Eye Pattern on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
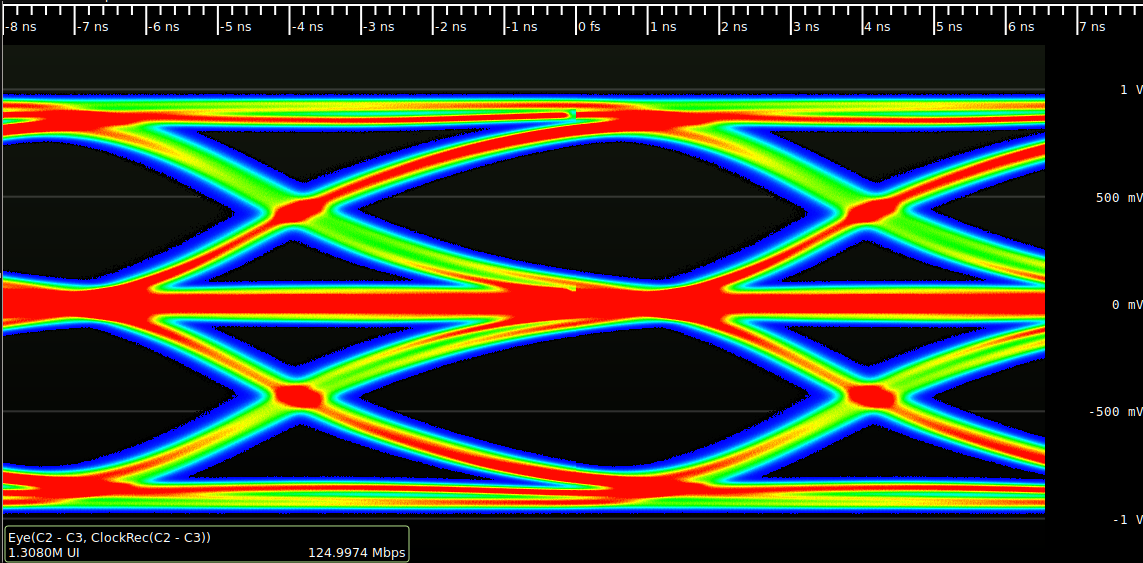
Eye_pattern_2.png, Eye pattern of twelve thousand UIs of a 1.25 Gbit/s signal
Eye_pattern_example.png, Eye pattern of eight million UIs (unit intervals) of a 1.25 Gbit/s signal




 As high frequency losses increase the overall shape of the eye gradually degrades into a sinusoid (once higher frequency harmonics of the data has been eliminated, all that remains is the fundamental) and decreases in amplitude.
As high frequency losses increase the overall shape of the eye gradually degrades into a sinusoid (once higher frequency harmonics of the data has been eliminated, all that remains is the fundamental) and decreases in amplitude.
 In the image below, an additional three inches of cable is added to the end of the same stub. The same "step" is present but is now four times as long, producing reflections at about 1280 ps or 1.6 UI. This produces extreme ISI (since the reflection of each UI arrives during the subsequent UI) which completely closes the eye.
In the image below, an additional three inches of cable is added to the end of the same stub. The same "step" is present but is now four times as long, producing reflections at about 1280 ps or 1.6 UI. This produces extreme ISI (since the reflection of each UI arrives during the subsequent UI) which completely closes the eye.

Understanding Data Eye Diagram Methodology for Analyzing High Speed Digital Signals
Data transmission
telecommunications
Telecommunication, often used in its plural form or abbreviated as telecom, is the transmission of information over a distance using electronic means, typically through cables, radio waves, or other communication technologies. These means of ...
, an eye pattern, also known as an eye diagram, is an oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
display in which a digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; ...
from a receiver is repetitively sampled and applied to the vertical input (''y-axis''), while the data rate is used to trigger the horizontal sweep (''x-axis''). It is so called because, for several types of coding, the pattern looks like a series of eyes between a pair of rails. It is a tool for the evaluation of the combined effects of channel noise, dispersion and intersymbol interference on the performance of a baseband pulse-transmission system. The technique was first used with the WWII
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
SIGSALY secure speech transmission system.
From a mathematical perspective, an eye pattern is a visualization of the probability density function
In probability theory, a probability density function (PDF), density function, or density of an absolutely continuous random variable, is a Function (mathematics), function whose value at any given sample (or point) in the sample space (the s ...
(PDF) of the signal, modulo
In computing and mathematics, the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division, after one number is divided by another, the latter being called the '' modulus'' of the operation.
Given two positive numbers and , mo ...
the unit interval
In mathematics, the unit interval is the closed interval , that is, the set of all real numbers that are greater than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1. It is often denoted ' (capital letter ). In addition to its role in real analysi ...
(UI). In other words, it shows the probability of the signal being at each possible voltage across the duration of the UI. Typically a color ramp is applied to the PDF in order to make small brightness differences easier to visualize.
Several system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its open system (systems theory), environment, is described by its boundaries, str ...
performance measurements can be derived by analyzing the display. If the signals are too long, too short, poorly synchronized with the system clock, too high, too low, too noisy, or too slow to change, or have too much undershoot or overshoot, this can be observed from the eye diagram. An open eye pattern corresponds to minimal signal distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
. Distortion of the signal waveform
In electronics, acoustics, and related fields, the waveform of a signal is the shape of its Graph of a function, graph as a function of time, independent of its time and Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude Scale (ratio), scales and of any dis ...
due to intersymbol interference and noise appears as closure of the eye pattern.
Calculation
Source data
The first step of computing an eye pattern is normally to obtain the waveform being analyzed in a quantized form. This may be done by measuring an actual electrical system with an oscilloscope of sufficient bandwidth, or by creating synthetic data with a circuit simulator in order to evaluate the signal integrity of a proposed design. A combination of the two approaches may be used as well: simulating the effects of an arbitrary circuit ortransmission line
In electrical engineering, a transmission line is a specialized cable or other structure designed to conduct electromagnetic waves in a contained manner. The term applies when the conductors are long enough that the wave nature of the transmis ...
on a measured signal, perhaps to determine whether a signal will still be intelligible after passing through a long cable. Interpolation
In the mathematics, mathematical field of numerical analysis, interpolation is a type of estimation, a method of constructing (finding) new data points based on the range of a discrete set of known data points.
In engineering and science, one ...
may also be applied at this time in order to increase the number of samples per unit interval (UI) and produce a smooth, gap-free plot which is more visually appealing and easier to understand.
Slicing
Next, the position of each sample within the UI must be determined. There are several methods for doing this depending on the characteristics of the signal and the capabilities of the oscilloscope and software in use. This step is critically important for accurate visualization ofjitter
In electronics and telecommunications, jitter is the deviation from true periodicity of a presumably periodic signal, often in relation to a reference clock signal. In clock recovery applications it is called timing jitter. Jitter is a signifi ...
in the eye.
Triggering
A very simple method of slicing is to set the oscilloscope display to be slightly more than one UI wide, trigger on both rising and falling edges in the signal, and enable display persistence so that all measured waveforms "stack" into a single plot. This has the advantage of being possible on almost any oscilloscope (even fully analog ones) and can provide decent visualization of noise and overall signal shape, but completely destroys the jitter content of the signal since the instrument's trigger re-synchronizes the plot to each UI. The only jitter visible with this method is that of the oscilloscope itself, as well as extremely high frequency jitter (frequencies with period less than the UI).Fixed rate
A simple way to have the eye pattern display jitter in the signal is to estimate the symbol rate of the signal (perhaps by counting the average number of zero crossings in a known window of time) and acquiring many UIs in a single oscilloscope capture. The first zero crossing in the capture is located and declared to be the start of the first UI, and the remainder of the waveform is divided into chunks one UI long. This approach can work adequately for stable signals in which the symbol rate remains exactly the same over time, however inaccuracies in the system mean that some drift is inevitable so it is rarely used in practice. In some protocols, such as SATA, the symbol rate is intentionally varied by use of spread spectrum clocking, so assuming a fixed rate will lead to the eye grossly exaggerating the actual jitter present on the signal. (While spread spectrum modulation on a clock is technically jitter in the strict sense, receivers for these systems are designed to track the modulation. The only jitter of interest to a signal integrity engineer is jitter much faster than the modulation rate, which the receiver cannot track effectively.)Reference clock
With some protocols, such asHDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary digital interface used to transmit high-quality video and audio signals between devices. It is commonly used to connect devices such as televisions, computer monitors, projectors, gam ...
, a reference clock is supplied along with the signal, either at the symbol rate or at a lower (but synchronized) frequency from which a symbol clock can be reconstructed. Since the actual receiver in the system uses the reference clock to sample the data, using this clock to determine UI boundaries allows the eye pattern to faithfully display the signal as the receiver sees it: only jitter between the signal and the reference clock is displayed.
Clock recovery
Most high speed serial signals, such as PCIe,DisplayPort
DisplayPort (DP) is a digital interface used to connect a video source, such as a Personal computer, computer, to a display device like a Computer monitor, monitor. Developed by the Video Electronics Standards Association (VESA), it can also car ...
, and most variants of Ethernet
Ethernet ( ) is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
, use a line code
In telecommunications, a line code is a pattern of voltage, current, or photons used to represent digital data transmission (telecommunications), transmitted down a communication channel or written to a storage medium. This repertoire of signal ...
which is intended to allow easy clock recovery by means of a PLL. Since this is how the actual receiver works, the most accurate way to slice data for the eye pattern is to implement a PLL with the same characteristics in software. Correct PLL configuration allows for the eye to conceal the effects of spread spectrum clocking and other long-term variation in the symbol rate which do not contribute to errors at the receiver, while still displaying higher frequency jitter.
Integration
The samples are then accumulated into a two-dimensionalhistogram
A histogram is a visual representation of the frequency distribution, distribution of quantitative data. To construct a histogram, the first step is to Data binning, "bin" (or "bucket") the range of values— divide the entire range of values in ...
, with the X axis representing time within the UI and the Y axis representing voltage. This is then normalized by dividing the value in each histogram bin by the value in the largest bin. Tone mapping
Tone mapping is a technique used in image processing and computer graphics to map one set of colors to another to approximate the appearance of high-dynamic-range (HDR) images in a medium that has a more limited dynamic range. Print-outs, C ...
, logarithmic scaling, or other mathematical transformations may be applied in order to emphasize different portions of the distribution, and a color gradient is applied to the final eye for display.
Large amounts of data may be needed to provide an accurate representation of the signal; tens to hundreds of millions of UIs are frequently used for a single eye pattern. In the example below, the eye using twelve thousand UIs only shows the basic shape of the eye, while the eye using eight million UIs shows far more nuance on the rising and falling edges.
Modulation
Each form of baseband modulation produces an eye pattern with a unique appearance.NRZ
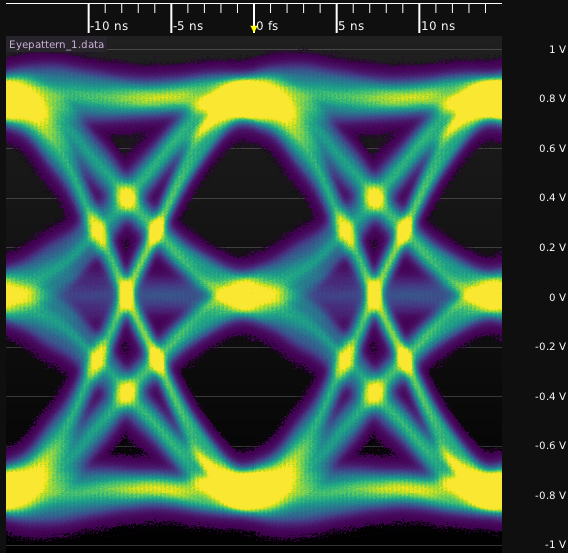
The eye pattern of a NRZ signal should consist of two clearly distinct levels with smooth transitions between them.
MLT-3
The eye pattern of a MLT-3 signal should consist of three clearly distinct levels (nominally -1, 0, +1 from bottom to top). The 0 level should be located at zero volts and the overall shape should be symmetric about the horizontal axis. The +1 and -1 states should have equal amplitude. There should be smooth transitions from the 0 state to the +1 and -1 states, however there should be no direct transitions from the -1 to +1 state (which would indicate the signal is PAM-3 rather than MLT-3).
PAM
The eye pattern of a PAM signal should consist of N clearly distinct levels (depending on the PAM order, for example PAM-4 should have four levels and PAM-3 should have three). The overall shape should be symmetric about the horizontal axis and the spacing of all levels should be uniform.
PSK
Channel effects
Many properties of a channel can be seen in the eye pattern.Emphasis
Emphasis applied to a signal produces an additional level for each value of the signal which is higher (for pre-emphasis) or lower (for de-emphasis) than the nominal value. The eye pattern for a signal with emphasis may be mistaken for that of a PAM signal at first glance, however closer inspection reveals some key differences. Most notably, an emphasized signal has a limited set of legal transitions: * Strong state to corresponding weak state (1-1 or 0-0 bit pattern) * Strong state to opposite strong state (second transition of a 1-0-1 or 0-1-0 bit pattern) * Weak state to opposite strong state (second transition of a 1-1-0 or 0-0-1 bit pattern) An emphasized signal will never transition from a weak state to the corresponding strong state, a weak state to another weak state, or remain in the same strong state for more than one UI. A PAM signal also normally has equally spaced levels while emphasized levels are normally closer to the nominal signal level.
High-Frequency Loss
Loss of printed circuit board traces and cables increases with frequency due to dielectric loss, which causes the channel to behave as alow-pass filter
A low-pass filter is a filter that passes signals with a frequency lower than a selected cutoff frequency and attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The exact frequency response of the filter depends on the filt ...
. The effect of this is an increase in signal rise/fall time. If the data rate is high enough or the channel is lossy enough, the signal may not even reach its full value during a fast 0-1-0 or 1-0-1 transition, and only stabilize after a run of several identical bits. This results in vertical closure of the eye.
The image below shows a 1.25 Gbit/s NRZ signal after passing through a lossy channel - an RG-188 coaxial cable approximately 12 feet (3.65 meters) in length. This channel has loss increasing in a fairly linear fashion from 0.1 dB at DC to 9 dB at 6 GHz.
The top and bottom "rails" of the eye show the final voltage the signal reaches after several consecutive bits with the same value. Since the channel has minimal loss at DC, the maximum signal amplitude is largely unaffected. Looking at the rising edge of the signal (a 0-1 pattern) we can see that the signal starts to level off around -300 ps, but continues to rise slowly over the duration of the UI. At around +300 ps, the signal either begins falling again (a 0-1-0 pattern) or continues rising slowly (an 0-1-1 pattern).
 As high frequency losses increase the overall shape of the eye gradually degrades into a sinusoid (once higher frequency harmonics of the data has been eliminated, all that remains is the fundamental) and decreases in amplitude.
As high frequency losses increase the overall shape of the eye gradually degrades into a sinusoid (once higher frequency harmonics of the data has been eliminated, all that remains is the fundamental) and decreases in amplitude.
Impedance Mismatches
Stubs, impedance mismatches, and other defects in a transmission line can cause reflections visible as defects in the edges of the signal. Reflections with a delay greater than one UI often render the eye completely unreadable due to inter-symbol interference (ISI), however those with a shorter delay can be easily seen in the shape of the eye. In the image below, a roughly one inch (25.4 mm) open circuited stub is present in the line, causing an initial low-impedance effect (reduced amplitude) followed by a positive reflection from the end of the stub with a delay of about 320 ps or 0.4 UIs. This can be clearly seen as a "step" in the rising edge in which the signal rises to a fraction of the full value, levels off for the round trip delay of the stub, then rises to its full value when the reflection arrives. In the image below, an additional three inches of cable is added to the end of the same stub. The same "step" is present but is now four times as long, producing reflections at about 1280 ps or 1.6 UI. This produces extreme ISI (since the reflection of each UI arrives during the subsequent UI) which completely closes the eye.
In the image below, an additional three inches of cable is added to the end of the same stub. The same "step" is present but is now four times as long, producing reflections at about 1280 ps or 1.6 UI. This produces extreme ISI (since the reflection of each UI arrives during the subsequent UI) which completely closes the eye.

Measurements
There are many measurements that can be obtained from an eye diagram: Amplitude measurements *Eye amplitude *Eye crossing amplitude *Eye crossing percentage *Eye height *Eye level *Eye signal-to-noise ratio *Quality factor *Vertical eye opening Time measurements *Deterministic jitter *Eye crossing time *Eye delay *Eye fall time *Eye rise time *Eye width *Horizontal eye opening *Peak-to-peak jitter *Random jitter *RMS jitter *CRC jitter *Total jitterInterpreting measurements
See also
* Constellation diagram * Signal integrity * Raised-cosine filter * Extinction ratioNotes
References
* *External links
* {{cite web , url = https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=my7CI84le5g , title = An Eye is Born , first = Hermann , last = Ruckerbauer , website =YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in ...
Gives an example video of construction of an eye pattern
Understanding Data Eye Diagram Methodology for Analyzing High Speed Digital Signals
Data transmission