Episiotomy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the
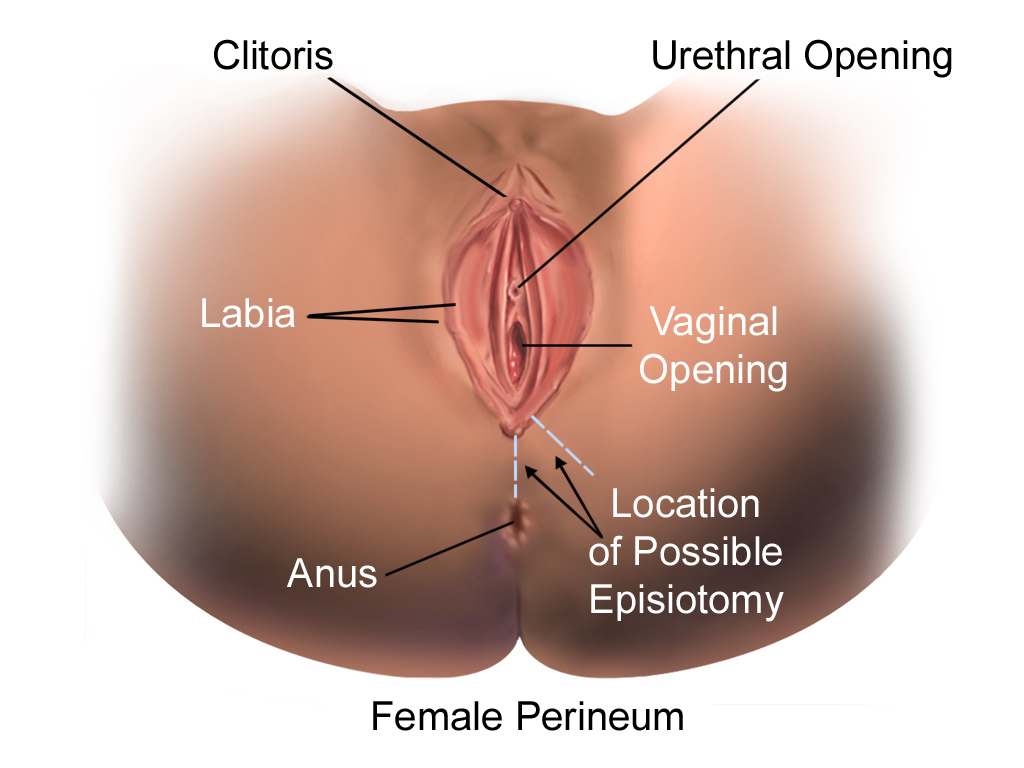
 There are four main types of episiotomy:
* Medio-lateral: The incision is made downward and outward from the midpoint of the fourchette either to the right or left. It is directed diagonally in a straight line which runs about away from the anus (midpoint between the anus and the ischial tuberosity).
* Median: The incision commences from the centre of the fourchette and extends on the posterior side along the midline for .
* Lateral: The incision starts from about away from the centre of the fourchette and extends laterally. Drawbacks include the chance of injury to the Bartholin's duct, therefore some practitioners have strongly discouraged lateral incisions.
* ''J''-shaped: The incision begins in the centre of the fourchette and is directed posteriorly along the midline for about and then directed downwards and outwards along the 5 or 7 o'clock position to avoid the internal and external anal sphincter. This procedure is also not widely practised.
There are four main types of episiotomy:
* Medio-lateral: The incision is made downward and outward from the midpoint of the fourchette either to the right or left. It is directed diagonally in a straight line which runs about away from the anus (midpoint between the anus and the ischial tuberosity).
* Median: The incision commences from the centre of the fourchette and extends on the posterior side along the midline for .
* Lateral: The incision starts from about away from the centre of the fourchette and extends laterally. Drawbacks include the chance of injury to the Bartholin's duct, therefore some practitioners have strongly discouraged lateral incisions.
* ''J''-shaped: The incision begins in the centre of the fourchette and is directed posteriorly along the midline for about and then directed downwards and outwards along the 5 or 7 o'clock position to avoid the internal and external anal sphincter. This procedure is also not widely practised.
Episiotomy
Merck Manual Professional Edition
Merck Manual Professional Edition-->
Merck Manual Professional Edition
What I Don’t Tell My Students About ‘The Husband Stitch’
Electricliterature.com
Episiotomy Animation
How That Might Be Used During Labor to Ease Delivery of the Baby? {{Obstetrical procedures Obstetrical procedures Theriogenology
perineum
The perineum (: perineums or perinea) in placentalia, placental mammals is the space between the anus and the genitals. The human perineum is between the anus and scrotum in the male or between the anus and vulva in the female. The perineum is ...
and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by an obstetrician. This is usually performed during the second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the aperture, allowing the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left (medio-lateral episiotomy), is performed under local anesthetic ( pudendal anesthesia), and is sutured after delivery.
Its routine use is no longer recommended, as perineal massage applied to the vaginal opening, is an alternative to enlarge the orifice for the baby. It was once one of the most common surgical procedures specific to women. In the United States, as of 2012, it was performed in 12% of vaginal births. It is also widely practiced in many parts of the world, including Korea
Korea is a peninsular region in East Asia consisting of the Korean Peninsula, Jeju Island, and smaller islands. Since the end of World War II in 1945, it has been politically Division of Korea, divided at or near the 38th parallel north, 3 ...
, Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
, Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia. The main geography of Taiwan, island of Taiwan, also known as ''Formosa'', lies between the East China Sea, East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocea ...
, China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, it is the list of countries by population (United Nations), second-most populous country after ...
, and Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
in the early 2000s.
Uses
Vaginal tears can occur during childbirth, most often at the introitus as the baby's head passes through, especially if the baby descends quickly. Episiotomies are used in an effort to prevent soft-tissue tearing ( perineal tear) which may involve the anal sphincter and rectum. Tears can involve the perineal skin or extend to the muscles and the anal sphincter and anus. The midwife or obstetrician may decide to make a surgical cut to the perineum with scissors or a scalpel to make the baby's birth easier and prevent severe injuries that can be difficult to repair. The cut is repaired with stitches (sutures). Some childbirth facilities have a policy of routine episiotomy. Specific reasons to do an episiotomy are unclear. Though indications on the need for episiotomy vary and may even be controversial (see discussion below), where the technique is applied, there are two main variations. Both are depicted in the above image. * In one variation, the midline episiotomy, the line of incision is central over the anus. This technique bifurcates the perineal body, which is essential for the integrity of the pelvic floor. Precipitous birth can also sever—and more severely sever—the perineal body, leading to long-term complications such as incontinence. Therefore, the oblique technique is often applied (also pictured above). * In the oblique technique, the perineal body is avoided, cutting only the vagina epithelium, skin, and muscles (transversalius and bulbospongiosus). This technique aids in avoiding trauma to the perineal body by either surgical or traumatic means. In 2009, a Cochrane meta-analysis based on studies with over 5,000 women concluded that: "Restrictive episiotomy policies appear to have a number of benefits compared to policies based on routine episiotomy. There is less posterior perineal trauma, less suturing and fewer complications, no difference for most pain measures and severe vaginal or perineal trauma, but there was an increased risk of anterior perineal trauma with restrictive episiotomy". The authors were unable to find quality studies that compared mediolateral versus midline episiotomy.Types

Controversy
Traditionally, physicians have used episiotomies in an effort to deflect the cut in the perineal skin away from the anal sphincter muscle, as control over stool (faeces) is an important function of the anal sphincter, i.e. lessen perineal trauma, minimize postpartum pelvic floor dysfunction, and as muscles have a good blood supply, by avoiding damaging the anal sphincter muscle, reduce the loss of blood during delivery, and protect against neonatal trauma. While episiotomy is employed to obviate issues such as post-partum pain, incontinence, and sexual dysfunction, some studies suggest that episiotomy surgery itself can cause all of these problems, the episiotomy and wound can continue as a tear and damage the ring of muscle around the lower part of the large bowel , the anal sphincter. Research has shown that natural tears typically are less severe (although this is perhaps surprising since an episiotomy is designed for when natural tearing will cause significant risks or trauma). Slow delivery of the head in between contractions will result in the least perineal damage. Studies in 2010 based on interviews with postpartum women have concluded that limiting perineal trauma during birth is conducive to continued sexual function after birth. At least one study has recommended that routine episiotomy be abandoned for this reason. In various countries, routine episiotomy has been an accepted medical practice for many years. Since about the 1960s, routine episiotomies have been rapidly losing popularity among obstetricians and midwives in almost all countries in Europe, Australia, Canada, and the United States. A nationwide U.S. population study suggested that 31% of women having babies in U.S. hospitals received episiotomies in 1997, compared with 56% in 1979. In Latin America, it remains popular and is performed in 90% of hospital births.Discussion
Having an episiotomy may increase perineal pain during postpartum recovery, resulting in trouble defecating, particularly in midline episiotomies. In addition, it may complicatesexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (also coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion of the Erection, erect male Human penis, penis inside the female vagina and followed by Pelvic thrust, thrusting motions for sexual pleasure ...
by making it painful and replacing erectile tissues in the vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, lab ...
with scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, t ...
tissue.
In cases where an episiotomy is indicated, a mediolateral incision may be preferable to a median (midline) incision, as the latter is associated with a higher risk of injury to the anal sphincter and the rectum. Damage to the anal sphincter caused by episiotomy can result in fecal incontinence
Fecal incontinence (FI), or in some forms, encopresis, is a lack of control over defecation, leading to involuntary loss of bowel contents—including flatus (gas), liquid stool elements and mucus, or solid feces. FI is a sign or a symptom ...
(loss of control over defecation). Conversely, one of the reasons episiotomy is performed is to prevent tearing of the anal sphincter, which is also associated with fecal incontinence.
Impacts on sexual intercourse
Some midwives compare routine episiotomy tofemale genital mutilation
Female genital mutilation (FGM) (also known as female genital cutting, female genital mutilation/cutting (FGM/C) and female circumcision) is the cutting or removal of some or all of the vulva for non-medical reasons. Prevalence of female ge ...
. One study found that women who underwent episiotomy reported more painful intercourse and insufficient lubrication 12–18 months after birth but did not find any problems with orgasm or arousal.
Pain management
Perineal pain after episiotomy has immediate and long-term negative effects on women and their babies. These effects can interfere with breastfeeding and the care of the infant. The pain from injection sites and episiotomy is managed by the frequent assessment of the report of pain from the mother. Pain can come from possible lacerations, incisions, uterine contractions and sore nipples. Appropriate medications are usually administered. Nonpharmacologic interventions can also be used: a warm salt bath increases blood flow to the area, decreases local discomfort, and promotes healing. Routine episiotomies have not been found to reduce the level of pain after the birth.See also
* Husband stitch * Perineal massage * Sheehan's syndromeReferences
External links
Episiotomy
Merck Manual Professional Edition
Merck Manual Professional Edition-->
Merck Manual Professional Edition
What I Don’t Tell My Students About ‘The Husband Stitch’
Electricliterature.com
Episiotomy Animation
How That Might Be Used During Labor to Ease Delivery of the Baby? {{Obstetrical procedures Obstetrical procedures Theriogenology