Englishman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The English people are an
 The influence of later invasions and migrations on the English population has been debated, as studies that sampled only modern DNA have produced uncertain results and have thus been subject to a large variety of interpretations. More recently, however, ancient DNA has been used to provide a clearer picture of the genetic effects of these movements of people.
One 2016 study, using Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon era DNA found at grave sites in Cambridgeshire, calculated that ten modern day eastern English samples had 38% Anglo-Saxon ancestry on average, while ten Welsh and Scottish samples each had 30% Anglo-Saxon ancestry, with a large statistical spread in all cases. However, the authors noted that the similarity observed between the various sample groups was likely to be due to more recent internal migration.
Another 2016 study conducted using evidence from burials found in northern England, found that a significant genetic difference was present in bodies from the Iron Age and the Roman period on the one hand, and the Anglo-Saxon period on the other. Samples from modern-day Wales were found to be similar to those from the Iron Age and Roman burials, while samples from much of modern England, East Anglia in particular, were closer to the Anglo-Saxon-era burial. This was found to demonstrate a "profound impact" from the Anglo-Saxon migrations on the modern English gene pool, though no specific percentages were given in the study.
A third study combined the ancient data from both of the preceding studies and compared it to a large number of modern samples from across Britain and Ireland. This study found that modern southern, central and eastern English populations were of "a predominantly Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry" while those from northern and southwestern England had a greater degree of indigenous origin.
A major 2020 study, which used DNA from Viking-era burials in various regions across Europe, found that modern English samples showed nearly equal contributions from a native British "North Atlantic" population and a Danish-like population. While much of the latter signature was attributed to the earlier settlement of the Anglo-Saxons, it was calculated that up to 6% of it could have come from Danish Vikings, with a further 4% contribution from a Norwegian-like source representing the Norwegian Vikings. The study also found an average 18% admixture from a source further south in Europe, which was interpreted as reflecting the legacy of French migration under the Normans.
A landmark 2022 study titled "The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool", found the English to be of plurality Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry, with heavy native Celtic Briton, and newly confirmed medieval French admixture. Significant regional variation was also observed.
The influence of later invasions and migrations on the English population has been debated, as studies that sampled only modern DNA have produced uncertain results and have thus been subject to a large variety of interpretations. More recently, however, ancient DNA has been used to provide a clearer picture of the genetic effects of these movements of people.
One 2016 study, using Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon era DNA found at grave sites in Cambridgeshire, calculated that ten modern day eastern English samples had 38% Anglo-Saxon ancestry on average, while ten Welsh and Scottish samples each had 30% Anglo-Saxon ancestry, with a large statistical spread in all cases. However, the authors noted that the similarity observed between the various sample groups was likely to be due to more recent internal migration.
Another 2016 study conducted using evidence from burials found in northern England, found that a significant genetic difference was present in bodies from the Iron Age and the Roman period on the one hand, and the Anglo-Saxon period on the other. Samples from modern-day Wales were found to be similar to those from the Iron Age and Roman burials, while samples from much of modern England, East Anglia in particular, were closer to the Anglo-Saxon-era burial. This was found to demonstrate a "profound impact" from the Anglo-Saxon migrations on the modern English gene pool, though no specific percentages were given in the study.
A third study combined the ancient data from both of the preceding studies and compared it to a large number of modern samples from across Britain and Ireland. This study found that modern southern, central and eastern English populations were of "a predominantly Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry" while those from northern and southwestern England had a greater degree of indigenous origin.
A major 2020 study, which used DNA from Viking-era burials in various regions across Europe, found that modern English samples showed nearly equal contributions from a native British "North Atlantic" population and a Danish-like population. While much of the latter signature was attributed to the earlier settlement of the Anglo-Saxons, it was calculated that up to 6% of it could have come from Danish Vikings, with a further 4% contribution from a Norwegian-like source representing the Norwegian Vikings. The study also found an average 18% admixture from a source further south in Europe, which was interpreted as reflecting the legacy of French migration under the Normans.
A landmark 2022 study titled "The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool", found the English to be of plurality Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry, with heavy native Celtic Briton, and newly confirmed medieval French admixture. Significant regional variation was also observed.
 The first people to be called "English" were the
The first people to be called "English" were the  The exact nature of the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons and their relationship with the Romano-British is a matter of debate. The traditional view is that a mass invasion by various Anglo-Saxon tribes largely displaced the indigenous British population in southern and eastern Britain (modern-day England with the exception of
The exact nature of the arrival of the Anglo-Saxons and their relationship with the Romano-British is a matter of debate. The traditional view is that a mass invasion by various Anglo-Saxon tribes largely displaced the indigenous British population in southern and eastern Britain (modern-day England with the exception of
 From about 800 AD, waves of Danish Viking assaults on the coastlines of the
From about 800 AD, waves of Danish Viking assaults on the coastlines of the
 The
The
Black Presence
'', Asian and Black History in Britain, 1500–1850: UK government website. Retrieved 21 July 2006. and a small Indian presence since at least the 17th century because of the
 In the 2020 United States census, English Americans were the largest group in the United States with 46.5 million Americans self-identifying as having some English origins (many combined with another heritage) representing (19.8%) of the
In the 2020 United States census, English Americans were the largest group in the United States with 46.5 million Americans self-identifying as having some English origins (many combined with another heritage) representing (19.8%) of the
 From the beginning of the colonial era until the mid-20th century, the vast majority of settlers to Australia were from the
From the beginning of the colonial era until the mid-20th century, the vast majority of settlers to Australia were from the
– Ancestry 2016
 English settlers arrived in
English settlers arrived in
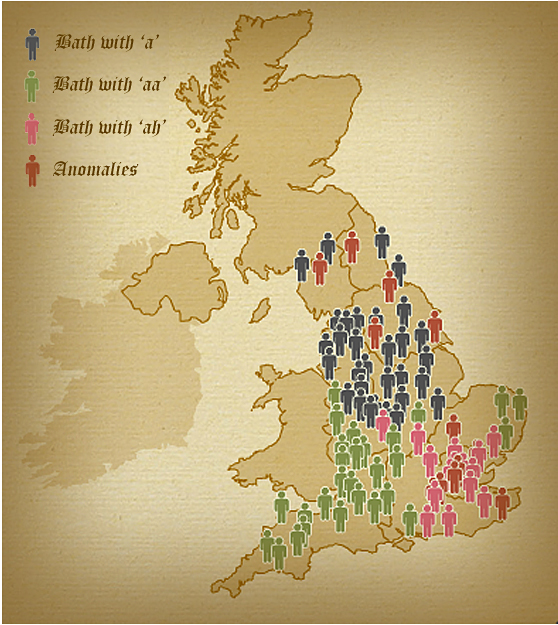 English people traditionally speak the
English people traditionally speak the
ethnic group
An ethnicity or ethnic group is a group of people with shared attributes, which they collectively believe to have, and long-term endogamy. Ethnicities share attributes like language, culture, common sets of ancestry, traditions, society, re ...
and nation
A nation is a type of social organization where a collective Identity (social science), identity, a national identity, has emerged from a combination of shared features across a given population, such as language, history, ethnicity, culture, t ...
native to England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, who speak the English language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
, a West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germ ...
language, and share a common ancestry, history, and culture. The English identity began with the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
, when they were known as the , meaning "Angle kin" or "English people". Their ethnonym
An ethnonym () is a name applied to a given ethnic group. Ethnonyms can be divided into two categories: exonyms (whose name of the ethnic group has been created by another group of people) and autonyms, or endonyms (whose name is created and used ...
is derived from the Angles, one of the Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were tribal groups who lived in Northern Europe in Classical antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. In modern scholarship, they typically include not only the Roman-era ''Germani'' who lived in both ''Germania'' and parts of ...
who invaded Britain
Britain most often refers to:
* Great Britain, a large island comprising the countries of England, Scotland and Wales
* The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, a sovereign state in Europe comprising Great Britain and the north-eas ...
around the 5th century AD.
The English largely descend from two main historical population groups: the West Germanic tribes, including the Angles, Saxons
The Saxons, sometimes called the Old Saxons or Continental Saxons, were a Germanic people of early medieval "Old" Saxony () which became a Carolingian " stem duchy" in 804, in what is now northern Germany. Many of their neighbours were, like th ...
, and Jutes
The Jutes ( ) were one of the Germanic people, Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the end of Roman rule in Britain, departure of the Roman Britain, Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic na ...
who settled in Southern Britain following the withdrawal of the Romans, and the partially Romanised Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', , ), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were the Celtic people who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age until the High Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh, ...
who already lived there.Martiniano, R., Caffell, A., Holst, M. et al. "Genomic signals of migration and continuity in Britain before the Anglo-Saxons". ''Nat Commun'' 7, 10326 (2016). Collectively known as the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
, they founded what was to become the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
by the 10th century, in response to the invasion and extensive settlement of Danes
Danes (, ), or Danish people, are an ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
History
Early history
Denmark ...
and other Norsemen
The Norsemen (or Northmen) were a cultural group in the Early Middle Ages, originating among speakers of Old Norse in Scandinavia. During the late eighth century, Scandinavians embarked on a Viking expansion, large-scale expansion in all direc ...
that began in the late 9th century. This was followed by the Norman Conquest
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
and limited settlement of Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; ; ) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and locals of West Francia. The Norse settlements in West Franc ...
in England in the late 11th century and a sizeable number of French Protestants
Protestantism in France has existed in its various forms, starting with Calvinism and Lutheranism since the Protestant Reformation. John Calvin was a Frenchman, as were numerous other Protestant Reformers including William Farel, Pierre Viret and ...
who emigrated between the 16th and 18th centuries.Campbell. ''The Anglo-Saxon State''. p. 10Higham, Nicholas J., and Martin J. Ryan. ''The Anglo-Saxon World''. Yale University Press, 2013. pp. 7–19 Some definitions of English people include, while others exclude, people descended from later migration into England.
England is the largest and most populous country of the United Kingdom. The majority of people living in England are British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies.
* British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture ...
citizens. In the Acts of Union 1707
The Acts of Union refer to two acts of Parliament, one by the Parliament of Scotland in March 1707, followed shortly thereafter by an equivalent act of the Parliament of England. They put into effect the international Treaty of Union agree ...
, the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from the late 9th century, when it was unified from various Heptarchy, Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland to f ...
and the Kingdom of Scotland
The Kingdom of Scotland was a sovereign state in northwest Europe, traditionally said to have been founded in 843. Its territories expanded and shrank, but it came to occupy the northern third of the island of Great Britain, sharing a Anglo-Sc ...
merged to become the Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
. Over the years, English customs and identity have become fairly closely aligned with British customs and identity in general. The demonyms for men and women from England are Englishman and Englishwoman.
English nationality
England itself has no devolved government. The 1990s witnessed a rise in English self-awareness. This is linked to the expressions of national self-awareness of the other British nations of Wales, Scotland and, to some extent, Northern Ireland which take their most solid form in the newdevolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
political arrangements within the United Kingdom and the waning of a shared British national identity with the growing distance between the end of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
and the present.
Many recent immigrants to England have assumed a solely British identity, while others have developed dual or mixed identities. Use of the word "English" to describe Britons from ethnic minorities
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority g ...
in England is complicated by most non-white people in England identifying as British rather than English. In their 2004 Annual Population Survey
The Annual Population Survey (APS) is a combined statistical survey of households in Great Britain which is conducted quarterly by the Office for National Statistics (ONS). It combines results from the Labour Force Survey (LFS) and the English ...
, the Office for National Statistics
The Office for National Statistics (ONS; ) is the executive office of the UK Statistics Authority, a non-ministerial department which reports directly to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK Parliament.
Overview
The ONS is responsible fo ...
compared the ethnic identities of British people with their perceived national identity
National identity is a person's identity or sense of belonging to one or more states or one or more nations. It is the sense of "a nation as a cohesive whole, as represented by distinctive traditions, culture, and language".
National identity ...
. They found that while 58% of white people
White is a Race (human categorization), racial classification of people generally used for those of predominantly Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry. It is also a Human skin color, skin color specifier, although the definition can var ...
in England described their nationality as "English", non-white people were more likely to describe themselves as "British". However, in the 2021 United Kingdom census
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in o ...
, 58.4% of respondants identified as "British" instead of "English" to 14.9%. Although, the Office for National Statistics states the reason for this change may partially be true, it is most likely due to changes to the question structure where "British" became the top response option in 2021 for England only.
Relationship to Britishness
It is unclear how many British people consider themselves English. The words "English" and "British" are often incorrectly used interchangeably, especially outside the UK. In his study of English identity, Krishan Kumar describes a common slip of the tongue in which people say "English, I mean British". He notes that this slip is normally made only by the English themselves and by foreigners: "Non-English members of the United Kingdom rarely say 'British' when they mean 'English. Kumar suggests that although this blurring is a sign of England's dominant position with the UK, it is also "problematic for the English ..when it comes to conceiving of their national identity. It tells of the difficulty that most English people have of distinguishing themselves, in a collective way, from the other inhabitants of the British Isles". In 1965, the historian A. J. P. Taylor wrote,When the ''However, although Taylor believed this blurring effect was dying out, in his book '' The Isles: A History'' (1999),Oxford History of England The Oxford History of England (1934–1965) was a book series on the history of the United Kingdom. Published by Oxford University Press, it was originally intended to span from Roman Britain to the outbreak of the First World War in fourteen vol ...'' was launched a generation ago, "England" was still an all-embracing word. It meant indiscriminately England and Wales; Great Britain; the United Kingdom; and even the British Empire. Foreigners used it as the name of aGreat Power A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power ...and indeed continue to do so.Bonar Law Andrew Bonar Law (; 16 September 1858 – 30 October 1923) was a British statesman and politician who was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from October 1922 to May 1923. Law was born in the British colony of New Brunswick (now a Canadi ..., by origin a Scotch Canadian, was not ashamed to describe himself as "Prime Minister of England" ..Now terms have become more rigorous. The use of "England" except for a geographic area brings protests, especially from the Scotch.
Norman Davies
Ivor Norman Richard Davies (born 8 June 1939) is a British and Polish historian, known for his publications on the history of Europe, Poland and the United Kingdom. He has a special interest in Central and Eastern Europe and is UNESCO Profes ...
lists numerous examples in history books of "British" still being used to mean "English" and vice versa.
In December 2010, Matthew Parris
Matthew Francis Parris (born 7 August 1949) is a British political writer, broadcaster, and former politician. He served as Member of Parliament for West Derbyshire from 1979 to 1986. Ideologically a liberal conservative, he is a member of t ...
in ''The Spectator
''The Spectator'' is a weekly British political and cultural news magazine. It was first published in July 1828, making it the oldest surviving magazine in the world. ''The Spectator'' is politically conservative, and its principal subject a ...
'', analysing the use of "English" over "British", argued that English identity, rather than growing, had existed all along but has recently been unmasked from behind a veneer of Britishness.
Historical and genetic origins
Replacement of Neolithic farmers by Bell Beaker populations
English people, like most Europeans, largely descend from three distinct lineages: Mesolithichunter-gatherer
A hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living in a community, or according to an ancestrally derived Lifestyle, lifestyle, in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local naturally occurring sources, esp ...
s, descended from a Cro-Magnon
Cro-Magnons or European early modern humans (EEMH) were the first early modern humans (''Homo sapiens'') to settle in Europe, migrating from western Asia, continuously occupying the continent possibly from as early as 56,800 years ago. They in ...
population that arrived in Europe about 45,000 years ago; Neolithic farmers who migrated from Anatolia during the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, also known as the First Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period in Afro-Eurasia from a lifestyle of hunter-gatherer, hunting and gathering to one of a ...
9,000 years ago; and Yamnaya Steppe pastoralists who expanded into Europe from the Pontic–Caspian steppe in the context of Indo-European migrations
The Indo-European migrations are hypothesized migrations of Proto-Indo-Europeans, peoples who spoke Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) and the derived Indo-European languages, which took place from around 4000 to 1000 BCE, ...
5,000 years ago.
Recent genetic studies have suggested that Britain's Neolithic population was largely replaced by a population from North Continental Europe characterised by the Bell Beaker culture around 2400 BC, associated with the Yamnaya
The Yamnaya ( ) or Yamna culture ( ), also known as the Pit Grave culture or Ochre Grave culture, is a late Copper Age to early Bronze Age archaeological culture of the region between the Southern Bug, Dniester, and Ural rivers (the Pontic–C ...
people from the Pontic-Caspian Steppe. This population lacked genetic affinity to some other Bell Beaker populations, such as the Iberian Bell Beakers, but appeared to be an offshoot of the Corded Ware single grave people, as developed in Western Europe. It is currently unknown whether these Beaker peoples went on to develop Celtic languages in the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
, or whether later Celtic migrations introduced Celtic languages to Britain.
The close genetic affinity of these Beaker people to Continental North Europeans means that British and Irish populations cluster genetically very closely with other Northwest European populations, regardless of how much Anglo-Saxon and Viking ancestry was introduced during the 1st millennium.
Anglo-Saxons, Vikings and Normans
 The influence of later invasions and migrations on the English population has been debated, as studies that sampled only modern DNA have produced uncertain results and have thus been subject to a large variety of interpretations. More recently, however, ancient DNA has been used to provide a clearer picture of the genetic effects of these movements of people.
One 2016 study, using Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon era DNA found at grave sites in Cambridgeshire, calculated that ten modern day eastern English samples had 38% Anglo-Saxon ancestry on average, while ten Welsh and Scottish samples each had 30% Anglo-Saxon ancestry, with a large statistical spread in all cases. However, the authors noted that the similarity observed between the various sample groups was likely to be due to more recent internal migration.
Another 2016 study conducted using evidence from burials found in northern England, found that a significant genetic difference was present in bodies from the Iron Age and the Roman period on the one hand, and the Anglo-Saxon period on the other. Samples from modern-day Wales were found to be similar to those from the Iron Age and Roman burials, while samples from much of modern England, East Anglia in particular, were closer to the Anglo-Saxon-era burial. This was found to demonstrate a "profound impact" from the Anglo-Saxon migrations on the modern English gene pool, though no specific percentages were given in the study.
A third study combined the ancient data from both of the preceding studies and compared it to a large number of modern samples from across Britain and Ireland. This study found that modern southern, central and eastern English populations were of "a predominantly Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry" while those from northern and southwestern England had a greater degree of indigenous origin.
A major 2020 study, which used DNA from Viking-era burials in various regions across Europe, found that modern English samples showed nearly equal contributions from a native British "North Atlantic" population and a Danish-like population. While much of the latter signature was attributed to the earlier settlement of the Anglo-Saxons, it was calculated that up to 6% of it could have come from Danish Vikings, with a further 4% contribution from a Norwegian-like source representing the Norwegian Vikings. The study also found an average 18% admixture from a source further south in Europe, which was interpreted as reflecting the legacy of French migration under the Normans.
A landmark 2022 study titled "The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool", found the English to be of plurality Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry, with heavy native Celtic Briton, and newly confirmed medieval French admixture. Significant regional variation was also observed.
The influence of later invasions and migrations on the English population has been debated, as studies that sampled only modern DNA have produced uncertain results and have thus been subject to a large variety of interpretations. More recently, however, ancient DNA has been used to provide a clearer picture of the genetic effects of these movements of people.
One 2016 study, using Iron Age and Anglo-Saxon era DNA found at grave sites in Cambridgeshire, calculated that ten modern day eastern English samples had 38% Anglo-Saxon ancestry on average, while ten Welsh and Scottish samples each had 30% Anglo-Saxon ancestry, with a large statistical spread in all cases. However, the authors noted that the similarity observed between the various sample groups was likely to be due to more recent internal migration.
Another 2016 study conducted using evidence from burials found in northern England, found that a significant genetic difference was present in bodies from the Iron Age and the Roman period on the one hand, and the Anglo-Saxon period on the other. Samples from modern-day Wales were found to be similar to those from the Iron Age and Roman burials, while samples from much of modern England, East Anglia in particular, were closer to the Anglo-Saxon-era burial. This was found to demonstrate a "profound impact" from the Anglo-Saxon migrations on the modern English gene pool, though no specific percentages were given in the study.
A third study combined the ancient data from both of the preceding studies and compared it to a large number of modern samples from across Britain and Ireland. This study found that modern southern, central and eastern English populations were of "a predominantly Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry" while those from northern and southwestern England had a greater degree of indigenous origin.
A major 2020 study, which used DNA from Viking-era burials in various regions across Europe, found that modern English samples showed nearly equal contributions from a native British "North Atlantic" population and a Danish-like population. While much of the latter signature was attributed to the earlier settlement of the Anglo-Saxons, it was calculated that up to 6% of it could have come from Danish Vikings, with a further 4% contribution from a Norwegian-like source representing the Norwegian Vikings. The study also found an average 18% admixture from a source further south in Europe, which was interpreted as reflecting the legacy of French migration under the Normans.
A landmark 2022 study titled "The Anglo-Saxon migration and the formation of the early English gene pool", found the English to be of plurality Anglo-Saxon-like ancestry, with heavy native Celtic Briton, and newly confirmed medieval French admixture. Significant regional variation was also observed.
History of English people
Anglo-Saxon settlement
 The first people to be called "English" were the
The first people to be called "English" were the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons, in some contexts simply called Saxons or the English, were a Cultural identity, cultural group who spoke Old English and inhabited much of what is now England and south-eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. They traced t ...
, a group of closely related Germanic tribes that began migrating to eastern and southern Britain, from southern Denmark and northern Germany, in the 5th century AD, after the Romans had withdrawn from Britain. The Anglo-Saxons gave their name to England ("Engla land", meaning "Land of the Angles") and to the English.
The Anglo-Saxons arrived in a land that was already populated by people commonly referred to as the "Romano-British
The Romano-British culture arose in Britain under the Roman Empire following the Roman conquest in AD 43 and the creation of the province of Britannia. It arose as a fusion of the imported Roman culture with that of the indigenous Britons, ...
"—the descendants of the native Brittonic-speaking population that lived in the area of Britain under Roman rule during the 1st–5th centuries AD. The multi-ethnic nature of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of ...
meant that small numbers of other peoples may have also been present in England before the Anglo-Saxons arrived. There is archaeological evidence, for example, of an early North African presence in a Roman garrison at Aballava, now Burgh-by-Sands, in Cumbria: a 4th-century inscription says that the Roman military unit "Numerus Maurorum Aurelianorum" ("unit of Aurelian Moors") from Mauretania (Morocco) was stationed there. Although the Roman Empire incorporated peoples from far and wide, genetic studies suggest the Romans did not significantly mix into the British population.
Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
). This is supported by the writings of Gildas
Gildas (English pronunciation: , Breton language, Breton: ''Gweltaz''; ) — also known as Gildas Badonicus, Gildas fab Caw (in Middle Welsh texts and antiquarian works) and ''Gildas Sapiens'' (Gildas the Wise) — was a 6th-century Britons (h ...
, who gives the only contemporary historical account of the period, and describes the slaughter and starvation of native Britons by invading tribes ('' aduentus Saxonum''). Furthermore, the English language contains no more than a handful of words borrowed from Brittonic sources.
This view was later re-evaluated by some archaeologists and historians, with a more small-scale migration being posited, possibly based around an elite of male warriors that took over the rule of the country and gradually acculturated the people living there. Within this theory, two processes leading to Anglo-Saxonisation have been proposed. One is similar to culture changes observed in Russia, North Africa and parts of the Islamic world, where a politically and socially powerful minority culture becomes, over a rather short period, adopted by a settled majority. This process is usually termed "elite dominance".Ward-Perkins, Bryan. "Why did the Anglo-Saxons not become more British?" ''The English Historical Review'' 115.462 (2000): 513–533. The second process is explained through incentives, such as the Wergild outlined in the law code of Ine of Wessex which produced an incentive to become Anglo-Saxon or at least English speaking. Historian Malcolm Todd writes, "It is much more likely that a large proportion of the British population remained in place and was progressively dominated by a Germanic aristocracy, in some cases marrying into it and leaving Celtic names in the, admittedly very dubious, early lists of Anglo-Saxon dynasties. But how we identify the surviving Britons in areas of predominantly Anglo-Saxon settlement, either archaeologically or linguistically, is still one of the deepest problems of early English history."
An emerging view is that the degree of population replacement by the Anglo-Saxons, and thus the degree of survival of the Romano-Britons, varied across England, and that as such the overall settlement of Britain by the Anglo-Saxons cannot be described by any one process in particular. Large-scale migration and population shift seems to be most applicable in the cases of eastern regions such as East Anglia and Lincolnshire, while in parts of Northumbria, much of the native population likely remained in place as the incomers took over as elites.Härke, Heinrich. "Anglo-Saxon Immigration and Ethnogenesis." ''Medieval Archaeology'' 55.1 (2011): 1–28. In a study of place names in northeastern England and southern Scotland, Bethany Fox found that the migrants settled in large numbers in river valleys, such as those of the Tyne and the Tweed, with the Britons moving to the less fertile hill country and becoming acculturated over a longer period. Fox describes the process by which English came to dominate this region as "a synthesis of mass-migration and elite-takeover models."
Vikings and the Danelaw
 From about 800 AD, waves of Danish Viking assaults on the coastlines of the
From about 800 AD, waves of Danish Viking assaults on the coastlines of the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
were gradually followed by a succession of Danish settlers in England. At first, the Vikings were very much considered a separate people from the English. This separation was enshrined when Alfred the Great
Alfred the Great ( ; – 26 October 899) was King of the West Saxons from 871 to 886, and King of the Anglo-Saxons from 886 until his death in 899. He was the youngest son of King Æthelwulf and his first wife Osburh, who both died when Alfr ...
signed the Treaty of Alfred and Guthrum
The Treaty of Alfred and Guthrum is a 9th-century peace agreement between Alfred of Wessex and Guthrum, the Viking ruler of East Anglia. It sets out the boundaries between Alfred and Guthrum's territories as well as agreements on peaceful trade, ...
to establish the Danelaw, a division of England between English and Danish rule, with the Danes occupying northern and eastern England.
However, Alfred's successors subsequently won military victories against the Danes, incorporating much of the Danelaw into the nascent kingdom of England. Danish invasions continued into the 11th century, and there were both English and Danish kings in the period following the unification of England (for example, Æthelred II
Æthelred (; ) or Ethelred () is an Old English personal name (a compound of ''wiktionary:æþele, æþele'' and ''wiktionary:ræd, ræd'', meaning "noble counsel" or "well-advised") and may refer to:
Anglo-Saxon England
* Æthelred and Æthelbe ...
(978–1013 and 1014–1016) was English but Cnut
Cnut ( ; ; – 12 November 1035), also known as Canute and with the epithet the Great, was King of England from 1016, King of Denmark from 1018, and King of Norway from 1028 until his death in 1035. The three kingdoms united under Cnut's rul ...
(1016–1035) was Danish).
Gradually, the Danes in England came to be seen as 'English'. They had a noticeable impact on the English language: many English words, such as ''anger'', ''ball'', ''egg'', ''got'', ''knife'', ''take'', and ''they'', are of Old Norse origin, and place names that end in ''-thwaite'' and ''-by'' are Scandinavian in origin.
English unification
The English population was not politically unified until the 10th century. Before then, there were a number ofpetty kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into t ...
s which gradually coalesced into a heptarchy
The Heptarchy was the division of Anglo-Saxon England between the sixth and eighth centuries into petty kingdoms, conventionally the seven kingdoms of East Anglia, Essex, Kent, Mercia, Northumbria, Sussex, and Wessex. The term originated wi ...
of seven states, the most powerful of which were Mercia
Mercia (, was one of the principal kingdoms founded at the end of Sub-Roman Britain; the area was settled by Anglo-Saxons in an era called the Heptarchy. It was centred on the River Trent and its tributaries, in a region now known as the Midlan ...
and Wessex
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon Heptarchy, kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886.
The Anglo-Sa ...
. The English nation state
A nation state, or nation-state, is a political entity in which the State (polity), state (a centralized political organization ruling over a population within a territory) and the nation (a community based on a common identity) are (broadly ...
began to form when the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms united against Danish Viking invasions, which began around 800 AD. Over the following century and a half England was for the most part a politically unified entity, and remained permanently so after 954.
The nation of England was formed in 12 July 927 by Æthelstan
Æthelstan or Athelstan (; ; ; ; – 27 October 939) was King of the Anglo-Saxons from 924 to 927 and King of the English from 927 to his death in 939. He was the son of King Edward the Elder and his first wife, Ecgwynn. Modern histori ...
of Wessex after the Treaty of Eamont Bridge, as Wessex grew from a relatively small kingdom in the South West to become the founder of the Kingdom of the English, incorporating all Anglo-Saxon kingdoms and the Danelaw. A. L. Rowse, ''The Story of Britain'', Artus 1979
Norman and Angevin rule
 The
The Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Normans, Norman, French people, French, Flemish people, Flemish, and Bretons, Breton troops, all led by the Du ...
during 1066 brought Anglo-Saxon and Danish rule of England to an end, as the new French-speaking
French ( or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European family. Like all other Romance languages, it descended from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. French evolved from Northern Old Gallo-Romance, a descendant of the Latin spoken in ...
Norman elite almost universally replaced the Anglo-Saxon aristocracy and church leaders. After the conquest, "English" normally included all natives of England, whether they were of Anglo-Saxon, Scandinavian or Celtic ancestry, to distinguish them from the Norman invaders, who were regarded as "Norman" even if born in England, for a generation or two after the Conquest. The Norman dynasty ruled England for 87 years until the death of King Stephen in 1154, when the succession passed to Henry II
Henry II may refer to:
Kings
* Saint Henry II, Holy Roman Emperor (972–1024), crowned King of Germany in 1002, of Italy in 1004 and Emperor in 1014
*Henry II of England (1133–89), reigned from 1154
*Henry II of Jerusalem and Cyprus (1271–1 ...
, House of Plantagenet
The House of Plantagenet (Help:IPA/English, /plænˈtædʒənət/ Help:Pronunciation respelling key, ''plan-TAJ-ə-nət'') was a royal house which originated from the Medieval France, French county of Anjou. The name Plantagenet is used by mo ...
(based in France), and England became part of the Angevin Empire
The Angevin Empire (; ) was the collection of territories held by the House of Plantagenet during the 12th and 13th centuries, when they ruled over an area covering roughly all of present-day England, half of France, and parts of Ireland and Wal ...
until its collapse in 1214.
Anglo-Norman and Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
continued to be the two languages used officially by the Plantagenet kings until Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots (Latin: Malleus Scotorum), was King of England from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he was Lord of Ireland, and from 125 ...
came to the throne, when Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
became used in official documents, but alongside Anglo-Norman and Latin. Over time the English language became more important even in the court, and the Normans were gradually assimilated, until, by the 14th century, both rulers and subjects regarded themselves as English and spoke the English language.
Despite the assimilation of the Normans, the distinction between 'English' and 'French' people survived in some official documents long after it had fallen out of common use, in particular in the legal process '' Presentment of Englishry'' (a rule by which a hundred
100 or one hundred (Roman numerals, Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 (number), 99 and preceding 101 (number), 101.
In mathematics
100 is the square of 10 (number), 10 (in scientific notation it is written as 102). The standar ...
had to prove an unidentified murdered body found on their soil to be that of an Englishman, rather than a Norman, if they wanted to avoid a fine). This law was abolished in 1340.
United Kingdom
Since the 18th century, England has been one part of a wider political entity covering all or part of the British Isles, which today is called the United Kingdom.Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic ...
was annexed
Annexation, in international law, is the forcible acquisition and assertion of legal title over one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. In current international law, it is generally held to ...
by England by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535–1542, which incorporated Wales into the English state. A new British identity was subsequently developed when James VI of Scotland
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until ...
became James I of England
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 unti ...
as well, and expressed the desire to be known as the monarch of Britain.
In 1707, England formed a union with Scotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
by passing an Act of Union in March 1707 that ratified the Treaty of Union
The Treaty of Union is the name usually now given to the treaty which led to the creation of the new political state of Great Britain. The treaty, effective since 1707, brought the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Ki ...
. The Parliament of Scotland
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
had previously passed its own Act of Union, so the Kingdom of Great Britain
Great Britain, also known as the Kingdom of Great Britain, was a sovereign state in Western Europe from 1707 to the end of 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, which united the Kingd ...
was born on 1 May 1707. In 1801, another Act of Union formed a union between the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland
The Kingdom of Ireland (; , ) was a dependent territory of Kingdom of England, England and then of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1542 to the end of 1800. It was ruled by the monarchs of England and then List of British monarchs ...
, creating the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was the union of the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland into one sovereign state, established by the Acts of Union 1800, Acts of Union in 1801. It continued in this form until ...
. In 1922, about two-thirds of the Irish population (those who lived in 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland), left the United Kingdom to form the Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-ye ...
. The remainder became the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, although this name was not introduced until 1927, after some years in which the term "United Kingdom" had been little used.
Throughout the history of the UK, the English have been dominant in population and in political weight. As a consequence, notions of 'Englishness' and 'Britishness' are often very similar. At the same time, after the Union of 1707, the English, along with the other peoples of the British Isles, have been encouraged to think of themselves as British rather than to identify themselves with the constituent nations.
Immigration and assimilation
England has been the destination of varied numbers of migrants at different periods from the 17th century onwards. While some members of these groups seek to practise a form of pluralism, attempting to maintain a separate ethnic identity, others have assimilated and intermarried with the English. SinceOliver Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English statesman, politician and soldier, widely regarded as one of the most important figures in British history. He came to prominence during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms, initially ...
's resettlement of the Jews in 1656, there have been waves of Jewish
Jews (, , ), or the Jewish people, are an ethnoreligious group and nation, originating from the Israelites of History of ancient Israel and Judah, ancient Israel and Judah. They also traditionally adhere to Judaism. Jewish ethnicity, rel ...
immigration from Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
in the 19th century and from Germany in the 20th.
After the French king Louis XIV
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
declared Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
illegal in 1685 in the Edict of Fontainebleau
The Edict of Fontainebleau (18 October 1685, published 22 October 1685) was an edict issued by French King Louis XIV and is also known as the Revocation of the Edict of Nantes. The Edict of Nantes (1598) had granted Huguenots the right to prac ...
, an estimated 50,000 Protestant Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
s fled to England. Due to sustained and sometimes mass emigration of the Irish, current estimates indicate that around 6 million people in the UK have at least one grandparent born in the Republic of Ireland.
There has been a small black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
presence in England since the 16th century due to the slave trade,Black Presence
'', Asian and Black History in Britain, 1500–1850: UK government website. Retrieved 21 July 2006. and a small Indian presence since at least the 17th century because of the
East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company that was founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to Indian Ocean trade, trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (South A ...
and British Raj
The British Raj ( ; from Hindustani language, Hindustani , 'reign', 'rule' or 'government') was the colonial rule of the British The Crown, Crown on the Indian subcontinent,
*
* lasting from 1858 to 1947.
*
* It is also called Crown rule ...
. Black
Black is a color that results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without chroma, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness.Eva Heller, ''P ...
and Asian populations have only grown throughout the UK generally, as immigration from the British Empire and the subsequent Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, often referred to as the British Commonwealth or simply the Commonwealth, is an International organization, international association of member states of the Commonwealth of Nations, 56 member states, the vast majo ...
was encouraged due to labour shortages during post World War II rebuilding.
However, these groups are often still considered to be ethnic minorities and research has shown that black and Asian people in the UK are more likely to identify as British rather than with one of the state's four constituent nations, including England.
A nationally representative survey published in June 2021 found that a majority of respondents thought that being English was not dependent on race. 77% of white respondents in England agreed that "Being English is open to people of different ethnic backgrounds who identify as English", whereas 14% were of the view that "Only people who are white count as truly English". Amongst ethnic minority respondents, the equivalent figures were 68% and 19%. Research has found that the proportion of people who consider being white to be a necessary component of Englishness has declined over time.
Current national and political identity
The 1990s witnessed a resurgence of English national identity. Survey data shows a rise in the number of people in England describing their national identity as English and a fall in the number describing themselves as British. Today, black and minority ethnic people of England still generally identify as British rather than English to a greater extent than their white counterparts; however, groups such as theCampaign for an English Parliament
The Campaign for an English Parliament (CEP) is a pressure group which seeks the establishment of a devolved English parliament. The CEP is the main organisation associated with an English Parliament. It was formed as a non-denominational lob ...
(CEP) suggest the emergence of a broader civic and multi-ethnic English nationhood. Scholars and journalists have noted a rise in English self-consciousness, with increased use of the English flag, particularly at football matches where the Union flag
The Union Jack or Union Flag is the ''de facto'' national flag of the United Kingdom. The Union Jack was also used as the official flag of several British colonies and dominions before they adopted their own national flags.
It is sometimes a ...
was previously more commonly flown by fans.
This perceived rise in English self-consciousness has generally been attributed to the devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territori ...
in the late 1990s of some powers to the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( ; ) is the Devolution in the United Kingdom, devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. It is located in the Holyrood, Edinburgh, Holyrood area of Edinburgh, and is frequently referred to by the metonym 'Holyrood'. ...
and National Assembly for Wales
The Senedd ( ; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, Its role is to scrutinise the Welsh Government and legislate on devolve ...
. In policy areas for which the devolved administrations in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland have responsibility, the UK Parliament votes on laws that consequently only apply to England. Because the Westminster Parliament is composed of MPs from throughout the United Kingdom, this has given rise to the " West Lothian question", a reference to the situation in which MPs representing constituencies outside England can vote on matters affecting only England, but MPs cannot vote on the same matters in relation to the other parts of the UK. Consequently, groups such as the CEP have called for the creation of a devolved English Parliament
A devolved English parliament is a proposed institution that would give separate decision-making powers to representatives for voters in England, similar to the representation given by the Senedd (Welsh Parliament), the Scottish Parliament and ...
, claiming that there is now a discriminatory democratic deficit against the English. The establishment of an English parliament has also been backed by a number of Scottish and Welsh nationalists. Writer Paul Johnson has suggested that like most dominant groups, the English have only demonstrated interest in their ethnic self-definition when they were feeling oppressed.
John Curtice argues that "In the early years of devolution...there was little sign" of an English backlash against devolution for Scotland and Wales, but that more recently survey data shows tentative signs of "a form of English nationalism...beginning to emerge among the general public". Michael Kenny, Richard English and Richard Hayton, meanwhile, argue that the resurgence in English nationalism predates devolution, being observable in the early 1990s, but that this resurgence does not necessarily have negative implications for the perception of the UK as a political union. Others question whether devolution has led to a rise in English national identity at all, arguing that survey data fails to portray the complex nature of national identities, with many people considering themselves both English ''and'' British. A 2017 survey by YouGov
YouGov plc is a international Internet-based market research and data analytics firm headquartered in the UK with operations in Europe, North America, the Middle East, and Asia-Pacific.
History
2000–2010
Stephan Shakespeare and Nadhim ...
found that 38% of English voters considered themselves both English and British, alongside 19% who felt English but not British.
Recent surveys of public opinion on the establishment of an English parliament have given widely varying conclusions. In the first five years of devolution for Scotland and Wales, support in England for the establishment of an English parliament was low at between 16 and 19%, according to successive British Social Attitudes Survey
The British Social Attitudes Survey (BSA) is an annual statistical survey conducted in Great Britain by National Centre for Social Research since 1983. The BSA involves in-depth interviews with over 3,300 respondents, selected using Survey samplin ...
s. A report, also based on the British Social Attitudes Survey, published in December 2010 suggests that only 29% of people in England support the establishment of an English parliament, though this figure had risen from 17% in 2007.
One 2007 poll carried out for BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
''Newsnight
''Newsnight'' is the BBC's news and current affairs programme, providing in-depth investigation and analysis of the stories behind the day's headlines. It is broadcast weeknights at 10:30 on BBC Two and the BBC News channel; it is also avail ...
'', however, found that 61 per cent would support such a parliament being established. Krishan Kumar notes that support for measures to ensure that only English MPs can vote on legislation that applies only to England is generally higher than that for the establishment of an English parliament, although support for both varies depending on the timing of the opinion poll and the wording of the question. Electoral support for English nationalist parties is also low, even though there is public support for many of the policies they espouse. The English Democrats gained just 64,826 votes in the 2010 UK general election, accounting for 0.3 per cent of all votes cast in England. Kumar argued in 2010 that "despite devolution and occasional bursts of English nationalism – more an expression of exasperation with the Scots or Northern Irish – the English remain on the whole satisfied with current constitutional arrangements".
English diaspora
From the earliest times, English people have left England to settle in other parts of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. It is impossible to identify their numbers, as British censuses have historically not invited respondents to identify themselves as English. However, the census does record place of birth, revealing that 8.1% of Scotland's population, 3.7% of the population of Northern Ireland and 20% of the Welsh population were born in England. Similarly, the census of the Republic of Ireland does not collect information on ethnicity, but it does record that there are over 200,000 people living in Ireland who were born inEngland and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the Law of the United Kingdom#Legal jurisdictions, three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Th ...
.
English ethnic descent and emigrant communities are found primarily in the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to various nations and state (polity), states in Western Europe, Northern America, and Australasia; with some debate as to whether those in Eastern Europe and Latin America also const ...
, and settled in significant numbers in some areas. Substantial populations descended from English colonists and immigrants exist in the United States, Canada, Australia, South Africa and New Zealand.
United States
 In the 2020 United States census, English Americans were the largest group in the United States with 46.5 million Americans self-identifying as having some English origins (many combined with another heritage) representing (19.8%) of the
In the 2020 United States census, English Americans were the largest group in the United States with 46.5 million Americans self-identifying as having some English origins (many combined with another heritage) representing (19.8%) of the White American
White Americans (sometimes also called Caucasian Americans) are Americans who identify as white people. In a more official sense, the United States Census Bureau, which collects demographic data on Americans, defines "white" as " person having ...
population. This includes 25.5 million (12.5%) who were "English alone" - one origin. However, demographers regard this as an undercount, as the index of inconsistency is high, and many, if not most, people from English stock have a tendency (since the introduction of a new 'American' category and ignoring the ancestry question in the 2000 census) to identify as simply Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
or if of mixed European ancestry, identify with a more recent and differentiated ethnic group.
Prior to this, in the 2000 census, 24,509,692 Americans described their ancestry
An ancestor, also known as a forefather, fore-elder, or a forebear, is a parent or ( recursively) the parent of an antecedent (i.e., a grandparent, great-grandparent, great-great-grandparent and so forth). ''Ancestor'' is "any person from ...
as wholly or partly English. In addition, 1,035,133 recorded British ancestry. This was a numerical decrease from the census in 1990
Important events of 1990 include the Reunification of Germany and the unification of Yemen, the formal beginning of the Human Genome Project (finished in 2003), the launch of the Hubble Space Telescope, the separation of Namibia from South ...
where 32,651,788 people or 13.1% of the population self-identified with English ancestry.
In 1980
Events January
* January 4 – U.S. President Jimmy Carter proclaims a United States grain embargo against the Soviet Union, grain embargo against the USSR with the support of the European Commission.
* January 6 – Global Positioning Sys ...
, over 49 million (49,598,035) Americans claimed English ancestry, at the time around 26.3% of the total population and largest reported group which, even today, would make them the largest ethnic group in the United States. Scots-Irish Americans
Scotch-Irish Americans are American descendants of primarily Ulster Scots people, who emigrated from Ulster (Ireland's northernmost province) to the United States between the 18th and 19th centuries, with their ancestors having originally mig ...
are descendants of Lowland Scots and Northern English (specifically: County Durham
County Durham, officially simply Durham, is a ceremonial county in North East England.UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. The county borders Northumberland and Tyne an ...
, Cumberland
Cumberland ( ) is an area of North West England which was historically a county. The county was bordered by Northumberland to the north-east, County Durham to the east, Westmorland to the south-east, Lancashire to the south, and the Scottish ...
, Northumberland
Northumberland ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North East England, on the Anglo-Scottish border, border with Scotland. It is bordered by the North Sea to the east, Tyne and Wear and County Durham to the south, Cumb ...
and Westmorland
Westmorland (, formerly also spelt ''Westmoreland''R. Wilkinson The British Isles, Sheet The British IslesVision of Britain/ref>) is an area of North West England which was Historic counties of England, historically a county. People of the area ...
) settlers who colonised Ireland during the Plantation of Ulster
The Plantation of Ulster (; Ulster Scots dialects, Ulster Scots: ) was the organised Settler colonialism, colonisation (''Plantation (settlement or colony), plantation'') of Ulstera Provinces of Ireland, province of Irelandby people from Great ...
in the 17th century.
Americans
Americans are the Citizenship of the United States, citizens and United States nationality law, nationals of the United States, United States of America.; ; Law of the United States, U.S. federal law does not equate nationality with Race (hu ...
of English heritage are often seen, and identify, as simply "American" due to the many historic cultural ties between England and the U.S. and their influence on the country's population. Relative to ethnic groups of other European origins, this may be due to the early establishment of English settlements; as well as to non-English groups having emigrated in order to establish significant communities.
Canada
In theCanada 2016 Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a change from its 2011 population of 33,476,688. The census, conducted by Statistics Canada, was Canada's seventh quinquennial censu ...
, 'English' was the most common ethnic origin (ethnic origin refers to the ethnic or cultural group(s) to which the respondent's ancestors belong) recorded by respondents; 6,320,085 people or 18.3% of the population self-identified themselves as wholly or partly English. On the other hand, people identifying as Canadian but not English may have previously identified as English before the option of identifying as Canadian was available.
Australia
 From the beginning of the colonial era until the mid-20th century, the vast majority of settlers to Australia were from the
From the beginning of the colonial era until the mid-20th century, the vast majority of settlers to Australia were from the British Isles
The British Isles are an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner Hebrides, Inner and Outer Hebr ...
, with the English being the dominant group. Among the leading ancestries, increases in Australian, Irish and German ancestries and decreases in English, Scottish and Welsh ancestries appear to reflect such shifts in perception or reporting. These reporting shifts at least partly resulted from changes in the design of the census question, in particular the introduction of a tick box format in 2001. English Australians have more often come from the south
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both west and east.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
than the north of England
Northern England, or the North of England, refers to the northern part of England and mainly corresponds to the historic counties of Cheshire, Cumberland, Durham, Lancashire, Northumberland, Westmorland and Yorkshire. Officially, it is a gr ...
.
Australians
Australians, colloquially known as Aussies, are the citizenship, citizens, nationality, nationals and individuals associated with the country of Australia. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or ethno-cultural. For most Aust ...
of English descent, are both the single largest ethnic group in Australia and the largest 'ancestry' identity in the Australian census. In the 2016 census, 7.8 million or 36.1% of the population identified as "English" or a combination including English, a numerical increase from 7.2 million over the 2011 census figure. The census also documented 907,572 residents or 3.9% of Australia as being born in England, and are the largest overseas-born population.Census of Population and Housing: Reflecting Australia– Ancestry 2016
New Zealand
English ancestry is the largest single ancestry New Zealanders share. Several million New Zealanders are estimated to have some English ancestry From 1840, the English comprised the largest single group among New Zealand's overseas-born, consistently being over 50 percent of the total population. Despite this, after the early 1850s, the English-born slowly fell from being a majority of the colonial population. In the 1851 census, 50.5% of the total population were born in England, this proportion fell to 36.5% (1861) and 24.3% by 1881.New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of isla ...
's foundational culture was English, given the strong representation in the mid and late-nineteenth century with the English being the largest in migration inflows.
In the 2013
2013 was the first year since 1987 to contain four unique digits (a span of 26 years).
2013 was designated as:
*International Year of Water Cooperation
*International Year of Quinoa
Events
January
* January 5 – 2013 Craig, Alask ...
census, there were 215,589 English-born representing 21.5% of all overseas-born residents or 5 percent of the total population and the most-common birthplace outside New Zealand.
In the recent 2018 census, 210,915 were born in England or 4.49% of the total population, a slight decrease from 2013.
Argentina
 English settlers arrived in
English settlers arrived in Buenos Aires
Buenos Aires, controlled by the government of the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Argentina. It is located on the southwest of the Río de la Plata. Buenos Aires is classified as an Alpha− glob ...
in 1806 (then a Spanish colony) in small numbers, mostly as businessmen, when Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
was an emerging nation and the settlers were welcomed for the stability they brought to commercial life. As the 19th century progressed, more English families arrived, and many bought land to develop the potential of the Argentine pampas for the large-scale growing of crops. The English founded banks, developed the export trade in crops and animal products and imported the luxuries that the growing Argentine middle classes sought.
As well as those who went to Argentina
Argentina, officially the Argentine Republic, is a country in the southern half of South America. It covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourt ...
as industrialists and major landowners, others went as railway engineers, civil engineer
A civil engineer is a person who practices civil engineering – the application of planning, designing, constructing, maintaining, and operating infrastructure while protecting the public and environmental health, as well as improving existing i ...
s and to work in bank
A bank is a financial institution that accepts Deposit account, deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital m ...
ing and commerce
Commerce is the organized Complex system, system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered large-scale exchange (distribution through Financial transaction, transactiona ...
. Others went to become whaler
A whaler or whaling ship is a specialized vessel, designed or adapted for whaling: the catching or processing of whales.
Terminology
The term ''whaler'' is mostly historic. A handful of nations continue with industrial whaling, and one, Jap ...
s, missionaries
A missionary is a member of a religious group who is sent into an area in order to promote its faith or provide services to people, such as education, literacy, social justice, health care, and economic development.Thomas Hale 'On Being a Miss ...
and simply to seek out a future. English families sent second and younger sons, or what were described as the black sheep
In the English language, black sheep is an idiom that describes a member of a group who is different from the rest, especially a family member who does not fit in. The term stems from sheep whose fleece is colored black rather than the more comm ...
of the family, to Argentina to make their fortunes in cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, bovid ungulates widely kept as livestock. They are prominent modern members of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Mature female cattle are calle ...
and wheat
Wheat is a group of wild and crop domestication, domesticated Poaceae, grasses of the genus ''Triticum'' (). They are Agriculture, cultivated for their cereal grains, which are staple foods around the world. Well-known Taxonomy of wheat, whe ...
. English settlers introduced football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kick (football), kicking a football (ball), ball to score a goal (sports), goal. Unqualified, football (word), the word ''football'' generally means the form of football t ...
to Argentina. Some English families owned sugar plantations
Plantations are farms specializing in cash crops, usually mainly planting a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Plantations, centered on a plantation house, grow crops including cotton, cannabis, tobac ...
.
Chile
Since the Port of Valparaíso opened its coasts to free trade in 1811, the English began to congregate in Valparaíso. The English eventually numbered more than 32,000 during the port of Valparaíso's boom period during the saltpeter bonanza at the end of the 19th and beginning of the 20th centuries.Culture
The culture of England is sometimes difficult to separate clearly from theculture of the United Kingdom
The culture of the United Kingdom is influenced by its History of the United Kingdom, combined nations' history, its interaction with the cultures of Europe, the individual diverse cultures of England, Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland, and ...
, so influential has English culture been on the cultures of the British Isles and, on the other hand, given the extent to which other cultures have influenced life in England.
Religion
The established religion of the realm is theChurch of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
, whose titular head is Charles III
Charles III (Charles Philip Arthur George; born 14 November 1948) is King of the United Kingdom and the 14 other Commonwealth realms.
Charles was born at Buckingham Palace during the reign of his maternal grandfather, King George VI, and ...
although the worldwide Anglican Communion
The Anglican Communion is a Christian Full communion, communion consisting of the Church of England and other autocephalous national and regional churches in full communion. The archbishop of Canterbury in England acts as a focus of unity, ...
is overseen by the General Synod
The General Synod is the title of the governing body of some church organizations. Anglican Communion
The General Synod of the Church of England, which was established in 1970 replacing the Church Assembly, is the legislative body of the Church ...
of its bishops under the authority of Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. 26 of the church's 42 bishops are Lords Spiritual
The Lords Spiritual are the bishops of the Church of England who sit in the House of Lords of the United Kingdom. Up to 26 of the 42 diocesan bishops and archbishops of the Church of England serve as Lords Spiritual (not including retired bish ...
, representing the church in the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
. In 2010, the Church of England counted 25 million baptised members out of the 41 million Christians in Great Britain's population of about 60 million; around the same time, it also claimed to baptise one in eight newborn children. Generally, anyone in England may marry or be buried at their local parish church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the Church (building), church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in com ...
, whether or not they have been baptised in the church. Actual attendance has declined steadily since 1890, with around one million, or 10% of the baptised population attending Sunday services on a regular basis (defined as once a month or more) and three million -roughly 15%- joining Christmas Eve and Christmas services.
Saint George
Saint George (;Geʽez: ጊዮርጊስ, , ka, გიორგი, , , died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was an early Christian martyr who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to holy tradition, he was a soldier in the ...
is recognised as the patron saint
A patron saint, patroness saint, patron hallow or heavenly protector is a saint who in Catholicism, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy or Oriental Orthodoxy is regarded as the heavenly advocate of a nation, place, craft, activity, class, clan, fa ...
of England, and the flag of England
The flag of England is the national flag of England, a constituent country of the United Kingdom. It is derived from Saint George's Cross (heraldic blazon: ''Argent, a cross gules''). The association of the red cross as an emblem of England ...
consists of his cross. Before Edward III, the patron saint was St Edmund; and St Alban is also honoured as England's first martyr.
A survey carried out in the end of 2008 by Ipsos MORI on behalf of The Catholic Agency For Overseas Development found the population of England and Wales to be 47.0% affiliated with the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
, which is also the state church, 9.6% with the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
and 8.7% were other Christians, mainly Free church Protestants
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
and Eastern Orthodox Christians
Eastern Orthodoxy, otherwise known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity or Byzantine Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millenni ...
. 4.8% were Muslim, 3.4% were members of other religions, 5.3% were agnostics, 6.8% were atheists and 15.0% were not sure about their religious affiliation or refused to answer to the question.
Religious observance of St George's Day
Saint George's Day is the Calendar of saints, feast day of Saint George, celebrated by Christian churches, countries, regions, and cities of which he is the Patronages of Saint George, patron saint, including Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bu ...
(23 April) changes when it is too close to Easter
Easter, also called Pascha ( Aramaic: פַּסְחָא , ''paskha''; Greek: πάσχα, ''páskha'') or Resurrection Sunday, is a Christian festival and cultural holiday commemorating the resurrection of Jesus from the dead, described in t ...
. According to the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
's calendar, when St George's Day falls between Palm Sunday
Palm Sunday is the Christian moveable feast that falls on the Sunday before Easter. The feast commemorates Christ's triumphal entry into Jerusalem, an event mentioned in each of the four canonical Gospels. Its name originates from the palm bran ...
and the Second Sunday of Easter inclusive, it is moved to the Monday after the Second Sunday of Easter.
Language
 English people traditionally speak the
English people traditionally speak the English language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples th ...
, a member of the West Germanic
The West Germanic languages constitute the largest of the three branches of the Germanic languages, Germanic family of languages (the others being the North Germanic languages, North Germanic and the extinct East Germanic languages, East Germ ...
language family
A language family is a group of languages related through descent from a common ancestor, called the proto-language of that family. The term ''family'' is a metaphor borrowed from biology, with the tree model used in historical linguistics ...
. The modern English language evolved from Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
(the form of language in use by the English people from the 12th to the 15th century); Middle English was influenced lexically by Norman-French, Old French
Old French (, , ; ) was the language spoken in most of the northern half of France approximately between the late 8th
of the Anglo-Saxon period; in the Northern and Eastern parts of England the language of Danish settlers had influenced the language, a fact still evident in Northern English dialects.
There were once many different dialects of modern English in England, which were recorded in projects such as the ''English Dialect Dictionary'' (late 19th century) and the Survey of English Dialects (mid 20th century), but there has been widespread dialect levelling in recent time as a result of education, the media and socio-economic pressures.
Cornish, a Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
. In the Middle English period Latin was the language of administration and the nobility spoke Norman French. Middle English was itself derived from the Old English language">Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...Celtic language
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves ...
, is one of three existing Brittonic languages; its usage has been revived in Cornwall
Cornwall (; or ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is also one of the Celtic nations and the homeland of the Cornish people. The county is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, ...
. Historically, another Brittonic Celtic language, Cumbric
Cumbric is an extinct Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North", in Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands. It was closely related to Old Welsh and the ot ...
, was spoken in Cumbria
Cumbria ( ) is a ceremonial county in North West England. It borders the Scottish council areas of Dumfries and Galloway and Scottish Borders to the north, Northumberland and County Durham to the east, North Yorkshire to the south-east, Lancash ...
in North West England
North West England is one of nine official regions of England and consists of the ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial counties of Cheshire, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire and Merseyside. The North West had a population of 7,4 ...
, but it died out in the 11th century although traces of it can still be found in the Cumbrian dialect. Early Modern English
Early Modern English (sometimes abbreviated EModEFor example, or EMnE) or Early New English (ENE) is the stage of the English language from the beginning of the Tudor period to the English Interregnum and Restoration, or from the transit ...
began in the late 15th century with the introduction of the printing press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a printing, print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in whi ...
to London and the Great Vowel Shift
The Great Vowel Shift was a series of English phonology, pronunciation changes in the vowels of the English language that took place primarily between the 1400s and 1600s (the transition period from Middle English to Early Modern English), begi ...
. Through the worldwide influence of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
, English spread around the world from the 17th to mid-20th centuries. Through newspapers, books, the telegraph, the telephone, phonograph records, radio, satellite television, broadcasters (such as the BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
) and the Internet, as well as the emergence of the United States as a global superpower, Modern English has become the international language of business
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or Trade, buying and selling Product (business), products (such as goods and Service (economics), services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for ...
, science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, communication
Communication is commonly defined as the transmission of information. Its precise definition is disputed and there are disagreements about whether Intention, unintentional or failed transmissions are included and whether communication not onl ...
, sports
Sport is a physical activity or game, often competitive and organized, that maintains or improves physical ability and skills. Sport may provide enjoyment to participants and entertainment to spectators. The number of participants in ...
, aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' include fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air aircraft such as h ...
, and diplomacy
Diplomacy is the communication by representatives of State (polity), state, International organization, intergovernmental, or Non-governmental organization, non-governmental institutions intended to influence events in the international syste ...
.
Literature
English literature begins withAnglo-Saxon literature
Old English literature refers to poetry (alliterative verse) and prose written in Old English in early medieval England, from the 7th century to the decades after the Norman Conquest of 1066, a period often termed Anglo-Saxon England. The 7th- ...
, which was written in Old English
Old English ( or , or ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the Early Middle Ages. It developed from the languages brought to Great Britain by Anglo-S ...
and produced epic works such as Beowulf
''Beowulf'' (; ) is an Old English poetry, Old English poem, an Epic poetry, epic in the tradition of Germanic heroic legend consisting of 3,182 Alliterative verse, alliterative lines. It is one of the most important and List of translat ...
and the fragmentary The Battle of Maldon
"The Battle of Maldon" is the name given to an Old English Old English literature, poem of uncertain date celebrating the real Battle of Maldon of 991, at which an Anglo-Saxon army failed to repulse a Viking raid. Only 325 lines of the poem are ...
, The Seafarer (poem), The Seafarer and The Wanderer (Old English poem), The Wanderer. For many years, Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
and French language, French were the preferred literary languages of England, but in the medieval period there was a flourishing of literature in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
; Geoffrey Chaucer is the most famous writer of this period.
The Elizabethan era is sometimes described as the golden age of English literature with writers such as William Shakespeare, Thomas Nashe, Edmund Spenser, Sir Philip Sidney, Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson.
Other famous English writers include Jane Austen, Arnold Bennett, Rupert Brooke, Agatha Christie, Charles Dickens, Thomas Hardy, A. E. Housman, George Orwell and the Lake Poets.
In 2003, the BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
carried out a UK survey entitled ''The Big Read'' in order to find the "nation's best-loved novel" of all time, with works by English novelists J. R. R. Tolkien, Jane Austen, Philip Pullman, Douglas Adams and J. K. Rowling making up the top five on the list.
See also
* List of English people * Old English (Ireland) * Celts, Celtic peoples * English art * Architecture of England * English nationalism * European ethnic groups * ''100% English'' (Channel 4 TV programme, 2006) * Social history of the United Kingdom (1945–present) * White British Language: * Anglicisation * English-speaking world Diaspora: * British diaspora in Africa * Anglo-Burmese * Anglo-Métis, Metis people * Anglo-Indian * Anglo-Irish * Anglo-Scot * English BrazilianNotes
References
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * ; Diaspora *External links
* {{DEFAULTSORT:English People English people, Ethnic groups in England Ethnic groups in the United Kingdom