Ephraimites on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 According to the
According to the
 According to the
According to the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
. '' pausa: , ''ʾEp̄rāyim'') was one of the
 The territory of Ephraim contained the early centers of Israelite religion - Shechem and Shiloh.''Jewish Encyclopedia'' These factors contributed to making Ephraim the most dominant of the tribes in the Kingdom of Israel, and led to ''Ephraim'' becoming a synonym for the entire kingdom.
Joshua 16:1-4 outlines the borders of the lands allocated to the "children of Joseph", i.e. Ephraim and Manasseh combined, and Joshua 16:5-8 defines the borders of the land allocated to the tribe of Ephraim in more detail.
Bethel was allocated by Joshua to the Tribe of Benjamin. However, even by the time of the prophetess Deborah, Bethel is described as being in the land of the Tribe of Ephraim. Some twenty years after the breakup of the
The territory of Ephraim contained the early centers of Israelite religion - Shechem and Shiloh.''Jewish Encyclopedia'' These factors contributed to making Ephraim the most dominant of the tribes in the Kingdom of Israel, and led to ''Ephraim'' becoming a synonym for the entire kingdom.
Joshua 16:1-4 outlines the borders of the lands allocated to the "children of Joseph", i.e. Ephraim and Manasseh combined, and Joshua 16:5-8 defines the borders of the land allocated to the tribe of Ephraim in more detail.
Bethel was allocated by Joshua to the Tribe of Benjamin. However, even by the time of the prophetess Deborah, Bethel is described as being in the land of the Tribe of Ephraim. Some twenty years after the breakup of the
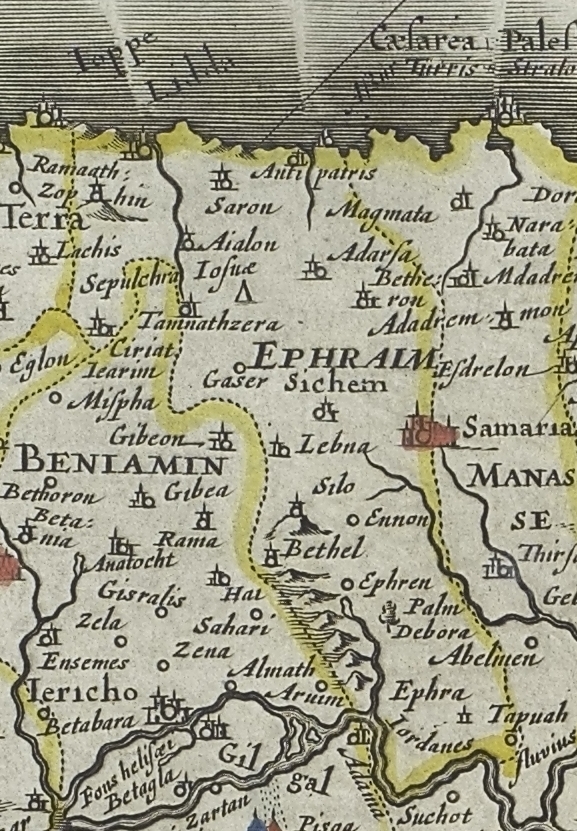
Map of the Tribal Territory of the Tribe of Ephraim
Fuller, 1650. Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ephraim, Tribe Of Twelve Tribes of Israel Samaritan culture and history Land of Israel Gilead
. '' pausa: , ''ʾEp̄rāyim'') was one of the
Twelve Tribes of Israel
The Twelve Tribes of Israel ( , ) are described in the Hebrew Bible as being the descendants of Jacob, a Patriarchs (Bible), Hebrew patriarch who was a son of Isaac and thereby a grandson of Abraham. Jacob, later known as Israel (name), Israel, ...
. The Tribe of Manasseh
According to the Hebrew Bible, the Tribe of Manasseh (; Hebrew: ''Ševet Mənašše,'' Tiberian: ''Šēḇeṭ Mănašše'') was one of the twelve tribes of Israel. After the catastrophic Assyrian invasion of 720 BCE, it is counted as one ...
, together with Ephraim, formed the Tribe of Joseph. It is one of the Ten Lost Tribes
The Ten Lost Tribes were those from the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel after it was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire around 720 BCE. They were the following ...
. The etymology of the name is disputed.For the etymology, see
Ephraim as portrayed in biblical narrative
According to the Bible, the Tribe of Ephraim is descended from a man named Ephraim, who is recorded as the son of Joseph, the son of Jacob, and Asenath, the daughter of Potiphera. The descendants of Joseph formed two of the tribes of Israel, whereas the other sons of Jacob were the founders of one tribe each. The Bible records that the Tribe of Ephraim entered the land ofCanaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
during its conquest by Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
, a descendant of Ephraim himself. However, many archeologists have abandoned the idea that Joshua carried out a conquest of Canaan similar to that described in the Book of Joshua, seeing Jews instead as indigenous Canaanites who developed a monotheistic religion over time.
From Joshua to the formation of the first Kingdom of Israel, the Tribe of Ephraim was a part of a loose confederation of Israelite tribes. No central government existed, and in times of crisis the people were led by ad hoc leaders known as Judges (see the Book of Judges
The Book of Judges is the seventh book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. In the narrative of the Hebrew Bible, it covers the time between the conquest described in the Book of Joshua and the establishment of a kingdom in the ...
).
With the growth of the threat from Philistine incursions, the Israelite tribes decided to form a strong centralised monarchy to meet the challenge. The Tribe of Ephraim joined the new kingdom with Saul
Saul (; , ; , ; ) was a monarch of ancient Israel and Judah and, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament, the first king of the United Monarchy, a polity of uncertain historicity. His reign, traditionally placed in the late eleventh c ...
as the first king. The widely accepted date for Saul's reign is approximately 1025–1005 BCE. Some scholars dispute this date range and place Saul later, perhaps as late as "the second half of the tenth century B.C.E."
After the death of Saul, the Bible records all the tribes other than Judah remained loyal to the House of Saul. After the death of Ishbosheth, Saul's son and successor to the throne of Israel, the Tribe of Ephraim joined the other northern Israelite tribes in making David
David (; , "beloved one") was a king of ancient Israel and Judah and the third king of the United Monarchy, according to the Hebrew Bible and Old Testament.
The Tel Dan stele, an Aramaic-inscribed stone erected by a king of Aram-Dam ...
, who was then the king of Judah, the king of a reunited Kingdom of Israel. According to archaeologist Israel Finkelstein, there is doubt about whether the biblical ordering for the reigns of the early monarchs is reliable, and that the sequence preserved in the Bible, in which David follows Saul as king of Israel, may not be historically accurate.
However, on the accession of Rehoboam, David's grandson, in c. 930 BCE the northern tribes split from the House of David to form the northern Kingdom of Israel. The first king of the northern kingdom was an Ephraimite, Jeroboam
Jeroboam I (; Hebrew language, Hebrew: ''Yārŏḇʿām''; ), frequently cited Jeroboam son of Nebat, was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first king of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel following a Jeroboam's Revol ...
, who likely ruled in 931–909 BCE.
The accents of the tribes were distinctive enough even at the time of the confederacy so that when the Israelites of Gilead, under the leadership of Jephthah, fought the Tribe of Ephraim, their pronunciation of '' shibboleth'' as ''sibboleth'' was considered sufficient evidence to single out individuals from Ephraim, so that they could be subjected to immediate death by the Israelites of Gilead.
Ephraim was a member of the Northern Kingdom until the kingdom was conquered by Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , ''māt Aššur'') was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization that existed as a city-state from the 21st century BC to the 14th century BC and eventually expanded into an empire from the 14th century BC t ...
in c. 723 BCE and the population deported. From that time, the Tribe of Ephraim has been counted as one of the Ten Lost Tribes
The Ten Lost Tribes were those from the Twelve Tribes of Israel that were said to have been exiled from the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel after it was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire around 720 BCE. They were the following ...
of Israel.
Ephraim is often seen as the tribe that embodies the entire Northern Kingdom and the royal house resided in the tribe's territory (just as Judah is the tribe that embodies the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
and provided its royal family).
Tribal territory
In the biblical account, following the completion of the conquest ofCanaan
CanaanThe current scholarly edition of the Septuagint, Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interprets. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : D ...
by the Israelite
Israelites were a Hebrew language, Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group, consisting of tribes that lived in Canaan during the Iron Age.
Modern scholarship describes the Israelites as emerging from indigenous Canaanites, Canaanite populations ...
Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
allocated the land among the twelve tribes. Kenneth Kitchen, a well-known conservative biblical scholar, dates this event to slightly after 1200 BC.Kitchen, Kenneth A. (2003), "On the Reliability of the Old Testament" (Grand Rapids, Michigan. William B. Eerdmans Publishing Company)() However, the consensus of modern scholars is that the conquest of Joshua as described in the Book of Joshua never occurred."Besides the rejection of the Albrightian ‘conquest' model, the general consensus among OT scholars is that the Book of Joshua has no value in the historical reconstruction. They see the book as an ideological retrojection from a later period — either as early as the reign of Josiah or as late as the Hasmonean period." "It behooves us to ask, in spite of the fact that the overwhelming consensus of modern scholarship is that Joshua is a pious fiction composed by the deuteronomistic school, how does and how has the Jewish community dealt with these foundational narratives, saturated as they are with acts of violence against others?" "Recent decades, for example, have seen a remarkable reevaluation of evidence concerning the conquest of the land of Canaan by Joshua. As more sites have been excavated, there has been a growing consensus that the main story of Joshua, that of a speedy and complete conquest (e.g. Josh. 11.23: 'Thus Joshua conquered the whole country, just as the had promised Moses') is contradicted by the archaeological record, though there are indications of ''some'' destruction and conquest at the appropriate time.
As recorded in the Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile. It tells of the ...
, the territory allocated to the Tribe of Ephraim was at the center of Canaan, west of the Jordan
Jordan, officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan, is a country in the Southern Levant region of West Asia. Jordan is bordered by Syria to the north, Iraq to the east, Saudi Arabia to the south, and Israel and the occupied Palestinian ter ...
, south of the territory of Manasseh, and north of the Tribe of Benjamin
According to the Torah, the Tribe of Benjamin () was one of the Twelve Tribes of Israel. The tribe was descended from Benjamin, the youngest son of the Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Jacob (later given the name Israel) and his wife Rachel. In the ...
. The region later named Samaria
Samaria (), the Hellenized form of the Hebrew name Shomron (), is used as a historical and Hebrew Bible, biblical name for the central region of the Land of Israel. It is bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The region is ...
(as distinguished from Judea
Judea or Judaea (; ; , ; ) is a mountainous region of the Levant. Traditionally dominated by the city of Jerusalem, it is now part of Palestine and Israel. The name's usage is historic, having been used in antiquity and still into the pres ...
or Galilee) consisted mostly of Ephraim's territory. The area was mountainous, giving it protection, and also highly fertile, giving prosperity,
United Monarchy
The Kingdom of Israel (Hebrew: מַמְלֶכֶת יִשְׂרָאֵל, ''Mamleḵeṯ Yīśrāʾēl'') was an Israelite kingdom that may have existed in the Southern Levant. According to the Deuteronomistic history in the Hebrew Bible ...
, Abijah, the second king of Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
, defeated Jeroboam
Jeroboam I (; Hebrew language, Hebrew: ''Yārŏḇʿām''; ), frequently cited Jeroboam son of Nebat, was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the first king of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel following a Jeroboam's Revol ...
of Israel
Israel, officially the State of Israel, is a country in West Asia. It Borders of Israel, shares borders with Lebanon to the north, Syria to the north-east, Jordan to the east, Egypt to the south-west, and the Mediterranean Sea to the west. Isr ...
and took back the towns of Bethel, Jeshanah and Ephron, with their surrounding villages. Ephron is believed to be the Ophrah that was also allocated to the Tribe of Benjamin by Joshua.
The wadi Qānā () of Joshua 17:9 divided Ephraim's territory to the south and Manasseh's territory to the north. The illegal Israeli settlement of Karnei Shomron is built near this gulch, which runs in an easterly-westerly direction.
The border of Ephraim extended from the Jordan River in the east to the Mediterranean Sea in the west. It incorporated within it the cities of Bethel (now Beitin), ʻAtarot, Lower Beth-Ḥoron (now Lower Bayt ʻUr), extending as far as Gezer (now Abu Shusha, formerly known as "Tell el Jezer") and the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea ( ) is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the east by the Levant in West Asia, on the north by Anatolia in West Asia and Southern Eur ...
. Gezer was said to have been inhabited by Canaanites long after Joshua had either killed or expelled the other Canaanites. According to French archaeologist, Charles Clermont-Ganneau, who identified the site in 1871 and later carried out excavations there, Gezer marked the extreme western point of the territory of Ephraim, and was "situated at the actual intersection of the boundaries of Ephraim, Dan and Judah." This view, however, does not seem to be supported by the Scriptures themselves which place the extent of Ephraim's border at the sea.
The tribe of Ephraim had by lot the land that extended in length from the river Jordan to Gezer; but in breadth as far as from Bethel, till it ended at the Great Plain.Spanish-Jewish traveller Benjamin of Tudela wrote that the southernmost bounds of the territory of Ephraim extended in a south-westerly direction as far as the town of Ibelin (now Yibna).
Origin
According to theTorah
The Torah ( , "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. The Torah is also known as the Pentateuch () ...
, the tribe consisted of descendants of Ephraim a son of Joseph, from whom it took its name; however some critical scholars view this also as postdiction, an eponym
An eponym is a noun after which or for which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. Adjectives derived from the word ''eponym'' include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Eponyms are commonly used for time periods, places, innovati ...
ous metaphor
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to cr ...
providing an aetiology of the connectedness of the tribe to others in the Israelite confederation.'' Peake's commentary on the Bible'' In the Biblical account, Joseph is one of the two children of Rachel
Rachel () was a Bible, Biblical figure, the favorite of Jacob's two wives, and the mother of Joseph (Genesis), Joseph and Benjamin, two of the twelve progenitors of the tribes of Israel. Rachel's father was Laban (Bible), Laban. Her older siste ...
and Jacob
Jacob, later known as Israel, is a Hebrew patriarch of the Abrahamic religions. He first appears in the Torah, where he is described in the Book of Genesis as a son of Isaac and Rebecca. Accordingly, alongside his older fraternal twin brother E ...
, a brother to Benjamin
Benjamin ( ''Bīnyāmīn''; "Son of (the) right") blue letter bible: https://www.blueletterbible.org/lexicon/h3225/kjv/wlc/0-1/ H3225 - yāmîn - Strong's Hebrew Lexicon (kjv) was the younger of the two sons of Jacob and Rachel, and Jacob's twe ...
, and father to both Ephraim, and his first son, Manasseh; although Manasseh was the eldest, Jacob foresaw that Ephraim's descendants would be greater than his brother's.
Though the biblical descriptions of the geographic boundary of the House of Joseph are fairly consistent, the descriptions of the boundaries between Manasseh and Ephraim are not, and each is portrayed as having exclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is s ...
s within the territory of the other. Furthermore, in the Blessing of Jacob, and elsewhere ascribed by textual scholars to a similar or earlier time period, Ephraim and Manasseh are treated as a single tribe, with ''Joseph'' appearing in their place. From this it is regarded as probable that originally Ephraim and Manasseh were considered one tribe — that of Joseph. According to several biblical scholars
Biblical studies is the academic application of a set of diverse academic discipline, disciplines to the study of the Bible, with ''Bible'' referring to the books of the Biblical canon#Jewish canons, canonical Hebrew Bible in mainstream Judais ...
, Benjamin was also originally part of the ''House of Joseph'', but the biblical account of this became lost; Benjamin being differentiated by being that part of Ephraim (House of Joseph) which joined the Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
rather than that of Israel.
A number of biblical scholars suspect that the ''Joseph tribes'' (including Benjamin) represent a second migration of Israelites to Israel, later than the main tribes, specifically that it was only the ''Joseph tribes'' which went to Egypt and returned, while the main Israelite tribes simply emerged as a subculture from the Canaanites and had remained in Canaan throughout; in the narrative in the Book of Joshua
The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian captivity, Babylonian exile. It tells of the ...
, which concerns the arrival in (and conquest of) Canaan by the Israelites from Egypt, the leader is Joshua
Joshua ( ), also known as Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' Literal translation, lit. 'Yahweh is salvation'), Jehoshua, or Josue, functioned as Moses' assistant in the books of Book of Exodus, Exodus and ...
, who was a member of the Ephraim tribe. According to this view, the story of Jacob's visit to Laban to obtain a wife began as a metaphor for the second migration, with Jacob's new family, possessions, and livestock, obtained from Laban, being representations of the new wave of migrants;
Professor David Frankel believes that ancient traditions regarding pre-conquest Ephraimite settlement in Canaan were unintentionally preserved in biblical passages such as 1 Chronicles 7:20-24. In 1 Chronicles 7:20-24, Ephraim's descendants, Ezer and Elead, were Canaanite residents who were killed by the Philistines, which was mourned by Ephraim and his brethren. This Ephraim was believed to be different from the more famous Ephraim and his brethren were believed to be the heads of other Israelite tribes. Professor Nili Wazana connects this with Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion
David Ben-Gurion ( ; ; born David Grün; 16 October 1886 – 1 December 1973) was the primary List of national founders, national founder and first Prime Minister of Israel, prime minister of the State of Israel. As head of the Jewish Agency ...
's argument for why the Jews were indigenous to Canaan, which was affirmed in the Israeli Declaration of Independence. Ben-Gurion argued that Abraham's migration to Canaan was a "renuion with indigenous Hebrews who shared his theological belief" and that not all Hebrews joined Jacob's family when they migrated to Egypt.
Character
In the account of the deuteronomic history, Ephraim is portrayed as domineering, haughty, discontented, and jealous, but in classical rabbinical literature, the biblical founder of the tribe is described as being modest and not selfish. These rabbinical sources allege that it was on account of modesty and selflessness, and a prophetic vision of Joshua, that Jacob gave Ephraim precedence over Manasseh, the elder of the two; in these sources, Jacob is regarded as sufficiently just that God upholds the blessing in his honour, and makes Ephraim the leading tribe. Nevertheless, other classical rabbinical texts mock the tribe for the character it has in the deuteronomic history, claiming that Ephraim, being headstrong, left Egypt 30 years prior tothe Exodus
The Exodus (Hebrew language, Hebrew: יציאת מצרים, ''Yəṣīʾat Mīṣrayīm'': ) is the Origin myth#Founding myth, founding myth of the Israelites whose narrative is spread over four of the five books of the Torah, Pentateuch (specif ...
, and on arrival in Canaan was subjected to a disastrous battle with the Philistines
Philistines (; LXX: ; ) were ancient people who lived on the south coast of Canaan during the Iron Age in a confederation of city-states generally referred to as Philistia.
There is compelling evidence to suggest that the Philistines origi ...
; in the Midrashic Jasher this is portrayed as a rebellion of Ephraim against God, resulting in the slaying of all but 10, and the bleached bones of the slaughtered being strewn across the roads, so much so that the circuitous route of the Exodus was simply an attempt by God to prevent the Israelites from having to suffer the sight of the remains.
Though from the point of view of an increasing majority of archaeologists, there were always two distinct cultures in Canaan, a strong and prosperous northern kingdom and a weaker and poorer southern one, in the Biblical account the Israelite tribes were initially united in a single kingdom, and only later fractured into the northern and southern kingdoms; this fracture is blamed by the Bible on the jealousy of Ephraim over the growing power of Judah. In the Book of Chronicles, Ephraim's act of splintering from Judah is denounced as forsaking God, and Ephraim is portrayed as becoming highly irreligious, particularly in their resistance to the reforms enacted by Hezekiah and Josiah.
It was not until the close of the first period of Jewish history that God 'refused the tabernacle of Joseph (Hebrew Bible), and chose not the tribe of Ephraim, but chose the tribe of Judah, the Mount Zion which he loved'. When the Ark was removed from Shiloh to Zion the power of Ephraim was sequestered.
Destiny
As part of the Kingdom of Israel, the territory of Ephraim was conquered by the Assyrians, and the tribe was mostly exiled; some in the tribe managed to flee to theKingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelites, Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries ...
, which lay just south of the territory of Ephraim. In any case, the manner of their exile and/or dispersal led to their further history being lost. However, several modern day groups claim descent, with varying levels of academic and rabbinical support. The Samaritans claim that some of their adherents are descended from this tribe, and many Persian Jews
Iranian Jews, (; ) also Persian Jews ( ) or Parsim, constitute one of the oldest communities of the Jewish diaspora. Dating back to the History of ancient Israel and Judah, biblical era, they originate from the Jews who relocated to Iran (his ...
claim to be descendants of Ephraim. Further afield, in India the Telugu Jews claim descent from Ephraim, and call themselves ''Bene Ephraim'', relating similar traditions to those of the Mizo Jews, whom the modern state of Israel regards as descendants of Manasseh.
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Restorationism, restorationist Christianity, Christian Christian denomination, denomination and the ...
teaches that a significant portion of its members are descended from or adopted into the tribe of Ephraim, believing that they are charged with restoring the lost tribes in the latter days, as prophesied by Isaiah. Along with members of the tribe of Judah, members of the tribe of Ephraim are believed to be playing important leadership roles for covenant Israel in the last days. They also believe that the main groups of the Book of Mormon ( Nephites and Lamanites) were parts of the tribes of Ephraim and Manasseh, as part fulfilment of the blessing of Jacob: "Joseph is a fruitful bough, even a fruitful bough by a well; whose branches run over the wall", interpreting the "wall" as the ocean). McConkie, Bruce R., ''The Millennial Messiah'', 1982, Chapter 16.
Notes
References
* McConkie, Bruce R, The Millennial Messiah, 1982, Chapter 16. *External links
Map of the Tribal Territory of the Tribe of Ephraim
Fuller, 1650. Eran Laor Cartographic Collection, The National Library of Israel. {{DEFAULTSORT:Ephraim, Tribe Of Twelve Tribes of Israel Samaritan culture and history Land of Israel Gilead