Extreme Weather Events on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Extreme weather includes unexpected, unusual,
Annex II: Glossary
öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) In
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, US, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029. In comparison, the term ''
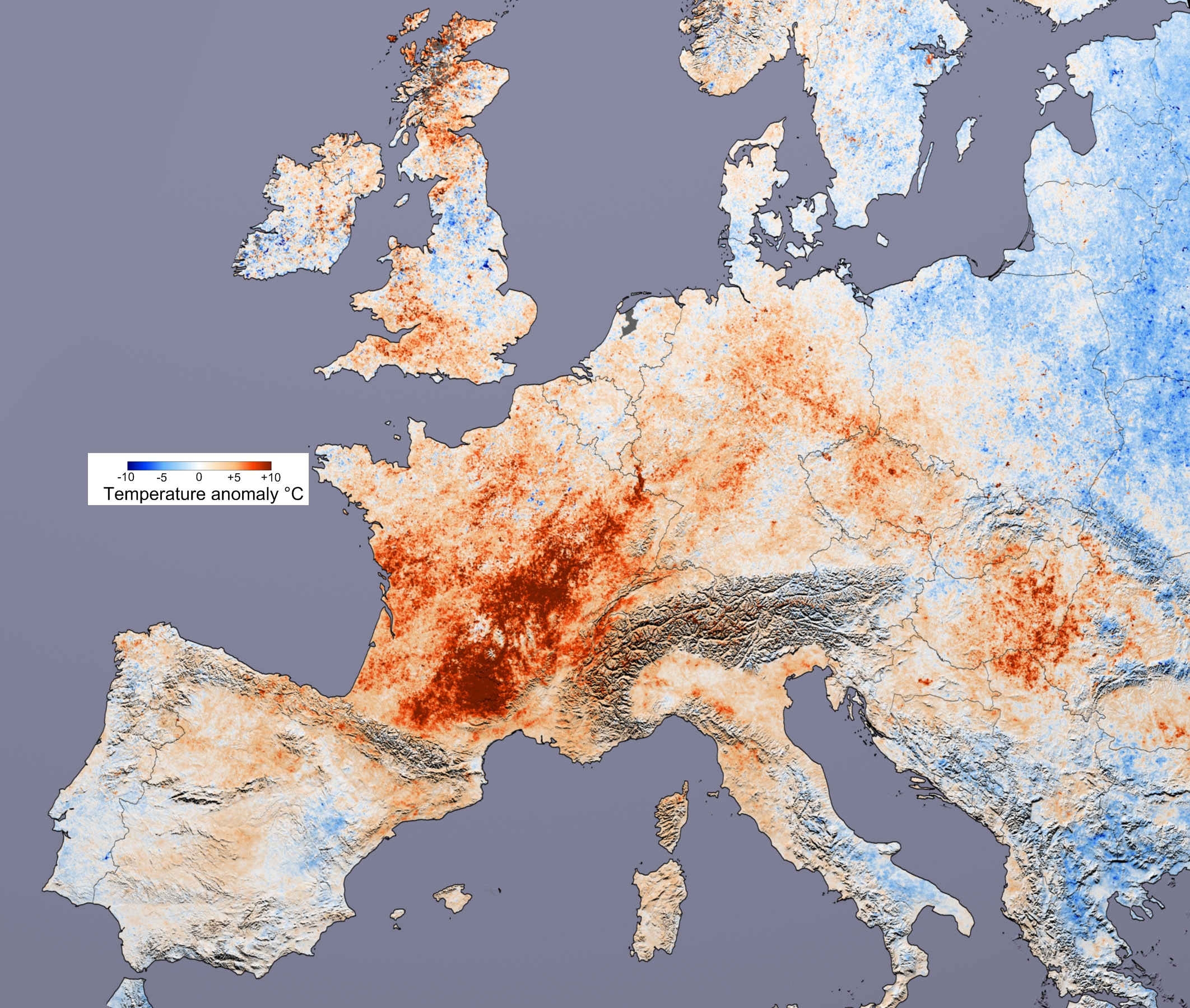 Heat waves are periods of abnormally high temperatures and
Heat waves are periods of abnormally high temperatures and
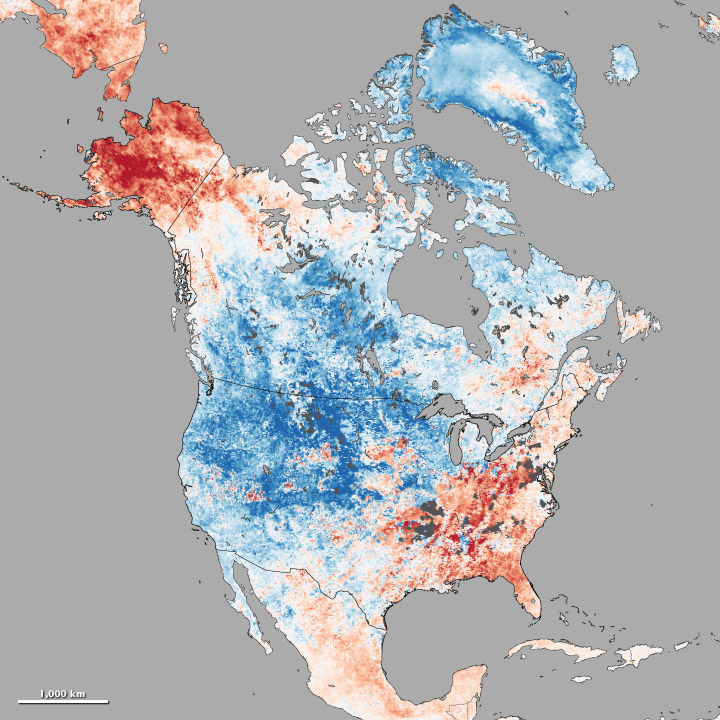 A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection for agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criterion for a cold wave is determined by the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year. Cold waves generally are capable of occurring at any geological location and are formed by large cool air masses that accumulate over certain regions, caused by movements of air streams.
A cold wave can cause death and injury to livestock and wildlife. Exposure to cold mandates greater caloric intake for all animals, including humans, and if a cold wave is accompanied by heavy and persistent snow, grazing animals may be unable to reach necessary food and water, and die of
A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection for agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criterion for a cold wave is determined by the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year. Cold waves generally are capable of occurring at any geological location and are formed by large cool air masses that accumulate over certain regions, caused by movements of air streams.
A cold wave can cause death and injury to livestock and wildlife. Exposure to cold mandates greater caloric intake for all animals, including humans, and if a cold wave is accompanied by heavy and persistent snow, grazing animals may be unable to reach necessary food and water, and die of
 Some studies assert a connection between rapidly warming arctic temperatures and thus a vanishing
Some studies assert a connection between rapidly warming arctic temperatures and thus a vanishing
Statistics of Weather and Climate Extremes
The
Research forecasts increased chances for stormy weather
,
Severe world weather overview
{{Authority control Weather hazards Severe weather and convection Effects of climate change Articles containing video clips
severe
Severity or Severely may refer to:
* ''Severity'' (video game), a canceled video game
* "Severely" (song), by South Korean band F.T. Island
See also
*
*
{{disambig ...
, or unseasonal weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloud cover, cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmo ...
; weather at the extremes of the historical distribution—the range that has been seen in the past. Extreme events are based on a location's recorded weather history. The main types of extreme weather include heat wave
A heat wave or heatwave, sometimes described as extreme heat, is a period of abnormally hot weather generally considered to be at least ''five consecutive days''. A heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the area and ...
s, cold wave
A cold wave (known in some regions as a cold snap, cold spell or Arctic Snap) is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temp ...
s, drought
A drought is a period of drier-than-normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, ...
s, and heavy precipitation or storm events, such as tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its locat ...
s. Extreme weather can have various effects, from natural hazards such as flood
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant con ...
s and landslide
Landslides, also known as landslips, rockslips or rockslides, are several forms of mass wasting that may include a wide range of ground movements, such as rockfalls, mudflows, shallow or deep-seated slope failures and debris flows. Landslides ...
s to social costs on human health and the economy. Severe weather
Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. These vary depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High ...
is a particular type of extreme weather which poses risks to life and property.
Weather patterns in a given region vary with time, and so extreme weather can be attributed, at least in part, to the natural climate variability
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more ...
that exists on Earth. For example, the El Niño-Southern Oscillation
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
(ENSO) or the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) are climate phenomena that impact weather patterns worldwide. Generally speaking, one event in extreme weather cannot be attributed to any one single cause. However, certain system wide changes to global weather systems can lead to increased frequency or intensity of extreme weather events.
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
might make some extreme weather events more frequent and more intense. This applies in particular to heat waves and cold waves. The extreme event attribution
Extreme event attribution, also known as attribution science, is the identification and quantification of the role that human-caused climate change plays in the frequency and intensity of Rare events, extreme weather events. Attribution science ai ...
sector looks at possible explanations behind extreme events. Climate model
Numerical climate models (or climate system models) are mathematical models that can simulate the interactions of important drivers of climate. These drivers are the atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. Scientists use climate models to st ...
s indicate that rising temperatures might make extreme weather events worse worldwide.
Extreme weather has serious impacts on human society and on ecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) is a system formed by Organism, organisms in interaction with their Biophysical environment, environment. The Biotic material, biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and en ...
s. There is loss of human lives, damage to infrastructure and ecosystem destruction. Some human activities can exacerbate the effects, for example poor urban planning
Urban planning (also called city planning in some contexts) is the process of developing and designing land use and the built environment, including air, water, and the infrastructure passing into and out of urban areas, such as transportatio ...
, wetland
A wetland is a distinct semi-aquatic ecosystem whose groundcovers are flooded or saturated in water, either permanently, for years or decades, or only seasonally. Flooding results in oxygen-poor ( anoxic) processes taking place, especially ...
destruction, and building homes along floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river. Floodplains stretch from the banks of a river channel to the base of the enclosing valley, and experience flooding during periods of high Discharge (hydrolog ...
s.
Definition
Extreme weather describes unusual weather events that are at the extremes of the historical distribution for a given area. TheIPCC Sixth Assessment Report
The Sixth Assessment Report (AR6) of the United Nations (UN) Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) is the sixth in a series of reports which assess the available scientific information on climate change. Three Working Groups (WGI, II, ...
defines an extreme weather event as follows: "An event that is rare at a particular place and time of year. Definitions of 'rare' vary, but an extreme weather event would normally be as rare as or rarer than the 10th or 90th percentile of a probability density function estimated from observations."IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary
öller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger (eds.) In
Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.) Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, US, pp. 2897–2930, doi:10.1017/9781009325844.029. In comparison, the term ''
severe weather
Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. These vary depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High ...
'' is any aspect of the weather that poses risks to life, property or requires the intervention of authorities. Severe weather is thus a particular type of extreme weather.
Types
Definitions of extreme weather vary in different parts of the community, changing the outcomes of research from those fields. Types of extreme weather can include, but are not limited to, heavy precipitation, droughts, heat waves, cold waves, tornadoes, and hurricanes.Heat waves
 Heat waves are periods of abnormally high temperatures and
Heat waves are periods of abnormally high temperatures and heat index
The heat index (HI) is an index that combines air temperature and relative humidity, in shade (shadow), shaded areas, to posit a human-perceived equivalent temperature, as how hot it would feel if the humidity were some other value in the Shade (s ...
. Definitions of a heatwave vary because of the variation of temperatures in different geographic locations. Excessive heat is often accompanied by high levels of humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog t ...
, but can also be catastrophically dry.
Because heat waves are not visible as other forms of severe weather, like hurricanes, tornadoes, and thunderstorms, they are one of the less known forms of extreme weather. Severely hot weather can damage populations and crops due to potential dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
or hyperthermia
Hyperthermia, also known as overheating, is a condition in which an individual's body temperature is elevated beyond normal due to failed thermoregulation. The person's body produces or absorbs more heat than it dissipates. When extreme te ...
, heat cramps
Heat cramps, a type of heat illness, are muscle spasms that result from loss of large amount of salt and water through exercise. Heat cramps are associated with cramping in the abdomen, arms and calves. This can be caused by inadequate consumption ...
, heat expansion
Thermal expansion is the tendency of matter to increase in length, area, or volume, changing its size and density, in response to an increase in temperature (usually excluding phase transitions).
Substances usually contract with decreasing temp ...
, and heat stroke
Heat stroke or heatstroke, also known as sun-stroke, is a severe heat illness that results in a body temperature greater than , along with red skin, headache, dizziness, and confusion. Sweating is generally present in exertional heatstro ...
. Dried soils are more susceptible to erosion, decreasing lands available for agriculture
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created ...
. Outbreaks of wildfires can increase in frequency as dry vegetation has an increased likelihood of igniting. The evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the Interface (chemistry), surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. A high concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evapora ...
of bodies of water can be devastating to marine populations, decreasing the size of the habitats available as well as the amount of nutrition present within the waters. Livestock and other animal populations may decline as well.
During excessive heat, plants shut their leaf pores (stomata
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spa ...
), a protective mechanism to conserve water but also curtails plants' absorption capabilities. This leaves more pollution and ozone in the air, which leads to higher mortality in the population. It has been estimated that extra pollution during the hot summer of 2006 in the UK, cost 460 lives. The European heat waves from summer 2003 are estimated to have caused 30,000 excess deaths, due to heat stress and air pollution
Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ...
. Over 200 U.S cities have registered new record high temperatures. The worst heat wave in the US occurred in 1936 and killed more than 5000 people directly. The worst heat wave in Australia occurred in 1938–39 and killed 438. The second worst was in 1896.
Power outages can also occur within areas experiencing heat waves due to the increased demand for electricity (i.e. air conditioning use). The urban heat island
Urban areas usually experience the urban heat island (UHI) effect; that is, they are significantly warmer than surrounding rural areas. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent when winds ar ...
effect can increase temperatures, particularly overnight.
Cold waves
 A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection for agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criterion for a cold wave is determined by the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year. Cold waves generally are capable of occurring at any geological location and are formed by large cool air masses that accumulate over certain regions, caused by movements of air streams.
A cold wave can cause death and injury to livestock and wildlife. Exposure to cold mandates greater caloric intake for all animals, including humans, and if a cold wave is accompanied by heavy and persistent snow, grazing animals may be unable to reach necessary food and water, and die of
A cold wave is a weather phenomenon that is distinguished by a cooling of the air. Specifically, as used by the U.S. National Weather Service, a cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within a 24-hour period requiring substantially increased protection for agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities. The precise criterion for a cold wave is determined by the rate at which the temperature falls, and the minimum to which it falls. This minimum temperature is dependent on the geographical region and time of year. Cold waves generally are capable of occurring at any geological location and are formed by large cool air masses that accumulate over certain regions, caused by movements of air streams.
A cold wave can cause death and injury to livestock and wildlife. Exposure to cold mandates greater caloric intake for all animals, including humans, and if a cold wave is accompanied by heavy and persistent snow, grazing animals may be unable to reach necessary food and water, and die of hypothermia
Hypothermia is defined as a body core temperature below in humans. Symptoms depend on the temperature. In mild hypothermia, there is shivering and mental confusion. In moderate hypothermia, shivering stops and confusion increases. In severe ...
or starvation. Cold waves often necessitate the purchase of fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agriculture, agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, domestic rabbit, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food ...
for livestock at a considerable cost to farmers. Human populations can be inflicted with frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when someone is exposed to extremely low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occ ...
when exposed for extended periods of time to cold and may result in the loss of limbs or damage to internal organs.
Extreme winter cold often causes poorly insulated water pipes
Pipe(s), PIPE(S) or piping may refer to:
Objects
* Pipe (fluid conveyance), a hollow cylinder following certain dimension rules
** Piping, the use of pipes in industry
* Smoking pipe
** Tobacco pipe
* Half-pipe and quarter pipe, semi-circu ...
to freeze. Even some poorly protected indoor plumbing
Plumbing is any system that conveys fluids for a wide range of applications. Plumbing uses piping, pipes, valves, piping and plumbing fitting, plumbing fixtures, Storage tank, tanks, and other apparatuses to convey fluids. HVAC, Heating and co ...
may rupture as frozen water expands within them, causing property damage. Fires, paradoxically, become more hazardous during extreme cold. Water mains may break and water supplies may become unreliable, making firefighting
Firefighting is a profession aimed at controlling and extinguishing fire. A person who engages in firefighting is known as a firefighter or fireman. Firefighters typically undergo a high degree of technical training. This involves structural fir ...
more difficult.
Cold waves that bring unexpected freezes and frosts during the growing season in mid-latitude zones can kill plants during the early and most vulnerable stages of growth. This results in crop failure as plants are killed before they can be harvest
Harvesting is the process of collecting plants, animals, or fish (as well as fungi) as food, especially the process of gathering mature crops, and "the harvest" also refers to the collected crops. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulses fo ...
ed economically. Such cold waves have caused famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food caused by several possible factors, including, but not limited to war, natural disasters, crop failure, widespread poverty, an Financial crisis, economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenom ...
s. Cold waves can also cause soil particles to harden and freeze, making it harder for plants and vegetation to grow within these areas. One extreme was the so-called Year Without a Summer
The year 1816 is known as the Year Without a Summer because of severe climate abnormalities that caused average global temperatures to decrease by . Summer temperatures in Europe were the coldest of any on record between 1766 and 2000, resultin ...
of 1816, one of several years during the 1810s in which numerous crops failed during freakish summer cold snaps after volcanic eruption
A volcanic eruption occurs when material is expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior h ...
s reduced incoming sunlight.
In some cases more frequent extremely cold winter weather – i.e. across parts of Asia and North America including the February 2021 North American cold wave
The February 2021 North American cold wave was an extreme weather event that brought record low temperatures to a significant portion of Canada, the United States and parts of northern Mexico during the first two-thirds of February 2021. The c ...
– can be a result of climate change such as due to changes in the Arctic. However, conclusions that link climate change to cold waves are considered to still be controversial. The JRC PESETA IV project concluded in 2020 that overall climate change will result in a decline in the intensity and frequency of extreme cold spells, with milder winters reducing fatalities from extreme cold, even if individual cold extreme weather may sometimes be caused by changes due to climate change and possibly even become more frequent in some regions.
According to a 2023 study, "weak extreme cold events (ECEs) significantly decrease in frequency, projection area and total area over the north hemisphere with global warming. However, the frequency, projection area and total area of strong ECEs show no significant trend, whereas they are increasing in Siberia and Canada."
Heavy rain and storms
Tropical cyclones
Less rain than usual
A shift in rainfall patterns can lead to greater amounts of precipitation in one area while another experiences much hotter, drier conditions, which can lead to drought. This is because an increase in temperatures also lead to an increase in evaporation at the surface of the earth, so more precipitation does not necessarily mean universally wetter conditions or a worldwide increase in drinking water.Causes and attribution
Attribution research
Generally speaking, one event in extreme weather cannot be attributed to any one cause. However, certain system wide changes to global weather systems can lead to increased frequency or intensity of extreme weather events. Early research in extreme weather focused on statements about predicting certain events. Contemporary research focuses more on the attribution of causes to trends in events. In particular the field is focusing onclimate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
alongside other causal factors for these events.
A 2016 report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), also known as the National Academies, is a Congressional charter, congressionally chartered organization that serves as the collective scientific national academy of the Uni ...
, recommended investing in improved shared practices across the field working on attribution research, improving the connection between research outcomes and weather forecasting.
As more research is done in this area, scientists have begun to investigate the connection between climate change and extreme weather events and what future impacts may arise. Much of this work is done through climate modeling. Climate models provide important predictions about the future characteristics of the atmosphere, oceans, and Earth using data collected in the modern day. However, while climate models are vital for studying more complex processes such as climate change or ocean acidification, they are still only approximations. Moreover, weather events are complex and cannot be tied to a singular cause—there are often many atmospheric variables such as temperature, pressure, or moisture to note on top of any influences from climate change or natural variability.
Natural variability
Aspects of our climate system have a certain level of natural variability, and extreme weather events can occur for several reasons beyond human impact, including changes in pressure or the movement of air. Areas along the coast or located in tropical regions are more likely to experience storms with heavy precipitation than temperate regions, although such events can occur. The atmosphere is a complex and dynamic system, influenced by several factors such as the natural tilt and orbit of the Earth, the absorption or reflection of solar radiation, the movement of air masses, and thewater cycle
The water cycle (or hydrologic cycle or hydrological cycle) is a biogeochemical cycle that involves the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth across different reservoirs. The mass of water on Earth remains fai ...
. Due to this, weather patterns can experience some variation, and so extreme weather can be attributed, at least in part, to the natural climate variability
Climate variability includes all the variations in the climate that last longer than individual weather events, whereas the term climate change only refers to those variations that persist for a longer period of time, typically decades or more ...
that exists on Earth.
Climatic phenomena such as the El Niño-Southern Oscillation
EL, El or el may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Fictional entities
* El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit
* Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things''
* El, fami ...
(ENSO) or the North Atlantic oscillation (NAO) impact weather patterns in specific regions of the world, influencing temperature and precipitation. The record-breaking extreme weather events that have been catalogued throughout the past two hundred years most likely arise when climate patterns like ENSO or NAO work "in the same direction as human‐induced warming."
Climate change
cryosphere
The cryosphere is an umbrella term for those portions of Earth's surface where water is in solid form. This includes sea ice, ice on lakes or rivers, snow, glaciers, ice caps, ice sheets, and frozen ground (which includes permafrost). Thus, there ...
to extreme weather in mid-latitudes. In a study published in Nature in 2019, scientists used several simulations to determine that the melting of ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica could affect overall sea level and sea temperature. Other models have shown that modern temperature rise and the subsequent addition of meltwater to the ocean could lead to a disruption of the thermohaline circulation, which is responsible for the movement of seawater and distribution of heat around the globe. A collapse of this circulation in the northern hemisphere could lead to an increase in extreme temperatures in Europe, as well as more frequent storms by throwing off natural climate variability and conditions. Thus, as increasing temperatures cause glaciers to melt, mid-latitudes could experience shifts in weather patterns or temperatures.
There were around 6,681 climate-related events reported during 2000-2019, compared to 3,656 climate-related events reported during 1980–1999. In this report, a 'climate-related event' refers to floods, storms, droughts, landslides, extreme temperatures (like heat waves or freezes), and wildfires; it excludes geophysical events such as volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, or mass movements. While there is evidence that a changing global climate, such as an increase in temperature, has impacted the frequency of extreme weather events, the most significant effects are likely to arise in the future. This is where climate models are useful, for they can provide simulations of how the atmosphere may behave over time and what steps need to be taken in the present day to mitigate any negative changes.
The increasing probability of record week-long heat extremes occurrence depends on warming rate, rather than global warming level.
Some researchers attribute increases in extreme weather occurrences to more reliable reporting systems. A difference in what qualifies as 'extreme weather' in varying climate systems could also be argued. Over or under reporting of casualties or losses can lead to inaccuracy in the impact of extreme weather. However, the UN reports show that, although some countries have experienced greater effects, there have been increases in extreme weather events on all continents. Current evidence and climate models show that an increasing global temperature will intensify extreme weather events around the globe, thereby amplifying human loss, damages and economic costs, and ecosystem destruction.
Tropical cyclones and climate change
In 2020, theNational Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA ) is an American scientific and regulatory agency charged with Weather forecasting, forecasting weather, monitoring oceanic and atmospheric conditions, Hydrography, charting the seas, ...
(NOAA) of the U.S. government predicted that, over the 21st Century, the frequency of tropical storms and Atlantic hurricanes would decline by 25 percent while their maximum intensity would rise by 5 percent.
Floods
Climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
has led to an increase in the frequency and/or intensity of certain types of extreme weather. Storms such as hurricanes or tropical cyclones may experience greater rainfall, causing major flooding events or landslides by saturating soil. This is because warmer air is able to 'hold' more moisture due to the water molecules having increased kinetic energy, and precipitation occurs at a greater rate because more molecules have the critical speed needed to fall as rain drops.
Human activities that exacerbate the effects
There are plenty of anthropogenic activities that can exacerbate the effects of extreme weather events. Urban planning often amplifiesurban flooding
Urban flooding is the inundation of land or property in cities or other built environment, caused by rainfall or coastal storm surges overwhelming the capacity of drainage systems, such as storm sewers. Urban flooding can occur regardless of whethe ...
impacts, especially in areas that are at increased risk of storms due to their location and climate variability. First, increasing the amount of impervious surfaces, such as sidewalks, roads, and roofs, means that less of the water from incoming storms is absorbed by the land. The destruction of wetlands, which act as a natural reservoir by absorbing water, can intensify the impact of floods and extreme precipitation. This can happen both inland and at the coast. However, wetland destruction along the coast can mean decreasing an area's natural 'cushion,' thus allowing storm surges and flood waters to reach farther inland during hurricanes or cyclones. Building homes below sea level or along a floodplain puts residents at increased risk of destruction or injury in an extreme precipitation event.
More urban areas can also contribute to the rise of extreme or unusual weather events. Tall structures can alter the way that wind moves throughout an urban area, pushing warmer air upwards and inducing convection, creating thunderstorms. With these thunderstorms comes increased precipitation, which, because of the large amounts of impervious surfaces in cities, can have devastating impacts. Impervious surfaces also absorb energy from the sun and warm the atmosphere, causing drastic increases in temperatures in urban areas. This, along with pollution and heat released from cars and other anthropogenic sources, contributes to urban heat islands.
Effects
Extreme weather affects a range of issues, from the economy to human health, and can lead to the occurrence of natural hazards, such as floods and landslides.Economic cost
In the face of record breaking extreme weather events,climate change adaptation
Climate change adaptation is the process of adjusting to the effects of climate change, both current and anticipated.IPCC, 2022Annex II: Glossary[Möller, V., R. van Diemen, J.B.R. Matthews, C. Méndez, S. Semenov, J.S. Fuglestvedt, A. Reisinger ...
efforts fall short while economists are confronted with inflation, the cost-of-living crisis, and economic uncertainty. In 2011 the IPCC estimated, that annual losses have ranged since 1980 from a few billion to above US$200 billion, with the highest economic losses occurring in 2005, the year of Hurricane Katrina
Hurricane Katrina was a powerful, devastating and historic tropical cyclone that caused 1,392 fatalities and damages estimated at $125 billion in late August 2005, particularly in the city of New Orleans and its surrounding area. ...
. The global weather-related disaster losses, such as loss of human lives, cultural heritage, and ecosystem services
Ecosystem services are the various benefits that humans derive from Ecosystem, ecosystems. The interconnected Biotic_material, living and Abiotic, non-living components of the natural environment offer benefits such as pollination of crops, clean ...
, are difficult to value and monetize, and thus they are poorly reflected in estimates of losses.
The World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an international non-governmental organization, international advocacy non-governmental organization and think tank, based in Cologny, Canton of Geneva, Switzerland. It was founded on 24 January 1971 by German ...
Global Risks Perception Survey 2023-2024 (GRPS) found that 66 percent of respondents selected extreme weather as top risk. The survey was conducted after the 2023 heat waves
A number of heat waves began across parts of the northern hemisphere in April 2023. Various heat records have been broken, with July being the hottest month ever recorded.
Scientists have Extreme event attribution, attributed the heat waves t ...
. According to the GRPS results, the perception of necessary short and long-term risk management
Risk management is the identification, evaluation, and prioritization of risks, followed by the minimization, monitoring, and control of the impact or probability of those risks occurring. Risks can come from various sources (i.e, Threat (sec ...
varies. Younger respondents prioritize environmental risks, including extreme weather, in the short-term. Respondents working in the private sector
The private sector is the part of the economy which is owned by private groups, usually as a means of establishment for profit or non profit, rather than being owned by the government.
Employment
The private sector employs most of the workfo ...
prioritize environmental risks as long-term.
Casualties
The death toll fromnatural disaster
A natural disaster is the very harmful impact on a society or community brought by natural phenomenon or Hazard#Natural hazard, hazard. Some examples of natural hazards include avalanches, droughts, earthquakes, floods, heat waves, landslides ...
s has declined over 90 percent since the 1920s, according to the International Disaster Database, even as the total human population on Earth quadrupled, and temperatures rose 1.3 °C. In the 1920s, 5.4 million people died from natural disasters while in the 2010s, just 400,000 did.
The most dramatic and rapid declines in deaths from extreme weather events have taken place in south Asia. Where a tropical cyclone in 1991 in Bangladesh killed 135,000 people, and a 1970 cyclone killed 300,000, the similarly-sized Cyclone Ampham, which struck India and Bangladesh in 2020, killed just 120 people in total.
On July 23, 2020, Munich Re announced that the 2,900 total global deaths from natural disasters for the first half of 2020 were a record-low, and "much lower than the average figures for both the last 30 years and the last 10 years."
A 2021 study found that 9.4% of global deaths between 2000 and 2019 – ~5 million annually – can be attributed to extreme temperature with cold-related ones making up the larger share and decreasing and heat-related ones making up ~0.91% and increasing.
A 2023 study published in ''The Lancet Planetary Health'' estimates that extreme cold events contributed to over 200,000 excess deaths and extreme heat events contributed to over 20,000 excess deaths in European urban areas between 2000 and 2019.
See also
*Heat burst
In meteorology, a heat burst is a rare atmospheric phenomenon characterized by a sudden, localized increase in air temperature near the Earth's surface. Heat bursts typically occur during night-time and are associated with decaying thunderstorm ...
*Lists of tornadoes and tornado outbreaks
These are some notable tornadoes, tornado outbreaks, and tornado outbreak sequences that have occurred around the globe.
# ''Exact death and injury counts are not possible; especially for large events and events before 1955.''
# ''Prior to 1950 ...
*List of weather records
The list of weather records includes the most extreme occurrences of weather phenomena for various categories. Many weather records are measured under specific conditions—such as surface temperature and wind speed—to keep consistency amon ...
*Downburst
In meteorology, a downburst is a strong downward and outward gushing wind system that emanates from a point source above and blows radially, that is, in straight lines in all directions from the area of impact at surface level. It originate ...
*Rogue wave A rogue wave is an abnormally large ocean wave.
Rogue wave may also refer to:
* Optical rogue waves, are rare pulses of light analogous to rogue or freak ocean waves.
* Rogue Wave Software, a software company
* Rogue Wave (band), an American in ...
*Severe weather
Severe weather is any dangerous meteorological phenomenon with the potential to cause damage, serious social disruption, or loss of human life. These vary depending on the latitude, altitude, topography, and atmospheric conditions. High ...
** List of severe weather phenomena
Severe weather phenomena are weather conditions that are hazardous to human life and property.
Severe weather can occur under a variety of situations, but three characteristics are generally needed: a temperature or moisture boundary, moisture, a ...
*Extreme weather events of 535–536
The volcanic winter of 536 was among the most severe and protracted episodes of climatic cooling in the Northern Hemisphere in the last 2,000 years. The volcanic winter was caused by at least three simultaneous eruptions of uncertain origin, wit ...
*Year Without a Summer
The year 1816 is known as the Year Without a Summer because of severe climate abnormalities that caused average global temperatures to decrease by . Summer temperatures in Europe were the coldest of any on record between 1766 and 2000, resultin ...
*Extreme event attribution
Extreme event attribution, also known as attribution science, is the identification and quantification of the role that human-caused climate change plays in the frequency and intensity of Rare events, extreme weather events. Attribution science ai ...
References
External links
Statistics of Weather and Climate Extremes
The
University Corporation for Atmospheric Research
The University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR) is a US nonprofit consortium of more than 100 colleges and universities providing research and training in the atmospheric and related sciences. UCAR manages the National Center for Atmosph ...
(UCAR)Research forecasts increased chances for stormy weather
,
Purdue University
Purdue University is a Public university#United States, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in West Lafayette, Indiana, United States, and the flagship campus of the Purdue University system. The university was founded ...
studySevere world weather overview
{{Authority control Weather hazards Severe weather and convection Effects of climate change Articles containing video clips