The colonial history of the United States covers the period of
European colonization of
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
from the late 15th century until the unifying of the
Thirteen British Colonies and creation of the
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
in 1776, during the
Revolutionary War. In the late 16th century,
England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
,
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
,
Spain
Spain, or the Kingdom of Spain, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe with territories in North Africa. Featuring the Punta de Tarifa, southernmost point of continental Europe, it is the largest country in Southern Eur ...
, and the
Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, commonly referred to in historiography as the Dutch Republic, was a confederation that existed from 1579 until the Batavian Revolution in 1795. It was a predecessor state of the present-day Netherlands ...
launched major colonization expeditions in North America.
The death rate was very high among early immigrants, and some early attempts disappeared altogether, such as the English
Lost Colony of Roanoke. Nevertheless, successful colonies were established within several decades.
European settlers came from a variety of social and religious groups, including adventurers, farmers, indentured servants, tradesmen, and a very few from the aristocracy. Settlers included the
Dutch of
New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
, the
Swedes
Swedes (), or Swedish people, are an ethnic group native to Sweden, who share a common ancestry, Culture of Sweden, culture, History of Sweden, history, and Swedish language, language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, ...
and
Finns
Finns or Finnish people (, ) are a Baltic Finns, Baltic Finnic ethnic group native to Finland. Finns are traditionally divided into smaller regional groups that span several countries adjacent to Finland, both those who are native to these cou ...
of
New Sweden
New Sweden () was a colony of the Swedish Empire between 1638 and 1655 along the lower reaches of the Delaware River in what is now Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania. Established during the Thirty Years' War when Sweden was a g ...
, the English
Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
of the
Province of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from ...
, the
English Puritans of
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, the Virginian Cavaliers, the English Catholics and Protestant
Nonconformists of the
Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an Kingdom of England, English and later British colonization of the Americas, British colony in North America from 1634 until 1776, when the province was one of the Thirteen Colonies that joined in supporting the A ...
, the "
worthy poor" of the
Province of Georgia
The Province of Georgia (also Georgia Colony) was one of the Southern Colonies in colonial-era British America. In 1775 it was the last of the Thirteen Colonies to support the American Revolution.
The original land grant of the Province of G ...
, the
Germans
Germans (, ) are the natives or inhabitants of Germany, or sometimes more broadly any people who are of German descent or native speakers of the German language. The Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany, constitution of Germany, imple ...
who settled the mid-Atlantic colonies, and the
Ulster Scots of the
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, are a mountain range in eastern to northeastern North America. The term "Appalachian" refers to several different regions associated with the mountain range, and its surrounding terrain ...
. These groups all became part of the United States when it gained its independence in 1776.
Russian America
Russian(s) may refer to:
*Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries
*A citizen of Russia
*Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages
*''The Russians'', a b ...
and parts of
New France
New France (, ) was the territory colonized by Kingdom of France, France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Kingdom of Great Br ...
and
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
were also incorporated into the United States at later times. The diverse colonists from these various regions built colonies of distinctive social, religious, political, and economic style.
Over time, non-British colonies East of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
were taken over and most of the inhabitants were assimilated. In
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, however, the British expelled the French Catholic
Acadians
The Acadians (; , ) are an ethnic group descended from the French colonial empire, French who settled in the New France colony of Acadia during the 17th and 18th centuries. Today, most descendants of Acadians live in either the Northern Americ ...
, and many relocated to
Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
. The two chief armed rebellions were short-lived failures in
Virginia in 1676 and in
New York in 1689–1691. Some of the colonies developed legalized systems of slavery, centered largely around the
Atlantic slave trade
The Atlantic slave trade or transatlantic slave trade involved the transportation by slave traders of Slavery in Africa, enslaved African people to the Americas. European slave ships regularly used the triangular trade route and its Middle Pass ...
. Wars were recurrent between the French and the British during the
French and Indian Wars
The French and Indian Wars were a series of conflicts that occurred in North America between 1688 and 1763, some of which indirectly were related to the European dynastic wars. The title ''French and Indian War'' in the singular is used in the U ...
. By 1760, France was defeated and its colonies were seized by Britain.
On the eastern seaboard, the four distinct English regions were
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, the
Middle Colonies, the
Chesapeake Bay Colonies (Upper South), and the
Southern Colonies (Lower South). Some historians add a fifth region of the "Frontier", which was never separately organized.
[Cooke, ed. ''North America in Colonial Times'' (1998)] The colonization of the United States resulted in a large
decline of the indigenous population primarily because of newly introduced
diseases
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that adversely affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism and is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that are asso ...
. A significant percentage of the American Indian tribes living in the eastern region had been ravaged by disease before 1620, possibly introduced to them decades before by explorers and sailors (although no conclusive cause has been established).
[Richard Middleton and Anne Lombard, ''Colonial America: A History to 1763'' (4th ed. 2011) p. 23 ]
Goals of colonization
Mercantilism
Mercantilism
Mercantilism is a economic nationalism, nationalist economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports of an economy. It seeks to maximize the accumulation of resources within the country and use those resources ...
was the basic policy imposed by Britain on its colonies from the 1660s, which meant that the government became a partner with merchants based in England to increase political power and private wealth. This was done to the exclusion of other empires and even other merchants in its own colonies. The government protected its London-based merchants and kept out others by trade barriers, regulations, and subsidies to domestic industries to maximize exports from the realm and minimize imports.
Freedom from religious persecution
The prospect of religious persecution by authorities of the crown and the
Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
prompted a significant number of colonization efforts. The
Pilgrims were separatist Puritans who fled persecution in England, first to the Netherlands and ultimately to
Plymouth Plantation in 1620. Over the following 20 years, people fleeing persecution from
King Charles I settled most of
New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
. Similarly, the
Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an Kingdom of England, English and later British colonization of the Americas, British colony in North America from 1634 until 1776, when the province was one of the Thirteen Colonies that joined in supporting the A ...
was founded in part to be a haven for
Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institut ...
.
Early colonial failures
After the turn of the 16th century, several European countries attempted to found colonies in what is now the United States. Most of those attempts ended in failure. The colonists themselves faced high rates of death from disease, starvation, inefficient resupply, conflict with Native Americans, attacks by rival European powers, and other causes.
Spain had numerous failed attempts, including
San Miguel de Gualdape in South Carolina (1526),
Pánfilo de Narváez's expedition to Florida's Gulf coast (1528–36), Pensacola in West Florida (1559–61),
Fort San Juan in North Carolina (1567–68), and the
Ajacán Mission in Virginia (1570–71). The French failed at Parris Island, South Carolina (1562–63),
Fort Caroline on Florida's Atlantic coast (1564–65), Saint Croix Island, Maine (1604–05), and
Fort Saint Louis, Texas (1685–89). The most notable English failures were the "
Lost Colony of Roanoke" (1583–90) in North Carolina and
Popham Colony in Maine (1607–08). It was at the Roanoke Colony that
Virginia Dare became the first English child born in America; her fate is unknown.
New Spain
Starting in the 16th century, Spain built a colonial empire in the Americas consisting of
New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( ; Nahuatl: ''Yankwik Kaxtillan Birreiyotl''), originally the Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain. It was one of several ...
and other vice-royalties. New Spain included territories in
Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, Alabama, Mississippi, much of the United States west of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, parts of
Latin America
Latin America is the cultural region of the Americas where Romance languages are predominantly spoken, primarily Spanish language, Spanish and Portuguese language, Portuguese. Latin America is defined according to cultural identity, not geogr ...
(including
Puerto Rico
; abbreviated PR), officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico, is a Government of Puerto Rico, self-governing Caribbean Geography of Puerto Rico, archipelago and island organized as an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territo ...
), and the
Spanish East Indies
The Spanish East Indies were the colonies of the Spanish Empire in Asia-Pacific, Asia and Oceania from 1565 to 1901, governed through the Captaincy General of the Philippines, captaincy general in Manila for the Monarchy of Spain, Spanish Crown, i ...
(including
Guam
Guam ( ; ) is an island that is an Territories of the United States, organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. Guam's capital is Hagåtña, Guam, Hagåtña, and the most ...
and the
Northern Mariana Islands
The Northern Mariana Islands, officially the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), is an Territories of the United States, unincorporated territory and Commonwealth (U.S. insular area), commonwealth of the United States consistin ...
). New Spain encompassed the
territory of Louisiana after the
Treaty of Fontainebleau (1762)
The Treaty of Fontainebleau, signed on November 3, 1762, was a secret agreement of 1762 in which the Kingdom of France ceded Louisiana to Spain. The treaty followed the last battle in the French and Indian War in North America, the Battle of Signa ...
, though Louisiana reverted to France in the 1800
Third Treaty of San Ildefonso
The Third Treaty of San Ildefonso was a secret agreement signed on 1 October 1800 between Spain and the French Republic by which Spain agreed in principle to exchange its North American colony of Louisiana for territories in Tuscany. The terms we ...
.
Many territories that had been part of New Spain became part of the United States after 1776 through various wars and treaties, including the
Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
(1803), the
Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
(1819), the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
(1846–1848), and the
Spanish–American War
The Spanish–American War (April 21 – August 13, 1898) was fought between Restoration (Spain), Spain and the United States in 1898. It began with the sinking of the USS Maine (1889), USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor in Cuba, and resulted in the ...
(1898). There were also several
Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, but Spain gave the United States all claims to the Pacific Northwest in the Adams–Onís Treaty. There were several thousand families in New Mexico and California who became American citizens in 1848, plus small numbers in the other colonies.
Florida
Spain established several small outposts in Florida in the early 16th century. The first was at
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only incorporated city, city in Escambia County, Florida, Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. ...
, in 1559 under
Tristán de Luna y Arellano
Tristán de Luna y Arellano (1510 – September 16, 1573) was a Spanish explorer and conquistador of the 16th century.Herbert Ingram Priestley, Tristan de Luna: Conquistador of the Old South: A Study of Spanish Imperial Strategy (1936). http://pa ...
, though it was short-lived. The most important was
St. Augustine, founded as
Mission Nombre de Dios in 1565 but repeatedly attacked and burned by pirates, privateers, and English forces, and nearly all the Spanish left after the
Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, also known as the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763 by the kingdoms of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain, Kingdom of France, France and Spanish Empire, Spain, with Kingdom of Portugal, Portugal in agree ...
ceded Florida to Great Britain. Certain First Spanish Period structures remain today, especially those made of
coquina
Coquina () is a sedimentary rock that is composed either wholly or almost entirely of the transported, abraded, and mechanically sorted fragments of mollusks, trilobites, brachiopods, or other invertebrates. The term ''coquina'' comes from the S ...
, a limestone quarried nearby.
The British attacked Spanish Florida during numerous wars. As early as 1687, the Spanish government had begun to offer asylum to slaves from British colonies, and the Spanish Crown officially proclaimed in 1693 that runaway slaves would find freedom in Florida in return for converting to Catholicism and four years of military service to the Spanish Crown. In effect, Spaniards created a maroon settlement in Florida as a front-line defense against English attacks from the north. This settlement was centered at
Fort Mose. Spain also intended to destabilize the plantation economy of the British colonies by creating a free black community to attract slaves. Notable British raids on St. Augustine were James Moore's 1702 raid and
James Oglethorpe
Lieutenant-General James Edward Oglethorpe (22 December 1696 – 30 June 1785) was a British Army officer, Tory politician and colonial administrator best known for founding the Province of Georgia in British North America. As a social refo ...
's 1740 siege.
In 1763, Spain traded Florida to Great Britain in exchange for control of
Havana, Cuba
Havana (; ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.[Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...](_bl ...<br></span></div>, which the British had captured during the <div class=)
. Florida was home to about 3,000 Spaniards at the time, and nearly all quickly left. Britain occupied Florida but did not send many settlers to the area. Dr.
Andrew Turnbull's failed colony at
New Smyrna, however, resulted in hundreds of Menorcans, Greeks, and Italians settling in St. Augustine in 1777. During the American Revolution, East and West Florida were
Loyalist colonies. Spain regained control of Florida in 1783 by the Peace of Paris which ended the Revolutionary War. Spain sent no more settlers or missionaries to Florida during the Second Spanish Period. The inhabitants of
West Florida revolted against the Spanish in 1810 and formed the
Republic of West Florida
The Republic of West Florida (, ), officially the State of Florida, was a short-lived unrecognized republic in the western region of Spanish West Florida for just over months during 1810. In December, 1810, the United States occupied and an ...
, which was quickly annexed by the United States. The United States took possession of
East Florida
East Florida () was a colony of Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of the Spanish Empire from 1783 to 1821. The British gained control over Spanish Florida in 1763 as part of the Treaty of Paris (1763), Tre ...
in 1821 according to the terms of the
Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Spanish Cession, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p. 168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to ...
.
Arizona and New Mexico
Throughout the 16th century, Spain explored the southwest from Mexico. The first expedition was the
Niza expedition in 1538.
Francisco Coronado followed with a larger expedition in 1539, throughout modern New Mexico and Arizona, arriving in New Mexico in 1540. The Spanish moved north from Mexico, settling villages in the upper valley of the Rio Grande, including much of the western half of the present-day state of New Mexico. The capital of
Santa Fe was settled in 1610 and remains one of the oldest continually European-inhabited settlements in the United States. Local Indians expelled the Spanish for 12 years following the
Pueblo Revolt of 1680; they returned in 1692 in the bloodless reoccupation of Santa Fe. Control was by Spain (223 years) and Mexico (25 years) until 1846, when the
American Army of the West took over in the
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, ...
. About a third of the population in the 21st century is descended from the Spanish settlers.
[Weber, ch 5]
California

Spanish explorers sailed along the coast of present-day
California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
starting with
Cabrillo in 1542–43. From 1565 to 1815,
Spanish galleons regularly arrived from Manila at
Cape Mendocino,
about 300 miles (480 km) north of San Francisco or farther south. Then they sailed south along the California coast to Acapulco, Mexico. Often they did not land, because of the rugged, foggy coast.
Spain wanted a safe harbor for galleons. They did not find
San Francisco Bay
San Francisco Bay (Chochenyo language, Chochenyo: 'ommu) is a large tidal estuary in the United States, U.S. state of California, and gives its name to the San Francisco Bay Area. It is dominated by the cities of San Francisco, California, San ...
, perhaps because of fog hiding the entrance.
In 1585 Gali charted the coast just south of San Francisco Bay,
[Development of Spanish ports and fleets on west coast]
/ref>
Alta California
Alta California (, ), also known as Nueva California () among other names, was a province of New Spain formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was made a separat ...
who created a series of missions operated by Franciscan
The Franciscans are a group of related organizations in the Catholic Church, founded or inspired by the Italian saint Francis of Assisi. They include three independent Religious institute, religious orders for men (the Order of Friars Minor bei ...
priests. They also operated ''presidios'' (forts), ''pueblos'' (settlements), and ranchos (land grant ranches), along the southern and central coast of California. Father Junípero Serra, founded the first missions in Spanish upper '' Las Californias'', starting with Mission San Diego de Alcalá
Mission Basilica San Diego de Alcalá (, lit. The Mission of Saint Didacus of Acalá) was the second Franciscan founded mission in the Californias (after San Fernando de Velicata), a province of New Spain. Located in present-day San Diego, C ...
in 1769. Through the Spanish and Mexican eras they eventually comprised a series of 21 missions to spread Roman Catholicism among the local Native Americans, linked by '' El Camino Real'' ("The Royal Road"). They were established to convert the indigenous peoples of California
Indigenous peoples of California, commonly known as Indigenous Californians or Native Californians, are a diverse group of nations and peoples that are indigenous to the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and afte ...
, while protecting historic Spanish claims to the area. The missions introduced European technology, livestock, and crops. The Indian Reductions converted the native peoples into groups of Mission Indians; they worked as laborers in the missions and the ranchos. In the 1830s the missions were disbanded and the lands sold to Californios. The indigenous Native American population was around 150,000; the ''Californios
Californios (singular Californio) are Californians of Spaniards, Spanish descent, especially those descended from settlers of the 17th through 19th centuries before California was annexed by the United States. California's Spanish language in C ...
'' (Mexican era Californians) around 10,000; including immigrant Americans and other nationalities involved in trade and business in California.
Puerto Rico
In September 1493, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus (; between 25 August and 31 October 1451 – 20 May 1506) was an Italians, Italian explorer and navigator from the Republic of Genoa who completed Voyages of Christopher Columbus, four Spanish-based voyages across the At ...
set sail on his second voyage with 17 ships from Cádiz
Cádiz ( , , ) is a city in Spain and the capital of the Province of Cádiz in the Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia. It is located in the southwest of the Iberian Peninsula off the Atlantic Ocean separated fr ...
.John the Baptist
John the Baptist ( – ) was a Jewish preacher active in the area of the Jordan River in the early first century AD. He is also known as Saint John the Forerunner in Eastern Orthodoxy and Oriental Orthodoxy, John the Immerser in some Baptist ...
. The first European colony, Caparra, was founded on August 8, 1508, by Juan Ponce de León, a lieutenant under Columbus, who was greeted by the Taíno Cacique Agüeybaná and who later became the first governor of the island. Ponce de Leon was actively involved in the Higuey massacre of 1503 in Puerto Rico. In 1508, Sir Ponce de Leon was chosen by the Spanish Crown to lead the conquest and enslavement of the Taíno Indians for gold mining operations.[Dietz, p. 38.] Also, early in the colonization of Puerto Rico, attempts were made to wrest control of Puerto Rico from Spain. The Caribs, a raiding tribe of the Caribbean, attacked Spanish settlements along the banks of the Daguao and Macao rivers in 1514 and again in 1521 but each time they were easily repelled by the superior Spanish firepower. However, these would not be the last attempts at control of Puerto Rico. The European powers quickly realized the potential of the lands not yet colonized by Europeans and attempted to gain control of them. Nonetheless, Puerto Rico remained a Spanish possession until the 19th century.
The last half of the 19th century was marked by the Puerto Rican struggle for sovereignty
Sovereignty can generally be defined as supreme authority. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within a state as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the person, body or institution that has the ultimate au ...
. A census conducted in 1860 revealed a population of 583,308. Of these, 300,406 (51.5%) were white and 282,775 (48.5%) were persons of color, the latter including people of primarily African heritage, mulatto
( , ) is a Race (human categorization), racial classification that refers to people of mixed Sub-Saharan African, African and Ethnic groups in Europe, European ancestry only. When speaking or writing about a singular woman in English, the ...
s and mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturall ...
s. The majority of the population in Puerto Rico was illiterate (83.7%) and lived in poverty, and the agricultural industry—at the time, the main source of income—was hampered by lack of road infrastructure, adequate tools and equipment, and natural disasters, including hurricanes and droughts. The economy also suffered from increasing tariffs and taxes imposed by the Spanish Crown. Furthermore, Spain had begun to exile or jail any person who called for liberal reforms. The Spanish–American War broke out in 1898, in the aftermath of the explosion of USS ''Maine'' in Havana Harbor. The U.S. defeated Spain by the end of the year, and won control of Puerto Rico in the ensuing peace treaty. In the Foraker Act of 1900, the U.S. Congress established Puerto Rico's status as an unincorporated territory.
New France
 New France was the vast area centered on the
New France was the vast area centered on the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (, ) is a large international river in the middle latitudes of North America connecting the Great Lakes to the North Atlantic Ocean. Its waters flow in a northeasterly direction from Lake Ontario to the Gulf of St. Lawrenc ...
, Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
, Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the main stem, primary river of the largest drainage basin in the United States. It is the second-longest river in the United States, behind only the Missouri River, Missouri. From its traditional source of Lake Ita ...
, and other major tributary rivers that was explored and claimed
"Claimed" is the eleventh episode of the The Walking Dead season 4, fourth season of the Apocalyptic and post-apocalyptic fiction, post-apocalyptic Horror fiction, horror television series ''The Walking Dead (TV series), The Walking Dead'', wh ...
by France starting in the early 17th century. It was composed of several colonies: Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region of Labrador, having a total size of . As of 2025 the population ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, Île-Royale (present-day Cape Breton Island
Cape Breton Island (, formerly '; or '; ) is a rugged and irregularly shaped island on the Atlantic coast of North America and part of the province of Nova Scotia, Canada.
The island accounts for 18.7% of Nova Scotia's total area. Although ...
), and Île Saint Jean (present-day Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island is an island Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. While it is the smallest province by land area and population, it is the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
). These colonies came under British or Spanish control after the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
, though France briefly re-acquired a portion of Louisiana in 1800. The United States would gain much of New France in the 1783 Treaty of Paris, and the U.S. would acquire another portion of French territory with the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. The remainder of New France became part of Canada, with the exception of the French islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Pierre and Miquelon ( ), officially the Territorial Collectivity of Saint Pierre and Miquelon (), is a self-governing territorial overseas collectivity of France in the northwestern Atlantic Ocean, located near the Canada, Canadian prov ...
.
The first French colonial empire
The French colonial empire () comprised the overseas Colony, colonies, protectorates, and League of Nations mandate, mandate territories that came under French rule from the 16th century onward. A distinction is generally made between the "Firs ...
stretched to over at its peak in 1710, which was the second largest colonial empire in the world, after the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered ...
.
Pays d'en Haut
By 1660, French fur trappers, missionaries, and military detachments based in Montreal pushed west along the Great Lakes upriver into the Pays d'en Haut and founded outposts at Green Bay, Fort de Buade and Saint Ignace (both at Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
), Sault Sainte Marie, Vincennes, and Detroit in 1701. During the French and Indian War (1754–1763) many of these settlements became occupied by the British. By 1773, the population of Detroit was 1,400. At the end of the War for Independence in 1783, the region south of the Great Lakes formally became part of the United States.
Arkansas and Illinois
 The Italian explorer Enrico Tonti, together with the French explorer
The Italian explorer Enrico Tonti, together with the French explorer René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and North American fur trade, fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada ...
, explored the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes spanning the Canada–United States border. The five lakes are Lake Superior, Superior, Lake Michigan, Michigan, Lake Huron, H ...
region. Enrico Tonti founded the first European settlement in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
in 1679 and in Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
in 1683, known as '' Poste de Arkansea'', making him "The Father of Arkansas".Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern United States. It borders on Lake Michigan to its northeast, the Mississippi River to its west, and the Wabash River, Wabash and Ohio River, Ohio rivers to its ...
and the Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, to its mouth and thereupon claimed the length of the Mississippi for Louis XIV of France
LouisXIV (Louis-Dieudonné; 5 September 16381 September 1715), also known as Louis the Great () or the Sun King (), was King of France from 1643 until his death in 1715. His verified reign of 72 years and 110 days is the List of longest-reign ...
.Peoria, Illinois
Peoria ( ) is a city in Peoria County, Illinois, United States, and its county seat. Located on the Illinois River, the city had a population of 113,150 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, making it the List of municipalities in Ill ...
.
Louisiana
French claims to French Louisiana
The term French Louisiana ( ; ) refers to two distinct regions:
* First, to Louisiana (New France), historic French Louisiana, comprising the massive, middle section of North America claimed by Early Modern France, France during the 17th and 18th ...
stretched thousands of miles from modern Louisiana north to the largely unexplored Midwest
The Midwestern United States (also referred to as the Midwest, the Heartland or the American Midwest) is one of the four census regions defined by the United States Census Bureau. It occupies the northern central part of the United States. It ...
, and west to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in great-circle distance, straight-line distance from the northernmost part of Western Can ...
. It was generally divided into Upper and Lower Louisiana. This vast tract was first settled at Mobile and Biloxi
Biloxi ( ; ) is a city in Harrison County, Mississippi, United States. It lies on the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast in southern Mississippi, bordering the city of Gulfport, Mississippi, Gulfport to its west. The adjacent cities ar ...
around 1700, and continued to grow reaching 7,000 French immigrants. René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle (; November 22, 1643 – March 19, 1687), was a 17th-century French explorer and North American fur trade, fur trader in North America. He explored the Great Lakes region of the United States and Canada ...
and Enrico Tonti founded New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
, and Enrico Tonti was governor of the Louisiana Territory for the next 20 years. Settlement proceeded very slowly; New Orleans became an important port as the gateway to the Mississippi River, but there was little other economic development because the city lacked a prosperous hinterland.
In 1763, Louisiana was ceded to Spain around New Orleans and west of the Mississippi River. In the 1780s, the western border of the newly independent United States stretched to the Mississippi River. The United States reached an agreement with Spain for navigation rights on the river and was content to let the "feeble" colonial power stay in control of the area. The situation changed when Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career ...
forced Spain to return Louisiana to France in 1802 and threatened to close the river to American vessels. Alarmed, the United States offered to buy New Orleans.
Napoleon needed funds to wage another war with Great Britain, and he doubted that France could defend such a huge and distant territory. He therefore offered to sell all of Louisiana for $15 million. The United States completed the Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase () was the acquisition of the Louisiana (New France), territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. This consisted of most of the land in the Mississippi River#Watershed, Mississipp ...
in 1803, doubling the size of the nation.
New Netherland
 ''Nieuw-Nederland'', or New Netherland, was a colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered in 1614, in what became New York,
''Nieuw-Nederland'', or New Netherland, was a colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered in 1614, in what became New York, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and parts of other neighboring states. The peak population was less than 10,000. The Dutch established a patroon
In the United States, a patroon (; from Dutch '' patroon'' ) was a landholder with manorial rights to large tracts of land in the 17th-century Dutch colony of New Netherland on the east coast of North America. Through the Charter of Free ...
system with feudal-like rights given to a few powerful landholders; they also established religious tolerance
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
and free trade. The colony's capital of New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam (, ) was a 17th-century Dutch Empire, Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''Factory (trading post), fac ...
was founded in 1625 and located at the southern tip of the island of Manhattan
Manhattan ( ) is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the Boroughs of New York City, five boroughs of New York City. Coextensive with New York County, Manhattan is the County statistics of the United States#Smallest, larg ...
, which grew to become a major world city.
The city was captured by the English in 1664; they took complete control of the colony in 1674 and renamed it New York. However the Dutch landholdings remained, and the Hudson River Valley maintained a traditional Dutch character until the 1820s.
Traces of Dutch influence remain in present-day northern New Jersey and southeastern New York State, such as homes, family surnames, and the names of roads and whole towns.
New Sweden
New Sweden () was a Swedish colony that existed along the Delaware River Valley from 1638 to 1655 and encompassed land in present-day Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
, southern New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and southeastern Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
. The several hundred settlers were centered around the capital of Fort Christina, at the location of what is today the city of Wilmington, Delaware
Wilmington is the List of municipalities in Delaware, most populous city in the U.S. state of Delaware. The city was built on the site of Fort Christina, the first Swedish colonization of the Americas, Swedish settlement in North America. It lie ...
. The colony also had settlements near the present-day location of Salem, New Jersey ( Fort Nya Elfsborg) and on Tinicum Island, Pennsylvania. The colony was captured by the Dutch in 1655 and merged into New Netherland
New Netherland () was a colony of the Dutch Republic located on the East Coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva Peninsula to Cape Cod. Settlements were established in what became the states ...
, with most of the colonists remaining. Years later, the entire New Netherland colony was incorporated into England's colonial holdings.
The colony of New Sweden introduced Lutheranism
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched ...
to America in the form of some of the continent's oldest European churches. The colonists also introduced the log cabin
A log cabin is a small log house, especially a minimally finished or less architecturally sophisticated structure. Log cabins have an ancient history in Europe, and in America are often associated with first-generation home building by settl ...
to America, and numerous rivers, towns, and families in the lower Delaware River Valley region derive their names from the Swedes.
Russian colonies
Russia explored the area that became Alaska, starting with the Second Kamchatka expedition
The Great Northern Expedition () or Second Kamchatka Expedition () was a major Russian Arctic expedition between roughly 1733 and 1743, which mapped most of the Arctic coast of Siberia and much of the Arctic coast of North America, greatly red ...
in the 1730s and early 1740s. Their first settlement was founded in 1784 by Grigory Shelikhov. The Russian-American Company was formed in 1799 with the influence of Nikolay Rezanov, for the purpose of buying sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of ...
s for their fur from native hunters. In 1867, the U.S. purchased Alaska, and nearly all Russians abandoned the area except a few missionaries of the Russian Orthodox Church
The Russian Orthodox Church (ROC; ;), also officially known as the Moscow Patriarchate (), is an autocephaly, autocephalous Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox Christian church. It has 194 dioceses inside Russia. The Primate (bishop), p ...
working among the natives.
English colonies
 England made its first successful efforts at the start of the 17th century for several reasons. During this era, English proto-nationalism and national assertiveness blossomed under the threat of Spanish invasion, assisted by a degree of Protestant militarism and the energy of Queen Elizabeth. At this time, however, there was no official attempt by the English government to create a colonial empire. Rather the motivation behind the founding of colonies was piecemeal and variable. Practical considerations played their parts, such as commercial enterprise, over-crowding, and the desire for freedom of religion. The main waves of settlement came in the 17th century. After 1700, most immigrants to Colonial America arrived as
England made its first successful efforts at the start of the 17th century for several reasons. During this era, English proto-nationalism and national assertiveness blossomed under the threat of Spanish invasion, assisted by a degree of Protestant militarism and the energy of Queen Elizabeth. At this time, however, there was no official attempt by the English government to create a colonial empire. Rather the motivation behind the founding of colonies was piecemeal and variable. Practical considerations played their parts, such as commercial enterprise, over-crowding, and the desire for freedom of religion. The main waves of settlement came in the 17th century. After 1700, most immigrants to Colonial America arrived as indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as payment for some good or ser ...
, young unmarried men and women seeking a new life in a much richer environment. The consensus view among economic historians and economists is that the indentured servitude occurred largely as "an institutional response to a capital market imperfection," but that it "enabled prospective migrants to borrow against their future earnings in order to pay the high cost of passage to America." Between the late 1610s and the American Revolution, the British shipped an estimated 50,000 to 120,000 convicts to its American colonies.
Alexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first U.S. secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795 dur ...
(1712–1756) was a Scottish-born doctor and writer who lived and worked in Annapolis, Maryland
Annapolis ( ) is the capital of the U.S. state of Maryland. It is the county seat of Anne Arundel County and its only incorporated city. Situated on the Chesapeake Bay at the mouth of the Severn River, south of Baltimore and about east ...
. Leo Lemay says that his 1744 travel diary ''Gentleman's Progress: The Itinerarium of Dr. Alexander Hamilton'' is "the best single portrait of men and manners, of rural and urban life, of the wide range of society and scenery in colonial America." His diary has been widely used by scholars, and covers his travels from Maryland to Maine. Biographer Elaine Breslaw says that he encountered:
:the relatively primitive social milieu of the New World. He faced unfamiliar and challenging social institutions: the labor system that relied on black slaves, extraordinarily fluid social statuses, distasteful business methods, unpleasant conversational quirks, as well as variant habits of dress, food, and drink.
Chesapeake Bay area
Virginia
The first successful English colony was Jamestown, established May 14, 1607, near Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula, including parts of the Ea ...
. The business venture was financed and coordinated by the London Virginia Company, a joint-stock company looking for gold. Its first years were extremely difficult, with very high death rates from disease and starvation, wars with local Amerindians, and little gold. The colony survived and flourished by turning to tobacco as a cash crop
A cash crop, also called profit crop, is an Agriculture, agricultural crop which is grown to sell for profit. It is typically purchased by parties separate from a farm. The term is used to differentiate a marketed crop from a staple crop ("subsi ...
. By the late 17th century, Virginia's export economy was largely based on tobacco, and new, richer settlers came in to take up large portions of land, build large plantations and import indentured servants and slaves. In 1676, Bacon's Rebellion
Bacon's Rebellion was an armed rebellion by Virginia settlers that took place from 1676 to 1677. It was led by Nathaniel Bacon against Colonial Governor William Berkeley, after Berkeley refused Bacon's request to drive Native American India ...
occurred, but was suppressed by royal officials. After Bacon's Rebellion, African slaves
Slavery is the ownership of a person as property, especially in regards to their labour. Slavery typically involves compulsory work, with the slave's location of work and residence dictated by the party that holds them in bondage. Enslavemen ...
rapidly replaced indentured servants as Virginia's main labor force.[Alan Taylor, ''American Colonies,'', 2001.][Ronald L. Heinemann, ''Old Dominion, New Commonwealth: A History of Virginia, 1607–2007'', 2008.]
The colonial assembly shared power with a royally appointed governor. On a more local level, governmental power was invested in county courts, which were self-perpetuating (the incumbents filled any vacancies and there never were popular elections). As cash crop producers, Chesapeake plantations were heavily dependent on trade with England. With easy navigation by river, there were few towns and no cities; planters shipped directly to Britain. High death rates and a very young population profile characterized the colony during its first years.
New England
Puritans
The Pilgrims were a small group of Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
separatists who felt that they needed to physically distance themselves from the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
. They initially moved to the Netherlands, then decided to re-establish themselves in America. The initial Pilgrim settlers sailed to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
in 1620 on the ''Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reac ...
''. Upon their arrival, they drew up the Mayflower Compact
The Mayflower Compact, originally titled Agreement Between the Settlers of New Plymouth, was the first governing document of Plymouth Colony. It was written by the men aboard the ''Mayflower,'' consisting of Separatist Puritans, adventurers, a ...
, by which they bound themselves together as a united community, thus establishing the small Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes spelled Plimouth) was the first permanent English colony in New England from 1620 and the third permanent English colony in America, after Newfoundland and the Jamestown Colony. It was settled by the passengers on t ...
. William Bradford was their main leader. After its founding, other settlers traveled from England to join the colony.
The non-separatist Puritans constituted a much larger group than the Pilgrims, and they established the Massachusetts Bay Colony
The Massachusetts Bay Colony (1628–1691), more formally the Colony of Massachusetts Bay, was an English settlement on the east coast of North America around Massachusetts Bay, one of the several colonies later reorganized as the Province of M ...
in 1629 with 400 settlers. They sought to reform the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
by creating a new, pure church in the New World. By 1640, 20,000 had arrived; many died soon after arrival, but the others found a healthy climate and an ample food supply. The Plymouth and Massachusetts Bay colonies together spawned other Puritan colonies in New England, including the New Haven
New Haven is a city of the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound. With a population of 135,081 as determined by the 2020 U.S. census, New Haven is the third largest city in Co ...
, Saybrook, and Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
colonies. During the 17th century, the New Haven and Saybrook colonies were absorbed by Connecticut.
The Puritans created a deeply religious, socially tight-knit, and politically innovative culture that still influences the modern United States. They hoped that this new land would serve as a " redeemer nation". They fled England and attempted to create a "nation of saints" or a " City upon a Hill" in America: an intensely religious, thoroughly righteous community designed to be an example for all of Europe.
Economically, Puritan New England fulfilled the expectations of its founders. The Puritan economy was based on the efforts of self-supporting farmsteads that traded only for goods which they could not produce themselves, unlike the cash crop-oriented plantations of the Chesapeake region. There was a generally higher economic standing and standard of living in New England than in the Chesapeake. New England became an important mercantile and shipbuilding center, along with agriculture, fishing, and logging, serving as the hub for trading between the southern colonies and Europe.[James Ciment, ed. ''Colonial America: An Encyclopedia of Social, Political, Cultural, and Economic History'', 2005.]
Other New England
Providence Plantation was founded in 1636 by Roger Williams
Roger Williams (March 1683) was an English-born New England minister, theologian, author, and founder of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, Providence Plantations, which became the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Pl ...
on land provided by Narragansett sachem Canonicus. Williams was a Puritan who preached religious tolerance
Religious tolerance or religious toleration may signify "no more than forbearance and the permission given by the adherents of a dominant religion for other religions to exist, even though the latter are looked on with disapproval as inferior, ...
, separation of Church and State
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and Jurisprudence, jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the State (polity), state. Conceptually, the term refers to ...
, and a complete break with the Church of England. He was banished from the Massachusetts Bay Colony over theological disagreements, and he and other settlers founded Providence Plantation based on an egalitarian constitution providing for majority rule "in civil things" and "liberty of conscience" in religious matters.Anne Hutchinson
Anne Hutchinson (; July 1591 – August 1643) was an English-born religious figure who was an important participant in the Antinomian Controversy which shook the infant Massachusetts Bay Colony from 1636 to 1638. Her strong religious formal d ...
established a second settlement on Aquidneck Island, also known as Rhode Island.
Other colonists settled to the north, mingling with adventurers and profit-oriented settlers to establish more religiously diverse colonies in New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
and Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
. These small settlements were absorbed by Massachusetts when it made significant land claims in the 1640s and 1650s, but New Hampshire was eventually given a separate charter in 1679. Maine remained a part of Massachusetts until achieving statehood in 1820.
Dominion of New England
Under King James II of England
James II and VII (14 October 1633 – 16 September 1701) was King of England and Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland as James II and King of Scotland as James VII from the death of his elder brother, Charles II of England, Charles II, on 6 February 1 ...
, the New England colonies, New York, and the Jerseys were briefly united as the Dominion of New England
The Dominion of New England in America (1686–1689) was a short-lived administrative union of English colonies covering all of New England and the Mid-Atlantic Colonies, with the exception of the Delaware Colony and the Province of Pennsylvani ...
(1686–1689). The administration was eventually led by Governor Sir Edmund Andros and seized colonial charters, revoked land titles, and ruled without local assemblies, causing anger among the population. The 1689 Boston revolt was inspired by England's Glorious Revolution
The Glorious Revolution, also known as the Revolution of 1688, was the deposition of James II and VII, James II and VII in November 1688. He was replaced by his daughter Mary II, Mary II and her Dutch husband, William III of Orange ...
against James II and led to the arrest of Andros, Boston Anglicans, and senior dominion officials by the Massachusetts militia. Andros was jailed for several months, then returned to England. The Dominion of New England was dissolved and governments resumed under their earlier charters.
However, the Massachusetts charter had been revoked in 1684, and a new one was issued in 1691 that combined Massachusetts and Plymouth into the Province of Massachusetts Bay
The Province of Massachusetts Bay was a colony in New England which became one of the thirteen original states of the United States. It was chartered on October 7, 1691, by William III and Mary II, the joint monarchs of the kingdoms of Eng ...
. King William III sought to unite the New England colonies militarily by appointing the Earl of Bellomont to three simultaneous governorships and military command over Connecticut and Rhode Island. However, these attempts at unified control failed.
Middle Colonies
The Middle Colonies consisted of the present-day states of New York, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
and were characterized by a large degree of religious, political, economic, and ethnic diversity.
The Dutch colony of New Netherland was taken over by the English and renamed New York. However, large numbers of Dutch remained in the colony, dominating the rural areas between New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
and Albany. Meanwhile, Yankees from New England started moving in, as did immigrants from Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
. New York City attracted a large polyglot population, including a large black slave population.
New Jersey began as a division of New York, and was divided into the proprietary colonies of East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Jersey for a time.
Pennsylvania was founded in 1681 as a proprietary colony of Quaker William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
. The main population elements included the Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally, others referred to them as Quakers ...
population based in Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
, a Scotch Irish population on the Western frontier, and numerous German colonies in between. Philadelphia became the largest city in the colonies with its central location, excellent port, and a population of about 30,000.
By the mid-18th century, Pennsylvania was basically a middle-class colony with limited deference to the small upper-class. A writer in the ''Pennsylvania Journal'' summed it up in 1756:
:The People of this Province are generally of the middling Sort, and at present pretty much upon a Level. They are chiefly industrious Farmers, Artificers or Men in Trade; they enjoy in re fond ofFreedom, and the ''meanest among them'' thinks he has a right to Civility from the greatest.
South
The predominant culture of the south was rooted in the settlement of the region by British colonists. In the seventeenth century, most voluntary colonists were of English origins who settled chiefly along the coastal regions of the Eastern seaboard. The majority of early British settlers were indentured servants
Indentured servitude is a form of labor in which a person is contracted to work without salary for a specific number of years. The contract called an "indenture", may be entered voluntarily for a prepaid lump sum, as payment for some good or ser ...
, who gained freedom after enough work to pay off their passage. The wealthier men who paid their way received land grants known as headrights, to encourage settlement.
The French and Spanish established colonies in Florida
Florida ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders the Gulf of Mexico to the west, Alabama to the northwest, Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia to the north, the Atlantic ...
, Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
, and Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the we ...
. The Spanish colonized Florida in the 16th century, with their communities reaching a peak in the late 17th century. In the British and French colonies, most colonists arrived after 1700. They cleared land, built houses and outbuildings, and worked on the large plantations that dominated export agriculture. Many were involved in the labor-intensive cultivation of tobacco, the first cash crop of Virginia. With a decrease in the number of British willing to go to the colonies in the eighteenth century, planters began importing more enslaved Africans, who became the predominant labor force on the plantations. Tobacco exhausted the soil quickly, requiring new fields to be cleared on a regular basis. Old fields were used as pasture and for crops such as corn and wheat, or allowed to grow into woodlots.
Rice cultivation in South Carolina became another major commodity crop. Some historians have argued that slaves from the lowlands of western Africa, where rice was a basic crop, provided key skills, knowledge and technology for irrigation and construction of earthworks to support rice cultivation. The early methods and tools used in South Carolina were congruent with those in Africa. British colonists would have had little or no familiarity with the complex process of growing rice in fields flooded by irrigation works.
In the mid- to late-18th century, large groups of Scots and Ulster-Scots (later called the Scots-Irish) immigrated and settled in the back country of Appalachia
Appalachia ( ) is a geographic region located in the Appalachian Mountains#Regions, central and southern sections of the Appalachian Mountains in the east of North America. In the north, its boundaries stretch from the western Catskill Mountai ...
and the Piedmont
Piedmont ( ; ; ) is one of the 20 regions of Italy, located in the northwest Italy, Northwest of the country. It borders the Liguria region to the south, the Lombardy and Emilia-Romagna regions to the east, and the Aosta Valley region to the ...
. They were the largest group of colonists from the British Isles before the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
. In a census taken in 2000 of Americans and their self-reported ancestries, areas where people reported ' American' ancestry were the places where, historically, many Scottish, Scotch-Irish and English Borderer Protestants settled in America: the interior as well as some of the coastal areas of the South, and especially the Appalachian region. The population with some Scots and Scots-Irish ancestry may number 47 million, as most people have multiple heritages, some of which they may not know.
The early colonists, especially the Scots-Irish in the back-country, engaged in warfare
War is an armed conflict between the armed forces of State (polity), states, or between governmental forces and armed groups that are organized under a certain command structure and have the capacity to sustain military operations, or betwe ...
, trade, and cultural exchanges. Those living in the backcountry were more likely to join with Creek Indians, Cherokee
The Cherokee (; , or ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, they were concentrated in their homelands, in towns along river valleys of what is now southwestern ...
, and Choctaw
The Choctaw ( ) people are one of the Indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States, originally based in what is now Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama. The Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choct ...
s and other regional native groups.
The oldest university in the South, The College of William & Mary, was founded in 1693 in Virginia; it pioneered in the teaching of political economy
Political or comparative economy is a branch of political science and economics studying economic systems (e.g. Marketplace, markets and national economies) and their governance by political systems (e.g. law, institutions, and government). Wi ...
and educated future U.S. Presidents Jefferson, Monroe and Tyler, all from Virginia. Indeed, the entire region dominated politics in the First Party System era: for example, four of the first five presidents— Washington, Jefferson, Madison, and Monroe—were from Virginia. The two oldest public universities are also in the South: the University of North Carolina
The University of North Carolina is the Public university, public university system for the state of North Carolina. Overseeing the state's 16 public universities and the North Carolina School of Science and Mathematics, it is commonly referre ...
(1795) and the University of Georgia
The University of Georgia (UGA or Georgia) is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university with its main campus in Athens, Georgia, United States. Chartered in 1785, it is the oldest public university in th ...
(1785).
The colonial South included the plantation colonies of the Chesapeake region (Virginia, Maryland, and, by some classifications, Delaware) and the lower South (Carolina, which eventually split into North and South Carolina; and Georgia).
Chesapeake society
The top five percent or so of the white population of Virginia and Maryland in the mid-18th century were planters who possessed growing wealth and increasing political power and social prestige. They controlled the local Anglican church, choosing ministers and handling church property and disbursing local charity. They sought election to the House of Burgesses or appointment as justice of the peace.
About 60 percent of white Virginians were part of a broad middle class that owned substantial farms. By the second generation, death rates from malaria and other local diseases had declined so much that a stable family structure was possible.
The bottom third owned no land and verged on poverty. Many were recent arrivals, recently released from indentured servitude. In some districts near present-day Washington DC, 70 percent of the land was owned by a handful of families, and three-fourths of the whites had no land at all. Large numbers of Irish and German Protestants had settled in the frontier districts, often moving down from Pennsylvania. Tobacco was not important here; farmers focused on hemp, grain, cattle, and horses. Entrepreneurs had begun to mine and melt the local iron ores.
Sports occupied a great deal of attention at every social level, starting at the top. In England, hunting was sharply restricted to landowners and enforced by armed gamekeepers. In America, game was plentiful. Everyone could and did hunt, including servants and slaves. Poor men with good rifle skills won praise; rich gentlemen who were off target won ridicule. In 1691, governor Sir Francis Nicholson organized competitions for the "better sort of Virginians onely who are Batchelors," and he offered prizes "to be shot for, wrestled, played at backswords, & Run for by Horse and foott."
Horse racing was the main event. The typical farmer did not own a horse in the first place, and racing was a matter for gentlemen only, but ordinary farmers were spectators and gamblers. The race was a major public event designed to demonstrate to the world the superior social status of the gentry through expensive breeding, training, boasting, and gambling, and especially winning the races themselves. Historian Timothy Breen explains that horse racing and high-stakes gambling were essential to maintaining the status of the gentry. When they publicly bet a large sum on their favorite horse, it told the world that competitiveness, individualism, and materialism were the core elements of gentry values.
By 1700, the Virginia population reached 70,000 and continued to grow rapidly from a high birth rate, low death rate, importation of slaves from the Caribbean, and immigration from Britain, Germany, and Pennsylvania. The climate was mild; the farm lands were cheap and fertile.
Carolinas
The Province of Carolina was the first attempted English settlement south of Virginia. It was a private venture, financed by a group of English Lords Proprietors
A lord proprietor is a person granted a royal charter for the establishment and government of an English colony in the 17th century. The plural of the term is "lords proprietors" or "lords proprietary".
Origin
In the beginning of the Europe ...
who obtained a royal charter
A royal charter is a formal grant issued by a monarch under royal prerogative as letters patent. Historically, they have been used to promulgate public laws, the most famous example being the English Magna Carta (great charter) of 1215, but ...
to the Carolinas in 1663, hoping that a new colony in the south would become profitable like Jamestown. Carolina was not settled until 1670, and even then the first attempt failed because there was no incentive for emigration to that area. Eventually, however, the Lords combined their remaining capital and financed a settlement mission to the area led by Sir John Colleton. The expedition located fertile and defensible ground at what became Charleston, originally Charles Town for Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651 and King of England, Scotland, and King of Ireland, Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest su ...
. The original settlers in South Carolina established a lucrative trade in food for the slave plantations in the Caribbean. The settlers came mainly from the English colony of Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
and brought enslaved Africans with them. Barbados was a wealthy sugarcane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of tall, Perennial plant, perennial grass (in the genus ''Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar Sugar industry, production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fib ...
plantation island, one of the early English colonies to use large numbers of Africans in plantation-style agriculture. The cultivation of rice was introduced during the 1690s and became an important export crop.
At first, South Carolina was politically divided. Its ethnic makeup included the original settlers (a group of rich, slave-owning English settlers from the island of Barbados) and Huguenots
The Huguenots ( , ; ) are a Religious denomination, religious group of French people, French Protestants who held to the Reformed (Calvinist) tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, ...
, a French-speaking community of Protestants. Nearly continuous frontier warfare during the era of King William's War and Queen Anne's War drove economic and political wedges between merchants and planters. The disaster of the 1715 Yamasee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee, who were supported by a number of allied Native Americans in ...
threatened the colony's viability and set off a decade of political turmoil. By 1729, the proprietary government had collapsed, and the Proprietors sold both colonies back to the British crown.
Georgia
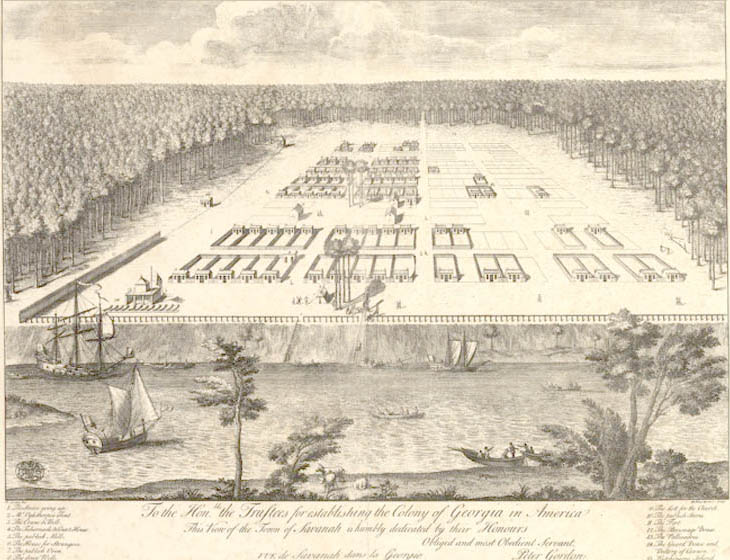 British Member of Parliament
British Member of Parliament James Oglethorpe
Lieutenant-General James Edward Oglethorpe (22 December 1696 – 30 June 1785) was a British Army officer, Tory politician and colonial administrator best known for founding the Province of Georgia in British North America. As a social refo ...
established the Georgia Colony in 1733 as a solution to two problems. At that time, tension was high between Spain and Great Britain, and the British feared that Spanish Florida was threatening the British Carolinas. Oglethorpe decided to establish a colony in the contested border region of Georgia and to populate it with debtors who would otherwise have been imprisoned according to standard British practice. This plan would both rid Great Britain of its undesirable elements and provide her with a base from which to attack Florida. The first colonists arrived in 1733.
East and West Florida
Spain ceded Florida to Great Britain in 1763, which established the colonies of East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Florida. The Floridas remained loyal to Great Britain during the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
. They were returned to Spain in 1783 in exchange for the Bahamas
The Bahamas, officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an archipelagic and island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the Atlantic Ocean. It contains 97 per cent of the archipelago's land area and 88 per cent of its population. ...
, at which time most of the British left. The Spanish then neglected the Floridas; few Spaniards lived there when the US bought the area in 1819.
Unification of the British colonies
Colonial wars
 Efforts began as early as the 1640s toward a common defense of the colonies, principally against shared threats from Indians, the French, and the Dutch. The Puritan colonies of New England formed a confederation to coordinate military and judicial matters. From the 1670s, several royal governors attempted to find means of coordinating defensive and offensive military matters, notably Sir Edmund Andros (who governed New York, New England, and Virginia at various times) and Francis Nicholson (governed Maryland, Virginia, Nova Scotia, and Carolina). After King Phillips War, Andros successfully negotiated the Covenant Chain, a series of Indian treaties that brought relative calm to the frontiers of the middle colonies for many years.
The northern colonies experienced numerous assaults from the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French from
Efforts began as early as the 1640s toward a common defense of the colonies, principally against shared threats from Indians, the French, and the Dutch. The Puritan colonies of New England formed a confederation to coordinate military and judicial matters. From the 1670s, several royal governors attempted to find means of coordinating defensive and offensive military matters, notably Sir Edmund Andros (who governed New York, New England, and Virginia at various times) and Francis Nicholson (governed Maryland, Virginia, Nova Scotia, and Carolina). After King Phillips War, Andros successfully negotiated the Covenant Chain, a series of Indian treaties that brought relative calm to the frontiers of the middle colonies for many years.
The northern colonies experienced numerous assaults from the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French from Acadia
Acadia (; ) was a colony of New France in northeastern North America which included parts of what are now the The Maritimes, Maritime provinces, the Gaspé Peninsula and Maine to the Kennebec River. The population of Acadia included the various ...
during the four French and Indian Wars
The French and Indian Wars were a series of conflicts that occurred in North America between 1688 and 1763, some of which indirectly were related to the European dynastic wars. The title ''French and Indian War'' in the singular is used in the U ...
, particularly present-day Maine
Maine ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the United States, and the northeasternmost state in the Contiguous United States. It borders New Hampshire to the west, the Gulf of Maine to the southeast, and the Provinces and ...
and New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
, as well as Father Rale's War and Father Le Loutre's War
Father Le Loutre's War (1749–1755), also known as the Indian War, the Mi'kmaq War and the Anglo-Mi'kmaq War, took place between King George's War and the French and Indian War in Acadia and Nova Scotia. On one side of the conflict, the Kingdo ...
.
One event that reminded colonists of their shared identity as British subjects was the War of the Austrian Succession
The War of the Austrian Succession was a European conflict fought between 1740 and 1748, primarily in Central Europe, the Austrian Netherlands, Italian Peninsula, Italy, the Atlantic Ocean and Mediterranean Sea. Related conflicts include King Ge ...
(1740–1748) in Europe. This conflict spilled over into the colonies, where it was known as "King George's War
King George's War (1744–1748) is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the War of the Austrian Succession (1740–1748). It was the third of the four French and Indian Wars. It took place primarily in ...
". The major battles took place in Europe, but American colonial troops fought the French and their Indian allies in New York, New England, and Nova Scotia with the Siege of Louisbourg (1745)
The siege of Louisbourg took place in 1745 when a New England colonial force aided by a British fleet captured Louisbourg, the capital of the French province of Île-Royale (present-day Cape Breton Island) during the War of the Austrian Succ ...
.
At the Albany Congress
The Albany Congress (June 19 – July 11, 1754), also known as the Albany Convention of 1754, was a meeting of representatives sent by the legislatures of seven of the British colonies in British America: Connecticut Colony, Connecticut, Prov ...
of 1754, Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
proposed that the colonies be united by a Grand Council overseeing a common policy for defense, expansion, and Indian affairs. The plan was thwarted by colonial legislatures and King George II, but it was an early indication that the British colonies of North America were headed towards unification.
French and Indian War

 The
The French and Indian War
The French and Indian War, 1754 to 1763, was a colonial conflict in North America between Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of France, France, along with their respective Native Americans in the United States, Native American ...
(1754–1763) was the American extension of the general European conflict known as the Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War, 1756 to 1763, was a Great Power conflict fought primarily in Europe, with significant subsidiary campaigns in North America and South Asia. The protagonists were Kingdom of Great Britain, Great Britain and Kingdom of Prus ...
. Previous colonial wars in North America had started in Europe and then spread to the colonies, but the French and Indian War is notable for having started in North America and spread to Europe. One of the primary causes of the war was increasing competition between Britain and France, especially in the Great Lakes and Ohio valley.[Fred Anderson, ''The War That Made America: A Short History of the French and Indian War'' (2006)]
The French and Indian War took on a new significance for the British North American colonists when William Pitt the Elder
William Pitt, 1st Earl of Chatham (15 November 170811 May 1778) was a British Whig statesman who served as Prime Minister of Great Britain from 1766 to 1768. Historians call him "Chatham" or "Pitt the Elder" to distinguish him from his son ...
decided that major military resources needed to be devoted to North America to win the war against France. For the first time, the continent became one of the main theaters of what could be termed a "world war
A world war is an international War, conflict that involves most or all of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World War I ...
". During the war, the position of the British colonies as part of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
was made truly apparent, as British military and civilian officials took on an increased presence in the lives of Americans.
The war also increased a sense of American unity in other ways. It caused men to travel across the continent who might otherwise have never left their own colony, fighting alongside men from decidedly different backgrounds who were nonetheless still "American". Throughout the course of the war, British officers trained American ones for battle, most notably George Washington
George Washington (, 1799) was a Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father and the first president of the United States, serving from 1789 to 1797. As commander of the Continental Army, Washington led Patriot (American Revoluti ...
, which benefitted the American cause during the Revolution. Also, colonial legislatures and officials had to cooperate intensively, for the first time, in pursuit of the continent-wide military effort.Louisiana
Louisiana ( ; ; ) is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It borders Texas to the west, Arkansas to the north, and Mississippi to the east. Of the 50 U.S. states, it ranks 31st in area and 25 ...
west of the Mississippi River the previous year. Before the war, Britain held the thirteen American colonies, most of present-day Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
, and most of the Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay, sometimes called Hudson's Bay (usually historically), is a large body of Saline water, saltwater in northeastern Canada with a surface area of . It is located north of Ontario, west of Quebec, northeast of Manitoba, and southeast o ...
watershed. Following the war, Britain gained all French territory east of the Mississippi River, including Quebec, the Great Lakes, and the Ohio River valley. Britain also gained Spanish Florida
Spanish Florida () was the first major European land-claim and attempted settlement-area in northern America during the European Age of Discovery. ''La Florida'' formed part of the Captaincy General of Cuba in the Viceroyalty of New Spain, and th ...
, from which it formed the colonies of East
East is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fact that ea ...
and West Florida. In removing a major foreign threat to the thirteen colonies, the war also largely removed the colonists' need of colonial protection.
The British and colonists triumphed jointly over a common foe. The colonists' loyalty to the mother country was stronger than ever before. However, disunity was beginning to form. British Prime Minister William Pitt the Elder had decided to wage the war in the colonies with the use of troops from the colonies and tax funds from Britain itself. This was a successful wartime strategy but, after the war was over, each side believed that it had borne a greater burden than the other. The British elite, the most heavily taxed of any in Europe, pointed out angrily that the colonists paid little to the royal coffers. The colonists replied that their sons had fought and died in a war that served European interests more than their own. This dispute was a link in the chain of events that soon brought about the American Revolution.
Ties to British Empire
The colonies were very different from one another but they were still a part of the British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It bega ...
in more than just name. Demographically, the majority of the colonists traced their roots to the British Isles and many of them still had family ties with Great Britain. Socially, the colonial elite of Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
, New York, Charleston, and Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
saw their identity as British. Many had never lived in Britain in over a few generations, yet they imitated British styles of dress, dance, and etiquette. This social upper echelon built its mansions in the Georgian style, copied the furniture designs of Thomas Chippendale, and participated in the intellectual currents of Europe, such as the Enlightenment. The seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Hamburg, Manc ...
cities of colonial America were truly British cities in the eyes of many inhabitants.[Daniel Vickers, ed. ''A Companion to Colonial America'' (2006), ch 13–16]
Many of the political structures of the colonies drew upon the republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology that encompasses a range of ideas from civic virtue, political participation, harms of corruption, positives of mixed constitution, rule of law, and others. Historically, it emphasizes the idea of self ...
expressed by opposition leaders in Britain, most notably the Commonwealth men and the Whig traditions. Many Americans at the time saw the colonies' systems of governance as modeled after the British constitution
The constitution of the United Kingdom comprises the written and unwritten arrangements that establish the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland as a political body. Unlike in most countries, no official attempt has been made to c ...
of the time, with the king corresponding to the governor, the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of ...
to the colonial assembly, and the House of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest ext ...
to the governor's council. The codes of law of the colonies were often drawn directly from English law
English law is the common law list of national legal systems, legal system of England and Wales, comprising mainly English criminal law, criminal law and Civil law (common law), civil law, each branch having its own Courts of England and Wales, ...
; indeed, English common law
Common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law primarily developed through judicial decisions rather than statutes. Although common law may incorporate certain statutes, it is largely based on prece ...
survives not only in Canada, but also throughout the United States. Eventually, it was a dispute over the meaning of some of these political ideals (especially political representation
Political representation is the activity of making citizens "present" in public policy-making processes when political actors act in the best interest of citizens according to Hanna Pitkin's ''Concept of Representation'' (1967).
This definition ...
) and republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology that encompasses a range of ideas from civic virtue, political participation, harms of corruption, positives of mixed constitution, rule of law, and others. Historically, it emphasizes the idea of self ...
that led to the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
.
Another point on which the colonies found themselves more similar than different was the booming import of British goods. The British economy had begun to grow rapidly at the end of the 17th century and, by the mid-18th century, small factories in Britain were producing much more than the nation could consume. Britain found a market for their goods in the British colonies of North America, increasing her exports to that region by 360% between 1740 and 1770. British merchants offered credit to their customers;Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlan ...
to Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
, all British subjects bought similar products, creating and anglicizing a sort of common identity.
Atlantic world
In recent years, historians have enlarged their perspective to cover the entire Atlantic world in a subfield now known as Atlantic history. Of special interest are such themes as international migration, trade, colonization, comparative military and governmental institutions, the transmission of religions and missionary work, and the slave trade. It was the Age of the Enlightenment
Age or AGE may refer to:
Time and its effects
* Age, the amount of time someone has been alive or something has existed
** East Asian age reckoning, an Asian system of marking age starting at 1
* Ageing or aging, the process of becoming older
...
, and ideas flowed back and forth across the Atlantic, with Philadelphian Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
playing a major role.
In 2008, Francois Furstenberg offered a different perspective on the historical period. He suggested that warfare was critical among the major imperial players: Britain, the American colonies, Spain, France, and the First Nations (Indians). They fought a series of conflicts from 1754 to 1815 that Furstenberg calls a "Long War for the West" over control of the region.
Women played a role in the emergence of the capitalist economy in the Atlantic world. The types of local commercial exchange in which they participated independently were well integrated with the trade networks between colonial merchants throughout the Atlantic region, especially markets in dairy and produce commodities. For example, local women merchants were important suppliers of foodstuffs to transatlantic shipping concerns.
Growing dissent and the American Revolution
In the colonial era, Americans insisted on their rights as Englishmen to have their own legislature raise all taxes. The British Parliament, however, asserted in 1765 that it held supreme authority to lay taxes, and a series of American protests began that led directly to the American Revolution. The first wave of protests attacked the Stamp Act of 1765, and marked the first time that Americans met together from each of the 13 colonies and planned a common front against British taxation. The Boston Tea Party
The Boston Tea Party was a seminal American protest, political and Mercantilism, mercantile protest on December 16, 1773, during the American Revolution. Initiated by Sons of Liberty activists in Boston in Province of Massachusetts Bay, colo ...
of 1773 dumped British tea into Boston Harbor because it contained a hidden tax that Americans refused to pay. The British responded by trying to crush traditional liberties in Massachusetts
Massachusetts ( ; ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders the Atlantic Ocean and the Gulf of Maine to its east, Connecticut and Rhode ...
, leading to the launch of the Revolutionary War in 1775.
The idea of independence steadily became more widespread, after being first proposed and advocated by a number of public figures and commentators throughout the colonies. One of the most prominent voices on behalf of independence was Thomas Paine
Thomas Paine (born Thomas Pain; – In the contemporary record as noted by Conway, Paine's birth date is given as January 29, 1736–37. Common practice was to use a dash or a slash to separate the old-style year from the new-style year. In ...
, whose pamphlet ''Common Sense
Common sense () is "knowledge, judgement, and taste which is more or less universal and which is held more or less without reflection or argument". As such, it is often considered to represent the basic level of sound practical judgement or know ...
'' was published in 1776. Another group that called for independence was the Sons of Liberty
The Sons of Liberty was a loosely organized, clandestine, sometimes violent, political organization active in the Thirteen American Colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. It p ...
, which had been founded in 1765 in Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
by Samuel Adams
Samuel Adams (, 1722 – October 2, 1803) was an American statesman, Political philosophy, political philosopher, and a Founding Father of the United States. He was a politician in Province of Massachusetts Bay, colonial Massachusetts, a le ...
and which was now becoming even more strident and numerous.
The British Parliament began a series of taxes and punishments which met more and more resistance: First Quartering Act (1765); Declaratory Act (1766); Townshend Revenue Act (1767); and Tea Act (1773). In response to the Boston Tea Party, Parliament passed the Intolerable Acts
The Intolerable Acts, sometimes referred to as the Insufferable Acts or Coercive Acts, were a series of five punitive laws passed by the British Parliament in 1774 after the Boston Tea Party. The laws aimed to punish Massachusetts colonists fo ...
: Second Quartering Act (1774); Quebec Act
The Quebec Act 1774 ( 14 Geo. 3. c. 83) () was an act of the Parliament of Great Britain which set procedures of governance in the Province of Quebec. One of the principal components of the act was the expansion of the province's territory t ...
(1774); Massachusetts Government Act (1774); Administration of Justice Act (1774); Boston Port Act (1774); Prohibitory Act (1775). By this point, the 13 colonies had organized themselves into the Continental Congress
The Continental Congress was a series of legislature, legislative bodies, with some executive function, for the Thirteen Colonies of British America, Great Britain in North America, and the newly declared United States before, during, and after ...
and begun setting up independent governments and drilling their militia in preparation for war.
Impacts of colonialism
The idea that nature and humans are separate entities can be traced back to European colonial views. To European settlers, land was an inherited right and was to be used to profit.
Colonial life
British colonial government
In the British colonies, the three forms of government were provincial ( royal colony), proprietary, and charter. These governments were all subordinate to the King of England, with no explicit relationship with the British Parliament
In modern politics and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: Representation (politics), representing the Election#Suffrage, electorate, making laws, and overseeing ...
. Beginning late in the 17th century, the administration of all British colonies was overseen by the Board of Trade
The Board of Trade is a British government body concerned with commerce and industry, currently within the Department for Business and Trade. Its full title is The Lords of the Committee of the Privy Council appointed for the consideration of ...
in London. Each colony had a paid colonial agent in London to represent its interests.
New Hampshire, New York, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, and eventually Massachusetts were crown colonies. The provincial colony was governed by commissions created at the pleasure of the king. A governor and (in some provinces) his council were appointed by the crown. The governor was invested with general executive powers and authorized to call a locally elected assembly. The governor's council would sit as an upper house when the assembly was in session, in addition to its role in advising the governor. Assemblies were made up of representatives elected by the freeholders and planters (landowners) of the province. The governor had the power of absolute veto and could prorogue
Prorogation in the Westminster system of government is the action of proroguing, or interrupting, a parliament, or the discontinuance of meetings for a given period of time, without a dissolution of parliament. The term is also used for the period ...
(i.e., delay) and dissolve the assembly. The assembly's role was to make all local laws and ordinances, ensuring that they were not inconsistent with the laws of England. In practice, this did not always occur, since many of the provincial assemblies sought to expand their powers and limit those of the governor and crown. Laws could be examined by the British Privy Council or Board of Trade, which also held veto power of legislation.
Pennsylvania (which included Delaware), New Jersey, and Maryland were proprietary colonies. They were governed much as royal colonies except that lord proprietors, rather than the king, appointed the governor. They were set up after the Restoration of 1660 and typically enjoyed greater civil and religious liberty.
Massachusetts, Providence Plantation, Rhode Island, Warwick, and Connecticut were charter colonies. The Massachusetts charter was revoked in 1684 and was replaced by a provincial charter that was issued in 1691. Charter governments were political corporations created by letters patent
Letters patent (plurale tantum, plural form for singular and plural) are a type of legal instrument in the form of a published written order issued by a monarch, President (government title), president or other head of state, generally granti ...
, giving the grantees control of the land and the powers of legislative government. The charters provided a fundamental constitution and divided powers among legislative, executive, and judicial functions, with those powers being vested in officials.
Political culture
The primary political cultures of the United States had their origins in the colonial period. Most theories of political culture identify New England, the Mid-Atlantic, and the South as having formed separate and distinct political cultures.
As Bonomi shows, the most distinctive feature of colonial society was the vibrant political culture, which attracted the most talented and ambitious young men into politics. First, suffrage was the most generous in the world, with every man allowed to vote who owned a certain amount of property. Fewer than one-percent of British men could vote, whereas a majority of American freemen were eligible. The roots of democracy were present, although deference was typically shown to social elites in colonial elections.
Second, a very wide range of public and private business was decided by elected bodies in the colonies, especially the assemblies and county governments in each colony. They handled land grants, commercial subsidies, and taxation, as well as oversight of roads, poor relief, taverns, and schools. Americans sued each other at a very high rate, with binding decisions made not by a great lord but by local judges and juries. This promoted the rapid expansion of the legal profession, so that the intense involvement of lawyers in politics became an American characteristic by the 1770s.
Third, the American colonies were exceptional in the world because of the representation of many different interest groups in political decision-making. The American political culture was open to economic, social, religious, ethnic, and geographical interests, with merchants, landlords, petty farmers, artisans, Anglicans, Presbyterians, Quakers, Germans, Scotch Irish, Yankees, Yorkers, and many other identifiable groups taking part. Elected representatives learned to listen to these interests because 90% of the men in the lower houses lived in their districts, unlike England where it was common to have an absentee member of Parliament. All of this was very unlike Europe, where aristocratic families and the established church were in control.
Finally, the Americans were fascinated by and increasingly adopted the political values of Republicanism
Republicanism is a political ideology that encompasses a range of ideas from civic virtue, political participation, harms of corruption, positives of mixed constitution, rule of law, and others. Historically, it emphasizes the idea of self ...
which stressed equal rights, the need for virtuous citizens, and the evils of corruption, luxury, and aristocracy. Republicanism provided the framework for colonial resistance to British schemes of taxation after 1763, which escalated into the Revolution.
None of the colonies had stable political parties of the sort that formed in the 1790s, but each had shifting factions that vied for power, especially in the perennial battles between the appointed governor and the elected assembly. There were often "country" and "court" factions, representing those opposed to the governor's agenda and those in favor of it, respectively. Massachusetts had particularly low requirements for voting eligibility and strong rural representation in its assembly from its 1691 charter; consequently, it also had a strong populist faction that represented the province's lower classes.
Up and down the colonies, non-English ethnic groups had clusters of settlements. The most numerous were Scottish Irish and German. Each group assimilated into the dominant English, Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divin ...
, commercial, and political culture, which included several local variations. They tended to vote in blocs, and politicians negotiated with group leaders for votes. They generally retained their historic languages and cultural traditions, even as they merged into the developing American culture.
Ethnocultural factors were most visible in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
. Between 1756 and 1776, the Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
were the largest faction in the legislature, but they were losing their dominance to the growing Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
faction based on Scotch-Irish votes, supported by Germans.
Medical conditions
Mortality was very high for new arrivals, and high for children in the colonial era. Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
was deadly to many new arrivals in the Southern colonies. For an example of newly arrived able-bodied young men, over one-fourth of the Anglican missionaries died within five years of their arrival in the Carolinas.
Mortality was high for infants and small children, especially from diphtheria
Diphtheria is an infection caused by the bacteria, bacterium ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae''. Most infections are asymptomatic or have a mild Course (medicine), clinical course, but in some outbreaks, the mortality rate approaches 10%. Signs a ...
, yellow fever, and malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomitin ...
. Most sick people turned to local healers and used folk remedies. Others relied upon the minister-physicians, barber-surgeons, apothecaries, midwives, and ministers; a few used colonial physicians trained either in Britain or an apprenticeship in the colonies. There was little government control, regulation of medical care, or attention to public health. Colonial physicians introduced modern medicine to the cities in the 18th century, following the models in England and Scotland, and made some advances in vaccination, pathology, anatomy, and pharmacology.
Religion
The first religious services held in colonial America were Anglican services held in Jamestown, Virginia
The Jamestown settlement in the Colony of Virginia was the first permanent British colonization of the Americas, English settlement in the Americas. It was located on the northeast bank of the James River, about southwest of present-day Willia ...
, according to the ''Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the title given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christianity, Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The Book of Common Prayer (1549), fi ...
''. The practice of the religion of the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the State religion#State churches, established List of Christian denominations, Christian church in England and the Crown Dependencies. It is the mother church of the Anglicanism, Anglican Christian tradition, ...
in Jamestown predates that of the Pilgrim
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star.
Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as ...
settlers who came on the ''Mayflower
''Mayflower'' was an English sailing ship that transported a group of English families, known today as the Pilgrims, from England to the New World in 1620. After 10 weeks at sea, ''Mayflower'', with 102 passengers and a crew of about 30, reac ...
'' in 1620 and whose separatist faith motivated their move from Europe. The Spanish set up a network of Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
missions in California
California () is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States that lies on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. It borders Oregon to the north, Nevada and Arizona to the east, and shares Mexico–United States border, an ...
, but they had all closed decades before 1848 when California became a state. There were a few important French Catholic churches and institutions in New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
.
Most of the settlers came from Protestant backgrounds in England and Western Europe, with a small proportion of Catholics, chiefly in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, and a few Jews in port cities. The English and the Germans brought along multiple Protestant denominations. Several colonies had an established church, which meant that local tax money went to the denomination. Freedom of religion became a basic American principle, and numerous new movements emerged, many of which became established denominations in their own right. The Puritans of New England kept in close touch with non-conformists in England, as did the Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
and the Methodists.
Church membership statistics by denomination are unreliable and scarce from the colonial period,American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which Am ...
and probably did not comprise even 30 percent of the population in the Southern Colonies (Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States between the East Coast of the United States ...
, North Carolina
North Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, South Carolina to the south, Georgia (U.S. stat ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the South Caucasus
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the southeastern United States
Georgia may also refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Georgia (name), a list of pe ...
) where the Church of England was the established church.Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
by the time of the Revolutionary War, of which 82 to 84 percent were affiliated with non-Anglican Protestant denominations, with 76 to 77 percent specifically affiliated with British Dissenter denominations (Congregational, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
, Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
, or Quaker) or continental Calvinists ( Dutch Reformed or German Reformed), 5 to 8 percent being Lutheran; there was also a population of approximately 10,000 Methodists. 14 to 16 percent remained Anglican but were declining in number, and the remaining 2 percent of the churches were Catholic
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwid ...
.Massachusetts Bay
Massachusetts Bay is a bay on the Gulf of Maine that forms part of the central coastline of Massachusetts.
Description
The bay extends from Cape Ann on the north to Plymouth Harbor on the south, a distance of about . Its northern and sout ...
, Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
, and New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
), while the Middle Colonies ( New York, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic and South Atlantic states, South Atlantic regions of the United States. It borders Maryland to its south and west, Pennsylvania to its north, New Jersey ...
) and the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations
The Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations was an English colony on the eastern coast of America, founded in 1636 by Puritan minister Roger Williams after his exile from the Massachusetts Bay Colony. It became a haven for religious d ...
had no established churches.Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion, which states that Jesus in Christianity, Jesus is the Son of God (Christianity), Son of God and Resurrection of Jesus, rose from the dead after his Crucifixion of Jesus, crucifixion, whose ...
was in the era of the American Revolution. Many of the founding fathers were active in a local church; some of them had Deist
Deism ( or ; derived from the Latin term '' deus'', meaning "god") is the philosophical position and rationalistic theology that generally rejects revelation as a source of divine knowledge and asserts that empirical reason and observation ...
sentiments, such as Jefferson, Franklin, and Washington. Catholics were few outside of Maryland; however, they joined the Patriot cause during the Revolution. Leaders such as George Washington strongly endorsed tolerance for them and indeed for all denominations.
Great Awakening
The First Great Awakening was the nation's first major religious revival, occurring in the middle of the 18th century, and it injected new vigor into Christian faith. It was a wave of religious enthusiasm among Protestants that swept the colonies in the 1730s and 1740s, leaving a permanent impact on American religion. Jonathan Edwards was a key leader and a powerful intellectual in colonial America. George Whitefield
George Whitefield (; 30 September 1770), also known as George Whitfield, was an English Anglican minister and preacher who was one of the founders of Methodism and the evangelical movement. Born in Gloucester, he matriculated at Pembroke Coll ...
came over from England and made many converts.
The Great Awakening emphasized the traditional Reformed virtues of Godly preaching, rudimentary liturgy, and a deep awareness of personal sin and redemption by Christ Jesus, spurred on by powerful preaching that deeply affected listeners. Pulling away from ritual and ceremony, the Great Awakening made religion personal to the average person.
The Awakening had a major impact in reshaping the Congregational church, Congregational, Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a historically Reformed Protestant tradition named for its form of church government by representative assemblies of elders, known as "presbyters". Though other Reformed churches are structurally similar, the word ''Pr ...
, Dutch Reformed Church, Dutch Reformed, and German Reformed denominations, and it strengthened the small Baptist
Baptists are a Christian denomination, denomination within Protestant Christianity distinguished by baptizing only professing Christian believers (believer's baptism) and doing so by complete Immersion baptism, immersion. Baptist churches ge ...
and Methodism, Methodist denominations. It brought Christianity to the slaves and was a powerful event in New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
that challenged established authority. It incited rancor and division between the new revivalists and the old traditionalists who insisted on ritual and liturgy. The Awakening had little impact on Anglicans and Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
.
The First Great Awakening focused on people who were already church members, unlike the Second Great Awakening that began around 1800 and reached out to the unchurched. It changed their rituals, their piety, and their self-awareness. The new style of sermons and the way that people practiced their faith breathed new life into religion in the United States, religion in America. People became passionately and emotionally involved in their religion, rather than passively listening to intellectual discourse in a detached manner. Ministers who used this new style of preaching were generally called "new lights", while the traditional-styled preachers were called "old lights".
People began to study the Bible at home, which effectively decentralized the means of informing the public on religious manners and was akin to the individualistic trends present in Europe during the Reformation, Protestant Reformation.
Women's roles
The experiences of women varied greatly from colony to colony during the colonial era. In New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
, the Puritan
The Puritans were English Protestants in the 16th and 17th centuries who sought to rid the Church of England of what they considered to be Roman Catholic practices, maintaining that the Church of England had not been fully reformed and should b ...
settlers brought their strong religious values with them to the New World, which dictated that a woman be submissive to her husband and dedicate herself to rearing God-fearing children to the best of her ability.
There were ethnic differences in the treatment of women. Among Puritan settlers in New England, wives almost never worked in the fields with their husbands. In German communities in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
, however, many women worked in fields and stables. German and Dutch immigrants granted women more control over property, which was not permitted in the local English law. Unlike English colonial wives, German and Dutch wives owned their own clothes and other items and were also given the ability to write wills disposing of the property brought into the marriage.
Like the many wives of founders and soldiers of the American Revolution
The American Revolution (1765–1783) was a colonial rebellion and war of independence in which the Thirteen Colonies broke from British America, British rule to form the United States of America. The revolution culminated in the American ...
, Mary Bartlett's life "shows how crucial a role these women played while their husbands fought the battles and formed the laws of the new nation. It was not just that they were making it all work at home, they were also passionate patriots themselves, engaged in the government and the war just as their husbands, sons, brothers, fathers, and friends were", according to Cokie Roberts in ''Founding Mothers : The women who raised our nation''.
Work for women included running establishments based on their culinary skills. The first restaurant in the colonies belonged to Goody Armitage in Massachusetts in 1643. Leisure activity for women of the time included playing the Clavier (instrument), clavier, harpsichord, clavichord and the Organ (music), organ. Women (as well as men) danced in Ball (dance party), balls especially after 1700. These dances had a strict social code with mistakes in choreography scrutinized and a loss of prestige would follow with excessive dance errors.
By the mid-18th century, the values of the American Enlightenment became established and weakened the view that husbands were natural "rulers" over their wives. There was a new sense of shared marriage. Legally, husbands took control of wives' property when marrying. Divorce was almost impossible until the late 18th century.
Slavery
Slaves transported to America:
* 1620–1700: 21,000
* 1701–1760: 189,000
* 1761–1770: 63,000
* 1771–1790: 56,000
* 1791–1800: 79,000
* 1801–1810: 124,000
* 1810–1865: 51,000
* Total: 583,000
About 305,326 slaves were transported to America, or less than 2% of the 12 million slaves taken from Africa. The great majority went to sugarcane-growing colonies in the Caribbean and Brazil, where life expectancy was short and the numbers had to be continually replenished. Life expectancy was much greater in the American colonies because of better food, less disease, lighter workloads, and better medical care, so the population grew rapidly, reaching 4 million by the 1860 census. From 1770 until 1860, the birth rate of American slaves was much greater than for the population of any nation in Europe, and was nearly twice as rapid as that of England.
The conditions the Caribbean and Brazilian enslaved populations endured in the early colonial years prompted many attempts at fleeing plantation work. Successfully escaped slaves often fled to "maroon communities'' which were populated with former slaves along with local Native Americans that helped shelter the recently escaped. Subsequent treaties with Maroons, Maroon communities suggest that these communities were a burden on South American and Caribbean plantations. While the inhumane working conditions coupled with slave revolts in the Caribbean Islands and Brazilian plantations called for the increased imports of African slaves, in the colonies many plantation owners recognized their ability to maintain a generation of slaves for the economic benefit of allowing natural reproduction to increase the population. This led to the following generations of the enslaved population to be American born.
Urban life
Historian Carl Bridenbaugh examined in depth five key cities: Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
(population 16,000 in 1760), Newport, Rhode Island (population 7500), New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
(population 18,000), Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
(population 23,000), and Charles Town (Charleston, South Carolina, Charlestown, South Carolina) (population 8000). He argues they grew from small villages to take major leadership roles in promoting trade, land speculation, immigration, and prosperity, and in disseminating the ideas of the Enlightenment, and new methods in medicine and technology. Furthermore, they sponsored a consumer taste for English amenities, developed a distinctly American educational system, and began systems for care of people in need. The colonial governments were much less powerful and intrusive than corresponding national governments in Europe. They experimented with new methods to raise revenue, build infrastructure, and solve urban problems. They were more democratic than European cities, in that a large fraction of the men could vote, and class lines were more fluid. Contrasted to Europe, printers (especially as newspaper editors) had a much larger role in shaping public opinion, and lawyers moved easily back and forth between politics and their profession. Bridenbaugh argues that by the mid-18th century, the middle-class businessmen, professionals, and skilled artisans dominated the cities.
There were few cities in the entire Southern United States, South, and Charleston (Charles Town) and New Orleans
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
were the most important before the American Civil War broke out in 1861. The Province of Carolina was settled mainly by Planter class, planters from the overpopulated British Sugar plantations in the Caribbean, sugar island colony of Barbados
Barbados, officially the Republic of Barbados, is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies and the easternmost island of the Caribbean region. It lies on the boundary of the South American ...
, who brought large numbers of African slaves from that island.
New England
In New England, the Puritans created self-governing communities of religious congregations of farmers, or Yeoman, yeomen, and their families. High-level politicians gave out plots of land to settlers, or proprietors, who then divided the land amongst themselves. Large portions were usually given to men of higher social standing, but every man who wasn't indentured or criminally bonded had enough land to support a family. Every male citizen had a voice in the town meeting. The town meeting levied taxes, built roads, and elected officials who managed town affairs. The towns did not have courts; that was a function of the county, whose officials were appointed by the state government.
The Congregational church which the Puritans founded was not automatically joined by all New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
residents because of Puritan beliefs that God singled out specific people for salvation. Instead, membership was limited to those who could convincingly "test" before members of the church that they had been saved. They were known as "the elect" or "Saints."
In 1652, the Massachusetts General Court authorized Boston silversmith John Hull (merchant), John Hull to produce pine tree shilling, local coinage in shilling, sixpence and threepence denominations to address a coin shortage in the colony. To that point, the colony's economy had been entirely dependent on barter and foreign currency, including English, Spanish, Dutch, Portuguese, and counterfeit coins. In 1661 after the Stuart Restoration, restoration of the monarchy, the English government considered the Boston mint to be treasonous. However, the colony ignored the English demands to cease operations until at least 1682, when Hull's contract as mintmaster expired, and the colony did not move to renew his contract or appoint a new mintmaster. The coinage was a contributing factor to the revocation of the Massachusetts Bay Colony charter in 1684.
Farm and family life
 A majority of
A majority of New England
New England is a region consisting of six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the ...
residents were small farmers. A man had complete power over the property within these small farm families. When married, an English woman gave up her maiden name. The role of wives was to raise and nurture healthy children and support their husbands. Most women carried out these duties. During the 18th century, couples usually married between the ages of 20–24, and 6–8 children were typical of a family, with three on average surviving to adulthood. Farm women provided most of the materials needed by the rest of the family by spinning yarn from wool and knitting sweaters and stockings, making candles and soap from ashes, and churning milk into butter.
Most New England parents tried to help their sons establish farms of their own. When sons married, fathers gave them gifts of land, livestock, or farming equipment; daughters received household goods, farm animals, or cash. Arranged marriages were very unusual; normally, children chose their own spouses from within a circle of suitable acquaintances who shared their race, religion, and social standing. Parents retained veto power over their children's marriages.
By the middle of the 18th century, New England's population had grown dramatically, going from about 100,000 people in 1700 to 250,000 in 1725 and 375,000 in 1750 thanks to high birth rates and relatively high overall life expectancy. (A 15-year-old boy in 1700 could expect to live to about 63.) Colonists in Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island continued to subdivide their land between farmers; the farms became too small to support single families, and this threatened the New England ideal of a society of independent yeoman farmers.
Some farmers obtained land grants to create farms in undeveloped land in Province of Massachusetts, Massachusetts and Connecticut
Connecticut ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the south. ...
or bought plots of land from speculators in New Hampshire
New Hampshire ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders Massachusetts to the south, Vermont to the west, Maine and the Gulf of Maine to the east, and the Canadian province of Quebec t ...
in what later became Vermont. Other farmers became agricultural innovators. They planted nutritious English grass such as Trifolium pratense, red clover and Timothy (grass), timothy-grass, which provided more feed for livestock, and potatoes, which provided a high production rate that was an advantage for small farms. Families increased their productivity by exchanging goods and labor with each other. They lent livestock and grazing land to one another and worked together to spin yarn, sew quilts, and shuck corn. Migration, agricultural innovation, and economic cooperation were creative measures that preserved New England's yeoman society until the 19th century.
Dwellings and material culture
 New England farming families generally lived in wooden houses because of the abundance of trees. A typical New England farmhouse was one-and-a-half stories tall and had a strong frame (usually made of large square timbers) that was covered by wooden clapboard siding. A large chimney stood in the middle of the house that provided cooking facilities and warmth during the winter. One side of the ground floor contained a hall, a general-purpose room where the family worked and ate meals. Adjacent to the hall was the parlor, a room used to entertain guests that contained the family's best furnishings and the parents' bed. Children slept in a loft above, while the kitchen was either part of the hall or was located in a shed along the back of the house. Colonial families were large, and these small dwellings had much activity and there was little privacy.
The furniture of the time was very basic, common household items include a trestle table, benches and stools, while chairs were rare. Bed frame, Bedsteads were expensive which lead to their rarity, so most people slept on mats, which were rolled up when not in use. People kept items in simple-made chests. The wealthy had larger bound chests including locks and cabinets, cupboards and dressers. The latter were used to store cups and cooking utensils. Glass-made items were also rare. For drinking cups, leather jacks and bombards were common.
New England farming families generally lived in wooden houses because of the abundance of trees. A typical New England farmhouse was one-and-a-half stories tall and had a strong frame (usually made of large square timbers) that was covered by wooden clapboard siding. A large chimney stood in the middle of the house that provided cooking facilities and warmth during the winter. One side of the ground floor contained a hall, a general-purpose room where the family worked and ate meals. Adjacent to the hall was the parlor, a room used to entertain guests that contained the family's best furnishings and the parents' bed. Children slept in a loft above, while the kitchen was either part of the hall or was located in a shed along the back of the house. Colonial families were large, and these small dwellings had much activity and there was little privacy.
The furniture of the time was very basic, common household items include a trestle table, benches and stools, while chairs were rare. Bed frame, Bedsteads were expensive which lead to their rarity, so most people slept on mats, which were rolled up when not in use. People kept items in simple-made chests. The wealthy had larger bound chests including locks and cabinets, cupboards and dressers. The latter were used to store cups and cooking utensils. Glass-made items were also rare. For drinking cups, leather jacks and bombards were common.
Town life
By the mid-18th century in New England, shipbuilding was a staple, particularly as the North American wilderness offered a seemingly endless supply of timber. The British crown often turned to the inexpensive yet strongly built American ships. There was a shipyard at the mouth of almost every river in New England.
By 1750, a variety of artisans, shopkeepers, and merchants provided services to the growing farming population. Blacksmiths, wheelwrights, and furniture makers set up shops in Rural areas in the United States, rural villages. There they built and repaired goods needed by farm families. Stores were set up by traders selling English manufactures such as cloth, iron utensils, and window glass, as well as West Indies, West Indian products such as sugar and molasses. The storekeepers of these shops sold their imported goods in exchange for crops and other local products, including roof shingles, potash, and barrel staves. These local goods were shipped to towns and cities all along the Atlantic Coast. Enterprising men set up stables and taverns along wagon roads to serve this transportation system.
These products were delivered to port towns such as Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
and Salem, Massachusetts, Salem in Massachusetts, New Haven, Connecticut, New Haven in Connecticut, and Newport, Rhode Island, Newport and Providence, Rhode Island, Providence in Rhode Island. Merchants then exported them to the West Indies, where they were traded for molasses, sugar, gold coins, and bills of exchange, also known as credit slips. They carried the West Indian products to New England factories, where the raw sugar was turned into granulated sugar and the molasses distilled into rum. The gold and credit slips were sent to England where they were exchanged for manufactures, which were shipped back to the colonies and sold along with the sugar and rum to farmers.
Other New England merchants took advantage of the rich fishing areas along the Atlantic Coast and financed a large fishing fleet, transporting its catch of mackerel and cod to the West Indies and Europe. Some merchants exploited the vast amounts of timber along the coasts and rivers of northern New England. They funded sawmills that supplied cheap wood for houses and shipbuilding. Hundreds of New England shipwrights built oceangoing ships, which they sold to British and American merchants.
Many merchants became very wealthy by providing their goods to the agricultural population, and ended up dominating the society of sea port cities. Unlike yeoman farmhouses, these merchants lived in elegant -story houses designed in the new Georgian style, imitating the lifestyle of the upper class of England. These Georgian houses had symmetrical façades with equal numbers of windows on both sides of the central door. The interior consisted of a passageway down the middle of the house with specialized rooms off the sides, such as a library, dining room, formal parlor, and master bedroom. Unlike the multi-purpose space of the yeoman houses, each of these rooms served a separate purpose. These houses contained bedrooms on the second floor that provided privacy to parents and children.
Culture and education
Education was primarily the responsibility of families, but numerous religious groups established tax-supported elementary schools, especially the Puritans in New England, so that their children could read the Bible. Nearly all the religious denominations set up their own schools and colleges to train ministers. Each city and most towns had private academies for the children of affluent families.
The practical sciences were of great interest to colonial Americans, who were engaged in the process of taming and settling a wild frontier country. The mainstream of intellectual activity in the colonies was on technological and engineering developments rather than more abstract topics such as politics or metaphysics. American scientific activity was pursued by such people as:
* David Rittenhouse, who constructed the first planetarium in the Western Hemisphere
* New York lieutenant governor Cadwallader Colden, botanist and anthropologist
* Benjamin Rush, physician, social reformer, and member of the American Philosophical Society
* Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, political philosopher.#britannica, Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the m ...
, founder of the American Philosophical Society who contributed important discoveries to physics such as electricity, but was more successful in his practical inventions, including stoves and lightning rods
The arts in colonial America were not as successful as the sciences. Literature in the European sense was nearly nonexistent, with histories being far more noteworthy. These included ''The History and present State of Virginia'' (1705) by Robert Beverley Jr., Robert Beverly and ''History of the Dividing Line'' (1728–29) by William Byrd, which was not published until a century later. Instead, the newspaper was the principal form of reading material. Printing was expensive, and most publications focused on purely practical matters, such as major news, advertisements, and business reports. Almanacs were very popular, also, Benjamin Franklin's ''Poor Richard's Almanack'' being the most famous. Literary magazines appeared at mid-century, but few were profitable and most went out of business after only a few years. American publications never approached the intellectual quality of European writers, but they were much more widespread and achieved a greater readership than anything produced by Voltaire, Locke, or Rousseau.
New Englanders wrote journals, pamphlets, books, and especially sermons, which exceeded those written by all other colonies combined. Boston
Boston is the capital and most populous city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts in the United States. The city serves as the cultural and Financial centre, financial center of New England, a region of the Northeas ...
minister Cotton Mather published ''Magnalia Christi Americana'' (''The Great Works of Christ in America'', 1702), and revivalist Jonathan Edwards wrote his philosophical work ''A Careful and Strict Enquiry Into...Notions of...Freedom of Will...'' (1754). Most music had a religious theme, as well, and was mainly the singing of Psalms. Because of New England's deep religious beliefs, artistic works that were insufficiently religious or too "worldly" were banned, especially the theater. The leading theologian and philosopher of the colonial era was Jonathan Edwards of Massachusetts, an interpreter of Calvinism and the leader of the First Great Awakening.
Art and drama were somewhat more successful than literature. Benjamin West was a noteworthy painter of historical subjects, and two first-rate portrait painters emerged in John Singleton Copley, John Copley and Gilbert Stuart, yet all three men spent much of their lives in London. Theater was more developed in the Southern colonies, especially South Carolina, but nowhere did stage works attain the level of Europe. Puritans in New England and Quakers in Pennsylvania opposed theatrical performances as immoral and ungodly.
Elementary education was widespread in New England. Early Puritan settlers believed that it was necessary to study the Bible, so children were taught to read at an early age. It was also required that each town pay for a primary school. About 10 percent enjoyed secondary schooling and funded grammar schools in larger towns. Most boys learned skills from their fathers on the farm or as apprentices to artisans. Few girls attended formal schools, but most were able to get some education at home or at so-called "Dame schools" where women taught basic reading and writing skills in their own houses. By 1750, nearly 90% of New England's women and almost all of its men could read and write.
Puritans founded Harvard College in Cambridge, Massachusetts in 1636 and, later, Yale College in New Haven, Connecticut in 1701. Later, Baptists founded Rhode Island College, which is now Brown University, in Providence, Rhode Island in 1764 and Congregational church, Congregationalists established Dartmouth College in Hanover, New Hampshire in 1769. Virginia founded the College of William & Mary, College of William and Mary in 1693; it was primarily Anglican. The colleges were designed for aspiring ministers, lawyers, or doctors. Every student shared the same curriculum, which focused on Latin and Greek, mathematics, and history, philosophy, logic, ethics, rhetoric, oratory, and a little basic science. There were no separate seminaries, law schools, or divinity schools. The first medical schools were founded late in the colonial era in Philadelphia and New York.
Delaware Valley and Mid-Atlantic region
Unlike New England, the Mid-Atlantic region gained much of its population from new immigration and, by 1750, the combined populations of New York, New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
, and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania, officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a U.S. state, state spanning the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern United States, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes region, Great Lakes regions o ...
had reached nearly 300,000 people. By 1750, about 60,000 Irish and 50,000 German Americans, Germans came to live in British North America, many of them settling in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region. William Penn
William Penn ( – ) was an English writer, religious thinker, and influential Quakers, Quaker who founded the Province of Pennsylvania during the British colonization of the Americas, British colonial era. An advocate of democracy and religi ...
founded the colony of Pennsylvania in 1682, and attracted an influx of British Quakers
Quakers are people who belong to the Religious Society of Friends, a historically Protestantism, Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations. Members refer to each other as Friends after in the Bible, and originally ...
with his policies of religious liberty and freehold ownership. The first major influx of settlers were the Scotch Irish, who headed to the frontier. Many Germans came to escape the religious conflicts and declining economic opportunities in Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It lies between the Baltic Sea and the North Sea to the north and the Alps to the south. Its sixteen States of Germany, constituent states have a total popu ...
and Switzerland.
Thousands of poor German farmers, chiefly from the Palatinate (region), Palatine region in Germany, migrated to upstate districts after 1700. They largely kept to themselves, married their own, spoke German language, German, attended Lutheranism, Lutheran churches, and retained their own customs and foods. They emphasized farm ownership. Some mastered English to become conversant with local legal and business opportunities. They ignored the Indians and tolerated slavery, although few were rich enough to own a slave.
Ways of life
 Much of the architecture of the Middle Colonies reflects the diversity of its people. In Albany and
Much of the architecture of the Middle Colonies reflects the diversity of its people. In Albany and New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
, a majority of the buildings were Dutch style with brick exteriors and high gables at each end, while many Dutch churches were octagonal. German and Welsh settlers in Pennsylvania used cut stone to build their houses, following the way of their homeland and completely ignoring the plethora of timber in the area. An example of this would be Germantown, Philadelphia, Germantown, Pennsylvania where 80 percent of the buildings in the town were made entirely of stone. On the other hand, settlers from Ireland took advantage of America's ample supply of timber and constructed sturdy log cabin
A log cabin is a small log house, especially a minimally finished or less architecturally sophisticated structure. Log cabins have an ancient history in Europe, and in America are often associated with first-generation home building by settl ...
s.
Ethnic cultures also affected styles of furniture. Rural Quakers preferred simple designs in furnishings such as tables, chairs, and chests, and shunned elaborate decorations. However, some urban Quakers had much more elaborate furniture. The city of Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
became a major center of furniture-making because of its massive wealth from Quaker and British merchants. Philadelphian cabinet makers built elegant desks and Tallboy (furniture), highboys. German artisans created intricately carved designs on their chests and other furniture, with painted scenes of flowers and birds. German potters also crafted a large array of jugs, pots, and plates of both elegant and traditional design.
By the time of the Revolutionary War, approximately 85 percent of white Americans were of English, Irish, Welsh, or Scottish descent. Approximately 8.8 percent of whites were of German ancestry, and 3.5 percent were of Dutch origin.
Farming
Ethnicity made a difference in agricultural practice. This can be seen where German farmers generally preferred oxen rather than horses to pull their plows, while Scotch-Irish Americans, Scots-Irish established a farming economy based on hogs and corn. Eventually, cows were brought with the horses. Almost all the farms had cows on their land. In Ireland, people farmed intensively, working small pieces of land trying to get the largest possible production rate from their crops. In the American colonies, settlers from Northern Ireland focused on mixed farming. Using this technique, they grew corn for human consumption and as feed for hogs and other livestock. Many improvement-minded farmers of all different backgrounds began using new agricultural practices to raise their output. During the 1750s, these agricultural innovators replaced the hand sickles and scythes used to harvest hay, wheat, and barley with the cradle scythe, a tool with wooden fingers that arranged the stalks of grain for easy collection. This tool was able to triple the amount of work done by farmers in one day. Farmers also began fertilizing their fields with dung and Agricultural lime, lime and crop rotation, rotating their crops to keep the soil fertile. By 1700, Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
was exporting 350,000 bushels of wheat and 18,000 tons of flour annually. The Southern colonies in particular relied on cash crops such as tobacco and cotton. South Carolina produced rice and indigo. North Carolina was somewhat less involved in the plantation economy, but because a major producer of naval stores. Virginia and Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
came to be almost totally dependent on tobacco, which would ultimately prove fatal at the end of the 18th century thanks to exhausted soil and collapsing prices, but for most of the century, the soil remained good and a single-crop economy profitable.
Before 1720, most colonists in the mid-Atlantic region worked with small-scale farming and paid for imported manufactures by supplying the West Indies with corn and flour. In New York, a fur-pelt export trade to Europe flourished adding additional wealth to the region. After 1720, mid-Atlantic farming stimulated with the international demand for wheat. A massive population explosion in Europe brought wheat prices up. By 1770, a bushel of wheat cost twice as much as it did in 1720. Farmers also expanded their production of Flax, flax seed and corn since flax was a high demand in the Irish linen industry and a demand for corn existed in the West Indies. Thus, by mid-century, most colonial farming was a commercial venture, although subsistence agriculture continued to exist in New England and the middle colonies. Some immigrants who just arrived purchased farms and shared in this export wealth, but many poor German and Irish immigrants were forced to work as agricultural wage laborers. Merchants and artisans also hired these homeless workers for a domestic system for the manufacture of cloth and other goods. Merchants often bought wool and flax from farmers and employed newly arrived immigrants, who had been textile workers in Ireland and Germany, to work in their homes spinning the materials into yarn and cloth. Large farmers and merchants became wealthy, while farmers with smaller farms and artisans only made enough for subsistence. The Mid-Atlantic region, by 1750, was divided by both ethnic background and wealth.
Seaports
Seaports that expanded from the wheat trade had more social classes than anywhere else in the Middle Colonies. By 1773, the population of the three largest cities had grown: Philadelphia
Philadelphia ( ), colloquially referred to as Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, most populous city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania and the List of United States cities by population, sixth-most populous city in the Unit ...
reached 40,000, New York City
New York, often called New York City (NYC), is the most populous city in the United States, located at the southern tip of New York State on one of the world's largest natural harbors. The city comprises five boroughs, each coextensive w ...
reached 25,000, and Baltimore reached 6,000. Merchants dominated seaport society, and about 40 merchants controlled half of Philadelphia's trade. Wealthy merchants in Philadelphia and New York, like their counterparts in New England, built elegant Georgian architecture, Georgian-style mansions such as those in List of houses in Fairmount Park, Fairmount Park.
Shopkeepers, artisans, shipwrights, butchers, cooper (profession), coopers, seamstresses, Shoemaking, cobblers, bakers, carpenters, masonry, masons, and many other specialized crafts made up the middle class of seaport society. Wives and husbands often worked as a team and taught their children their skills to pass it on through the family. Many of these artisans and traders made enough money to create a modest life. Laborers stood at the bottom of seaport society. These poor people worked on the docks unloading inbound vessels and loading outbound vessels with wheat, corn, and flax seed. Many of these were African American; some were free, while others were enslaved. In 1750, blacks made up about 10 percent of the population of New York and Philadelphia. Hundreds of seamen worked as sailors on merchant ships, some of whom were African American.
Southern Colonies
The Southern Colonies were mainly dominated by the wealthy planters in Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It borders the states of Virginia to its south, West Virginia to its west, Pennsylvania to its north, and Delaware to its east ...
, Virginia, and South Carolina. They owned increasingly large plantations that were worked by African slaves. Of the 650,000 inhabitants of the South in 1750, about 250,000 or 40 percent, were slaves. The plantations grew tobacco, indigo and rice for export, and raised most of their own food supplies. In addition, many small subsistence farms were family owned and operated by Plain Folk of the Old South, yeoman. Most white men owned some land, and therefore could vote.
Women in the South
Historians have paid special attention to the role of women, family, and gender in the colonial South since the social history revolution in the 1970s.[Ben Marsh, ''Georgia's Frontier Women: Female Fortunes in a Southern Colony'' (2007)]
Very few women were present in the early Chesapeake Bay, Chesapeake colonies. In 1650, estimates put Maryland's total population near 600 with fewer than 200 women present.
See also
* British North America
* Chronology of the colonization of North America
* Colonial American military history
* Credit in the Thirteen Colonies
* Cuisine of the Thirteen Colonies
* Disease in colonial America
* Early American publishers and printers
* European colonization of the Americas
* Indigenous peoples of the Americas
* List of incidents of civil unrest in Colonial North America
* List of North American settlements by year of foundation
* Political culture of the United States
* Slavery in the colonial United States
* Social history of soldiers and veterans in the United States
* Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America.
The Thirteen C ...
* United Colonies, the name for the emerging nation, 1775–1776, before independence
References
Further reading
Reference books
* , Biographies of every major figure
*
*
**
* Faragher, John Mack. ''The Encyclopedia of Colonial and Revolutionary America'' (1996
online
* Gallay, Alan, ed. ''Colonial Wars of North America, 1512–1763: An Encyclopedia'' (1996
excerpt and text search
* Gipson, Lawrence. ''The British Empire Before the American Revolution'' (15 volumes) (1936–1970), Pulitzer Prize; highly detailed discussion of every British colony in the New World
* Pencak, William. ''Historical Dictionary of Colonial America'' (2011) excerpt and text search; 400 entries; 492pp
* Taylor, Dale. ''The Writer's Guide to Everyday Life in Colonial America, 1607–1783'' (2002
excerpt and text search
* Vickers, Daniel, ed. ''A Companion to Colonial America'' (2006), long topics essays by scholars
Surveys
* Adams, James Truslow. ''The Founding of New England'' (1921). s:The Founding of New England, online
* (the standard overview in four volumes)
* Barck, Jr., and Hugh Talmage Lefler. ''Colonial America'' (2nd ed. Macmillan, 1968
online
* (online at American Council of Learned Societies, ACLS History e-book project; als
online
* Butler, Jon. ''Religion in Colonial America'' (Oxford University Press, 2000
online
* Canny, Nicholas, ed. ''The Origins of Empire: British Overseas Enterprise to the Close of the Seventeenth Century'' (1988), passim; vol 1 of "The Oxford history of the British Empire"
* Conforti, Joseph A. ''Saints and Strangers: New England in British North America'' (2006). 236pp; the latest scholarly history of New England
* Greene, Evarts Boutelle. ''Provincial America, 1690–1740'' (1905) old, comprehensive overview by schola
online
* Hoffer, Peter Charles. ''The Brave New World: A History of Early America'' (2nd ed. 2006).
* Kupperman, Karen Ordahl, ed. ''Major Problems in American Colonial History: Documents and Essays'' (1999) short excerpts from scholars and primary sources
* McNeese, Tim. ''Colonial America 1543–1763'' (2010), short survey for secondary school
online
* Marshall, P.J. and Alaine Low, eds. ''Oxford History of the British Empire, Vol. 2: The Eighteenth Century'' (Oxford UP, 1998), passim.
* Middleton, Richard and Anne Lombard. ''Colonial America: A History, 1565–1776'' (4th ed 2011), 624pp
* Nettels Curtis P. ''Roots Of American Civilization'' (1940) online 800pp; a major survey of social and cultural histor
online
* Rose, Holland et al. eds. ''The Cambridge History of the British Empire: Vol. I The old empire from the beginnings to 1783'' (1929
online
* Savelle, Max. ''Seeds of Liberty: The Genesis of the American Mind'' (1965) comprehensive survey of intellectual histor
online
* Taylor, Alan. ''American Colonies,'' (2001) survey by leading scholar; [Taylor, Alan. excerpt]
** Taylor, Alan. ''Colonial America: A Very Short Introduction'' (2012) 168pp
Special topics
*
*
online
*
* Beeman, Richard R. ''The Varieties of Political Experience in Eighteenth-Century America'' (2006
excerpt and text search
* Beer, George Louis. "British Colonial Policy, 1754–1765," ''Political Science Quarterly,'' vol 22 (March 1907) pp 1–48;
* Berkin, Carol. ''First Generations: Women in Colonial America'' (1997) 276pp
excerpt and text search
*
*
* Bradburn, Douglas M., and John C. Coombs. "Smoke and Mirrors: Reinterpreting the society and economy of the seventeenth-century Chesapeake." ''Atlantic Studies'' 3.2 (2006): 131–157; argues need to study regional tobacco cultures, trade with Caribbean, trade with the Indians, internal markets, shipbuilding, and western land development.
* Bremer, Francis J. ''The Puritan Experiment: New England Society from Bradford to Edwards'' (1995).
* Brown, Kathleen M. ''Good Wives, Nasty Wenches, and Anxious Patriarchs: Gender, Race, and Power in Colonial Virginia'' (1996) 512p
excerpt and text search
* Brown-Pérez, Kathleen A. (2017)
''By Whatever Means Necessary: The U.S. Government’s Ongoing Attempts to Remove Indigenous Peoples During an Era of Self-(De)termination''
New Diversities, 19(2), 7–23.
* Bruce, Philip A. ''Economic History of Virginia in the Seventeenth Century: An Inquiry into the Material Condition of the People, Based on Original and Contemporaneous Records.'' (1896), very old fashioned history
* Carr, Lois Green and Philip D. Morgan. ''Colonial Chesapeake Society'' (1991), 524pp
excerpt and text search
*
*
* Curran, Robert Emmett. ''Papist Devils: Catholics in British America, 1574–1783'' (2014)
* Daniels, Bruce C. "Economic Development in Colonial and Revolutionary Connecticut: An Overview," ''William and Mary Quarterly'' (1980) 37#3 pp. 429–450 ]
* Daniel, Bruce. ''Puritans at Play: Leisure and Recreation in Colonial New England'' (1996
excerpt
* David Hackett Fischer, Fischer, David Hackett. ''Albion's Seed: Four British Folkways in America'' (1989), comprehensive look at major ethnic group
excerpt and text search
* Fogleman, Aaron. ''Hopeful Journeys: German Immigration, Settlement, and Political Culture in Colonial America, 1717–1775'' (University of Pennsylvania Press, 1996)
* Games, Alison. ''Migration and the Origins of the English Atlantic World'' (Harvard UP, 1999).
* Hatfield, April Lee. ''Atlantic Virginia: Intercolonial Relations in the Seventeenth Century'' (2007
excerpt and text search
* Illick, Joseph E. ''Colonial Pennsylvania: A History,'' (1976
online
* Kammen, Michael. ''Colonial New York: A History,'' (1975
online
* Katz, Stanley, et al. eds. ''Colonial America: Essays in Politics and Social Development'' (6th ed. 2010), 606pp; essays by 28 leading scholar
* Kidd, Thomas S. ''The Great Awakening: The Roots of Evangelical Christianity in Colonial America'' (2009)
*
* Labaree, Benjamin Woods. ''Colonial Massachusetts: A History,'' (1979)
* Mancall, Peter C. "Pigs for Historians: Changes in the Land and Beyond" ''William and Mary Quarterly'' (2010) 67#2 pp. 347–375, covers historiography of environmental history
* Morgan, Edmund S. ''American Slavery, American Freedom: The Ordeal of Colonial Virginia'' (1975) Pulitzer Prize
* Nagl, Dominik. ''No Part of the Mother Country, but Distinct Dominions – Law, State Formation and Governance in England, Massachusetts und South Carolina, 1630–1769'' (2013
online edition
* Norton, Mary Beth. ''1774: The Long Year of Revolution'' (2020)
* Rohrer, S. Scott. ''Wandering souls : Protestant migrations in America, 1630–1865'' (2010)
* Savelle, Max. ''Empires to nations : expansion in America, 1713–1824'' (1974
online
* Savelle, Max. ''The Origins of American Diplomacy: The International History of Anglo-America, 1492–1763'' (1968
online free to borrow
* Struna, Nancy L. ''People of Prowess Sport Leisure and Labor in Early Anglo-America'' (1996
excerpt
* Tate, Thad W. ''Chesapeake in the Seventeenth Century'' (1980
excerpt and text search
* Wilson, Thomas D. ''The Ashley Cooper Plan: The Founding of Carolina and the Origins of Southern Political Culture'' (U of North Carolina Press, 2016).
* Wood, Betty. ''Slavery in Colonial America, 1619–1776'' (2005)
Military history
* Anderson, Fred. ''The War That Made America a Short History of the French and Indian War'' (2006
online
* Anderson, Fred. "A People's Army: Provincial Military Service in Massachusetts during the Seven Years' War." '' William and Mary Quarterly'' (1983) 40#4: 500–527 .
* Chartrand, René. ''Colonial American Troops 1610–1774'' (Osprey, 2002), heavily illustrated; focus on uniforms and equipment.
* Ferling, John E. ''Struggle for a continent: the wars of early America'' (1993), short scholarly summary
* Gallay, Alan. ''Colonial Wars of North America, 1512–1763: An Encyclopedia'' (Routledge, 2015).
* Grenier, John. "Warfare during the Colonial Era, 1607–1765." In ''Companion to American Military History'' ed by James C. Bradford, (2010) pp 9–21. Historiography
* Leach, Douglas Edward. ''Roots of Conflict: British Armed Forces and Colonial Americans, 1677–1763'' (Univ of North Carolina Press, 1989
online
* LePore, Jill. ''In the Name of War: King Philip's War and the Origins of American Identity'' (Knopf, 1998)
* Pargellis, Stanley McCrory. "Braddock’s Defeat", ''American Historical Review'' 41 (1936): 253–269.
* Peckham, Howard H. ''The Colonial Wars, 1689–1762'' (1964
online
Primary sources
* Kavenagh, W. Keith, ed. ''Foundations of Colonial America: A Documentary History'' (1973) 4 vol. 22
* Ulrich Bonnell Phillips, Phillips, Ulrich B. ''Plantation and Frontier Documents, 1649–1863; Illustrative of Industrial History in the Colonial and Antebellum South: Collected from MSS. and Other Rare Sources.'' 2 Volumes. (1909)
vol 1 & 2 online edition
* Rushforth, Brett, Paul Mapp, and Alan Taylor, eds. ''North America and the Atlantic World: A History in Documents'' (2008)
* Sarson, Steven, and Jack P. Greene, eds. ''The American Colonies and the British Empire, 1607–1783'' (8 vol, 2010); primary sources
Online sources
at Thayer's American History site
*
Colonial North America
Worlds of Change: Colonial North America at Harvard Library
External links
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20100307180656/http://www.history.com/topics/colonial-culture Colonial American Culture]
*
*
{{Authority control
Colonization history of the United States,
Eras of United States history
European colonization of North America, United States
History of the Thirteen Colonies
History of the United States by topic
 Spanish explorers sailed along the coast of present-day
Spanish explorers sailed along the coast of present-day  The Italian explorer Enrico Tonti, together with the French explorer
The Italian explorer Enrico Tonti, together with the French explorer  ''Nieuw-Nederland'', or New Netherland, was a colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered in 1614, in what became New York,
''Nieuw-Nederland'', or New Netherland, was a colonial province of the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands chartered in 1614, in what became New York,  England made its first successful efforts at the start of the 17th century for several reasons. During this era, English proto-nationalism and national assertiveness blossomed under the threat of Spanish invasion, assisted by a degree of Protestant militarism and the energy of Queen Elizabeth. At this time, however, there was no official attempt by the English government to create a colonial empire. Rather the motivation behind the founding of colonies was piecemeal and variable. Practical considerations played their parts, such as commercial enterprise, over-crowding, and the desire for freedom of religion. The main waves of settlement came in the 17th century. After 1700, most immigrants to Colonial America arrived as
England made its first successful efforts at the start of the 17th century for several reasons. During this era, English proto-nationalism and national assertiveness blossomed under the threat of Spanish invasion, assisted by a degree of Protestant militarism and the energy of Queen Elizabeth. At this time, however, there was no official attempt by the English government to create a colonial empire. Rather the motivation behind the founding of colonies was piecemeal and variable. Practical considerations played their parts, such as commercial enterprise, over-crowding, and the desire for freedom of religion. The main waves of settlement came in the 17th century. After 1700, most immigrants to Colonial America arrived as  Efforts began as early as the 1640s toward a common defense of the colonies, principally against shared threats from Indians, the French, and the Dutch. The Puritan colonies of New England formed a confederation to coordinate military and judicial matters. From the 1670s, several royal governors attempted to find means of coordinating defensive and offensive military matters, notably Sir Edmund Andros (who governed New York, New England, and Virginia at various times) and Francis Nicholson (governed Maryland, Virginia, Nova Scotia, and Carolina). After King Phillips War, Andros successfully negotiated the Covenant Chain, a series of Indian treaties that brought relative calm to the frontiers of the middle colonies for many years.
The northern colonies experienced numerous assaults from the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French from
Efforts began as early as the 1640s toward a common defense of the colonies, principally against shared threats from Indians, the French, and the Dutch. The Puritan colonies of New England formed a confederation to coordinate military and judicial matters. From the 1670s, several royal governors attempted to find means of coordinating defensive and offensive military matters, notably Sir Edmund Andros (who governed New York, New England, and Virginia at various times) and Francis Nicholson (governed Maryland, Virginia, Nova Scotia, and Carolina). After King Phillips War, Andros successfully negotiated the Covenant Chain, a series of Indian treaties that brought relative calm to the frontiers of the middle colonies for many years.
The northern colonies experienced numerous assaults from the Wabanaki Confederacy and the French from 
 The
The  New England farming families generally lived in wooden houses because of the abundance of trees. A typical New England farmhouse was one-and-a-half stories tall and had a strong frame (usually made of large square timbers) that was covered by wooden clapboard siding. A large chimney stood in the middle of the house that provided cooking facilities and warmth during the winter. One side of the ground floor contained a hall, a general-purpose room where the family worked and ate meals. Adjacent to the hall was the parlor, a room used to entertain guests that contained the family's best furnishings and the parents' bed. Children slept in a loft above, while the kitchen was either part of the hall or was located in a shed along the back of the house. Colonial families were large, and these small dwellings had much activity and there was little privacy.
The furniture of the time was very basic, common household items include a trestle table, benches and stools, while chairs were rare. Bed frame, Bedsteads were expensive which lead to their rarity, so most people slept on mats, which were rolled up when not in use. People kept items in simple-made chests. The wealthy had larger bound chests including locks and cabinets, cupboards and dressers. The latter were used to store cups and cooking utensils. Glass-made items were also rare. For drinking cups, leather jacks and bombards were common.
New England farming families generally lived in wooden houses because of the abundance of trees. A typical New England farmhouse was one-and-a-half stories tall and had a strong frame (usually made of large square timbers) that was covered by wooden clapboard siding. A large chimney stood in the middle of the house that provided cooking facilities and warmth during the winter. One side of the ground floor contained a hall, a general-purpose room where the family worked and ate meals. Adjacent to the hall was the parlor, a room used to entertain guests that contained the family's best furnishings and the parents' bed. Children slept in a loft above, while the kitchen was either part of the hall or was located in a shed along the back of the house. Colonial families were large, and these small dwellings had much activity and there was little privacy.
The furniture of the time was very basic, common household items include a trestle table, benches and stools, while chairs were rare. Bed frame, Bedsteads were expensive which lead to their rarity, so most people slept on mats, which were rolled up when not in use. People kept items in simple-made chests. The wealthy had larger bound chests including locks and cabinets, cupboards and dressers. The latter were used to store cups and cooking utensils. Glass-made items were also rare. For drinking cups, leather jacks and bombards were common.