari Paltiel, Michel Sepulchre, Irene Kornilenko, Martin MaldonadoLong‐Range Population Projections for Israel: 2009‐2059
Israeli Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 2014-04-21. The overall growth rate of Israeli Jews, Jews in Israel is 1.7% annually. The Jewish diaspora, diaspora countries, by contrast, have low Jewish birth rates, an increasingly elderly age composition, and a negative balance of people leaving Judaism versus those joining. There is also a trend of Orthodox movements reaching out to Jewish secularism, secular Jews in order to give them a stronger Jewish identity so there is less chance of Intermarriage in Judaism, intermarriage. As a result of the efforts by these and other Jewish groups over the past 25 years, there has been a trend (known as the Baal teshuva movement) for secular Jews to become more religiously observant, though the demographic implications of the trend are unknown. Additionally, there is also a growing rate of conversion to Jews by Choice of gentiles who make the decision to head in the direction of becoming Jews.
 Rates of Interfaith marriage, interreligious marriage vary widely: In the United States, it is just under 50 percent, in the United Kingdom, around 53 percent; in France; around 30 percent, and in Australia and Mexico, as low as 10 percent. In the United States, only about a third of children from intermarriages affiliate with Jewish religious practice. The result is that most countries in the Diaspora have steady or slightly declining religiously Historical Jewish population comparisons, Jewish populations as Jews continue to assimilate into the countries in which they live.
In 1939, the core Jewish population reached its historical peak of 17 million (0.8% of the global population). Because of the Holocaust, the number had been reduced to 11 million by the end of 1945. The population grew again to around 13 million by the 1970s, but has since recorded near-zero growth until around 2005 due to low fertility rates and to Jewish assimilation, assimilation. Since 2005, the world's Jewish population has been growing modestly at a rate of around 0.78% (in 2013). This increase primarily reflects the rapid growth of Haredi and some Orthodox Jews, Orthodox sectors, who are becoming a growing proportion of Jews.
According to the
Rates of Interfaith marriage, interreligious marriage vary widely: In the United States, it is just under 50 percent, in the United Kingdom, around 53 percent; in France; around 30 percent, and in Australia and Mexico, as low as 10 percent. In the United States, only about a third of children from intermarriages affiliate with Jewish religious practice. The result is that most countries in the Diaspora have steady or slightly declining religiously Historical Jewish population comparisons, Jewish populations as Jews continue to assimilate into the countries in which they live.
In 1939, the core Jewish population reached its historical peak of 17 million (0.8% of the global population). Because of the Holocaust, the number had been reduced to 11 million by the end of 1945. The population grew again to around 13 million by the 1970s, but has since recorded near-zero growth until around 2005 due to low fertility rates and to Jewish assimilation, assimilation. Since 2005, the world's Jewish population has been growing modestly at a rate of around 0.78% (in 2013). This increase primarily reflects the rapid growth of Haredi and some Orthodox Jews, Orthodox sectors, who are becoming a growing proportion of Jews.
According to the Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
published on 2010, religious conversion may have little impact on the Jewish population between 2010 and 2050; Jews are expected to lose 0.3 million adherents, between 2010 and 2050. According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, over the next four decades the number of Jews around the world is expected to increase from 14.2 million in 2015 to 16.3 million in 2060.
Baháʼí Faith

 As of around 2020, there were about 8 million Bahá'ís in the world. In 2013, two scholars of demography wrote that, "The Baha'i Faith is the only religion to have grown faster in every United Nations region over the past 100 years than the general population; Bahaʼi [sic] was thus the fastest-growing religion between 1910 and 2010, growing at least twice as fast as the population of almost every UN region."
The largest proportions of the total world Bahá'í population were found in sub-Saharan Africa (29.9%) and South Asia (26.8%), followed by Southeast Asia (12.7%) and Latin America (12.2%). Lesser populations are found in North America (7.6%) and the Middle East/North Africa (6.2%), while the smallest populations in Europe (2.0%), Australasia (1.6%), and Northeast Asia (0.9%). In 2015, the internationally recognized religion was the second-largest international religion in Iran, Panama, Belize, Bolivia, Zambia, and Papua New Guinea; and the third-largest in Chad, and Kenya.
From the Bahá'í Faith's origins in the 19th century until the 1950s, the vast majority of Baháʼís were found in Iran; converts from outside Iran were mostly found in India and the Western world. From having roughly 200,000 Baháʼís in 1950, the religion grew to having over 4 million by the late 1980s, with a widespread international distribution. Most of the growth in the late 20th century was seeded out of North America by means of the planned migration of individuals. Yet, rather than being a cultural spread from either Iran or North America, in 2001, sociologist David Barrett wrote that the Baháʼí Faith is, "A world religion with no racial or national focus". However, the growth has not been even. From the late 1920s to the late 1980s the religion was harassed and banned in the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc, and then again from the 1970s into the 1990s across some countries in sub-Saharan Africa. The most intense opposition has been in Iran and neighboring Shia Islam, Shia-majority countries, considered by some scholars and watch agencies as a case of attempted genocide. Meanwhile in other times or places the religion has experienced surges in growth. Before it was banned in certain countries, the religion "hugely increased" in sub-Saharan Africa. In 1989 the Universal House of Justice named Bolivia, Bangladesh, Haiti, India, Liberia, Peru, the Philippines, and Taiwan as countries where growth in the religion had been notable in the previous decades. Bahá'í sources state "more than five million" Bahá'ís in 1991-2. However, since around 2001 the Universal House of Justice has prioritized statistics of the community by their levels of activity rather than simply their population of avowed adherents or numbers of local assemblies.
Because Bahá'ís do not represent the majority of the population in any country, and most often represent only a tiny fraction of countries' total populations, there are problems of under-reporting. In addition, there are examples where the adherents have their highest density among minorities in societies who face their own challenges.
As of around 2020, there were about 8 million Bahá'ís in the world. In 2013, two scholars of demography wrote that, "The Baha'i Faith is the only religion to have grown faster in every United Nations region over the past 100 years than the general population; Bahaʼi [sic] was thus the fastest-growing religion between 1910 and 2010, growing at least twice as fast as the population of almost every UN region."
The largest proportions of the total world Bahá'í population were found in sub-Saharan Africa (29.9%) and South Asia (26.8%), followed by Southeast Asia (12.7%) and Latin America (12.2%). Lesser populations are found in North America (7.6%) and the Middle East/North Africa (6.2%), while the smallest populations in Europe (2.0%), Australasia (1.6%), and Northeast Asia (0.9%). In 2015, the internationally recognized religion was the second-largest international religion in Iran, Panama, Belize, Bolivia, Zambia, and Papua New Guinea; and the third-largest in Chad, and Kenya.
From the Bahá'í Faith's origins in the 19th century until the 1950s, the vast majority of Baháʼís were found in Iran; converts from outside Iran were mostly found in India and the Western world. From having roughly 200,000 Baháʼís in 1950, the religion grew to having over 4 million by the late 1980s, with a widespread international distribution. Most of the growth in the late 20th century was seeded out of North America by means of the planned migration of individuals. Yet, rather than being a cultural spread from either Iran or North America, in 2001, sociologist David Barrett wrote that the Baháʼí Faith is, "A world religion with no racial or national focus". However, the growth has not been even. From the late 1920s to the late 1980s the religion was harassed and banned in the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc, and then again from the 1970s into the 1990s across some countries in sub-Saharan Africa. The most intense opposition has been in Iran and neighboring Shia Islam, Shia-majority countries, considered by some scholars and watch agencies as a case of attempted genocide. Meanwhile in other times or places the religion has experienced surges in growth. Before it was banned in certain countries, the religion "hugely increased" in sub-Saharan Africa. In 1989 the Universal House of Justice named Bolivia, Bangladesh, Haiti, India, Liberia, Peru, the Philippines, and Taiwan as countries where growth in the religion had been notable in the previous decades. Bahá'í sources state "more than five million" Bahá'ís in 1991-2. However, since around 2001 the Universal House of Justice has prioritized statistics of the community by their levels of activity rather than simply their population of avowed adherents or numbers of local assemblies.
Because Bahá'ís do not represent the majority of the population in any country, and most often represent only a tiny fraction of countries' total populations, there are problems of under-reporting. In addition, there are examples where the adherents have their highest density among minorities in societies who face their own challenges.
Nonreligious
In terms of absolute numbers, irreligion appears to be increasing (along with secularization generally). (See the Demographics of atheism#Geographic distribution, geographic distribution of atheism.) According toPew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey in 2012, religiously unaffiliated (include agnostic and atheist) make up about 18.2% of Europe's population, and they make up the majority of the population in only two European countries: Czech Republic (76%) and Estonia (60%). According to a 2017 Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
survey, between 2010 and 2015 "an estimated 68 million babies were born to religiously unaffiliated mothers and roughly 42 million religiously unaffiliated died, meaning that the natural increase in the religiously unaffiliated population – i.e., the number of births minus the number of deaths – was 26 million over this period". As for religious conversion, the religiously unaffiliated is expected to have the largest net gains through religious conversion between 2010 and 2050, notably on Europe and Americas. However, religiously unaffiliated is expected to grow slightly due to a decrease in the fertility rate among the religiously unaffiliated population.
The American Religious Identification Survey gave nonreligious groups the largest gain in terms of absolute numbers: 14.3 million (8.4% of the population) to 29.4 million (14.1% of the population) for the period 1990–2001 in the U.S.American Religious Identification Survey, Full PDF DocumentThe Graduate Center of the City University of New York A 2012 study by the Pew Research Center, Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life reports, "The number of Americans who do not identify with any religion continues to grow at a rapid pace. One-fifth of the U.S. public – and a third of adults under 30 – are religiously unaffiliated today, the highest percentages ever in Pew Research Center polling." A similar pattern has been found in other countries such as Australia, Canada, and Mexico. According to statistics in Canada, the number of "Nones" increased by about 60% between 1985 and 2004. In Australia, census data from the Australian Bureau of Statistics give "no religion" the largest gains in absolute numbers over the 15 years from 1991 to 2006, from 2,948,888 (18.2% of the population that answered the question) to 3,706,555 (21.0% of the population that answered the question). According to INEGI, in Mexico, the number of atheists grows annually by 5.2%, while the number of Catholics grows by 1.7%. In New Zealand, 39% of the population are irreligious, making it the country with the largest irreligious population percentage in the Oceania region. According to a religious forecast for 2050 by Pew Research Center, the percentage of the world's population that is unaffiliated or nonreligious is expected to drop, from 16% of the world's total population in 2010 to 13% in 2050. The decline is largely due to the advanced age (median age of 34) and low fertility among unaffiliated or Nonreligious (1.7 children per woman in the 2010–2015 period). Sociologist Phil Zuckerman's global studies on atheism have indicated that global atheism may be in decline due to irreligious countries having the lowest birth rates in the world and religious countries having higher birth rates in general. According to Pew Research Center, Pew Forum on Religion & Public Life, by 2050 unaffiliated or nonreligious are expected to account for 27% of North America total population (up from 17.1% as in 2010), and 23% of Europe total population (up from 18% as in 2010). The religiously unaffiliated are stationed largely in the Asia-Pacific region, where 76% resided in that region in 2010, and is expected to be 68% by 2050. The share of the global unaffiliated population living in Europe is projected to grow from 12% in 2010 to 13% in 2050. The proportion of the global religiously unaffiliated living in North America will rise from 5% in 2010, to 9% in 2050. According to the Pew Research Center, religious conversion may have a modest impact on religiously unaffiliated population between 2010 and 2050; religiously unaffiliated are expected to gain 61 million adherents. The largest net movement is expected to be into the religiously unaffiliated category between 2010 and 2050.
Sikhism
Sikhism was founded by Guru Nanak in the 15th century. The religion began in Punjab, the region of Punjab in easternPakistan
Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of over 241.5 million, having the Islam by country# ...
and Northwest India. Today, India is home to the largest Sikh population with 1.7% of its population, or about 20 million people identifying as Sikh. Within India, a majority of Sikhs live in the Punjab, India, state of Punjab. Outside of India, the largest Sikh communities are in the Anglosphere, core Anglosphere, with around 771,790 in Sikhism in Canada, Canada (2.1% Sikh), 524,529 in the Sikhism in the United Kingdom, United Kingdom (0.8% Sikh), 280,000 in the Sikhism in the United States, United States (0.08% Sikh), 210,400 in Sikhism in Australia, Australia (0.8% Sikh), and 40,908 in Sikhism in New Zealand, New Zealand (0.9% Sikh).
Primarily for socio-economic reasons (Sikhs being the wealthiest and most educated of India's Religion in India, four major religious groups), Sikhism in India, Indian Sikhs have the lowest adjusted growth rate of any major religious group in India, at 8.4% per decade (from 2001 to 2011), compared to the national rate of 17.7% per decade. Sikhs have the lowest fertility rate amongst India's four major religious groups, at 1.6 children per woman in 2019-20. The Sikh population has the lowest gender balance in India, with only 903 women per 1,000 men according to the 2011 Indian census, although the sex ratio at birth for Indian Sikhs has rapidly improved from 130 male births per 100 female births in 2001 to 110 male births per 100 female births in 2019-21, now only slightly above the average for India as a whole (108 male births per 100 female births). In contrast to the religion's slowing growth in India, Sikhism is the fastest growing religion in Canada, Australia and New Zealand.
Johnson and Barrett (2004) estimate that the global Sikh population increases annually by 392,633 (1.7% per year, based on 2004 figures); this percentage includes births, deaths, and conversions. The estimated world's Sikh population was over 30 million in 2020, and it will reach 42 million by 2050. It is expected to increase up to 62 million by 2100, given that the anticipated growth rate of 1.7% per year and adding at least 400,000 followers annually. By 2050, according to Pew research center based on growth rate of current Sikh population between (2001–2011), India will have 27,129,086 Sikhs by half-century which will be more than that of any country including the Western world.
Wicca
The American Religious Identification Survey gives Wicca an average annual growth of 143% for the period 1990 to 2001 (from 8,000 to 134,000 – ''U.S. data'' / similar for Canada & Australia). According to Anne Elizabeth Wynn of ''The Statesman'', "The two most recent American Religious Identification Surveys declare Wicca, one form of paganism, as the fastest growing spiritual identification in America". Mary Jones says Wicca is one of the fastest-growing religions in the United States as well. Wicca, which is largely a "Pagan" religion primarily attracts followers of nature-based religions in, as an example, the Southeast Valley region of the Phoenix, Arizona metropolitan area.Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism ( ), also called Mazdayasnā () or Beh-dīn (), is an Iranian religions, Iranian religion centred on the Avesta and the teachings of Zoroaster, Zarathushtra Spitama, who is more commonly referred to by the Greek translation, ...
was founded during the early Persian Empire in the 6th century BCE by Zoroaster, Zarathustra. It served as the state religion of the History of Iran, ancient Iranian empires for more than a millennium, from around 600 BCE to 650 CE, but Islamization of Iran, declined from the 7th century onwards following the Muslim conquest of Persia of 633–654. Zoroastrianism declined as forced conversion increased with the rise of Islam. From the 10th century onwards,, Volume 2 Zoroastrians emigrated to Gujarat, India where they found asylum from unjust persecutions and since then are called Parsi, since Indians called Persia Faras and hence named them Parsi. Recent estimates place the current number of Zoroastrians at around 110,000–120,000, at most with the majority living in India, Iran, and North America; their number has been thought to be declining.
India has the world's largest Zoroastrian population who are called Parsis. According to the 2011 Census of India, there are 57,264 Parsis in India. According to the National Commission for Minorities, there are a "variety of causes that are responsible for this steady decline in the population of the community", the most significant of which were childlessness and migration. Demographic trends project that by the year 2020 the Parsis will number only 23,000. The Parsis will then cease to be called a community and will be labeled a 'tribe'. One-fifth of the decrease in population is attributed to migration. A slower birthrate than deathrate accounts for the rest: as of 2001, Parsis over the age of 60 make up for 31% of the community. Only 4.7% of the Parsi community are under 6 years of age, which translates to 7 births per year per 1,000 individuals. Concerns have been raised in recent years over the rapidly declining population of the Parsi community in India.
There has been recent conversions of Kurds from Islam to Zoroastrianism in Kurdistan for different reasons, including a sense of national and/or ethnic identity or for recent conflicts with radical Muslims, which had been enthusiastically received by Zoroastrians worldwide.
The number of Kurdish Zoroastrians, along with those of non-ethnic converts, has been estimated differently. The Zoroastrian Representative of the Kurdistan Regional Government in Iraq has said that as many as 14,000 people in Iraqi Kurdistan have converted to Zoroastrianism recently, with community leaders repeating this and speculating that even more Zoroastrians in the region are practicing their faith secretly. However, this has not been confirmed by independent sources.
Overall statistics
Data collection
Statistics on religious adherence are difficult to gather and often contradictory; statistics for the change of religious adherence are even more so, requiring multiple surveys separated by many years using the same data gathering rules. This has only been achieved in rare cases, and then only for particular countries, such as the American Religious Identification Survey in the United States, or census data from Australia (which has included a voluntary religious question since 1911).Historical growth
The World Religion Database (WRD) is a peer-reviewed database of international religious statistics based on research conducted at the Institute on Culture, Religion & World Affairs atBoston University
Boston University (BU) is a Private university, private research university in Boston, Massachusetts, United States. BU was founded in 1839 by a group of Boston Methodism, Methodists with its original campus in Newbury (town), Vermont, Newbur ...
. It is published by Brill Publishers, Brill and is the most comprehensive database of religious demographics available to scholars, providing data for all of the world's countries. Adherence data is largely compiled from census and surveys. The database groups adherents into 18 broadly defined categories: Agnostics, Atheists, Baháʼís, Buddhists, Chinese folk-religionists, Christians, Confucianists, Daoists, Ethnoreligionists, Hindus, Jains, Jews, Muslims, New Religionists, Shintoists, Sikhs, Spiritists, and Zoroastrians. The WRD is edited by demographers Todd M. Johnson and Brian J. Grim.
Future change
Projections of future religious adherence are based on assumptions that trends, total fertility rates, life expectancy, political climate, conversion rates, secularization, etc. will continue. Such forecasts cannot be validated empirically and are contentious, but are useful for comparison.Todd M. JohnsonReligious Projections for the Next 200 Years
fro
World Network of Religious Futurists
/ref>
Future change by conversion
According to thePew Research Center
The Pew Research Center (also simply known as Pew) is a nonpartisan American think tank based in Washington, D.C. It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the world. It ...
published in 2010, religious conversion may have little impact on religious demographics between 2010 and 2050. Christianity is expected to lose a net of 66 million adherents mostly to religiously unaffiliated, while religiously unaffiliated are expected to gain 61 million adherents. Islam is expected to gain 3.2 million followers, while Buddhists and Jews are expected to lose 2.9 million and 0.3 million adherents, respectively.
The largest net gains for the religiously unaffiliated between 2010 and 2050 are expected in North America (+26 million), Europe (+24 million), Latin America (+6 million), and the Asia-Pacific, Asia-Pacific region (4 million). Islam is projected to have a net gain of followers in Sub-Saharan Africa (+2.9 million) and Asia-Pacific (+0.95 million), but net loss of followers in North America (-0.58 million) and Europe (-0.06 million). Christianity is expected to have the largest net loss of followers between 2010 and 2050 in North America (-28 million), Europe (-24 million), Latin America and the Caribbean (-9.5 million), sub-Saharan Africa (-3 million), and Asia-Pacific (2.4 million).
Only in recent decades have surveys begun to measure changes in religious identity among individuals. Religious switching is a sensitive topic in India, and carries social and legal repercussions including the death penalty for apostasy in Muslim-majority countries. In China it is difficult to project rates at which Christianity, Islam and Buddhism are gaining converts, nor what are the retention rates among converts.
These forecasts lack reliable data on religious conversion in China, but according to media reports and expert assessments, it is possible that the rapid growth of Christianity in China may maintain, or even increase, the current numerical advantage of Christianity as the largest religion in the world and may negatively affect the growth of the Religiously Unaffiliated. This scenario (Chinese scenario) is based primarily on sensitivity tests.
According to Pew Research Center surveys of nearly 80,000 people across 36 countries, individuals raised as Christians or Buddhists are more likely to abandon their religion later in life, often becoming unaffiliated and not adhering to any faith. In contrast, religions such as Hinduism and Islam have not been significantly affected by religious switching. According to the study, although these figures indicate religious trends in the 36 countries surveyed, they may not accurately represent the global population as a whole.
In nearly all of the 27 countries analyzed—mostly in the West— the majorities of adults who were raised Christian still identify as Christian today, yet more people have left Christianity than have joined it in many of these countries. Many of those who have converted to Christianity say they were raised as Buddhists or with no religious background. In contrast, most individuals who have left Christianity now identify as religiously unaffiliated.
Meanwhile, in countries such as Singapore and South Korea and Argentina, the highest share of people report being raised with no religious affiliation but now identify with a religion—mostly Christianity. In 13 countries analyzed, most individuals who have left Islam either no longer identify with any religion or now identify as Christian. Except in the United States, where more than a quarter of those raised as Muslims have left Islam, in most of the 13 countries surveyed, only a very small percentage of adults have either left or converted to Islam.
Among the six surveyed countries, Buddhism has declined in some due to religious switching, such as in Japan and South Korea and Singapore, while in others, it has remained relatively stable, such as in Thailand and Sri Lanka. Both Israel and the U.S. show strong levels of Jewish identity retention. In Israel, almost all individuals who grew up Jewish continue to identify as such, while in the U.S., 76% of those with a Jewish upbringing still consider themselves Jewish.
See also
*History of religion *List of religious populations *Major religious groups **Major religious groups#Trends in adherence, Trends in adherenceNotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Carolyn Chen, Russell Jeung. ''Sustaining Faith Traditions: Race, Ethnicity, and Religion among the Latino and Asian American Second Generation''. NYU Press, 2012. . * Miikka Ruokanen, Paulos Zhanzhu Huang. ''Christianity and Chinese Culture''. William B. Eerdmans Publishing, 2011. . *Religion on the Move!: New Dynamics of Religious Expansion in a Globalizing World
', BRILL, 21 November 2012, Afe Adogame, Shobana Shankar, 2012. * The report provides a comprehensive analysis of the global religious landscape, revealing the size and distribution o
major religious groups as of 2023.
External links
Think religion is in decline? Look at who is 'going forth and multiplying'
, ''Vancouver Sun'', 2014
''Shall the Religious Inherit the Earth?: Demography and Politics in the Twenty-First Century''
by Eric Kaufmann, Belfer Center, Harvard University/Birkbeck College, University of London (PDF) *
Religious Projections for the Next 200 Years
fro
World Network of Religious Futurists
{{DEFAULTSORT:Claims To Be The Fastest-Growing Religion Religious studies Religious demographics