FAM178B on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
FAM178B is a protein coding that is located on the plus strand of chromosome 2.FAM178B - Protein FAM178B - Homo sapiens (Human) - FAM178B gene & protein. (n.d.). Retrieved February 25, 2019, from https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8IXR5 The locus for the gene is 2q11.2. It is also known by the aliases Family with Sequence Similarity 178, Member B, and HSPC234. In total there are 24


 The promoter region of FAM178B is highly conserved across its most related orthologs, and is almost identical across the human, gorilla, chimp, bonobo and gibbon organisms.
The promoter region of FAM178B is highly conserved across its most related orthologs, and is almost identical across the human, gorilla, chimp, bonobo and gibbon organisms.
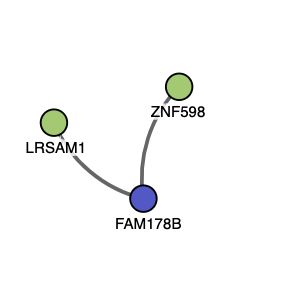 MENTHA interacting proteins for FAM178B.
MENTHA interacting proteins for FAM178B.
 STRING interacting proteins for FAM178B.
STRING interacting proteins for FAM178B.
exons
An exon is any part of a gene that will form a part of the final mature RNA produced by that gene after introns have been removed by RNA splicing. The term ''exon'' refers to both the DNA sequence within a gene and to the corresponding sequence ...
in the gene. FAM178B spans 110,720 base pairs, and contains 827 amino acids.
Forms
There are two isoforms of the gene transcript that exist byalternative splicing
Alternative splicing, or alternative RNA splicing, or differential splicing, is an alternative splicing process during gene expression that allows a single gene to code for multiple proteins. In this process, particular exons of a gene may be ...
, and one gene precursor.
SLF2 (FAM178A) is an important paralog of FAM178B. SLF2 is predicted to play a role in the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway by regulating post-replication repair of UV-damaged DNA, and genomic stability maintenance.
Protein structure
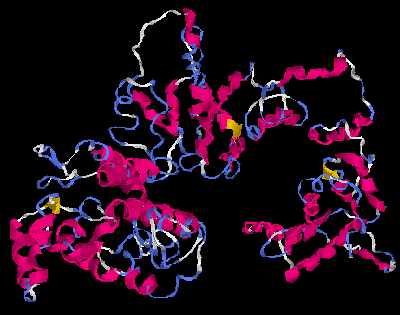
The molecular weight of the protein is 76.5 kilodaltons, and the isoelectric point is 5.47.The gene has 6 transcript splice variants. The protein has been phenotypically associated with bipolar disease due to its locus, as well asbody mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and he ...
(BMI), and cell adhesion
Cell adhesion is the process by which cells interact and attach to neighbouring cells through specialised molecules of the cell surface. This process can occur either through direct contact between cell surfaces such as cell junctions or indir ...
. A proposed structure for the protein can be found in the images for proposed structures. The secondary structure
Protein secondary structure is the three dimensional conformational isomerism, form of ''local segments'' of proteins. The two most common Protein structure#Secondary structure, secondary structural elements are alpha helix, alpha helices and beta ...
for the FAM178B protein is predicted to be primarily alpha helices. The tertiary structure of the protein may assume a coiled coil structure.

Expression
FAM178B is most highly expressed in theskeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
and brain tissues.The structure in which it is highly concentrated is in the corpus callosum of the brain. Additionally, it is of high levels in the trigeminal nerve and spinal cord. Further, there is also high concentrations of the gene found near the heart, testes and olfactory regions.
According to the Allen Brain Atlas
The Allen Mouse and Human Brain Atlases are projects within the Allen Institute for Brain Science which seek to combine genomics with neuroanatomy by creating gene expression maps for the mouse and human brain. They were initiated in September 2 ...
, the olfactory regions, and the hippocampus of the mouse brain showed the greatest expressions of the gene when tested experimentally.

DNA Level Regulation
The proposed promoter region of FAM178B protein is below. A table of relevant transcription factor binding sites that correspond to the sequence and colors highlighted in the promoter region is also included.
 The promoter region of FAM178B is highly conserved across its most related orthologs, and is almost identical across the human, gorilla, chimp, bonobo and gibbon organisms.
The promoter region of FAM178B is highly conserved across its most related orthologs, and is almost identical across the human, gorilla, chimp, bonobo and gibbon organisms.
Protein Level Regulation
Below is a table that shows the protein modifications that could be potentially made to FAM178B, and the potential effects of these modifications on the protein itself:.Homology and Evolution
An important paralog of the gene is SLF2, which plays a role in the DNA damage response (DDR) pathway by regulating post replication repair of UV-damaged DNA. It also helps maintain genomic stability. There are 74 known orthologs of the protein, and it can be traced back as far back as crustaceans. FAM178B is heavily found in both vertebrates and invertebrates. The ortholog space for the protein FAM178B is quite large as it can be traced back 794 millions of years ago (mya) to mollusks with the apple snail, and Pacific Oyster. There are 134 known orthologs of FAM178B. However, the protein is not found in arthropods, or insects, which is interesting because those organisms also existed in that time period meaning that it was conserved across some taxa, but not others. The protein is most readily found in primates, and other non-primate mammals. The protein is also conserved across reptiles, some bony fish, and cartilaginous fish, and birds. Below is a table illustrating some of the orthologs for FAM178B using BLAST and BLAT. Timetree for FAM178BInteracting Proteins
There are 2 proteins that have high predicted values of interaction with FAM178B: LRSAM 1 and ZNF598. LRSAM1 is also known as leucine rich repeat and sterile alpha motif protein 1. The value for the protein is .29 and the evidence is physical from hybrid pooling approaches. LRSAM1 was previously known as Tsg-associated ligase and is located on the LRSAM1 gene. Mutations have been associated with periphery neuropathy, and sensory disorders. It is highly expressed in the spinal cord, as is FAM178B. There is currently no known structure for the protein. ZNF598 is a zinc finger protein and the value is .13. It plays a key role in ribosome quality control. The predicted structures are below for both proteins. MENTHA interacting proteins for FAM178B.
MENTHA interacting proteins for FAM178B.
 STRING interacting proteins for FAM178B.
STRING interacting proteins for FAM178B.
References
Further reading
# # {{Cite journal, last1=Stelzl, first1=Ulrich, last2=Worm, first2=Uwe, last3=Lalowski, first3=Maciej, last4=Haenig, first4=Christian, last5=Brembeck, first5=Felix H., last6=Goehler, first6=Heike, last7=Stroedicke, first7=Martin, last8=Zenkner, first8=Martina, last9=Schoenherr, first9=Anke, date=2005-09-23, title=A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome, url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed?cmd=search&term=16169070&dopt=b, journal=Cell, volume=122, issue=6, pages=957–968, doi=10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029, issn=0092-8674, pmid=16169070, hdl=11858/00-001M-0000-0010-8592-0, s2cid=8235923, hdl-access=free # Cloning and functional analysis of cDNAs with open reading frames for 300 previously undefined genes expressed in CD34+ hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells Protein classification