Explorer I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the
 Explorer 1 was designed and built by
Explorer 1 was designed and built by 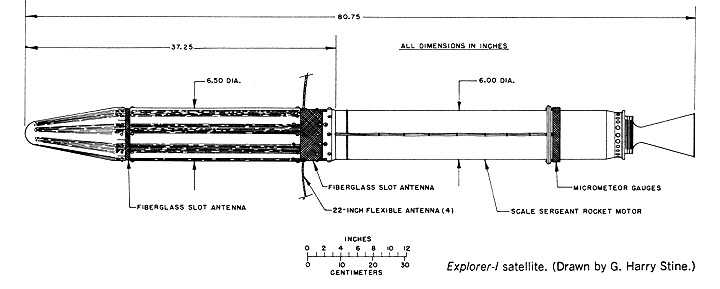
 After a jet stream-related delay on 28 January 1958, at 03:47:56 GMT on 1 February 1958 the Juno I rocket was launched, putting Explorer 1 into orbit with a
After a jet stream-related delay on 28 January 1958, at 03:47:56 GMT on 1 February 1958 the Juno I rocket was launched, putting Explorer 1 into orbit with a  The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
Explorer I Characteristics.jpg , Explorer 1 statistics and orbital diagram
Explorer I 02.jpg, Officials with Explorer 1 model at
NASA images and videos of Explorer 1 and other early satellites
Department of Astronautics,
Explorer I Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
* * *
Lecture with detailed evaluation of the Explorer 1 rotation anomaly
{{Orbital launches in 1958 Spacecraft launched in 1958 1958 in the United States Satellites formerly orbiting Earth Explorers Program Individual spacecraft in the Smithsonian Institution First artificial satellites of a country Spacecraft which reentered in 1970 Articles containing video clips Geospace monitoring satellites
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; ), also referred to as the third International Polar Year, was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War w ...
(IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites, both launched by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
during the previous year, Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (, , ''Satellite 1''), sometimes referred to as simply Sputnik, was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program ...
and Sputnik 2
Sputnik 2 (, , ''Satellite 2'', or Prosteyshiy Sputnik 2 (PS-2, , ''Simplest Satellite 2'', launched on 3 November 1957, was the second spacecraft launched into Earth orbit, and the first to carry an animal into orbit, a Soviet space dog named ...
. This began a Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
during the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
between the two nations.
Explorer 1 was launched on 1 February 1958 at 03:47:56 GMT (or 31 January 1958 at 22:47:56 Eastern Time) atop the first Juno I
The Juno I was a four-stage American space launch vehicle, used to launch lightweight payloads into low Earth orbit. The launch vehicle was used between January 1958 to December 1959. The launch vehicle is a member of the Redstone launch vehi ...
booster from LC-26A at the Cape Canaveral Missile Test Center of the Atlantic Missile Range
The Eastern Range (ER) is an American rocket range (Spaceport) that supports missile and rocket launches from the two major List of rocket launch sites, launch heads located at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station and the Kennedy Space Center ( ...
(AMR), in Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
. It was the first spacecraft to detect the Van Allen radiation belt
The Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others ma ...
, returning data until its batteries were exhausted after nearly four months. It remained in orbit until 1970.
Explorer 1 was given Satellite Catalog Number 00004 and the Harvard designation 1958 Alpha 1, the forerunner to the modern International Designator.
Background
The U.S. Earth satellite program began in 1954 as a joint U.S. Army and U.S. Navy proposal, called Project Orbiter, to put a scientific satellite into orbit during theInternational Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; ), also referred to as the third International Polar Year, was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War w ...
. The proposal, using a military Redstone missile, was rejected in 1955 by the Eisenhower administration in favor of the Navy's Project Vanguard
Project Vanguard was a program managed by the United States Navy Naval Research Laboratory (NRL), which intended to launch the first Satellite, artificial satellite into low Earth orbit using a Vanguard (rocket), Vanguard rocket as the launch ...
, using a booster advertised as more civilian in nature. Following the launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 on 4 October 1957, the initial Project Orbiter program was revived as the Explorer program to catch up with the Soviet Union.
Explorer 1 was designed and built by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
(JPL), while a Jupiter-C
The Jupiter-C was an American research and development vehicle developed from the Jupiter-A. Jupiter-C was used for three Uncrewed vehicle, uncrewed sub-orbital spaceflights in 1956 and 1957 to test Re-entry vehicle, re-entry nosecones that were ...
rocket was modified by the Army Ballistic Missile Agency
The Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) was formed to develop the U.S. Army's first large ballistic missile. The agency was established at Redstone Arsenal on 1 February 1956, and commanded by Major General John B. Medaris with Wernher v ...
(ABMA) to accommodate a satellite payload; the resulting rocket known as the Juno I. The Jupiter-C design used for the launch had already been flight-tested in nose cone reentry tests for the Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the List of Solar System objects by size, largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a Jupiter mass, mass more than 2.5 times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined a ...
intermediate-range ballistic missile
An intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) is a ballistic missile with a range (aeronautics), range between (), categorized between a medium-range ballistic missile (MRBM) and an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM). Classifying ball ...
(IRBM) and was modified into Juno I. Working closely together, ABMA and JPL completed the job of modifying the Jupiter-C and building Explorer 1 in 84 days. However, before work was completed, the Soviet Union launched a second satellite, Sputnik 2
Sputnik 2 (, , ''Satellite 2'', or Prosteyshiy Sputnik 2 (PS-2, , ''Simplest Satellite 2'', launched on 3 November 1957, was the second spacecraft launched into Earth orbit, and the first to carry an animal into orbit, a Soviet space dog named ...
, on 3 November 1957. The U.S. Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is the world's most powerful navy with the largest displacement, at 4.5 million tons in 2021. It has the world's largest aircraft ...
attempted to put the first U.S. satellite into orbit but failed with the launch of the Vanguard TV-3
Vanguard TV-3 (also called Vanguard Test Vehicle-Three), was the first attempt of the United States to launch a satellite into orbit around the Earth, after the successful Soviet launches of Sputnik 1 and Sputnik 2. Vanguard TV-3 was a small s ...
on 6 December 1957.
Spacecraft
 Explorer 1 was designed and built by
Explorer 1 was designed and built by California Institute of Technology
The California Institute of Technology (branded as Caltech) is a private research university in Pasadena, California, United States. The university is responsible for many modern scientific advancements and is among a small group of institutes ...
's JPL under the direction of Dr. William Hayward Pickering. It was the second satellite to carry a mission payload (Sputnik 2 was the first).
The total mass of the satellite was , of which were instrumentation. In comparison, the mass of the first Soviet satellite Sputnik 1 was . The instrument section at the front end of the satellite and the empty scaled-down fourth-stage rocket casing orbited as a single unit, spinning around its long axis at 750 revolutions per minute.
Data from the scientific instruments was transmitted to the ground by two antennas. A 60 milliwatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of power or radiant flux in the International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantify the rate of energy transfer. The watt is named in honor o ...
transmitter fed a dipole antenna
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet
is one of the two simplest and most widely used antenna types, types of antenna; the other is the monopole antenna, monopole. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producin ...
consisting of two fiberglasses slot antenna
A slot antenna consists of a metal surface, usually a flat plate, with one or more holes or slots cut out. When the plate is driven element, driven as an antenna (radio), antenna by an applied radio frequency current, the slot radiates electromag ...
s in the body of the satellite operating on 108.03 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), often described as being equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose formal expression in terms of SI base u ...
, and four flexible whips forming a turnstile antenna were fed by a 10 milliwatt transmitter operating on 108.00 MHz.
Because of the limited space available and the requirements for low weight, the payload instrumentation was designed and built with simplicity and high reliability in mind, using germanium
Germanium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid or a nonmetal in the carbon group that is chemically ...
and silicon
Silicon is a chemical element; it has symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic lustre, and is a tetravalent metalloid (sometimes considered a non-metal) and semiconductor. It is a membe ...
transistors in its electronics. A total of 20 transistors were used in Explorer 1, plus additional ones in the Army's micrometeorite amplifier. Electrical power was provided by mercury chemical batteries that made up approximately 40% of the payload weight.
The external skin of the instrument section was sandblasted stainless steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromi ...
with white stripes. Several other color schemes had been tested, resulting in backup articles, models, and photographs showing different configurations, including alternate white and green striping and blue stripes alternating with copper. The final color scheme was determined by studies of shadow–sunlight intervals based on firing time, trajectory, orbit and inclination.

Science payload
The Explorer 1 payload consisted of the IowaCosmic Ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
Instrument without a tape data recorder which was not modified in time to make it onto the spacecraft. The real-time data received on the ground was therefore very sparse and puzzling showing normal counting rates and no counts at all. The later Explorer 3 mission, which included a tape data recorder in the payload, provided the additional data for confirmation of the earlier Explorer 1 data.
The scientific instrumentation of Explorer 1 was designed and built under the direction of Dr. James Van Allen
James Alfred Van Allen (September 7, 1914August 9, 2006) was an American space physicist at the University of Iowa. He was instrumental in establishing the field of magnetospheric research in space.
The Van Allen radiation belts were named af ...
of the University of Iowa
The University of Iowa (U of I, UIowa, or Iowa) is a public university, public research university in Iowa City, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1847, it is the oldest and largest university in the state. The University of Iowa is organized int ...
containing:
* Anton 314 omnidirectional Geiger–Müller tube
The Geiger–Müller tube or G–M tube is the sensing element of the Geiger counter instrument used for the detection of ionizing radiation. It is named after Hans Geiger, who invented the principle in 1908, and Walther Müller, who collaborate ...
, designed by Dr. George H. Ludwig of Iowa's Cosmic Ray Laboratory, to detect cosmic ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the ...
s. It could detect protons with E>30 MeV and electrons with E>3 MeV. Most of the time the instrument was saturated;
* Five temperature sensors (one internal, three external and one on the nose cone);
* Acoustic detector (crystal transducer
A transducer is a device that Energy transformation, converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another.
Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, M ...
and solid-state amplifier
An amplifier, electronic amplifier or (informally) amp is an electronic device that can increase the magnitude of a signal (a time-varying voltage or current). It is a two-port electronic circuit that uses electric power from a power su ...
) to detect micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. T ...
(cosmic dust
Cosmic dustalso called extraterrestrial dust, space dust, or star dustis dust that occurs in outer space or has fallen onto Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and , such as micrometeoroids (30 μm). Cosmic dust can ...
) impacts. It responded to micrometeorite impacts on the spacecraft skin in such a way that each impact would be a function of mass and velocity. Its effective area was 0.075 m2 and the average threshold sensitivity was 2.5 g cm/s;
* Wire grid detector, also to detect micrometeorite impacts. It consisted of 12 parallel connected cards mounted in a fiberglass supporting ring. Each card was wound with two layers of enameled nickel alloy wire with a diameter of 17 μm (21 μm with the enamel insulation included) in such way that a total area of was completely covered. If a micrometeorite
A micrometeorite is a micrometeoroid that has survived entry through the Earth's atmosphere. Usually found on Earth's surface, micrometeorites differ from meteorites in that they are smaller in size, more abundant, and different in composition. T ...
of about 10 μm impacted, it would fracture the wire, destroy the electrical connection, and thus record the event.
Flight
 After a jet stream-related delay on 28 January 1958, at 03:47:56 GMT on 1 February 1958 the Juno I rocket was launched, putting Explorer 1 into orbit with a
After a jet stream-related delay on 28 January 1958, at 03:47:56 GMT on 1 February 1958 the Juno I rocket was launched, putting Explorer 1 into orbit with a perigee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
of and an apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values.
Apsides perta ...
of having a period of 114.80 minutes, and an inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object.
For a satellite orbiting the Eart ...
of 33.24°. Goldstone Tracking Station could not report after 90 minutes as planned whether the launch had succeeded because the orbit was larger than expected. At about 06:30 GMT, after confirming that Explorer 1 was indeed in orbit, a news conference was held in the Great Hall at the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly known as Washington or D.C., is the capital city and federal district of the United States. The city is on the Potomac River, across from Virginia, and shares land borders with ...
to announce it to the world.
 The original expected lifetime of the satellite before
The original expected lifetime of the satellite before orbital decay
Orbital decay is a gradual decrease of the distance between two orbiting bodies at their closest approach (the periapsis) over many orbital periods. These orbiting bodies can be a planet and its satellite, a star and any object orbiting it, or ...
was three years. Mercury batteries
A mercury battery (also called mercuric oxide battery, mercury cell, button cell, or Ruben-Mallory) is a non-rechargeable battery (electricity), electrochemical battery, a primary cell. Mercury batteries use a reaction between mercuric oxide and ...
powered the high-power transmitter for 31 days and the low-power transmitter for 105 days. Explorer 1 stopped transmission of data on 23 May 1958, when its batteries died, but remained in orbit for more than 12 years. It reentered the atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
on 31 March 1970 after more than 58,400 orbits.
Results
Explorer 1 changed rotation axis after launch. The elongated body of the spacecraft had been designed to spin about its long (least-inertia) axis but refused to do so, and instead started precessing due to energydissipation
In thermodynamics, dissipation is the result of an irreversible process that affects a thermodynamic system. In a dissipative process, energy ( internal, bulk flow kinetic, or system potential) transforms from an initial form to a final form, wh ...
from flexible structural elements. Later it was understood that on general grounds, the body ends up in the spin state that minimizes the kinetic rotational energy for a fixed angular momentum (this being the maximal-inertia axis). This motivated the first further development of the Eulerian theory of rigid body dynamics after nearly 200 years – to address this kind of momentum-preserving energy dissipation.
Sometimes the instrumentation reported the expected cosmic ray count (approximately 30 counts per second) but other times it would show a peculiar zero counts per second. The University of Iowa (under James Van Allen) observed that all of the zero counts per second reports were from an altitude of more than over South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a considerably smaller portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as the southern Subregion#Americas, subregion o ...
, while passes at would show the expected level of cosmic rays. Later, after Explorer 3, it was concluded that the original Geiger counter had been overwhelmed ("saturated") by strong radiation coming from a belt of charged particles trapped in space by the Earth's magnetic field. This belt of charged particles is now known as the Van Allen radiation belt
The Van Allen radiation belt is a zone of energetic charged particles, most of which originate from the solar wind, that are captured by and held around a planet by that planet's magnetosphere. Earth has two such belts, and sometimes others ma ...
. The discovery was considered to be one of the outstanding discoveries of the International Geophysical Year.
The acoustic micrometeorite detector detected 145 impacts of cosmic dust in 78,750 seconds. This calculates to an average impact rate of 8.0−3 impacts per second per square meter, or 29 impacts per hour per square meter, over the twelve-day period.
Legacy
Explorer 1 was the first of the long-running Explorers program. Four follow-up satellites of the Explorer series were launched by the Juno I launch vehicle in 1958. Of these, Explorer 3 and 4 were successful, while Explorer 2 and 5 failed to reach orbit. The final flight of the Juno I booster, the satellite Beacon-1, also failed. The Juno I vehicle was replaced by theJuno II
Juno II was an American space launch vehicle used during the late 1950s and early 1960s. It was derived from the Jupiter missile, which was used as the first stage.
Development
Solid-fueled rocket motors derived from the MGM-29 Sergeant we ...
launch vehicle in 1959.
A follow-up to the first mission, Explorer-1 Prime Unit 2, was successfully launched aboard a Delta II
Delta II was an expendable launch system, originally designed and built by McDonnell Douglas, and sometimes known as the Thorad Delta 1. Delta II was part of the Delta rocket family, derived directly from the Delta 3000, and entered service in ...
launch vehicle in late October 2011. The Prime was built using modern satellite construction techniques. The orbiting satellite was a backup, because the initial Explorer-1 Prime, launched on 4 March 2011, did not reach orbit due to a launch vehicle failure.
An identically constructed flight backup of Explorer 1 is on display in the Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
's National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, ...
, Milestones of Flight Gallery in Washington, D.C., LC-26A was deactivated in 1963 and was designated for use as a museum in 1964, the Air Force Space and Missile Museum. Here too, a full-scale Explorer 1 is on display, but this one is a mock-up.
Gallery
Redstone Arsenal
Redstone Arsenal is a United States Army base adjacent to Huntsville, Alabama in the Wheeler National Wildlife Refuge. A census-designated place in Madison County, Alabama, United States, it is part of the Huntsville-Decatur Combined Statistica ...
, including Maj. Gen. John Medaris (3rd from left), Walter Haeussermann, Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
and Ernst Stuhlinger
Explorer1 people.jpg, William Hayward Pickering, James Van Allen
James Alfred Van Allen (September 7, 1914August 9, 2006) was an American space physicist at the University of Iowa. He was instrumental in establishing the field of magnetospheric research in space.
The Van Allen radiation belts were named af ...
, and Wernher von Braun
Wernher Magnus Maximilian Freiherr von Braun ( ; ; 23 March 191216 June 1977) was a German–American aerospace engineer and space architect. He was a member of the Nazi Party and '' Allgemeine SS'', the leading figure in the development of ...
display a full-scale model of Explorer 1 at a crowded news conference in Washington, D.C. after confirmation the satellite was in orbit.
Explorer 1 During the Installation to Jupiter-C.jpg, Explorer 1 in spin test facility
Jupier c explorer1 pad.jpg, Explorer 1 and Juno I booster in gantry at LC-26A
Explorer 1 in Gantry.jpg, Close-up of Explorer 1 atop Juno I booster
Launch of Jupiter C with Explorer 1.jpg, Launch of Explorer 1 on 1 February 1958
207457main antenna-331-2426a-516.jpg, Preliminary satellite tracking tests in a field near Jet Propulsion Laboratory
The Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center (FFRDC) in La Cañada Flintridge, California, Crescenta Valley, United States. Founded in 1936 by Cali ...
207469main_computers-p-163-500.jpg, Trajectory calculations were done by hand by this group of women.
See also
*Timeline of artificial satellites and space probes
This timeline of artificial satellites and space probes includes uncrewed spacecraft including technology demonstrators, observatories, lunar probes, and interplanetary probes. First satellites from each country are included. Not included are most ...
* Explorer program
References
Bibliography
External links
NASA images and videos of Explorer 1 and other early satellites
Department of Astronautics,
National Air and Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration.
Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, ...
, Smithsonian Institution
The Smithsonian Institution ( ), or simply the Smithsonian, is a group of museums, Education center, education and Research institute, research centers, created by the Federal government of the United States, U.S. government "for the increase a ...
Explorer I Collection, The University of Alabama in Huntsville Archives and Special Collections
* * *
Lecture with detailed evaluation of the Explorer 1 rotation anomaly
{{Orbital launches in 1958 Spacecraft launched in 1958 1958 in the United States Satellites formerly orbiting Earth Explorers Program Individual spacecraft in the Smithsonian Institution First artificial satellites of a country Spacecraft which reentered in 1970 Articles containing video clips Geospace monitoring satellites