Facial symmetry on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Facial symmetry is one specific measure of bodily
 Aurofacial asymmetry (from
Aurofacial asymmetry (from
Alex Dodge 2012 left.jpg, 2 right sides
Alex Dodge 2012.jpg, Original
Alex Dodge 2012 right.jpg, 2 left sides
Conclusions derived from face mirroring, however, have been called into question, because it has been shown that mirroring face-halves creates artificial features. For example, if the nose of an individual is slightly bent to the right side, then mirroring the right side of the face will lead to an over-sized nose, while mirroring the left side will lead to an unnaturally small nose.
FaceResearch
– Online studies on facial symmetry by researchers affiliated with University of Aberdeen (Scotland) School of Psychology, and University of St. Andrews (Scotland). *
A facial symmetry plugin for the GIMP
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190405150525/http://www.andyshelley.co.uk/gimpsymmetry/index.php , date=2019-04-05 "—Try experimenting with facial symmetry, using open source software. *
Psychological Image Collection at Stirling (PICS)
Free Database of pictures of faces *
FaceBase
An interdisciplinary research consortium for facial symmetry *
Tübinger Face Database
An open research database of 200 merged 3-D faces *
A facial symmetry app for iPhone
Experiment with facial symmetry, using a free iPhone app.
AI-Driven Facial Symmetry Tool by FaceAuraAI
– interactive analysis and visualization of human facial symmetry. Body shape Facial features Physical attractiveness Anthropometry Symmetry
symmetry
Symmetry () in everyday life refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, the term has a more precise definition and is usually used to refer to an object that is Invariant (mathematics), invariant und ...
. Along with traits such as averageness and youthfulness, it influences judgments of aesthetic
Aesthetics (also spelled esthetics) is the branch of philosophy concerned with the nature of beauty and taste, which in a broad sense incorporates the philosophy of art.Slater, B. H.Aesthetics ''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy,'' , acces ...
traits of physical attractiveness
Physical attractiveness is the degree to which a person's physical features are considered aesthetics, aesthetically pleasing or beauty, beautiful. The term often implies sexual attraction, sexual attractiveness or desirability, but can also be d ...
and beauty
Beauty is commonly described as a feature of objects that makes them pleasure, pleasurable to perceive. Such objects include landscapes, sunsets, humans and works of art. Beauty, art and taste are the main subjects of aesthetics, one of the fie ...
. For instance, in mate selection, people have been shown to have a preference for symmetry.
Facial bilateral symmetry is typically defined as fluctuating asymmetry of the face comparing random differences in facial features of the two sides of the face. The human face also has systematic, directional asymmetry
Asymmetry is the absence of, or a violation of, symmetry (the property of an object being invariant to a transformation, such as reflection). Symmetry is an important property of both physical and abstract systems and it may be displayed in pre ...
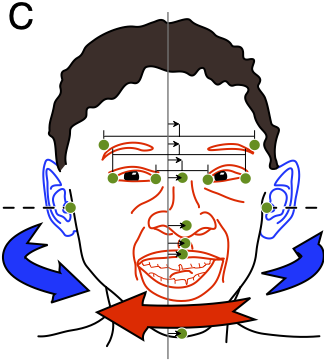
: on average, the face (mouth, nose and eyes) sits systematically to the left with respect to the axis through the ears, the so-called '' aurofacial asymmetry''.
Directional asymmetry
Directional asymmetry is systematic. The average across the population is not "symmetric", but statistically significantly biased on one direction. That means, that individuals of a species can be symmetric, or even asymmetric to the opposite side (see, e.g.,handedness
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to and causing it to be stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dext ...
), but most individuals are asymmetric to the same side. The relation between ''directional'' and ''fluctuating'' asymmetry is comparable to the concepts of accuracy and precision
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value''.
''Precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other.
The ...
in empirical measurements.
There are examples from the brain
The brain is an organ (biology), organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It consists of nervous tissue and is typically located in the head (cephalization), usually near organs for ...
(Yakovlevian torque
Yakovlevian torque (also known as occipital bending (OB) or counterclockwise brain torque) is the tendency of the right side of the human brain to be warped slightly forward relative to the left and the left side of the human brain to be warped sl ...
) and spine, and inner organs (see axial twist theory), but also from various animals (see Symmetry in biology
Symmetry in biology refers to the symmetry observed in organisms, including plants, animals, fungi, and bacteria. External symmetry can be easily seen by just looking at an organism. For example, the face of a human being has a plane of symme ...
).
Aurofacial asymmetry
 Aurofacial asymmetry (from
Aurofacial asymmetry (from Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
''auris'' ' ear' and ''facies'' 'face
The face is the front of the head that features the eyes, nose and mouth, and through which animals express many of their emotions. The face is crucial for human identity, and damage such as scarring or developmental deformities may affect th ...
') is an example of directed asymmetry of the face. It refers to the left-sided offset of the face (i.e. eyes
An eye is a sensory organ that allows an organism to perceive visual information. It detects light and converts it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons (neurones). It is part of an organism's visual system.
In higher organisms, the ey ...
, nose
A nose is a sensory organ and respiratory structure in vertebrates. It consists of a nasal cavity inside the head, and an external nose on the face. The external nose houses the nostrils, or nares, a pair of tubes providing airflow through the ...
, and mouth
A mouth also referred to as the oral is the body orifice through which many animals ingest food and animal communication#Auditory, vocalize. The body cavity immediately behind the mouth opening, known as the oral cavity (or in Latin), is also t ...
) with respect to the ears. On average, the face's offset is slightly to the left, meaning that the right side of the face appears larger than the left side. The offset is larger in newborns and reduces gradually during growth.
Anatomy and definition
In contrast to ''fluctuating'' asymmetry, ''directional asymmetry'' is systematic, i.e. across the population it is systematically more often in one direction than in the other. It means that across the population a deviation is more often to one direction than to the other, i.e., there is a statistically significantbias
Bias is a disproportionate weight ''in favor of'' or ''against'' an idea or thing, usually in a way that is inaccurate, closed-minded, prejudicial, or unfair. Biases can be innate or learned. People may develop biases for or against an individ ...
to one direction. In case of directional asymmetry, most individuals of a species are asymmetric to the same side, even though some individuals can be symmetric, or even asymmetric to the opposite side (cf., e.g., handedness
In human biology, handedness is an individual's preferential use of one hand, known as the dominant hand, due to and causing it to be stronger, faster or more Fine motor skill, dextrous. The other hand, comparatively often the weaker, less dext ...
). The relation between ''directional'' and ''fluctuating'' asymmetry is comparable to the concepts of accuracy and precision
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''.
''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements (observations or readings) are to their ''true value''.
''Precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other.
The ...
in empirical measurements.
The aurofacial asymmetry is defined as the position of the face (mouth, nose and eyes) with respect to the mid plane of the axis through the ears. The asymmetry is expressed as an angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two R ...
( degrees), i.e. by how many degrees facial landmarks (e.g. tip of the nose) or pairs of landmarks (e.g. inner corners of the eyes ( endocanthions are rotated away from the mid plane between the ears.
Magnitude across the face and development
On average, the aurofacial asymmetry is slightly larger for the eyes than for the nose, as shown by the figure. In humans asymmetric growth leads to a gradual reduction of the aurofacial asymmetry. As shown in the graph, the asymmetry decreases from about 2° atbirth
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the f ...
to about 0.5° in adults.
Theory and evolution
The aurofacial asymmetry was discovered after it was predicted by the axial twist theory. According to the theory the facial asymmetry is related to theYakovlevian torque
Yakovlevian torque (also known as occipital bending (OB) or counterclockwise brain torque) is the tendency of the right side of the human brain to be warped slightly forward relative to the left and the left side of the human brain to be warped sl ...
of the cerebrum
The cerebrum (: cerebra), telencephalon or endbrain is the largest part of the brain, containing the cerebral cortex (of the two cerebral hemispheres) as well as several subcortical structures, including the hippocampus, basal ganglia, and olfac ...
, asymmetric heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrie ...
and bowels
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The tract is the largest of the body's systems, after the cardiovascular system. T ...
and the spine. It is predicted to be common in vertebrates
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
, but this has never been tested.
The axial twist occurs in the early embryo. Shortly after the neurulation
Neurulation refers to the folding process in vertebrate embryos, which includes the transformation of the neural plate into the neural tube. The embryo at this stage is termed the neurula.
The process begins when the notochord induces the formati ...
, the anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to describe unambiguously the anatomy of humans and other animals. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ...
head region makes a half-turn around the body axis in anti-clockwise direction (looking from tail to head), whereas the rest of the body (except heart and bowels) make a half-turn in clockwise direction. Since the axial twist is located between the ear-region and the forebrain-face-region, it is predicted that the face grows from the left to the midline, as is indeed the case.
Fluctuating asymmetry
Fluctuating asymmetry is the non-systematic variation of individual facial landmarks with respect to the facial midline, i.e., the line perpendicular to the line through the eyes, which crosses the tip of the nose and the chin. A wide variety of methods have been used to examine the claim that facial symmetry plays a role in judgments of beauty. ''Blending of multiple faces'' to create a composite and ''face-half mirroring'' have been among the techniques used.Attractiveness
Facial symmetry has been found to increase ratings of attractiveness in human faces. More symmetrical faces are perceived as more attractive in both males and females, although facial symmetry plays a larger role in judgments of attractiveness concerning female faces. Studies have shown that nearly symmetrical faces are considered highly attractive as compared to asymmetrical ones.Dynamic asymmetries
Highly conspicuous directional asymmetries can be temporary ones. For example, during speech, most people (76%) tend to express greater amplitude of movement on the right side of their mouth. This is most likely caused by the uneven strengths of contralateral neural connections between the left hemisphere of the brain (linguistic localization) and the right side of the face.Facial averageness vs. symmetry
Experiments suggest that symmetry and averageness make independent contributions to attractiveness.Aging
Facial symmetry is also a valid marker of cognitive aging. Progressive changes occurring throughout life in the soft tissues of the face will cause more prominent facial asymmetry in older faces. Therefore, symmetrical transformation of older faces generally increases their attractiveness while symmetrical transformation in young adults and children will decrease their attractiveness.Physiognomy
''Physiognomy'' or ''face reading'' is the practice of assessing a person's character or personality from their outer appearance—especially the face. Physiognomy as a practice meets the contemporary definition of pseudoscience and is regarded as such by academics because of its unsupported claims. Nevertheless, the subject is topic of serious scientific research. Statistical correlations does not inform about possible causal dependence, so if observers judge the personality of (pictures of) symmetric faces differently than asymmetric ones, this might be due tocultural
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes ...
prejudice
Prejudice can be an affect (psychology), affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived In-group and out-group, social group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classifi ...
.
Research indicates that a correlation exists between facial symmetry and the 'big-five' model of personality. The five factors are:
* Openness to experience
Openness to experience is one of the domains which are used to describe personality psychology, human personality in the Big Five personality traits, Five Factor Model. Openness involves six Facet (psychology), facets, or dimensions: active imagina ...
(''inventive/curious'' vs. ''consistent/cautious'')
* Conscientiousness
Conscientiousness is the personality trait of being responsible, :wikt:careful, careful, or :wikt:diligent, diligent. Conscientiousness implies a desire to do a task well, and to take obligations to others seriously. Conscientious people tend to ...
(''efficient/organized'' vs. ''easy-going/careless'')
* Extraversion
Extraversion and introversion are a central trait dimension in human personality theory. The terms were introduced into psychology by Carl Jung, though both the popular understanding and current psychological usage are not the same as Jung's ...
(''outgoing/energetic'' vs. ''solitary/reserved'')
* Agreeableness
Agreeableness is the trait theory, personality trait of being kind, Sympathy, sympathetic, cooperative, warm, honest, straightforward, and considerate. In personality psychology, agreeableness is one of the Big Five personality traits, five major ...
(''friendly/compassionate'' vs. ''challenging/detached'')
* Neuroticism
Neuroticism is a personality trait associated with negative emotions. It is one of the Big Five traits. Individuals with high scores on neuroticism are more likely than average to experience such feelings as anxiety, worry, fear, anger, shame ...
(''sensitive/nervous'' vs. ''secure/confident'')
Accordingly, a positive correlation was found between facial symmetry and extraversion, as judged by others from photographs, as well as by the subjects themselves. More symmetrical faces are also judged to be lower on neuroticism but higher on conscientiousness and agreeableness (asymmetrical faces were rated as less agreeable than normal ones, but the more symmetrical were again rated as somewhat less agreeable than the normal). More symmetrical faces are also more likely to have more desirable social attributes assigned to them, such as sociable, intelligent or lively.
The correlation of facial symmetry and ''neuroticism'', ''openness'', ''agreeableness'' and ''conscientiousness'' has remained unclear. Openness and agreeableness appear to be significantly negatively correlated to facial symmetry, while neuroticism and conscientiousness do not seem to be correlated to facial symmetry. With respect to trustworthiness
Trust is the belief that another person will do what is expected. It brings with it a willingness for one party (the trustor) to become vulnerable to another party (the trustee), on the presumption that the trustee will act in ways that benefit ...
it has been found that the facial muscles become imbalanced when lying.
Evolution and sexual selection
Sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
is a theoretical construct within evolution theory
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certai ...
. According to sexual selection, mate choice
Mate choice is one of the primary mechanisms under which evolution can occur. It is characterized by a "selective response by animals to particular stimuli" which can be observed as behavior.Bateson, Paul Patrick Gordon. "Mate Choice." Mate Choi ...
can have profound influence on the preferred features. Sexual selection can only influence features that potential mates can perceive, such as smell, audition
An audition is a sample performance by an actor, singer, musician, dancer or other performer. It typically involves the performer displaying their talent through a previously memorized and rehearsed solo piece or by performing a work or piece gi ...
(e.g. song
A song is a musical composition performed by the human voice. The voice often carries the melody (a series of distinct and fixed pitches) using patterns of sound and silence. Songs have a structure, such as the common ABA form, and are usu ...
) and vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
. Such features might be reliable indicators of hidden fitness parameters such as a good immune system
The immune system is a network of biological systems that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to bacteria, as well as Tumor immunology, cancer cells, Parasitic worm, parasitic ...
or developmental stability.
It has been argued that more symmetric faces are preferred because symmetry might be a reliable sign of such hidden fitness parameters. However it is possible that high facial symmetry in an individual is not due to their superior genetics but due to a lack of exposure to stressors, such as alcohol, during prenatal development.
It has been found that more symmetrical faces are rated as healthier than less symmetrical faces. Indeed, facial symmetry was found to be positively associated with the perceived healthiness of the facial skin. Also, facial asymmetry was found to be correlated with physiological, psychological and emotional distress.
Some evidence suggests that face preferences in adults might be correlated to infections in childhood.
See also
*Beauty
Beauty is commonly described as a feature of objects that makes them pleasure, pleasurable to perceive. Such objects include landscapes, sunsets, humans and works of art. Beauty, art and taste are the main subjects of aesthetics, one of the fie ...
* Symmetry in nature
* Patterns in nature
Patterns in nature are visible regularities of form found in the natural world. These patterns recur in different contexts and can sometimes be modelled mathematically. Natural patterns include symmetries, trees, spirals, meanders, wave ...
* Physical attractiveness
Physical attractiveness is the degree to which a person's physical features are considered aesthetics, aesthetically pleasing or beauty, beautiful. The term often implies sexual attraction, sexual attractiveness or desirability, but can also be d ...
References
External links
FaceResearch
– Online studies on facial symmetry by researchers affiliated with University of Aberdeen (Scotland) School of Psychology, and University of St. Andrews (Scotland). *
A facial symmetry plugin for the GIMP
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20190405150525/http://www.andyshelley.co.uk/gimpsymmetry/index.php , date=2019-04-05 "—Try experimenting with facial symmetry, using open source software. *
Psychological Image Collection at Stirling (PICS)
Free Database of pictures of faces *
FaceBase
An interdisciplinary research consortium for facial symmetry *
Tübinger Face Database
An open research database of 200 merged 3-D faces *
A facial symmetry app for iPhone
Experiment with facial symmetry, using a free iPhone app.
AI-Driven Facial Symmetry Tool by FaceAuraAI
– interactive analysis and visualization of human facial symmetry. Body shape Facial features Physical attractiveness Anthropometry Symmetry