Estonian Navy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Estonian Navy () are the unified naval forces among the

 The ''Merevägi'' was founded on November 21, 1918. The foundation and development of the Estonian Navy rely greatly on the
The ''Merevägi'' was founded on November 21, 1918. The foundation and development of the Estonian Navy rely greatly on the
 The top priority for the Estonian Navy is the development of mine countermeasures capability that is also one of the Navy's peacetime responsibilities: during
The top priority for the Estonian Navy is the development of mine countermeasures capability that is also one of the Navy's peacetime responsibilities: during
Estonian Navy
{{Authority control Military units and formations established in 1918 Military units and formations disestablished in 1940 Military units and formations established in 1991 1991 establishments in Estonia
Estonian Defence Forces
The Estonian Defence Forces () is the unified military force of the Republic of Estonia. The Estonian Defence Forces consists of the Estonian Land Forces, the Estonian Navy, the Estonian Air Force, and the paramilitary Estonian Defence Leagu ...
.
With only six commissioned ships and displacement well under 10,000 tonnes, the Estonian navy is one of the smallest navies in the world. Its ship prefix is EML (''Eesti Mereväe Laev''/Estonian Navy Ship). The Estonian Navy has participated numerous times in NATO's naval joint-exercises.
History
Interwar period
Foundation

 The ''Merevägi'' was founded on November 21, 1918. The foundation and development of the Estonian Navy rely greatly on the
The ''Merevägi'' was founded on November 21, 1918. The foundation and development of the Estonian Navy rely greatly on the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
which operated in the Gulf of Finland as an ally to Estonia during the Estonian War of Independence. The first Estonian navy warships were the destroyers '' Lennuk'' and '' Wambola'' and were gifts from the UK's Royal Navy after they had been captured from the Russian Baltic Fleet in 1919.
Marine Infantry
The Meredessantpataljon was a short-lived marine infantry - Naval landing battalion of the Estonian Defence Forces subject to the Estonian Navy. The battalion was created from the crews of the Estonian surface warships and was based in Tallinn.Coastal batteries
Since the end of the 19th century, the Russian Empire began to build coastal fortresses and naval strongholds in Estonia which was annexed to the empire after theGreat Northern War
In the Great Northern War (1700–1721) a coalition led by the Tsardom of Russia successfully contested the supremacy of the Swedish Empire in Northern Europe, Northern, Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe. The initial leaders of the ant ...
in 1721. Tallinn, having been historically an important trading center between the East and the West, became one of the main naval bases of the Imperial Russian Baltic Fleet
The Baltic Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Baltic Sea.
Established 18 May 1703, under Tsar Peter the Great as part of the Imperial Russian Navy, the Baltic Fleet is the oldest Russian fleet. In 1918, the fleet w ...
. A systematic coastal defence network and naval gun installations were ordered, and the construction works began at the end of the 1890s.
During the Estonian War of Independence
The Estonian War of Independence, also known as the War of Freedom in Estonia, was a defensive campaign of the Estonian Army and its allies, most notably the United Kingdom, against the Soviet Russian westward offensive of 1918–1919 and the ...
and after the Treaty of Tartu the Estonian Navy began to rebuild and develop the coastal defence network. From 1918 to 1940 Estonia invested millions of kroons into the renovation and development of coastal defences. By 1939 the coastal batteries presented a considerable naval force and were considered among the Estonian Navy elite forces. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
and later the Soviet occupation of Estonia, little has remained of the former coastal defence lines and fortifications. Today some buildings and firing positions can be seen at various places of which the best-preserved ones are located on the island of Aegna.
After restoration of independence
20th century
In 1998 the Baltic Naval Squadron BALTRON was inaugurated. The main responsibility of BALTRON is to improve the co-operation between the Baltic States in the areas of naval defence and security. Constant readiness to contribute units to NATO-led operations is assured through BALTRON. Each Baltic state appoints one or two ships to BALTRON for certain periods and staff members for one year. Service in BALTRON provides both, the crews and staff officers, with an excellent opportunity to serve in an international environment and acquire valuable experience in mine countermeasures. Estonia provides BALTRON with on-shore facilities for the staff. Since 1995 Estonian Navy ships have participated in most of the major international exercises and operations carried out in the Baltic Sea. Even though it was not until 1993 when the Navy was re-established, and despite the fact that it incorporates one of the smallest fleets in the world, the young crews of the Navy ships have demonstrated excellent interoperability during international exercises and have proved to be equal partners with other navies.21st century
From May 2005 to March 2006, was assigned as the Command and Support Ship ofNATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO ; , OTAN), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental organization, intergovernmental Transnationalism, transnational military alliance of 32 Member states of NATO, member s ...
's Standing NRF Mine Countermeasures Group 1 which is part of the NATO Response Force's maritime capability. ENS Admiral Pitka was the first vessel from the Baltic navies to be part of the force. SNMCMG1 is also one of the Estonian Navy's main NATO partners.
In 2020, the Estonian Defence Forces started planning the development of new defensive capabilities, which included procuring naval mine
A naval mine is a self-contained explosive weapon placed in water to damage or destroy surface ships or submarines. Similar to anti-personnel mine, anti-personnel and other land mines, and unlike purpose launched naval depth charges, they are ...
s and anti-ship missile
An anti-ship missile (AShM or ASM) is a guided missile that is designed for use against ships and large boats. Most anti-ship missiles are of the sea-skimming variety, and many use a combination of inertial guidance and active radar homing. ...
systems. In 2021, Estonia signed a contract with a Finnish company for the procurement of naval mines. In October, Estonia also signed a contract for Blue Spear 5G SSM anti-ship missiles.
In November 2021, the Estonian government decided to merge the fleet of the Police and Border Guard Board to the Estonian Navy. The navy would take over the ships, personnel and tasks of the Police and Border Guard Board. The merger would be completed by 1 January 2023.
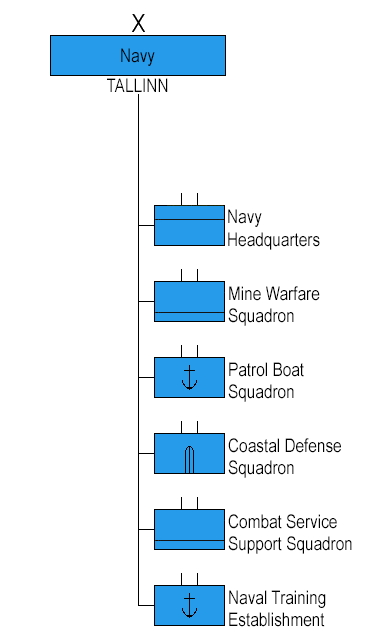
Organisation
Commanders
Operating forces
 The top priority for the Estonian Navy is the development of mine countermeasures capability that is also one of the Navy's peacetime responsibilities: during
The top priority for the Estonian Navy is the development of mine countermeasures capability that is also one of the Navy's peacetime responsibilities: during World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
and World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo ...
more than 80,000 sea mines were laid in the Baltic Sea. Since 1995 a number of mine clearance operations have been carried out in Estonian waters by the Estonian Mineships Division in close co-operation with other navies of the Baltic Sea region in order to find and dispose of ordnance and contribute to safe seagoing.
The Estonian Navy uses a small number of different vessels and weapon systems. Since the restoration of the Estonian Defence Forces on 3 September 1991 and the Estonian Navy on 1 July 1993, the naval force has developed tremendously. Then-Commander Estonian Naval Defence Forces, Commodore Roland Leit, was interviewed by Jane's Defence Weekly
''Jane's Defence Weekly'' (abbreviated as ''JDW'') is a weekly magazine reporting on military and corporate affairs, edited by Peter Felstead. It is one of a number of military-related publications named after John F. T. Jane, an Englishman who ...
on 9 July 1994. 'When the Soviet Navy
The Soviet Navy was the naval warfare Military, uniform service branch of the Soviet Armed Forces. Often referred to as the Red Fleet, the Soviet Navy made up a large part of the Soviet Union's strategic planning in the event of a conflict with t ...
left the Tallinn Naval Base, they sabotaged the facilities and scuttled about 10 of their ships in the harbour. They broke all the windows, all the heating, and all the electrical equipment. When they came in 1939, they took over our port facilities in good order. Now they are leaving us a mess, he said bitterly.' 'We got nothing from the Russian Navy. The ''Griff'' class patrol craft we got not from them but from a Russian firm that had bought the hulls first. Their navigation and radio systems are broken, too. We hope to have it all repaired and bring the craft into service before the end of the year.'
Although the Soviet legacy's clean-up and military infrastructure rebuilding has taken most of the defence budget resources away from the Navy, the armament and equipment has improved a great deal.
Naval Flotilla
Although theEstonian Defence Forces
The Estonian Defence Forces () is the unified military force of the Republic of Estonia. The Estonian Defence Forces consists of the Estonian Land Forces, the Estonian Navy, the Estonian Air Force, and the paramilitary Estonian Defence Leagu ...
have a relatively small selection of marine vessel
A watercraft or waterborne vessel is any vehicle designed for travel across or through water bodies, such as a boat, ship, hovercraft, submersible or submarine.
Types
Historically, watercraft have been divided into two main categories.
*Raf ...
s, the Navy still has a variety of different light-combat craft, coastal patrol-craft and support vessels. The first crafts that entered the service in the restored Estonian Navy in 1993 were mainly German background mine-layers and mine-hunters. Within the last 15 years, the Navy logistics support has increased year by year. Most of the modern navy vessels have either been received as foreign aid or been bought from Germany, Finland, United Kingdom and Denmark. In 2006, Estonia purchased three from the UK to enhance the Estonian Navy's mine-hunting capabilities.
In 2012, the Estonian Navy received a former Estonian Maritime Administration vessel EVA-321. It was renamed "Lood" (A530) and became a diving support vessel.
In September 2013, it was reported that the Estonian Navy was interested in acquiring the 1979-built Finnish minelayer ''Pohjanmaa'' that had been decommissioned by the Finnish Navy
The Finnish Navy ( , ) is one of the branches of the Finnish Defence Forces. The navy employs 2,300 people and about 4,300 conscripts are trained each year. Finnish Navy vessels are given the ship prefix "FNS", short for "Finnish Navy ship", but ...
and was offered for sale. However, all of this speculation came to nought; in March 2016, a Finnish State-owned company (Meritaito) acquired the vessel.
In July 2018, it was reported that three Sandown-class minehunters were set to be modernized between 2018 and 2019. The modernization would include improvements in mine clearance and marine surveillance capabilities. The estimated cost of the project would be €30 million.
In April 2020, the Ministry of Defence announced that it would buy two force protection patrol boats. The boats would be manufactured by Baltic Workboats AS for a total sum of €3.9 million. They would enter service in 2021 and would be used for force protection at sea and in ports, and could also provide support for other agencies, including the Police and Border Guard Board. In December 2020, the Estonian Defence Forces received the two boats and named them Roland and Risto. In April 2024, Roland and Risto were donated to Ukraine..
Naval Base
The "Merevägi" has operated a number of naval bases and war harbors, most of them being located on the western coast and the islands. Until 1939 there were more than ten smaller and bigger war harbors and bases; including Aegna, Paldiski, Virtsu, Rohuküla, Mõntu, Kuressaare, Kõiguste, Papisaare, Jaagurahu, Tagalaht, Küdema, Sõru, Kärdla, Kallaste, Mustvee and Tallinn harbor. Currently, there is only one major naval harbor Miinisadam which is located in northern Tallinn. The Miinisadam is a base for the Mineships Division.Personnel
Most Estonian Navy officers have been trained in European or American naval academies (notably the US Naval Academy). In 2003, the Navy established its own Centre of Naval Education and Training (CNET) to train junior petty officers. Each Baltic State shares its limited training resources with the others. For instance, Estonia provides communications training at the Baltic Naval Communications School inTallinn
Tallinn is the capital city, capital and List of cities in Estonia, most populous city of Estonia. Situated on a Tallinn Bay, bay in north Estonia, on the shore of the Gulf of Finland of the Baltic Sea, it has a population of (as of 2025) and ...
, and Latvia hosts a common Baltic Naval Diving Training Centre in Liepāja
Liepāja () (formerly: Libau) is a Administrative divisions of Latvia, state city in western Latvia, located on the Baltic Sea. It is the largest city in the Courland region and the third-largest in the country after Riga and Daugavpils. It is an ...
.
Ranks
Commissioned officer ranks
The rank insignia ofcommissioned officer
An officer is a person who holds a position of authority as a member of an armed force or uniformed service.
Broadly speaking, "officer" means a commissioned officer, a non-commissioned officer (NCO), or a warrant officer. However, absent ...
s.
Other ranks
The rank insignia ofnon-commissioned officer
A non-commissioned officer (NCO) is an enlisted rank, enlisted leader, petty officer, or in some cases warrant officer, who does not hold a Commission (document), commission. Non-commissioned officers usually earn their position of authority b ...
s and enlisted personnel
An enlisted rank (also known as an enlisted grade or enlisted rate) is, in some armed services, any rank below that of a commissioned officer. The term can be inclusive of non-commissioned officers or warrant officers, except in United States ...
.
See also
* Finnish–Estonian defense cooperationReferences
External links
Estonian Navy
{{Authority control Military units and formations established in 1918 Military units and formations disestablished in 1940 Military units and formations established in 1991 1991 establishments in Estonia