Fab Fragment on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
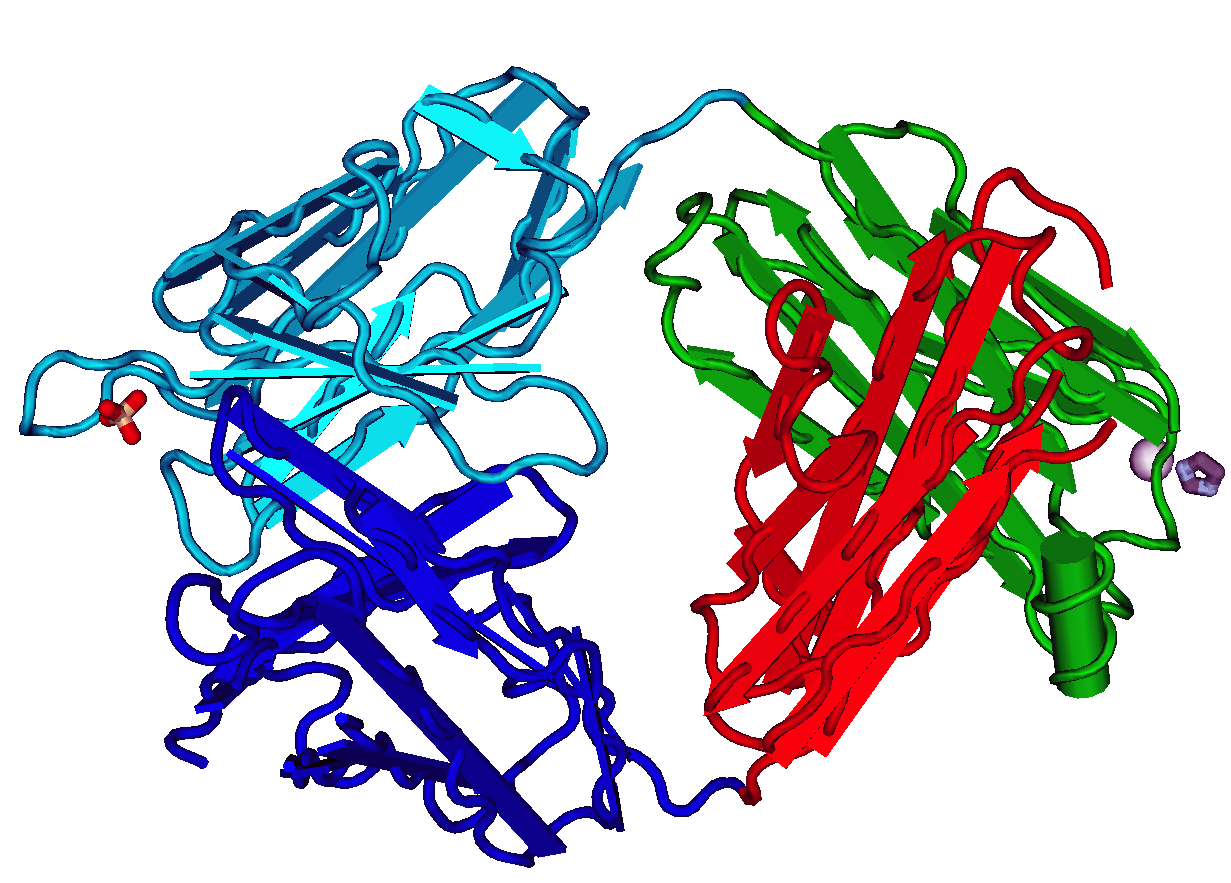 The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
File:Antibody je2.png, Heavy and light chains, variable and constant regions of an antibody.
File:2fab fc.svg, An antibody digested by
The variable regions of the heavy and light chains can be fused together to form a
 The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
The fragment antigen-binding region (Fab region) is a region on an antibody that binds to antigens. It is composed of one constant and one variable domain of each of the heavy and the light chain. The variable domain contains the paratope (the antigen-binding site), comprising a set of complementarity-determining regions, at the amino terminal end of the monomer. Each arm of the Y thus binds an epitope on the antigen.
Preparation
In an experimental setting, Fc and Fab fragments can be generated in the laboratory. The enzymepapain
Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease () enzyme present in papaya (''Carica papaya'') and mountain papaya (''Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis''). It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
It has wide ...
can be used to cleave an immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
monomer into two Fab fragments and an Fc fragment. Conversely, the enzyme pepsin cleaves below the hinge region, so the result instead is a F(ab')2 fragment and a pFc' fragment. Recently another enzyme for generation of F(ab')2 has been commercially available. The enzyme IdeS (Immunoglobulin degrading enzyme from '' Streptococcus pyogenes'', trade name FabRICATOR) cleaves IgG in a sequence specific manner at neutral pH. The F(ab')2 fragment can be split into two Fab' fragments by mild reduction.
papain
Papain, also known as papaya proteinase I, is a cysteine protease () enzyme present in papaya (''Carica papaya'') and mountain papaya (''Vasconcellea cundinamarcensis''). It is the namesake member of the papain-like protease family.
It has wide ...
yields three fragments: two Fab fragments and one Fc fragment
File:F ab2 pFc.png, An antibody digested by pepsin yields two fragments: a F(ab')2 fragment and a pFc' fragment
single-chain variable fragment
A single-chain variable fragment (scFv) is not actually a fragment of an antibody, but instead is a fusion protein of the variable regions of the heavy (VH) and light chains (VL) of immunoglobulins, connected with a short linker peptide of te ...
(scFv), which is only half the size of the Fab fragment, yet retains the original specificity of the parent immunoglobulin.
Applications
Fabs have seen some therapeutic use inemergency medicine
Emergency medicine is the medical speciality concerned with the care of illnesses or injuries requiring immediate medical attention. Emergency physicians (often called “ER doctors” in the United States) continuously learn to care for unsche ...
as an antidote. Marketed applications include digoxin immune fab
Digoxin immune fab or digoxin-specific antibody is an antidote for overdose of digoxin. It is made from Antibody, immunoglobulin fragments from sheep that have already been immunized with a digoxin derivative, digoxindicarboxymethoxylamine (DDMA). ...
and Crofab, a mixture of Fabs for rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small anim ...
bites. Fabs against colchicine and tricyclic antidepressant
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) are a class of medications that are used primarily as antidepressants, which is important for the management of depression. They are second-line drugs next to SSRIs. TCAs were discovered in the early 1950s and we ...
s has also been produced but are yet to see approval.
Fabs are a common form-factor for monoclonal antibodies
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
Monoclonal antibodies ca ...
designated for therapeutic use. The Fab abciximab, which inhibits blood clotting, works by disabling glycoprotein IIb/IIIa found on platelets. Ranibizumab, a treatment for macular degeneration, targets vascular endothelial growth factor A, a protein involved in the growth of blood vessels. Certolizumab pegol is a Fab chemically linked to PEG, and it treats various inflammatory disorders by binding away TNFα
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
.
Fab antibodies also have diagnostic use. Arcitumomab is a mouse antibody that recognizes carcinoembryonic antigen
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) describes a set of highly related glycoproteins involved in cell adhesion. CEA is normally produced in gastrointestinal tissue during fetal development, but the production stops before birth. Consequently, CEA is ...
, an antigen over-expressed in 95% of colorectal cancers. It is conjugated to a radioactive element, which will label the tumors when viewed with single-photon emission computed tomography
Single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT, or less commonly, SPET) is a nuclear medicine tomographic imaging technique using gamma rays. It is very similar to conventional nuclear medicine planar imaging using a gamma camera (that is, ...
. Sulesomab
Technetium (99mTc) sulesomab (trade name LeukoScan) is a radio-pharmaceutical composed of anti-human mouse monoclonal antibody that targets the granulocyte associated NCA-90 cell antigen and a conjugated technetium-99m radionuclide. After intrave ...
, an antigen that recognizes proteins on the surface of granulocyte
Granulocytes are
cells in the innate immune system characterized by the presence of specific granules in their cytoplasm. Such granules distinguish them from the various agranulocytes. All myeloblastic granulocytes are polymorphonuclear. They ha ...
s, is used to label out infections, again using the 99mTc isotope.
Fab fragments are often fused to small proteins (<100 kDa) that have lower scattering, resulting in images with less contrast.
See also
*Fragment crystallizable region
The fragment crystallizable region (Fc region) is the tail region of an antibody that interacts with cell surface receptors called Fc receptors and some proteins of the complement system. This property allows antibodies to activate the immune ...
References
Antibodies {{immunology-stub