Farinograph Absorption on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 In
In
 The points of interest on the graph are fivefold:
#Arrival Time (Absorption) – Absorption is the point chosen by the baking industry which represents a target water to flour ratio in
The points of interest on the graph are fivefold:
#Arrival Time (Absorption) – Absorption is the point chosen by the baking industry which represents a target water to flour ratio in
US Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service.American Association of Cereal Chemists
Dough Mixers
{{Bread Baking Food analysis Measuring instruments

 In
In baking
Baking is a method of preparing food that uses dry heat, typically in an oven, but it can also be done in hot ashes, or on hot Baking stone, stones. Bread is the most commonly baked item, but many other types of food can also be baked. Heat is ...
, a farinograph measures specific properties of flour
Flour is a powder made by Mill (grinding), grinding raw grains, List of root vegetables, roots, beans, Nut (fruit), nuts, or seeds. Flours are used to make many different foods. Cereal flour, particularly wheat flour, is the main ingredie ...
. It was first developed and launched in 1928. The farinograph is a tool used for measuring the shear and viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's rate-dependent drag (physics), resistance to a change in shape or to movement of its neighboring portions relative to one another. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of ''thickness''; for e ...
of a mixture of flour and water. The primary units of the farinograph are Brabender Units, an arbitrary unit
In science and technology, an arbitrary unit (abbreviated arb. unit, '' see below'')
or procedure defined unit (p.d.u.)
is a relative unit of measurement to show the ratio of amount of substance, intensity, or other quantities, to a predetermin ...
of measuring the viscosity of a fluid.
A baker can formulate end products by using the farinograph's results to determine the following:
*Water absorption
*Dough viscosity, including peak water to gluten
Gluten is a structural protein naturally found in certain Cereal, cereal grains. The term ''gluten'' usually refers to the elastic network of a wheat grain's proteins, gliadin and glutenin primarily, that forms readily with the addition of water ...
ratio prior to gluten breakdown
*Peak mixing time to arrive at desired water/gluten ratio
*The stability of flour under mixing
*The tolerance of a flour's gluten
Method
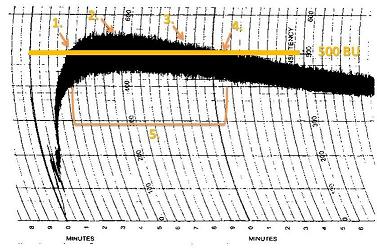
The farinograph is drawn on a curved graph with the vertical axis labeled in Brabender Units (BU) and the horizontal axis labeled as time in minutes. The graph is generally hockey-stick shaped, with the curve being more or less acute depending on the strength of the gluten in the flour. The points of interest on the graph are fivefold:
#Arrival Time (Absorption) – Absorption is the point chosen by the baking industry which represents a target water to flour ratio in
The points of interest on the graph are fivefold:
#Arrival Time (Absorption) – Absorption is the point chosen by the baking industry which represents a target water to flour ratio in bread
Bread is a baked food product made from water, flour, and often yeast. It is a staple food across the world, particularly in Europe and the Middle East. Throughout recorded history and around the world, it has been an important part of many cu ...
. This ratio is marked at the 500 BU line and is taken as a rule of thumb
In English language, English, the phrase ''rule of thumb'' refers to an approximate method for doing something, based on practical experience rather than theory. This usage of the phrase can be traced back to the 17th century and has been associat ...
for desired taste, texture, and dough performance during proofing and baking. All other measurements are based on this 500 BU standard. (For comparison, the accepted BU is 1000 or greater for noodles
Noodles are a type of food made from unleavened dough which is either rolled flat and cut, stretched, or extruded, into long strips or strings. Noodles are a staple food in many cultures and made into a variety of shapes. The most common noo ...
). Thus on the graph above, Arrival time is the point on the graph where the top of the curve reaches the 500 BU point and indicates the rate of absorption (minutes/BU).
#Peak time – Peak time is reached at the highest point on the curve, and indicates when the dough has reached is maximum viscosity before gluten strands begin to break down.
#Mixing Tolerance Index (MTI) – MTI is found by taking the difference in BU between the peak time point (on the graph above 3 minutes, 30 seconds) and 5 minutes after peak time is reached. This is used by bakers to determine the amount that a dough will soften over a period of mixing. MTI may be expressed as a value in BU or as a percentage of BU lost over time ().
#Departure Time – Departure time is defined as the point at which the top of the curve goes below the 500 BU line. This point is generally considered the point at which gluten is breaking down and dough has become over mixed.
#Stability – Stability is the point between arrival time and departure time and generally indicates the strength of a flour (how much gluten a flour has and how strong it is).
Applications
The Farinograph is used worldwide by bakers and food technicians in building bakery formulations. The farinograph gives bakers a good snapshot of the flour's properties and how the flour will react in different stages of baking, which helps them pick a certain flour for any given purpose. Millers use the Brabender Farinograph to access the properties of the flour, to ascertain whether changes need to be made in the mill. The miller also uses the farinograph to prepare dough for further testing for extensibility after a resting period (akin to proofing) with the Brabender Extensograph. The industrial application of these five points is far reaching. A baker may use, for example, the arrival time as a bare minimum time when planning full product floor time for a batch of dough. A baker may also use MTI as guideline to judge the response of a dough to the addition of other ingredients. Peak time may be used as a target mix time for optimal gluten structure and resilience. Stability may be used as a method of determining desired cell structure before irreparable gluten breakdown occurs.Notes and references
Sources
*''Starch in food: structure, function and applications''. Ann-Charlotte Eliasson. CRC Press, 2004. ,US Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service.
External links
*Dough Mixers
{{Bread Baking Food analysis Measuring instruments