Engineering Physicist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Engineering is the practice of using
Engineering is the practice of using
 Engineering has existed since ancient times, when
Engineering has existed since ancient times, when
 The
The
A 13th Century Programmable Robot (Archive)
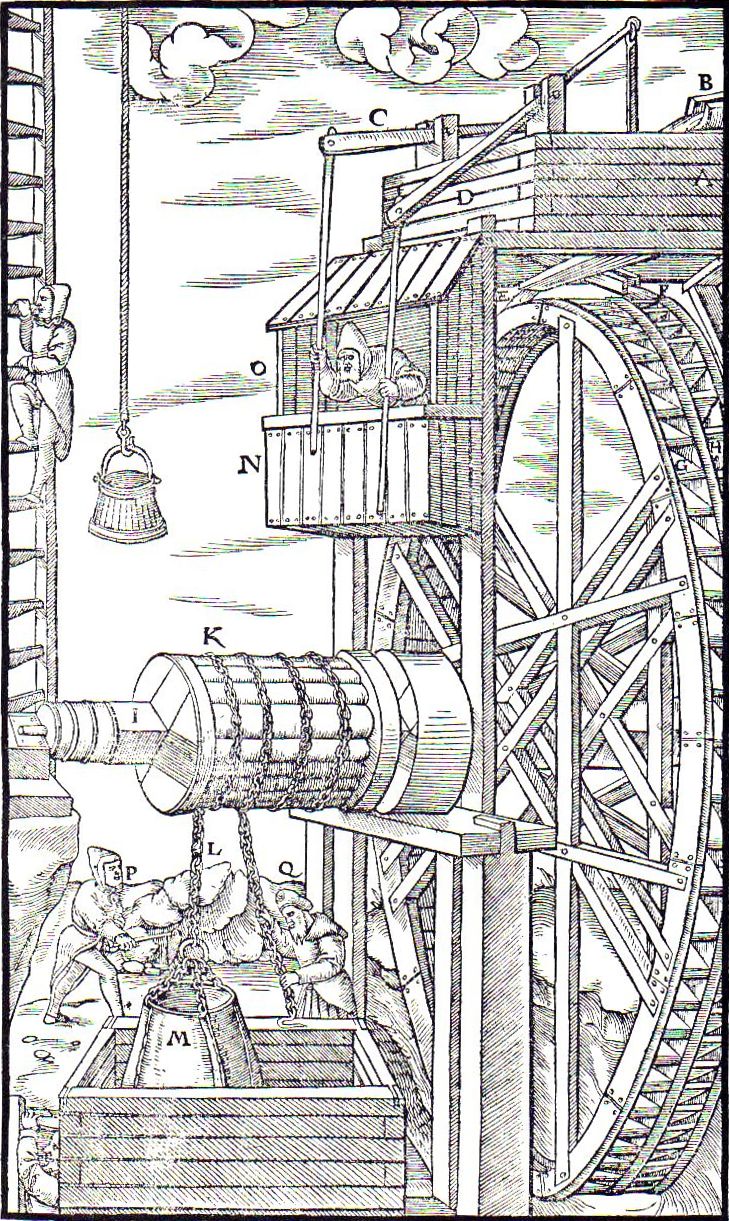 Before the development of modern engineering, mathematics was used by artisans and craftsmen, such as
Before the development of modern engineering, mathematics was used by artisans and craftsmen, such as
 The application of steam-powered cast iron blowing cylinders for providing pressurized air for
The application of steam-powered cast iron blowing cylinders for providing pressurized air for  The
The  Aeronautical engineering deals with
Aeronautical engineering deals with
 Engineering is a broad discipline that is often broken down into several sub-disciplines. Although most engineers will usually be trained in a specific discipline, some engineers become multi-disciplined through experience. Engineering is often characterized as having five main branches:The Engineering Profession
Engineering is a broad discipline that is often broken down into several sub-disciplines. Although most engineers will usually be trained in a specific discipline, some engineers become multi-disciplined through experience. Engineering is often characterized as having five main branches:The Engineering Profession
by Sir James Hamilton, UK Engineering Council Quote: "The Civilingenior degree encompasses the main branches of engineering civil, mechanical, electrical, chemical." (From the Internet Archive) chemical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering, materials science and engineering, and mechanical engineering. Below is a list of recognized branches of engineering. There are additional sub-disciplines as well.
 In the
In the
 Engineers use their knowledge of
Engineers use their knowledge of
 As with all modern scientific and technological endeavors, computers and software play an increasingly important role. As well as the typical business
As with all modern scientific and technological endeavors, computers and software play an increasingly important role. As well as the typical business  One of the most widely used
One of the most widely used
 The engineering profession engages in a range of activities, from collaboration at the societal level, and smaller individual projects. Almost all engineering projects are obligated to a funding source: a company, a set of investors, or a government. The types of engineering that are less constrained by such a funding source, are ''
The engineering profession engages in a range of activities, from collaboration at the societal level, and smaller individual projects. Almost all engineering projects are obligated to a funding source: a company, a set of investors, or a government. The types of engineering that are less constrained by such a funding source, are '' Overseas development and relief NGOs make considerable use of engineers, to apply solutions in disaster and development scenarios. Some charitable organizations use engineering directly for development:
*
Overseas development and relief NGOs make considerable use of engineers, to apply solutions in disaster and development scenarios. Some charitable organizations use engineering directly for development:
*
Engineering companies in more developed economies face challenges with regard to the number of engineers being trained, compared with those retiring. This problem is prominent in the UK where engineering has a poor image and low status. There are negative economic and political issues that this can cause, as well as ethical issues. It is agreed the engineering profession faces an "image crisis". The UK holds the most engineering companies compared to other European countries, together with the United States.
 There exists an overlap between the sciences and engineering practice; in engineering, one applies science. Both areas of endeavor rely on accurate observation of materials and phenomena. Both use mathematics and classification criteria to analyze and communicate observations.
Scientists may also have to complete engineering tasks, such as designing experimental apparatus or building prototypes. Conversely, in the process of developing technology, engineers sometimes find themselves exploring new phenomena, thus becoming, for the moment, scientists or more precisely "engineering scientists".
In the book ''
There exists an overlap between the sciences and engineering practice; in engineering, one applies science. Both areas of endeavor rely on accurate observation of materials and phenomena. Both use mathematics and classification criteria to analyze and communicate observations.
Scientists may also have to complete engineering tasks, such as designing experimental apparatus or building prototypes. Conversely, in the process of developing technology, engineers sometimes find themselves exploring new phenomena, thus becoming, for the moment, scientists or more precisely "engineering scientists".
In the book ''
 The study of the human body, albeit from different directions and for different purposes, is an important common link between medicine and some engineering disciplines.
The study of the human body, albeit from different directions and for different purposes, is an important common link between medicine and some engineering disciplines.  Modern medicine can replace several of the body's functions through the use of artificial organs and can significantly alter the function of the human body through artificial devices such as, for example,
Modern medicine can replace several of the body's functions through the use of artificial organs and can significantly alter the function of the human body through artificial devices such as, for example,
Both fields provide solutions to real world problems. This often requires moving forward before phenomena are completely understood in a more rigorous scientific sense and therefore experimentation and empirical knowledge is an integral part of both. Medicine, in part, studies the function of the human body. The human body, as a biological machine, has many functions that can be modeled using engineering methods.Royal Academy of Engineering and Academy of Medical Sciences: Systems Biology: a vision for engineering and medicine in pdf: quote1: Systems Biology is an emerging methodology that has yet to be defined quote2: It applies the concepts of systems engineering to the study of complex biological systems through iteration between computational or mathematical modelling and experimentation.
The heart for example functions much like a pump, the skeleton is like a linked structure with levers,
the brain produces electrical signals etc. These similarities as well as the increasing importance and application of engineering principles in medicine, led to the development of the field of
 There are connections between engineering and art, for example,
There are connections between engineering and art, for example,
The
Among famous historical figures,
 Engineering is the practice of using
Engineering is the practice of using natural science
Natural science or empirical science is one of the branches of science concerned with the description, understanding and prediction of natural phenomena, based on empirical evidence from observation and experimentation. Mechanisms such as peer ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, and the engineering design process
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeat ...
to solve problems within technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
, increase efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
...
and productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production proce ...
, and improve systems
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is exp ...
. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
ing and improving infrastructure
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and pri ...
, machinery
A machine is a physical system that uses power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolec ...
, vehicles
A vehicle () is a machine designed for self-propulsion, usually to transport people, cargo, or both. The term "vehicle" typically refers to land vehicles such as human-powered vehicles (e.g. bicycles, tricycles, velomobiles), animal-powered tr ...
, electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
, materials
A material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their ge ...
, and energy system
An energy system is a system primarily designed to supply #Energy-services, energy-services to end user, end-users. The intent behind energy systems is to minimise energy losses to a negligible level, as well as to ensure the efficient use of ...
s.
The discipline
Discipline is the self-control that is gained by requiring that rules or orders be obeyed, and the ability to keep working at something that is difficult. Disciplinarians believe that such self-control is of the utmost importance and enforce a ...
of engineering encompasses a broad range of more specialized fields of engineering
Engineering is the discipline and profession that applies scientific theories, mathematical methods, and empirical evidence to design, create, and analyze technological solutions, balancing technical requirements with concerns or constraints on s ...
, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
and science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
. See glossary of engineering
This glossary is split across multiple pages due to technical limitations.
By alphabetical order
* Glossary of engineering: A–L
* Glossary of engineering: M–Z
By category
* Glossary of civil engineering
* Glossary of electrical and e ...
.
The word ''engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
'' is derived from the Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
.
Definition
TheAmerican Engineers' Council for Professional Development
The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development or simply the Engineers' Council for Professional Development (ECPD), established in June 1932, was an engineering professional body dedicated to the education, accreditation, regulatio ...
(the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology
ABET (pronounced A-bet), formerly known as the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology, Inc., is a non-governmental accreditation organization for post-secondary programs in engineering, engineering technology, computing, and appli ...
aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as:
History
humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing ...
devised inventions such as the wedge
A wedge is a triangle, triangular shaped tool, a portable inclined plane, and one of the six simple machines. It can be used to separate two objects or portions of an object, lift up an object, or hold an object in place. It functions by conver ...
, lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam (structure), beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '':wikt:fulcrum, fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, l ...
, wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
and pulley
Sheave without a rope
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft enabling a taut cable or belt passing over the wheel to move and change direction, or transfer power between itself and a shaft.
A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flan ...
, etc.
The term ''engineering'' is derived from the word ''engineer'', which itself dates back to the 14th century when an ''engine'er'' (literally, one who builds or operates a ''siege engine
A siege engine is a device that is designed to break or circumvent heavy castle doors, thick city walls and other fortifications in siege warfare. Some are immobile, constructed in place to attack enemy fortifications from a distance, while othe ...
'') referred to "a constructor of military engines". In this context, now obsolete, an "engine" referred to a military machine, ''i.e.'', a mechanical contraption used in war (for example, a catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
). Notable examples of the obsolete usage which have survived to the present day are military engineering corps, ''e.g.'', the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USACE) is the military engineering branch of the United States Army. A direct reporting unit (DRU), it has three primary mission areas: Engineer Regiment, military construction, and civil wor ...
.
The word "engine" itself is of even older origin, ultimately deriving from the Latin (), meaning "innate quality, especially mental power, hence a clever invention."
Later, as the design of civilian structures, such as bridges and buildings, matured as a technical discipline, the term civil engineering
Civil engineering is a regulation and licensure in engineering, professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads ...
entered the lexicon as a way to distinguish between those specializing in the construction of such non-military projects and those involved in the discipline of military engineering
Military engineering is loosely defined as the art, science, and practice of designing and building military works and maintaining lines of military transport and military communications. Military engineers are also responsible for logistics b ...
.
Ancient era
 The
The pyramids
A pyramid () is a Nonbuilding structure, structure whose visible surfaces are triangular in broad outline and converge toward the top, making the appearance roughly a Pyramid (geometry), pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid ca ...
in ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
, ziggurats
A ziggurat (; Cuneiform: 𒅆𒂍𒉪, Akkadian (language), Akkadian: ', D-stem of ' 'to protrude, to build high', cognate with other Semitic languages like Hebrew ''zaqar'' (זָקַר) 'protrude'), (Persian language, Persian: Chogha Zanbilچغ� ...
of Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
, the Acropolis
An acropolis was the settlement of an upper part of an ancient Greek city, especially a citadel, and frequently a hill with precipitous sides, mainly chosen for purposes of defense. The term is typically used to refer to the Acropolis of Athens ...
and Parthenon
The Parthenon (; ; ) is a former Ancient Greek temple, temple on the Acropolis of Athens, Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the Greek gods, goddess Athena. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of c ...
in Greece
Greece, officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. Located on the southern tip of the Balkan peninsula, it shares land borders with Albania to the northwest, North Macedonia and Bulgaria to the north, and Turkey to th ...
, the Roman aqueduct
The Romans constructed aqueducts throughout their Republic and later Empire, to bring water from outside sources into cities and towns. Aqueduct water supplied public baths, latrines, fountains, and private households; it also supported min ...
s, Via Appia
The Appian Way (Latin and Italian: Via Appia) is one of the earliest and strategically most important Roman roads of the ancient republic. It connected Rome to Brindisi, in southeast Italy. Its importance is indicated by its common name, recor ...
and Colosseum
The Colosseum ( ; , ultimately from Ancient Greek word "kolossos" meaning a large statue or giant) is an Ellipse, elliptical amphitheatre in the centre of the city of Rome, Italy, just east of the Roman Forum. It is the largest ancient amphi ...
, Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan (; Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'', ; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City.
Teotihuacan is known today as ...
, and the Brihadeeswarar Temple
Brihadishvara Temple, called Rajarajesvaram () by its builder, and known locally as ''Thanjai Periya Kovil'' () and ''Peruvudaiyar Kovil'', is a Shaivite Hindu temple built in a Chola architectural style located on the south bank of the Cau ...
of Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art ...
, among many others, stand as a testament to the ingenuity and skill of ancient civil and military engineers. Other monuments, no longer standing, such as the Hanging Gardens of Babylon
The Hanging Gardens of Babylon were one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World listed by Hellenic culture. They were described as a remarkable feat of engineering with an ascending series of tiered gardens containing a wide variety of tree ...
and the Pharos of Alexandria
The Lighthouse of Alexandria, sometimes called the Pharos of Alexandria, was a lighthouse built by the Ptolemaic Kingdom of Ancient Egypt, during the reign of Ptolemy II Philadelphus (280–247 BC). It has been estimated to have been at least ...
, were important engineering achievements of their time and were considered among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, also known as the Seven Wonders of the World or simply the Seven Wonders, is a list of seven notable structures present during classical antiquity, first established in the 1572 publication '' Octo Mundi M ...
.
The six classic simple machines
Simple Machines was an American independent record label in Arlington, Virginia. The label was founded by Derek Denckla and Jenny Toomey and Brad Sigal while both were living in the Positive Force House in north Arlington, but Sigal and even ...
were known in the ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was home to many cradles of civilization, spanning Mesopotamia, Egypt, Iran (or Persia), Anatolia and the Armenian highlands, the Levant, and the Arabian Peninsula. As such, the fields of ancient Near East studies and Nea ...
. The wedge
A wedge is a triangle, triangular shaped tool, a portable inclined plane, and one of the six simple machines. It can be used to separate two objects or portions of an object, lift up an object, or hold an object in place. It functions by conver ...
and the inclined plane
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
(ramp) were known since prehistoric
Prehistory, also called pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the first known use of stone tools by hominins million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use o ...
times. The wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machin ...
, along with the wheel and axle
The wheel and axle is a simple machine, consisting of a wheel attached to a smaller axle so that these two parts rotate together, in which a force is transferred from one to the other. The wheel and axle can be viewed as a version of the lever, w ...
mechanism, was invented in Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia is a historical region of West Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the Fertile Crescent. Today, Mesopotamia is known as present-day Iraq and forms the eastern geographic boundary of ...
(modern Iraq) during the 5th millennium BC. The lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam (structure), beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or '':wikt:fulcrum, fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, l ...
mechanism first appeared around 5,000 years ago in the Near East
The Near East () is a transcontinental region around the Eastern Mediterranean encompassing the historical Fertile Crescent, the Levant, Anatolia, Egypt, Mesopotamia, and coastal areas of the Arabian Peninsula. The term was invented in the 20th ...
, where it was used in a simple balance scale
A scale or balance is a device used to measure weight or mass. These are also known as mass scales, weight scales, mass balances, massometers, and weight balances.
The traditional scale consists of two plates or bowls suspended at equal dis ...
, and to move large objects in ancient Egyptian technology
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the inclined plane, ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope t ...
. The lever was also used in the shadoof
A shadoof or shaduf, well pole, well sweep, sweep,Knight, Edward Henry. ''Knight's American mechanical dictionary''. Vol. 3. New York, Hurd and Houghton: Riverside Press, 1877. 2,468. Print. swape, or simply a lift is a tool that is used to lift w ...
water-lifting device, the first crane machine, which appeared in Mesopotamia , and then in ancient Egyptian technology
Ancient Egyptian technology describes devices and technologies invented or used in Ancient Egypt. The Egyptians invented and used many simple machines, such as the inclined plane, ramp and the lever, to aid construction processes. They used rope t ...
. The earliest evidence of pulley
Sheave without a rope
A pulley is a wheel on an axle or shaft enabling a taut cable or belt passing over the wheel to move and change direction, or transfer power between itself and a shaft.
A pulley may have a groove or grooves between flan ...
s date back to Mesopotamia in the early 2nd millennium BC, and ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt () was a cradle of civilization concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in Northeast Africa. It emerged from prehistoric Egypt around 3150BC (according to conventional Egyptian chronology), when Upper and Lower E ...
during the Twelfth Dynasty
The Twelfth Dynasty of ancient Egypt (Dynasty XII) is a series of rulers reigning from 1991–1802 BC (190 years), at what is often considered to be the apex of the Middle Kingdom (Dynasties XI–XIV). The dynasty periodically expanded its terr ...
(1991–1802 BC). The screw
A screw is an externally helical threaded fastener capable of being tightened or released by a twisting force (torque) to the screw head, head. The most common uses of screws are to hold objects together and there are many forms for a variety ...
, the last of the simple machines to be invented, first appeared in Mesopotamia during the Neo-Assyrian
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew to dominate the ancient Near East and parts of South Caucasus, Nort ...
period (911–609) BC. The Egyptian pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids are ancient masonry structures located in Egypt. Most were built as tombs for the pharaohs and their consorts during the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old and Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom periods. At least 138 identi ...
were built using three of the six simple machines, the inclined plane, the wedge, and the lever, to create structures like the Great Pyramid of Giza
The Great Pyramid of Giza is the largest Egyptian pyramid. It served as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu, who ruled during the Fourth Dynasty of Egypt, Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt, Old Kingdom. Built , over a period of about 26 years ...
.
The earliest civil engineer known by name is Imhotep
Imhotep (; "(the one who) comes in peace"; ) was an Egyptian chancellor to the King Djoser, possible architect of Djoser's step pyramid, and high priest of the sun god Ra at Heliopolis. Very little is known of Imhotep as a historical figur ...
. As one of the officials of the Pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian language, Egyptian: ''wikt:pr ꜥꜣ, pr ꜥꜣ''; Meroitic language, Meroitic: 𐦲𐦤𐦧, ; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') was the title of the monarch of ancient Egypt from the First Dynasty of Egypt, First Dynasty ( ...
, Djosèr, he probably designed and supervised the construction of the Pyramid of Djoser
The pyramid of Djoser, sometimes called the Step Pyramid of Djoser or Step Pyramid of Horus Netjerikhet, is an archaeological site in the Saqqara necropolis, Egypt, northwest of the ruins of Memphis.Bard, Kathryn A., and Jean-Philipee Lauer, ed ...
(the Step Pyramid
A step pyramid or stepped pyramid is an architectural structure that uses flat platforms, or steps, receding from the ground up, to achieve a completed shape similar to a geometric pyramid. Step pyramids – typically large and made of several la ...
) at Saqqara
Saqqara ( : saqqāra ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in the markaz (county) of Badrashin in the Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for ...
in Egypt around 2630–2611 BC. The earliest practical water-power
Hydropower (from Ancient Greek -, "water"), also known as water power or water energy, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or ki ...
ed machines, the water wheel
A water wheel is a machine for converting the kinetic energy of flowing or falling water into useful forms of power, often in a watermill. A water wheel consists of a large wheel (usually constructed from wood or metal), with numerous b ...
and watermill
A watermill or water mill is a mill that uses hydropower. It is a structure that uses a water wheel or water turbine to drive a mechanical process such as mill (grinding), milling (grinding), rolling, or hammering. Such processes are needed in ...
, first appeared in the Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the larg ...
, in what are now Iraq and Iran, by the early 4th century BC.
Kush
KUSH 1600 AM is a radio station licensed to Cushing, Oklahoma. The station broadcasts a Full service format, consisting of local and national talk, sports
Sport is a physical activity or game, often competitive and organized, tha ...
developed the Sakia
A sāqiyah or saqiya (), also spelled sakia or saqia) is a mechanical water lifting device. It is also called a Persian wheel, tablia, rehat, and in Latin tympanum. It is similar in function to a scoop wheel, which uses buckets, jars, or scoops ...
during the 4th century BC, which relied on animal power instead of human energy. Hafirs were developed as a type of reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of wa ...
in Kush to store and contain water as well as boost irrigation.Fritz Hintze, Kush XI; pp. 222–224. Sappers
A sapper, also called a combat engineer, is a combatant or soldier who performs a variety of military engineering duties, such as breaching fortifications, demolitions, bridge-building, laying or clearing minefields, preparing field defenses, ...
were employed to build causeways
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Tr ...
during military campaigns. Kushite ancestors built speos
The Speos Artemidos (; Grotto of Artemis) is an archaeological site in Egypt. It is located about 2 km south of the Middle Kingdom of Egypt, Middle Kingdom tombs at Beni Hasan, and about 28 km south of Al Minya, Egypt, Al Minya. Today, ...
during the Bronze Age between 3700 and 3250 BC. Bloomeries and blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure.
In a ...
s were also created during the 7th centuries BC in Kush.
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically r ...
developed machines in both civilian and military domains. The Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( , ) is an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery (model of the Solar System). It is the oldest known example of an Analog computer, analogue computer. It could be used to predict astronomy, astronomical ...
, an early known mechanical analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computation machine (computer) that uses physical phenomena such as Electrical network, electrical, Mechanics, mechanical, or Hydraulics, hydraulic quantities behaving according to the math ...
, and the mechanical inventions
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
of Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse ( ; ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek Greek mathematics, mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and Invention, inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse, Sicily, Syracuse in History of Greek and Hellenis ...
, are examples of Greek mechanical engineering. Some of Archimedes' inventions, as well as the Antikythera mechanism, required sophisticated knowledge of differential gearing or epicyclic gearing
An epicyclic gear train (also known as a planetary gearset) is a gear reduction assembly consisting of two gears mounted so that the center of one gear (the "planet") revolves around the center of the other (the "sun"). A carrier connects the ...
, two key principles in machine theory that helped design the gear train
A gear train or gear set is a machine element of a mechanical system formed by mounting two or more gears on a frame such that the teeth of the gears engage.
Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each oth ...
s of the Industrial Revolution, and are widely used in fields such as robotics
Robotics is the interdisciplinary study and practice of the design, construction, operation, and use of robots.
Within mechanical engineering, robotics is the design and construction of the physical structures of robots, while in computer s ...
and automotive engineering
Automotive engineering, along with aerospace engineering and naval architecture, is a branch of vehicle engineering, incorporating elements of Mechanical engineering, mechanical, Electrical engineering, electrical, Electronic engineering, electro ...
.
Ancient Chinese, Greek, Roman and Hunnic armies employed military machines and inventions such as artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and l ...
which was developed by the Greeks around the 4th century BC, the trireme
A trireme ( ; ; cf. ) was an ancient navies and vessels, ancient vessel and a type of galley that was used by the ancient maritime civilizations of the Mediterranean Sea, especially the Phoenicians, ancient Greece, ancient Greeks and ancient R ...
, the ballista
The ballista (Latin, from Ancient Greek, Greek βαλλίστρα ''ballistra'' and that from βάλλω ''ballō'', "throw"), plural ballistae or ballistas, sometimes called bolt thrower, was an Classical antiquity, ancient missile weapon tha ...
and the catapult
A catapult is a ballistics, ballistic device used to launch a projectile at a great distance without the aid of gunpowder or other propellants – particularly various types of ancient and medieval siege engines. A catapult uses the sudden rel ...
, the trebuchet
A trebuchet () is a type of catapult that uses a hinged arm with a sling attached to the tip to launch a projectile. It was a common powerful siege engine until the advent of gunpowder. The design of a trebuchet allows it to launch projectiles ...
by Chinese circa 6th-5th century BCE.
Middle Ages
The earliest practical wind-powered machines, thewindmill
A windmill is a machine operated by the force of wind acting on vanes or sails to mill grain (gristmills), pump water, generate electricity, or drive other machinery.
Windmills were used throughout the high medieval and early modern period ...
and wind pump
A windpump is a wind-driven device which is used for pumping water.
Windpumps were used to pump water since at least the 9th century in what is now Afghanistan, Iran and Pakistan. The use of wind pumps became widespread across the Muslim world a ...
, first appeared in the Muslim world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
during the Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of scientific, economic, and cultural flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 13th century.
This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign o ...
, in what are now Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, by the 9th century AD. The earliest practical steam-power
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs Work (physics), mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a Cylinder (locomotive), cyl ...
ed machine was a steam jack
A roasting jack is a machine which rotates meat roasting on a spit. It can also be called a spit jack, a spit engine or a turnspit, although this name can also refer to a human turning the spit, or a turnspit dog. Cooking meat on a spit dates ...
driven by a steam turbine
A steam turbine or steam turbine engine is a machine or heat engine that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work utilising a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Sir Charles Par ...
, described in 1551 by Taqi al-Din Muhammad ibn Ma'ruf
Taqi ad-Din Muhammad ibn Ma'ruf ash-Shami al-Asadi (; ; 1526–1585) was an Ottoman polymath active in Cairo and Istanbul. He was the author of more than ninety books on a wide variety of subjects, including astronomy, clocks, engineering ...
in Ottoman Egypt
Ottoman Egypt was an administrative division of the Ottoman Empire after the conquest of Mamluk Egypt by the Ottomans in 1517. The Ottomans administered Egypt as a province (''eyalet'') of their empire (). It remained formally an Ottoman prov ...
.
The cotton gin
A cotton gin—meaning "cotton engine"—is a machine that quickly and easily separates cotton fibers from their seeds, enabling much greater productivity than manual cotton separation.. Reprinted by McGraw-Hill, New York and London, 1926 (); ...
was invented in India by the 6th century AD, and the spinning wheel
A spinning wheel is a device for spinning thread or yarn from fibres. It was fundamental to the textile industry prior to the Industrial Revolution. It laid the foundations for later machinery such as the spinning jenny and spinning frame, ...
was invented in the Islamic world
The terms Islamic world and Muslim world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs, politics, and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is ...
by the early 11th century, both of which were fundamental to the growth of the cotton industry
Cotton (), first recorded in ancient India, is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure ce ...
. The spinning wheel was also a precursor to the spinning jenny
The spinning jenny is a multi- spindle spinning frame, and was one of the key developments in the industrialisation of textile manufacturing during the early Industrial Revolution. It was invented in 1764–1765 by James Hargreaves in Stan ...
, which was a key development during the early Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
in the 18th century.
The earliest programmable machines were developed in the Muslim world. A music sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling Musical note, note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open ...
, a programmable musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make Music, musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person ...
, was the earliest type of programmable machine. The first music sequencer was an automated flute
The flute is a member of a family of musical instruments in the woodwind group. Like all woodwinds, flutes are aerophones, producing sound with a vibrating column of air. Flutes produce sound when the player's air flows across an opening. In th ...
player invented by the Banu Musa
Banu or BANU may refer to:
* Banu (name)
* Banu (Arabic), Arabic word for "the sons of" or "children of"
* Banu (makeup artist), an Indian makeup artist
* Banu Chichek, a character in the ''Book of Dede Korkut''
* Bulgarian Agrarian National Union ...
brothers, described in their ''Book of Ingenious Devices
The ''Book of Ingenious Devices'' (, ) is a large illustrated work on mechanical devices, including automata, published in 850 by the three brothers of Persian descent, the Banū Mūsā brothers (Ahmad, Muhammad and Hasan ibn Musa ibn Shakir) ...
'', in the 9th century. In 1206, Al-Jazari invented programmable automata
An automaton (; : automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions. Some automata, such as bellstrikers i ...
/robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
s. He described four automaton
An automaton (; : automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions. Some automata, such as bellstrikers i ...
musicians, including drummers operated by a programmable drum machine
A drum machine is an electronic musical instrument that creates percussion sounds, drum beats, and patterns. Drum machines may imitate drum kits or other percussion instruments, or produce unique sounds, such as synthesized electronic tones. A d ...
, where they could be made to play different rhythms and different drum patterns.Professor Noel SharkeyA 13th Century Programmable Robot (Archive)
University of Sheffield
The University of Sheffield (informally Sheffield University or TUOS) is a public university, public research university in Sheffield, South Yorkshire, England. Its history traces back to the foundation of Sheffield Medical School in 1828, Fir ...
.
 Before the development of modern engineering, mathematics was used by artisans and craftsmen, such as
Before the development of modern engineering, mathematics was used by artisans and craftsmen, such as millwright
A millwright is a craftsman or skilled tradesman who installs, dismantles, maintains, repairs, reassembles, and moves machinery in factories, power plants, and construction sites.
The term ''millwright'' (also known as ''industrial mechanic'') ...
s, clockmaker
A clockmaker is an artisan who makes and/or repairs clocks. Since almost all clocks are now factory-made, most modern clockmakers only repair clocks. Modern clockmakers may be employed by jewellers, antique shops, and places devoted strictly t ...
s, instrument makers and surveyors. Aside from these professions, universities were not believed to have had much practical significance to technology.
A standard reference for the state of mechanical arts during the Renaissance is given in the mining engineering treatise '' De re metallica'' (1556), which also contains sections on geology, mining, and chemistry. ''De re metallica'' was the standard chemistry reference for the next 180 years.
Modern era
The science ofclassical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a Theoretical physics, physical theory describing the motion of objects such as projectiles, parts of Machine (mechanical), machinery, spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. The development of classical mechanics inv ...
, sometimes called Newtonian mechanics, formed the scientific basis of much of modern engineering. With the rise of engineering as a profession
A profession is a field of Work (human activity), work that has been successfully professionalized. It can be defined as a disciplined group of individuals, professionals, who adhere to ethical standards and who hold themselves out as, and are ...
in the 18th century, the term became more narrowly applied to fields in which mathematics and science were applied to these ends. Similarly, in addition to military and civil engineering, the fields then known as the mechanic arts became incorporated into engineering.
Canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface ...
building was an important engineering work during the early phases of the Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
.
John Smeaton
John Smeaton (8 June 1724 – 28 October 1792) was an English civil engineer responsible for the design of bridges, canals, harbours and lighthouses. He was also a capable mechanical engineer and an eminent scholar, who introduced various ...
was the first self-proclaimed civil engineer and is often regarded as the "father" of civil engineering. He was an English civil engineer responsible for the design of bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, whi ...
s, canals, harbor
A harbor (American English), or harbour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be moored. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is ...
s, and lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lens (optics), lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Ligh ...
s. He was also a capable mechanical engineer
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations o ...
and an eminent physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
. Using a model water wheel, Smeaton conducted experiments for seven years, determining ways to increase efficiency. Smeaton introduced iron axles and gears to water wheels. Smeaton also made mechanical improvements to the Newcomen steam engine
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is sometimes referred to as the Newcomen fire engine (see below) or Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam being drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating ...
. Smeaton designed the third Eddystone Lighthouse
The Eddystone Lighthouse is a lighthouse on the Eddystone Rocks, south of Rame Head in Cornwall, England. The rocks are submerged below the surface of the sea and are composed of Precambrian gneiss. View at 1:50000 scale
The current structu ...
(1755–59) where he pioneered the use of 'hydraulic lime
Hydraulic lime (HL) is a general term for a variety of lime different from calcium oxide (quicklime), that sets by hydration and consists of calcium silicate and calcium aluminate, compounds that can harden in contact with water. This contras ...
' (a form of mortar
Mortar may refer to:
* Mortar (weapon), an indirect-fire infantry weapon
* Mortar (masonry), a material used to fill the gaps between blocks and bind them together
* Mortar and pestle, a tool pair used to crush or grind
* Mortar, Bihar, a village i ...
which will set under water) and developed a technique involving dovetailed blocks of granite in the building of the lighthouse. He is important in the history, rediscovery of, and development of modern cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
, because he identified the compositional requirements needed to obtain "hydraulicity" in lime; work which led ultimately to the invention of Portland cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar (masonry), mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in th ...
.
Applied science led to the development of the steam engine. The sequence of events began with the invention of the barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis ...
and the measurement of atmospheric pressure by Evangelista Torricelli
Evangelista Torricelli ( ; ; 15 October 160825 October 1647) was an Italian people, Italian physicist and mathematician, and a student of Benedetto Castelli. He is best known for his invention of the barometer, but is also known for his advances i ...
in 1643, demonstration of the force of atmospheric pressure by Otto von Guericke
Otto von Guericke ( , , ; spelled Gericke until 1666; – ) was a German scientist, inventor, mathematician and physicist. His pioneering scientific work, the development of experimental methods and repeatable demonstrations on the physics of ...
using the Magdeburg hemispheres
The Magdeburg hemispheres are a pair of large copper hemispheres with mating rims that were used in a famous 1654 experiment to demonstrate the power of atmospheric pressure. When the rims were sealed with grease and the air was pumped out, the sph ...
in 1656, laboratory experiments by Denis Papin
Denis Papin FRS (; 22 August 1647 – 26 August 1713) was a French physicist, mathematician and inventor, best known for his pioneering invention of the steam digester, the forerunner of the pressure cooker, the steam engine, the centrifug ...
, who built experimental model steam engines and demonstrated the use of a piston
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder a ...
, which he published in 1707. Edward Somerset, 2nd Marquess of Worcester
Edward Somerset, 2nd Marquess of Worcester (9 March 1602 or 9 March 16033 April 1667), styled Lord Herbert of Raglan from 1628 to 1644, was an English nobleman involved in royalist politics, and an inventor.
While Earl of Glamorgan, he was ...
published a book of 100 inventions containing a method for raising waters similar to a coffee percolator
A coffee percolator is a type of pot used for the brewing of coffee by continually cycling the boiling or nearly boiling brew through the grounds (coffee), grounds using gravity until the required strength is reached. The grounds are held in a ...
. Samuel Morland
Sir Samuel Morland, 1st Baronet (1625 – 30 December 1695), or Moreland, was an English academic, diplomat, spy, inventor and mathematician of the 17th century, a polymath credited with early developments in relation to computing, hydraulic ...
, a mathematician and inventor who worked on pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
s, left notes at the Vauxhall Ordinance Office on a steam pump design that Thomas Savery
Thomas Savery (; c. 1650 – 15 May 1715) was an English inventor and engineer. He invented the first commercially used steam-powered device, a steam pump which is often referred to as the "Savery engine". Savery's steam pump was a revolutiona ...
read. In 1698 Savery built a steam pump called "The Miner's Friend". It employed both vacuum and pressure. Iron merchant Thomas Newcomen
Thomas Newcomen (; February 1664 – 5 August 1729) was an English inventor, creator of the Newcomen atmospheric engine, atmospheric engine in 1712, Baptist lay preacher, preacher by calling and ironmonger by trade.
He was born in Dart ...
, who built the first commercial piston steam engine in 1712, was not known to have any scientific training.
 The application of steam-powered cast iron blowing cylinders for providing pressurized air for
The application of steam-powered cast iron blowing cylinders for providing pressurized air for blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure.
In a ...
s lead to a large increase in iron production in the late 18th century. The higher furnace temperatures made possible with steam-powered blast allowed for the use of more lime in blast furnace
A blast furnace is a type of metallurgical furnace used for smelting to produce industrial metals, generally pig iron, but also others such as lead or copper. ''Blast'' refers to the combustion air being supplied above atmospheric pressure.
In a ...
s, which enabled the transition from charcoal to coke. These innovations lowered the cost of iron, making horse railways and iron bridges practical. The puddling process, patented by Henry Cort
Henry Cort (c. 1740 – 23 May 1800) was an English ironware producer who was formerly a Navy pay agent. During the Industrial Revolution in England, Cort began refining iron from pig iron to wrought iron (or bar iron) using innovative productio ...
in 1784 produced large scale quantities of wrought iron. Hot blast
Hot blast is the preheated air blown into a blast furnace or other metallurgical process. This technology, which considerably reduces the fuel consumed, was one of the most important technologies developed during the Industrial Revolution. Hot b ...
, patented by James Beaumont Neilson
James Beaumont Neilson (22 June 1792 – 18 January 1865) was a British inventor whose hot-blast process greatly increased the efficiency of smelting iron.
Life
He was the son of the engineer Walter Neilson, a millwright and later engine ...
in 1828, greatly lowered the amount of fuel needed to smelt iron. With the development of the high pressure steam engine, the power to weight ratio of steam engines made practical steamboats and locomotives possible. New steel making processes, such as the Bessemer process
The Bessemer process was the first inexpensive industrial process for the mass production of steel from molten pig iron before the development of the open hearth furnace. The key principle is steelmaking, removal of impurities and undesired eleme ...
and the open hearth furnace, ushered in an area of heavy engineering in the late 19th century.
One of the most famous engineers of the mid-19th century was Isambard Kingdom Brunel
Isambard Kingdom Brunel ( ; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was an English civil engineer and mechanical engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history", "one of the 19th-century engi ...
, who built railroads, dockyards and steamships.
 The
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution, sometimes divided into the First Industrial Revolution and Second Industrial Revolution, was a transitional period of the global economy toward more widespread, efficient and stable manufacturing processes, succee ...
created a demand for machinery with metal parts, which led to the development of several machine tools
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, boring, grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some sort of tool that does the cutting or shaping. All ...
. Boring cast iron cylinders with precision was not possible until John Wilkinson invented his boring machine, which is considered the first machine tool
A machine tool is a machine for handling or machining metal or other rigid materials, usually by cutting, Boring (manufacturing), boring, grinding (abrasive cutting), grinding, shearing, or other forms of deformations. Machine tools employ some s ...
. Other machine tools included the screw cutting lathe
A screw-cutting lathe is a machine (specifically, a lathe) capable of cutting very accurate screw threads via single-point screw-cutting, which is the process of guiding the linear motion of the tool bit in a precisely known ratio to the rotati ...
, milling machine
Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying directions on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of ...
, turret lathe
A turret lathe is a form of lathe (metal), metalworking lathe that is used for repetitive production of duplicate parts, which by the nature of their cutting process are usually interchangeable parts, interchangeable. It evolved from earlier lath ...
and the metal planer. Precision machining techniques were developed in the first half of the 19th century. These included the use of gigs to guide the machining tool over the work and fixtures to hold the work in the proper position. Machine tools and machining techniques capable of producing interchangeable parts
Interchangeable parts are parts (wikt:component#Noun, components) that are identical for practical purposes. They are made to specifications that ensure that they are so nearly identical that they will fit into any assembly of the same type. One ...
lead to large scale factory production by the late 19th century.
The United States Census of 1850 listed the occupation of "engineer" for the first time with a count of 2,000. There were fewer than 50 engineering graduates in the U.S. before 1865. The first PhD
A Doctor of Philosophy (PhD, DPhil; or ) is a terminal degree that usually denotes the highest level of academic achievement in a given discipline and is awarded following a course of graduate study and original research. The name of the deg ...
in engineering (technically, ''applied science and engineering'') awarded in the United States went to Josiah Willard Gibbs
Josiah Willard Gibbs (; February 11, 1839 – April 28, 1903) was an American mechanical engineer and scientist who made fundamental theoretical contributions to physics, chemistry, and mathematics. His work on the applications of thermodynami ...
at Yale University
Yale University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in New Haven, Connecticut, United States. Founded in 1701, Yale is the List of Colonial Colleges, third-oldest institution of higher education in the United Stat ...
in 1863; it was also the second PhD awarded in science in the U.S. In 1870 there were a dozen U.S. mechanical engineering graduates, with that number increasing to 43 per year in 1875. In 1890, there were 6,000 engineers in civil, mining
Mining is the Resource extraction, extraction of valuable geological materials and minerals from the surface of the Earth. Mining is required to obtain most materials that cannot be grown through agriculture, agricultural processes, or feasib ...
, mechanical and electrical. There was no chair of applied mechanism and applied mechanics at Cambridge until 1875, and no chair of engineering at Oxford until 1907. Germany established technical universities earlier.
The foundations of electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is an engineering discipline concerned with the study, design, and application of equipment, devices, and systems that use electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It emerged as an identifiable occupation in the l ...
in the 1800s included the experiments of Alessandro Volta
Alessandro Giuseppe Antonio Anastasio Volta (, ; ; 18 February 1745 – 5 March 1827) was an Italian chemist and physicist who was a pioneer of electricity and Power (physics), power, and is credited as the inventor of the electric battery a ...
, Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday (; 22 September 1791 – 25 August 1867) was an English chemist and physicist who contributed to the study of electrochemistry and electromagnetism. His main discoveries include the principles underlying electromagnetic inducti ...
, Georg Ohm
Georg Simon Ohm (; ; 16 March 1789 – 6 July 1854) was a German mathematician and physicist. As a school teacher, Ohm began his research with the new electrochemical cell, invented by Italian scientist Alessandro Volta. Using equipment of his o ...
and others and the invention of the electric telegraph
Electrical telegraphy is Point-to-point (telecommunications), point-to-point distance communicating via sending electric signals over wire, a system primarily used from the 1840s until the late 20th century. It was the first electrical telecom ...
in 1816 and the electric motor
An electric motor is a machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a electromagnetic coil, wire winding to gene ...
in 1872. The theoretical work of James Maxwell (see: Maxwell's equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, Electrical network, electr ...
) and Heinrich Hertz
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz (; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism.
Biography
Heinri ...
in the late 19th century gave rise to the field of electronics
Electronics is a scientific and engineering discipline that studies and applies the principles of physics to design, create, and operate devices that manipulate electrons and other Electric charge, electrically charged particles. It is a subfield ...
. The later inventions of the vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
and the transistor
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electric power, power. It is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semicondu ...
further accelerated the development of electronics to such an extent that electrical and electronics engineers currently outnumber their colleagues of any other engineering specialty.
Chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of the operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials ...
developed in the late nineteenth century. Industrial scale manufacturing demanded new materials and new processes and by 1880 the need for large scale production of chemicals was such that a new industry was created, dedicated to the development and large scale manufacturing of chemicals in new industrial plants. The role of the chemical engineer was the design of these chemical plants and processes. Originally deriving from the manufacture of ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant, and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcela ...
s and its putative derivative metallurgy, materials science is one of the oldest forms of engineering. Modern materials science evolved directly from metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the ...
, which itself evolved from the use of fire. Important elements of modern materials science were products of the Space Race
The Space Race (, ) was a 20th-century competition between the Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between t ...
; the understanding and engineering of the metallic alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which in most cases at least one is a metal, metallic element, although it is also sometimes used for mixtures of elements; herein only metallic alloys are described. Metallic alloys often have prop ...
s, and silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
and carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalence, tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 ...
materials, used in building space vehicles enabling the exploration of space. Materials science has driven, and been driven by, the development of revolutionary technologies such as rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds.
Types of polyisoprene ...
s, plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding ...
s, semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping level ...
s, and biomaterial
A biomaterial is a substance that has been Biological engineering, engineered to interact with biological systems for a medical purpose – either a therapeutic (treat, augment, repair, or replace a tissue function of the body) or a Medical diag ...
s.
 Aeronautical engineering deals with
Aeronautical engineering deals with aircraft design process
The aircraft design process is a loosely defined method used to balance many competing and demanding requirements to produce an aircraft that is strong, lightweight, economical and can carry an adequate payload while being sufficiently reliable to ...
design while aerospace engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is s ...
is a more modern term that expands the reach of the discipline by including spacecraft
A spacecraft is a vehicle that is designed spaceflight, to fly and operate in outer space. Spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth observation, Weather s ...
design. Its origins can be traced back to the aviation pioneers around the start of the 20th century although the work of Sir George Cayley
Sir George Cayley, 6th Baronet (27 December 1773 – 15 December 1857) was an English engineer, inventor, and aviator. He is one of the most important people in the history of aeronautics. Many consider him to be the first true scientific ae ...
has recently been dated as being from the last decade of the 18th century. Early knowledge of aeronautical engineering was largely empirical with some concepts and skills imported from other branches of engineering. Only a decade
A decade (from , , ) is a period of 10 years. Decades may describe any 10-year period, such as those of a person's life, or refer to specific groupings of calendar years.
Usage
Any period of ten years is a "decade". For example, the statement ...
after the successful flights by the Wright brothers
The Wright brothers, Orville Wright (August 19, 1871 – January 30, 1948) and Wilbur Wright (April 16, 1867 – May 30, 1912), were American aviation List of aviation pioneers, pioneers generally credited with inventing, building, and flyin ...
, there was extensive development of aeronautical engineering through development of military aircraft that were used in World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
. Meanwhile, research to provide fundamental background science continued by combining theoretical physics
Theoretical physics is a branch of physics that employs mathematical models and abstractions of physical objects and systems to rationalize, explain, and predict List of natural phenomena, natural phenomena. This is in contrast to experimental p ...
with experiments.
Branches of engineering
 Engineering is a broad discipline that is often broken down into several sub-disciplines. Although most engineers will usually be trained in a specific discipline, some engineers become multi-disciplined through experience. Engineering is often characterized as having five main branches:The Engineering Profession
Engineering is a broad discipline that is often broken down into several sub-disciplines. Although most engineers will usually be trained in a specific discipline, some engineers become multi-disciplined through experience. Engineering is often characterized as having five main branches:The Engineering Professionby Sir James Hamilton, UK Engineering Council Quote: "The Civilingenior degree encompasses the main branches of engineering civil, mechanical, electrical, chemical." (From the Internet Archive) chemical engineering, civil engineering, electrical engineering, materials science and engineering, and mechanical engineering. Below is a list of recognized branches of engineering. There are additional sub-disciplines as well.
Interdisciplinary engineering
Interdisciplinary engineering draws from more than one of the principle branches of the practice. Historically,naval engineering
Naval architecture, or naval engineering, is an engineering discipline incorporating elements of mechanical, electrical, electronic, software and safety engineering as applied to the engineering design process, shipbuilding, maintenance, and op ...
and mining engineering
Mining engineering is the extraction of minerals from the ground. It is associated with many other disciplines, such as mineral processing, exploration, excavation, geology, metallurgy, geotechnical engineering and surveying. A mining engineer m ...
were major branches. Other engineering fields are manufacturing engineering
Manufacturing engineering or production engineering is a branch of professional engineering that shares many common concepts and ideas with other fields of engineering such as mechanical, chemical, electrical, and industrial engineering.
Manufac ...
, acoustical engineering
Acoustical engineering (also known as acoustic engineering) is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typical ...
, corrosion engineering
Corrosion engineering is an engineering specialty that applies scientific, technical, engineering skills, and knowledge of natural laws and physical resources to design and implement materials, structures, devices, systems, and procedures to mana ...
, instrumentation and control, automotive, information engineering
Information engineering is the engineering discipline that deals with the generation, distribution, analysis, and use of information, data, and knowledge in electrical systems. The field first became identifiable in the early 21st century.
Th ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil or simply oil, is a naturally occurring, yellowish-black liquid chemical mixture found in geological formations, consisting mainly of hydrocarbons. The term ''petroleum'' refers both to naturally occurring un ...
, systems
A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is exp ...
, audio
Audio most commonly refers to sound, as it is transmitted in signal form. It may also refer to:
Sound
*Audio signal, an electrical representation of sound
*Audio frequency, a frequency in the audio spectrum
*Digital audio, representation of sound ...
, software
Software consists of computer programs that instruct the Execution (computing), execution of a computer. Software also includes design documents and specifications.
The history of software is closely tied to the development of digital comput ...
, architectural
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, biosystems
''BioSystems'' is a monthly peer review, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering experimental, computational, and theoretical research that links biology, evolution, and the Information processing (psychology), information processing sciences. ...
, and textile
Textile is an Hyponymy and hypernymy, umbrella term that includes various Fiber, fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, Staple (textiles)#Filament fiber, filaments, Thread (yarn), threads, and different types of #Fabric, fabric. ...
engineering
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, s ...
. These and other branches of engineering are represented in the 36 licensed member institutions of the UK Engineering Council
The Engineering Council (formerly Engineering Council UK; colloquially known as EngC) is the UK's regulatory authority for registration of Chartered and Incorporated engineers and engineering technician. The Engineering Council holds the nat ...
.
New specialties sometimes combine with the traditional fields and form new branches – for example, Earth systems engineering and management Earth systems engineering and management (ESEM) is a discipline used to analyze, design, engineer and manage complex environmental systems. It entails a wide range of subject areas including anthropology, engineering, environmental science, ethics ...
involves a wide range of subject areas including engineering studies
Engineering studies is an interdisciplinary branch of social sciences and humanities devoted to the study of engineers and their activities, often considered a part of Science and Technology Studies, science and technology studies (STS), and inte ...
, environmental science, engineering ethics
Engineering ethics is the field concerned with the system of moral principles that apply to the practice of engineering. The field examines and sets the obligations by engineers to society, to their clients, and to the profession. As a scholarly ...
and philosophy of engineering The philosophy of engineering is an emerging discipline that considers what engineering is, what engineers do, and how their work affects society, and thus includes aspects of ethics and aesthetics, as well as the ontology, epistemology, etc. that m ...
.
Practice
One who practices engineering is called anengineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
, and those licensed to do so may have more formal designations such as Professional Engineer
A professional is a member of a profession or any person who works in a specified professional activity. The term also describes the standards of education and training that prepare members of the profession with the particular knowledge and ski ...
, Chartered Engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thr ...
, Incorporated Engineer
An engineering technologist is a professional trained in certain aspects of development and implementation of a respective area of technology. An education in engineering technology concentrates more on application and less on theory than do ...
, Ingenieur
An engineer's degree is an advanced academic degree in engineering which is conferred in Europe, some countries of Asia and Latin America, North Africa and a few institutions in the United States. The degree may require a thesis but always require ...
, European Engineer
European Engineer (EUR ING) is an international professional qualification and title for highly qualified engineers used in over 32 European countries. Contemporary EUR ING engineers are degree-qualified and have gained the highest level of profes ...
, or Designated Engineering Representative.
Methodology
 In the
In the engineering design
The engineering design process, also known as the engineering method, is a common series of steps that engineers use in creating functional products and processes. The process is highly iterative – parts of the process often need to be repeat ...
process, engineers apply mathematics and sciences such as physics to find novel solutions to problems or to improve existing solutions. Engineers need proficient knowledge of relevant sciences for their design projects. As a result, many engineers continue to learn new material throughout their careers.
If multiple solutions exist, engineers weigh each design choice based on their merit and choose the solution that best matches the requirements. The task of the engineer is to identify, understand, and interpret the constraints on a design in order to yield a successful result. It is generally insufficient to build a technically successful product, rather, it must also meet further requirements.
Constraints may include available resources, physical, imaginative or technical limitations, flexibility for future modifications and additions, and other factors, such as requirements for cost, safety
Safety is the state of being protected from harm or other danger. Safety can also refer to the control of recognized hazards in order to achieve an acceptable level of risk.
Meanings
The word 'safety' entered the English language in the 1 ...
, marketability, productivity, and serviceability. By understanding the constraints, engineers derive specifications
A specification often refers to a set of documented requirements to be satisfied by a material, design, product, or service. A specification is often a type of technical standard.
There are different types of technical or engineering specificati ...
for the limits within which a viable object or system may be produced and operated.
Problem solving
 Engineers use their knowledge of
Engineers use their knowledge of science
Science is a systematic discipline that builds and organises knowledge in the form of testable hypotheses and predictions about the universe. Modern science is typically divided into twoor threemajor branches: the natural sciences, which stu ...
, mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...
, logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure o ...
, economics
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ...
, and appropriate experience or tacit knowledge to find suitable solutions to a particular problem. Creating an appropriate mathematical model
A mathematical model is an abstract and concrete, abstract description of a concrete system using mathematics, mathematical concepts and language of mathematics, language. The process of developing a mathematical model is termed ''mathematical m ...
of a problem often allows them to analyze it (sometimes definitively), and to test potential solutions.
More than one solution to a design problem usually exists so the different design choice
A design choice describes the planned way to satisfy an engineering development requirement in a way that could be satisfied differently. Often, there are multiple ways to satisfy a requirement, which necessitates making choices to select from pos ...
s have to be evaluated on their merits before the one judged most suitable is chosen. Genrich Altshuller
Genrikh Saulovich Altshuller (, ; 15 October 1926 – 24 September 1998) was a Soviet engineer, inventor, and writer. He is most notable for creating the TRIZ, Theory of Inventive Problem Solving, better known by its Russian acronym TRIZ. He fou ...
, after gathering statistics on a large number of patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an sufficiency of disclosure, enabling discl ...
s, suggested that compromise
To compromise is to make a deal between different parties where each party gives up part of their demand. In arguments, compromise means finding agreement through communication, through a mutual acceptance of terms—often involving variations fr ...
s are at the heart of "low-level
High-level and low-level, as technical terms, are used to classify, describe and point to specific goals of a systematic operation; and are applied in a wide range of contexts, such as, for instance, in domains as widely varied as computer scienc ...
" engineering designs, while at a higher level the best design is one which eliminates the core contradiction causing the problem.
Engineers typically attempt to predict how well their designs will perform to their specifications prior to full-scale production. They use, among other things: prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and Software prototyping, software programming. A prototype ...
s, scale model
A scale model is a physical model that is geometrically similar to an object (known as the ''prototype''). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small protot ...
s, simulation
A simulation is an imitative representation of a process or system that could exist in the real world. In this broad sense, simulation can often be used interchangeably with model. Sometimes a clear distinction between the two terms is made, in ...
s, destructive tests, nondestructive tests, and stress tests. Testing ensures that products will perform as expected but only in so far as the testing has been representative of use in service. For products, such as aircraft, that are used differently by different users failures and unexpected shortcomings (and necessary design changes) can be expected throughout the operational life of the product.
Engineers take on the responsibility of producing designs that will perform as well as expected and, except those employed in specific areas of the arms industry, will not harm people. Engineers typically include a factor of safety
In engineering, a factor of safety (FoS) or safety factor (SF) expresses how much stronger a system is than it needs to be for its specified maximum load. Safety factors are often calculated using detailed analysis because comprehensive testing i ...
in their designs to reduce the risk of unexpected failure.
The study of failed products is known as forensic engineering
Forensic engineering has been defined as "the investigation of failures—ranging from serviceability to catastrophic—which may lead to legal activity, including both civil and criminal". The forensic engineering field is very broad in terms o ...
. It attempts to identify the cause of failure to allow a redesign of the product and so prevent a re-occurrence. Careful analysis is needed to establish the cause of failure of a product. The consequences of a failure may vary in severity from the minor cost of a machine breakdown to large loss of life in the case of accidents involving aircraft and large stationary structures like buildings and dams.
Computer use
 As with all modern scientific and technological endeavors, computers and software play an increasingly important role. As well as the typical business
As with all modern scientific and technological endeavors, computers and software play an increasingly important role. As well as the typical business application software
Application software is any computer program that is intended for end-user use not operating, administering or programming the computer. An application (app, application program, software application) is any program that can be categorized as ...
there are a number of computer aided applications (computer-aided technologies
Computer-aided technologies (CAx) is the use of computer technology to aid in the design, analysis, and manufacture of products.
Advanced CAx tools merge many different aspects of product lifecycle management (PLM), including design, finite elem ...
) specifically for engineering. Computers can be used to generate models of fundamental physical processes, which can be solved using numerical method
In numerical analysis, a numerical method is a mathematical tool designed to solve numerical problems. The implementation of a numerical method with an appropriate convergence check in a programming language is called a numerical algorithm.
Mathem ...
s.
 One of the most widely used
One of the most widely used design tool
Design tools are objects, media, or computer programs, which can be used to design. They may influence the process of production, expression and perception of design ideas and therefore need to be applied skillfully.
Objects
New ideas can com ...
s in the profession is computer-aided design
Computer-aided design (CAD) is the use of computers (or ) to aid in the creation, modification, analysis, or optimization of a design. This software is used to increase the productivity of the designer, improve the quality of design, improve c ...
(CAD) software. It enables engineers to create 3D models, 2D drawings, and schematics of their designs. CAD together with digital mockup
A digital mockup (or digital mock-up) is the digital description of a product, usually in three dimensions. The product design engineers, the manufacturing engineers, and the support engineers work together to create and manage the mock-up. As a ...
(DMU) and CAE software such as finite element method analysis or analytic element method The analytic element method (AEM) is a numerical method used for the solution of partial differential equations. It was initially developed by O.D.L. Strack at the University of Minnesota. It is similar in nature to the boundary element method (BE ...
allows engineers to create models of designs that can be analyzed without having to make expensive and time-consuming physical prototypes.
These allow products and components to be checked for flaws; assess fit and assembly; study ergonomics; and to analyze static and dynamic characteristics of systems such as stresses, temperatures, electromagnetic emissions, electrical currents and voltages, digital logic levels, fluid flows, and kinematics. Access and distribution of all this information is generally organized with the use of product data management software.
There are also many tools to support specific engineering tasks such as computer-aided manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) also known as computer-aided modeling or computer-aided machining is the use of software to control machine tools in the manufacturing of work pieces. This is not the only definition for CAM, but it is the most ...
(CAM) software to generate CNC
Computer numerical control (CNC) or CNC machining is the automated control of machine tools by a computer. It is an evolution of numerical control (NC), where machine tools are directly managed by data storage media such as punched cards or ...
machining instructions; manufacturing process management
Manufacturing process management (MPM) is a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. MPM differs from ERP/MRP which is used to plan the ordering of materials and other resources, set manufacturing ...
software for production engineering; EDA for printed circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB), also called printed wiring board (PWB), is a Lamination, laminated sandwich structure of electrical conduction, conductive and Insulator (electricity), insulating layers, each with a pattern of traces, planes ...
(PCB) and circuit schematic
A schematic, or schematic diagram, is a designed representation of the elements of a system using abstract, graphic symbols rather than realistic pictures. A schematic usually omits all details that are not relevant to the key information the sc ...
s for electronic engineers; MRO applications for maintenance management; and Architecture, engineering and construction (AEC) software for civil engineering.
In recent years the use of computer software to aid the development of goods has collectively come to be known as product lifecycle management
In industry, product lifecycle management (PLM) is the process of managing the entire lifecycle of a product from its inception through the engineering, design, and manufacture, as well as the service and disposal of manufactured products. ...
(PLM).
Social context
 The engineering profession engages in a range of activities, from collaboration at the societal level, and smaller individual projects. Almost all engineering projects are obligated to a funding source: a company, a set of investors, or a government. The types of engineering that are less constrained by such a funding source, are ''
The engineering profession engages in a range of activities, from collaboration at the societal level, and smaller individual projects. Almost all engineering projects are obligated to a funding source: a company, a set of investors, or a government. The types of engineering that are less constrained by such a funding source, are ''pro bono
( English: 'for the public good'), usually shortened to , is a Latin phrase for professional work undertaken voluntarily and without payment. The term traditionally referred to provision of legal services by legal professionals for people who a ...
'', and open-design
The open-design movement involves the development of physical products, machines and systems through use of publicly shared design information. This includes the making of both free and open-source software (FOSS) as well as open-source hardwar ...
engineering.
Engineering has interconnections with society, culture and human behavior. Most products and constructions used by modern society, are influenced by engineering. Engineering activities have an impact on the environment, society, economies, and public safety.
Engineering projects can be controversial. Examples from different engineering disciplines include: the development of nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission or atomic bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions (thermonuclear weapon), producing a nuclear exp ...
s, the Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam (), officially known as Yangtze River Three Gorges Water Conservancy Project () is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River near Sandouping in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downs ...
, the design and use of sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle (SUV) is a car classification that combines elements of road-going passenger cars with features from off-road vehicles, such as raised ground clearance and four-wheel drive.
There is no commonly agreed-upon definitio ...
s and the extraction of oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) and lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturate ...
. In response, some engineering companies have enacted serious corporate and social responsibility policies.
The attainment of many of the Millennium Development Goals
In the United Nations, the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were eight international development goals for the year 2015 created following the Millennium Summit, following the adoption of the United Nations Millennium Declaration. These w ...
requires the achievement of sufficient engineering capacity to develop infrastructure and sustainable technological development.
 Overseas development and relief NGOs make considerable use of engineers, to apply solutions in disaster and development scenarios. Some charitable organizations use engineering directly for development:
*
Overseas development and relief NGOs make considerable use of engineers, to apply solutions in disaster and development scenarios. Some charitable organizations use engineering directly for development:
* Engineers Without Borders
The term Engineers Without Borders (EWB; , ISF) is used by a number of non-governmental organizations in various countries to describe their activity based on engineering and oriented to international development work. All of these groups work wor ...
* Engineers Against Poverty
* Registered Engineers for Disaster Relief
* Engineers for a Sustainable World
* Engineering for Change
Engineering for Change (E4C) is an online platform and international community of engineers, scientists, non-governmental organizations, local community advocates and other innovators working to solve problems in sustainable global development. T ...
* Engineering Ministries InternationalHome page for EMIEngineering companies in more developed economies face challenges with regard to the number of engineers being trained, compared with those retiring. This problem is prominent in the UK where engineering has a poor image and low status. There are negative economic and political issues that this can cause, as well as ethical issues. It is agreed the engineering profession faces an "image crisis". The UK holds the most engineering companies compared to other European countries, together with the United States.
Code of ethics
Manyengineering societies
An engineering society is a professional organization for engineers of various disciplines. Some are umbrella type organizations which accept many different disciplines, while others are discipline-specific. Many award professional designations, s ...
have established codes of practice and codes of ethics to guide members and inform the public at large. The National Society of Professional Engineers
The National Society of Professional Engineers (abbreviate as NSPE) is a professional association representing licensed professional engineers in the United States. NSPE is the recognized voice and advocate of licensed Professional Engineers repr ...
code of ethics states:
In Canada, engineers wear the Iron Ring
The Iron Ring is a ring worn by many Canadian engineers as a symbol and reminder of the obligations and ethics associated with their profession. The ring is presented in a private ceremony known as the Ritual of the Calling of an Engineer.
as a symbol and reminder of the obligations and ethics associated with their profession.
Relationships with other disciplines
Science
 There exists an overlap between the sciences and engineering practice; in engineering, one applies science. Both areas of endeavor rely on accurate observation of materials and phenomena. Both use mathematics and classification criteria to analyze and communicate observations.
Scientists may also have to complete engineering tasks, such as designing experimental apparatus or building prototypes. Conversely, in the process of developing technology, engineers sometimes find themselves exploring new phenomena, thus becoming, for the moment, scientists or more precisely "engineering scientists".
In the book ''
There exists an overlap between the sciences and engineering practice; in engineering, one applies science. Both areas of endeavor rely on accurate observation of materials and phenomena. Both use mathematics and classification criteria to analyze and communicate observations.
Scientists may also have to complete engineering tasks, such as designing experimental apparatus or building prototypes. Conversely, in the process of developing technology, engineers sometimes find themselves exploring new phenomena, thus becoming, for the moment, scientists or more precisely "engineering scientists".
In the book ''What Engineers Know and How They Know It
''What Engineers Know and How they Know It: Analytical Studies from Aeronautical History'' (The Johns Hopkins University Press, 1990) is a historical reflection on engineering practice in US aeronautics from 1908 to 1953 written by Walter Vincen ...
'', Walter Vincenti asserts that engineering research has a character different from that of scientific research. First, it often deals with areas in which the basic physics
Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...
or chemistry
Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...
are well understood, but the problems themselves are too complex to solve in an exact manner.
There is a "real and important" difference between engineering and physics as similar to any science field has to do with technology. Physics is an exploratory science that seeks knowledge of principles while engineering uses knowledge for practical applications of principles. The former equates an understanding into a mathematical principle while the latter measures variables involved and creates technology. For technology, physics is an auxiliary and in a way technology is considered as applied physics. Though physics and engineering are interrelated, it does not mean that a physicist is trained to do an engineer's job. A physicist would typically require additional and relevant training. Physicists and engineers engage in different lines of work. But PhD physicists who specialize in sectors of engineering physics
Engineering physics (EP), sometimes engineering science, is the field of study combining pure science disciplines (such as physics, mathematics, chemistry or biology) and engineering disciplines (computer, nuclear, electrical, aerospace, medic ...
and applied physics
Applied physics is the application of physics to solve scientific or engineering problems. It is usually considered a bridge or a connection between physics and engineering.
"Applied" is distinguished from "pure" by a subtle combination of fac ...
are titled as Technology officer, R&D Engineers and System Engineers.
An example of this is the use of numerical approximations to the Navier–Stokes equations
The Navier–Stokes equations ( ) are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances. They were named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and the Irish physicist and mathematician Georg ...
to describe aerodynamic flow over an aircraft, or the use of the finite element method
Finite element method (FEM) is a popular method for numerically solving differential equations arising in engineering and mathematical modeling. Typical problem areas of interest include the traditional fields of structural analysis, heat tran ...
to calculate the stresses in complex components. Second, engineering research employs many semi-empirical methods
Empirical research is research using empirical evidence. It is also a way of gaining knowledge by means of direct and indirect observation or experience. Empiricism values some research more than other kinds. Empirical evidence (the record of o ...
that are foreign to pure scientific research, one example being the method of parameter variation.
As stated by Fung ''et al.'' in the revision to the classic engineering text ''Foundations of Solid Mechanics'':
Engineering is quite different from science. Scientists try to understand nature. Engineers try to make things that do not exist in nature. Engineers stress innovation and invention. To embody an invention the engineer must put his idea in concrete terms, and design something that people can use. That something can be a complex system, device, a gadget, a material, a method, a computing program, an innovative experiment, a new solution to a problem, or an improvement on what already exists. Since a design has to be realistic and functional, it must have its geometry, dimensions, and characteristics data defined. In the past engineers working on new designs found that they did not have all the required information to make design decisions. Most often, they were limited by insufficient scientific knowledge. Thus they studiedAlthough engineering solutions make use of scientific principles, engineers must also take into account safety, efficiency, economy, reliability, and constructability or ease of fabrication as well as the environment, ethical and legal considerations such as patent infringement or liability in the case of failure of the solution.mathematics Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many ar ...,physics Physics is the scientific study of matter, its Elementary particle, fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge whi ...,chemistry Chemistry is the scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a physical science within the natural sciences that studies the chemical elements that make up matter and chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules a ...,biology Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...andmechanics Mechanics () is the area of physics concerned with the relationships between force, matter, and motion among Physical object, physical objects. Forces applied to objects may result in Displacement (vector), displacements, which are changes of .... Often they had to add to the sciences relevant to their profession. Thus engineering sciences were born.
Medicine and biology
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for patients, managing the Medical diagnosis, diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, ...
aims to sustain, repair, enhance and even replace functions of the human body
The human body is the entire structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently Organ (biology), organs and then Organ system, org ...
, if necessary, through the use of technology
Technology is the application of Conceptual model, conceptual knowledge to achieve practical goals, especially in a reproducible way. The word ''technology'' can also mean the products resulting from such efforts, including both tangible too ...
.
 Modern medicine can replace several of the body's functions through the use of artificial organs and can significantly alter the function of the human body through artificial devices such as, for example,
Modern medicine can replace several of the body's functions through the use of artificial organs and can significantly alter the function of the human body through artificial devices such as, for example, brain implant
Brain implants, often referred to as neural implants, are technological devices that connect directly to a biological subject's brain – usually placed on the surface of the brain, or attached to the brain's cortex. A common purpose of modern bra ...
s and pacemakers
A pacemaker, also known as an artificial cardiac pacemaker, is an implanted medical device that generates electrical pulses delivered by electrodes to one or more of the chambers of the heart. Each pulse causes the targeted chamber(s) to co ...
. The fields of bionics
Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design of engineering systems and modern technology.
The word ''bionic'', coined by Jack E. Steele in August 195 ...
and medical bionics are dedicated to the study of synthetic implants pertaining to natural systems.
Conversely, some engineering disciplines view the human body as a biological machine worth studying and are dedicated to emulating many of its functions by replacing biology
Biology is the scientific study of life and living organisms. It is a broad natural science that encompasses a wide range of fields and unifying principles that explain the structure, function, growth, History of life, origin, evolution, and ...
with technology. This has led to fields such as artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the capability of computer, computational systems to perform tasks typically associated with human intelligence, such as learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and decision-making. It is a field of re ...
, neural networks
A neural network is a group of interconnected units called neurons that send signals to one another. Neurons can be either Cell (biology), biological cells or signal pathways. While individual neurons are simple, many of them together in a netwo ...
, fuzzy logic
Fuzzy logic is a form of many-valued logic in which the truth value of variables may be any real number between 0 and 1. It is employed to handle the concept of partial truth, where the truth value may range between completely true and completely ...
, and robot
A robot is a machine—especially one Computer program, programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions Automation, automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the robot control, co ...
ics. There are also substantial interdisciplinary interactions between engineering and medicine.Institute of Medicine and Engineering: Mission statement The mission of the Institute for Medicine and Engineering (IME) is to stimulate fundamental research at the interface between biomedicine and engineering/physical/computational sciences leading to innovative applications in biomedical research and clinical practice.Both fields provide solutions to real world problems. This often requires moving forward before phenomena are completely understood in a more rigorous scientific sense and therefore experimentation and empirical knowledge is an integral part of both. Medicine, in part, studies the function of the human body. The human body, as a biological machine, has many functions that can be modeled using engineering methods.Royal Academy of Engineering and Academy of Medical Sciences: Systems Biology: a vision for engineering and medicine in pdf: quote1: Systems Biology is an emerging methodology that has yet to be defined quote2: It applies the concepts of systems engineering to the study of complex biological systems through iteration between computational or mathematical modelling and experimentation.
The heart for example functions much like a pump, the skeleton is like a linked structure with levers,
the brain produces electrical signals etc. These similarities as well as the increasing importance and application of engineering principles in medicine, led to the development of the field of
biomedical engineering
Biomedical engineering (BME) or medical engineering is the application of engineering principles and design concepts to medicine and biology for healthcare applications (e.g., diagnostic or therapeutic purposes). BME also integrates the logica ...
that uses concepts developed in both disciplines.
Newly emerging branches of science, such as systems biology
Systems biology is the computational modeling, computational and mathematical analysis and modeling of complex biological systems. It is a biology-based interdisciplinary field of study that focuses on complex interactions within biological system ...
, are adapting analytical tools traditionally used for engineering, such as systems modeling and computational analysis, to the description of biological systems.
Art
 There are connections between engineering and art, for example,
There are connections between engineering and art, for example, architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and construction, constructi ...
, landscape architecture
Landscape architecture is the design of outdoor areas, landmarks, and structures to achieve environmental, social-behavioural, or aesthetic outcomes. It involves the systematic design and general engineering of various structures for constructio ...
and industrial design
Industrial design is a process of design applied to physical Product (business), products that are to be manufactured by mass production. It is the creative act of determining and defining a product's form and features, which takes place in adva ...
(even to the extent that these disciplines may sometimes be included in a university's Faculty of Engineering).MIT World:The Art of Engineering: Inventor James Dyson on the Art of Engineering: quote: A member of the British Design Council, James Dyson has been designing products since graduating from the Royal College of Art in 1970.The
Art Institute of Chicago
The Art Institute of Chicago, founded in 1879, is one of the oldest and largest art museums in the United States. The museum is based in the Art Institute of Chicago Building in Chicago's Grant Park (Chicago), Grant Park. Its collection, stewa ...
, for instance, held an exhibition about the art of NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States ...
's aerospace design. Robert Maillart
Robert Maillart (16 February 1872 – 5 April 1940) was a Swiss civil engineer who revolutionized the use of structural reinforced concrete with such designs as the three-hinged arch and the deck-stiffened arch for bridges, and the beamless f ...
's bridge design is perceived by some to have been deliberately artistic. At the University of South Florida
The University of South Florida (USF) is a Public university, public research university with its main campus located in Tampa, Florida, Tampa, Florida, United States, and other campuses in St. Petersburg, Florida, St. Petersburg and Sarasota, ...
, an engineering professor, through a grant with the National Science Foundation
The U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) is an Independent agencies of the United States government#Examples of independent agencies, independent agency of the Federal government of the United States, United States federal government that su ...
, has developed a course that connects art and engineering.quote:..the tools of artists and the perspective of engineers..Among famous historical figures,
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 1452 - 2 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially rested o ...
is a well-known Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and sur ...
artist and engineer, and a prime example of the nexus between art and engineering.Bjerklie, David. "The Art of Renaissance Engineering." ''MIT's Technology Review'' Jan./Feb.1998: 54–59. Article explores the concept of the "artist-engineer", an individual who used his artistic talent in engineering. Quote from article: Da Vinci reached the pinnacle of "artist-engineer"-dom, Quote2: "It was Leonardo da Vinci who initiated the most ambitious expansion in the role of artist-engineer, progressing from astute observer to inventor to theoretician." (Bjerklie 58)Drew U: user website: cites Bjerklie paperBusiness
Business engineering
A business process, business method, or business function is a collection of related, structured activities or tasks performed by people or equipment in which a specific sequence produces a service or product (that serves a particular business g ...
deals with the relationship between professional engineering, IT systems, business administration and change management
Change management (CM) is a discipline that focuses on managing changes within an organization. Change management involves implementing approaches to prepare and support individuals, teams, and leaders in making organizational change. Change mana ...
. Engineering management
Engineering management is the application of engineering methods, tools, and techniques to business management systems. Engineering management is a career that brings together the technological problem-solving ability of engineering and the organi ...
or "Management engineering" is a specialized field of management
Management (or managing) is the administration of organizations, whether businesses, nonprofit organizations, or a Government agency, government bodies through business administration, Nonprofit studies, nonprofit management, or the political s ...
concerned with engineering practice or the engineering industry sector. The demand for management-focused engineers (or from the opposite perspective, managers with an understanding of engineering), has resulted in the development of specialized engineering management degrees that develop the knowledge and skills needed for these roles. During an engineering management course, students will develop industrial engineering
Industrial engineering (IE) is concerned with the design, improvement and installation of integrated systems of people, materials, information, equipment and energy. It draws upon specialized knowledge and skill in the mathematical, physical, an ...
skills, knowledge, and expertise, alongside knowledge of business administration, management techniques, and strategic thinking. Engineers specializing in change management must have in-depth knowledge of the application of industrial and organizational psychology
Industrial and organizational psychology (I-O psychology) "focuses the lens of psychological science on a key aspect of human life, namely, their work lives. In general, the goals of I-O psychology are to better understand and optimize the effec ...
principles and methods. Professional engineers often train as certified management consultant
"Certified management consultant" (CMC) is an international professional certification established in 1967 for management consulting professionals, awarded by institutes in 50 countries (as of February 2014). The CMC enjoys global reciprocity; cons ...
s in the very specialized field of management consulting
Management consulting is the practice of providing consulting services to organizations to improve their performance or in any way to assist in achieving organizational objectives. Organizations may draw upon the services of management consultant ...
applied to engineering practice or the engineering sector. This work often deals with large scale complex business transformation
In management it has been said that business transformation involves making fundamental changes in how business is conducted in order to help cope with shifts in market environment. However this is a relatively narrow definition that overlooks o ...
or business process management
Business process management (BPM) is the discipline in which people use various methods to Business process discovery, discover, Business process modeling, model, Business analysis, analyze, measure, improve, optimize, and Business process auto ...
initiatives in aerospace and defence, automotive, oil and gas, machinery, pharmaceutical, food and beverage, electrical and electronics, power distribution and generation, utilities and transportation systems. This combination of technical engineering practice, management consulting practice, industry sector knowledge, and change management expertise enables professional engineers who are also qualified as management consultants to lead major business transformation initiatives. These initiatives are typically sponsored by C-level executives.
Other fields
Inpolitical science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
, the term ''engineering'' has been borrowed for the study of the subjects of social engineering and political engineering In political science, political engineering is the designing of political institutions in a society and often involves the use of paper decrees, in the form of laws, referendums, ordinances, or otherwise, to try to achieve some desired effect.
The ...
, which deal with forming political
Politics () is the set of activities that are associated with decision-making, making decisions in social group, groups, or other forms of power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of Social sta ...
and social structure
In the social sciences, social structure is the aggregate of patterned social arrangements in society that are both emergent from and determinant of the actions of individuals. Likewise, society is believed to be grouped into structurally rel ...
s using engineering methodology coupled with political science
Political science is the scientific study of politics. It is a social science dealing with systems of governance and Power (social and political), power, and the analysis of political activities, political philosophy, political thought, polit ...
principles. Marketing engineering Marketing engineering is currently defined as "a systematic approach to harness data and knowledge to drive effective marketing decision making and implementation through a technology-enabled and model-supported decision process".
History
The term ...
and financial engineering
Financial engineering is a multidisciplinary field involving financial theory, methods of engineering, tools of mathematics and the practice of programming. It has also been defined as the application of technical methods, especially from mathe ...
have similarly borrowed the term.
See also
;Lists *List of aerospace engineering topics
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to aerospace engineering. For a broad overview of engineering, see List of engineering topics. For biographies, see List of engineers.
A
*Ablative laser propulsion —
*Absolute va ...
* List of basic chemical engineering topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to chemical engineering:
Chemical engineering – deals with the application of physical science (e.g., chemistry and physics), and life sciences (e.g., biology, microbio ...
* List of electrical engineering topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to electrical engineering.
Electrical engineering – field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electroma ...
* List of engineering societies
An engineering society is a professional organization for engineers of various disciplines. Some are umbrella type organizations which accept many different disciplines, while others are discipline-specific. Many award professional designations, ...
* List of engineering topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to engineering:
Engineering is the scientific discipline and profession that applies scientific theories, mathematical methods, and empirical evidence to design, create, and ...
* List of engineers
Types of engineer include:
* Chartered Engineer
* European Engineer
* Incorporated Engineer
* Professional Engineer
* Royal Engineer
Lists of individual engineers by discipline include:
* List of aerospace engineers
* List of canal enginee ...
* List of genetic engineering topics
* List of mechanical engineering topics
This is an alphabetical list of articles pertaining specifically to mechanical engineering. For a broad overview of engineering, please see List of engineering topics. For biographies please see List of engineers.
A
Acceleration –
Accuracy an ...
* List of nanoengineering topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to nanotechnology:
Nanotechnology is science, engineering, and technology conducted at the nanoscale, which is about 1 to 100 nanometers.
Branches of nanotechnology
* ...
* List of software engineering topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to software engineering:
Software engineering – application of a systematic, disciplined, quantifiable approach to the development, operation, and maintenance of softwar ...
;Glossaries
* Glossary of areas of mathematics
Mathematics is a broad subject that is commonly divided in many areas or branches that may be defined by their objects of study, by the used methods, or by both. For example, analytic number theory is a subarea of number theory devoted to the u ...
* Glossary of biology
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions ...
* Glossary of chemistry
* Glossary of engineering
This glossary is split across multiple pages due to technical limitations.
By alphabetical order
* Glossary of engineering: A–L
* Glossary of engineering: M–Z
By category
* Glossary of civil engineering
* Glossary of electrical and e ...
* Glossary of physics
This glossary of physics is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to physics, its sub-disciplines, and related fields, including mechanics, materials science, nuclear physics, particle physics, and thermodynamics. For more inclusiv ...
;Related subjects
* Controversies over the term Engineer
Regulation and licensure in engineering is established by various jurisdictions of the world to encourage life, public welfare, safety, well-being, then environment and other interests of the general public and to define the licensure process thr ...
* Design
A design is the concept or proposal for an object, process, or system. The word ''design'' refers to something that is or has been intentionally created by a thinking agent, and is sometimes used to refer to the inherent nature of something ...
* Earthquake engineering
* Engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
* Engineering economics
Engineering economics, previously known as engineering economy, is a subset of economics concerned with the use and "...application of economic principles"Dharmaraj, E.. Engineering Economics. Mumbai, IN: Himalaya Publishing House, 2009. ProQu ...
* Engineering education
Engineering education is the activity of teaching knowledge and principles to the professional practice of engineering. It includes an initial education ( Dip.Eng.)and (B.Eng.) or ( M.Eng.), and any advanced education and specializations th ...
* Engineering education research
* Environmental engineering science
Environmental engineering science (EES) is a multidisciplinary field of engineering science that combines the biological, chemical and physical sciences with the field of engineering. This major traditionally requires the student to take basic en ...
* Global Engineering Education
Global Engineering Education is a field of study that focuses on the impact of globalization on the engineering industry.
History
Over the past decade or so educators and researchers have made an effort to transform engineering education in li ...
* Green engineering
Green is the color between cyan and yellow on the visible spectrum. It is evoked by light which has a dominant wavelength of roughly 495570 nm. In subtractive color systems, used in painting and color printing, it is created by a combin ...
* Reverse engineering
Reverse engineering (also known as backwards engineering or back engineering) is a process or method through which one attempts to understand through deductive reasoning how a previously made device, process, system, or piece of software accompl ...
* Structural failure
Structural integrity and failure is an aspect of engineering that deals with the ability of a structure to support a designed structural load (weight, force, etc.) without breaking and includes the study of past structural failures in order to ...
* Sustainable engineering
Sustainable engineering is the process of designing or operating systems such that they use energy and resources sustainably, in other words, at a rate that does not compromise the natural environment, or the ability of future generations to meet ...
* Women in engineering
Women are often under-represented in the academic and professional fields of engineering; however, many women have contributed to the diverse fields of engineering historically and currently. A number of organizations and programs have been creat ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * *External links
* * * * {{Authority control Engineering occupations Philosophy of science Main topic articles