
In
estimation theory
Estimation theory is a branch of statistics that deals with estimating the values of parameters based on measured empirical data that has a random component. The parameters describe an underlying physical setting in such a way that their val ...
, estimation of signal parameters via rotational invariant techniques (ESPRIT) is a technique to determine parameters of a mixture of
sinusoid
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the ''sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in ...
s in a background noise. This technique is first proposed for frequency estimation, however, with the introduction of
phased-array
In antenna theory, a phased array usually means an electronically scanned array, a computer-controlled array of antennas which creates a beam of radio waves that can be electronically steered to point in different directions without moving th ...
systems in daily use technology, it is also used for
Angle of arrival
The angle of arrival (AoA) of a signal is the direction from which the signal (e.g. radio, optical or acoustic) is received.
Measurement
Measurement of AoA can be done by determining the direction of propagation of a radio-frequency wave incident ...
estimations
[Volodymyr Vasylyshyn. Direction of arrival estimation using ESPRIT with sparse arrays.// Proc. 2009 European Radar Conference (EuRAD). – 30 Sept.-2 Oct. 2009. - Pp. 246 - 249. ]
/ref> as well.
General description
Dividing into virtual sub-arrays
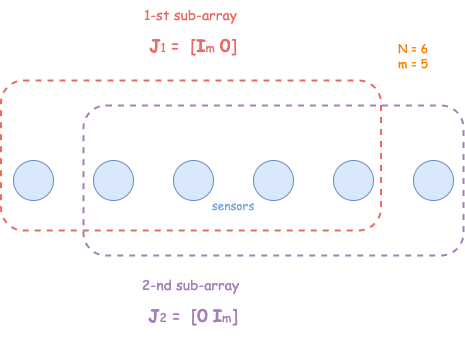 Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a
Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a Vandermonde matrix
In linear algebra, a Vandermonde matrix, named after Alexandre-Théophile Vandermonde, is a matrix with the terms of a geometric progression in each row: an matrix
:V=\begin
1 & x_1 & x_1^2 & \dots & x_1^\\
1 & x_2 & x_2^2 & \dots & x_2^\\
1 & x ...
for number of sinusoids can be constructed, as in
 In
In  Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a
Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a
 In
In  Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a
Defining a signal vector as,
where represents the radial frequency of -th sinusoid, a