Etonitazene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Etonitazene, also known as EA-4941 or CS-4640, is a benzimidazole opioid, first reported in 1957, that has been shown to have approximately 1,000 to 1,500 times the
 The most versatile synthesis developed by the Swiss team first involved
The most versatile synthesis developed by the Swiss team first involved  A particularly novel, high-yielding synthesis of etonitazene was developed by FI Carroll and MC Coleman in the mid-1970s The authors were tasked with the preparation of large quantities of etonitazene, but found the conventional synthesis to be inadequate. The problem with the conventional synthesis was the lability of the imino ether reactant, 2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-acetimidic acid ethyl ester (prepared by reacting 4-ethoxyphenylacetonitrile with ethanolic HCl). The imino ether necessitated the use of
A particularly novel, high-yielding synthesis of etonitazene was developed by FI Carroll and MC Coleman in the mid-1970s The authors were tasked with the preparation of large quantities of etonitazene, but found the conventional synthesis to be inadequate. The problem with the conventional synthesis was the lability of the imino ether reactant, 2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-acetimidic acid ethyl ester (prepared by reacting 4-ethoxyphenylacetonitrile with ethanolic HCl). The imino ether necessitated the use of  A 2011 publication . Org. Chem., 2011, 76(23), 9577-9583from a South Korean team outlined a novel, one-pot synthesis for substituted and unsubstituted 2-benzyl-benzimidazoles that can be easily adapted to the preparation of etonitazene. The three component synthesis of the direct etonitazene precursor, 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole, consists of a 2-Bromo- or 2-Iodo-5-nitro-phenylamine (1.0 molar equivalent), a 4-substituted
A 2011 publication . Org. Chem., 2011, 76(23), 9577-9583from a South Korean team outlined a novel, one-pot synthesis for substituted and unsubstituted 2-benzyl-benzimidazoles that can be easily adapted to the preparation of etonitazene. The three component synthesis of the direct etonitazene precursor, 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole, consists of a 2-Bromo- or 2-Iodo-5-nitro-phenylamine (1.0 molar equivalent), a 4-substituted 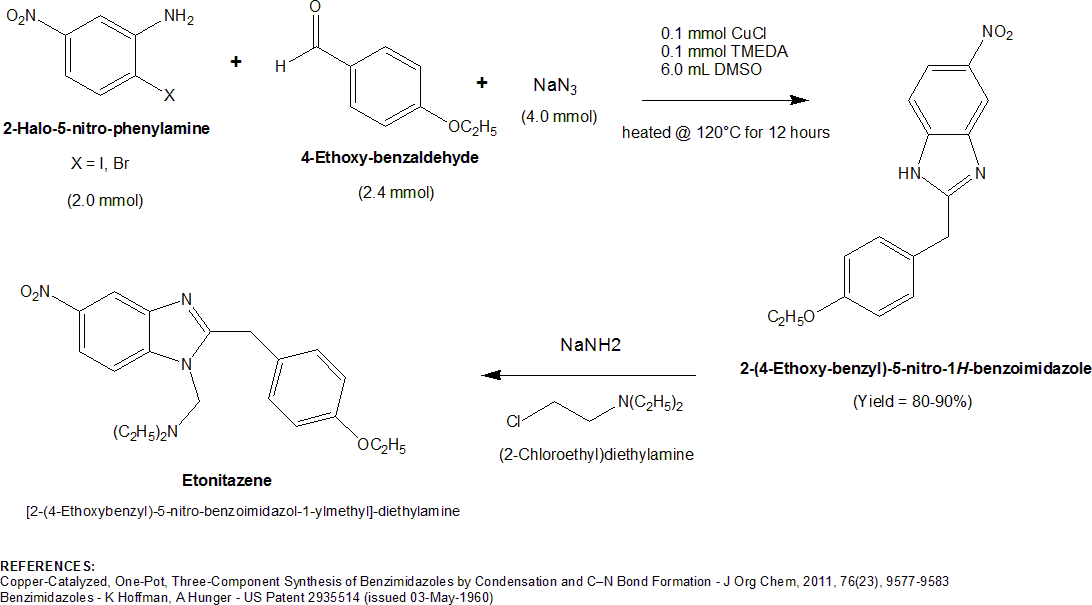
potency
Potency may refer to:
* Potency (pharmacology), a measure of the activity of a drug in a biological system
* Virility
* Cell potency, a measure of the differentiation potential of stem cells
* In homeopathic dilutions, potency is a measure of ho ...
of morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
in animals.
Because it is characterized by a strong dependency potential and a tendency to produce profound respiratory depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapni ...
, it is not used in humans. It is, however, useful in animal models for addiction
Addiction is a neuropsychological disorder characterized by a persistent and intense urge to use a drug or engage in a behavior that produces natural reward, despite substantial harm and other negative consequences. Repetitive drug use can ...
studies, particularly those requiring the animals to drink or ingest the agent, because it is not as bitter as opiate salts like morphine sulfate
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are ...
.
Synthesis
Etonitazene and relatednitazene
Benzimidazole opioids are a class of synthetic opioids that contain a benzimidazole core structure. The analgesic, pain-relieving properties of these substances were discovered in the mid-1950s by the Swiss company Ciba Specialty Chemicals, Ciba ...
opioid
Opioids are a class of Drug, drugs that derive from, or mimic, natural substances found in the Papaver somniferum, opium poppy plant. Opioids work on opioid receptors in the brain and other organs to produce a variety of morphine-like effects, ...
s were discovered in the late 1950s, by a team of Swiss researchers working at the pharmaceutical firm CIBA (now Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical company, pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland. Novartis is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world and was the eighth largest by re ...
). One of the first compounds investigated by the Swiss team was 1-(β-diethylaminoethyl)-2-benzylbenzimidazole, which was found to possess 10% of the analgesic activity of morphine when tested in rodent bioassays.
This finding encouraged the group to begin a comprehensive systematic study of 2-benzylbenzimidazoles and to establish the structure-activity relationship of this new family of analgesics. Two general synthetic methods were developed for the preparation of these compounds.
The first method involved the condensation of o-phenylenediamine
''o''-Phenylenediamine (OPD) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH2)2. This aromatic diamine is an important precursor to many heterocyclic compounds. OPD is a white compound although samples appear darker owing to oxidation by air. I ...
with para-ethoxy- phenylacetonitrile to form a 2-benzylbenzimidazole. The benzimidazole is then alkylated with the desired 1-chloro-2-dialkylaminoethane, forming the final product. This particular procedure was most useful for the preparation of benzimidazoles that lacked substituents on the benzene rings. A diagram of this method is displayed below.
alkylation Alkylation is a chemical reaction that entails transfer of an alkyl group. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting al ...
of 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (O2N)2C6H3Cl. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It is an intermediate for the industrial production of other compounds.
Preparation and reac ...
with 1-amino-2-diethylaminoethane to form N-(β-Diethylaminoethyl)-2,4-dinitroaniline (also known as N'-(2,4-Dinitrophenyl)-N,N-diethyl-ethane-1,2-diamine). The 2-nitro substituent on the 2,4-dinitroaniline compound is then selectively reduced
Reduction, reduced, or reduce may refer to:
Science and technology Chemistry
* Reduction (chemistry), part of a reduction-oxidation (redox) reaction in which atoms have their oxidation state changed.
** Organic redox reaction, a redox reacti ...
to the corresponding primary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
by utilizing ammonium sulfide
Ammonium hydrosulfide is the chemical compound with the formula .
Composition
It is the salt derived from the ammonium cation and the hydrosulfide anion. The salt exists as colourless, water-soluble, micaceous crystals. On Earth the compound is e ...
as the reducing agent
In chemistry, a reducing agent (also known as a reductant, reducer, or electron donor) is a chemical species that "donates" an electron to an (called the , , , or ).
Examples of substances that are common reducing agents include hydrogen, carbon ...
.
The ammonium sulfide can be formed by the addition of concentrated aqueous ammonium hydroxide
Ammonia solution, also known as ammonia water, ammonium hydroxide, ammoniacal liquor, ammonia liquor, aqua ammonia, aqueous ammonia, or (inaccurately) ammonia, is a solution of ammonia in water. It can be denoted by the symbols NH3(aq). Although ...
followed by saturation of the solution with hydrogen sulfide
Hydrogen sulfide is a chemical compound with the formula . It is a colorless chalcogen-hydride gas, and is toxic, corrosive, and flammable. Trace amounts in ambient atmosphere have a characteristic foul odor of rotten eggs. Swedish chemist ...
gas. The intermediate formed by the selective reduction of the 2-nitro substituent, 2-(β-Diethylaminoethylamino)-5-nitroaniline The term nitroaniline in chemistry refers to a derivative of aniline (C6H5NH2) containing a nitro group (—NO2) There are three simple nitroanilines of formula C6H4(NH2)(NO2) which differ only in the position of the nitro group:
* 2-Nitroaniline
...
, is then reacted with the hydrochloride
In chemistry, a hydrochloride is an acid salt resulting, or regarded as resulting, from the reaction of hydrochloric acid with an organic base (e.g. an amine). An alternative name is chlorhydrate, which comes from French. An archaic alternati ...
salt of the imino ethyl ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R� ...
of 4-ethoxy phenylacetonitrile (aka: p-ethoxybenzyl cyanide).
The imino ether, 2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-acetimidic acid ethyl ester
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an acid (either organic or inorganic) in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group () of that acid is replaced by an organyl group (R). These compounds contain a distin ...
hydrochloride, is prepared by dissolving the 4-substituted benzyl cyanide
Benzyl cyanide (abbreviated BnCN) is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH2CN. This colorless oily aromatic liquid is an important precursor to numerous compounds in organic chemistry.
It is also an important pheromone in certain s ...
in a mixture of anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
and chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
and then saturating this solution with dry hydrogen chloride
The Chemical compound, compound hydrogen chloride has the chemical formula and as such is a hydrogen halide. At room temperature, it is a colorless gas, which forms white fumes of hydrochloric acid upon contact with atmospheric water vapor. Hyd ...
gas. The reaction between the 2-(β-dialkylaminoalkylamine)-5-nitroaniline and the HCl salt of the imino ethyl ether results in the formation of etonitazene. This procedure is particularly useful in the preparation of the 4-, 5-, 6-, and 7-nitrobenzimidazoles.
Varying the choice of the substituted phenylacetic acid imino ether affords compounds with a diversity of substituents on the benzene ring at the 2- position. A diagram of this particular synthesis as it applies to the preparation of etonitazene is shown below.
 A particularly novel, high-yielding synthesis of etonitazene was developed by FI Carroll and MC Coleman in the mid-1970s The authors were tasked with the preparation of large quantities of etonitazene, but found the conventional synthesis to be inadequate. The problem with the conventional synthesis was the lability of the imino ether reactant, 2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-acetimidic acid ethyl ester (prepared by reacting 4-ethoxyphenylacetonitrile with ethanolic HCl). The imino ether necessitated the use of
A particularly novel, high-yielding synthesis of etonitazene was developed by FI Carroll and MC Coleman in the mid-1970s The authors were tasked with the preparation of large quantities of etonitazene, but found the conventional synthesis to be inadequate. The problem with the conventional synthesis was the lability of the imino ether reactant, 2-(4-Ethoxyphenyl)-acetimidic acid ethyl ester (prepared by reacting 4-ethoxyphenylacetonitrile with ethanolic HCl). The imino ether necessitated the use of anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
reaction conditions and was inconvenient to prepare in large quantities. This led the authors to experiment with the use of a coupling reagent, EEDQ (N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline), in order to promote the condensation of 2-(2-diethylaminoethylamino)-5-nitroaniline with 4-ethoxyphenylacetic acid. The authors discovered that when this condensation was performed in the presence of 2 or more molar equivalents of EEDQ (added portionwise in 3 steps) in THF
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is ma ...
at 50 °C for 192 hours (8 days), a near quantitative yield (100%) of etonitazene was obtained. In addition to the impressive improvement in yield over the conventional procedure, the work up procedure was greatly simplified since quinoline
Quinoline is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C9H7N. It is a colorless hygroscopic liquid with a strong odor. Aged samples, especially if exposed to light, become yellow and later brown. Quinoline is only sl ...
, carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalent bond, covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in a gas state at room temperature and at norma ...
, and ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
were the only by-products formed. A diagram of this procedure is shown below.
 A 2011 publication . Org. Chem., 2011, 76(23), 9577-9583from a South Korean team outlined a novel, one-pot synthesis for substituted and unsubstituted 2-benzyl-benzimidazoles that can be easily adapted to the preparation of etonitazene. The three component synthesis of the direct etonitazene precursor, 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole, consists of a 2-Bromo- or 2-Iodo-5-nitro-phenylamine (1.0 molar equivalent), a 4-substituted
A 2011 publication . Org. Chem., 2011, 76(23), 9577-9583from a South Korean team outlined a novel, one-pot synthesis for substituted and unsubstituted 2-benzyl-benzimidazoles that can be easily adapted to the preparation of etonitazene. The three component synthesis of the direct etonitazene precursor, 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole, consists of a 2-Bromo- or 2-Iodo-5-nitro-phenylamine (1.0 molar equivalent), a 4-substituted benzaldehyde
Benzaldehyde (C6H5CHO) is an organic compound consisting of a benzene ring with a formyl substituent. It is among the simplest aromatic aldehydes and one of the most industrially useful.
It is a colorless liquid with a characteristic almond-li ...
(1.2 equiv), and sodium azide
Sodium azide is an inorganic compound with the formula . This colorless salt is the gas-forming component in some car airbag systems. It is used for the preparation of other azide compounds. It is highly soluble in water and is acutely poisonou ...
(2 equiv). The 2-Halo-5-nitro-phenylamine requires a bromo or iodo group for optimal activity. 2-Chloro-phenylamines are completely unreactive. In addition to these three components, the reaction was optimized in the presence of 0.05 molar equivalents (5 mol%) of a catalyst, copper(I) chloride, and 5 mol% of ligand, TMEDA (tetramethylethylenediamine
Tetramethylethylenediamine (TMEDA or TEMED) is a chemical compound with the formula (CH3)2NCH2CH2N(CH3)2. This species is derived from ethylenediamine by replacement of the four amine hydrogens with four methyl groups. It is a colorless liquid, ...
). After heating these components at 120 °C for 12 hours in DMSO
Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula . This colorless liquid is the sulfoxide most widely used commercially. It is an important polar aprotic solvent that dissolves both polar and nonpolar compounds and is ...
, the direct etonitazene precursor, 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole, was formed in an approx 80-90% yield. The secondary amine
In chemistry, amines (, ) are organic compounds that contain carbon-nitrogen bonds. Amines are formed when one or more hydrogen atoms in ammonia are replaced by alkyl or aryl groups. The nitrogen atom in an amine possesses a lone pair of elec ...
nitrogen of 2-(4-Ethoxybenzyl)-5-nitro-1H-benzoimidazole was then alkylated with (2-Chloroethyl)diethylamine to form etonitazene. A diagram of this synthesis is shown below.

Analogs
A number of analogues are known, with the only other well-known compound to come out of the original 1950s research being clonitazene, which is much weaker than etonitazene (around 3x morphine). More recently since around late 2018 a number ofdesigner
A designer is a person who plans the form or structure of something before it is made, by preparing drawings or plans. In practice, anyone who creates tangible or intangible objects, products, processes, laws, games, graphics, services, or exper ...
analogues have started to appear on illicit markets around the world, with the most prominent compounds being metonitazene
Metonitazene is an analgesic compound related to etonitazene, which was first reported in 1957, and has been shown to have approximately 100 times the potency of morphine by central routes of administration, but if used orally it has been shown t ...
, isotonitazene
Isotonitazene is a synthetic opioid analgesic drug from the nitazene class and structural homolog of etonitazene, which has been sold as a designer drug. It has only around half the potency of etonitazene in animal studies, but it is likely eve ...
and etazene, though others have continued to appear.
Of these analogues, only etonitazene and clonitazene are explicitly listed under UN conventions and so are controlled throughout the world. The rest would only be illegal in countries such as the US, Australia and New Zealand that have laws equivalent to the Federal Analog Act
The Federal Analogue Act, , is a section of the United States Controlled Substances Act passed in 1986 which allows any chemical "substantially similar" to a controlled substance listed in Schedule I or II to be treated as if it were listed ...
. In the United States Etonitazene is a Schedule I narcotic controlled substance
A controlled substance is generally a drug or chemical whose manufacture, possession and use is regulated by a government, such as illicitly used drugs or prescription medications that are designated by law. Some treaties, notably the Sing ...
with a DEA ACSCN of 9624 and a 25 gram ( oz) manufacturing quota as of 2022.
Illicit production
Illicit production and sale of etonitazene has been limited. Identified on theMoscow
Moscow is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Russia by population, largest city of Russia, standing on the Moskva (river), Moskva River in Central Russia. It has a population estimated at over 13 million residents with ...
illegal drug market in 1998, it was primarily smoked in laced cigarettes. A chemist at Morton Thiokol
Thiokol was an American corporation concerned initially with rubber and related chemicals, and later with rocket and missile propulsion systems. Its name is a portmanteau of the Greek words for sulfur () and glue (), an allusion to the company's ...
synthesized the compound for his own use. The drug was produced in Russia in 1996 and sold as 'Chinese Dwarf'. The drug resulted in an unconfirmed number of deaths due to its uncertain potency. It appears to have a steep dose-response curve, and unpredictable pharmacokinetics especially when injected, in a similar manner to some other potent opioids such as dextromoramide
Dextromoramide (Palfium, Palphium, Jetrium, Dimorlin) is a powerful opioid analgesic approximately three times more potent than morphine but shorter acting. It is subject to drug prohibition regimes, both internationally through UN treaties and b ...
, which may cause etonitazene to be especially hazardous when compared to opioids of similar potency such as fentanyl
Fentanyl is a highly potent synthetic piperidine opioid primarily used as an analgesic (pain medication). It is 30 to 50 times more Potency (pharmacology), potent than heroin and 50 to 100 times more potent than morphine. Its primary Medici ...
.
See also
*Etazen
Etodesnitazene (also known as desnitroetonitazene, etazen, etazene, and etazone) is a benzimidazole-derived opioid analgesic drug, which was originally developed in the late 1950s alongside etonitazene and a range of related derivatives. It is m ...
(desnitroetonitazene)
References
{{Chemical agents Benzimidazole opioids Phenol ethers Mu-opioid receptor agonists Diethylamino compounds Nitroarenes Incapacitating agents Ethoxy compounds