Extinct Birds Of Asia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Extinction is the termination of an
 A species is extinct when the last existing member dies. Extinction therefore becomes a certainty when there are no surviving individuals that can reproduce and create a new generation. A species may become
A species is extinct when the last existing member dies. Extinction therefore becomes a certainty when there are no surviving individuals that can reproduce and create a new generation. A species may become  In
In
Extinct in the Wild" ''The Extinction Website''. URL accessed January 26 2007.
When possible, modern
 As long as species have been evolving, species have been going extinct. It is estimated that over 99.9% of all species that ever lived are extinct. The average lifespan of a species is 1–10 million years, although this varies widely between taxa.
A variety of causes can contribute directly or indirectly to the extinction of a species or group of species. "Just as each species is unique", write Beverly and Stephen C. Stearns, "so is each extinction ... the causes for each are varied—some subtle and complex, others obvious and simple". Most simply, any species that cannot
As long as species have been evolving, species have been going extinct. It is estimated that over 99.9% of all species that ever lived are extinct. The average lifespan of a species is 1–10 million years, although this varies widely between taxa.
A variety of causes can contribute directly or indirectly to the extinction of a species or group of species. "Just as each species is unique", write Beverly and Stephen C. Stearns, "so is each extinction ... the causes for each are varied—some subtle and complex, others obvious and simple". Most simply, any species that cannot
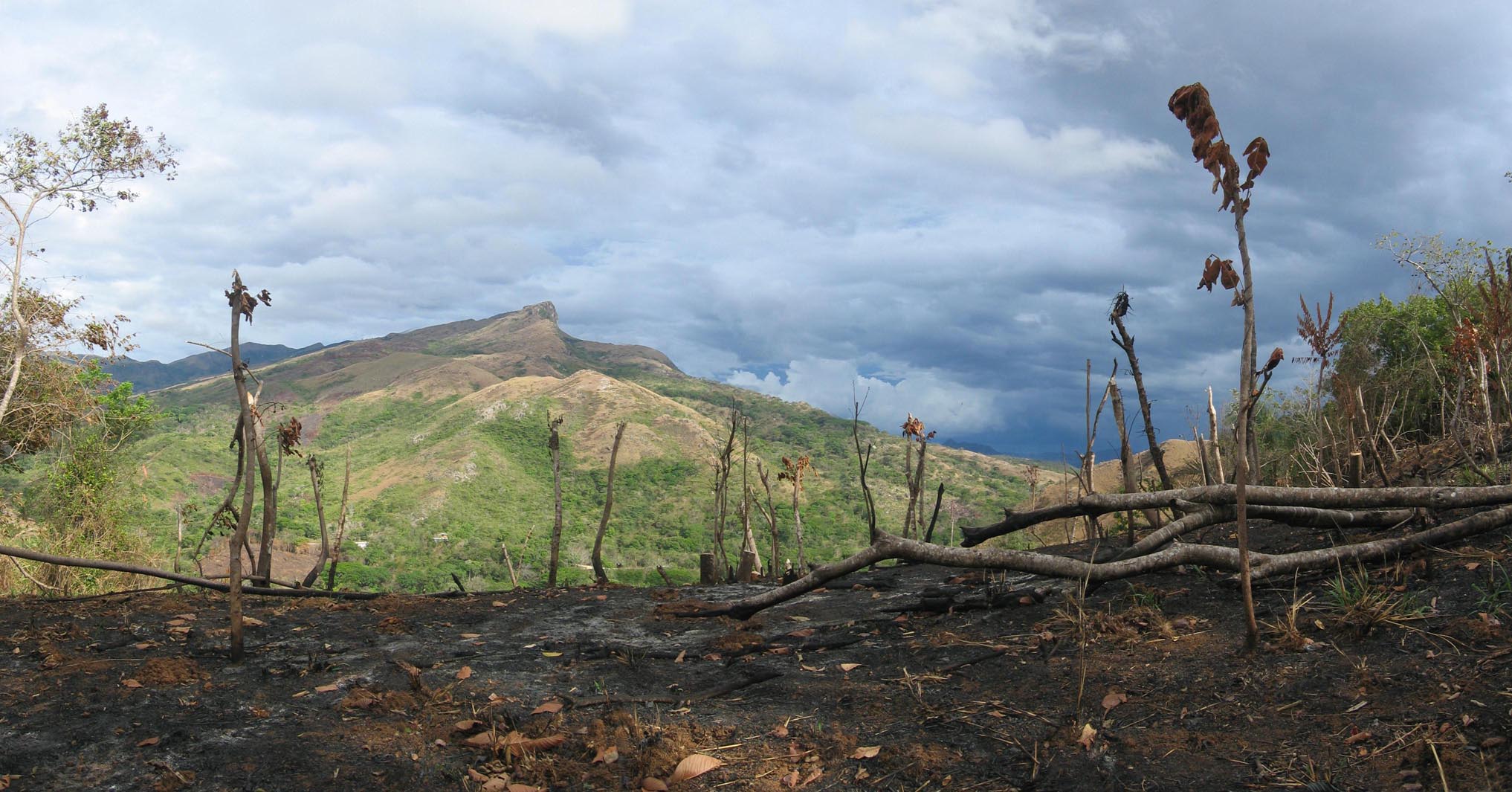 Habitat degradation is currently the main anthropogenic cause of species extinctions. The main cause of habitat degradation worldwide is agriculture, with
Habitat degradation is currently the main anthropogenic cause of species extinctions. The main cause of habitat degradation worldwide is agriculture, with
 In the natural course of events, species become extinct for a number of reasons, including but not limited to: extinction of a necessary host, prey or pollinator,
In the natural course of events, species become extinct for a number of reasons, including but not limited to: extinction of a necessary host, prey or pollinator,
The Pleistocene Overkill Hypothesis
." ''University of California at Berkeley Geography Program.'' Retrieved January 11, 2007.
 Coextinction refers to the loss of a species due to the extinction of another; for example, the extinction of parasitic insects following the loss of their hosts. Coextinction can also occur when a species loses its
Coextinction refers to the loss of a species due to the extinction of another; for example, the extinction of parasitic insects following the loss of their hosts. Coextinction can also occur when a species loses its
 According to a 1998 survey of 400 biologists conducted by New York City, New York's American Museum of Natural History, nearly 70% believed that the Earth is currently in the early stages of a human-caused mass extinction,American Museum of Natural History.
According to a 1998 survey of 400 biologists conducted by New York City, New York's American Museum of Natural History, nearly 70% believed that the Earth is currently in the early stages of a human-caused mass extinction,American Museum of Natural History.
National Survey Reveals Biodiversity Crisis – Scientific Experts Believe We are in the Midst of the Fastest Mass Extinction in Earth's History
". Retrieved September 20, 2006. known as the Holocene extinction. In that survey, the same proportion of respondents agreed with the prediction that up to 20% of all living populations could become extinct within 30 years (by 2028). A 2014 special edition of ''Science (journal), Science'' declared there is widespread consensus on the issue of human-driven mass species extinctions. A 2020 study published in ''PNAS'' stated that the contemporary extinction crisis "may be the most serious environmental threat to the persistence of civilization, because it is irreversible." A 2025 study found that human activities are to blame for biodiversity loss across all species and ecosystems. Biologist E. O. Wilson estimated in 2002 that if current rates of human destruction of the biosphere continue, one-half of all plant and animal species of life on earth will be extinct in 100 years. E.O. Wilson repeats his estimation in 2012. More significantly, the current rate of global species extinctions is estimated as 100 to 1,000 times "background" rates (the average extinction rates in the
 For much of history, the modern understanding of extinction as the end of a
For much of history, the modern understanding of extinction as the end of a
 Extinction is an important research topic in the field of zoology, and biology in general, and has also become an area of concern outside the scientific community. A number of organizations, such as the WWF (conservation organization), Worldwide Fund for Nature, have been created with the goal of preserving species from extinction. Governments have attempted, through enacting laws, to avoid habitat destruction, agricultural over-harvesting, and
Extinction is an important research topic in the field of zoology, and biology in general, and has also become an area of concern outside the scientific community. A number of organizations, such as the WWF (conservation organization), Worldwide Fund for Nature, have been created with the goal of preserving species from extinction. Governments have attempted, through enacting laws, to avoid habitat destruction, agricultural over-harvesting, and
Extinction
. Bioscience at University of Arizona. Retrieved July 26, 2006.Committee on Recently Extinct Organisms.
". Retrieved July 30, 2006. In modern times, commercial and industrial interests often have to contend with the effects of production on plant and animal life. However, some technologies with minimal, or no, proven harmful effects on ''Homo sapiens'' can be devastating to wildlife (for example, DDT).International Programme on Chemical Safety (1989).
DDT and its Derivatives – Environmental Aspects
". Environmental Health Criteria 83. Retrieved September 20, 2006. Biogeography, Biogeographer Jared Diamond notes that while big business may label environmental concerns as "exaggerated", and often cause "devastating damage", some corporations find it in their interest to adopt good conservation practices, and even engage in preservation efforts that surpass those taken by national parks. Governments sometimes see the loss of native species as a loss to ecotourism,Drewry, Rachel.
Ecotourism: Can it save the orangutans?
" ''Inside Indonesia''. Retrieved January 26, 2007. and can enact laws with severe punishment against the trade in native species in an effort to prevent extinction in the wild. Nature preserves are created by governments as a means to provide continuing habitats to species crowded by human expansion. The 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity has resulted in international Biodiversity Action Plan programmes, which attempt to provide comprehensive guidelines for government biodiversity conservation. Advocacy groups, such as The Wildlands ProjectThe Wildlands Project
. Retrieved January 26, 2007. and the Alliance for Zero Extinctions, work to educate the public and pressure governments into action. People who live close to nature can be dependent on the survival of all the species in their environment, leaving them highly exposed to extinction risks. However, people prioritize day-to-day survival over species conservation; with human overpopulation in tropical developing country, developing countries, there has been enormous pressure on forests due to subsistence agriculture, including slash-and-burn agricultural techniques that can reduce endangered species's habitats. Antinatalist philosopher David Benatar concludes that any popular concern about non-human species extinction usually arises out of concern about how the loss of a species will impact human wants and needs, that "we shall live in a world impoverished by the loss of one aspect of faunal diversity, that we shall no longer be able to behold or use that species of animal." He notes that typical concerns about possible human extinction, such as the loss of individual members, are not considered in regards to non-human species extinction. Anthropologist Jason Hickel speculates that the reason humanity seems largely indifferent to anthropogenic mass species extinction is that we see ourselves as separate from the natural world and the organisms within it. He says that this is due in part to the logic of capitalism: "that the world is not really alive, and it is certainly not our kin, but rather just stuff to be extracted and discarded – and that includes most of the human beings living here too."
 Some, such as Harvard geneticist George M. Church, believe that ongoing technological advances will let us "bring back to life" an extinct species by Cloning#Cloning extinct and endangered species, cloning, using DNA from the remains of that species. Proposed targets for cloning include the
Some, such as Harvard geneticist George M. Church, believe that ongoing technological advances will let us "bring back to life" an extinct species by Cloning#Cloning extinct and endangered species, cloning, using DNA from the remains of that species. Proposed targets for cloning include the
Committee on recently extinct organisms
The age of extinction
series in ''The Guardian''
Extincion events connected with New theory of evolution
{{Authority control Extinction, Biota by conservation status Environmental conservation Evolutionary biology IUCN Red List
organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have be ...
by the death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
of its last member. A taxon
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; : taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and ...
may become functionally extinct
Functional extinction is the extinction of a species or other taxon such that:
#It disappears from the fossil record, or historic reports of its existence cease;
#The reduced population no longer plays a significant role in ecosystem function;
#T ...
before the death of its last member if it loses the capacity to reproduce
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual.
In asexual reprod ...
and recover. As a species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
) after a period of apparent absence.
Over five billion species are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote
The eukaryotes ( ) constitute the Domain (biology), domain of Eukaryota or Eukarya, organisms whose Cell (biology), cells have a membrane-bound cell nucleus, nucleus. All animals, plants, Fungus, fungi, seaweeds, and many unicellular organisms ...
s globally, possibly many times more if microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe, is an organism of microscopic scale, microscopic size, which may exist in its unicellular organism, single-celled form or as a Colony (biology)#Microbial colonies, colony of cells. The possible existence of unseen ...
s are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats
Machairodontinae (from Ancient Greek μάχαιρα ''Makhaira, machaira,'' a type of Ancient Greek sword and ὀδόντος ''odontos'' meaning tooth) is an extinct subfamily of carnivoran mammals of the cat family Felidae, representing the ...
, and mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
s. Through evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
, species arise through the process of speciation
Speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species. The biologist Orator F. Cook coined the term in 1906 for cladogenesis, the splitting of lineages, as opposed to anagenesis, phyletic evolution within ...
. Species become extinct when they are no longer able to survive in changing conditions or against superior competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
. The relationship between animals and their ecological niches has been firmly established. A typical species becomes extinct within 10 million years of its first appearance, although some species, called living fossil
A living fossil is a Deprecation, deprecated term for an extant taxon that phenotypically resembles related species known only from the fossil record. To be considered a living fossil, the fossil species must be old relative to the time of or ...
s, survive with little to no morphological change for hundreds of millions of years.
Mass extinctions are relatively rare events; however, isolated extinctions of species and clades are quite common, and are a natural part of the evolutionary process. Only recently have extinctions been recorded with scientists alarmed at the current high rate of extinctions. Most species that become extinct are never scientifically documented. Some scientists estimate that up to half of presently existing plant and animal species may become extinct by 2100. Wilson, E.O., ''The Future of Life'' (2002) (). See also: Leakey, Richard, ''The Sixth Extinction : Patterns of Life and the Future of Humankind'', A 2018 report indicated that the phylogenetic diversity of 300 mammalian species erased during the human era since the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
would require 5 to 7 million years to recover.
According to the 2019 ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
The ''Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services'' is a report by the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services, on the global state of biodiversity. A summary for policymakers was relea ...
'' by IPBES, the biomass of wild mammals has fallen by 82%, natural ecosystems have lost about half their area and a million species are at risk of extinction—all largely as a result of human actions. Twenty-five percent of plant and animal species are threatened with extinction. In a subsequent report, IPBES listed unsustainable fishing, hunting and logging as being some of the primary drivers of the global extinction crisis. In June 2019, one million species of plants and animals were at risk of extinction. At least 571 plant species have been lost since 1750. The main cause of the extinctions is the destruction of natural habitats by human activities, such as cutting down forests and converting land into fields for farming.
A dagger symbol (†) placed next to the name of a species or other taxon normally indicates its status as extinct.
Definition
 A species is extinct when the last existing member dies. Extinction therefore becomes a certainty when there are no surviving individuals that can reproduce and create a new generation. A species may become
A species is extinct when the last existing member dies. Extinction therefore becomes a certainty when there are no surviving individuals that can reproduce and create a new generation. A species may become functionally extinct
Functional extinction is the extinction of a species or other taxon such that:
#It disappears from the fossil record, or historic reports of its existence cease;
#The reduced population no longer plays a significant role in ecosystem function;
#T ...
when only a handful of individuals survive, which cannot reproduce due to poor health, age, sparse distribution over a large range, a lack of individuals of both sexes (in sexually reproducing
Sexual reproduction is a type of reproduction that involves a complex life cycle in which a gamete (haploid reproductive cells, such as a sperm or egg cell) with a single set of chromosomes combines with another gamete to produce a zygote that d ...
species), or other reasons.
Pinpointing the extinction (or pseudoextinction) of a species requires a clear definition of that species. If it is to be declared extinct, the species in question must be uniquely distinguishable from any ancestor or daughter species, and from any other closely related species. Extinction of a species (or replacement by a daughter species) plays a key role in the punctuated equilibrium
In evolutionary biology, punctuated equilibrium (also called punctuated equilibria) is a Scientific theory, theory that proposes that once a species appears in the fossil record, the population will become stable, showing little evolution, evol ...
hypothesis of Stephen Jay Gould
Stephen Jay Gould ( ; September 10, 1941 – May 20, 2002) was an American Paleontology, paleontologist, Evolutionary biology, evolutionary biologist, and History of science, historian of science. He was one of the most influential and widely re ...
and Niles Eldredge.
 In
In ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere lev ...
, ''extinction'' is sometimes used informally to refer to local extinction
Local extinction, also extirpation, is the termination of a species (or other taxon) in a chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere. Local extinctions are contrasted with extinction, global extinctions.
Local extinctions ...
, in which a species ceases to exist in the chosen area of study, despite still existing elsewhere. Local extinctions may be made good by the reintroduction of individuals of that species taken from other locations; wolf reintroduction
Wolf reintroduction involves the reintroduction of a portion of grey wolves in areas where native wolves have been extirpated. More than 30 subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and grey wolves, as colloquially understood, compr ...
is an example of this. Species that are not globally extinct are termed extant
Extant or Least-concern species, least concern is the opposite of the word extinct. It may refer to:
* Extant hereditary titles
* Extant literature, surviving literature, such as ''Beowulf'', the oldest extant manuscript written in English
* Exta ...
. Those species that are extant, yet are threatened with extinction, are referred to as threatened or endangered species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, inv ...
.
Currently, an important aspect of extinction is human attempts to preserve critically endangered species. These are reflected by the creation of the conservation status
The conservation status of a group of organisms (for instance, a species) indicates whether the group still exists and how likely the group is to become extinct in the near future. Many factors are taken into account when assessing conservation ...
"extinct in the wild" (EW). Species listed under this status by the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN) are not known to have any living specimens in the wild and are maintained only in zoos or other artificial environments. Some of these species are functionally extinct, as they are no longer part of their natural habitat and it is unlikely the species will ever be restored to the wild.Maas, Peter.Extinct in the Wild" ''The Extinction Website''. URL accessed January 26 2007.
When possible, modern
zoological
Zoology ( , ) is the scientific study of animals. Its studies include the anatomy, structure, embryology, Biological classification, classification, Ethology, habits, and distribution of all animals, both living and extinction, extinct, and ...
institutions try to maintain a viable population for species preservation and possible future reintroduction to the wild, through use of carefully planned breeding programs.
The extinction of one species' wild population can have knock-on effects, causing further extinctions. These are also called "chains of extinction". This is especially common with extinction of keystone species
A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance. The concept was introduced in 1969 by the zoologist Robert T. Paine. Keystone species play a critical role in main ...
.
A 2018 study indicated that the sixth mass extinction started in the Late Pleistocene
The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as the Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth division ...
could take up to 5 to 7 million years to restore mammal diversity to what it was before the human era.
Pseudoextinction
Extinction of a parent species where daughter species or subspecies are still extant is called pseudoextinction or phyletic extinction. Effectively, the old taxon vanishes, transformed (anagenesis
Anagenesis is the gradual evolution of a species that continues to exist as an interbreeding population. This contrasts with cladogenesis, which occurs when branching or splitting occurs, leading to two or more lineages and resulting in separate ...
) into a successor, or split into more than one (cladogenesis
Cladogenesis is an evolutionary splitting of a parent species into two distinct species, forming a clade.
This event usually occurs when a few organisms end up in new, often distant areas or when environmental changes cause several extinctions, ...
).
Pseudoextinction is difficult to demonstrate unless one has a strong chain of evidence linking a living species to members of a pre-existing species. For example, it is sometimes claimed that the extinct ''Hyracotherium
''Hyracotherium'' ( ; "hyrax-like beast") is an extinction, extinct genus of small (about 60 cm in length) perissodactyl ungulates that was found in the London Clay formation. This small, fox-sized animal is (for some scientists) considered t ...
'', which was an early horse that shares a common ancestor with the modern horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 mi ...
, is pseudoextinct, rather than extinct, because there are several extant species of '' Equus'', including zebra
Zebras (, ) (subgenus ''Hippotigris'') are African equines with distinctive black-and-white striped coats. There are three living species: Grévy's zebra (''Equus grevyi''), the plains zebra (''E. quagga''), and the mountain zebra (''E. ...
and donkey
The donkey or ass is a domesticated equine. It derives from the African wild ass, ''Equus africanus'', and may be classified either as a subspecies thereof, ''Equus africanus asinus'', or as a separate species, ''Equus asinus''. It was domes ...
; however, as fossil species typically leave no genetic material behind, one cannot say whether ''Hyracotherium'' evolved into more modern horse species or merely evolved from a common ancestor with modern horses. Pseudoextinction is much easier to demonstrate for larger taxonomic groups.
Lazarus taxa
A Lazarus taxon or Lazarus species refers to instances where a species or taxon was thought to be extinct, but was later rediscovered. It can also refer to instances where large gaps in the fossil record of a taxon result in fossils reappearing much later, although the taxon may have ultimately become extinct at a later point. Thecoelacanth
Coelacanths ( ) are an ancient group of lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii) in the class Actinistia. As sarcopterygians, they are more closely related to lungfish and tetrapods (the terrestrial vertebrates including living amphibians, reptiles, bi ...
, a fish related to lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the class Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, inc ...
and tetrapod
A tetrapod (; from Ancient Greek :wiktionary:τετρα-#Ancient Greek, τετρα- ''(tetra-)'' 'four' and :wiktionary:πούς#Ancient Greek, πούς ''(poús)'' 'foot') is any four-Limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animal of the clade Tetr ...
s, is an example of a Lazarus taxon that was known only from the fossil record and was considered to have been extinct since the end of the Cretaceous Period
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ninth and longest geologi ...
. In 1938, however, a living specimen was found off the Chalumna River (now Tyolomnqa) on the east coast of South Africa. '' Calliostoma bullatum'', a species of deepwater sea snail
Sea snails are slow-moving marine (ocean), marine gastropod Mollusca, molluscs, usually with visible external shells, such as whelk or abalone. They share the Taxonomic classification, taxonomic class Gastropoda with slugs, which are distinguishe ...
originally described from fossils in 1844 proved to be a Lazarus species when extant individuals were described in 2019.
Attenborough's long-beaked echidna (''Zaglossus attenboroughi'') is an example of a Lazarus species from Papua New Guinea
Papua New Guinea, officially the Independent State of Papua New Guinea, is an island country in Oceania that comprises the eastern half of the island of New Guinea and offshore islands in Melanesia, a region of the southwestern Pacific Ocean n ...
that had last been sighted in 1962 and believed to be possibly extinct, until it was recorded again in November 2023.
Some species thought to be extinct have had ongoing speculation that they may still exist, and in the event of rediscovery would be considered Lazarus species. Examples include the thylacine
The thylacine (; binomial name ''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, was a carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmani ...
, or Tasmanian tiger (''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), the last known example of which died in Hobart Zoo in Tasmania in 1936; the Japanese wolf (''Canis lupus hodophilax''), last sighted over 100 years ago; the American ivory-billed woodpecker (''Campephilus principalis''), with the last universally accepted sighting in 1944; and the slender-billed curlew (''Numenius tenuirostris''), not seen since 2007.
Causes
 As long as species have been evolving, species have been going extinct. It is estimated that over 99.9% of all species that ever lived are extinct. The average lifespan of a species is 1–10 million years, although this varies widely between taxa.
A variety of causes can contribute directly or indirectly to the extinction of a species or group of species. "Just as each species is unique", write Beverly and Stephen C. Stearns, "so is each extinction ... the causes for each are varied—some subtle and complex, others obvious and simple". Most simply, any species that cannot
As long as species have been evolving, species have been going extinct. It is estimated that over 99.9% of all species that ever lived are extinct. The average lifespan of a species is 1–10 million years, although this varies widely between taxa.
A variety of causes can contribute directly or indirectly to the extinction of a species or group of species. "Just as each species is unique", write Beverly and Stephen C. Stearns, "so is each extinction ... the causes for each are varied—some subtle and complex, others obvious and simple". Most simply, any species that cannot survive
Survival or survivorship, the act of surviving, is the propensity of something to continue existing, particularly when this is done despite conditions that might kill or destroy it. The concept can be applied to humans and other living things ...
and reproduce
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual.
In asexual reprod ...
in its environment and cannot move to a new environment where it can do so, dies out and becomes extinct. Extinction of a species may come suddenly when an otherwise healthy species is wiped out completely, as when toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
renders its entire habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
unliveable; or may occur gradually over thousands or millions of years, such as when a species gradually loses out in competition for food to better adapted competitors. Extinction may occur a long time after the events that set it in motion, a phenomenon known as extinction debt.
Assessing the relative importance of genetic factors compared to environmental ones as the causes of extinction has been compared to the debate on nature and nurture
Nature versus nurture is a long-standing debate in biology and society about the relative influence on human beings of their genetic inheritance (nature) and the environmental conditions of their development ( nurture). The alliterative expression ...
. The question of whether more extinctions in the fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
record have been caused by evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
or by competition or by predation or by disease or by catastrophe is a subject of discussion; Mark Newman, the author of ''Modeling Extinction'', argues for a mathematical model that falls in all positions. By contrast, conservation biology
Conservation biology is the study of the conservation of nature and of Earth's biodiversity with the aim of protecting species, their habitats, and ecosystems from excessive rates of extinction and the erosion of biotic interactions. It is an i ...
uses the extinction vortex model to classify extinctions by cause. When concerns about human extinction have been raised, for example in Sir Martin Rees' 2003 book '' Our Final Hour'', those concerns lie with the effects of climate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
or technological
Technology is the application of conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible tools such as ute ...
disaster.
Human-driven extinction started as humans migrated out of Africa more than 60,000 years ago. Currently, environmental groups and some governments are concerned with the extinction of species caused by humanity, and they try to prevent further extinctions through a variety of conservation programs. Humans can cause extinction of a species through overharvesting
Overexploitation, also called overharvesting or ecological overshoot, refers to harvesting a renewable resource to the point of diminishing returns. Continued overexploitation can lead to the destruction of the resource, as it will be unable to ...
, pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
, habitat destruction
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
, introduction of invasive species
An invasive species is an introduced species that harms its new environment. Invasive species adversely affect habitats and bioregions, causing ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage. The term can also be used for native spec ...
(such as new predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s and food competitors
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
), overhunting, and other influences. Explosive, unsustainable human population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
and increasing per capita consumption are essential drivers of the extinction crisis. According to the International Union for Conservation of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. Founded in 1948, IUCN has become the global authority on the stat ...
(IUCN), 784 extinctions have been recorded since the year 1500, the arbitrary date selected to define "recent" extinctions, up to the year 2004; with many more likely to have gone unnoticed. Several species have also been listed as extinct since 2004.
Genetics and demographic phenomena
Ifadaptation
In biology, adaptation has three related meanings. Firstly, it is the dynamic evolutionary process of natural selection that fits organisms to their environment, enhancing their evolutionary fitness. Secondly, it is a state reached by the p ...
increasing population fitness is slower than environmental degradation
Environment most often refers to:
__NOTOC__
* Natural environment, referring respectively to all living and non-living things occurring naturally and the physical and biological factors along with their chemical interactions that affect an organism ...
plus the accumulation of slightly deleterious mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
s, then a population will go extinct. Smaller populations have fewer beneficial mutations entering the population each generation, slowing adaptation. It is also easier for slightly deleterious mutations to fix in small populations; the resulting positive feedback loop between small population size and low fitness can cause mutational meltdown.
Limited geographic range is the most important determinant of genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In bino ...
extinction at background rates but becomes increasingly irrelevant as mass extinction
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occ ...
arises. Limited geographic range is a cause both of small population size and of greater vulnerability to local environmental catastrophes.
Extinction rates can be affected not just by population size, but by any factor that affects evolvability, including balancing selection, cryptic genetic variation, phenotypic plasticity
Phenotypic plasticity refers to some of the changes in an organism's behavior, morphology and physiology in response to a unique environment. Fundamental to the way in which organisms cope with environmental variation, phenotypic plasticity encompa ...
, and robustness
Robustness is the property of being strong and healthy in constitution. When it is transposed into a system
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, ...
. A diverse or deep gene pool
The gene pool is the set of all genes, or genetic information, in any population, usually of a particular species.
Description
A large gene pool indicates extensive genetic diversity, which is associated with robust populations that can survi ...
gives a population a higher chance in the short term of surviving an adverse change in conditions. Effects that cause or reward a loss in genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
can increase the chances of extinction of a species. Population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as genocide, speciocide, wid ...
s can dramatically reduce genetic diversity by severely limiting the number of reproducing individuals and make inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
more frequent.
Genetic pollution
Extinction sometimes results for species evolved to specific ecologies that are subjected togenetic pollution
Genetic pollution is a term for uncontrolled gene flow into wild populations. It is defined as "the dispersal of contaminated altered genes from genetically engineered organisms to natural organisms, esp. by cross-pollination", but has come to be ...
—i.e., uncontrolled hybridization, introgression
Introgression, also known as introgressive hybridization, in genetics is the transfer of genetic material from one species into the gene pool of another by the repeated backcrossing of an interspecific hybrid with one of its parent species. Introg ...
and genetic swamping that lead to homogenization or out-competition from the introduced ( or hybrid) species. Endemic populations can face such extinctions when new populations are imported or selectively bred by people, or when habitat modification brings previously isolated species into contact. Extinction is likeliest for rare species
A rare species is a group of organisms that are very uncommon, scarce, or infrequently encountered. This designation may be applied to either a plant or animal taxon, and is distinct from the term ''endangered species, endangered'' or ''threatened ...
coming into contact with more abundant ones; interbreeding can swamp the rarer gene pool and create hybrids, depleting the purebred gene pool (for example, the endangered wild water buffalo is most threatened with extinction by genetic pollution from the abundant domestic water buffalo). Such extinctions are not always apparent from morphological (non-genetic) observations. Some degree of gene flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent ...
is a normal evolutionary process; nevertheless, hybridization (with or without introgression) threatens rare species' existence.
The gene pool of a species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
or a population
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and pl ...
is the variety of genetic information in its living members. A large gene pool (extensive genetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
) is associated with robust populations that can survive bouts of intense selection
Selection may refer to:
Science
* Selection (biology), also called natural selection, selection in evolution
** Sex selection, in genetics
** Mate selection, in mating
** Sexual selection in humans, in human sexuality
** Human mating strat ...
. Meanwhile, low genetic diversity (see inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely genetic distance, related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genet ...
and population bottlenecks) reduces the range of adaptions possible. Replacing native with alien genes narrows genetic diversity within the original population,
thereby increasing the chance of extinction.
Habitat degradation
 Habitat degradation is currently the main anthropogenic cause of species extinctions. The main cause of habitat degradation worldwide is agriculture, with
Habitat degradation is currently the main anthropogenic cause of species extinctions. The main cause of habitat degradation worldwide is agriculture, with urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city". Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted ...
, logging, mining, and some fishing practices close behind. The degradation of a species' habitat
In ecology, habitat refers to the array of resources, biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species' habitat can be seen as the physical manifestation of its ...
may alter the fitness landscape to such an extent that the species is no longer able to survive and becomes extinct. This may occur by direct effects, such as the environment becoming toxic
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect on a subst ...
, or indirectly, by limiting a species' ability to compete effectively for diminished resources or against new competitor species.
Habitat destruction, particularly the removal of vegetation that stabilizes soil, enhances erosion and diminishes nutrient availability in terrestrial ecosystems. This degradation can lead to a reduction in agricultural productivity. Furthermore, increased erosion contributes to poorer water quality by elevating the levels of sediment and pollutants in rivers and streams.
Habitat degradation through toxicity can kill off a species very rapidly, by killing all living members through contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that renders something unsuitable, unfit or harmful for the physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
Within the scien ...
or sterilizing them. It can also occur over longer periods at lower toxicity levels by affecting life span, reproductive capacity, or competitiveness.
Habitat degradation can also take the form of a physical destruction of niche habitats. The widespread destruction of tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are dense and warm rainforests with high rainfall typically found between 10° north and south of the Equator. They are a subset of the tropical forest biome that occurs roughly within the 28° latitudes (in the torrid zo ...
s and replacement with open pastureland is widely cited as an example of this; elimination of the dense forest eliminated the infrastructure needed by many species to survive. For example, a fern
The ferns (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta) are a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. They differ from mosses by being vascular, i.e., having specialized tissue ...
that depends on dense shade for protection from direct sunlight can no longer survive without forest to shelter it. Another example is the destruction of ocean floors by bottom trawling
Bottom trawling is trawling (towing a trawl, which is a fishing net) along the seafloor. It is also referred to as "dragging". The scientific community divides bottom trawling into benthic trawling and Demersal zone, demersal trawling. Benthic tra ...
.
Diminished resources or introduction of new competitor species also often accompany habitat degradation. Global warming
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes ...
has allowed some species to expand their range, bringing competition to other species that previously occupied that area. Sometimes these new competitors are predators and directly affect prey species, while at other times they may merely outcompete vulnerable species for limited resources. Vital resources including water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
and food can also be limited during habitat degradation, leading to extinction.
Predation, competition, and disease
 In the natural course of events, species become extinct for a number of reasons, including but not limited to: extinction of a necessary host, prey or pollinator,
In the natural course of events, species become extinct for a number of reasons, including but not limited to: extinction of a necessary host, prey or pollinator, interspecific competition
Interspecific competition, in ecology, is a form of competition in which individuals of ''different'' species compete for the same resources in an ecosystem (e.g. food or living space). This can be contrasted with mutualism, a type of symbiosis. ...
, inability to deal with evolving diseases and changing environmental conditions (particularly sudden changes) which can act to introduce novel predators, or to remove prey. Recently in geological time, humans have become an additional cause of extinction of some species, either as a new mega-predator or by transporting animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the Biology, biological Kingdom (biology), kingdom Animalia (). With few exceptions, animals heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, ...
s and plant
Plants are the eukaryotes that form the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae; they are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic. This means that they obtain their energy from sunlight, using chloroplasts derived from endosymbiosis with c ...
s from one part of the world to another. Such introductions have been occurring for thousands of years, sometimes intentionally (e.g. livestock
Livestock are the Domestication, domesticated animals that are raised in an Agriculture, agricultural setting to provide labour and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, Egg as food, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The t ...
released by sailors on islands as a future source of food) and sometimes accidentally (e.g. rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents. Species of rats are found throughout the order Rodentia, but stereotypical rats are found in the genus ''Rattus''. Other rat genera include '' Neotoma'' (pack rats), '' Bandicota'' (bandicoo ...
s escaping from boats). In most cases, the introductions are unsuccessful, but when an invasive alien species does become established, the consequences can be catastrophic. Invasive alien species can affect native species directly by eating them, competing with them, and introducing pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
s or parasite
Parasitism is a Symbiosis, close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives (at least some of the time) on or inside another organism, the Host (biology), host, causing it some harm, and is Adaptation, adapted str ...
s that sicken or kill them; or indirectly by destroying or degrading their habitat. Human populations may themselves act as invasive predators. According to the "overkill hypothesis", the swift extinction of the megafauna
In zoology, megafauna (from Ancient Greek, Greek μέγας ''megas'' "large" and Neo-Latin ''fauna'' "animal life") are large animals. The precise definition of the term varies widely, though a common threshold is approximately , this lower en ...
in areas such as Australia (40,000 years before present), North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
(12,000 years before present), Madagascar
Madagascar, officially the Republic of Madagascar, is an island country that includes the island of Madagascar and numerous smaller peripheral islands. Lying off the southeastern coast of Africa, it is the world's List of islands by area, f ...
, Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
(AD 300–1000), and New Zealand (AD 1300–1500), resulted from the sudden introduction of human beings to environments full of animals that had never seen them before and were therefore completely unadapted to their predation techniques.Lee, Anita.The Pleistocene Overkill Hypothesis
." ''University of California at Berkeley Geography Program.'' Retrieved January 11, 2007.
Coextinction
 Coextinction refers to the loss of a species due to the extinction of another; for example, the extinction of parasitic insects following the loss of their hosts. Coextinction can also occur when a species loses its
Coextinction refers to the loss of a species due to the extinction of another; for example, the extinction of parasitic insects following the loss of their hosts. Coextinction can also occur when a species loses its pollinator
A pollinator is an animal that moves pollen from the male anther of a flower to the female carpel, stigma of a flower. This helps to bring about fertilization of the ovules in the flower by the male gametes from the pollen grains.
Insects are ...
, or to predator
Predation is a biological interaction in which one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common List of feeding behaviours, feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation ...
s in a food chain
A food chain is a linear network of links in a food web, often starting with an autotroph (such as grass or algae), also called a producer, and typically ending at an apex predator (such as grizzly bears or killer whales), detritivore (such as ...
who lose their prey. "Species coextinction is a manifestation of one of the interconnectednesses of organisms in complex ecosystems ... While coextinction may not be the most important cause of species extinctions, it is certainly an insidious one." Coextinction is especially common when a keystone species
A keystone species is a species that has a disproportionately large effect on its natural environment relative to its abundance. The concept was introduced in 1969 by the zoologist Robert T. Paine. Keystone species play a critical role in main ...
goes extinct. Models suggest that coextinction is the most common form of biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss happens when plant or animal species disappear completely from Earth (extinction) or when there is a decrease or disappearance of species in a specific area. Biodiversity loss means that there is a reduction in Biodiversity, b ...
. There may be a cascade of coextinction across the trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food web. Within a food web, a food chain is a succession of organisms that eat other organisms and may, in turn, be eaten themselves. The trophic level of an organism is the ...
s. Such effects are most severe in mutualistic and parasitic relationships. An example of coextinction is the Haast's eagle and the moa: the Haast's eagle was a predator that became extinct because its food source became extinct. The moa were several species of flightless birds that were a food source for the Haast's eagle.
Climate change
Extinction as a result ofclimate change
Present-day climate change includes both global warming—the ongoing increase in Global surface temperature, global average temperature—and its wider effects on Earth's climate system. Climate variability and change, Climate change in ...
has been confirmed by fossil studies. Particularly, the extinction of amphibians during the Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse
The Carboniferous rainforest collapse (CRC) was a minor extinction event that occurred around 305 million years ago in the Carboniferous period. The event occurred at the end of the Moscovian and continued into the early Kasimovian stages of th ...
, 305 million years ago. A 2003 review across 14 biodiversity research centers predicted that, because of climate change, 15–37% of land species would be "committed to extinction" by 2050. The ecologically rich areas that would potentially suffer the heaviest losses include the Cape Floristic Region
The Cape Floral Region is a floristic region located near the southern tip of South Africa. It is the only floristic region of the Cape Floristic Kingdom, and includes only one floristic province, known as the Cape Floristic Province.
The Cap ...
and the Caribbean Basin. These areas might see a doubling of present carbon dioxide levels and rising temperatures that could eliminate 56,000 plant and 3,700 animal species. Climate change has also been found to be a factor in habitat loss
Habitat destruction (also termed habitat loss or habitat reduction) occurs when a natural habitat is no longer able to support its native species. The organisms once living there have either moved elsewhere, or are dead, leading to a decrease ...
and desertification
Desertification is a type of gradual land degradation of Soil fertility, fertile land into arid desert due to a combination of natural processes and human activities.
The immediate cause of desertification is the loss of most vegetation. This i ...
.
Sexual selection and male investment
Studies of fossils following species from the time they evolved to their extinction show that species with highsexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where sexes of the same species exhibit different Morphology (biology), morphological characteristics, including characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most dioecy, di ...
, especially characteristics in males that are used to compete for mating, are at a higher risk of extinction and die out faster than less sexually dimorphic species, the least sexually dimorphic species surviving for millions of years while the most sexually dimorphic species die out within mere thousands of years. Earlier studies based on counting the number of currently living species in modern taxa have shown a higher number of species in more sexually dimorphic taxa which have been interpreted as higher survival in taxa with more sexual selection, but such studies of modern species only measure indirect effects of extinction and are subject to error sources such as dying and doomed taxa speciating more due to splitting of habitat ranges into more small isolated groups during the habitat retreat of taxa approaching extinction. Possible causes of the higher extinction risk in species with more sexual selection shown by the comprehensive fossil studies that rule out such error sources include expensive sexually selected ornaments having negative effects on the ability to survive natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the Heredity, heritable traits characteristic of a population over generation ...
, as well as sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex ...
removing a diversity of genes that under current ecological conditions are neutral for natural selection but some of which may be important for surviving climate change.
Mass extinctions
There have been at least five mass extinctions in the history of life on earth, and four in the last 350 million years in which many species have disappeared in a relatively short period of geological time. A massive eruptive event that released large quantities oftephra
Tephra is fragmental material produced by a Volcano, volcanic eruption regardless of composition, fragment size, or emplacement mechanism.
Volcanologists also refer to airborne fragments as pyroclasts. Once clasts have fallen to the ground, ...
particles into the atmosphere is considered to be one likely cause of the "Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic extinction event (also known as the P–T extinction event, the Late Permian extinction event, the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian extinction event, and colloquially as the Great Dying,) was an extinction ...
" about 250 million years ago, which is estimated to have killed 90% of species then existing. There is also evidence to suggest that this event was preceded by another mass extinction, known as Olson's Extinction
Olson's Extinction was a mass extinction that occurred in the late Cisuralian or early Guadalupian epoch of the Permian period, predating the much larger Permian–Triassic extinction event.
The event is named after American paleontologist E ...
. The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event, also known as the K–T extinction, was the extinction event, mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth approximately 66 million years ago. The event cau ...
(K–Pg) occurred 66 million years ago, at the end of the Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
period; it is best known for having wiped out non-avian dinosaurs, among many other species.
Modern extinctions
 According to a 1998 survey of 400 biologists conducted by New York City, New York's American Museum of Natural History, nearly 70% believed that the Earth is currently in the early stages of a human-caused mass extinction,American Museum of Natural History.
According to a 1998 survey of 400 biologists conducted by New York City, New York's American Museum of Natural History, nearly 70% believed that the Earth is currently in the early stages of a human-caused mass extinction,American Museum of Natural History.National Survey Reveals Biodiversity Crisis – Scientific Experts Believe We are in the Midst of the Fastest Mass Extinction in Earth's History
". Retrieved September 20, 2006. known as the Holocene extinction. In that survey, the same proportion of respondents agreed with the prediction that up to 20% of all living populations could become extinct within 30 years (by 2028). A 2014 special edition of ''Science (journal), Science'' declared there is widespread consensus on the issue of human-driven mass species extinctions. A 2020 study published in ''PNAS'' stated that the contemporary extinction crisis "may be the most serious environmental threat to the persistence of civilization, because it is irreversible." A 2025 study found that human activities are to blame for biodiversity loss across all species and ecosystems. Biologist E. O. Wilson estimated in 2002 that if current rates of human destruction of the biosphere continue, one-half of all plant and animal species of life on earth will be extinct in 100 years. E.O. Wilson repeats his estimation in 2012. More significantly, the current rate of global species extinctions is estimated as 100 to 1,000 times "background" rates (the average extinction rates in the
evolution
Evolution is the change in the heritable Phenotypic trait, characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, re ...
ary time scale of planet Earth), faster than at any other time in human history, while future rates are likely 10,000 times higher. However, some groups are going extinct much faster. Biologists Paul R. Ehrlich and Stuart Pimm, among others, contend that human population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. The World population, global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to 8.2 billion in 2025. Actual global human population growth amounts to aroun ...
and overconsumption are the main drivers of the modern extinction crisis.
In January 2020, the UN's Convention on Biological Diversity drafted a plan to mitigate the contemporary extinction crisis by establishing a deadline of 2030 to protect 30% of the Earth's land and oceans and reduce pollution by 50%, with the goal of allowing for the restoration of ecosystems by 2050. The 2020 United Nations' ''Global Biodiversity Outlook'' report stated that of the 20 biodiversity goals laid out by the Aichi Biodiversity Targets in 2010, only 6 were "partially achieved" by the deadline of 2020. The report warned that biodiversity will continue to decline if the status quo is not changed, in particular the "currently unsustainable patterns of production and consumption, population growth and technological developments". In a 2021 report published in the journal ''Frontiers in Conservation Science'', some top scientists asserted that even if the Aichi Biodiversity Targets set for 2020 had been achieved, it would not have resulted in a significant mitigation of biodiversity loss. They added that failure of the global community to reach these targets is hardly surprising given that biodiversity loss is "nowhere close to the top of any country's priorities, trailing far behind other concerns such as employment, healthcare, economic growth, or currency stability."
History of scientific understanding

 For much of history, the modern understanding of extinction as the end of a
For much of history, the modern understanding of extinction as the end of a species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), ...
was incompatible with the prevailing worldview. Prior to the 19th century, much of Western society adhered to the belief that the world was created by God and as such was complete and perfect. This concept reached its heyday in the 1700s with the peak popularity of a theological concept called the great chain of being, in which all life on earth, from the tiniest microorganism to God, is linked in a continuous chain. The extinction of a species was impossible under this model, as it would create gaps or missing links in the chain and destroy the natural order. Thomas Jefferson was a firm supporter of the great chain of being and an opponent of extinction, famously denying the extinction of the woolly mammoth on the grounds that nature never allows a race of animals to become extinct.
A series of fossils were discovered in the late 17th century that appeared unlike any living species. As a result, the scientific community embarked on a voyage of creative rationalization, seeking to understand what had happened to these species within a framework that did not account for total extinction. In October 1686, Robert Hooke presented an impression of a nautilus to the Royal Society that was more than two feet in diameter, and morphologically distinct from any known living species. Robert Hooke, Hooke theorized that this was simply because the species lived in the deep ocean and no one had discovered them yet. While he contended that it was possible a species could be "lost", he thought this highly unlikely. Similarly, in 1695, Sir Thomas Molyneux published an account of enormous antlers found in Ireland that did not belong to any extant taxa in that area. Molyneux reasoned that they came from the North American moose and that the animal had once been common on the British Isles. Rather than suggest that this indicated the possibility of species going extinct, he argued that although organisms could become locally extinct, they could never be entirely lost and would continue to exist in some unknown region of the globe. The antlers were later confirmed to be from the extinct deer ''Megaloceros''. Hooke and Molyneux's line of thinking was difficult to disprove. When parts of the world had not been thoroughly examined and charted, scientists could not rule out that animals found only in the fossil record were not simply "hiding" in unexplored regions of the Earth.''Ideas: A History from Fire to Freud'' (Peter Watson (business writer), Peter Watson Weidenfeld & Nicolson )
Georges Cuvier is credited with establishing the modern conception of extinction in a 1796 lecture to the French Institute, though he would spend most of his career trying to convince the wider scientific community of his theory. Cuvier was a well-regarded geologist, lauded for his ability to reconstruct the anatomy of an unknown species from a few fragments of bone. His primary evidence for extinction came from mammoth skulls found near Paris. Cuvier recognized them as distinct from any known living species of elephant, and argued that it was highly unlikely such an enormous animal would go undiscovered. In 1798, he studied a fossil from the Paris Basin that was first observed by Robert de Lamanon in 1782, first hypothesizing that it belonged to a canine but then deciding that it instead belonged to an animal that was unlike living ones. His study paved the way to his naming of the extinct mammal genus ''Palaeotherium'' in 1804 based on the skull and additional fossil material along with another extinct contemporary mammal genus ''Anoplotherium''. In both genera, he noticed that their fossils shared some similarities with other mammals like ruminants and rhinoceroses but still had distinct differences. In 1812, Cuvier, along with Alexandre Brongniart and Isidore Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, Geoffroy Saint-Hilaire, mapped the Stratum, strata of the Paris basin. They saw alternating saltwater and freshwater deposits, as well as patterns of the appearance and disappearance of fossils throughout the record. From these patterns, Cuvier inferred historic cycles of catastrophic flooding, extinction, and repopulation of the earth with new species.
Cuvier's fossil evidence showed that very different life forms existed in the past than those that exist today, a fact that was accepted by most scientists. The primary debate focused on whether this turnover caused by extinction was gradual or abrupt in nature. Cuvier understood extinction to be the result of cataclysmic events that wipe out huge numbers of species, as opposed to the gradual decline of a species over time. His catastrophic view of the nature of extinction garnered him many opponents in the newly emerging school of uniformitarianism.
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, a Gradualism, gradualist and colleague of Cuvier, saw the fossils of different life forms as evidence of the mutable character of species. While Lamarck did not deny the possibility of extinction, he believed that it was exceptional and rare and that most of the change in species over time was due to gradual change. Unlike Cuvier, Lamarck was skeptical that catastrophic events of a scale large enough to cause total extinction were possible. In his geological history of the earth titled Hydrogeologie, Lamarck instead argued that the surface of the earth was shaped by gradual erosion and deposition by water, and that species changed over time in response to the changing environment.
Charles Lyell, a noted geologist and founder of uniformitarianism, believed that past processes should be understood using present day processes. Like Lamarck, Lyell acknowledged that extinction could occur, noting the total extinction of the dodo and the extirpation of History of the horse in Britain, indigenous horses to the British Isles. He similarly argued against mass extinctions, believing that any extinction must be a gradual process. Lyell also showed that Cuvier's original interpretation of the Parisian strata was incorrect. Instead of the catastrophic floods inferred by Cuvier, Lyell demonstrated that patterns of saltwater and freshwater Deposition (geology), deposits, like those seen in the Paris basin, could be formed by a slow rise and fall of sea levels.
The concept of extinction was integral to Charles Darwin's ''On the Origin of Species'', with less fit lineages disappearing over time. For Darwin, extinction was a constant side effect of competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indi ...
. Because of the wide reach of ''On the Origin of Species'', it was widely accepted that extinction occurred gradually and evenly (a concept now referred to as Background extinction rate, background extinction). It was not until 1982, when David M. Raup, David Raup and Jack Sepkoski published their seminal paper on mass extinctions, that Cuvier was vindicated and catastrophic extinction was accepted as an important mechanism. The current understanding of extinction is a synthesis of the cataclysmic extinction events proposed by Cuvier, and the background extinction events proposed by Lyell and Darwin.
Human attitudes and interests
 Extinction is an important research topic in the field of zoology, and biology in general, and has also become an area of concern outside the scientific community. A number of organizations, such as the WWF (conservation organization), Worldwide Fund for Nature, have been created with the goal of preserving species from extinction. Governments have attempted, through enacting laws, to avoid habitat destruction, agricultural over-harvesting, and
Extinction is an important research topic in the field of zoology, and biology in general, and has also become an area of concern outside the scientific community. A number of organizations, such as the WWF (conservation organization), Worldwide Fund for Nature, have been created with the goal of preserving species from extinction. Governments have attempted, through enacting laws, to avoid habitat destruction, agricultural over-harvesting, and pollution
Pollution is the introduction of contaminants into the natural environment that cause harm. Pollution can take the form of any substance (solid, liquid, or gas) or energy (such as radioactivity, heat, sound, or light). Pollutants, the component ...
. While many human-caused extinctions have been accidental, humans have also engaged in the deliberate destruction of some species, such as dangerous viruses, and the total destruction of other problematic species has been suggested. Other species were deliberately driven to extinction, or nearly so, due to poaching or because they were "undesirable", or to push for other human agendas. One example was the near extinction of the American bison, which was nearly wiped out by mass hunts sanctioned by the United States government, to force the removal of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans, many of whom relied on the bison for food.
Biologist Bruce Walsh (scientist), Bruce Walsh states three reasons for scientific interest in the preservation of species: genetic resources, ecosystem stability, and ethics; and today the scientific community "stress[es] the importance" of maintaining biodiversity.Bruce Walsh (scientist), Walsh, BruceExtinction
. Bioscience at University of Arizona. Retrieved July 26, 2006.Committee on Recently Extinct Organisms.
". Retrieved July 30, 2006. In modern times, commercial and industrial interests often have to contend with the effects of production on plant and animal life. However, some technologies with minimal, or no, proven harmful effects on ''Homo sapiens'' can be devastating to wildlife (for example, DDT).International Programme on Chemical Safety (1989).
DDT and its Derivatives – Environmental Aspects
". Environmental Health Criteria 83. Retrieved September 20, 2006. Biogeography, Biogeographer Jared Diamond notes that while big business may label environmental concerns as "exaggerated", and often cause "devastating damage", some corporations find it in their interest to adopt good conservation practices, and even engage in preservation efforts that surpass those taken by national parks. Governments sometimes see the loss of native species as a loss to ecotourism,Drewry, Rachel.
Ecotourism: Can it save the orangutans?
" ''Inside Indonesia''. Retrieved January 26, 2007. and can enact laws with severe punishment against the trade in native species in an effort to prevent extinction in the wild. Nature preserves are created by governments as a means to provide continuing habitats to species crowded by human expansion. The 1992 Convention on Biological Diversity has resulted in international Biodiversity Action Plan programmes, which attempt to provide comprehensive guidelines for government biodiversity conservation. Advocacy groups, such as The Wildlands ProjectThe Wildlands Project
. Retrieved January 26, 2007. and the Alliance for Zero Extinctions, work to educate the public and pressure governments into action. People who live close to nature can be dependent on the survival of all the species in their environment, leaving them highly exposed to extinction risks. However, people prioritize day-to-day survival over species conservation; with human overpopulation in tropical developing country, developing countries, there has been enormous pressure on forests due to subsistence agriculture, including slash-and-burn agricultural techniques that can reduce endangered species's habitats. Antinatalist philosopher David Benatar concludes that any popular concern about non-human species extinction usually arises out of concern about how the loss of a species will impact human wants and needs, that "we shall live in a world impoverished by the loss of one aspect of faunal diversity, that we shall no longer be able to behold or use that species of animal." He notes that typical concerns about possible human extinction, such as the loss of individual members, are not considered in regards to non-human species extinction. Anthropologist Jason Hickel speculates that the reason humanity seems largely indifferent to anthropogenic mass species extinction is that we see ourselves as separate from the natural world and the organisms within it. He says that this is due in part to the logic of capitalism: "that the world is not really alive, and it is certainly not our kin, but rather just stuff to be extracted and discarded – and that includes most of the human beings living here too."
Planned extinction
Completed
* The smallpox virus is now extinct in the wild, although samples are retained in laboratory settings. * The rinderpest virus, which Cattle diseases, infected domestic cattle, is now extinct in the wild.Proposed
= Disease agents
= The poliovirus is now confined to small parts of the world due to extermination efforts. ''Dracunculus medinensis'', or Guinea worm, a parasitic worm which causes the disease dracunculiasis, is now close to eradication thanks to efforts led by the Carter Center. ''Treponema pallidum, Treponema pallidum pertenue'', a bacterium which causes the disease yaws, is in the process of being eradicated.= Disease vectors
= Biologist Olivia Judson has advocated the deliberate extinction of certain disease-carrying mosquito species. In an article in ''The New York Times'' on 25 September 2003, she advocated "specicide" of thirty mosquito species by introducing a genetic element that can insert itself into another crucial gene, to create recessive "Gene knockout, knockout genes". She says that the ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes (which spread malaria) and ''Aedes'' mosquitoes (which spread dengue fever, yellow fever, elephantiasis tropica, elephantiasis, and other diseases) represent only 30 of around 3,500 mosquito species; eradicating these would save at least one million human lives per year, at a cost of reducing thegenetic diversity
Genetic diversity is the total number of genetic characteristics in the genetic makeup of a species. It ranges widely, from the number of species to differences within species, and can be correlated to the span of survival for a species. It is d ...
of the family Culicidae by only 1%. She further argues that since species become extinct "all the time" the disappearance of a few more will not destroy the ecosystem: "We're not left with a wasteland every time a species vanishes. Removing one species sometimes causes shifts in the populations of other species—but different need not mean worse." In addition, anti-malarial and Mosquito#Control, mosquito control programs offer little realistic hope to the 300 million people in developing nations who will be infected with acute illnesses this year. Although trials are ongoing, she writes that if they fail "we should consider the ultimate swatting".
Biologist E. O. Wilson has advocated the eradication of several species of mosquito, including malaria vector ''Anopheles gambiae''. Wilson stated, "I'm talking about a very small number of species that have co-evolved with us and are preying on humans, so it would certainly be acceptable to remove them. I believe it's just common sense."
There have been many campaigns – some successful – to locally eradicate tsetse fly, tsetse flies and their trypanosoma, trypanosomes in areas, countries, and islands of Africa (including Príncipe). (Other ) There are currently serious efforts to do away with them all across Africa, and this is generally viewed as beneficial and morally necessary, although not always.
Cloning
 Some, such as Harvard geneticist George M. Church, believe that ongoing technological advances will let us "bring back to life" an extinct species by Cloning#Cloning extinct and endangered species, cloning, using DNA from the remains of that species. Proposed targets for cloning include the
Some, such as Harvard geneticist George M. Church, believe that ongoing technological advances will let us "bring back to life" an extinct species by Cloning#Cloning extinct and endangered species, cloning, using DNA from the remains of that species. Proposed targets for cloning include the mammoth
A mammoth is any species of the extinct elephantid genus ''Mammuthus.'' They lived from the late Miocene epoch (from around 6.2 million years ago) into the Holocene until about 4,000 years ago, with mammoth species at various times inhabi ...
, the thylacine
The thylacine (; binomial name ''Thylacinus cynocephalus''), also commonly known as the Tasmanian tiger or Tasmanian wolf, was a carnivorous marsupial that was native to the Mainland Australia, Australian mainland and the islands of Tasmani ...
, and the Pyrenean ibex. For this to succeed, enough individuals would have to be cloned, from the DNA of different individuals (in the case of sexually reproducing organisms) to create a viable population. Though bioethics, bioethical and philosophy, philosophical objections have been raised, the cloning of extinct creatures seems theoretically possible.
In 2003, scientists tried to clone the extinct Pyrenean ibex (''C. p. pyrenaica''). This attempt failed: of the 285 embryos reconstructed, 54 were transferred to 12 Spanish ibexes and ibex–domestic goat hybrids, but only two survived the initial two months of gestation before they, too, died. In 2009, a second attempt was made to clone the Pyrenean ibex: one clone was born alive, but died seven minutes later, due to physical defects in the lungs.
See also
References
Further reading
* * * *External links
Committee on recently extinct organisms
The age of extinction
series in ''The Guardian''
Extincion events connected with New theory of evolution
{{Authority control Extinction, Biota by conservation status Environmental conservation Evolutionary biology IUCN Red List